THE ANIMAL KINGDOM UNIT 8
|
|
|
- Marjorie Hamilton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE ANIMAL KINGDOM UNIT 8 All animals have got common characteristics: They are multicellular. They are made up of many cells. These cells have a specific function. Their cells are eukaryotic cells. They have got nucleus but have not got cell wall. They are heterotrophus. They are consumers so they have to take food from the environment. Depending on their nutrition (the things they eat) we can divide this kingdom into three different groups: Herbivores. They eat plants ( for example cows and horses) Carnivores. They hunt other animals and eat fresh meat ( for example lions) Omnivores. They eat both plants and animals (for example pigs and chimpanzees) They have got keen senses. They can detect changes in their environment. This information goes through the sensory organs. The majority of them can move, look for food or escape from danger. (Vocabulary: to hunt: cazar / keen senses: sentidos finos, agudos / environment: medio ambiente / fresh meat: carne fresca / sensory organs: órganos de los sentidos / to look for: buscar / danger: peligro) Match the words on the left column with the sentences on the right 1 Multicellular A With them animals can detect changes in their environment 2 Heterotrophus B Animals that eat both plants and animals (for example pigs) 3 Eukaryotic cells C Animals that hunt other animals and eat fresh meat (for example lions) 4 Herbivores D Animals that eat plants (for example cows and horses) 5 Carnivores E Living beings that are made up of many cells 6 Omnivores F They are cells that have got nucleus 7 Sensory organs G They have to take food from the environment Answers: Fill the gaps with the following words from the list Multicellular environment nucleus cell wall function sensory heterotrophus chimpanzees herbivores meat carnivores omnivores. All the animals are... living beings. They are made up of many cells. These cells have got a specific... The animal cells are eukaryotic cells. They have got... but have not got... Animals are...,so they have to take food from the environment. When animals eat plants (for example cows and horses), they are called... Animals are called... when they hunt other animals and eat fresh... (for example lions). When animals eat both plants and animals (for example pigs and...), they are called... Animals can detect changes in their... This information goes through the...organs. 1. What kind of cells have animals got?... 1
2 2. Are animals unicellular or multicellular living beings? Why are animals heterotrophus? What are carnivorous animals? What is the diet of omnivorous animals? What have a lion and a chimpanzee in common in relation to their diet? Does a horse eat other animals? Why can animals detect changes in their environment? Can all animals move? Why do animals move?... Vertebrates and invertebrates Depending on their backbone or spinal column we can distinguish two groups: Vertebrates. They are animals that have got a backbone. It is a part of an internal skeleton. Invertebrates They are animals that have not got an internal skeleton with a backbone. Some of them have not got a skeleton (like worms and jelly-fish) and others have got an external skeleton (like insects, spiders, and crabs). Vertebrates All vertebrates have got a backbone that is part of an internal skeleton or endoskeleton. It is made up of joint pieces called vertebra. Vertebrates are divided in five groups: Mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Their bodies are divided in three parts: head, trunk, and tail. Some of them, like apes, have not got tail. Vertebrates have got joint limbs, such as legs, wings, and fins. Some of them, like snakes, have not got limbs. They have got a complex and well-developed nervous system. The main part is the brain in the skull covered by the cranium. Most sensory organs are in the head. Vertebrates have got bilateral symmetry. This means that their bodies can be divided in two equal parts. 2
3 (Vocabulary: backbone: columna vertebral / ape: simio / worm: gusano / jelly-fish: medusa / crab: cangrejo / joint pieces: piezas articuladas / limb: extremidad / joint limbs: extremidades articuladas / trunk: tronco / leg: pata / wing: ala / fin: aleta / brain: cerebro / complex: complejo / well-developed: bien desarrollado / cranium: cráneo / skull: calavera / to mean: significar / equal: igual) Fill the boxes marked in the picture Match the words in the left column with the sentences on the right 1 Vertebrates A It is made up of joint pieces called vertebra 2 Invertebrates B Their body can be divided in two equal parts 3 Backbone C It is the main part of the nervous system 4 Bilateral symmetry D They are animals that have got an internal skeleton 5 Brain E They are animals that can have an external skeleton Answers: Fill the gaps with the following words from the list trunk backbone equal internal skeleton joint limbs head tail snakes bilateral symmetry three invertebrates joint pieces brain fins jelly-fish skull Vertebrates are animals that have got a... It is a part of an... skeleton. Some... have not got a skeleton (like worms and... ) and others have got an external... (like insects, spiders, and crabs) The backbone is formed by... called vertebras. The vertebrate s body is divided in... parts: head,..., and tail Some vertebrates, like apes, have not got... Vertebrates have got..., such as legs, wings, and... Some of them, like... have not got limbs. The main part of the nervous system in vertebrates is the... It is in the... covered by the cranium. Most sensory organs are in the... The vertebrate s body has got... This means that their bodies can be divided in two... parts 3
4 1. What is the main difference between vertebrate and invertebrate animals? Give two examples of invertebrate animals that have not got skeleton at all What is the difference between a worm and a spider? What is the name of the joint pieces that form the backbone? Give an example of vertebrate with no tail Have snakes got limbs? What is the main part of the nervous system in vertebrates? What does bilateral symmetry mean?... Mammals An elephant, a mouse, and a dog are mammals. Most of them are terrestrial animals. But dolphins are aquatic animals and bats are mammals that can fly. The body The head is close to the trunk by the neck. The backbone reaches the tail. They are the only vertebrates that have got ears. Mammals have got four limbs. The limbs are adapted to the kind of mobility. The limbs are legs in terrestrial mammals, fins in aquatic mammals, and wings in bats. Mammals have got hair or fur covering their body. It is useful as a temperature insulator, helping to keep them warm. Aquatic mammals, like whales, have got fins and a smooth skin with no hair. They have got lips and teeth in their mouth. The shape of the teeth is different depending on their diet (the food they eat). Mammals have got many glands. For example, the sweat glands or the mammary glands which produce milk Functions All mammals are homeothermal or warm-blooded animals. They keep their body temperature constant and independent from the environment Mammals breathe through lungs. Aquatic mammals have to come up to surface of water to breathe Their diet is varied. They can be herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores Mammals have got internal fertilization. The young mammals grow inside the mother s womb. They are viviparous animals; they are born from their mothers through live birth. The babies feed on their mother s milk. Parents look after them. (Vocabulary: kind of: tipo de / bat: murciélago / to reach: llegar hasta / limb:extremidad / fur: piel / useful: útil / insulator: aislante / warm: cálido, caliente / whale: ballena / smooth: suave / sweat gland: glándula sudorípara /mammary gland: glándula mamaria / homeothermal, warm-blooded: homeotermo / to come up: subir / to breathe: respirar / lung: pulmón / to look after: cuidar / to grow: crecer, desarrollarse / womb: útero / live birth: parto / to feed: alimentarse) 4
5 Fill the boxes marked in the picture Match the words on the left column with the setences on the right 1 Bat A It is the place where young mammals grow 2 Whale B It is part of the internal skeleton 3 Womb C With this organ mammals can hear 4 Homeothermal D They are mammals that can fly 5 Ear E They are mammals that live in sea 6 Sweat gland F It is a gland that makes body temperature decrease 7 Backbone G They are animals with constant temperature Answers: Fill the gaps with the following words from the list aquatic terrestrial bats whales ears milk four insulator womb environment warm-blooded viviparous neck diet wings smooth lips hair mobility glands fins Most of mammals are... animals. But dolphins are... animals and... are mammals that can fly. The head of mammals is close to the trunk by the... Mammals are the only vertebrates that have got... Mammals have got... limbs. The limbs are adapted to the kind of... The limbs are legs in terrestrial mammals,... in aquatic mammals, and... in bats. Most mammals have got... covering their body. It is useful as a temperature... Aquatic mammals, like..., have got fins and a... skin with no hair. The teeth of mammals are different depending on their... They have got... and teeth in their mouth Mammals have got many... ; like the mammary glands which produce... All the mammals are... animals. They keep their body temperature constant and independent from the... The young mammals grow inside the mother s..., so they are... animals 5
6 1. How is the trunk close to the head in mammals? What kind of limbs have dolphins got? How does a horse breathe? What does homoeothermic mean? Give an example of omnivorous mammals What is the importance of hair in mammals? Do the young mammals eat for themselves? How does a whale breathe? What is the function of mammary glands? What is the name of mammals which eat plants?... Birds A canary, an owl, and a duck are birds. Birds are terrestrial vertebrates. Most of them can fly. Only some birds like ostriches cannot fly. The body Their bodies have got an aerodynamic shape, adapted for flight. The head is close to the trunk by the neck. In the stork the neck is very long. Birds have got four limbs. The back limbs are legs with four fingers, and covered by scales. The fore limbs are wings Their body is covered in feathers, which stop heat being lost through the skin. The skeleton of birds has got very lightweight bones. Their bones are hollow. For this reason their bodies are light, which is very important for the flight. The sternum or chestbone is very developed as a keel for the attachment of strong flight muscles that move the wings. Birds have a hornlike beak and they have not got teeth. The beak is adapted to their diet. Functions Birds are homoeothermic or warm-blooded animals. They keep their temperature (around 42 0 C) constant and independent from the environment. All birds breathe through lungs. These lungs connect with cavities filled with air, called air sacs. All this benefits the breathing and the flight Birds are oviparous animals; they lay eggs.they have got internal fertilization. They are born from eggs with hard shells. The eggs are incubated until the chicks hatch. Adults look after their babies until they grow and can leave the nest. Their diet is varied. They can be carnivores, herbivores and omnivores. The shape of a bird s beak depends on the food it eats: They can eat grain, fruit, insects, and meat 6
7 (Vocabulary: owl: buho / ostrich: avestruz / stork: cigüeña / flight: vuelo / neck: cuello / fore limb: extremidad delantera / scale: escama / feather: pluma/ to fill: llenar/ air sac: saco aéreo / lightweight: ligero, liviano / hollow: hueco / chestbone: esternón / to develop: desarrollar / keel: quilla / attachment: unión, acoplamiento / to benefit: favorecer / hornlike: córneo / beak: pico / to lay eggs: poner huevos / shell: cáscara / to incubate: incubar / chicks: pollos / to hatch: salir del huevo, eclosionar / to look after: cuidar / nest: nido) Fill the boxes in the following picture Match the words in the left column with the sentences on the right 1 Skeleton A It covers the main part of a bird body 2 Oviparous B It is very developed as a keel 3 Feather C It has got very lightweight bones 4 Beak D It depends on the kind of food. 5 Chestbone E It means that they lay eggs Answers: Fill the gaps with the following words from the list trunk hollow neck scales chestbone four feathers keel teeth air sacs fore lightweight lungs aerodynamic beak flight The birds bodies have got an... shape, so they can fly. The head is close to the... by the neck. In the stork the... is very long. Birds have got four limbs. The back limbs are legs with... fingers, and covered by... The... limbs are wings The birds body are covered with... The skeleton of birds has got very... bones, and they are... For this reason their bodies are light. The sternum or... is very developed as a... for the attachment of strong flight muscles that move the wings. Birds have got a hornlike... and they have not got... Birds... connect with cavities filled with air, called... All this benefits the breathing and the What is the reason of the aerodynamic shape body of birds?... 7
8 2. Has the birds body got scales? Where? Why are the birds bones hollow? What kind of fertilization have birds got? Have birds got beak or teeth? Are young birds born from eggs or from live birth? What is the name of the cavities inside the birds body? How is the temperature of birds in relation to their environment? What is the name of the structures which cover the birds body? Why does the chestbone of birds have shape of keel?... Reptiles A snake, a crocodile, a lizard, and a turtle are reptiles. They are terrestrial vertebrates, although turtles are aquatic vertebrates. The body All of them have got four limbs or legs, except snakes, that have no limbs. Their bodies are covered with hard scales that are close together to avoid drying Lizards and snakes shed their skin. Turtles have got a hard shell called carapace The function Reptiles are poikilotherms or cold-blooded vertebrates, because the temperature of their body depends on the environment All reptiles breathe through lungs Most reptiles are carnivores. They have got teeth to capture their preys. Turtles have got a hornlike beak with no teeth, and snakes have got fangs connected with poison glands. Reptiles are oviparous animals and they have got internal fertilization. Their eggs are protected by a leathery shell to avoid drying. The eggs are not incubated. Some snakes are ovoviviparous; the embryo develops inside an egg that remains inside the female until hatching and gives birth to living young. (Vocabulary: snake: serpiente / lizard: lagarto / turtle: tortuga marina / to avoid: evitar / drying: desecación / to shed: mudar / carapace: caparazón / cold-blooded: poiquilotermo / environment entorno / preys: presas / hornlike: córneo / poison: veneno / fang: colmillo / leathery shell: cáscara correosa, como de cuero / to develop: desarrollar / to remain: permanecer / hatching: eclosión, salida del huevo / female: hembra) 8
9 Fill the boxes marked in the picture Match the words in the left column with the setences on the right 1 Scales A They have not got limbs. 2 Eggs B They are close together to avoid drying 3 Fangs C It means that temperature of the body depends on its environment 4 Poikilotherm D They are connected with poison glands 5 Snakes E They are not incubated. Answers: Fill the gaps with the following words from the list cold-blooded fangs skin snakes legs hard scales hornlike drying shell environment All reptiles have got four..., except..., that have not got limbs. Reptiles bodies are covered in... that are close together to avoid... Lizards and snakes change their... Turtles have got a... Reptiles are... vertebrates, because the temperature of their body depends on their... Turtles have got a... beak, and snakes have got connected with poison glands. 1. How many legs have snakes got? Do you know any aquatic reptiles? Why are reptiles called poikilotherm vertebrates? What is the difference between reptiles and birds in relation with eggs? Why are some snakes dangerous? What is a carapace? What is the difference between eggs laided by birds and the ones laided by reptiles? Do you know any reptiles which give birth to live youngs?... Amphibians A frog, a toad, a newt, and a salamander are amphibians. They are born in the water and when they grow up they can live on land. They were the first vertebrates to colonize land even though they still depend on water to reproduce. Amphibians can be divided into two groups: 9
10 Anurans have not got a tail. They are frogs and toads. Urodeles have got a tail. They include salamanders and newts The body Amphibians body is divided into the head and trunk. Amphibians have not got a neck. The head, which is joined directly to the trunk, has got a wide mouth with thin teeth and a muscular tongue. Amphibians have got prominent eyes with moving eyelids and auditory openings covered by a membrane or eardrum. The trunk of the adult amphibian has got four limbs or legs. The fore legs have got four toes and the back legs have got five toes. All the toes of the back legs are joined together by membranes to make swimming easier (webbed feet). Frogs have got back legs very developed so they can make big jumps. All amphibians have got smooth, moist, thin skin, with no hair or scales. It is not protected against drying out. For this reason, amphibians need water to survive. Frogs and toads have not got a tail. The babies, called tadpoles, have got tail and no legs. Functions Amphibians are poikilotherms or cold-blooded vertebrates. They cannot control their temperature, for this reason they do not live in cold places. Adult amphibians breathe through lungs and through the skin so they need humidity to survive. Young amphibians are called tadpoles. They are aquatic and breathe through gills. Most of amphibians are carnivores when they are adults, they usually eat insects. But tadpoles are herbivores. Most of amphibians are oviparous, although salamanders are ovoviviparous. They can have external and internal fertilization. The females lay eggs, in a jelly-like mass, in the water and the tadpoles hatch from the eggs. The tadpoles change enormously as they are adults. This change is called metamorphosis. (Vocabulary: frog: rana / toad: sapo / newt: tritón / anurans: anuros / urodeles: urodelos / gills: branquias / to grow up: crecer / to colonise: colonizar / even though: aunque / still: todavía / swimming : la natación / webbed feet: patas membranosas / developed: desarrollado / drying out: desecación / to jump: saltar / thin: delgado / tongue: lengua / prominent: prominente, saltón / eyelid: párpado / auditory openings: orificios auditivos / eardrum: tímpano / tadpole: renacuajo / moist: húmedo / humidity: humedad / to lay: poner, depositar / to hatch: salir del huevo, eclosionar / to become: convertirse en) Fill the boxes in the following picture 1
11 Match the words in the left column with the sentences on the right 1 Poikilotherm A It is the change from tadpoles to adults 2 Tadpoles B It is smooth with no hair or scales. 3 Salamanders C They have got four legs and tail 4 Metamorphosis D They have got tail and no legs 5 Skin E They cannot control their temperature Answers: Fill the gaps with the following words from the list smooth water tadpoles back toads land humidity jumps metamorphosis fertilization hair gills cold lungs hatch Amphibians are born in the... and when they grow up they can live on... Frogs have got... limbs very developed so they can make big... All amphibians have got... thin skin, with no... or scales. Frogs and... have not got a tail. Salamanders have got a tail. The young, called..., have got tail and no legs Amphibians do not live in... places because they are poikilotherm vertebrates Adult animals breathe through... and through the skin so they need... to survive. The tadpoles are aquatic and breathe through... Amphibians can have external and internal... The females lay eggs into the water and the tadpoles... from the eggs. The tadpoles change enormously as they become adults. This change is called What is the difference between fore and back limbs in frogs? How is the amphibians skin? How many legs have tadpoles got? What is the difference between adult amphibians and tadpoles breathings? What is the name of the change that tadpoles suffer when they become adults? Why do amphibians have to live in humid places? Do the frogs incubate its eggs? What are the differences in the external shape between an adult frog and a tadpole?... FISH A trout, a shark, a ray, and a tuna are fish. All fish are aquatic vertebrates. Some of them, like sharks, live in the sea and some of them live in fresh waters, like the trout The body Fish are tube-shaped or fusiform. Their body is wide in the middle and narrow in the end. This reduces water resistance and makes movement easier. 1
12 Fish limbs are called fins. Fins are located in thorax, stomach, back, and tail. Fins allow them to propel themselves and change direction easily. Their body is covered by scales. This protect them and helps them move in water Fish have got a lateral line. It is a sensory organ that helps the animal feel the vibrations through the water. Most of fish have got swim-bladder. It is an organ with the shape of a bag which is filled with air and so the fish controls the depth. Functions Fish cannot control their temperature. They are poikilotherms or cold-blooded vertebrates. Fish breathe through gills. The gills are behind the head, and they are protected by a kind of bone called operculum (gills covers). Water enters the mouth and passes through the gills. Sharks and rays have not got operculum but five gill slits. Most of fish are carnivores, but there are omnivores and herbivores as well. Fish are oviparous animals with external fertilization (the male deposits its sperms on the ovules that the female lays in the water). The young fish hatch from the eggs. They are called fry. (Vocabulary: trout: trucha / shark: tiburón / ray: raya / tuna: atún / tube-shaped: forma hidrodinámica / wide: ancho / narrow: estrecho / to propel: impulsar lateral line: linea lateral / swimbladder: vejiga natatoria / depth: profundidad / gills: branquias / operculum: opérculo / gill slits: hendiduras branquiales / as well: también / to deposit: depositar / sperm: espermatozoide / ovule: óvulo / to lay: poner, depositar / to hatch: salir del huevo, eclosionar / fry: alevin) Fill the boxes in the following picture Match the words in the left column with the sentences on the right 1 Operculum A This means that the body is wide in the middle and narrow in the end. 2 Swim-bladder B It is a sensory organ to feel the vibrations through the water. 3 Tube-shaped C It is an organ with the shape of a bag, so the animal controls the depth. 4 Fry D It is a bone that protects the gills 5 Lateral line. E They are young fish that hatch from the eggs Answers:
13 Fill the gaps with the following words from the list Lateral line fry wide tube-shaped gills end sea swim-bladder depth scales trout fins operculum vibrations bag water Some fish, like sharks, live in the... and some of them live in fresh waters, like the... Fish are..., their body is... in the middle and narrow in the... Fish have got... and their body is covered by... All fish have got a... It is a sensory organ that helps the animal feel the... through the water. Most of fish have got... It is an organ with the shape of a... which is filled with air and so the animal controls the... Fish breathe through... They are behind the head protected by the... (gills covers). Fish females lay eggs in the... The young fish, called..., hatch from the eggs. 1. Do all fish live in salty waters? How is the body of fish? How do fish breathe? What is the function of swim-bladder? Is fish fertilization internal or external?... Complete the following table Limbs shapes Skin covering Temperature control Type of breathing Type of diet Type of reproduction Mammals Birds Reptiles Amphibians Fish 1. Give the name of a mammal that has got fins Do all birds fly? If not, give the name of one that cannot fly What have a turtle and a duck got in common in relation to the mouth? Why cannot a whale stay under the water for a long time?... 1
14 5. What is the main difference between a tadpole and a fry? What are the main similarities between a tadpole and a fry? What have a dolphin and a turtle got in common in relation to the mouth?... Complete the following table Vertebrate organs Backbone What are they? What group do they belong to? Lungs Fins Swim-bladder Lateral line Carapace Wings 1
I.E.S LA ESCRIBANA 1º E.S.O.
 I.E.S LA ESCRIBANA Lesson 4 1º E.S.O. Sección Bilingüe Vertebrate Animals I.E.S LA ESCRIBANA 1º E.S.O. Lesson 1: Vertebrate Animals ANIMAL KINGDOM All animals share some common characteristics: They are
I.E.S LA ESCRIBANA Lesson 4 1º E.S.O. Sección Bilingüe Vertebrate Animals I.E.S LA ESCRIBANA 1º E.S.O. Lesson 1: Vertebrate Animals ANIMAL KINGDOM All animals share some common characteristics: They are
3rd GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UDI 2.- FAUNIA. ANIMALS-VERTEBRATES (7)
 VERTEBRATES 3rd GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UDI 2.- FAUNIA. ANIMALS-VERTEBRATES (7) Vertebrates are animals which have a backbone and an internal skeleton. The skeleton protects vital organs and supports the
VERTEBRATES 3rd GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UDI 2.- FAUNIA. ANIMALS-VERTEBRATES (7) Vertebrates are animals which have a backbone and an internal skeleton. The skeleton protects vital organs and supports the
T. 6. THE VERTEBRATES
 T. 6. THE VERTEBRATES 1.- Relate the following concepts to their definition. Later, relate each concept to one of the pictures you are going to see. 1.- FIN a.- mammals with their babies 2.- GILLS b.-
T. 6. THE VERTEBRATES 1.- Relate the following concepts to their definition. Later, relate each concept to one of the pictures you are going to see. 1.- FIN a.- mammals with their babies 2.- GILLS b.-
Read the following texts 1. Living Things. Both animals and plants are living things because they are born, grow up, reproduce and die.
 Read the following texts 1. Living Things. Both animals and plants are living things because they are born, grow up, reproduce and die. All living things perform all of these functions. A tiger, a deer,
Read the following texts 1. Living Things. Both animals and plants are living things because they are born, grow up, reproduce and die. All living things perform all of these functions. A tiger, a deer,
Name Date When you put food away in the kitchen, you sort the food into groups. You put foods that are alike in certain ways into the same
 1 Name Date When you put food away in the kitchen, you sort the food into groups. You put foods that are alike in certain ways into the same group. Scientists do the same thing with animals, plants and
1 Name Date When you put food away in the kitchen, you sort the food into groups. You put foods that are alike in certain ways into the same group. Scientists do the same thing with animals, plants and
Vertebrates. Vertebrates are animals that have a backbone and an endoskeleton.
 Vertebrates Vertebrates are animals that have a backbone and an endoskeleton. The backbone replaces the notochord and contains bones called vertebrae. An endoskeleton is an internal skeleton that protects
Vertebrates Vertebrates are animals that have a backbone and an endoskeleton. The backbone replaces the notochord and contains bones called vertebrae. An endoskeleton is an internal skeleton that protects
Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals
 Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish,
Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish,
CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS
 CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS Natural Science 5º - 2016/2017 Unit 2: Classification of animals 1-What are the common features of the vertebrate animals? Complete the sentences using the words head spinal column
CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS Natural Science 5º - 2016/2017 Unit 2: Classification of animals 1-What are the common features of the vertebrate animals? Complete the sentences using the words head spinal column
Vertebrate Structure and Function
 Vertebrate Structure and Function Part 1 - Comparing Structure and Function Classification of Vertebrates a. Phylum: Chordata Common Characteristics: Notochord, pharyngeal gill slits, hollow dorsal nerve
Vertebrate Structure and Function Part 1 - Comparing Structure and Function Classification of Vertebrates a. Phylum: Chordata Common Characteristics: Notochord, pharyngeal gill slits, hollow dorsal nerve
Fishes, Amphibians, Reptiles
 Fishes, Amphibians, Reptiles Section 1: What is a Vertebrate? Characteristics of CHORDATES Most are Vertebrates (have a spinal cord) Some point in life cycle all chordates have: Notochord Nerve cord that
Fishes, Amphibians, Reptiles Section 1: What is a Vertebrate? Characteristics of CHORDATES Most are Vertebrates (have a spinal cord) Some point in life cycle all chordates have: Notochord Nerve cord that
Let s learn about ANIMALS. Level : School:.
 Let s learn about ANIMALS Name: Level : School:. 1. CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS There are many different animals and we can classify them according to: Their skeleton: Vertebrates have a skeleton but Invertebrates
Let s learn about ANIMALS Name: Level : School:. 1. CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS There are many different animals and we can classify them according to: Their skeleton: Vertebrates have a skeleton but Invertebrates
Essential Question: What are the characteristics of invertebrate animals? What are the characteristics of vertebrate animals?
 Essential Question: What are the characteristics of invertebrate animals? What are the characteristics of vertebrate animals? Key Concept: The animal kingdom is divided up into 35 phyla. These phyla can
Essential Question: What are the characteristics of invertebrate animals? What are the characteristics of vertebrate animals? Key Concept: The animal kingdom is divided up into 35 phyla. These phyla can
Vertebrates. skull ribs vertebral column
 Vertebrates skull ribs vertebral column endoskeleton in cells working together tissues tissues working together organs working together organs systems Blood carries oxygen to the cells carries nutrients
Vertebrates skull ribs vertebral column endoskeleton in cells working together tissues tissues working together organs working together organs systems Blood carries oxygen to the cells carries nutrients
All living things are classified into groups based on the traits they share. Taxonomy is the study of classification. The largest groups into which
 All living things are classified into groups based on the traits they share. Taxonomy is the study of classification. The largest groups into which the scientists divide the groups are called kingdoms.
All living things are classified into groups based on the traits they share. Taxonomy is the study of classification. The largest groups into which the scientists divide the groups are called kingdoms.
Phylum Chordata. Fish, Amphibians, Reptiles
 Phylum Chordata Fish, Amphibians, Reptiles Chordates Three different groups Vertebrates Lancelets Tunicates At some point in their lives, they all have four special body parts Notocord Hollow nerve cord
Phylum Chordata Fish, Amphibians, Reptiles Chordates Three different groups Vertebrates Lancelets Tunicates At some point in their lives, they all have four special body parts Notocord Hollow nerve cord
Kingdom Animalia. All animals are multicellular organisms with real tissues and heterotrophic nutrition
 Keywords Kingdom Animalia Poriferan, -s Coelenterate,-s Echinoderm, -s Mollusc, -s Medusa, -s Polyp, -s Arthropod, -s Arachnid, -s Crustacean, -s Myriapod, -s Radula Exoskeleton / endoskeleton Atrial cavity
Keywords Kingdom Animalia Poriferan, -s Coelenterate,-s Echinoderm, -s Mollusc, -s Medusa, -s Polyp, -s Arthropod, -s Arachnid, -s Crustacean, -s Myriapod, -s Radula Exoskeleton / endoskeleton Atrial cavity
Diversity of Animals
 Classifying Animals Diversity of Animals Animals can be classified and grouped based on similarities in their characteristics. Animals make up one of the major biological groups of classification. All
Classifying Animals Diversity of Animals Animals can be classified and grouped based on similarities in their characteristics. Animals make up one of the major biological groups of classification. All
DO NOW: Invertebrate POP Quiz. Sit Quietly and clear off your desk/table of everything EXCEPT and blank piece of white lined paper and a pen/pencil.
 DO NOW: Invertebrate POP Quiz Sit Quietly and clear off your desk/table of everything EXCEPT and blank piece of white lined paper and a pen/pencil. DO NOW: Invertebrate POP Quiz Question 1: What is an
DO NOW: Invertebrate POP Quiz Sit Quietly and clear off your desk/table of everything EXCEPT and blank piece of white lined paper and a pen/pencil. DO NOW: Invertebrate POP Quiz Question 1: What is an
Name Class Date. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 14 2 The Animal Kingdom SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is diversity? What are vertebrates? What
CHAPTER 14 2 The Animal Kingdom SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is diversity? What are vertebrates? What
Animals Classification
 Animals Classification By Piyush & Ilaxi Grouping & Identifying Living Things 2 Classifying Living Things Classifying Living Things Biological Classification is the way in which scientists use to categorize
Animals Classification By Piyush & Ilaxi Grouping & Identifying Living Things 2 Classifying Living Things Classifying Living Things Biological Classification is the way in which scientists use to categorize
Most amphibians begin life as aquatic organisms and then live on land as adults.
 Section 3: Most amphibians begin life as aquatic organisms and then live on land as adults. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What were the kinds of adaptations
Section 3: Most amphibians begin life as aquatic organisms and then live on land as adults. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What were the kinds of adaptations
Natural Science 1º ESO
 Unit 5 y 6. Animals. NAME Adapted from Natural Science. 1º ESO. Anaya Natural Science 1º ESO 0 INDEX 1. VOCABULARY... 1 2. VOCABULARIO... 2 3. UNIT CHART...Cover and 3 4. UNIT ACTIVITIES AND NOTES... 4-14
Unit 5 y 6. Animals. NAME Adapted from Natural Science. 1º ESO. Anaya Natural Science 1º ESO 0 INDEX 1. VOCABULARY... 1 2. VOCABULARIO... 2 3. UNIT CHART...Cover and 3 4. UNIT ACTIVITIES AND NOTES... 4-14
#8964 Standards-Based Science Investigations 2 Teacher Created Resources, Inc.
 Introduction...4 Locating Simple Science Materials...5 Standards Correlation....7 Thinking About Inquiry Investigations...9 Inquiry Assessment Rubric...12 Student Inquiry Worksheets...13 Sample Inquiry
Introduction...4 Locating Simple Science Materials...5 Standards Correlation....7 Thinking About Inquiry Investigations...9 Inquiry Assessment Rubric...12 Student Inquiry Worksheets...13 Sample Inquiry
Some Facts about... Amphibians
 Amphibians Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates that live part of their lives in water and part on land. Amphibians eggs are laid in water and they are born there. They begin their lives with gills
Amphibians Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates that live part of their lives in water and part on land. Amphibians eggs are laid in water and they are born there. They begin their lives with gills
VERTEBRATE READING. Fishes
 VERTEBRATE READING Fishes The first vertebrates to become a widespread, predominant life form on earth were fishes. Prior to this, only invertebrates, such as mollusks, worms and squid-like animals, would
VERTEBRATE READING Fishes The first vertebrates to become a widespread, predominant life form on earth were fishes. Prior to this, only invertebrates, such as mollusks, worms and squid-like animals, would
Animals WORKSHEET 3.1 Animals
 Animals WORKSHEET 3.1 Animals 1. Are these sentences true or false? Correct the false ones. a) A butterfly is a non-living thing. b) Water is a non-living thing. c) Living things are born, die, reproduce
Animals WORKSHEET 3.1 Animals 1. Are these sentences true or false? Correct the false ones. a) A butterfly is a non-living thing. b) Water is a non-living thing. c) Living things are born, die, reproduce
30-3 Amphibians Slide 1 of 47
 1 of 47 What Is an Amphibian? What Is an Amphibian? An amphibian is a vertebrate that, with some exceptions: lives in water as a larva and on land as an adult breathes with lungs as an adult has moist
1 of 47 What Is an Amphibian? What Is an Amphibian? An amphibian is a vertebrate that, with some exceptions: lives in water as a larva and on land as an adult breathes with lungs as an adult has moist
5 pt. 10 pt. 15 pt. 20 pt. 25 pt
 Final Jeopardy Characteristics of Vertebrates Characteristics of Fish Amphibians Reptiles Chapter 16 Vocabulary 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 20 pt
Final Jeopardy Characteristics of Vertebrates Characteristics of Fish Amphibians Reptiles Chapter 16 Vocabulary 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 10 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 15 pt 20 pt
Name Class Date. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 14 4 Vertebrates SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are vertebrates different from invertebrates? How
CHAPTER 14 4 Vertebrates SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are vertebrates different from invertebrates? How
Classification of Animals. adapted from
 Classification of Animals Animals With Backbones AMPHIBIAN FISH MAMMAL BIRD REPTILE Animals With Backbones Animals with backbones are called vertebrates. Vertebrates include many different kinds of animals.
Classification of Animals Animals With Backbones AMPHIBIAN FISH MAMMAL BIRD REPTILE Animals With Backbones Animals with backbones are called vertebrates. Vertebrates include many different kinds of animals.
Sec KEY CONCEPT Amphibians evolved from lobe-finned fish.
 Wed 4/26 Activities Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Students will describe the adaptations of amphibians that help them
Wed 4/26 Activities Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Students will describe the adaptations of amphibians that help them
1. Examine the specimens of sponges on the lab table. Which of these are true sponges? Explain your answers.
 Station #1 - Porifera 1. Examine the specimens of sponges on the lab table. Which of these are true sponges? Explain your answers. 2. Sponges are said to have an internal special skeleton. Examine the
Station #1 - Porifera 1. Examine the specimens of sponges on the lab table. Which of these are true sponges? Explain your answers. 2. Sponges are said to have an internal special skeleton. Examine the
Amphibians. Land and Water Dwellers
 Amphibians Land and Water Dwellers Amphibians Most amphibians do not live completely in the water or completely on land and most must return to water to reproduce http://potch74.files.wordpress.com/2007/09/amphibians.jpg
Amphibians Land and Water Dwellers Amphibians Most amphibians do not live completely in the water or completely on land and most must return to water to reproduce http://potch74.files.wordpress.com/2007/09/amphibians.jpg
Let s Learn About: Vertebrates & Invertebrates. Informational passages, graphic organizers, study guide, flashcards, and MORE!
 Let s Learn About: Vertebrates & Invertebrates Informational passages, graphic organizers, study guide, flashcards, and MORE! Let s Learn About Vertebrates The animal kingdom is comprised of two main categories
Let s Learn About: Vertebrates & Invertebrates Informational passages, graphic organizers, study guide, flashcards, and MORE! Let s Learn About Vertebrates The animal kingdom is comprised of two main categories
Topic 3: Animals Ch.17 Characteristics of Animals p.338. Distinguishing Characteristics pp
 Topic 3: Animals Ch.17 Characteristics of Animals p.338 - Animals are: - Multicellular. - Ingestive heterotrophs. - Have a division of labour (tissues, organs, systems). - Motile at some stage in their
Topic 3: Animals Ch.17 Characteristics of Animals p.338 - Animals are: - Multicellular. - Ingestive heterotrophs. - Have a division of labour (tissues, organs, systems). - Motile at some stage in their
AP Biology. Animal Characteristics. Kingdom: Animals. Body Cavity. Animal Evolution. Invertebrate: Porifera. Invertebrate: Cnidaria.
 Kingdom: Animals Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Animal Characteristics Heterotrophs must ingest others for nutrients Multicellular complex bodies No cell walls allows active movement Sexual reproduction
Kingdom: Animals Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Animal Characteristics Heterotrophs must ingest others for nutrients Multicellular complex bodies No cell walls allows active movement Sexual reproduction
Phylogeny of Animalia (overview)
 The Diversity of Animals 2 Chapter 23 Phylogeny of Animalia (overview) Key features of Chordates Phylum Chordata (the Chordates) includes both invertebrates and vertebrates that share (at some point in
The Diversity of Animals 2 Chapter 23 Phylogeny of Animalia (overview) Key features of Chordates Phylum Chordata (the Chordates) includes both invertebrates and vertebrates that share (at some point in
Today s Class. Go over viewfinder lab A closer look at the Animal Kingdom Taxonomy Worksheet
 Kingdom Animalia Today s Class Go over viewfinder lab A closer look at the Animal Kingdom Taxonomy Worksheet Viewfinder Kingdom: Animalia Cells: multicellular Food: eats other organisms Movement: moves
Kingdom Animalia Today s Class Go over viewfinder lab A closer look at the Animal Kingdom Taxonomy Worksheet Viewfinder Kingdom: Animalia Cells: multicellular Food: eats other organisms Movement: moves
Biology Slide 1 of 50
 Biology 1 of 50 2 of 50 What Is a Reptile? What are the characteristics of reptiles? 3 of 50 What Is a Reptile? What Is a Reptile? A reptile is a vertebrate that has dry, scaly skin, lungs, and terrestrial
Biology 1 of 50 2 of 50 What Is a Reptile? What are the characteristics of reptiles? 3 of 50 What Is a Reptile? What Is a Reptile? A reptile is a vertebrate that has dry, scaly skin, lungs, and terrestrial
Reproduction in Seed Plants (pp )
 Structure and Function of Plants Reading/Notetaking Guide Reproduction in Seed Plants (pp. 388 397) This section gives examples of the group of seed plants known as gymnosperms and angiosperms and describes
Structure and Function of Plants Reading/Notetaking Guide Reproduction in Seed Plants (pp. 388 397) This section gives examples of the group of seed plants known as gymnosperms and angiosperms and describes
! Three things needed to survive on land were: ! 1. Have lungs and breathe air. ! 2. Have a body resistant to drying out.
 Marine Reptiles, Birds and Mammals Vertebrates! Invaded the land and are descendants from the bony fish and were able to withstand the conditions on the land.! They evolved two sets of limbs (even snakes)
Marine Reptiles, Birds and Mammals Vertebrates! Invaded the land and are descendants from the bony fish and were able to withstand the conditions on the land.! They evolved two sets of limbs (even snakes)
Week 19 KSE pp What are three characteristics of amphibians? (Amphibians are the smallest group of vertebrates. Amphibians are cold-blooded.
 Week 18 KSE pp. 78-79 1. What are the three types of fish and their main characteristics? (The three main types of fish are bony fish, cartilaginous fish and jawless fish. Cartilaginous fish have skeletons
Week 18 KSE pp. 78-79 1. What are the three types of fish and their main characteristics? (The three main types of fish are bony fish, cartilaginous fish and jawless fish. Cartilaginous fish have skeletons
Vertebrates. Vertebrate Characteristics. 444 Chapter 14
 4 Vertebrates Key Concept All vertebrates have a backbone, which supports other specialized body structures and functions. What You Will Learn Vertebrates have an endoskeleton that provides support and
4 Vertebrates Key Concept All vertebrates have a backbone, which supports other specialized body structures and functions. What You Will Learn Vertebrates have an endoskeleton that provides support and
Fish 2/26/13. Chordates 2. Sharks and Rays (about 470 species) Sharks etc Bony fish. Tetrapods. Osteichthans Lobe fins and lungfish
 Chordates 2 Sharks etc Bony fish Osteichthans Lobe fins and lungfish Tetrapods ns Reptiles Birds Feb 27, 2013 Chordates ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME Notochord Common ancestor of chordates Head Vertebral column
Chordates 2 Sharks etc Bony fish Osteichthans Lobe fins and lungfish Tetrapods ns Reptiles Birds Feb 27, 2013 Chordates ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME Notochord Common ancestor of chordates Head Vertebral column
What is the body structure of a sponge? Do they have specialized cells? Describe the process of reproduction in sponges.
 11.2 Sponges and Cnidarians What are the main characteristics of Sponges? Where are sponges found? What is the body structure of a sponge? Do they have specialized cells? Do sponges have separate sexes?
11.2 Sponges and Cnidarians What are the main characteristics of Sponges? Where are sponges found? What is the body structure of a sponge? Do they have specialized cells? Do sponges have separate sexes?
B-Division Herpetology Test. By: Brooke Diamond
 B-Division Herpetology Test By: Brooke Diamond Rules: - Play each slide for 2 minutes and answer the questions on the test sheet. - Use only pages attached to your binder, you may not use stray pages.
B-Division Herpetology Test By: Brooke Diamond Rules: - Play each slide for 2 minutes and answer the questions on the test sheet. - Use only pages attached to your binder, you may not use stray pages.
Unit 19.3: Amphibians
 Unit 19.3: Amphibians Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in amphibians. Outline the reproduction and development of amphibians. Identify the three living amphibian orders. Describe how amphibians
Unit 19.3: Amphibians Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in amphibians. Outline the reproduction and development of amphibians. Identify the three living amphibian orders. Describe how amphibians
How Animals Live. Chapter 2 Review
 How Animals Live Chapter 2 Review What do animals need to survive? Water Food Air (oxygen) Shelter Butterfly life cycle During the larva stage, the butterfly is called a caterpillar. During the pupa stage,
How Animals Live Chapter 2 Review What do animals need to survive? Water Food Air (oxygen) Shelter Butterfly life cycle During the larva stage, the butterfly is called a caterpillar. During the pupa stage,
WHAT ARE HERPTILES? WHICH IS WHICH? 1. Vertebrates are animals that have 2. Complete the following chart of vertebrate groups: EGGS LAID WHERE?
 WHAT ARE HERPTILES? 1. Vertebrates are animals that have 2. Complete the following chart of vertebrate groups: SKIN COVERING? GILLS OR LUNGS? EGGS LAID WHERE? ENDOTHERMIC OR ECTOTHERMIC Fish AMPHIBIANS
WHAT ARE HERPTILES? 1. Vertebrates are animals that have 2. Complete the following chart of vertebrate groups: SKIN COVERING? GILLS OR LUNGS? EGGS LAID WHERE? ENDOTHERMIC OR ECTOTHERMIC Fish AMPHIBIANS
First Facts by Rebecca Johnson
 First Facts by Rebecca Johnson Use these activity sheets to teach your science content in combination with literacy. There are two photocopiable worksheets to support each of the eight books in the series.
First Facts by Rebecca Johnson Use these activity sheets to teach your science content in combination with literacy. There are two photocopiable worksheets to support each of the eight books in the series.
Biology. Slide 1of 50. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 50 2of 50 Phylogeny of Chordates Nonvertebrate chordates Jawless fishes Sharks & their relatives Bony fishes Reptiles Amphibians Birds Mammals Invertebrate ancestor 3of 50 A vertebrate dry,
Biology 1of 50 2of 50 Phylogeny of Chordates Nonvertebrate chordates Jawless fishes Sharks & their relatives Bony fishes Reptiles Amphibians Birds Mammals Invertebrate ancestor 3of 50 A vertebrate dry,
A. Body Temperature Control Form and Function in Mammals
 Taxonomy Chapter 22 Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Mammals Characteristics Evolution of Mammals Have hair and First appear in the mammary glands Breathe air, 4chambered heart, endotherms
Taxonomy Chapter 22 Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Mammals Characteristics Evolution of Mammals Have hair and First appear in the mammary glands Breathe air, 4chambered heart, endotherms
Characteristics of a Reptile. Vertebrate animals Lungs Scaly skin Amniotic egg
 Reptiles Characteristics of a Reptile Vertebrate animals Lungs Scaly skin Amniotic egg Characteristics of Reptiles Adaptations to life on land More efficient lungs and a better circulator system were develope
Reptiles Characteristics of a Reptile Vertebrate animals Lungs Scaly skin Amniotic egg Characteristics of Reptiles Adaptations to life on land More efficient lungs and a better circulator system were develope
DEUTEROSTOMES. This presentation contains copyrighted material under the educational fair use exemption to the U.S. copyright law.
 DEUTEROSTOMES This presentation contains copyrighted material under the educational fair use exemption to the U.S. copyright law. Deuterostome Echinodermata body plan! Body plan! Larvae are bilateral!
DEUTEROSTOMES This presentation contains copyrighted material under the educational fair use exemption to the U.S. copyright law. Deuterostome Echinodermata body plan! Body plan! Larvae are bilateral!
Animal Diversity wrap-up Lecture 9 Winter 2014
 Animal Diversity wrap-up Lecture 9 Winter 2014 1 Animal phylogeny based on morphology & development Fig. 32.10 2 Animal phylogeny based on molecular data Fig. 32.11 New Clades 3 Lophotrochozoa Lophophore:
Animal Diversity wrap-up Lecture 9 Winter 2014 1 Animal phylogeny based on morphology & development Fig. 32.10 2 Animal phylogeny based on molecular data Fig. 32.11 New Clades 3 Lophotrochozoa Lophophore:
What Is a Vertebrate?
 Name Date _ Class What Is a Vertebrate? This section explains the charactertsftcs of apt:mals With backbones. Use Target Reading Skills After you read the section, reread the paragraphs that contatn definition
Name Date _ Class What Is a Vertebrate? This section explains the charactertsftcs of apt:mals With backbones. Use Target Reading Skills After you read the section, reread the paragraphs that contatn definition
Get the other MEGA courses!
 www.thesimplehomeschool.com Simple Schooling BUGS MEGA course is ten weeks of all about bugs! This course grabs your student s attention and never lets go! Grades K-3 Get the other MEGA courses! Simple
www.thesimplehomeschool.com Simple Schooling BUGS MEGA course is ten weeks of all about bugs! This course grabs your student s attention and never lets go! Grades K-3 Get the other MEGA courses! Simple
I will learn to talk about. groups of animals animal characteristics animal habitats. Unit Unit 7
 I am a mammal with both fur and wings. I sleep during the day, and I hunt for food at night. I use high-pitched sounds to find my way around. What am I? I will learn to talk about groups of animals animal
I am a mammal with both fur and wings. I sleep during the day, and I hunt for food at night. I use high-pitched sounds to find my way around. What am I? I will learn to talk about groups of animals animal
Characteristics of Tetrapods
 Marine Tetrapods Characteristics of Tetrapods Tetrapod = four-footed Reptiles, Birds, & Mammals No marine species of amphibian Air-breathing lungs Class Reptilia Saltwater Crocodiles, Sea turtles, sea
Marine Tetrapods Characteristics of Tetrapods Tetrapod = four-footed Reptiles, Birds, & Mammals No marine species of amphibian Air-breathing lungs Class Reptilia Saltwater Crocodiles, Sea turtles, sea
Animals and Their Environments II
 Animals and Their Environments II Grade Level: K, 2 Content Area: Life science Core Area: Exploring Organisms and Their Environments, Animals and Their Environments Lesson Overview: Students will compare
Animals and Their Environments II Grade Level: K, 2 Content Area: Life science Core Area: Exploring Organisms and Their Environments, Animals and Their Environments Lesson Overview: Students will compare
Exceptions: Somebody liked snakes. Some people disliked dogs, geese, sharks
 Unit 1: ANIMALS Exceptions: Somebody liked snakes Some people disliked dogs, geese, sharks Both animals are fascinating & worthy of our interest ANIMAL NAMES Taxonomy is a branch of biology that categorizes
Unit 1: ANIMALS Exceptions: Somebody liked snakes Some people disliked dogs, geese, sharks Both animals are fascinating & worthy of our interest ANIMAL NAMES Taxonomy is a branch of biology that categorizes
35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external
 35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical characteristics. All animals share several common characteristics:
35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical characteristics. All animals share several common characteristics:
2019 Herpetology (B/C)
 2019 Herpetology (B/C) Information shared by: Emily Burrell - Piedmont Herpetology Coach Maya Marin - NC State Herpetology Club Corina Mota - Piedmont Head Coach Adapted from KAREN LANCOUR - National Bio
2019 Herpetology (B/C) Information shared by: Emily Burrell - Piedmont Herpetology Coach Maya Marin - NC State Herpetology Club Corina Mota - Piedmont Head Coach Adapted from KAREN LANCOUR - National Bio
Biology Lesson 12: From Fishes to Birds
 Biology Lesson 12: From Fishes to Birds This stunning bird is a peacock. Do you know why he is spreading out his big, colorful tail feathers like a fan? He is trying to attract a female for mating. Both
Biology Lesson 12: From Fishes to Birds This stunning bird is a peacock. Do you know why he is spreading out his big, colorful tail feathers like a fan? He is trying to attract a female for mating. Both
Reptiles Amphibians ( am-fib-ee-anz ) Fish Birds Mammals
 Chapter 11: Page 94 In the last chapter, you learned how plants go through a natural cycle of life. It is not just plants that go through a life cycle! Animals do too! Remember the definition of species?
Chapter 11: Page 94 In the last chapter, you learned how plants go through a natural cycle of life. It is not just plants that go through a life cycle! Animals do too! Remember the definition of species?
Vocabulary. 1. the group of vertebrates that have hair and nourish their young with milk
 Vocabulary migration prey jacobsons gland endothermic predator ectothermic hibernate mammal habitat vertebrate reptile invertebrate fish camouflage amphibian physical adaptation bird swim bladder Matching
Vocabulary migration prey jacobsons gland endothermic predator ectothermic hibernate mammal habitat vertebrate reptile invertebrate fish camouflage amphibian physical adaptation bird swim bladder Matching
Classification. Grouping & Identifying Living Things
 Classification Grouping & Identifying Living Things Taxonomy The study of how living things are classified Classification is the sorting of organisms based on similar characteristics Carolus Linnaeus is
Classification Grouping & Identifying Living Things Taxonomy The study of how living things are classified Classification is the sorting of organisms based on similar characteristics Carolus Linnaeus is
The Evolution of Chordates
 The Evolution of Chordates Phylum Chordata belongs to clade Deuterostomata. Deuterostomes have events of development in common with one another. 1. Coelom from archenteron surrounded by mesodermal tissue.
The Evolution of Chordates Phylum Chordata belongs to clade Deuterostomata. Deuterostomes have events of development in common with one another. 1. Coelom from archenteron surrounded by mesodermal tissue.
Time of Day. Teacher Lesson Plan Nocturnal Animals Pre-Visit Lesson. Overview
 Teacher Lesson Plan Nocturnal Animals Pre-Visit Lesson Duration: 40-50 minutes Minnesota State Science Standard Correlations: 3.4.1.1.2. Wisconsin State Science Standard Correlations: B 4.6, C.4.1, C.4.2
Teacher Lesson Plan Nocturnal Animals Pre-Visit Lesson Duration: 40-50 minutes Minnesota State Science Standard Correlations: 3.4.1.1.2. Wisconsin State Science Standard Correlations: B 4.6, C.4.1, C.4.2
*Using the 2018 List. Use the image below to answer question 6.
 Herpetology Test 1. Hearts in all herps other than consists of atria and one ventricle somewhat divided by a septum. (2 pts) a. snakes; two b. crocodiles; two c. turtles; three d. frogs; four 2. The food
Herpetology Test 1. Hearts in all herps other than consists of atria and one ventricle somewhat divided by a septum. (2 pts) a. snakes; two b. crocodiles; two c. turtles; three d. frogs; four 2. The food
Page # Diversity of Arthropoda Crustacea Morphology. Diversity of Arthropoda. Diversity of Arthropoda. Diversity of Arthropoda. Arthropods, from last
 Arthropods, from last time Crustacea are the dominant marine arthropods Crustacea are the dominant marine arthropods any terrestrial crustaceans? Should we call them shellfish? sowbugs 2 3 Crustacea Morphology
Arthropods, from last time Crustacea are the dominant marine arthropods Crustacea are the dominant marine arthropods any terrestrial crustaceans? Should we call them shellfish? sowbugs 2 3 Crustacea Morphology
Birds & Mammals. Chapter 15
 Birds & Mammals Chapter 15 What is a Bird? Vertebrate Endothermic Feathered 4 chambered heart Egg laying Fore-limbs adapted for flight Bones nearly hollow (allow for lighter weight) Bird Internal Anatomy
Birds & Mammals Chapter 15 What is a Bird? Vertebrate Endothermic Feathered 4 chambered heart Egg laying Fore-limbs adapted for flight Bones nearly hollow (allow for lighter weight) Bird Internal Anatomy
Animal phyla. Prior Knowledge Questions:
 1 Name: Animal phyla Core: Prior Knowledge Questions: What do Tim & Moby say about Invertebrates? 2 Want to watch the video again? Go to Invertebrates Brainpop (Username: nfmsbrain password: pop) Word
1 Name: Animal phyla Core: Prior Knowledge Questions: What do Tim & Moby say about Invertebrates? 2 Want to watch the video again? Go to Invertebrates Brainpop (Username: nfmsbrain password: pop) Word
MAMMAL LESSON PLAN. Understanding (s)/goals Students will understand that mammals are a unique group within the animal kingdom.
 MAMMAL LESSON PLAN Lesson Topic: Mammals Grade level: Elementary Grades Length of lesson: Approximately 5 days; will vary based on age and ability Curriculum Developer: Jennifer Mooney, M.Ed. Stage 1 Desired
MAMMAL LESSON PLAN Lesson Topic: Mammals Grade level: Elementary Grades Length of lesson: Approximately 5 days; will vary based on age and ability Curriculum Developer: Jennifer Mooney, M.Ed. Stage 1 Desired
Vertebrates. What is a vertebrate?
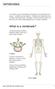 Vertebrates In a modern system of classification, all animals can be divided into two groups vertebrates and invertebrates. Vertebrates are animals that have a skeleton inside their bodies. Biologists
Vertebrates In a modern system of classification, all animals can be divided into two groups vertebrates and invertebrates. Vertebrates are animals that have a skeleton inside their bodies. Biologists
ADAPTATION IN ANIMALS. 1. Which body feature of a frog MAINLY helps it to capture a flying insect? Ans
 Name : Subject : Science Class : V Roll No. : Date : SECTION A Choose the correct alternative ADAPTATION IN ANIMALS 1. Which body feature of a frog MAINLY helps it to capture a flying insect? a. Long,
Name : Subject : Science Class : V Roll No. : Date : SECTION A Choose the correct alternative ADAPTATION IN ANIMALS 1. Which body feature of a frog MAINLY helps it to capture a flying insect? a. Long,
Table of Contents. Sample file
 Table of Contents What are Amphibians? The Defense Mechanisms of Amphibians The Order of Amphibians The Life Cycle of a Frog What is a Food Chain? The Amphibian Food Chain Amphibian Habitats The Amazing
Table of Contents What are Amphibians? The Defense Mechanisms of Amphibians The Order of Amphibians The Life Cycle of a Frog What is a Food Chain? The Amphibian Food Chain Amphibian Habitats The Amazing
Biology Review: Amphibians
 Name: Biology Review: Amphibians NOTE: USE THE SCANNED CHAPTER ON MY WEBSITE, NOT YOUR TEXTBOOK FOR THIS ASSIGNMENT 1-6. Amphibians were the first group of vertebrates to adapt to a land existence. What
Name: Biology Review: Amphibians NOTE: USE THE SCANNED CHAPTER ON MY WEBSITE, NOT YOUR TEXTBOOK FOR THIS ASSIGNMENT 1-6. Amphibians were the first group of vertebrates to adapt to a land existence. What
! Taxonomic Scheme of the 2018 Official Science Olympiad NATIONAL HERPETOLOGY List
 DISCLAIMER This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may be some changes in the final copy of the rules. The rules which will be in your Coaches Manual and Student Manuals will be the official
DISCLAIMER This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may be some changes in the final copy of the rules. The rules which will be in your Coaches Manual and Student Manuals will be the official
Animals and Their Environments II
 Animals and Their Environments II Grade Level: K, 2 Content Area: Life science Core Area: Exploring Organisms and Their Environments, Animals and Their Environments Lesson Overview: Students will compare
Animals and Their Environments II Grade Level: K, 2 Content Area: Life science Core Area: Exploring Organisms and Their Environments, Animals and Their Environments Lesson Overview: Students will compare
Teacher s Guide. All About Baby Animals series
 Teacher s Guide All About Baby Animals series Introduction This teacher s guide helps educate young children about baby animals. Animals live in many different habitats. Some live in grasslands, rainforests,
Teacher s Guide All About Baby Animals series Introduction This teacher s guide helps educate young children about baby animals. Animals live in many different habitats. Some live in grasslands, rainforests,
ì<(sk$m)=bdibci< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Labels Diagram Glossary Animals Scott Foresman Science 3.2 ì
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Labels Diagram Glossary Animals Scott Foresman Science 3.2 ì
There are 35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical
 Name 1 There are 35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical characteristics. All animals share several common
Name 1 There are 35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical characteristics. All animals share several common
08 AMPHIBIANS & REPTILES (B) AND HERPETOLOGY (C) TRAINING HANDOUT By Karen L. Lancour
 08 AMPHIBIANS & REPTILES (B) AND HERPETOLOGY (C) TRAINING HANDOUT By Karen L. Lancour This event will test knowledge of amphibians, turtles, crocodiles & reptiles. The Official National List will be used
08 AMPHIBIANS & REPTILES (B) AND HERPETOLOGY (C) TRAINING HANDOUT By Karen L. Lancour This event will test knowledge of amphibians, turtles, crocodiles & reptiles. The Official National List will be used
Lab 9: Inventing Life Forms
 Name: Section: Date: Lab 9: Inventing Life Forms 1 Instructions The purpose of this lab is to create a life form that may have evolved on a planet other than Earth. Follow the instructions below detailing
Name: Section: Date: Lab 9: Inventing Life Forms 1 Instructions The purpose of this lab is to create a life form that may have evolved on a planet other than Earth. Follow the instructions below detailing
Class Reptilia Testudines Squamata Crocodilia Sphenodontia
 Class Reptilia Testudines (around 300 species Tortoises and Turtles) Squamata (around 7,900 species Snakes, Lizards and amphisbaenids) Crocodilia (around 23 species Alligators, Crocodiles, Caimans and
Class Reptilia Testudines (around 300 species Tortoises and Turtles) Squamata (around 7,900 species Snakes, Lizards and amphisbaenids) Crocodilia (around 23 species Alligators, Crocodiles, Caimans and
2 nd Term Final. Revision Sheet. Students Name: Grade: 11 A/B. Subject: Biology. Teacher Signature. Page 1 of 11
 2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 11 A/B Subject: Biology Teacher Signature Page 1 of 11 Nour Al Maref International School Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Biology Worksheet (2 nd Term) Chapter-26
2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 11 A/B Subject: Biology Teacher Signature Page 1 of 11 Nour Al Maref International School Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Biology Worksheet (2 nd Term) Chapter-26
Taxonomy. Chapter 20. Evolutionary Development Diagram. I. Evolution 2/24/11. Kingdom - Animalia Phylum - Chordata Class Reptilia.
 Taxonomy Chapter 20 Reptiles Kingdom - Animalia Phylum - Chordata Class Reptilia Order Testudines - turtles Order Crocodylia - crocodiles, alligators Order Sphenodontida - tuataras Order Squamata - snakes
Taxonomy Chapter 20 Reptiles Kingdom - Animalia Phylum - Chordata Class Reptilia Order Testudines - turtles Order Crocodylia - crocodiles, alligators Order Sphenodontida - tuataras Order Squamata - snakes
What is an. Amphibian?
 Editors: Brian A. Jerome Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Lyndsey Tomasi What is an Graphics: Fred Thodal Amphibian? Teacher s Guide Visual Learning Company 1-800-453-8481 www.visuallearningco.com
Editors: Brian A. Jerome Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Lyndsey Tomasi What is an Graphics: Fred Thodal Amphibian? Teacher s Guide Visual Learning Company 1-800-453-8481 www.visuallearningco.com
CHAPTER 3 EATING HABIT OF ANIMALS
 JABAL FARASAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL, RABEGH KSA Affiliated to CBSE New Delhi SCIENCE-CLASS III-CHAPTER-WISE WORKSHEET-2 STUDENT NAME... ROLL NO. DATE CHAPTER 3 EATING HABIT OF ANIMALS I. FILL IN THE BLANKS
JABAL FARASAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL, RABEGH KSA Affiliated to CBSE New Delhi SCIENCE-CLASS III-CHAPTER-WISE WORKSHEET-2 STUDENT NAME... ROLL NO. DATE CHAPTER 3 EATING HABIT OF ANIMALS I. FILL IN THE BLANKS
CHAPTER 26. Animal Evolution The Vertebrates
 CHAPTER 26 Animal Evolution The Vertebrates Impacts, Issues: Interpreting and Misinterpreting the Past No one was around to witness the transitions in the history of life Fossils allow us glimpses into
CHAPTER 26 Animal Evolution The Vertebrates Impacts, Issues: Interpreting and Misinterpreting the Past No one was around to witness the transitions in the history of life Fossils allow us glimpses into
7.7.1 Species. 110 minutes. 164 marks. Page 1 of 47
 7.7.1 Species 110 minutes 164 marks Page 1 of 47 Q1. Ospreys can live in places where the weather is sometimes cold. (a) Explain how an osprey s feathers insulate it in cold weather. Ospreys hunt for fish
7.7.1 Species 110 minutes 164 marks Page 1 of 47 Q1. Ospreys can live in places where the weather is sometimes cold. (a) Explain how an osprey s feathers insulate it in cold weather. Ospreys hunt for fish
Diatoms are producers. They are found very near the surface of the sea.
 1. A food chain found in the sea is: very small small animals called animals called diatoms copepods krill whales Diatoms are producers. They are found very near the surface of the sea. (i) Where in the
1. A food chain found in the sea is: very small small animals called animals called diatoms copepods krill whales Diatoms are producers. They are found very near the surface of the sea. (i) Where in the
What is the evidence for evolution?
 What is the evidence for evolution? 1. Geographic Distribution 2. Fossil Evidence & Transitional Species 3. Comparative Anatomy 1. Homologous Structures 2. Analogous Structures 3. Vestigial Structures
What is the evidence for evolution? 1. Geographic Distribution 2. Fossil Evidence & Transitional Species 3. Comparative Anatomy 1. Homologous Structures 2. Analogous Structures 3. Vestigial Structures
CHARACTERISTICS OF AMPHIBIANS
 AMPHIBIAN NOTES "Amphibian" comes from the Greek meaning "both life". Amphibians can live on water and on land. Scientist infer that amphibians evolved from lobe-finned fishes called crossopterygians.
AMPHIBIAN NOTES "Amphibian" comes from the Greek meaning "both life". Amphibians can live on water and on land. Scientist infer that amphibians evolved from lobe-finned fishes called crossopterygians.
MANSFIELD SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL / SCIENCE / A. There is no God. B. All living things on Earth are related.
 The Evidence of Evolution Name: Date: 1. Biological Evolutions makes 2 very bold claims about living creatures.what are they circle 2. A. There is no God. B. All living things on Earth are related. C.
The Evidence of Evolution Name: Date: 1. Biological Evolutions makes 2 very bold claims about living creatures.what are they circle 2. A. There is no God. B. All living things on Earth are related. C.
HUMAN APPENDIX BATS & TROPICAL FLOWERS
 HUMAN APPENDIX In humans, the appendix is a short piece of tissue off the large intestine. It is not used by humans for digestive functions. In other mammals, like rabbits and deer, the cecum is a large
HUMAN APPENDIX In humans, the appendix is a short piece of tissue off the large intestine. It is not used by humans for digestive functions. In other mammals, like rabbits and deer, the cecum is a large
Sec KEY CONCEPT Reptiles, birds, and mammals are amniotes.
 Thu 4/27 Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Activities Students will describe the evolutionary significance of amniotic
Thu 4/27 Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Activities Students will describe the evolutionary significance of amniotic
JoJoKeKe s Herpetology Exam
 ~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~ JoJoKeKe s Herpetology Exam (SSSS) 2:30 to be given at each station- B/C Station 1: 1.) What is the family & genus of the shown
~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~ JoJoKeKe s Herpetology Exam (SSSS) 2:30 to be given at each station- B/C Station 1: 1.) What is the family & genus of the shown
Name Date Class. From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence.
 Name Date Class Structure and Function of Vertebrates Review and Reinforce Birds Understanding Main Ideas Answer the following questions. 1. What are four characteristics that all birds share? 2. What
Name Date Class Structure and Function of Vertebrates Review and Reinforce Birds Understanding Main Ideas Answer the following questions. 1. What are four characteristics that all birds share? 2. What
