Mammalogy Laboratory 3 Chiroptera, Primates, Scandentia, & Dermoptera. Order Chiroptera
|
|
|
- Jodie Warren
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mammalogy Laboratory 3 Chiroptera, Primates, Scandentia, & Dermoptera We have representation of the first three of these orders, and there are local chiropteran species. The Order Chiroptera has received a great deal of attention from systematists because an Australian neurobiologist has discovered that one group, the Pteropodidea (the megabats), has neuronal pathways that are very similar to those found in primates, and not at all similar to those of Microchiroptera. A flurry of molecular papers followed that examined the hypothesis of nonmonophyly of Chiroptera, and most could reject it. The data therefore indicate that the classical hypothesis of a monophyletic Chiroptera is supported. Furthermore, some recent papers have indicated that the megabats have evolved from within microbats, making the latter a paraphyletic group. Some difficult names have resulted; Yangochiroptera, which includes most of the microbats, and Yinpterochiroptera, which includes the megabats (Pteropodidae) and a few microbat families (e.g., Craseonycteridae, Hipposideridae, Megadermatidae, Rhinolophidae, etc.). Order Chiroptera General Comments: This is a very diverse group. Chiroptera is the second largest order of mammals, containing approximately 925 species; ca. 20% of all mammals are bats. The biology of bats and their morphological diversity are truly fascinating. In general the northern latitudes have a relatively depauperate bat fauna; all our local bats belong to a single family. Diagnosis: flying mammals with well-developed wings; hand and forefingers greatly elongated (except for the thumb); never > 2 pairs of upper incisors; never > 22 milk teeth; baculum present; manubrium often keeled. Range: Cosmopolitan (worldwide) Family Pteropodidae (fruit bats or flying foxes) Diagnosis: foredigit 2 retains some degree of independence, and is often clawed; mandible with angular process broad and low or practically absent; post-orbital process well-developed; bony palate extends posteriorly beyond last molar; tragus absent; no nose leafs; eyes well developed. Habits: Frugivores or nectivores; crepuscular/nocturnal; usually locate food by smell; have excellent vision; don t echolocate (except Rousettus); do not hibernate; long life span with low reproductive potential (usually one young per year). Range: Old World tropics: Representative Genera: Pteropus, Rousettus, Dobsonia, Micropteropus, Cynopterus. Material in Lab: Pteropus (skeleton) 1
2 yangochiropteran families Diagnosis: foredigit 2 scarcely, if at all independent, closely appressed against third digit, and lacking a claw; mandible with angular process well developed, usually long and narrow; postorbital process usually absent or rudimentary, occasionally well-developed; bony palate usually not extended posteriorly beyond last molars; tragus often present; eyes relatively small; effective echolocation in all groups. Range: cosmopolitan, including New Zealand. Families (those in parentheses are probably more closely related to megabats than to other microbats): Phyllostomidae Natalidae Furipteridae Thyropteridae Myzopodidae Mormoopidae Emballonuridae Noctilionidae Vespertilionidae Mystacinidae Nycteridae Molossidae Family Vespertilionidae (vespertilionid or common bats) Diagnosis: foredigit 3 with three phalanges, foredigit two with metacarpal and one small phalanx; nose-leaf absent or rudimentary; tragus present and well-developed; premaxillae separate; no post-orbital process; tail long, extending to end of wide interfemoral membrane; molars always 3/3, with well-developed W-shaped ectolophs (Dilambdodont). Habits: usually insectivorous, a few species piscivorous; migration and hibernation common; usually one young per year, but a few species have up to four; some tropical species polyestrous; may live as long as 30 years or more. Range: Cosmopolitan Representative Genera: 36 genera, 314 species. Material in Lab: Corynorhinus (Plecotus) townsendii (Townsends s big-eared bat) Lasiurus borealis (red bat)* Lasiurus cinereus (hoary bat) Eptesicus fuscus (big brown bat) Lasionycterus noctivagans (silver-haired bat) Myotis lucifugus (little brown bat) M. thysanodes (fringed myotis) M. evotis (long-eared myotis) M. volans (long-legged myotis) M. yumanensis (Yuma myotis) Pipistrellus hesperus (western pipistrelle) Antrozous pallidus (pallid bat) 2
3 Idaho Forms not represented: Euderma maculatum (spotted bat) Myotis californicus (California myotis) M. ciliolabrum (leibii) (western small-footed myotis) Key to Myotis species occurring in Idaho: 1. Uropatagium fringed with well-developed stiff hairs....m. thysanodes Uropatagium not visibly fringed Ears extending past rostrum when laid forward Ears not extending past rostrum when laid forward Ears > 16 mm, extending > 2 mm beyond rostrum.....m. evotis Ears < 16 mm Black facial marking present.m. ciliolabrum Black facial marking absent; sparse hair extending onto uropatagium...m. californicus 5. Uropatagium furred..m. volans Uropatagium not furred; calcar not keeled.6 6. Pelage glossy, with distinct sheen; greatest length of skull usually > 14 mm..m. lucifugus Pelage dull, often pale, without sheen; greatest length of skull < 14 mm.. M. yumanensis Family Molossidae (free-tailed bats and mastiff bats) Diagnosis: muzzle broad and obtuse; foredigit 3 with three phalanges; lips large, upper lip often furrowed by vertical wrinkles; ears usually large and broad, often united across forehead; tragus present but small; interfemoral membrane narrow, with tail extending far beyond distal edge; no postorbital process. Habits: insectivorous; inhabit caves, buildings or other similar structures; fast fliers (recorded up to 95 km/hr); some species migratory; some species hibernate but generally not as deeply as vespertilionids; most species colonial, with colonies of 20,000,000 known for Tadarida brasiliensis; typically one young per year. Range: widespread in tropical and subtropical forests; occur in the southern half of US Representative Genera: Tadarida, Otomops, Meoplatymops, Platymops, Sauromys, Eumops, Molossus. Martial in Lab: Tadarida brasiliensis* 3
4 Order Primates Diagnosis: plantigrade; herbivorous, omnivorous, rarely insectivorous or carnivorous; mostly arboreal, but some terrestrial; primarily pentadactyl; radius and ulna unfused, permitting free pronation and supination; molars brachydont and tuberculo-sectorial or bunodont; mandibular symphysis firmly ossified in some groups; orbits directed forward and separated from temporal fenestra by post-orbital bar or plate; baculum usually present (except in Tarsius, some cebids, and Homo); mammae usually in a single pectoral pair. Range: Pantropical, except Australia; Homo is cosmopolitan. Classification: Suborder Strepsirhini (informally prosimians ) Family Lemuridae Family Indriidae Family Daubentoniidea Family Lorisidae Family Cheirogaleidae Family Lepilemuridae Family Galagidae Suborder Haplorhini (informally anthropoids ) Infraorder Tarsiiformes Family Tarsiidae Infraorder Platyrrhini Family Callithricidae Family Callimiconidae Family Cebidae Infraorder Catarrhini Family Cercopithecidae Family Hylobatidae Family Hominidae (includes Pongidae) Family Cebidae (New World monkeys) Diagnosis: Small to medium sized; arboreal; nails on digits; pollex only slightly opposable or absent; tail variable in length but moderately to strongly prehensile; internarial septum broad, nostrils well -separated and laterally directed (platyrrhine condition); no cheek pouches or ischial callosities; molars usually bunodont; facial vibrissae reduced, but present; orbits large and directed forward; dental fromula 2/2 1/1 3/3 2-3/2-3 = 32 or 36; palate shorter than in catarrhines; jugal contributes to post-orbital plate and meets parietal. Habits: primarily herbivorous, but also omnivorous; usually live in territorial family groups; arboreal, climb quadrupedally; diurnal of nocturnal; engage in personal and social grooming; extremely vocal; possess well-developed color vision. Range: Amazon basin of South America, north to southern Mexico. Representative Genera: Saimiri, Aotus, Callicebus, Alouatta, Cacajao, Cebus, Ateles 4
5 Material in Lab: Cebus apella * (capuchin monkey) Family Cercopithecidae (Old World monkeys) Diagnosis: medium sized, arboreal to semiterrestrail; flattened nails on all digits; rostrum often lengthened; ischial collosities present; auditory bulla extends laterally as a bony tube; P 1 with anterior root sloping anteriorly into dentary, occluding with upper canine; tail not prehensile; dental formula typically 2/2 1/1 2/2 3/3 = 32; bunodont. Habits: omnivorous to herbivorous; well-developed social groups; usually diurnal; life spans up to 50 years; well-developed vocalizations, used primarily in social interactions; possess welldeveloped color vision. Range: Old World, from Africa east through southern Asia. Representative Genera: Miopithecus, Cercopithecus, Papio, Presbytis Material in Lab: Macaca (macaque)* Order Scandentia (tree shrews) Diagnosis: squirrel-like in size and form (19-40 cm); molars with w-shaped ectolophs (dilambdodont); post-orbital process contacts zygomatic arch to form postorbital bar; tail often tufted. Habits: inhabit deciduous forests; nest in trees, fallen logs, or holes in ground; rather omnivorous; diurnal. Range: southeastern Asia Family Tupaiidae Material in Lab: Tupaia* Skin & Skull *Not an Idaho form. Other Representative Genera: Ptilocercus, Urogale 5
Family Tupaiidae: tree shrews (5 genera) Genus to know: Tupaia Diurnal frugivores or insectivores, live in forests in Southeastern Asia
 Family Tupaiidae: tree shrews (5 genera) Genus to know: Tupaia Diurnal frugivores or insectivores, live in forests in Southeastern Asia Diagnosis: Looks like a squirrel with elongated snout, dilambodont
Family Tupaiidae: tree shrews (5 genera) Genus to know: Tupaia Diurnal frugivores or insectivores, live in forests in Southeastern Asia Diagnosis: Looks like a squirrel with elongated snout, dilambodont
Appendix 4: Keys to the bats of the Greater Yellowstone Network
 Appendix 4: Keys to the bats of the Greater Yellowstone Network Page 66 Dichotomous Key to the Bats of the Greater Yellowstone Network Doug Keinath, WYNDD, dkeinath@uwyo.edu # If this is true then go to
Appendix 4: Keys to the bats of the Greater Yellowstone Network Page 66 Dichotomous Key to the Bats of the Greater Yellowstone Network Doug Keinath, WYNDD, dkeinath@uwyo.edu # If this is true then go to
New York State Mammals
 New York State Mammals ORDER CHIROPTERA Family: Vespertilionidae 1. Little brown myotis (Myotis lucifugus) 2. Northern long-eared myotis (Myotis septentrionalis) 3. Indiana myotis (Myotis sodalis) 4. Small-footed
New York State Mammals ORDER CHIROPTERA Family: Vespertilionidae 1. Little brown myotis (Myotis lucifugus) 2. Northern long-eared myotis (Myotis septentrionalis) 3. Indiana myotis (Myotis sodalis) 4. Small-footed
Survey of the Primates
 Survey of the Primates Classification of the order Primates Classification of the order Primates Superfamily: End -OIDEA Family: End -IDAE CebOIDEA CebIDAE Subfamily: End -INAE Genus and species: Both
Survey of the Primates Classification of the order Primates Classification of the order Primates Superfamily: End -OIDEA Family: End -IDAE CebOIDEA CebIDAE Subfamily: End -INAE Genus and species: Both
One group (Tarsiers) is off on it's own (note clear where they belong). All tarsiers are endangered or threatened to some extent.
 Primates, part II Suborder Haplorrhini Divided into two clades (Infraorders?) Platyrrhini (flat noses, with nostrils to side) Catarrhini (nostrils pointing down) One group (Tarsiers) is off on it's own
Primates, part II Suborder Haplorrhini Divided into two clades (Infraorders?) Platyrrhini (flat noses, with nostrils to side) Catarrhini (nostrils pointing down) One group (Tarsiers) is off on it's own
ANTHR 1L Biological Anthropology Lab
 ANTHR 1L Biological Anthropology Lab Name: DEFINING THE ORDER PRIMATES Humans belong to the zoological Order Primates, which is one of the 18 Orders of the Class Mammalia. Today we will review some of
ANTHR 1L Biological Anthropology Lab Name: DEFINING THE ORDER PRIMATES Humans belong to the zoological Order Primates, which is one of the 18 Orders of the Class Mammalia. Today we will review some of
Mammalogy Lab 1: Skull, Teeth, and Terms
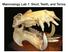 Mammalogy Lab 1: Skull, Teeth, and Terms Be able to: Goals of today s lab Locate all structures listed on handout Define all terms on handout what they are or what they look like Give examples of mammals
Mammalogy Lab 1: Skull, Teeth, and Terms Be able to: Goals of today s lab Locate all structures listed on handout Define all terms on handout what they are or what they look like Give examples of mammals
Occasional Papers. Field Identification Key and Guide for Bats of the United States of. Museum of Texas Tech University Number January 2019
 Occasional Papers Museum of Texas Tech University Number 360 17 January 2019 Field Identification Key and Guide for Bats of the United States of America Clint N. Morgan, Loren K. Ammerman, Krysta D. Demere,
Occasional Papers Museum of Texas Tech University Number 360 17 January 2019 Field Identification Key and Guide for Bats of the United States of America Clint N. Morgan, Loren K. Ammerman, Krysta D. Demere,
Minnesota_mammals_Info_10.doc 11/09/09 -- DRAFT Page 11 of 50
 Minnesota_mammals_Info_10.doc 11/09/09 -- DRAFT Page 11 of 50 Order Chiroptera Bats are the only mammals with wings and the only mammals that fly. Bats fly slower than birds, and all Minnesota bats are
Minnesota_mammals_Info_10.doc 11/09/09 -- DRAFT Page 11 of 50 Order Chiroptera Bats are the only mammals with wings and the only mammals that fly. Bats fly slower than birds, and all Minnesota bats are
Mammalogy Lecture 4B - Therian Mammal Diversity: Eutherians
 Mammalogy Lecture 4B - Therian Mammal Diversity: Eutherians VI. Eutherian Groups. We won t go through the diversity here in as great detail as we did for Marsupials - We ll leave a lot of details for the
Mammalogy Lecture 4B - Therian Mammal Diversity: Eutherians VI. Eutherian Groups. We won t go through the diversity here in as great detail as we did for Marsupials - We ll leave a lot of details for the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Primitive bat from the Early Eocene of Wyoming: flight and the evolution of echolocation Nancy B. Simmons 1, Kevin L. Seymour 2, Jörg Habersetzer 3 & Gregg F. Gunnell 4 1 American Museum of Natural History,
Primitive bat from the Early Eocene of Wyoming: flight and the evolution of echolocation Nancy B. Simmons 1, Kevin L. Seymour 2, Jörg Habersetzer 3 & Gregg F. Gunnell 4 1 American Museum of Natural History,
During the summer, two species primarily roost in structures (house bats) And four roost in trees and rocky outcrops (forest bats).
 Vermont has nine species of bats, each relying on specific summer and winter habitats. Six species hibernate in caves and mines during the winter and are known as cave bats. During the summer, two species
Vermont has nine species of bats, each relying on specific summer and winter habitats. Six species hibernate in caves and mines during the winter and are known as cave bats. During the summer, two species
Mammalogy Laboratory 1 - Mammalian Anatomy
 Mammalogy Laboratory 1 - Mammalian Anatomy I. The Goal. The goal of the lab is to teach you skeletal anatomy of mammals. We will emphasize the skull because many of the taxonomically important characters
Mammalogy Laboratory 1 - Mammalian Anatomy I. The Goal. The goal of the lab is to teach you skeletal anatomy of mammals. We will emphasize the skull because many of the taxonomically important characters
Overall structure is similar to humans, but again there are differences. Some features that are unique to mammals: Found in eutherian mammals.
 Mammalian anatomy and physiology (part II): Nervous system: Brain: Sensory input: Overall structure is similar to humans, but again there are differences. Some features that are unique to mammals: Smell:
Mammalian anatomy and physiology (part II): Nervous system: Brain: Sensory input: Overall structure is similar to humans, but again there are differences. Some features that are unique to mammals: Smell:
Bats. Order Chiroptera
 Bats Order Chiroptera First, the myths. I know what you re thinking. Flying mice. Wrong! If ever an animal suffered from superstitions and misconceptions it is the bat. First of all, bats are not rodents.
Bats Order Chiroptera First, the myths. I know what you re thinking. Flying mice. Wrong! If ever an animal suffered from superstitions and misconceptions it is the bat. First of all, bats are not rodents.
New York State Mammals. Morphology Ecology Identification Classification Distribution
 New York State Mammals Morphology Ecology Identification Classification Distribution ORDER: Didelphimorphia FAMILY: Didelphidae Common Name: Virginia opossum Scientific Name: (Didelphis virginiana) Marsupial
New York State Mammals Morphology Ecology Identification Classification Distribution ORDER: Didelphimorphia FAMILY: Didelphidae Common Name: Virginia opossum Scientific Name: (Didelphis virginiana) Marsupial
Mammals. Introduction (page 821) Evolution of Mammals (page 821) Form and Function in Mammals (pages ) Chapter 32.
 Chapter 32 Mammals Section 32 1 Introduction to the Mammals (pages 821 827) This section describes the characteristics common to all mammals, as well as how mammals carry out life functions. It also briefly
Chapter 32 Mammals Section 32 1 Introduction to the Mammals (pages 821 827) This section describes the characteristics common to all mammals, as well as how mammals carry out life functions. It also briefly
ASSESSMENT. Assessment
 ASSESSMENT Assessment This section provides some possible questions that could be incorporated into a pre and/or postassessment of student learning regarding concepts covered with the Bone Box Resource
ASSESSMENT Assessment This section provides some possible questions that could be incorporated into a pre and/or postassessment of student learning regarding concepts covered with the Bone Box Resource
New York State Mammals. Order Lagomorpha Order Rodentia
 New York State Mammals Order Lagomorpha Order Rodentia FAMILY: LEPORIDAE Rabbits and hares Conspicuous tail Fenestra appears as bony latticework Some species molt seasonally Presence of a second incisor
New York State Mammals Order Lagomorpha Order Rodentia FAMILY: LEPORIDAE Rabbits and hares Conspicuous tail Fenestra appears as bony latticework Some species molt seasonally Presence of a second incisor
Monograph. A key to the bats (Mammalia: Chiroptera) of South Asia
 Monograph A key to the bats (Mammalia: Chiroptera) of South Asia C. Srinivasulu, Paul A. Racey & Shahroukh Mistry Journal of Threatened Taxa 1001 Journal of Threatened Taxa ISSN 0974-7907 (online) 0974-7893
Monograph A key to the bats (Mammalia: Chiroptera) of South Asia C. Srinivasulu, Paul A. Racey & Shahroukh Mistry Journal of Threatened Taxa 1001 Journal of Threatened Taxa ISSN 0974-7907 (online) 0974-7893
Approximately 220 species of wild mammals occur in California and the
 Approximately 220 species of wild mammals occur in California and the surrounding waters (including introduced species, but not domestic species such as house cats). Amazingly, the state of California
Approximately 220 species of wild mammals occur in California and the surrounding waters (including introduced species, but not domestic species such as house cats). Amazingly, the state of California
Lab 8 Order Carnivora: Families Canidae, Felidae, and Ursidae Need to know Terms: carnassials, digitigrade, reproductive suppression, Jacobson s organ
 Lab 8 Order Carnivora: Families Canidae, Felidae, and Ursidae Need to know Terms: carnassials, digitigrade, reproductive suppression, Jacobson s organ Family Canidae Canis latrans ID based on skull, photos,
Lab 8 Order Carnivora: Families Canidae, Felidae, and Ursidae Need to know Terms: carnassials, digitigrade, reproductive suppression, Jacobson s organ Family Canidae Canis latrans ID based on skull, photos,
Family Soricidae Masked shrew Southeastern shrew (long-tailed shrews)
 Masked shrew Southeastern shrew (long-tailed shrews) Solitary, insectivorous & primarily nocturnal Prefers moist habitats Breeds summer-fall Has 1-2 litters per breeding season Family Soricidae Family
Masked shrew Southeastern shrew (long-tailed shrews) Solitary, insectivorous & primarily nocturnal Prefers moist habitats Breeds summer-fall Has 1-2 litters per breeding season Family Soricidae Family
New York State Mammals. Order Rodentia (cont.) Order Lagomorpha
 New York State Mammals Order Rodentia (cont.) Order Lagomorpha FAMILY: CRICETIDAE New World rats, mice, voles, hamsters, etc. Diverse & species rich Most terrestrial, 1 in NYS is aquatic Muskrat Subfamily
New York State Mammals Order Rodentia (cont.) Order Lagomorpha FAMILY: CRICETIDAE New World rats, mice, voles, hamsters, etc. Diverse & species rich Most terrestrial, 1 in NYS is aquatic Muskrat Subfamily
Minnesota_mammals_Info_9.doc 11/04/09 -- DRAFT Page 1 of 64. Minnesota mammals
 Minnesota_mammals_Info_9.doc 11/04/09 -- DRAFT Page 1 of 64 Minnesota mammals This is a short guide to Minnesota mammals, with information drawn from Hazard s Mammals of, Walker s Mammals of the World,
Minnesota_mammals_Info_9.doc 11/04/09 -- DRAFT Page 1 of 64 Minnesota mammals This is a short guide to Minnesota mammals, with information drawn from Hazard s Mammals of, Walker s Mammals of the World,
Skulls & Evolution. 14,000 ya cro-magnon. 300,000 ya Homo sapiens. 2 Ma Homo habilis A. boisei A. robustus A. africanus
 Skulls & Evolution Purpose To illustrate trends in the evolution of humans. To demonstrate what you can learn from bones & fossils. To show the adaptations of various mammals to different habitats and
Skulls & Evolution Purpose To illustrate trends in the evolution of humans. To demonstrate what you can learn from bones & fossils. To show the adaptations of various mammals to different habitats and
Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy
 Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy Presented by BIOBUGS: Biology Inquiry and Outreach with Boston University Graduate Students In association with LERNet and The BU Biology Teaching Laboratory Designed and
Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy Presented by BIOBUGS: Biology Inquiry and Outreach with Boston University Graduate Students In association with LERNet and The BU Biology Teaching Laboratory Designed and
B ats and Rabies. A Public Health Guide. Eastern Red Bat (Lasiurus borealis)
 B ats and Rabies A Public Health Guide Eastern Red Bat (Lasiurus borealis) What is rabies and how do people get it? Rabies is an infectious viral disease that affects the nervous system of humans and other
B ats and Rabies A Public Health Guide Eastern Red Bat (Lasiurus borealis) What is rabies and how do people get it? Rabies is an infectious viral disease that affects the nervous system of humans and other
Plestiodon (=Eumeces) fasciatus Family Scincidae
 Plestiodon (=Eumeces) fasciatus Family Scincidae Living specimens: - Five distinct longitudinal light lines on dorsum - Juveniles have bright blue tail - Head of male reddish during breeding season - Old
Plestiodon (=Eumeces) fasciatus Family Scincidae Living specimens: - Five distinct longitudinal light lines on dorsum - Juveniles have bright blue tail - Head of male reddish during breeding season - Old
Rabies in Bats from Alabama
 Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 43(2), 2007, pp. 291 299 # Wildlife Disease Association 2007 Rabies in Bats from Alabama Laura C. Hester, 1,3 Troy L. Best, 1 and M. Keith Hudson 21 Department of Biological
Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 43(2), 2007, pp. 291 299 # Wildlife Disease Association 2007 Rabies in Bats from Alabama Laura C. Hester, 1,3 Troy L. Best, 1 and M. Keith Hudson 21 Department of Biological
MAMMAL SPECIES SEEN AT SCOTTSDALE COMMUNITY COLLEGE INDEX OF 14 SPECIES
 MAMMAL SPECIES SEEN AT SCOTTSDALE COMMUNITY COLLEGE INDEX OF 14 SPECIES References at end. Text written by staff. Photos by Roy Barnes, Emma Olsen and Dr. John Weser. Bailey's Pocket Mouse Black-tailed
MAMMAL SPECIES SEEN AT SCOTTSDALE COMMUNITY COLLEGE INDEX OF 14 SPECIES References at end. Text written by staff. Photos by Roy Barnes, Emma Olsen and Dr. John Weser. Bailey's Pocket Mouse Black-tailed
ALLOMETRY OF LITTER MASS IN BATS: MATERNAL SIZE, WING MORPHOLOGY, AND PHYLOGENY
 ALLOMETRY OF LITTER MASS IN BATS: MATERNAL SIZE, WING MORPHOLOGY, AND PHYLOGENY V. HAYSSEN AND T. H. KUNZ Department of Biological Sciences, Smith College, Northampton, MA 01063 (VH) Department of Biology,
ALLOMETRY OF LITTER MASS IN BATS: MATERNAL SIZE, WING MORPHOLOGY, AND PHYLOGENY V. HAYSSEN AND T. H. KUNZ Department of Biological Sciences, Smith College, Northampton, MA 01063 (VH) Department of Biology,
SAMPLE PAGE. Bats Express (Quick) Lapbook. Any Age. A Journey Through Learning
 A J T L Any Age Bats Express (Quick) Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guides, Coloring Sheets, and Activities A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2015 A Journey Through Learning
A J T L Any Age Bats Express (Quick) Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guides, Coloring Sheets, and Activities A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2015 A Journey Through Learning
Title: Phylogenetic Methods and Vertebrate Phylogeny
 Title: Phylogenetic Methods and Vertebrate Phylogeny Central Question: How can evolutionary relationships be determined objectively? Sub-questions: 1. What affect does the selection of the outgroup have
Title: Phylogenetic Methods and Vertebrate Phylogeny Central Question: How can evolutionary relationships be determined objectively? Sub-questions: 1. What affect does the selection of the outgroup have
SKELETONS: Museum of Osteology Tooth and Eye Dentification Teacher Resource
 SKELETONS: Museum of Osteology Tooth and Eye Dentification Teacher Resource Grade Levels: 3 rd 5 th Grade 3 rd Grade: SC.3.N.1.1 - Raise questions about the natural world, investigate them individually
SKELETONS: Museum of Osteology Tooth and Eye Dentification Teacher Resource Grade Levels: 3 rd 5 th Grade 3 rd Grade: SC.3.N.1.1 - Raise questions about the natural world, investigate them individually
Introduction to the Care and Rehabilitation of Microbats
 Introduction to the Care and Rehabilitation of Microbats (Focussing on Species of South East Queensland) WILDCARE AUSTRALIA INC. PO Box 2379, Nerang Mail Centre Qld 4211 Telephone: (07) 5527 2444 Facsimile:
Introduction to the Care and Rehabilitation of Microbats (Focussing on Species of South East Queensland) WILDCARE AUSTRALIA INC. PO Box 2379, Nerang Mail Centre Qld 4211 Telephone: (07) 5527 2444 Facsimile:
Description of Malacomys verschureni, a new Murid-species from Central Africa
 (Rev. ZooI. afr., 91, no 3) (A paru Ie 30 septembre 1977). Description of Malacomys verschureni, a new Murid-species from Central Africa (Mammalia - Muridae) By W.N. VERHEYEN ANDE. VAN DER STRAETEN * (Antwerpen)
(Rev. ZooI. afr., 91, no 3) (A paru Ie 30 septembre 1977). Description of Malacomys verschureni, a new Murid-species from Central Africa (Mammalia - Muridae) By W.N. VERHEYEN ANDE. VAN DER STRAETEN * (Antwerpen)
Virginia Opossum (Didelphis virginiana)
 Virginia Opossum (Didelphis virginiana) ORDER: Didelphimorphia FAMILY: Didelphidae FIELD GUIDE TO NORTH AMERICAN MAMMALS The Virginia opossum, the only marsupial found north of Mexico, is an adaptable
Virginia Opossum (Didelphis virginiana) ORDER: Didelphimorphia FAMILY: Didelphidae FIELD GUIDE TO NORTH AMERICAN MAMMALS The Virginia opossum, the only marsupial found north of Mexico, is an adaptable
New Carnivorous Dinosaurs from the Upper Cretaceous of Mongolia
 1955 Doklady, Academy of Sciences USSR 104 (5):779-783 New Carnivorous Dinosaurs from the Upper Cretaceous of Mongolia E. A. Maleev (translated by F. J. Alcock) The present article is a summary containing
1955 Doklady, Academy of Sciences USSR 104 (5):779-783 New Carnivorous Dinosaurs from the Upper Cretaceous of Mongolia E. A. Maleev (translated by F. J. Alcock) The present article is a summary containing
Animal Evolution The Chordates. Chapter 26 Part 2
 Animal Evolution The Chordates Chapter 26 Part 2 26.10 Birds The Feathered Ones Birds are the only animals with feathers Descendants of flying dinosaurs in which scales became modified as feathers Long
Animal Evolution The Chordates Chapter 26 Part 2 26.10 Birds The Feathered Ones Birds are the only animals with feathers Descendants of flying dinosaurs in which scales became modified as feathers Long
Your Eye, My Eye, and the Eye of the Aye Aye: Evolution of Human Vision from 65 Million Years Ago to the Present
 # 75 Your Eye, My Eye, and the Eye of the Aye Aye: Evolution of Human Vision from 65 Million Years Ago to the Present Dr. Christopher Kirk December 2, 2011 Produced by and for Hot Science - Cool Talks
# 75 Your Eye, My Eye, and the Eye of the Aye Aye: Evolution of Human Vision from 65 Million Years Ago to the Present Dr. Christopher Kirk December 2, 2011 Produced by and for Hot Science - Cool Talks
Mammalogy 4764 Lab Practical page 1 Name Key
 Mammalogy 4764 Lab Practical page 1 Name Key Comments on exam (LP_2 is this Lab practical): As is kind of typical for the final, students know the taxonomy and identification well, or not so well. I usually
Mammalogy 4764 Lab Practical page 1 Name Key Comments on exam (LP_2 is this Lab practical): As is kind of typical for the final, students know the taxonomy and identification well, or not so well. I usually
Introduction to the Care and Rehabilitation of Microbats
 Introduction to the Care and Rehabilitation of Microbats (Focussing on Species of South East Queensland) The entire contents of these notes (except where specified) should be considered copyright and no
Introduction to the Care and Rehabilitation of Microbats (Focussing on Species of South East Queensland) The entire contents of these notes (except where specified) should be considered copyright and no
'~:~~:h\2l' Mammals Marshall White, Reginald H. Barrett, Allan S. Boss, Thomas F. Newman, Thomas]. Rahn, and Daniel F. Williams J..::J.' ~~.
!['~:~~:h\2l' Mammals Marshall White, Reginald H. Barrett, Allan S. Boss, Thomas F. Newman, Thomas]. Rahn, and Daniel F. Williams J..::J.' ~~. '~:~~:h\2l' Mammals Marshall White, Reginald H. Barrett, Allan S. Boss, Thomas F. Newman, Thomas]. Rahn, and Daniel F. Williams J..::J.' ~~.](/thumbs/81/83098177.jpg) Mammals Marshall White, Reginald H. Barrett, Allan S. Boss, Thomas F. Newman, Thomas]. Rahn, and Daniel F. Williams I This chapter offers information on the status, distribution by habitat, and basic life
Mammals Marshall White, Reginald H. Barrett, Allan S. Boss, Thomas F. Newman, Thomas]. Rahn, and Daniel F. Williams I This chapter offers information on the status, distribution by habitat, and basic life
Reproducing: Cockroaches hatch from eggs. See if you can spot the smallest cockroach in the enclosure.
 Madagascan Hissing Cockroaches (Gromphadorhina portentosa) These cockroaches come from the rainforests of Madagascar. They live on the forest floor and in the trees. Moving: Most cockroaches have wings
Madagascan Hissing Cockroaches (Gromphadorhina portentosa) These cockroaches come from the rainforests of Madagascar. They live on the forest floor and in the trees. Moving: Most cockroaches have wings
Night Life Pre-Visit Packet
 Night Life Pre-Visit Packet The activities in this pre-visit packet have been designed to help you and your students prepare for your upcoming Night Life program at the St. Joseph County Parks. The information
Night Life Pre-Visit Packet The activities in this pre-visit packet have been designed to help you and your students prepare for your upcoming Night Life program at the St. Joseph County Parks. The information
.56 m. (22 in.). COMPSOGNATHOID DINOSAUR FROM THE. Medicine Bow, Wyoming, by the American Museum Expedition
 Article XII.-ORNITHOLESTES HERMANNI, A NEW COMPSOGNATHOID DINOSAUR FROM THE UPPER JURASSIC. By HENRY FAIRFIELD OSBORN. The type skeleton (Amer. Mus. Coll. No. 6I9) of this remarkable animal was discovered
Article XII.-ORNITHOLESTES HERMANNI, A NEW COMPSOGNATHOID DINOSAUR FROM THE UPPER JURASSIC. By HENRY FAIRFIELD OSBORN. The type skeleton (Amer. Mus. Coll. No. 6I9) of this remarkable animal was discovered
Lab 5: Rodentia and Lagomorpha
 Lab 5: Rodentia and Lagomorpha (8 families in B.C.) Sciuridae squirrels (16 species in B.C.) Muridae mice, rats, lemmings, voles (16) Aplodontidae mountain beaver (1) Castoridae beaver (1) Dipodidae jumping
Lab 5: Rodentia and Lagomorpha (8 families in B.C.) Sciuridae squirrels (16 species in B.C.) Muridae mice, rats, lemmings, voles (16) Aplodontidae mountain beaver (1) Castoridae beaver (1) Dipodidae jumping
1. Hair 2. Mammary glands produce milk 3. Specialized teeth 4. 3 inner ear bones 5. Endothermic 6. Diaphragm 7. Sweat, oil and scent glands 8.
 Class Mammalia The Mammals Key Characteristics of Mammals 1. Hair 2. Mammary glands produce milk 3. Specialized teeth 4. 3 inner ear bones 5. Endothermic 6. Diaphragm 7. Sweat, oil and scent glands 8.
Class Mammalia The Mammals Key Characteristics of Mammals 1. Hair 2. Mammary glands produce milk 3. Specialized teeth 4. 3 inner ear bones 5. Endothermic 6. Diaphragm 7. Sweat, oil and scent glands 8.
Select Mammals of Loudoun County
 Select Mammals of Loudoun County Class Mammalia Warm-blooded Fur Produce Milk Most bear live young Order: Marsupialia Marsupials The Pouched Mammals Opossum (Didelphis virginianus) Only marsupial in North
Select Mammals of Loudoun County Class Mammalia Warm-blooded Fur Produce Milk Most bear live young Order: Marsupialia Marsupials The Pouched Mammals Opossum (Didelphis virginianus) Only marsupial in North
Standards-Based Module (Lesson/Unit Plan) Cover Page. Title of Lesson/Unit: Mammal Teeth and Skulls - Adaptations and Identification
 Standards-Based Module (Lesson/Unit Plan) Cover Page Content Area: Life Science Grade Level: 6, 7, or 8 Title of Lesson/Unit: Mammal Teeth and Skulls - Adaptations and Identification Original Lesson by:
Standards-Based Module (Lesson/Unit Plan) Cover Page Content Area: Life Science Grade Level: 6, 7, or 8 Title of Lesson/Unit: Mammal Teeth and Skulls - Adaptations and Identification Original Lesson by:
Beaver. Mammal Rodent
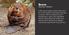 Beaver Rodent Is the second largest rodent in the world. It is a semi-aquatic rodent that is primarily nocturnal. They are mainly known for building dams, canals, and lodges(their homes). Large sharp front
Beaver Rodent Is the second largest rodent in the world. It is a semi-aquatic rodent that is primarily nocturnal. They are mainly known for building dams, canals, and lodges(their homes). Large sharp front
What we ve covered so far:
 What we ve covered so far: Didelphimorphia Didelphidae opossums (1 B.C. species) Soricomorpha Soricidae shrews (9 B.C. species) Talpidae moles (3 B.C. species) What s next: Rodentia Sciuridae squirrels
What we ve covered so far: Didelphimorphia Didelphidae opossums (1 B.C. species) Soricomorpha Soricidae shrews (9 B.C. species) Talpidae moles (3 B.C. species) What s next: Rodentia Sciuridae squirrels
Anatomy. Name Section. The Vertebrate Skeleton
 Name Section Anatomy The Vertebrate Skeleton Vertebrate paleontologists get most of their knowledge about past organisms from skeletal remains. Skeletons are useful for gleaning information about an organism
Name Section Anatomy The Vertebrate Skeleton Vertebrate paleontologists get most of their knowledge about past organisms from skeletal remains. Skeletons are useful for gleaning information about an organism
PRIMATE SUB-ORDER: PROSIMIANS
 PRIMATE SUB-ORDER: PROSIMIANS Are prosimians primitive? Prosimii means before apes or nearly monkeys. Prosimians also have features resembling primate fossils from about 50 million years ago and unlike
PRIMATE SUB-ORDER: PROSIMIANS Are prosimians primitive? Prosimii means before apes or nearly monkeys. Prosimians also have features resembling primate fossils from about 50 million years ago and unlike
Exceptional fossil preservation demonstrates a new mode of axial skeleton elongation in early ray-finned fishes
 Supplementary Information Exceptional fossil preservation demonstrates a new mode of axial skeleton elongation in early ray-finned fishes Erin E. Maxwell, Heinz Furrer, Marcelo R. Sánchez-Villagra Supplementary
Supplementary Information Exceptional fossil preservation demonstrates a new mode of axial skeleton elongation in early ray-finned fishes Erin E. Maxwell, Heinz Furrer, Marcelo R. Sánchez-Villagra Supplementary
Mammalogy Lecture 3 - Early Mammals & Monotremes
 Mammalogy Lecture 3 - Early Mammals & Monotremes I. Early mammals There are several early groups known as Mesozoic mammals. There have been lots of groups discovered rather recently, and we ll only address
Mammalogy Lecture 3 - Early Mammals & Monotremes I. Early mammals There are several early groups known as Mesozoic mammals. There have been lots of groups discovered rather recently, and we ll only address
Class Reptilia Testudines Squamata Crocodilia Sphenodontia
 Class Reptilia Testudines (around 300 species Tortoises and Turtles) Squamata (around 7,900 species Snakes, Lizards and amphisbaenids) Crocodilia (around 23 species Alligators, Crocodiles, Caimans and
Class Reptilia Testudines (around 300 species Tortoises and Turtles) Squamata (around 7,900 species Snakes, Lizards and amphisbaenids) Crocodilia (around 23 species Alligators, Crocodiles, Caimans and
Coyote (Canis latrans)
 Coyote (Canis latrans) Coyotes are among the most adaptable mammals in North America. They have an enormous geographical distribution and can live in very diverse ecological settings, even successfully
Coyote (Canis latrans) Coyotes are among the most adaptable mammals in North America. They have an enormous geographical distribution and can live in very diverse ecological settings, even successfully
Keys to the Mammals and Mammal Skulls of the Northern Coastal Plain of Virginia
 Virginia Journal of Science Volume 54, Number 1 Spring 2003 Keys to the Mammals and Mammal Skulls of the Northern Coastal Plain of Virginia John F. Pagels 1, Department of Biology, Virginia Commonwealth
Virginia Journal of Science Volume 54, Number 1 Spring 2003 Keys to the Mammals and Mammal Skulls of the Northern Coastal Plain of Virginia John F. Pagels 1, Department of Biology, Virginia Commonwealth
The Primates. compiled by Dana Visalli. A male Mandrill
 The Primates compiled by Dana Visalli A male Mandrill Primates arose from ancestors that lived in the trees of tropical forests; many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging
The Primates compiled by Dana Visalli A male Mandrill Primates arose from ancestors that lived in the trees of tropical forests; many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging
Examples of herbivorous animals: rabbits, deer and beaver
 Mammal Adaptations Mammals are a group of animals that fit together because they all 1)have fur or hair 2) bear live young 3) feed their young with milk from specialized mammary glands. We are going to
Mammal Adaptations Mammals are a group of animals that fit together because they all 1)have fur or hair 2) bear live young 3) feed their young with milk from specialized mammary glands. We are going to
RELATIVE BRAIN SIZE AND FEEDING STRATEGIES IN THE CHIROPTERA
 Evolution, 32(4), 1978, pp. 740-751 RELATIVE BRAIN SIZE AND FEEDING STRATEGIES IN THE CHIROPTERA JOHN F. EISENBERG AND DON E, WILSON National Zoological Park, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C.,
Evolution, 32(4), 1978, pp. 740-751 RELATIVE BRAIN SIZE AND FEEDING STRATEGIES IN THE CHIROPTERA JOHN F. EISENBERG AND DON E, WILSON National Zoological Park, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C.,
Temporal lines. More forwardfacing. tubular orbits than in the African forms 3. Orbits larger relative to skull size than in the other genera 2.
 Asian lorises More forwardfacing and tubular orbits than in the African forms 3. Characterized by a marked extension of the ectotympanic into a tubular meatus and a more angular auditory bulla than in
Asian lorises More forwardfacing and tubular orbits than in the African forms 3. Characterized by a marked extension of the ectotympanic into a tubular meatus and a more angular auditory bulla than in
Chapter 2 Mammalian Origins. Fig. 2-2 Temporal Openings in the Amniotes
 Chapter 2 Mammalian Origins Fig. 2-2 Temporal Openings in the Amniotes 1 Synapsida 1. monophyletic group 2. Single temporal opening below postorbital and squamosal 3. Dominant terrestrial vertebrate group
Chapter 2 Mammalian Origins Fig. 2-2 Temporal Openings in the Amniotes 1 Synapsida 1. monophyletic group 2. Single temporal opening below postorbital and squamosal 3. Dominant terrestrial vertebrate group
FRINGED MYOTIS. Evaluation Species. Myotis thysanodes
 Mammals FRINGED MYOTIS Myotis thysanodes Mouse-eared Bat Family Roger W. Barbour Description: A medium-sized (wingspread: 26-30 cm [10-12 in.]; mass: 5-7 g [0.18-0.25 oz]), buffy brown bat with relatively
Mammals FRINGED MYOTIS Myotis thysanodes Mouse-eared Bat Family Roger W. Barbour Description: A medium-sized (wingspread: 26-30 cm [10-12 in.]; mass: 5-7 g [0.18-0.25 oz]), buffy brown bat with relatively
Forests. By: Elyse Jacoby-Jacoby Jungle
 Forests There are forests in North America, Europe, Asia, South America, Africa, and Australia. The growing season in these forests is about 6 months long. Temperature and Precipitation: The average temperature
Forests There are forests in North America, Europe, Asia, South America, Africa, and Australia. The growing season in these forests is about 6 months long. Temperature and Precipitation: The average temperature
Mammalogy Lecture 3 - Early Mammals/Monotremes
 Mammalogy Lecture 3 - Early Mammals/Monotremes I. Early mammals - These groups are known as Mesozoic mammals, and there are several groups. Again, there have been lots of new groups discovered, and we
Mammalogy Lecture 3 - Early Mammals/Monotremes I. Early mammals - These groups are known as Mesozoic mammals, and there are several groups. Again, there have been lots of new groups discovered, and we
Goog le. Conepatus leuconotus
 from the Midwest, Canadian prairie provinces, and northeastern parts of the United States and Canada (Rosatte and Lariviere 2003). (Colorado typically has few cases of rabies in skunks.) Canine distemper
from the Midwest, Canadian prairie provinces, and northeastern parts of the United States and Canada (Rosatte and Lariviere 2003). (Colorado typically has few cases of rabies in skunks.) Canine distemper
What Can I Learn From a Skull?
 What Can I Learn From a Skull? Pennsylvania Envirothon 2018 Skulls- Herbivores, Omnivores, and Carnivores Lesson Overview Grade level(s): Elementary School (K-5), Middle School Subjects(s): Biology/Life
What Can I Learn From a Skull? Pennsylvania Envirothon 2018 Skulls- Herbivores, Omnivores, and Carnivores Lesson Overview Grade level(s): Elementary School (K-5), Middle School Subjects(s): Biology/Life
PKPS MEETING 9:00 AM May 8th, 2010
 PKPS MEETING 9:00 AM May 8th, 2010 Our Hosts: Steve and Kathy Wakeman, located, 3104 W. Summerbend Ct. Peoria DIRECTIONS: Travel North on N. Knoxville (Rt.40) going past Northpoint Shopping Center and
PKPS MEETING 9:00 AM May 8th, 2010 Our Hosts: Steve and Kathy Wakeman, located, 3104 W. Summerbend Ct. Peoria DIRECTIONS: Travel North on N. Knoxville (Rt.40) going past Northpoint Shopping Center and
The Anatomy of the Hyoid Region of Molossus Molossus and its Implication in Systematics
 Illinois Wesleyan University Digital Commons @ IWU Honors Projects Biology 1991 The Anatomy of the Hyoid Region of Molossus Molossus and its Implication in Systematics Natawadee Prasertphon '91 Illinois
Illinois Wesleyan University Digital Commons @ IWU Honors Projects Biology 1991 The Anatomy of the Hyoid Region of Molossus Molossus and its Implication in Systematics Natawadee Prasertphon '91 Illinois
Is That Mammal a Carnivore, Herbivore or Omnivore?
 Name: Is That Mammal a Carnivore, by Guy Belleranti A mammal can be a carnivore (meat eater), herbivore (plant eater) or omnivore (meat and plant eater). By looking at the teeth, eye position and feet
Name: Is That Mammal a Carnivore, by Guy Belleranti A mammal can be a carnivore (meat eater), herbivore (plant eater) or omnivore (meat and plant eater). By looking at the teeth, eye position and feet
Mammalogy Laboratory 6 - Rodents II: Castorimorpha and Myomorpha
 Mammalogy Laboratory 6 - Rodents II: Castorimorpha and Myomorpha Suborder Castorimorpha Family Castoridae (Beavers) Diagnosis: Skull massive; sciuromorphous zygomasseteric condition; infraorbital foramen
Mammalogy Laboratory 6 - Rodents II: Castorimorpha and Myomorpha Suborder Castorimorpha Family Castoridae (Beavers) Diagnosis: Skull massive; sciuromorphous zygomasseteric condition; infraorbital foramen
complex in cusp pattern. (3) The bones of the coyote skull are thinner, crests sharper and the
 DISTINCTIONS BETWEEN THE SKULLS OF S AND DOGS Grover S. Krantz Archaeological sites in the United States frequently yield the bones of coyotes and domestic dogs. These two canines are very similar both
DISTINCTIONS BETWEEN THE SKULLS OF S AND DOGS Grover S. Krantz Archaeological sites in the United States frequently yield the bones of coyotes and domestic dogs. These two canines are very similar both
Station #4. All information Adapted from:http://school.discoveryeducation.com/lessonplans/activities/makeitahabitat/adaptations.html and other sites
 Adaptation Homework Station #1 GOAL: Avoid the Sun s heat and keep themselves cool. Animals spend the daylight hours hiding in burrows or behind boulders. They come out at night to hunt and forage for
Adaptation Homework Station #1 GOAL: Avoid the Sun s heat and keep themselves cool. Animals spend the daylight hours hiding in burrows or behind boulders. They come out at night to hunt and forage for
Identifying Plant and Animal Adaptations Answer Key
 Identifying Plant and Animal Adaptations Answer Key Instructions: Review the provided photos on the ipad. Try to identify as many adaptations for each plant or animal and determine how each adaptation
Identifying Plant and Animal Adaptations Answer Key Instructions: Review the provided photos on the ipad. Try to identify as many adaptations for each plant or animal and determine how each adaptation
Fossil primates. Fossil primates 1. Family Parapithecidae (extinct Oligocene monkeys) Infraorder Platyrrhini (New World anthropoids)
 Fossil primates 1 Fossil primates Extinct members of the order of mammals to which humans belong. All current classifications divide the living primates into two major groups (suborders), but zoologists
Fossil primates 1 Fossil primates Extinct members of the order of mammals to which humans belong. All current classifications divide the living primates into two major groups (suborders), but zoologists
PRIMATE SUB-ORDER: PROSIMIANS
 PRIMATE SUB-ORDER: PROSIMIANS Are prosimians primitive? Prosimii means before apes or nearly monkeys. Prosimians also have features resembling primate fossils from about 50 million years ago and unlike
PRIMATE SUB-ORDER: PROSIMIANS Are prosimians primitive? Prosimii means before apes or nearly monkeys. Prosimians also have features resembling primate fossils from about 50 million years ago and unlike
A. Body Temperature Control Form and Function in Mammals
 Taxonomy Chapter 22 Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Mammals Characteristics Evolution of Mammals Have hair and First appear in the mammary glands Breathe air, 4chambered heart, endotherms
Taxonomy Chapter 22 Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Mammals Characteristics Evolution of Mammals Have hair and First appear in the mammary glands Breathe air, 4chambered heart, endotherms
56 Zootaxa Magnolia Press
 Class Mammalia Linnaeus, 1758 1, 2 (2 subclasses) Subclass Prototheria Gill, 1872 (1 order) Order Monotremata Bonaparte, 1837 (2 families) Family Tachyglossidae Gill, 1872 (2 genera, 4 species) Family
Class Mammalia Linnaeus, 1758 1, 2 (2 subclasses) Subclass Prototheria Gill, 1872 (1 order) Order Monotremata Bonaparte, 1837 (2 families) Family Tachyglossidae Gill, 1872 (2 genera, 4 species) Family
HONR219D Due 3/29/16 Homework VI
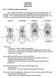 Part 1: Yet More Vertebrate Anatomy!!! HONR219D Due 3/29/16 Homework VI Part 1 builds on homework V by examining the skull in even greater detail. We start with the some of the important bones (thankfully
Part 1: Yet More Vertebrate Anatomy!!! HONR219D Due 3/29/16 Homework VI Part 1 builds on homework V by examining the skull in even greater detail. We start with the some of the important bones (thankfully
Game Ranging / Field Guiding Course. Small Mammals
 1 Module # 7 Component # 2 Small The term small mammals is not a taxonomic one. Small mammals are not inter-related unless viewed from a much broader sense in that they are mammals and small in size. One
1 Module # 7 Component # 2 Small The term small mammals is not a taxonomic one. Small mammals are not inter-related unless viewed from a much broader sense in that they are mammals and small in size. One
ARIEGE POINTING DOG (Braque de l Ariège)
 FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) 07.08.1998/EN FCI-Standard N 177 ARIEGE POINTING DOG (Braque de l Ariège) 2 TRANSLATION
FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) 07.08.1998/EN FCI-Standard N 177 ARIEGE POINTING DOG (Braque de l Ariège) 2 TRANSLATION
Mammalogy Laboratory 4 - Rodents I: Hystricomorpha, Sciuromorpha
 Mammalogy Laboratory 4 - Rodents I: Hystricomorpha, Sciuromorpha General Comments: We ll spend two weeks on the order Rodentia. This may seem like a lot of time, but almost half (~2552 species) of all
Mammalogy Laboratory 4 - Rodents I: Hystricomorpha, Sciuromorpha General Comments: We ll spend two weeks on the order Rodentia. This may seem like a lot of time, but almost half (~2552 species) of all
MANSFIELD SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL / SCIENCE / A. There is no God. B. All living things on Earth are related.
 The Evidence of Evolution Name: Date: 1. Biological Evolutions makes 2 very bold claims about living creatures.what are they circle 2. A. There is no God. B. All living things on Earth are related. C.
The Evidence of Evolution Name: Date: 1. Biological Evolutions makes 2 very bold claims about living creatures.what are they circle 2. A. There is no God. B. All living things on Earth are related. C.
The Primates. compiled by Dana Visalli. A male Mandrill
 The Primates compiled by Dana Visalli A male Mandrill Primates arose from ancestors that lived in the trees of tropical forests; many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging
The Primates compiled by Dana Visalli A male Mandrill Primates arose from ancestors that lived in the trees of tropical forests; many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging
W(h)ither Fossils? Studying Morphological Character Evolution in the Age of Molecular Sequences
 San Jose State University SJSU ScholarWorks Faculty Publications Geology April 2008 W(h)ither Fossils? Studying Morphological Character Evolution in the Age of Molecular Sequences Elizabeth J. Hermsen
San Jose State University SJSU ScholarWorks Faculty Publications Geology April 2008 W(h)ither Fossils? Studying Morphological Character Evolution in the Age of Molecular Sequences Elizabeth J. Hermsen
Name. Compare the bones found in the foot, as well as the number of digits.
 MAMMALOGY LAB 4 LIMBS & LOCOMOTION Today s exercise focuses on the variation in limbs and lifestyles of mammals. You will be interpreting the lifestyles of a number of mammals based on various aspects
MAMMALOGY LAB 4 LIMBS & LOCOMOTION Today s exercise focuses on the variation in limbs and lifestyles of mammals. You will be interpreting the lifestyles of a number of mammals based on various aspects
Animal Adaptations Woodland Animal Fact Sheet
 Post Visit Resource 5 Animal Adaptations Woodland Animal Fact Sheet Fox Food: Foxes will eat almost anything they can get hold of. They eat small mammals such as rabbits and voles, insects and invertebrates,
Post Visit Resource 5 Animal Adaptations Woodland Animal Fact Sheet Fox Food: Foxes will eat almost anything they can get hold of. They eat small mammals such as rabbits and voles, insects and invertebrates,
Evolutionary Trade-Offs in Mammalian Sensory Perceptions: Visual Pathways of Bats. By Adam Proctor Mentor: Dr. Emma Teeling
 Evolutionary Trade-Offs in Mammalian Sensory Perceptions: Visual Pathways of Bats By Adam Proctor Mentor: Dr. Emma Teeling Visual Pathways of Bats Purpose Background on mammalian vision Tradeoffs and bats
Evolutionary Trade-Offs in Mammalian Sensory Perceptions: Visual Pathways of Bats By Adam Proctor Mentor: Dr. Emma Teeling Visual Pathways of Bats Purpose Background on mammalian vision Tradeoffs and bats
Primates. BIOL 111 Announcements. BIOL 111 Organismal Biology. Which statement is not TRUE regarding mammal evolution?
 BIOL 111 Announcements Final lab exam, Monday November 23, 6:30-7:30pm CORRECTION: Vertebrate hearts: amphibians + Flip-flop atria and ventricle(s) lungs body Clicker participation: 25 lectures + 2 (maybe
BIOL 111 Announcements Final lab exam, Monday November 23, 6:30-7:30pm CORRECTION: Vertebrate hearts: amphibians + Flip-flop atria and ventricle(s) lungs body Clicker participation: 25 lectures + 2 (maybe
2016 LANCASTER COUNTY JUNIOR ENVIROTHON STUDY GUIDE: MAMMALS OF PENNSYLVANIA S FIELD HABITATS
 2016 LANCASTER COUNTY JUNIOR ENVIROTHON STUDY GUIDE: MAMMALS OF PENNSYLVANIA S FIELD HABITATS RED FOX: A common carnivore in Pennsylvania, the red fox measures 36 to 40 in length, weighs between 8 to 10
2016 LANCASTER COUNTY JUNIOR ENVIROTHON STUDY GUIDE: MAMMALS OF PENNSYLVANIA S FIELD HABITATS RED FOX: A common carnivore in Pennsylvania, the red fox measures 36 to 40 in length, weighs between 8 to 10
Xiao-Ming Gu 1, *, Shu-Yan He 1, and Lei Ao 2
 Zoological Studies 47(3): 368-378 (2008) Molecular Phylogenetics among Three Families of Bats (Chiroptera: Rhinolophidae, Hipposideridae, and Vespertilionidae) Based on Partial Sequences of the Mitochondrial
Zoological Studies 47(3): 368-378 (2008) Molecular Phylogenetics among Three Families of Bats (Chiroptera: Rhinolophidae, Hipposideridae, and Vespertilionidae) Based on Partial Sequences of the Mitochondrial
Comparative morphology of the tongue in free-tailed bats (Chiroptera, Molossidae) 213 ABSTRACT
 Comparative morphology of the tongue in free-tailed bats (Chiroptera, Molossidae) 213 COMPARATIVE MORPHOLOGY OF THE TONGUE IN FREE-TAILED BATS (CHIROPTERA, MOLOSSIDAE) ABSTRACT Renato Gregorin 1 Descriptive
Comparative morphology of the tongue in free-tailed bats (Chiroptera, Molossidae) 213 COMPARATIVE MORPHOLOGY OF THE TONGUE IN FREE-TAILED BATS (CHIROPTERA, MOLOSSIDAE) ABSTRACT Renato Gregorin 1 Descriptive
Equipment and Room Requirements. Three large tables (or desks moved to create three stations) with adequate space for students to move around.
 FROM MICE TO MOOSE MAMMALS OF MAINE From Mice to Moose is an activity-based program where students participate in hands-on activities to develop an understanding of the mammals of Maine. Through the use
FROM MICE TO MOOSE MAMMALS OF MAINE From Mice to Moose is an activity-based program where students participate in hands-on activities to develop an understanding of the mammals of Maine. Through the use
Evolution as Fact. The figure below shows transitional fossils in the whale lineage.
 Evolution as Fact Evolution is a fact. Organisms descend from others with modification. Phylogeny, the lineage of ancestors and descendants, is the scientific term to Darwin's phrase "descent with modification."
Evolution as Fact Evolution is a fact. Organisms descend from others with modification. Phylogeny, the lineage of ancestors and descendants, is the scientific term to Darwin's phrase "descent with modification."
Where are Tropical Rainforests Found? 1. The Layers of the Rainforest 2. Critters of the Rainforest 2-3. Tortoises of the Rainforest 3
 Fish Tales A T L A N T I C C I T Y A Q U A R I UM Atlantic City Aquarium 800 N. New Hampshire Avenue Atlantic City, NJ 08401 609-348-2880 www.acaquarium.com Totally Tropical Rainforest In our area of the
Fish Tales A T L A N T I C C I T Y A Q U A R I UM Atlantic City Aquarium 800 N. New Hampshire Avenue Atlantic City, NJ 08401 609-348-2880 www.acaquarium.com Totally Tropical Rainforest In our area of the
SCIUROPTERUS MINDANENSIS SP. NOV., A NEW SPECIES OF FLYING SQUIRREL FROM MINDANAO
 SCIUROPTERUS MINDANENSIS SP. NOV., A NEW SPECIES OF FLYING SQUIRREL FROM MINDANAO By DioscoRO S. Rabor Of the Division of Fisheries^ Department of Agriculture and Commerce Manila FOUR PLATES In August,
SCIUROPTERUS MINDANENSIS SP. NOV., A NEW SPECIES OF FLYING SQUIRREL FROM MINDANAO By DioscoRO S. Rabor Of the Division of Fisheries^ Department of Agriculture and Commerce Manila FOUR PLATES In August,
Appendix 1. Small Mammals in the Muskwa-Kechika Management Area
 Appendix 1. Small Mammals in the Muskwa-Kechika Management Area This list includes only species actually recorded (museum specimens and observational records from published and unpublished sources) in
Appendix 1. Small Mammals in the Muskwa-Kechika Management Area This list includes only species actually recorded (museum specimens and observational records from published and unpublished sources) in
