objective Students will learn that organisms are related to each other, based on shared (morphological) characteristics
|
|
|
- Francine Sophie Tyler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AIS Group members: Christine, Seojung, Andrew Meeting time: Mondays, 3-4pm Science standard 3d (evolution) students know how to construct a branching diagram classify living groups of organisms by shared derived characteristics objective Students will learn that organisms are related to each other, based on shared (morphological) characteristics assessment completion of the assignment in closing, question-based discussion introduction (10-15 min.) Andrew Students suggest animals, we put them into columns (without telling students what we re doing) based on how organisms are related ask students to suggest ideas why organisms are grouped together in that way ie mammals, reptiles, fish, etc--what are the differences? hair, vertebrae, live young, etc make list-->sort--> ideas for the groupings--> rules that separated the animals rules: shared features between birds, mammal, fish, reptiles, etc categories -- at least 2 per category leaders suggest animals, ask students to group based on what s on board already differentiate animals w/in broad categories have an other category Find an example of tree Add animals they suggested! guided discussion (5-10 min.) Christine very brief, extension from intro and prepares for activity (review evolutionary adaptations) explain branching diagrams-- shared, derived characteristics --what types of traits make things related (refer to images) these shared, derived characteristics can arise as a result of evolutionary adaptations--ask class to explain these ie types of symmetry, birth, hair/shells/etc... symmetry--bilateral, radial, assymetrical (define) types of birth? live, eggs, etc hair/skin/shells all things are related (focus on animals, what makes something an animal) activity (10 min.) ALL give students a list of animals/photos with short facts provided have students group animals based on the facts/their own knowledge make them group/branch things from a base point (all animals) students should connect organisms based on similarities (ie more similar = less branches between)
2 students write down what they noticed each student group gets one group from below: 1. Marine invertebrates 2. Fish 3. Mammals 4. Birds 5. Reptiles 6. Amphibians FOR notes on the animals-- provide hint that suggest why ALL of the group is in common provide hint to suggest why a few are in common (maybe) provide hint to suggest why individual is unique closing (15 min.) Seojung bring all groups back together have students present their branching diagrams to the class speculate on how different groups could be related to each other (ie evolution from inverts--fish-- amphibians--reptiles--birds--mammals) ^^maybe not asking about that Instead expose to tree of life Dl to flash drive and bring!!! show animal taxonomic tree? to show where each group is located. review and add technical terms generalization to future/next lesson a branching diagram organizes organisms based on physical and/or genetic characteristics tree of life: everything! from bacteria to humans come from single ancestor terms phylogeny clade kingdom, phyla, etc. evolutionary time (length of branches relates to when species diverged) Marine invertebrates What do they all have in common? No backbone (no vertebrae) Can you think of other animals you would include in this category? Questions to ask about these animals to help find what s related 1. What kind of symmetry does it have? (none, radial, bilateral) 2. What kind of bones and skin does it have? 3. How does it move? 4. How does it feed? 5. What other physical features can you spot? cnidara--gastropod--bivalve--echnioderm--arthropod--cephalopods 1. Brain coral (Faviidae) have stinging cells called nematocysts
3 2 body types -- can you guess what they are? polyp (most coral, can t move) medusa (babies, before settling) radial 2. Moon jelly (Aurelia aurita have stinging cells called nematocysts 2 body types polyp (babies, before settling) medusa (adults, swimming) radial 3. Spanish shawl nudibranch (Flabellina iodine) Uses a muscular foot to move symmetry? assymetrical 4. Kellet s whelk (Kelletia kelletii) it can withdraw from it s shell how does it move? uses a muscular foot to move symmetry? assymetrical 5. Pismo clam (Tivela stultorum) how many shells does it have? 2 use muscular foot to dig into sand use siphon to feed (Extends out of body) 6. Pacific oyster (Crassotrea gigas) how many shells does it have? 2 attach to hard surfaces with byssal threads (which are produced by an organ in the foot ) 7. Red sea urchin (Stronglylocentrotus franciscanus) pentamorous radial symmetry what do you think pentamorous means? (hint, penta = 5) how do they move? tube feet what kind of skeleton do they have? external skeleton with fused plates 8. Leather star (Dermasterias imbricate) hint, it is radial pentamorous radial symmetry how do they move? tube feet what kind of skeleton external skeleton plates are loosely attached 9. Giant pacific octopus (Enteroctopus) no skeleton
4 how do they move? by jet propulsion, squirt water how do they feed and catch things? use tentacles/suckers bilateral 10. Humboldt squid (Dosidicus gigas) internal skeleton how do they move? jet propulsion how do they feed and catch things? use tentacles/suckers in half (called bilateral) Marine fish What do they all have in common? swim, gills to breathe underwater, fins, backbone (vertebrae) Can you think of other animals you would include in this category? Questions to ask about these animals? 1. What shape do they have? 2. what kind of skin and bones do they have? 3. what kind of fins do they have? 4. how do they eat? 1. Great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) has a lateral line that detects sound and movement in the water (good for hunting) flexible skin is made of a certain type of scales, called dermal denticles which are similar to what makes their teeth, and makes their skin rough if touched in the wrong direction 2. Whale shark (Rhincodon typus) largest fish in the world flexible skin is made of dermal denticles 3. California skate (Raja inornata) skin is made of dermal denticles What kind of fins do they have? pectoral (side) fins are fused to the whole body 4. Bat ray (Myliobatis californica) skin is made of dermal denticles what kinds of fins do they have? how do they feed?
5 go along ocean bottom, mouth is on ventral (bottom) side of body 6. California halibut (Paralichthys californicus) bony skeleton and fins supported by bones 7. Leafy seadragon (Phycodurus eques) fins supported by bones males care for the young body shape? 8. Pacific seahorse (Hippocampus ingens) fins supported by bones males care for the young body shape? 9. Striped marlin (Tetrapturus audax) bony skeleton fins supported by bones 10. California sheephead (Semicossyphus pulcher) bony skeleton females can change to males 11. Zebra moray eel ( Gymnomuraena zebra) smooth skin, no scales top fin (dorsal) runs along the whole body missing side fins (pectoral, pelvic) Questions to ask: What does their skin look like (or appear to feel like)? How many toes do they have, if any? How do their legs, if any, compare to each other? What kinds of eggs does it lay? Reptiles - scales, dry skin, lay eggs, cold-blooded snakes- forked tongue, no limbs, extremely flexible, (closest relatives = lizards) lizards - five toes on front feet, four legs, long tail, clawed feet crocs - partially webbed feet, long tails turtles - bony shells, do not have teeth 1. Red Racer (Coluber flagellum piceus) dry skin forked tonuge 2. Kingsnake (Lampropeltis getula californiae) extremely flexible forked tongue has scaly skin 3. Sierra Garter Snake (Thamnophis couchi) how does this animal move around? has scaly skin where does this animal generally live (land or water?) 4. Nile Crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus) what does this animals feet look like? what kind of skin does this animal have? 5. North American Alligator (Alligator mississippiensis)
6 partially webbed feet what kind of skin does this animal have? 6. Western Fence Lizard (Sceloporus occidentalis occidentalis) how big is this animal look? how many toes does this animal have? 7. Coast Horned Lizard (Phrynosoma blainvillii) how does this animal move around (walk, slither, swim)? what of skin does this animal have? 8. Peninsular Banded Gecko (Coleonyx switaki switaki) how big does this animal look? how many toes does this animal have? 9. Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas) how does this animal move around (walk, slither, swim)? does not have teeth 10. Spider Tortoise (Pyxis arachnoides) does not have teeth how would you describe some main features about this animal? Amphibians - live on land and water, breathe with lungs and gills, lay many eggs, cold blooded salamander - soft & moist skin, no scales, eggs are surrounded by clear jelly, four toes on front feet frog - two bulging eyes, webbed hind feet, smooth or slimy skin, lays eggs in clusters toad - short hind legs, warty & dry skin, lays eggs in chains 1. Arboreal Salamander (Aneides lugubris) breathes with lungs and gills four toes on front feet 2. California Tiger Salamander (Ambystoma californiense) four toes on front feet no scales 3. Black-bellied Slender Salamander (Batrachoseps nigriventris) eggs are surrounded by a clear jelly no scales 4. Sierra Newt (Taricha sierrae) soft & moist skin four toes on front feet 5. Green Tree Frog (Hyla cinerea) webbed hind feet in clusters 6. American Bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus)
7 in clusters smooth or slimy skin 7. Yosemite Toad (Anaxyrus canorus) warty and dry skin in a chain 8. Rocky Mountain Toad (Anaxyrus woodhousii woodhousii) in a chain short hind legs Mammals What do they all have in common? Mothers feed milk to their young. Can you think of other animals you would include in this category? Questions to ask about these animals: 1. What do they eat? 2. What are some categories of animals? a. What makes them different? 3. How are they different from birds, reptiles, etc? 1. Koala (Phascolarctos cinereus) Young are carried in a pouch Herbivores Has fingerprints like humans Mostly silent and nocturnal 2. Indian elephants (Elephas maximus indicus) Odd number of toes on hooves Tusks present on males Shoulder height between 2 and 3.5m How are their young born? 3. Kangaroo (Macropus rufus) Large feet Long muscular tail for balance Chews cud Where do they keep their young? 4. white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) Antlers on males Long legs How are their young born? How many toes do they have on their hooves? 5. gray wolves (Canis lupus) Pups are born live Long snout and nonretractile claws Long legs Relatively small paws Short and sturdy teeth 6. zebras (Equus quagga) 1 toe per hoof Have great night vision
8 Can turn ears in almost any direction How are their young born? 7. Golden retriever Long snout and nonretractile claws What makes them such good runners? How are their children born? 8. Hippos (Hippopotamus amphibius) What do their feet look like? o Even-toed Semi-aquatic life in freshwater Skeleton that has adapted to carry a lot of weight How are their young born? 9. Western African lions Retractile claws How are their young born? Large external ears 10. Hyenas (Crocuta crocuta) How are their young born? Noticeable downward sloped back Primarily nocturnal 11. aardvark (Orycteropus afer) Hoofed feet Very thick tail Disproportionately long ears Young are born live 12. Asian black bear (Ursus thibetanus) Children are born live Long snout and nonretractile claws Mostly omnivorous 12. Shetland pony How many toes do they have on their hooves? (Think horses!) Strongest of all horse and pony breeds More likely to have heart problems How are young born? Birds What do all of them have in common? Winged, warm-blooded, egg-laying Animals that go in this category? Questions: 1. What is another group of animals lays eggs? 2. What are some characteristics of birds that can help you group them? 1. Ostriches (Struthio camelus) Tail and flight feathers are only decorative 2 toes on each foot Wings used in courtship and predator distraction 2. Canada geese (Branta canadensis) What do their feet look like? Monogamous Where do they live? 3. Gentoo penguins (Pygoscelis papua) Where do they live?
9 What do they use their wings for? Can drink salt water 4. Booted eagle (Aquila pennata) Sharply hooked beak Heavy head and beak Females larger than males 5. Mandarin duck (Aix galericulata) What do their feet look like? Feeds mainly during dawn or dusk Perch in trees or on ground during the day 6. Painted Bush quails (Perdicula erythrorhyncha) Ground feeding Rounded bodies Dust-bathe in morning and evening Deep red bills 7. Peregrine falcons Fastest moving creatures on Earth What do their beaks look like? o How do they catch their prey? Thin tapered wings 8. Australian Bustard (type of turkey) (Ardeotis australis) What shape do their bodies have? Fleshy wattle at top of beak 9. Northern Goshawk What do their beaks look like? Sharp vision Long tail Marine invertebrates What do they all have in common? Can you think of other animals you would include in this category? Questions to ask about these animals to help find what s related 1. What kind of symmetry does it have? (none, radial, bilateral) 2. What kind of bones and skin does it have? 3. How does it move? 4. How does it feed? 5. What other physical features can you spot? 1. Brain coral (Faviidae) have stinging cells called nematocysts 2 body types polyp (attached, don t move) medusa (young, before settling) radial symmetry 2. Moon jelly (Aurelia aurita) have stinging cells called nematocysts 2 body types polyp (young) medusa (adults, swimming) 3. Spanish shawl nudibranch (Flabellina iodine)
10 Uses a muscular foot to move assymetrical 4. Kellet s whelk (Kelletia kelletii) it can withdraw from it s shell how does it move? assymetrical 5. Pismo clam (Tivela stultorum) how many shells does it have? uses muscular foot to dig into sand uses siphon to feed (Extends out of body) 6. Pacific oyster (Crassotrea gigas) how many shells does it have? attaches to hard surfaces with byssal threads (which are produced by an organ in the foot ) 7. Red sea urchin (Stronglylocentrotus franciscanus) pentamorous radial symmetry what do you think pentamorous means? (hint, penta = 5) move with tube feet external skeleton with fused plates 8. Leather star (Dermasterias imbricate) hint: radial move with tube feet external skeleton plates are loosely attached 9. Giant pacific octopus (Enteroctopus) no skeleton move by jet propulsion (use water pressure to propel themselve) how do they feed and catch things? 10. Humboldt squid (Dosidicus gigas) internal skeleton move by jet propulsion how do they feed and catch things? Marine fish What do they all have in common? Can you think of other animals you would include in this category? Questions to ask about these animals 1. What shape do they have? 2. what kind of skin and bones do they have? 3. what kind of fins do they have? 4. how do they eat? 1. Great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) has a lateral line that detects sound and movement in the water (good for hunting) (very flexible)
11 skin is made of a certain type of scales, called dermal denticles which are similar to what makes their teeth, and makes their skin rough if touched in the wrong direction 2. Whale shark (Rhincodon typus) largest fish in the world skin is made of dermal denticles 3. California skate (Raja inornata) skin is made of dermal denticles What kind of fins do they have? how do they feed? 4. Bat ray (Myliobatis californica) skin is made of dermal denticles how do they feed? 6. California halibut (Paralichthys californicus) bony skeleton and fins supported by bones what body type does it have? 7. Leafy seadragon (Phycodurus eques) fins supported by bones males care for the young what body type does it have? 8. Pacific seahorse (Hippocampus ingens) fins supported by bones males care for the young what body type does it have? 9. Striped marlin (Tetrapturus audax) bony skeleton fins supported by bones 10. California sheephead (Semicossyphus pulcher) bony skeleton females can change to males 11. Zebra moray eel ( Gymnomuraena zebra) smooth skin, no scales top fin (dorsal) runs along the whole body Questions to ask: What does their skin look like (or appear to feel like)? How many toes do they have, if any? How do their legs, if any, compare to each other? What kinds of eggs does it lay? Reptiles 1. Red Racer (Coluber flagellum piceus) dry skin forked tongue 2. Kingsnake (Lampropeltis getula californiae) extremely flexible
12 forked tongue has scaly skin 3. Sierra Garter Snake (Thamnophis couchi) how does this animal move around? has scaly skin where does this animal generally live (land or water?) 4. Nile Crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus) what does this animals feet look like? what kind of skin does this animal have? 5. North American Alligator (Alligator mississippiensis) partially webbed feet what kind of skin does this animal have? 6. Western Fence Lizard (Sceloporus occidentalis occidentalis) how big is this animal look? how many toes does this animal have? 7. Coast Horned Lizard (Phrynosoma blainvillii) how does this animal move around (walk, slither, swim)? what of skin does this animal have? 8. Peninsular Banded Gecko (Coleonyx switaki switaki) how big does this animal look? how many toes does this animal have? 9. Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas) how does this animal move around (walk, slither, swim)? does not have teeth 10. Spider Tortoise (Pyxis arachnoides) does not have teeth how would you describe some main features about this animal? Amphibians What do they all have in common? Questions to ask: 1. What kind of toes and legs do they have? 2. What kind of eggs do they lay? 3. What is their skin like? 1. Arboreal Salamander (Aneides lugubris) breathes with lungs and gills four toes on front feet 2. California Tiger Salamander (Ambystoma californiense)
13 four toes on front feet no scales 3. Black-bellied Slender Salamander (Batrachoseps nigriventris) eggs are surrounded by a clear jelly no scales 4. Sierra Newt (Taricha sierrae) soft & moist skin four toes on front feet 5. Green Tree Frog (Hyla cinerea) webbed hind feet in clusters 6. American Bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus) in clusters smooth or slimy skin 7. Yosemite Toad (Anaxyrus canorus) warty and dry skin in a chain 8. Rocky Mountain Toad (Anaxyrus woodhousii woodhousii) in a chain short hind legs
Some Facts about... Amphibians
 Amphibians Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates that live part of their lives in water and part on land. Amphibians eggs are laid in water and they are born there. They begin their lives with gills
Amphibians Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates that live part of their lives in water and part on land. Amphibians eggs are laid in water and they are born there. They begin their lives with gills
Name Class Date. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 14 2 The Animal Kingdom SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is diversity? What are vertebrates? What
CHAPTER 14 2 The Animal Kingdom SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is diversity? What are vertebrates? What
Animals Classification
 Animals Classification By Piyush & Ilaxi Grouping & Identifying Living Things 2 Classifying Living Things Classifying Living Things Biological Classification is the way in which scientists use to categorize
Animals Classification By Piyush & Ilaxi Grouping & Identifying Living Things 2 Classifying Living Things Classifying Living Things Biological Classification is the way in which scientists use to categorize
Name Date When you put food away in the kitchen, you sort the food into groups. You put foods that are alike in certain ways into the same
 1 Name Date When you put food away in the kitchen, you sort the food into groups. You put foods that are alike in certain ways into the same group. Scientists do the same thing with animals, plants and
1 Name Date When you put food away in the kitchen, you sort the food into groups. You put foods that are alike in certain ways into the same group. Scientists do the same thing with animals, plants and
Vertebrates. Vertebrates are animals that have a backbone and an endoskeleton.
 Vertebrates Vertebrates are animals that have a backbone and an endoskeleton. The backbone replaces the notochord and contains bones called vertebrae. An endoskeleton is an internal skeleton that protects
Vertebrates Vertebrates are animals that have a backbone and an endoskeleton. The backbone replaces the notochord and contains bones called vertebrae. An endoskeleton is an internal skeleton that protects
Essential Question: What are the characteristics of invertebrate animals? What are the characteristics of vertebrate animals?
 Essential Question: What are the characteristics of invertebrate animals? What are the characteristics of vertebrate animals? Key Concept: The animal kingdom is divided up into 35 phyla. These phyla can
Essential Question: What are the characteristics of invertebrate animals? What are the characteristics of vertebrate animals? Key Concept: The animal kingdom is divided up into 35 phyla. These phyla can
T. 6. THE VERTEBRATES
 T. 6. THE VERTEBRATES 1.- Relate the following concepts to their definition. Later, relate each concept to one of the pictures you are going to see. 1.- FIN a.- mammals with their babies 2.- GILLS b.-
T. 6. THE VERTEBRATES 1.- Relate the following concepts to their definition. Later, relate each concept to one of the pictures you are going to see. 1.- FIN a.- mammals with their babies 2.- GILLS b.-
Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals
 Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish,
Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish,
DO NOW: Invertebrate POP Quiz. Sit Quietly and clear off your desk/table of everything EXCEPT and blank piece of white lined paper and a pen/pencil.
 DO NOW: Invertebrate POP Quiz Sit Quietly and clear off your desk/table of everything EXCEPT and blank piece of white lined paper and a pen/pencil. DO NOW: Invertebrate POP Quiz Question 1: What is an
DO NOW: Invertebrate POP Quiz Sit Quietly and clear off your desk/table of everything EXCEPT and blank piece of white lined paper and a pen/pencil. DO NOW: Invertebrate POP Quiz Question 1: What is an
3rd GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UDI 2.- FAUNIA. ANIMALS-VERTEBRATES (7)
 VERTEBRATES 3rd GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UDI 2.- FAUNIA. ANIMALS-VERTEBRATES (7) Vertebrates are animals which have a backbone and an internal skeleton. The skeleton protects vital organs and supports the
VERTEBRATES 3rd GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UDI 2.- FAUNIA. ANIMALS-VERTEBRATES (7) Vertebrates are animals which have a backbone and an internal skeleton. The skeleton protects vital organs and supports the
VERTEBRATE READING. Fishes
 VERTEBRATE READING Fishes The first vertebrates to become a widespread, predominant life form on earth were fishes. Prior to this, only invertebrates, such as mollusks, worms and squid-like animals, would
VERTEBRATE READING Fishes The first vertebrates to become a widespread, predominant life form on earth were fishes. Prior to this, only invertebrates, such as mollusks, worms and squid-like animals, would
Today s Class. Go over viewfinder lab A closer look at the Animal Kingdom Taxonomy Worksheet
 Kingdom Animalia Today s Class Go over viewfinder lab A closer look at the Animal Kingdom Taxonomy Worksheet Viewfinder Kingdom: Animalia Cells: multicellular Food: eats other organisms Movement: moves
Kingdom Animalia Today s Class Go over viewfinder lab A closer look at the Animal Kingdom Taxonomy Worksheet Viewfinder Kingdom: Animalia Cells: multicellular Food: eats other organisms Movement: moves
Classification of Animals. adapted from
 Classification of Animals Animals With Backbones AMPHIBIAN FISH MAMMAL BIRD REPTILE Animals With Backbones Animals with backbones are called vertebrates. Vertebrates include many different kinds of animals.
Classification of Animals Animals With Backbones AMPHIBIAN FISH MAMMAL BIRD REPTILE Animals With Backbones Animals with backbones are called vertebrates. Vertebrates include many different kinds of animals.
All living things are classified into groups based on the traits they share. Taxonomy is the study of classification. The largest groups into which
 All living things are classified into groups based on the traits they share. Taxonomy is the study of classification. The largest groups into which the scientists divide the groups are called kingdoms.
All living things are classified into groups based on the traits they share. Taxonomy is the study of classification. The largest groups into which the scientists divide the groups are called kingdoms.
Diversity of Animals
 Classifying Animals Diversity of Animals Animals can be classified and grouped based on similarities in their characteristics. Animals make up one of the major biological groups of classification. All
Classifying Animals Diversity of Animals Animals can be classified and grouped based on similarities in their characteristics. Animals make up one of the major biological groups of classification. All
Phylogeny of Animalia (overview)
 The Diversity of Animals 2 Chapter 23 Phylogeny of Animalia (overview) Key features of Chordates Phylum Chordata (the Chordates) includes both invertebrates and vertebrates that share (at some point in
The Diversity of Animals 2 Chapter 23 Phylogeny of Animalia (overview) Key features of Chordates Phylum Chordata (the Chordates) includes both invertebrates and vertebrates that share (at some point in
#8964 Standards-Based Science Investigations 2 Teacher Created Resources, Inc.
 Introduction...4 Locating Simple Science Materials...5 Standards Correlation....7 Thinking About Inquiry Investigations...9 Inquiry Assessment Rubric...12 Student Inquiry Worksheets...13 Sample Inquiry
Introduction...4 Locating Simple Science Materials...5 Standards Correlation....7 Thinking About Inquiry Investigations...9 Inquiry Assessment Rubric...12 Student Inquiry Worksheets...13 Sample Inquiry
Let s Learn About: Vertebrates & Invertebrates. Informational passages, graphic organizers, study guide, flashcards, and MORE!
 Let s Learn About: Vertebrates & Invertebrates Informational passages, graphic organizers, study guide, flashcards, and MORE! Let s Learn About Vertebrates The animal kingdom is comprised of two main categories
Let s Learn About: Vertebrates & Invertebrates Informational passages, graphic organizers, study guide, flashcards, and MORE! Let s Learn About Vertebrates The animal kingdom is comprised of two main categories
Fishes, Amphibians, Reptiles
 Fishes, Amphibians, Reptiles Section 1: What is a Vertebrate? Characteristics of CHORDATES Most are Vertebrates (have a spinal cord) Some point in life cycle all chordates have: Notochord Nerve cord that
Fishes, Amphibians, Reptiles Section 1: What is a Vertebrate? Characteristics of CHORDATES Most are Vertebrates (have a spinal cord) Some point in life cycle all chordates have: Notochord Nerve cord that
Animal phyla. Prior Knowledge Questions:
 1 Name: Animal phyla Core: Prior Knowledge Questions: What do Tim & Moby say about Invertebrates? 2 Want to watch the video again? Go to Invertebrates Brainpop (Username: nfmsbrain password: pop) Word
1 Name: Animal phyla Core: Prior Knowledge Questions: What do Tim & Moby say about Invertebrates? 2 Want to watch the video again? Go to Invertebrates Brainpop (Username: nfmsbrain password: pop) Word
CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS
 CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS Natural Science 5º - 2016/2017 Unit 2: Classification of animals 1-What are the common features of the vertebrate animals? Complete the sentences using the words head spinal column
CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS Natural Science 5º - 2016/2017 Unit 2: Classification of animals 1-What are the common features of the vertebrate animals? Complete the sentences using the words head spinal column
Yr 3-4. excursion activity pack. Year 3 to Year 4
 Yr 3-4 excursion activity pack Year 3 to Year 4 1 great southern coast leafy seadragons pineapplefish old wives shark egg, jaws, teeth & models Region quiz: read these questions before you enter the region
Yr 3-4 excursion activity pack Year 3 to Year 4 1 great southern coast leafy seadragons pineapplefish old wives shark egg, jaws, teeth & models Region quiz: read these questions before you enter the region
Read the following texts 1. Living Things. Both animals and plants are living things because they are born, grow up, reproduce and die.
 Read the following texts 1. Living Things. Both animals and plants are living things because they are born, grow up, reproduce and die. All living things perform all of these functions. A tiger, a deer,
Read the following texts 1. Living Things. Both animals and plants are living things because they are born, grow up, reproduce and die. All living things perform all of these functions. A tiger, a deer,
Kingdom Animalia. All animals are multicellular organisms with real tissues and heterotrophic nutrition
 Keywords Kingdom Animalia Poriferan, -s Coelenterate,-s Echinoderm, -s Mollusc, -s Medusa, -s Polyp, -s Arthropod, -s Arachnid, -s Crustacean, -s Myriapod, -s Radula Exoskeleton / endoskeleton Atrial cavity
Keywords Kingdom Animalia Poriferan, -s Coelenterate,-s Echinoderm, -s Mollusc, -s Medusa, -s Polyp, -s Arthropod, -s Arachnid, -s Crustacean, -s Myriapod, -s Radula Exoskeleton / endoskeleton Atrial cavity
Animal Diversity III: Mollusca and Deuterostomes
 Animal Diversity III: Mollusca and Deuterostomes Objectives: Be able to identify specimens from the main groups of Mollusca and Echinodermata. Be able to distinguish between the bilateral symmetry on a
Animal Diversity III: Mollusca and Deuterostomes Objectives: Be able to identify specimens from the main groups of Mollusca and Echinodermata. Be able to distinguish between the bilateral symmetry on a
Vertebrate Structure and Function
 Vertebrate Structure and Function Part 1 - Comparing Structure and Function Classification of Vertebrates a. Phylum: Chordata Common Characteristics: Notochord, pharyngeal gill slits, hollow dorsal nerve
Vertebrate Structure and Function Part 1 - Comparing Structure and Function Classification of Vertebrates a. Phylum: Chordata Common Characteristics: Notochord, pharyngeal gill slits, hollow dorsal nerve
! Three things needed to survive on land were: ! 1. Have lungs and breathe air. ! 2. Have a body resistant to drying out.
 Marine Reptiles, Birds and Mammals Vertebrates! Invaded the land and are descendants from the bony fish and were able to withstand the conditions on the land.! They evolved two sets of limbs (even snakes)
Marine Reptiles, Birds and Mammals Vertebrates! Invaded the land and are descendants from the bony fish and were able to withstand the conditions on the land.! They evolved two sets of limbs (even snakes)
Phylum Chordata. Fish, Amphibians, Reptiles
 Phylum Chordata Fish, Amphibians, Reptiles Chordates Three different groups Vertebrates Lancelets Tunicates At some point in their lives, they all have four special body parts Notocord Hollow nerve cord
Phylum Chordata Fish, Amphibians, Reptiles Chordates Three different groups Vertebrates Lancelets Tunicates At some point in their lives, they all have four special body parts Notocord Hollow nerve cord
How Animals Live. Chapter 2 Review
 How Animals Live Chapter 2 Review What do animals need to survive? Water Food Air (oxygen) Shelter Butterfly life cycle During the larva stage, the butterfly is called a caterpillar. During the pupa stage,
How Animals Live Chapter 2 Review What do animals need to survive? Water Food Air (oxygen) Shelter Butterfly life cycle During the larva stage, the butterfly is called a caterpillar. During the pupa stage,
Let s learn about ANIMALS. Level : School:.
 Let s learn about ANIMALS Name: Level : School:. 1. CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS There are many different animals and we can classify them according to: Their skeleton: Vertebrates have a skeleton but Invertebrates
Let s learn about ANIMALS Name: Level : School:. 1. CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS There are many different animals and we can classify them according to: Their skeleton: Vertebrates have a skeleton but Invertebrates
Animal Instincts. Modified from a lesson found at
 Animal Instincts Modified from a lesson found at Materials Paper for writing and drawing assembled into a log Reference materials for researching animals Dice Procedure 1. The first task for your group
Animal Instincts Modified from a lesson found at Materials Paper for writing and drawing assembled into a log Reference materials for researching animals Dice Procedure 1. The first task for your group
First Facts by Rebecca Johnson
 First Facts by Rebecca Johnson Use these activity sheets to teach your science content in combination with literacy. There are two photocopiable worksheets to support each of the eight books in the series.
First Facts by Rebecca Johnson Use these activity sheets to teach your science content in combination with literacy. There are two photocopiable worksheets to support each of the eight books in the series.
 2014 Animal Reports Brady Did you know that the Polar Bear may also hunt by swimming beneath ice? Polar bears live in the arctic habitat with other animals like reindeer, arctic wolves, and arctic foxes.
2014 Animal Reports Brady Did you know that the Polar Bear may also hunt by swimming beneath ice? Polar bears live in the arctic habitat with other animals like reindeer, arctic wolves, and arctic foxes.
DEUTEROSTOMES. This presentation contains copyrighted material under the educational fair use exemption to the U.S. copyright law.
 DEUTEROSTOMES This presentation contains copyrighted material under the educational fair use exemption to the U.S. copyright law. Deuterostome Echinodermata body plan! Body plan! Larvae are bilateral!
DEUTEROSTOMES This presentation contains copyrighted material under the educational fair use exemption to the U.S. copyright law. Deuterostome Echinodermata body plan! Body plan! Larvae are bilateral!
AP Biology. Animal Characteristics. Kingdom: Animals. Body Cavity. Animal Evolution. Invertebrate: Porifera. Invertebrate: Cnidaria.
 Kingdom: Animals Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Animal Characteristics Heterotrophs must ingest others for nutrients Multicellular complex bodies No cell walls allows active movement Sexual reproduction
Kingdom: Animals Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Animal Characteristics Heterotrophs must ingest others for nutrients Multicellular complex bodies No cell walls allows active movement Sexual reproduction
Vertebrates. skull ribs vertebral column
 Vertebrates skull ribs vertebral column endoskeleton in cells working together tissues tissues working together organs working together organs systems Blood carries oxygen to the cells carries nutrients
Vertebrates skull ribs vertebral column endoskeleton in cells working together tissues tissues working together organs working together organs systems Blood carries oxygen to the cells carries nutrients
Animal Diversity wrap-up Lecture 9 Winter 2014
 Animal Diversity wrap-up Lecture 9 Winter 2014 1 Animal phylogeny based on morphology & development Fig. 32.10 2 Animal phylogeny based on molecular data Fig. 32.11 New Clades 3 Lophotrochozoa Lophophore:
Animal Diversity wrap-up Lecture 9 Winter 2014 1 Animal phylogeny based on morphology & development Fig. 32.10 2 Animal phylogeny based on molecular data Fig. 32.11 New Clades 3 Lophotrochozoa Lophophore:
The Animal Kingdom. Animal Diversity. Key Concept Animals are a diverse group of organisms that have adaptations to live in water and on land.
 2 The Animal Kingdom Key Concept Animals are a diverse group of organisms that have adaptations to live in water and on land. What You Will Learn The animal kingdom is made up of many different kinds of
2 The Animal Kingdom Key Concept Animals are a diverse group of organisms that have adaptations to live in water and on land. What You Will Learn The animal kingdom is made up of many different kinds of
Lab 9: Inventing Life Forms
 Name: Section: Date: Lab 9: Inventing Life Forms 1 Instructions The purpose of this lab is to create a life form that may have evolved on a planet other than Earth. Follow the instructions below detailing
Name: Section: Date: Lab 9: Inventing Life Forms 1 Instructions The purpose of this lab is to create a life form that may have evolved on a planet other than Earth. Follow the instructions below detailing
Page # Diversity of Arthropoda Crustacea Morphology. Diversity of Arthropoda. Diversity of Arthropoda. Diversity of Arthropoda. Arthropods, from last
 Arthropods, from last time Crustacea are the dominant marine arthropods Crustacea are the dominant marine arthropods any terrestrial crustaceans? Should we call them shellfish? sowbugs 2 3 Crustacea Morphology
Arthropods, from last time Crustacea are the dominant marine arthropods Crustacea are the dominant marine arthropods any terrestrial crustaceans? Should we call them shellfish? sowbugs 2 3 Crustacea Morphology
I will learn to talk about. groups of animals animal characteristics animal habitats. Unit Unit 7
 I am a mammal with both fur and wings. I sleep during the day, and I hunt for food at night. I use high-pitched sounds to find my way around. What am I? I will learn to talk about groups of animals animal
I am a mammal with both fur and wings. I sleep during the day, and I hunt for food at night. I use high-pitched sounds to find my way around. What am I? I will learn to talk about groups of animals animal
Time of Day. Teacher Lesson Plan Nocturnal Animals Pre-Visit Lesson. Overview
 Teacher Lesson Plan Nocturnal Animals Pre-Visit Lesson Duration: 40-50 minutes Minnesota State Science Standard Correlations: 3.4.1.1.2. Wisconsin State Science Standard Correlations: B 4.6, C.4.1, C.4.2
Teacher Lesson Plan Nocturnal Animals Pre-Visit Lesson Duration: 40-50 minutes Minnesota State Science Standard Correlations: 3.4.1.1.2. Wisconsin State Science Standard Correlations: B 4.6, C.4.1, C.4.2
HUMAN APPENDIX BATS & TROPICAL FLOWERS
 HUMAN APPENDIX In humans, the appendix is a short piece of tissue off the large intestine. It is not used by humans for digestive functions. In other mammals, like rabbits and deer, the cecum is a large
HUMAN APPENDIX In humans, the appendix is a short piece of tissue off the large intestine. It is not used by humans for digestive functions. In other mammals, like rabbits and deer, the cecum is a large
Australian Animals. Andrea Buford Arkansas State University
 Australian Animals Andrea Buford Arkansas State University Andrea.buford@smail.astate.edu Animals of Australia Many people visit Australia for its unique animals. Australia has more than 378 mammal species,
Australian Animals Andrea Buford Arkansas State University Andrea.buford@smail.astate.edu Animals of Australia Many people visit Australia for its unique animals. Australia has more than 378 mammal species,
Amphibians. Land and Water Dwellers
 Amphibians Land and Water Dwellers Amphibians Most amphibians do not live completely in the water or completely on land and most must return to water to reproduce http://potch74.files.wordpress.com/2007/09/amphibians.jpg
Amphibians Land and Water Dwellers Amphibians Most amphibians do not live completely in the water or completely on land and most must return to water to reproduce http://potch74.files.wordpress.com/2007/09/amphibians.jpg
Classification. Grouping & Identifying Living Things
 Classification Grouping & Identifying Living Things Taxonomy The study of how living things are classified Classification is the sorting of organisms based on similar characteristics Carolus Linnaeus is
Classification Grouping & Identifying Living Things Taxonomy The study of how living things are classified Classification is the sorting of organisms based on similar characteristics Carolus Linnaeus is
Reptile Round Up. An Educator s Guide to the Program
 Reptile Round Up An Educator s Guide to the Program GRADES: K-3 PROGRAM DESCRIPTION: This guide provided by the Oklahoma Aquarium explores reptiles and their unique characteristics. The Reptile Round Up
Reptile Round Up An Educator s Guide to the Program GRADES: K-3 PROGRAM DESCRIPTION: This guide provided by the Oklahoma Aquarium explores reptiles and their unique characteristics. The Reptile Round Up
Teacher s Guide. All About Baby Animals series
 Teacher s Guide All About Baby Animals series Introduction This teacher s guide helps educate young children about baby animals. Animals live in many different habitats. Some live in grasslands, rainforests,
Teacher s Guide All About Baby Animals series Introduction This teacher s guide helps educate young children about baby animals. Animals live in many different habitats. Some live in grasslands, rainforests,
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT. Zoology Quarter 3. Animal Behavior (Duration 2 Weeks)
 HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Zoology Quarter 3 Animal Behavior (Duration 2 Weeks) Big Idea: Essential Questions: 1. Compare and contrast innate and learned behavior 2. Compare
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Zoology Quarter 3 Animal Behavior (Duration 2 Weeks) Big Idea: Essential Questions: 1. Compare and contrast innate and learned behavior 2. Compare
Reptiles Amphibians ( am-fib-ee-anz ) Fish Birds Mammals
 Chapter 11: Page 94 In the last chapter, you learned how plants go through a natural cycle of life. It is not just plants that go through a life cycle! Animals do too! Remember the definition of species?
Chapter 11: Page 94 In the last chapter, you learned how plants go through a natural cycle of life. It is not just plants that go through a life cycle! Animals do too! Remember the definition of species?
1. Examine the specimens of sponges on the lab table. Which of these are true sponges? Explain your answers.
 Station #1 - Porifera 1. Examine the specimens of sponges on the lab table. Which of these are true sponges? Explain your answers. 2. Sponges are said to have an internal special skeleton. Examine the
Station #1 - Porifera 1. Examine the specimens of sponges on the lab table. Which of these are true sponges? Explain your answers. 2. Sponges are said to have an internal special skeleton. Examine the
The platypus lives in streams, ponds, and rivers in Australia. It closes its eyes under water and uses its bill to dig in the mud to find its food.
 The platypus lives in streams, ponds, and rivers in Australia. It closes its eyes under water and uses its bill to dig in the mud to find its food. The hyena, found in Africa and parts of Asia, weighs
The platypus lives in streams, ponds, and rivers in Australia. It closes its eyes under water and uses its bill to dig in the mud to find its food. The hyena, found in Africa and parts of Asia, weighs
Topic 3: Animals Ch.17 Characteristics of Animals p.338. Distinguishing Characteristics pp
 Topic 3: Animals Ch.17 Characteristics of Animals p.338 - Animals are: - Multicellular. - Ingestive heterotrophs. - Have a division of labour (tissues, organs, systems). - Motile at some stage in their
Topic 3: Animals Ch.17 Characteristics of Animals p.338 - Animals are: - Multicellular. - Ingestive heterotrophs. - Have a division of labour (tissues, organs, systems). - Motile at some stage in their
CHAPTER 3 EATING HABIT OF ANIMALS
 JABAL FARASAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL, RABEGH KSA Affiliated to CBSE New Delhi SCIENCE-CLASS III-CHAPTER-WISE WORKSHEET-2 STUDENT NAME... ROLL NO. DATE CHAPTER 3 EATING HABIT OF ANIMALS I. FILL IN THE BLANKS
JABAL FARASAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL, RABEGH KSA Affiliated to CBSE New Delhi SCIENCE-CLASS III-CHAPTER-WISE WORKSHEET-2 STUDENT NAME... ROLL NO. DATE CHAPTER 3 EATING HABIT OF ANIMALS I. FILL IN THE BLANKS
Vertebrates. What is a vertebrate?
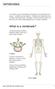 Vertebrates In a modern system of classification, all animals can be divided into two groups vertebrates and invertebrates. Vertebrates are animals that have a skeleton inside their bodies. Biologists
Vertebrates In a modern system of classification, all animals can be divided into two groups vertebrates and invertebrates. Vertebrates are animals that have a skeleton inside their bodies. Biologists
students a hint to which habitat the animal could live in. If this information is above your students reading level, you may want
 tocutthecardsinhalfandonlyusethepictures. Note to teacher: The text on these cards is designed to give students a hint to which habitat the animal could live in. If this information is above your students
tocutthecardsinhalfandonlyusethepictures. Note to teacher: The text on these cards is designed to give students a hint to which habitat the animal could live in. If this information is above your students
There are 35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical
 Name 1 There are 35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical characteristics. All animals share several common
Name 1 There are 35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical characteristics. All animals share several common
5 pt. 10 pt. 15 pt. 20 pt. 25 pt
 Final Jeopardy Characteristics of Vertebrates Characteristics of Fish Amphibians Reptiles Chapter 16 Vocabulary 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 20 pt
Final Jeopardy Characteristics of Vertebrates Characteristics of Fish Amphibians Reptiles Chapter 16 Vocabulary 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 20 pt
May 10, SWBAT analyze and evaluate the scientific evidence provided by the fossil record.
 May 10, 2017 Aims: SWBAT analyze and evaluate the scientific evidence provided by the fossil record. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing our AIMS: E.3-Examining
May 10, 2017 Aims: SWBAT analyze and evaluate the scientific evidence provided by the fossil record. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing our AIMS: E.3-Examining
Class Reptilia Testudines Squamata Crocodilia Sphenodontia
 Class Reptilia Testudines (around 300 species Tortoises and Turtles) Squamata (around 7,900 species Snakes, Lizards and amphisbaenids) Crocodilia (around 23 species Alligators, Crocodiles, Caimans and
Class Reptilia Testudines (around 300 species Tortoises and Turtles) Squamata (around 7,900 species Snakes, Lizards and amphisbaenids) Crocodilia (around 23 species Alligators, Crocodiles, Caimans and
Mollusks. Ch. 13, pgs
 Mollusks Ch. 13, pgs. 364-368 368 Characteristics of Mollusks Mollusks have Bilateral Symmetry Most mollusks live in water, but some live on land. Examples of mollusks are snails, clams, and squids. Body
Mollusks Ch. 13, pgs. 364-368 368 Characteristics of Mollusks Mollusks have Bilateral Symmetry Most mollusks live in water, but some live on land. Examples of mollusks are snails, clams, and squids. Body
Chapter 7. Marine Animals Without a Backbone
 Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Echinoderms Characteristics of Phylum: Name means "Spiny Skin" Endoskeleton Skeleton on inside of body Covered by tissue All 7000 species exclusively marine
Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Echinoderms Characteristics of Phylum: Name means "Spiny Skin" Endoskeleton Skeleton on inside of body Covered by tissue All 7000 species exclusively marine
Suitable age group: 10 and older These printable lessons will be added to as time goes along. (Solutions to questions are not provided)
 Suitable age group: 10 and older These printable lessons will be added to as time goes along. (Solutions to questions are not provided) 1 Australian Mammals 1 Provide information about each animal, including
Suitable age group: 10 and older These printable lessons will be added to as time goes along. (Solutions to questions are not provided) 1 Australian Mammals 1 Provide information about each animal, including
"Mr. Schreiter's Mixed Up Animals" By Mr. Schreiter's Class
 This is my jellyuar. It has tentacles like a jellyfish. It has sharp teeth like a jaguar. It sounds like a jellyfish. It eats fish and deer and pigs. The jellyuar has no bones like a jellyfish. It explores
This is my jellyuar. It has tentacles like a jellyfish. It has sharp teeth like a jaguar. It sounds like a jellyfish. It eats fish and deer and pigs. The jellyuar has no bones like a jellyfish. It explores
Review Inverts 4/17/15. What Invertebrates have we learned about so far? Porifera. Cnidaria. Ctenophora. Molluscs
 Review Inverts What Invertebrates have we learned about so far? Porifera sponges Cnidaria jellyfishes, sea anemones, coral Ctenophora comb jellies Molluscs snails, bivalves, octopuses, squid, cuglefish
Review Inverts What Invertebrates have we learned about so far? Porifera sponges Cnidaria jellyfishes, sea anemones, coral Ctenophora comb jellies Molluscs snails, bivalves, octopuses, squid, cuglefish
ADAPTATION IN ANIMALS. 1. Which body feature of a frog MAINLY helps it to capture a flying insect? Ans
 Name : Subject : Science Class : V Roll No. : Date : SECTION A Choose the correct alternative ADAPTATION IN ANIMALS 1. Which body feature of a frog MAINLY helps it to capture a flying insect? a. Long,
Name : Subject : Science Class : V Roll No. : Date : SECTION A Choose the correct alternative ADAPTATION IN ANIMALS 1. Which body feature of a frog MAINLY helps it to capture a flying insect? a. Long,
08 AMPHIBIANS & REPTILES (B) AND HERPETOLOGY (C) TRAINING HANDOUT By Karen L. Lancour
 08 AMPHIBIANS & REPTILES (B) AND HERPETOLOGY (C) TRAINING HANDOUT By Karen L. Lancour This event will test knowledge of amphibians, turtles, crocodiles & reptiles. The Official National List will be used
08 AMPHIBIANS & REPTILES (B) AND HERPETOLOGY (C) TRAINING HANDOUT By Karen L. Lancour This event will test knowledge of amphibians, turtles, crocodiles & reptiles. The Official National List will be used
Use your Fact Files to circle the correct lion facts. Which food would the lion rather eat? About how many years does a lion live?
 Use your Fact Files to circle the correct lion facts. Which food would the lion rather eat? About how many years does a lion live? 25 50 1 16 GRADE ONE ZOO ANIMALS SCIENCE 001 Which lion would typically
Use your Fact Files to circle the correct lion facts. Which food would the lion rather eat? About how many years does a lion live? 25 50 1 16 GRADE ONE ZOO ANIMALS SCIENCE 001 Which lion would typically
Animals and Their Environments II
 Animals and Their Environments II Grade Level: K, 2 Content Area: Life science Core Area: Exploring Organisms and Their Environments, Animals and Their Environments Lesson Overview: Students will compare
Animals and Their Environments II Grade Level: K, 2 Content Area: Life science Core Area: Exploring Organisms and Their Environments, Animals and Their Environments Lesson Overview: Students will compare
MANSFIELD SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL / SCIENCE / A. There is no God. B. All living things on Earth are related.
 The Evidence of Evolution Name: Date: 1. Biological Evolutions makes 2 very bold claims about living creatures.what are they circle 2. A. There is no God. B. All living things on Earth are related. C.
The Evidence of Evolution Name: Date: 1. Biological Evolutions makes 2 very bold claims about living creatures.what are they circle 2. A. There is no God. B. All living things on Earth are related. C.
Amphibians and Reptiles Division B
 Amphibians and Reptiles Division B Amphibians and Reptiles KEY (corrected) Station I siren 1. Write the scientific name of this specimen (siren lacertian) 2. To which order do these belong?
Amphibians and Reptiles Division B Amphibians and Reptiles KEY (corrected) Station I siren 1. Write the scientific name of this specimen (siren lacertian) 2. To which order do these belong?
Field Lesson: Reptiles and Amphibians
 Field Lesson: Reptiles and Amphibians State Core Standards 5.2 Interaction and Change: Force, energy, matter, and organisms interact within living and non-living systems Content Standards 5.2L.1 Explain
Field Lesson: Reptiles and Amphibians State Core Standards 5.2 Interaction and Change: Force, energy, matter, and organisms interact within living and non-living systems Content Standards 5.2L.1 Explain
35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external
 35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical characteristics. All animals share several common characteristics:
35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical characteristics. All animals share several common characteristics:
What is the evidence for evolution?
 What is the evidence for evolution? 1. Geographic Distribution 2. Fossil Evidence & Transitional Species 3. Comparative Anatomy 1. Homologous Structures 2. Analogous Structures 3. Vestigial Structures
What is the evidence for evolution? 1. Geographic Distribution 2. Fossil Evidence & Transitional Species 3. Comparative Anatomy 1. Homologous Structures 2. Analogous Structures 3. Vestigial Structures
ì<(sk$m)=bdhiaa< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Infer Call Outs Captions Labels Glossary Living Things Scott Foresman Science 2.4 ì
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Infer Call Outs Captions Labels Glossary Living Things Scott Foresman Science 2.4 ì
Characteristics of Tetrapods
 Marine Tetrapods Characteristics of Tetrapods Tetrapod = four-footed Reptiles, Birds, & Mammals No marine species of amphibian Air-breathing lungs Class Reptilia Saltwater Crocodiles, Sea turtles, sea
Marine Tetrapods Characteristics of Tetrapods Tetrapod = four-footed Reptiles, Birds, & Mammals No marine species of amphibian Air-breathing lungs Class Reptilia Saltwater Crocodiles, Sea turtles, sea
2018 Copyright Jolie Canoli and Friends. For personal and educational use only. Find more resources at joliecanoli.com
 PHYLUM: BODY PLANS After the classification of Kingdom comes the category Phylum. The Phylum category of Animals puts animals with similar body types together. There are many phylum, but we will study
PHYLUM: BODY PLANS After the classification of Kingdom comes the category Phylum. The Phylum category of Animals puts animals with similar body types together. There are many phylum, but we will study
Outline. Identifying Idaho Amphibians and Reptiles
 Identifying Idaho Amphibians and Reptiles Wildlife Ecology, University of Idaho Fall 2011 Charles R. Peterson Herpetology Laboratory Department of Biological Sciences, Idaho Museum of Natural History Idaho
Identifying Idaho Amphibians and Reptiles Wildlife Ecology, University of Idaho Fall 2011 Charles R. Peterson Herpetology Laboratory Department of Biological Sciences, Idaho Museum of Natural History Idaho
Museum of Zoology Department Vision Message Objectives
 Museum of Zoology Department The museum of Zoology department was established in Shawwal 1390 H (1970) with a few samples of birds and some young mammals. The number of specimens in the museum increased
Museum of Zoology Department The museum of Zoology department was established in Shawwal 1390 H (1970) with a few samples of birds and some young mammals. The number of specimens in the museum increased
Objectives: Outline: Idaho Amphibians and Reptiles. Characteristics of Amphibians. Types and Numbers of Amphibians
 Natural History of Idaho Amphibians and Reptiles Wildlife Ecology, University of Idaho Fall 2005 Charles R. Peterson Herpetology Laboratory Department of Biological Sciences, Idaho Museum of Natural History
Natural History of Idaho Amphibians and Reptiles Wildlife Ecology, University of Idaho Fall 2005 Charles R. Peterson Herpetology Laboratory Department of Biological Sciences, Idaho Museum of Natural History
Doug Scull s Science and Nature
 THE SNAKES PART ONE Doug Scull s Science and Nature Feared by some, worshiped by others, snakes are some of the most misunderstood animals on Earth. Some people are fearful of snakes Some people worship
THE SNAKES PART ONE Doug Scull s Science and Nature Feared by some, worshiped by others, snakes are some of the most misunderstood animals on Earth. Some people are fearful of snakes Some people worship
Class Reptilia. Lecture 19: Animal Classification. Adaptations for life on land
 Lecture 19: Animal Classification Class Reptilia Adaptations for life on land بيض جنيني egg. Amniotic Water-tight scales. One occipital condyle one point of attachement of the skull with the vertebral
Lecture 19: Animal Classification Class Reptilia Adaptations for life on land بيض جنيني egg. Amniotic Water-tight scales. One occipital condyle one point of attachement of the skull with the vertebral
! Taxonomic Scheme of the 2018 Official Science Olympiad NATIONAL HERPETOLOGY List
 DISCLAIMER This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may be some changes in the final copy of the rules. The rules which will be in your Coaches Manual and Student Manuals will be the official
DISCLAIMER This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may be some changes in the final copy of the rules. The rules which will be in your Coaches Manual and Student Manuals will be the official
Bones and Bellies Clue Card 1
 Bones and Bellies Clue Card 1 Land Animals to the land food web. Animal A I am a carnivorous marsupial. My upper canine teeth are slightly larger than the lower canines. My molar teeth are sharp and pointy
Bones and Bellies Clue Card 1 Land Animals to the land food web. Animal A I am a carnivorous marsupial. My upper canine teeth are slightly larger than the lower canines. My molar teeth are sharp and pointy
Effective August 2007 All indicators in Standard / 11
 6.3.1 Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds,
6.3.1 Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds,
Magic Story-telling Souvenir Coloring Books
 Magic Story-telling Souvenir Coloring Books The following are a few pages from our second book My Zoo Adventure Coloring Book. Actual page sizes are approximately 8.5 x 12 For wholesale prices to the souvenir
Magic Story-telling Souvenir Coloring Books The following are a few pages from our second book My Zoo Adventure Coloring Book. Actual page sizes are approximately 8.5 x 12 For wholesale prices to the souvenir
Biology. Slide 1of 50. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 50 2of 50 Phylogeny of Chordates Nonvertebrate chordates Jawless fishes Sharks & their relatives Bony fishes Reptiles Amphibians Birds Mammals Invertebrate ancestor 3of 50 A vertebrate dry,
Biology 1of 50 2of 50 Phylogeny of Chordates Nonvertebrate chordates Jawless fishes Sharks & their relatives Bony fishes Reptiles Amphibians Birds Mammals Invertebrate ancestor 3of 50 A vertebrate dry,
A. Body Temperature Control Form and Function in Mammals
 Taxonomy Chapter 22 Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Mammals Characteristics Evolution of Mammals Have hair and First appear in the mammary glands Breathe air, 4chambered heart, endotherms
Taxonomy Chapter 22 Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Mammals Characteristics Evolution of Mammals Have hair and First appear in the mammary glands Breathe air, 4chambered heart, endotherms
EXTERNAL FEATURES TEACHER RESOURCE BOOKLET
 EXTERNAL FEATURES TEACHER RESOURCE BOOKLET Koala, Phascolarctos cinereus. Image: QM. Saltwater crocodile, Crocodylus porosus. Image: QM. Poinciana Longicorn Beetle, Agrianome spinicollis. Image: Jeff Wright,
EXTERNAL FEATURES TEACHER RESOURCE BOOKLET Koala, Phascolarctos cinereus. Image: QM. Saltwater crocodile, Crocodylus porosus. Image: QM. Poinciana Longicorn Beetle, Agrianome spinicollis. Image: Jeff Wright,
Animals and Their Environments II
 Animals and Their Environments II Grade Level: K, 2 Content Area: Life science Core Area: Exploring Organisms and Their Environments, Animals and Their Environments Lesson Overview: Students will compare
Animals and Their Environments II Grade Level: K, 2 Content Area: Life science Core Area: Exploring Organisms and Their Environments, Animals and Their Environments Lesson Overview: Students will compare
Draw a line from the names below to the animals they match. Red Fox. Wild Turkey. Wood Duck. White-tailed Deer. Black Bear
 Science and Nature Cente Draw a line from the names below to the animals they match. Which animal do you like the best that you see in the nature center? Red Fox Wild Turkey Wood Duck White-tailed Deer
Science and Nature Cente Draw a line from the names below to the animals they match. Which animal do you like the best that you see in the nature center? Red Fox Wild Turkey Wood Duck White-tailed Deer
Life Cycles Learning Journal
 Life Cycles Learning Journal Zoologist: Lesson 1 Name Date Animal Classification Choose an animal that you read about today. How can you classify this animal? Use details from the text to support your
Life Cycles Learning Journal Zoologist: Lesson 1 Name Date Animal Classification Choose an animal that you read about today. How can you classify this animal? Use details from the text to support your
Teacher Workbooks. Language Arts Series Internet Reading Comprehension Oceans Theme, Vol. 1
 Teacher Workbooks Language Arts Series Internet Reading Comprehension Oceans Theme, Vol. 1 Copyright 2003 Teachnology Publishing Company A Division of Teachnology, Inc. For additional information, visit
Teacher Workbooks Language Arts Series Internet Reading Comprehension Oceans Theme, Vol. 1 Copyright 2003 Teachnology Publishing Company A Division of Teachnology, Inc. For additional information, visit
Natural Science 1º ESO
 Unit 5 y 6. Animals. NAME Adapted from Natural Science. 1º ESO. Anaya Natural Science 1º ESO 0 INDEX 1. VOCABULARY... 1 2. VOCABULARIO... 2 3. UNIT CHART...Cover and 3 4. UNIT ACTIVITIES AND NOTES... 4-14
Unit 5 y 6. Animals. NAME Adapted from Natural Science. 1º ESO. Anaya Natural Science 1º ESO 0 INDEX 1. VOCABULARY... 1 2. VOCABULARIO... 2 3. UNIT CHART...Cover and 3 4. UNIT ACTIVITIES AND NOTES... 4-14
Get the other MEGA courses!
 www.thesimplehomeschool.com Simple Schooling BUGS MEGA course is ten weeks of all about bugs! This course grabs your student s attention and never lets go! Grades K-3 Get the other MEGA courses! Simple
www.thesimplehomeschool.com Simple Schooling BUGS MEGA course is ten weeks of all about bugs! This course grabs your student s attention and never lets go! Grades K-3 Get the other MEGA courses! Simple
Pasig Catholic College. Grade School Department 103 S.Y Be with Jesus, be with the Poor. Science 5 SECOND QUARTER Activity Sheet # 1
 PCC @ 103 Be with Jesus, be with the Poor Activity Sheet # 1 TYPE OF ACTIVITY: Discussion on Animal Adaptations: Natural Habitat : Natural Habitat of Animals Learning Objectives : Describe the different
PCC @ 103 Be with Jesus, be with the Poor Activity Sheet # 1 TYPE OF ACTIVITY: Discussion on Animal Adaptations: Natural Habitat : Natural Habitat of Animals Learning Objectives : Describe the different
What Is a Vertebrate?
 Name Date _ Class What Is a Vertebrate? This section explains the charactertsftcs of apt:mals With backbones. Use Target Reading Skills After you read the section, reread the paragraphs that contatn definition
Name Date _ Class What Is a Vertebrate? This section explains the charactertsftcs of apt:mals With backbones. Use Target Reading Skills After you read the section, reread the paragraphs that contatn definition
UNIT: INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS 1º ESO BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY
 UNIT: INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS 1º ESO BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 2015/2016 What do they have in common? What are their differences? What is the theme for the next unit? Vertebrates and Invertebrates 1 Label the animals
UNIT: INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS 1º ESO BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 2015/2016 What do they have in common? What are their differences? What is the theme for the next unit? Vertebrates and Invertebrates 1 Label the animals
ì<(sk$m)=bdibci< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Labels Diagram Glossary Animals Scott Foresman Science 3.2 ì
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Labels Diagram Glossary Animals Scott Foresman Science 3.2 ì
