Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater
|
|
|
- Eleanore Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AQUATIC ORGANISMS PLATES Plate 1A. Cyanobacteria and green algae. Dimensions refer to individual cells or filaments. All organisms inhabit fresh water. Cyanobacteria (Phylum Cyanophyta): A Aphanizomenon, aggregate of filaments (3 6 µm) B Aphanizomenon, detail
2 C Gloeotrichia, portion of colony (cells 7 9 µm diameter)
3 D Gloeotrichia, detail Green algae (Phylum Chlorophyta): E Dictyosphaerium (8 14 µm)
4 F Westella (5 7 µm)
5 G Selenastrum (6 7 µm)
6 H Tetrastrum (5 9 µm)
7 I Crucigenia (5 8 µm)
8 J Ankistrodesmus (2 3 µm)
9 K Schizomeris(12 18 µm)
10 Plate 1B. Yellow-green, green, and golden-brown algae. Dimensions refer to individual cells or filaments. All organisms inhabit fresh water. Yellow-green algae (Phylum Xanthophyta): L Botrydium (1 2 µm)
11 Green algae (Phylum Chlorophyta): M Stichococcus (3 µm)
12 N Hyalotheca (12 30 µm) O Pithopora ( µm)
13 P Microthamnion (2 4 µm)
14 Q Dichotomosiphon( µm) Golden-brown algae (Phylum Chrysophyta) (diatoms):
15 R Cocconeis (10 µm) S Achnanthes (10 µm) T Cyclotella (10 µm)
16 U Coscinodiscus (120 µm)
17 V Rhizosolenia (5 15 µm) W Skeletonema (5 15 µm)
18 X Biddulphia (100 µm) Plate 2A. Types of large marine algae.
19 Green algae (Phylum Chlorophyta): A Sponge weed, Codium (30 40 cm) B Sea lettuce, Ulva (20 cm)
20 C Sargassum ( cm) Brown algae (Phylum Phaeophyta):
21 D Rockweed, Fucus (75 cm) E Giant kelp, Macrocystis (30 m)
22 F Enteromorpha (40 cm)
23 G Bull whip, Nereocystis (20 m) Plate 2B. Types of large marine algae and marine grasses: Red algae (Phylum Rhodophyta): H Corallina (4 cm)
24 I Gracilaria (50 cm)
25 J Gigartina (30 40 cm) K Plocamium (30 cm)
26 L Champia (1 6 cm) Marine grasses (Phylum Spermatophyta):
27 M Eelgrass, Vallisneria (50 cm) N Eelgrass, Zostera (45 cm)
28 Plate 3A. Higher plants. All floating, freshwater inhabitants. Phylum Spermatophyta: A Great duckweed, Spirodela (8 mm)
29 B Water hyacinth, Eichhornia (22 cm)
30 C Lesser duckweed, Lemna (5 cm) D Watermeal, Wolffia (1 1.5 mm) Phylum Pteridophyta:
31 E Water velvet, Azolla (1 cm) F Water fern, Salvinia (4 cm)
32 Plate 3B. Higher plants. All freshwater inhabitants (Phylum Spermatophyta). Submerged: G Pondweed, Potamogeton (30 60 cm)
33 H Coontail, Ceratophyllum (30 cm)
34 I Waterweed, Elodea (15 cm) J Water milfoil, Myriophyllum (30 cm)
35 K Naiad, Najas (60 cm) Emersed:
36 L Pickerelweed, Pontederia (60 cm) Plate 3C. Higher plants. All freshwater inhabitants (Phylum Spermatophyta), emersed. M Sweet flag, Acorus (30 cm)
37 N Spike rush, Eleocharis (30 cm) O Cattail, Typha (1 2 m)
38 Plate 4A. Flagellates. Pigmented flagellates, various phyla. Freshwater inhabitants. A Pteromonas (5 18 µm)
39 B Lobomonas (5 14 µm) C Haematococcus (40 45 µm)
40 D Chromulina (4 10 µm) E Cryptomonas (6 12 µm)
41 F Ochromonas (7 14 µm) G Chloramoeba (10 15 µm)
42 H Platydorina (66 70 µm, colony)
43 Plate 4B. Flagellates. Freshwater inhabitants except as noted. Pigmented (various phyla): I Pleodorina (8 10 µm) J Gonyaulax (marine) (10 µm) K Gymnodinium (marine) (10 µm)
44 Nonpigmented (Phylum Protozoa): L Astasia (40 50 µm) M Bodo (11 22 µm)
45 N Dinomonas (15 16 µm) O Oikomonas (5 20 µm) P Anisonema (14 60 µm)
46 Q Cercomonas (10 36 µm) R Tetramitus (11 30 µm) S Dendromonas (8 µm)
47 Plate 5A. Amoebas (Phylum Protozoa). A Naegleria, (a) amoeboid stage, (b) flagellated stage, (c) cyst stage (10 36 µm) B Amoeba, (a) amoeboid state, (c) cyst stage ( µm)
48 C Acanthamoeba (Hartmannella), (a) amoeboid stage, (c) cyst stage (15 25 µm) D Amoeba radiosa ( µm) E Pelomyxa ( mm)
49 F Difflugia (40 µm) G Actinophrys (25 50 µm) Plate 5B. Amoebas and nonpigmented flagellates (Phylum Protozoa). Amoebas: H Arcella (side view) ( µm)
50 I Arcella (top view) ( µm) Nonpigmented flagellates: J Peranema (40 70 µm)
51 K Mastigamoeba ( µm)
52 L Anthophysa (5 6 µm)
53 M Monas (5 16 µm) Plate 6. Ciliates (Phylum Protozoa). A Lionotus (100 µm) B Pleuronema ( µm)
54 C Paramecium ( µm) D Colpoda ( µm)
55 E Stylonychia ( µm) F Euplotes ( µm)
56 G Aspidisca (30 50 µm) H Vorticella ( µm)
57 I Tintinnidium ( µm) Plate 7. Sponges and coelenterates.
58 Sponges (Phylum Porifera): A Vase sponge, marine B Sponge spicule types
59 C Trochospongilla, 3 gemmules, freshwater D Purple sponge, Haliclona, marine Coelenterates (Phylum Cnidaria): E Hydra extended with bud, freshwater
60 F Obelia extended (a) and contracted (b) hydranth and gonothe (c), marine
61 G Jellyfish (medusoid stage), Craspedascusta, freshwater H Sea anemone, Anthopleura, marine
62 Plate 8. Rotifers (Phylum Rotifera). All freshwater inhabitants. Dimensions include spines. A Epiphanes (0.6 mm)
63 B Philodina (0.4 mm) C Euchlanis (0.25 mm)
64 D Proales (0.45 mm) E Brachionus (0.2 mm)
65 F Monostyla (0.15 mm) G Kellicottia (1 mm)
66 H Keratella (0.2 mm) I Notholca (0.2 mm)
67 J Trichocerca (0.6 mm) K Synchaeta (0.26 mm)
68 L Filinia (0.15 mm) M Polyarthra (0.175 mm)
69 Plate 9. Roundworms, flatworms, and segmented worms. (a) anterior end, (b) posterior end, (c) tubes, (d) mud surface, (e) setae, (f) anterior sucker, (g) posterior sucker. All freshwater inhabitants. Roundworms (Phylum Nematoda): A Plectus (1.0 mm)
70 B Tripyla (1.0 mm) Flatworms (Phylum Platyhelminthes):
71 C Planaria (5 13 mm) Segmented worms (Phylum Annelida, Class Oligochaeta): D Tubifex, sludgeworm (2.5 5 cm)
72 E Dero (3 7 mm) Segmented worms (Phylum Annelida, Class Polychaeta):
73 F Manayunkia, lives in tube (5 mm) Segmented worms (Phylum Annelida, Class Hirudinea): G Leech (3 6 cm)
74 H Leech (3 6 cm)
75 Plate 10. Segmented marine worms (Phylum Annelida, Class Polychaeta). A Scale worm, Halosydna (5 cm) B Syllids, Typosyllis (2 5 cm)
76 C Nereid, Nereis (4 15 cm) D Nephtyid, Nephtys (5 25 cm) E Onuphid, Diopatra, in tube covered with shells (5 25 cm)
77 F Spionid, Polydora (2 4 cm) G Capitellid, Capitella (2 4 cm)
78 H Ice cream cone worm, Pectinaria (1 3 cm) I Feather duster worm, Sabella (10 15 cm)
79 J Chaetopterid, Chaetopterus, lives in U-shaped tube (10 20 cm) K Terebellid, Pista (10 15 cm)
80 Plate 11. Crustaceans (Phylum Arthropoda) all freshwater inhabitants, except as noted. Order Cladocera: A Leptodora (9 mm)
2018 Copyright Jolie Canoli and Friends. For personal and educational use only. Find more resources at joliecanoli.com
 PHYLUM: BODY PLANS After the classification of Kingdom comes the category Phylum. The Phylum category of Animals puts animals with similar body types together. There are many phylum, but we will study
PHYLUM: BODY PLANS After the classification of Kingdom comes the category Phylum. The Phylum category of Animals puts animals with similar body types together. There are many phylum, but we will study
Waneta and Lamoka Lakes 2008 Plant Community Response to the Application of the Herbicide Triclopyr to Control Eurasian Watermilfoil
 Waneta and Lamoka Lakes 2008 Plant Community Response to the Application of the Herbicide Triclopyr to Control Eurasian Watermilfoil Robert L. Johnson rlj5@cornell.edu Nicholas Sledziona tiohero@gmail.com
Waneta and Lamoka Lakes 2008 Plant Community Response to the Application of the Herbicide Triclopyr to Control Eurasian Watermilfoil Robert L. Johnson rlj5@cornell.edu Nicholas Sledziona tiohero@gmail.com
AP Biology. Animal Characteristics. Kingdom: Animals. Body Cavity. Animal Evolution. Invertebrate: Porifera. Invertebrate: Cnidaria.
 Kingdom: Animals Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Animal Characteristics Heterotrophs must ingest others for nutrients Multicellular complex bodies No cell walls allows active movement Sexual reproduction
Kingdom: Animals Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Animal Characteristics Heterotrophs must ingest others for nutrients Multicellular complex bodies No cell walls allows active movement Sexual reproduction
Marine Invertebrate STUDY GUIDE
 Marine Invertebrate STUDY GUIDE Invertebrate Basics: What do all invertebrates have in common? A. Phylum Porifera: Example organism: Symmetry: Movement Type: Feeding type: Pores: Ostia: Oscula: Choanocyte:
Marine Invertebrate STUDY GUIDE Invertebrate Basics: What do all invertebrates have in common? A. Phylum Porifera: Example organism: Symmetry: Movement Type: Feeding type: Pores: Ostia: Oscula: Choanocyte:
Sponges and cnidarians were the first animals to evolve from a multicellular ancestor.
 Section 3: Sponges and cnidarians were the first animals to evolve from a multicellular ancestor. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review diploid New filter feeder sessile
Section 3: Sponges and cnidarians were the first animals to evolve from a multicellular ancestor. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review diploid New filter feeder sessile
Chapter 33. Table of Contents. Section 1 Porifera. Section 2 Cnidaria and Ctenophora. Sponges, Cnidarians, and Ctenophores
 Sponges, Cnidarians, and Ctenophores Table of Contents Section 1 Porifera Section 2 Cnidaria and Ctenophora Section 1 Porifera Objectives Describe the basic body plan of a sponge. Describe the process
Sponges, Cnidarians, and Ctenophores Table of Contents Section 1 Porifera Section 2 Cnidaria and Ctenophora Section 1 Porifera Objectives Describe the basic body plan of a sponge. Describe the process
Animal phyla. Prior Knowledge Questions:
 1 Name: Animal phyla Core: Prior Knowledge Questions: What do Tim & Moby say about Invertebrates? 2 Want to watch the video again? Go to Invertebrates Brainpop (Username: nfmsbrain password: pop) Word
1 Name: Animal phyla Core: Prior Knowledge Questions: What do Tim & Moby say about Invertebrates? 2 Want to watch the video again? Go to Invertebrates Brainpop (Username: nfmsbrain password: pop) Word
Objectives. Chapter 8. Objectives. I. What Are Animals? II. Sponges. Marine Phyla
 Objectives Chapter 8 Sponges, Cnidarians, Comb Jellies, and Marine Worms Describe the structure and function of sponge biology. Understand the role sponges play in ecoystems. Differentiate between Cnidarians
Objectives Chapter 8 Sponges, Cnidarians, Comb Jellies, and Marine Worms Describe the structure and function of sponge biology. Understand the role sponges play in ecoystems. Differentiate between Cnidarians
#1 Porifera (Sponges)
 Virtual Coral Reef #1 Porifera (Sponges) Sea sponges, are Sessile animals; they don t move. They pick a spot on a rock, sandy ocean floor or even another animal, latch on and stay put. They have no organs
Virtual Coral Reef #1 Porifera (Sponges) Sea sponges, are Sessile animals; they don t move. They pick a spot on a rock, sandy ocean floor or even another animal, latch on and stay put. They have no organs
Porifera. subtidal. Porifera. porifera. Cnidaria. Haliclona ecbasis Purplish intertidal sponge Worldwide distribution
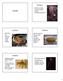 Porifera subtidal Haliclona ecbasis Purplish intertidal sponge Worldwide distribution porifera Porifera Suberites sp. Often on shells of hermit crabs, subtidal Myxilla incrustans Rough scallop sponge Can
Porifera subtidal Haliclona ecbasis Purplish intertidal sponge Worldwide distribution porifera Porifera Suberites sp. Often on shells of hermit crabs, subtidal Myxilla incrustans Rough scallop sponge Can
Topic Page: Invertebrates
 Topic Page: Invertebrates Definition: invertebrate from The Penguin Dictionary of Science General term of convenience given to an animal species that is not a member of the chordate subphylum Vertebrata.
Topic Page: Invertebrates Definition: invertebrate from The Penguin Dictionary of Science General term of convenience given to an animal species that is not a member of the chordate subphylum Vertebrata.
1. Examine the specimens of sponges on the lab table. Which of these are true sponges? Explain your answers.
 Station #1 - Porifera 1. Examine the specimens of sponges on the lab table. Which of these are true sponges? Explain your answers. 2. Sponges are said to have an internal special skeleton. Examine the
Station #1 - Porifera 1. Examine the specimens of sponges on the lab table. Which of these are true sponges? Explain your answers. 2. Sponges are said to have an internal special skeleton. Examine the
Table 1. Nitrogen Preference of Aquatic Plant Species [My book (p. 108) cites the original scientific papers with the experimental data.
 1 PLANTS versus FILTERS By Diana Walstad July 2014 Ammonium and nitrite are detrimental to fish health. 1 Most hobbyists rely on filters (i.e., biological filtration or nitrification) to remove these toxins
1 PLANTS versus FILTERS By Diana Walstad July 2014 Ammonium and nitrite are detrimental to fish health. 1 Most hobbyists rely on filters (i.e., biological filtration or nitrification) to remove these toxins
Some Facts about... Amphibians
 Amphibians Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates that live part of their lives in water and part on land. Amphibians eggs are laid in water and they are born there. They begin their lives with gills
Amphibians Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates that live part of their lives in water and part on land. Amphibians eggs are laid in water and they are born there. They begin their lives with gills
Cnidaria. BIO2135 Animal Form & Function. Page 1. Gap (septate) junctions (Connexon) Symmetry types
 Cnidaria 1 Animal innovations Gap (Septate) junctions Loss of the choanocytes Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora Rotifera Annelida Mollusca Sipuncula
Cnidaria 1 Animal innovations Gap (Septate) junctions Loss of the choanocytes Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora Rotifera Annelida Mollusca Sipuncula
Analyzing Organismal Traits through Cladograms
 Analyzing Organismal Traits through Cladograms Above you will see a cladogram of marine taxa. Your focus will be only on Phyla Porifera, Cnidaria, and Echinodermata and the cladogram that they show. Directions:
Analyzing Organismal Traits through Cladograms Above you will see a cladogram of marine taxa. Your focus will be only on Phyla Porifera, Cnidaria, and Echinodermata and the cladogram that they show. Directions:
BIOL 1220 General Biology II Minimum contact hours/minutes 6 contact hours per week * 15 weeks = 90 contact hours per course
 COURSE ADDENDUM The following information identifies the requirements for each course delivered as dual enrollment (College Credit Plus) at a high school. As part of the Memorandum of Understanding for
COURSE ADDENDUM The following information identifies the requirements for each course delivered as dual enrollment (College Credit Plus) at a high school. As part of the Memorandum of Understanding for
Today s Class. Go over viewfinder lab A closer look at the Animal Kingdom Taxonomy Worksheet
 Kingdom Animalia Today s Class Go over viewfinder lab A closer look at the Animal Kingdom Taxonomy Worksheet Viewfinder Kingdom: Animalia Cells: multicellular Food: eats other organisms Movement: moves
Kingdom Animalia Today s Class Go over viewfinder lab A closer look at the Animal Kingdom Taxonomy Worksheet Viewfinder Kingdom: Animalia Cells: multicellular Food: eats other organisms Movement: moves
Marine Consumers OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5
 Marine Consumers OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Goetze/Peijnenburg Consumer Types Grazers (Herbivore) Predators Parasites Kill their prey (Herbivore, Carnivore, or Omnivore) Scavengers Detritivores Decomposers
Marine Consumers OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Goetze/Peijnenburg Consumer Types Grazers (Herbivore) Predators Parasites Kill their prey (Herbivore, Carnivore, or Omnivore) Scavengers Detritivores Decomposers
Kingdom: Phylum: Simple Sponge drawing (labeled) Name: Ocean Zone: Ocean Classification Station Activity Station 1: Sponges
 Station 1: Sponges Sponge Observations: Simple Sponge drawing (labeled) Types of Sponges in your Ocean Zone: (illustrated) Description of Sponge from Animals book: Station 2: Jellyfish, Corals and Anemones
Station 1: Sponges Sponge Observations: Simple Sponge drawing (labeled) Types of Sponges in your Ocean Zone: (illustrated) Description of Sponge from Animals book: Station 2: Jellyfish, Corals and Anemones
Pasig Catholic College. Grade School Department 103 S.Y Be with Jesus, be with the Poor. Science 5 SECOND QUARTER Activity Sheet # 1
 PCC @ 103 Be with Jesus, be with the Poor Activity Sheet # 1 TYPE OF ACTIVITY: Discussion on Animal Adaptations: Natural Habitat : Natural Habitat of Animals Learning Objectives : Describe the different
PCC @ 103 Be with Jesus, be with the Poor Activity Sheet # 1 TYPE OF ACTIVITY: Discussion on Animal Adaptations: Natural Habitat : Natural Habitat of Animals Learning Objectives : Describe the different
Back to the life forms!
 Remember that the environment is not simply the geography, but it includes other living things around it. So as one organism changes, it changes the environment for other organisms living around it. In
Remember that the environment is not simply the geography, but it includes other living things around it. So as one organism changes, it changes the environment for other organisms living around it. In
Marine Consumers OCN 201 Biology Lecture 6
 Marine Consumers OCN 201 Biology Lecture 6 Goetze/Peijnenburg Consumer Types Grazers (Herbivore) Predators Parasites Scavengers Detritivores Decomposers Feeding on algae or phytoplankton, consuming the
Marine Consumers OCN 201 Biology Lecture 6 Goetze/Peijnenburg Consumer Types Grazers (Herbivore) Predators Parasites Scavengers Detritivores Decomposers Feeding on algae or phytoplankton, consuming the
Pacing Guide for 7-12 Curriculum
 Pacing Guide for 7-12 Curriculum Course Title: Zoology Length of Course: 36 Weeks Week Number Week 1 Week 2 Chapter COS Objectives Student Will Be Able To: Biology COS 1- Select Successfully follow appropriate
Pacing Guide for 7-12 Curriculum Course Title: Zoology Length of Course: 36 Weeks Week Number Week 1 Week 2 Chapter COS Objectives Student Will Be Able To: Biology COS 1- Select Successfully follow appropriate
Flatworms Flatworms Platyhelminthes dorsoventrally free-living planarian parasitic fluke tapeworm label three body layers ectoderm mesoderm
 Flatworms Flatworms are in the phylum Platyhelminthes. Flatworms are flattened dorsoventrally (top to bottom). The group includes the freshwater, free-living planarian and the parasitic fluke and tapeworm.
Flatworms Flatworms are in the phylum Platyhelminthes. Flatworms are flattened dorsoventrally (top to bottom). The group includes the freshwater, free-living planarian and the parasitic fluke and tapeworm.
Review Inverts 4/17/15. What Invertebrates have we learned about so far? Porifera. Cnidaria. Ctenophora. Molluscs
 Review Inverts What Invertebrates have we learned about so far? Porifera sponges Cnidaria jellyfishes, sea anemones, coral Ctenophora comb jellies Molluscs snails, bivalves, octopuses, squid, cuglefish
Review Inverts What Invertebrates have we learned about so far? Porifera sponges Cnidaria jellyfishes, sea anemones, coral Ctenophora comb jellies Molluscs snails, bivalves, octopuses, squid, cuglefish
Topic 3: Animals Ch.17 Characteristics of Animals p.338. Distinguishing Characteristics pp
 Topic 3: Animals Ch.17 Characteristics of Animals p.338 - Animals are: - Multicellular. - Ingestive heterotrophs. - Have a division of labour (tissues, organs, systems). - Motile at some stage in their
Topic 3: Animals Ch.17 Characteristics of Animals p.338 - Animals are: - Multicellular. - Ingestive heterotrophs. - Have a division of labour (tissues, organs, systems). - Motile at some stage in their
Nematoda. Round worms Feeding and Parasitism
 Nematoda Round worms Feeding and Parasitism Nematoda Have pseudocoelom Live in many environments Parasitic Important decomposers Covered with cuticle Trichinella spiralis see fig 18.8B Nematode Diets and
Nematoda Round worms Feeding and Parasitism Nematoda Have pseudocoelom Live in many environments Parasitic Important decomposers Covered with cuticle Trichinella spiralis see fig 18.8B Nematode Diets and
UNIT: INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS 1º ESO BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY
 UNIT: INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS 1º ESO BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 2015/2016 What do they have in common? What are their differences? What is the theme for the next unit? Vertebrates and Invertebrates 1 Label the animals
UNIT: INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS 1º ESO BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 2015/2016 What do they have in common? What are their differences? What is the theme for the next unit? Vertebrates and Invertebrates 1 Label the animals
Chapter 7 Study Guide. True/False: If the statement is true, write True. If it is false explain why it is false.
 Name: Date of Quiz: Per: Chapter 7 Study Guide Complete this study guide, using complete sentences when appropriate, and turn it in with all of your class notes on the day of the quiz. True/False: If the
Name: Date of Quiz: Per: Chapter 7 Study Guide Complete this study guide, using complete sentences when appropriate, and turn it in with all of your class notes on the day of the quiz. True/False: If the
Animal Diversity Lecture 8 Winter 2014
 Animal Phylogeny 1 Animal Diversity Lecture 8 Winter 2014 Fig. 32.10 Phylum Porifera (sponges) 2 Phylum Cnidaria (corals, jellies, hydras, sea anemones) 3a ~5,500 species Primarily marine Suspension feeders
Animal Phylogeny 1 Animal Diversity Lecture 8 Winter 2014 Fig. 32.10 Phylum Porifera (sponges) 2 Phylum Cnidaria (corals, jellies, hydras, sea anemones) 3a ~5,500 species Primarily marine Suspension feeders
Classification of Animals. adapted from
 Classification of Animals Animals With Backbones AMPHIBIAN FISH MAMMAL BIRD REPTILE Animals With Backbones Animals with backbones are called vertebrates. Vertebrates include many different kinds of animals.
Classification of Animals Animals With Backbones AMPHIBIAN FISH MAMMAL BIRD REPTILE Animals With Backbones Animals with backbones are called vertebrates. Vertebrates include many different kinds of animals.
Kingdom Animalia. ii. iii.
 Kingdom Animalia 1. General Measures of Complexity a. Embryonic development i. The embryos of all animals go through the same stages during development so this can t be used as a measure of development
Kingdom Animalia 1. General Measures of Complexity a. Embryonic development i. The embryos of all animals go through the same stages during development so this can t be used as a measure of development
The Worms / Chapter 34 and Partial 35 (pgs )
 Name: The Worms / Chapter 34 and Partial 35 (pgs.712-716) 1-6. Worms are not the simple organisms most people think of at first sight. List three specific features that support the idea that worms are
Name: The Worms / Chapter 34 and Partial 35 (pgs.712-716) 1-6. Worms are not the simple organisms most people think of at first sight. List three specific features that support the idea that worms are
Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms
 Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms The Acoelomates The acoelomates are animals that lack a coelom. Acoelomates lack a body cavity, and instead the space between the body wall and the digestive tract is filled
Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms The Acoelomates The acoelomates are animals that lack a coelom. Acoelomates lack a body cavity, and instead the space between the body wall and the digestive tract is filled
All living things are classified into groups based on the traits they share. Taxonomy is the study of classification. The largest groups into which
 All living things are classified into groups based on the traits they share. Taxonomy is the study of classification. The largest groups into which the scientists divide the groups are called kingdoms.
All living things are classified into groups based on the traits they share. Taxonomy is the study of classification. The largest groups into which the scientists divide the groups are called kingdoms.
Classification. Class Scyphozoa Jellyfish Class Anthozoa Sea Anemones & Corals Class Hydrozoa - Hydra
 Phylum Cnidaria Classification Class Scyphozoa Jellyfish Class Anthozoa Sea Anemones & Corals Class Hydrozoa - Hydra General Characteristics Stinging tentacles Arranged in ring around mouth Saclike digestive
Phylum Cnidaria Classification Class Scyphozoa Jellyfish Class Anthozoa Sea Anemones & Corals Class Hydrozoa - Hydra General Characteristics Stinging tentacles Arranged in ring around mouth Saclike digestive
The Animal Kingdom. Animal Diversity. Key Concept Animals are a diverse group of organisms that have adaptations to live in water and on land.
 2 The Animal Kingdom Key Concept Animals are a diverse group of organisms that have adaptations to live in water and on land. What You Will Learn The animal kingdom is made up of many different kinds of
2 The Animal Kingdom Key Concept Animals are a diverse group of organisms that have adaptations to live in water and on land. What You Will Learn The animal kingdom is made up of many different kinds of
CTENOPHORA. PHYLUM Sea walnuts / Comb jellies
 PHYLUM Sea walnuts / Comb jellies CTENOPHORA TISSUE level of body org. RADIAL Symmetry Bodies often transparent &/or luminescent Locomotion = most are free-swimming 8 rows of ciliated combs = ctenes for
PHYLUM Sea walnuts / Comb jellies CTENOPHORA TISSUE level of body org. RADIAL Symmetry Bodies often transparent &/or luminescent Locomotion = most are free-swimming 8 rows of ciliated combs = ctenes for
Characteristics of Worms
 Worms Reading Preview Key Concepts What are the three main phyla of worms? What are the main characteristics of each phylum of worms? Key Terms parasite host free-living organism scavenger anus closed
Worms Reading Preview Key Concepts What are the three main phyla of worms? What are the main characteristics of each phylum of worms? Key Terms parasite host free-living organism scavenger anus closed
NATURAL BRIDGES SB TIDEPOOLS EXPLORATION
 NATURAL BRIDGES SB TIDEPOOLS EXPLORATION Difficulty: Moderate, Accessibile: No, Duration: 2.0 hrs Natural Bridges SB Tidepools The intertidal rocks at Natural Bridges State Beach are covered in life: sea
NATURAL BRIDGES SB TIDEPOOLS EXPLORATION Difficulty: Moderate, Accessibile: No, Duration: 2.0 hrs Natural Bridges SB Tidepools The intertidal rocks at Natural Bridges State Beach are covered in life: sea
Name Class Date. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 14 2 The Animal Kingdom SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is diversity? What are vertebrates? What
CHAPTER 14 2 The Animal Kingdom SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is diversity? What are vertebrates? What
Echinodermata. BIO3334 Invertebrate Zoology. Page 1. Phylum Echinodermata. Extant Animalia ~1,300,000 species. Dipleurula larva.
 Phylum Adrian Pingstone 1 Deuterostomia Blastopore becomes the anus Tripartite coelom Dipleurula larval stage Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora
Phylum Adrian Pingstone 1 Deuterostomia Blastopore becomes the anus Tripartite coelom Dipleurula larval stage Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora
Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals
 Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish,
Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish,
Echinodermata. BIO3334 Invertebrate Zoology. Page 1. Phylum Echinodermata. Dipleurula larva 1 4:43 AM. Deuterostomia
 Phylum Adrian Pingstone 1 Deuterostomia Blastopore becomes the anus Tripartite coelom Dipleurula larval stage Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora
Phylum Adrian Pingstone 1 Deuterostomia Blastopore becomes the anus Tripartite coelom Dipleurula larval stage Porifera Placozoa Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Gastrotricha Gnathostomulida Cycliophora
Chapter 33B: An Introduction to Vertebrates II The Bilateria. 1. Lophotrochozoa 2. Ecdysozoa 3. Deuterostomia
 Chapter 33B: An Introduction to Vertebrates II The Bilateria 1. Lophotrochozoa 2. Ecdysozoa 3. Deuterostomia Invertebrates Porifera ANCESTRAL PROTIST Cnidaria Common ancestor of all animals Eumetazoa Bilateria
Chapter 33B: An Introduction to Vertebrates II The Bilateria 1. Lophotrochozoa 2. Ecdysozoa 3. Deuterostomia Invertebrates Porifera ANCESTRAL PROTIST Cnidaria Common ancestor of all animals Eumetazoa Bilateria
Invertebrate Characteristic Lab
 Insects Draw and list the Characteristics of the following insects: Grasshopper, Termite, Squash bug, Beetle, Butterfly, and Honey Bee. Make sure you match up all of the characteristics with each insect,
Insects Draw and list the Characteristics of the following insects: Grasshopper, Termite, Squash bug, Beetle, Butterfly, and Honey Bee. Make sure you match up all of the characteristics with each insect,
Phylum: Cnidaria. Dr. Khalid M. Salih
 Phylum: Cnidaria Dr. Khalid M. Salih Definition Cnidaria comes from the Greek word "cnidos" which means stinging (nettle). Formerly known as coelenterata (Gr. Koilos = hollow, enteron = gut) take its name
Phylum: Cnidaria Dr. Khalid M. Salih Definition Cnidaria comes from the Greek word "cnidos" which means stinging (nettle). Formerly known as coelenterata (Gr. Koilos = hollow, enteron = gut) take its name
Sea Turtle, Terrapin or Tortoise?
 Sea Turtles Sea Turtle, Terrapin or Tortoise? Based on Where it lives (ocean, freshwater or land) Retraction of its flippers and head into its shell All 3 lay eggs on land All 3 are reptiles Freshwater
Sea Turtles Sea Turtle, Terrapin or Tortoise? Based on Where it lives (ocean, freshwater or land) Retraction of its flippers and head into its shell All 3 lay eggs on land All 3 are reptiles Freshwater
Essential Question: What are the characteristics of invertebrate animals? What are the characteristics of vertebrate animals?
 Essential Question: What are the characteristics of invertebrate animals? What are the characteristics of vertebrate animals? Key Concept: The animal kingdom is divided up into 35 phyla. These phyla can
Essential Question: What are the characteristics of invertebrate animals? What are the characteristics of vertebrate animals? Key Concept: The animal kingdom is divided up into 35 phyla. These phyla can
NOTES 839 ON THE POLYCHAETE GAJTYANA DELUDENS FAUVEL ASSOCIATED WITH THE HERMIT CRAB DIOGENES DIOGENES HERBST AND D.
 NOTES 89 ON THE POLYCHAETE GAJTYANA DELUDENS FAUVEL ASSOCIATED WITH THE HERMIT CRAB DIOGENES DIOGENES HERBST AND D. CUSTOS FABRICIUS ABSTRACT The commensal habits of Gattyana deludens Fauvel with the hermit
NOTES 89 ON THE POLYCHAETE GAJTYANA DELUDENS FAUVEL ASSOCIATED WITH THE HERMIT CRAB DIOGENES DIOGENES HERBST AND D. CUSTOS FABRICIUS ABSTRACT The commensal habits of Gattyana deludens Fauvel with the hermit
Classification. Chapter 17. Classification. Classification. Classification
 Classification Chapter 17 Classification Classification is the arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities. Classification shows how organisms are related and different. Classification
Classification Chapter 17 Classification Classification is the arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities. Classification shows how organisms are related and different. Classification
Practical-2 Classification. Protozoa, Porifera and Coelenterata
 Practical-2 Classification Protozoa, Porifera and Coelenterata 1 Euglena Phylum:-Protozoa SubPhylum:-Plasmodroma Class:- Mastigophora Type:- Euglena Character 1 Euglena is minute, elongated and spindle
Practical-2 Classification Protozoa, Porifera and Coelenterata 1 Euglena Phylum:-Protozoa SubPhylum:-Plasmodroma Class:- Mastigophora Type:- Euglena Character 1 Euglena is minute, elongated and spindle
Animals. Chapters Exam November 22, 2011
 Animals Chapters 32-35 Exam November 22, 2011 Overview of Animals Chapter 32 General Features of Animals and Evolution of the Body Plan General Features of Animals Heterotrophs Multicellular No Cell Walls
Animals Chapters 32-35 Exam November 22, 2011 Overview of Animals Chapter 32 General Features of Animals and Evolution of the Body Plan General Features of Animals Heterotrophs Multicellular No Cell Walls
Cnidarians and Ctenophores
 Cnidarians and Ctenophores Characteristics All carnivorous Contain a jelly-like layer between epidermis and gastrodermis called mesoglea Single opening (mouth/anus) to gastrovascular cavity where food
Cnidarians and Ctenophores Characteristics All carnivorous Contain a jelly-like layer between epidermis and gastrodermis called mesoglea Single opening (mouth/anus) to gastrovascular cavity where food
Life of the intertidal zones and tide pools
 Life of the intertidal zones and tide pools Marine habitats and intertidal zonation Tim Hall Life zones of the sea Of the life zones of the sea the intertidal is very small- and a tide pool- even smaller
Life of the intertidal zones and tide pools Marine habitats and intertidal zonation Tim Hall Life zones of the sea Of the life zones of the sea the intertidal is very small- and a tide pool- even smaller
Echinodermata. Gr: spine skin 6500 spp all marine except for few estuarine, none freshwater. *larvae bilateral symmetrical. mesodermally-derived
 Echinodermata Gr: spine skin 6500 spp all marine except for few estuarine, none freshwater 1) pentamerous radial symmetry (adults) 2) spines *larvae bilateral symmetrical 3) endoskeleton mesodermally-derived
Echinodermata Gr: spine skin 6500 spp all marine except for few estuarine, none freshwater 1) pentamerous radial symmetry (adults) 2) spines *larvae bilateral symmetrical 3) endoskeleton mesodermally-derived
Chapter 7 - Cnidarians. Animals with stinging tentacles, including: jellyfish, corals, sea anemones, and hydra
 Chapter 7 - Cnidarians Animals with stinging tentacles, including: jellyfish, corals, sea anemones, and hydra Cnidarians Cnidarians are soft-bodied animals. Have stinging tentacles arranged in circles
Chapter 7 - Cnidarians Animals with stinging tentacles, including: jellyfish, corals, sea anemones, and hydra Cnidarians Cnidarians are soft-bodied animals. Have stinging tentacles arranged in circles
Classification. Grouping & Identifying Living Things
 Classification Grouping & Identifying Living Things Taxonomy The study of how living things are classified Classification is the sorting of organisms based on similar characteristics Carolus Linnaeus is
Classification Grouping & Identifying Living Things Taxonomy The study of how living things are classified Classification is the sorting of organisms based on similar characteristics Carolus Linnaeus is
Animals Classification
 Animals Classification By Piyush & Ilaxi Grouping & Identifying Living Things 2 Classifying Living Things Classifying Living Things Biological Classification is the way in which scientists use to categorize
Animals Classification By Piyush & Ilaxi Grouping & Identifying Living Things 2 Classifying Living Things Classifying Living Things Biological Classification is the way in which scientists use to categorize
UNIT 9. THE ANIMAL KINGDOM: INVERTEBRATES
 UNIT 9. THE ANIMAL KINGDOM: INVERTEBRATES 1. The simplest invertebrates 2. Annelids, molluscs and echinoderms 3. Arthropods 4. Insects All living beings belong to the Animal Kingdom have got the following
UNIT 9. THE ANIMAL KINGDOM: INVERTEBRATES 1. The simplest invertebrates 2. Annelids, molluscs and echinoderms 3. Arthropods 4. Insects All living beings belong to the Animal Kingdom have got the following
Figure 1. Numerical Distribution of Named Animal Taxa.
 Arthropod Review Sheet The Phylum Arthropoda is the largest and most diverse of all animal phyla (Fig 1). More than three quarters of the animals on earth are arthropods, and most of these are insects.
Arthropod Review Sheet The Phylum Arthropoda is the largest and most diverse of all animal phyla (Fig 1). More than three quarters of the animals on earth are arthropods, and most of these are insects.
Chapter 3: Impact of Invasive Aquatic Plants on Waterfowl
 Chapter 3: Impact of Invasive Aquatic Plants on Waterfowl Ryan M. Wersal: Lonza Specialty Ingredients, Alpharetta GA 30004; ryan.wersal@lonza.com Kurt D. Getsinger: US Army ERDC, Vicksburg MS; Kurt.D.Getsinger@usace.army.mil
Chapter 3: Impact of Invasive Aquatic Plants on Waterfowl Ryan M. Wersal: Lonza Specialty Ingredients, Alpharetta GA 30004; ryan.wersal@lonza.com Kurt D. Getsinger: US Army ERDC, Vicksburg MS; Kurt.D.Getsinger@usace.army.mil
Cnidarians: Jellies, anemones, hydroids & corals
 Cnidarians: Jellies, anemones, hydroids & corals Doug Stark Aggregating / pink-tipped anemone Anthopleura elegantissima Pink-tipped green anemone a.k.a. Aggregating anemone Anthopleura elegantissima Doug
Cnidarians: Jellies, anemones, hydroids & corals Doug Stark Aggregating / pink-tipped anemone Anthopleura elegantissima Pink-tipped green anemone a.k.a. Aggregating anemone Anthopleura elegantissima Doug
Field Guide: Teacher Notes
 Field Guide: Teacher Notes Bob Winters Classification Objectives After completing this activity, students will be able to: Investigate how living things are classified. Group, or classify organisms according
Field Guide: Teacher Notes Bob Winters Classification Objectives After completing this activity, students will be able to: Investigate how living things are classified. Group, or classify organisms according
Chapter 17 The Evolution of Animals Biology and Society: The Discovery of the Hobbit People
 Chapter 17 The Evolution of Animals Biology and Society: The Discovery of the Hobbit People In 2003, anthropologists discovered bones on the Indonesian island of Flores, dating back about 18,000 years,
Chapter 17 The Evolution of Animals Biology and Society: The Discovery of the Hobbit People In 2003, anthropologists discovered bones on the Indonesian island of Flores, dating back about 18,000 years,
ì<(sk$m)=bdjbgd< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Life Science Genre Comprehension Skills Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Compare and Contrast Labels Captions Classifying Organisms Diagrams Glossary Scott Foresman Science 5.1 by Wade Lind ì
Life Science Genre Comprehension Skills Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Compare and Contrast Labels Captions Classifying Organisms Diagrams Glossary Scott Foresman Science 5.1 by Wade Lind ì
species at-a-glance How many living species are there? Taxon (and common name)
 species at-a-glance How many living species are there? * (sea squirts only) Taxon (and common name) New Species World (2008) 1 Total 2 Insecta (insects) 8,794 (48.25%) 1,013,692 3 Plantae (vascular, including
species at-a-glance How many living species are there? * (sea squirts only) Taxon (and common name) New Species World (2008) 1 Total 2 Insecta (insects) 8,794 (48.25%) 1,013,692 3 Plantae (vascular, including
DIVERSITY IV Animalia II: Ecdysozoan Protostomes and Deuterostomes
 NAME: PARTNER: DATE: DIVERSITY IV Animalia II: Ecdysozoan Protostomes and Deuterostomes In this laboratory session we will conclude our examination of organismal diversity by looking at the ecdysozoa the
NAME: PARTNER: DATE: DIVERSITY IV Animalia II: Ecdysozoan Protostomes and Deuterostomes In this laboratory session we will conclude our examination of organismal diversity by looking at the ecdysozoa the
Echinodermata. Phylum Echinodermata. Derived from the Greek meaning Spiny Skinned. Ancient animal group that evolved over 600 ma
 Echinodermata Phylum Echinodermata Derived from the Greek meaning Spiny Skinned Ancient animal group that evolved over 600 ma Six classes living today Sea stars (Asteroidea) Sea urchins (Echinoidea) Sea
Echinodermata Phylum Echinodermata Derived from the Greek meaning Spiny Skinned Ancient animal group that evolved over 600 ma Six classes living today Sea stars (Asteroidea) Sea urchins (Echinoidea) Sea
Reef Check California Copy of RCCA Data Sheets xls
 Site Description Report Site Information Temperature in Celsius Site Name Air City / Island Surface County 5 Meters State California 10 Meters Latitude (deg min.min) North Distance in Meters Longitude
Site Description Report Site Information Temperature in Celsius Site Name Air City / Island Surface County 5 Meters State California 10 Meters Latitude (deg min.min) North Distance in Meters Longitude
A Survey of Marine Animal Kingdoms
 A Survey of Marine Animal Kingdoms Phylum Cnidaria Has Diversity Hydroids Jellyfish Sea Anemone Coral polyps 2 2 Corals, Anemones, Sea Fans and Jellyfish Phylum Cnidaria Radial symmetry symmetry around
A Survey of Marine Animal Kingdoms Phylum Cnidaria Has Diversity Hydroids Jellyfish Sea Anemone Coral polyps 2 2 Corals, Anemones, Sea Fans and Jellyfish Phylum Cnidaria Radial symmetry symmetry around
Dietary intake of Mute Swans, Cygnus olor, in relation to. reproduction on the lower Great Lakes
 Dietary intake of Mute Swans, Cygnus olor, in relation to reproduction on the lower Great Lakes Submitted to Dr. R. Podesta, Dr. R.J. Scott, and Dr. L. Zanette April 7, 2003 Investigator: Supervisor: Co-supervisor:
Dietary intake of Mute Swans, Cygnus olor, in relation to reproduction on the lower Great Lakes Submitted to Dr. R. Podesta, Dr. R.J. Scott, and Dr. L. Zanette April 7, 2003 Investigator: Supervisor: Co-supervisor:
DO NOT OPEN EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO
 Name: Last KEY First Biological Sciences 1B Dr. Herrlinger Summer Sessions I 2001 Final Exam August 3, 2001 ID# Lab. Date and Time Lab. TA DO NOT OPEN EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO Multiple Choice Questions
Name: Last KEY First Biological Sciences 1B Dr. Herrlinger Summer Sessions I 2001 Final Exam August 3, 2001 ID# Lab. Date and Time Lab. TA DO NOT OPEN EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO Multiple Choice Questions
T. 6. THE VERTEBRATES
 T. 6. THE VERTEBRATES 1.- Relate the following concepts to their definition. Later, relate each concept to one of the pictures you are going to see. 1.- FIN a.- mammals with their babies 2.- GILLS b.-
T. 6. THE VERTEBRATES 1.- Relate the following concepts to their definition. Later, relate each concept to one of the pictures you are going to see. 1.- FIN a.- mammals with their babies 2.- GILLS b.-
INTERTIDAL VIEWING. Fun Fact: Fun Fact: - They change their angle in the sand as the tide goes in and out so that they can continuously feed.
 Orange Sea Cucumber: Cucumaria minata Along rock intertidal areas, keep your eyes open for these animals that tend to look like brightly coloured dill pickles! They attach themselves to rocks or other
Orange Sea Cucumber: Cucumaria minata Along rock intertidal areas, keep your eyes open for these animals that tend to look like brightly coloured dill pickles! They attach themselves to rocks or other
Diversity of Animals
 Classifying Animals Diversity of Animals Animals can be classified and grouped based on similarities in their characteristics. Animals make up one of the major biological groups of classification. All
Classifying Animals Diversity of Animals Animals can be classified and grouped based on similarities in their characteristics. Animals make up one of the major biological groups of classification. All
Concept 1: sponges are basal animals that lack true tissues
 Concept 1: sponges are basal animals that lack true tissues Sponges are basal animals ( arise from the base of animal tree) and lack true tissues. Sponges belong to phylum Porifera and are thought to be
Concept 1: sponges are basal animals that lack true tissues Sponges are basal animals ( arise from the base of animal tree) and lack true tissues. Sponges belong to phylum Porifera and are thought to be
true tissue Ancestral Protist
 Phylum Mollusca Platyhelminthes Mollusca Arthropoda Chordata Porifera Cnidaria Nematoda Annelida Echinodermata acoelom pseudoc oelom Protostome: schizocoelem segmentation Deuterostomes: eucoelom radial
Phylum Mollusca Platyhelminthes Mollusca Arthropoda Chordata Porifera Cnidaria Nematoda Annelida Echinodermata acoelom pseudoc oelom Protostome: schizocoelem segmentation Deuterostomes: eucoelom radial
Chapter 7. Marine Animals Without a Backbone
 Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Echinoderms Characteristics of Phylum: Name means "Spiny Skin" Endoskeleton Skeleton on inside of body Covered by tissue All 7000 species exclusively marine
Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Echinoderms Characteristics of Phylum: Name means "Spiny Skin" Endoskeleton Skeleton on inside of body Covered by tissue All 7000 species exclusively marine
8/25/ Opening Questions: Are you an animal? What traits do you share with a jellyfish? Chapter 10 Biodiversity 3: Animals
 Chapter 10 Biodiversity 3: Animals 10.1 Animals are consumers 10.2 Sponges and cnidarians 10.3 Three phyla of worms 10.4 Mollusks 10.5 Arthropods 10.6 Echinoderms 10.7 Vertebrates 10.8 Fishes 10.9 Amphibians
Chapter 10 Biodiversity 3: Animals 10.1 Animals are consumers 10.2 Sponges and cnidarians 10.3 Three phyla of worms 10.4 Mollusks 10.5 Arthropods 10.6 Echinoderms 10.7 Vertebrates 10.8 Fishes 10.9 Amphibians
What is the body structure of a sponge? Do they have specialized cells? Describe the process of reproduction in sponges.
 11.2 Sponges and Cnidarians What are the main characteristics of Sponges? Where are sponges found? What is the body structure of a sponge? Do they have specialized cells? Do sponges have separate sexes?
11.2 Sponges and Cnidarians What are the main characteristics of Sponges? Where are sponges found? What is the body structure of a sponge? Do they have specialized cells? Do sponges have separate sexes?
SELECTIVE FEEDING BY WILD DUCKLINGS
 SELECTIVE FEEDING BY WILD DUCKLINGS OF DIFFERENT SPECIES NICHOLAS E. COLLIAS AND ELSIE C. COLLIAS T the Delta Waterfowl Research Station at the south end of Lake Mani- A toba, where this work was done,
SELECTIVE FEEDING BY WILD DUCKLINGS OF DIFFERENT SPECIES NICHOLAS E. COLLIAS AND ELSIE C. COLLIAS T the Delta Waterfowl Research Station at the south end of Lake Mani- A toba, where this work was done,
Comparative Anatomy Lab 1: Cnidarians
 Comparative Anatomy Lab 1: Cnidarians The Cnidarians are an ancient assemblage of organisms whose ancestry can be traced back more than 700 million years. This marks them as one of the earliest stock of
Comparative Anatomy Lab 1: Cnidarians The Cnidarians are an ancient assemblage of organisms whose ancestry can be traced back more than 700 million years. This marks them as one of the earliest stock of
Comparison Of The Major Animal Phyla
 Comparison Of The Major Animal Phyla Free PDF ebook Download: Comparison Of The Major Animal Phyla Download or Read Online ebook comparison of the major animal phyla in PDF Format From The Best User Guide
Comparison Of The Major Animal Phyla Free PDF ebook Download: Comparison Of The Major Animal Phyla Download or Read Online ebook comparison of the major animal phyla in PDF Format From The Best User Guide
Unit 18: Biology Part 1
 SUPERCHARGED SCIENCE Unit 18: Biology Part 1 www.sciencelearningspace.com Appropriate for Grades: Grades K-8 (see notes on each lesson) Duration: 3-25 hours, depending on how many activities you do! Animals
SUPERCHARGED SCIENCE Unit 18: Biology Part 1 www.sciencelearningspace.com Appropriate for Grades: Grades K-8 (see notes on each lesson) Duration: 3-25 hours, depending on how many activities you do! Animals
Classifying Organisms. Classifying Organisms. Classifying Organisms. Classifying Organisms.
 Intro to Life and Animals Life, as we call it. I suppose that before we talk about life, we should somehow name it. Classifying Organisms You have at least a two part name..your first, and your last. For
Intro to Life and Animals Life, as we call it. I suppose that before we talk about life, we should somehow name it. Classifying Organisms You have at least a two part name..your first, and your last. For
Introduction to Helminthology
 Introduction to Helminthology HELMINTHES (WORMS) - Characteristics Eukaryotic, multicellular animals that usually have digestive, circulatory, nervous, excretory, and reproductive systems. Worms with bilateral
Introduction to Helminthology HELMINTHES (WORMS) - Characteristics Eukaryotic, multicellular animals that usually have digestive, circulatory, nervous, excretory, and reproductive systems. Worms with bilateral
26-3 Cnidarians Slide 2 of 47
 2 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What is a cnidarian? 3 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What Is a Cnidarian? Cnidarians are soft-bodied, carnivorous animals that have stinging tentacles arranged in circles around
2 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What is a cnidarian? 3 of 47 What Is a Cnidarian? What Is a Cnidarian? Cnidarians are soft-bodied, carnivorous animals that have stinging tentacles arranged in circles around
Return to the sea: Marine birds, reptiles and pinnipeds
 Figure 34.14 The origin of tetrapods Return to the sea: Marine birds, reptiles and pinnipeds Phylum Chordata Free swimmers Nekton Now we move to reptiles (Class Reptilia) and birds (Class Aves), then on
Figure 34.14 The origin of tetrapods Return to the sea: Marine birds, reptiles and pinnipeds Phylum Chordata Free swimmers Nekton Now we move to reptiles (Class Reptilia) and birds (Class Aves), then on
Phylum Echinodermata. Biology 11
 Phylum Echinodermata Biology 11 General characteristics Spiny Radial symmetry Water vascular system Endoskeleton Endoskeleton Hard, spiny, or bumpy endoskeleton covered with a thin epidermis. Endoskeleton
Phylum Echinodermata Biology 11 General characteristics Spiny Radial symmetry Water vascular system Endoskeleton Endoskeleton Hard, spiny, or bumpy endoskeleton covered with a thin epidermis. Endoskeleton
27 The Rise of Animal Diversity
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 27 The Rise of Animal Diversity Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Life Becomes Dangerous
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 27 The Rise of Animal Diversity Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Life Becomes Dangerous
Study Questions. to Tiny Travelers. naturalists. Young
 Young naturalists Study Questions to Tiny Travelers Study and learn facts and ideas based on this Young Naturalists nonfiction story in Minnesota Conservation Volunteer, September October 2016, www.mndnr.gov/mcvmagazine.
Young naturalists Study Questions to Tiny Travelers Study and learn facts and ideas based on this Young Naturalists nonfiction story in Minnesota Conservation Volunteer, September October 2016, www.mndnr.gov/mcvmagazine.
Aquatic Macroinvertebrates
 Aquatic Macroinvertebrates Brazoria NWR (Big Slough and Crosstrails Pond) Nov. 2015 - Nov. 2016 Photos by Pete and Peggy Romfh SCUD (SIDE-SWIMMERS) Arthropoda, Sub-Phylum Crustacea, Class Malacostraca,
Aquatic Macroinvertebrates Brazoria NWR (Big Slough and Crosstrails Pond) Nov. 2015 - Nov. 2016 Photos by Pete and Peggy Romfh SCUD (SIDE-SWIMMERS) Arthropoda, Sub-Phylum Crustacea, Class Malacostraca,
Distribution and Habitat Analysis for Freshwater Turtles of River Indus and some of its Tributaries in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Punjab, Pakistan
 Journal of Bioresource Management Volume 2 Issue 3 Article 8 2015 Distribution and Habitat Analysis for Freshwater Turtles of River Indus and some of its Tributaries in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Punjab, Pakistan
Journal of Bioresource Management Volume 2 Issue 3 Article 8 2015 Distribution and Habitat Analysis for Freshwater Turtles of River Indus and some of its Tributaries in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Punjab, Pakistan
Phylum Mollusca (mollis, soft)
 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca (mollis, soft) Body usually an anterior head, ventral foot and a dorsal visceral mass. Covered by a fleshy outgrowth of the body wall called a mantle. Shell if present is
Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca (mollis, soft) Body usually an anterior head, ventral foot and a dorsal visceral mass. Covered by a fleshy outgrowth of the body wall called a mantle. Shell if present is
CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS. Learning Objectives : To explain how animals are classified into groups. Key Words:
 CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS Learning Objectives : To explain how animals are classified into groups. Key Words: How do we identify living from non living? 7A Signs of life The meaning of life There are seven
CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS Learning Objectives : To explain how animals are classified into groups. Key Words: How do we identify living from non living? 7A Signs of life The meaning of life There are seven
Echinochloa crus-galli (dawa-dawa) and Digitaria sanguinalis (saka-saka) are weeds which are alternative hosts to abaca and corn mosaic viruses.
 Jatropha curcas (tuba-tuba/tubang bakod) is popular due to its being an alternative source of bio-fuel. Although known to have medicinal properties, its seed is poisonous. The fruits which are usually
Jatropha curcas (tuba-tuba/tubang bakod) is popular due to its being an alternative source of bio-fuel. Although known to have medicinal properties, its seed is poisonous. The fruits which are usually
Additional copies may be obtained from the following address:
 Turtle Coloring and Activity Book Art and Text By Holly Dumas Gulfport High School Additional copies may be obtained from the following address: Gulf Coast Research Laboratory The University of Southern
Turtle Coloring and Activity Book Art and Text By Holly Dumas Gulfport High School Additional copies may be obtained from the following address: Gulf Coast Research Laboratory The University of Southern
