CA-MRSA lesions: What works, what doesn t
|
|
|
- Diane Cole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 For mass reproduction, content licensing and permissions contact Dowden Health Media. FAMILY David McBride, MD University Student Health Services and the Department of Family Medicine, Boston University IN THIS ARTICLE CA-MRSA treatments Page 590 Simple precautions Page 591 CA-MRSA lesions: What works, what doesn t Incision and drainage are key, with antibiotics usually held in reserve; forego screening patients household contacts Practice recommendations Community-acquired methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) abscesses are best managed surgically; postprocedure antibiotics do not substantially improve outcomes. Cure rates with incision and Copyright Dowden Health Media drainage alone are at least 90% (A). If incision and drainage fail to promote healing within 7 days, the oral antibiotics of choice are trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole and tetracycline (C). Eradication of nasal carriage of CA-MRSA is generally not useful in preventing spread of clinical MRSA infections in communities (B). Strength of recommendation (SOR) For personal use only A Good quality patient-oriented evidence B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series Apreviously healthy law student arrives at your office complaining of abdominal pain. You discover on examination that she has an erythematous, indurated, and tender 3-cm lesion on her suprapubic region. The lesion has no point, but its center is boggy. The patient s temperature is normal. Would you give her an antibiotic? Would you cover immediately for communityacquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA)? What other factors might influence your decision? The incidence of MRSA is increasing in communities across the United States, challenging our assumptions about evaluation and management of skin and softtissue infections. In this article, I outline a rational approach to managing patients who have lesions likely to have been caused by CA-MRSA (TABLE). When to suspect MRSA skin infection Patients with CA-MRSA skin infection often report a spider bite, as lesions appear suddenly and unexpectedly in areas without a history of trauma. 1 The lesions very often are pustular with central necrosis, and there may be purulent drainage, redness, tenderness, and palpable fluctuance. CA-MRSA can cause impetigo, but the often benign nature of this clinical infection makes management decisions less crucial. CA-MRSA skin lesions can occur anywhere on the body, though most often they appear in the axillae or the groin and buttocks. Patients may or may not have a fever. Individuals who are at increased risk for CA-MRSA disease include users of health clubs or participants in contact sports, men who have sex with men, chil- 588 VOL 57, NO 9 / SEPTEMBER 2008 FAMILY
2 dren younger than 2 years of age, users of intravenous drugs, military personnel, and prisoners. 2,3 However, the absence of these factors in a patient with a skin or softtissue infection does not rule out MRSA. 4 Regardless of the lesion s appearance or the patient s epidemiologic history, consider CA-MRSA if its prevalence in your community reaches 10% to 15%. Hospitalize any patient who exhibits fever or hypothermia, tachycardia greater than 100 beats per minute, or hypotension with a systolic blood pressure <90 mm Hg or 20 mm Hg lower than baseline. A skin lesion >5 cm is also likely to require hospitalization and parenteral antibiotics. 5 Treatment: Incision and drainage most important Several management schemes have been proposed to guide the appropriate level of therapy based on presenting patient characteristics. 6,7 If a lesion is clearly fluctuant, incise it and drain the fluid, or refer the patient for surgical consultation. If the lesion is not clearly fluctuant, needle aspiration may help to determine the need for more extensive incision and drainage or to collect a specimen for culture. Although culture of skin lesions may not have been routine in the past, the advent of CA-MRSA has made it so, particularly given that MRSA lesions may not be clinically distinguishable from those caused by nonresistant S aureus. Periodic postprocedure follow-up is indicated to ensure resolution of the infection. At our health center, patients return every few days for an appointment with nursing staff for wound irrigation and packing change until the lesion visibly improves. Systemic effects from the infection are monitored, as well. Adult patients in 1 study were treated with incision and drainage by a surgeon. 8 The technique described in the article used an 11 blade and a sawing motion, creating a wide opening. The wound cavity was explored for loculations and packed. This technique is identical to that used in the office. There is CA-MRSA fast facts Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) causes up to 74% of purulent skin and soft-tissue infections in communities throughout the United States. 1 By definition, this infection occurs in patients who have not been hospitalized and have not undergone medical procedures within the prior year. 12 The annual incidence of CA-MRSA was reported to be cases per 100,000 population between 2001 and Clusters of CA-MRSA have been identified among Alaskan natives, Native American Indians, and Pacific Islanders. 12 Most often this organism causes skin and softtissue infections, though cardiac, respiratory, blood, and bone infections can also occur. 14 CA-MRSA species are genotypically distinct from hospital-acquired MRSA. One marker for CA-MRSA, Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL), is most often detected in cases of severe and systemic infection, and it may be a virulence factor. 15 However, the presence of PVL does not necessarily correlate directly with antibiotic resistance. Historically, CA-MRSA was primarily resistant to beta-lactams and erythromycin. More recent strains have also demonstrated resistance to tetracycline and clindamycin. Retrospective analyses show that patients with CA-MRSA tend to receive inadequate initial antibiotic coverage, and, independent of this, they tend to have worse clinical outcomes than those infected by methicillin-sensitive strains VOL 57, NO 9 / SEPTEMBER
3 FAMILY TABLE Suspect CA-MRSA? Consider this treatment approach 6,7 CLASS PATIENT CRITERIA MANAGEMENT ANTIBIOTIC CHOICES 1 Afebrile and healthy; lesion nonfluctuant 2 Fluctuant or pustular lesion <5 cm; with or without fever 3 Toxic appearance or at least 1 unstable comorbidity or a limb-threatening infection; lesion >5 cm 4 Sepsis syndrome or life-threatening infection (necrotizing fasciitis) If no drainable abscess, give common first-line antibiotic for SSTI; reassess for response Surgical drainage of abscess if possible. Use I&D presumptively for MRSA and monitor closely for response; inpatient management may be indicated Hospital admission with broadspectrum antibiotics for MRSA coverage; consider infectious disease consultation Above plus aggressive surgical debridement Semisynthetic penicillin, oral first- or second-generation cephalosporin, macrolide, clindamycin Trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole, tetracycline, clindamycin Broad-spectrum, including vancomycin Above with infectious disease guidance CA-MRSA, community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; I&D, incision and drainage; MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; SSTI, skin and soft-tissue infection. FAST TRACK Regardless of the lesion s appearance, consider CA-MRSA if its prevalence in your community reaches 10% to 15% one caveat, though: This study included abscesses larger than 5 cm and patients with compromised immune systems situations not routinely managed in the primary care office. Are antibiotics indicated after incision and drainage for MRSA? In this same study, cure rates with incision and drainage alone were just over 90%. 8 The cure rate in the treatment arm also receiving an antibiotic was 84% (difference was not statistically significant), and coverage was inadequate for MRSA. Treatment with cephalexin after incision and drainage resulted in 1 patient harmed for every 14 treated (NNH=14). A pediatric study also showed that antibiotics do not affect the outcome of skin lesions following incision and drainage. 5 When deciding whether to prescribe postprocedure antibiotics, keep in mind the need to avoid contributing further to bacterial resistance. Generally if incision and drainage fail to promote healing of the MRSA lesion within 7 days, start the patient on trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or tetracycline. Clindamycin is an option, though resistance to it is becoming more common. Adjust the antibiotic choice as needed when culture and sensitivity results become available. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is generally well tolerated at the recommended dose of 1 to 2 double-strength tablets (160 mg TMP, 800 mg SMX) twice daily for adults. If a patient s creatinine clearance is 15 to 30 ml/min, reduce the dose by half. The rate of sulfa allergy is similar to other antibiotics, at 3%. Tetracycline s dosing schedule for adults, 250 or 500 mg 4 times daily makes it difficult to use. Gastrointestinal upset, phototoxicity, and hepatotoxicity can occur. The possibility of tooth discoloration precludes tetracycline s use in children. Clindamycin carries a high rate of gastrointestinal-related problems, Clostridium difficile infection in particular (10% incidence administered in any route). Inducible resistance to clindamycin is 50% in MRSA infections. 9 Recent use of antibiotics may increase the likelihood of clindamycin resistance, with erythromycin in particular inducing this resistance. Its dosage typically is 150 to 300 mg every 6 hours. Doxycycline and minocycline are not recommended, as they carry a 21% failure rate VOL 57, NO 9 / SEPTEMBER 2008 FAMILY
4 CA-MRSA lesions: What works, what doesn t Linezolid is costly and has many drug interactions. In particular, linezolid has the potential to cause serotonin syndrome with agents that affect the serotonergic system. Linezolid may also interact with medications that affect the adrenergic system (pressors). Its routine use in the community without infectious disease consultation is not advised. For lesions that are not fluctuant or purulent, appropriate first-line antibiotics are semisynthetic penicillins (dicloxacillin), first- or second-generation oral cephalosporins, macrolides, and clindamycin. 9 These antibiotics are preferable for group A streptococcal infections, erysipelas (which can be quite aggressive), and impetigo. Adjustments can be made as culture results become available or if the clinical response is inadequate. There is no particular utility in waiting to administer oral antibiotics in cases of erysipelas or impetigo, though topical antibiotics can often be used for limited cases of impetigo. Prevention: Simple precautions are the rule Most CA-MRSA infections result from direct contact with a patient s wound or from wound drainage on environmental surfaces. In the medical office. In addition to using sterile technique during incision and drainage, be sure that all staff members wash their hands with soap and water or with an alcohol-based sanitizer. For the most part, MRSA remains susceptible to triclosan, a topical antiseptic in commercially available hand soaps. Clean equipment as needed with 10% sodium hypochlorite solution or another agent effective against MRSA. Surgical instruments should be disposable or sterilized after each use. At the patient s home. Instruct patients to clean wounds wearing fresh disposable gloves each time and to cover wounds with new, dry dressings. Tell families to avoid sharing linens and clothing unless they have been washed in hot soap and water and dried in a heated dryer. MRSA can live for weeks to months on surfaces exposed to infected wounds, 10 and these surfaces can be disinfected with a 10% bleach solution. Sports environments. Athletes with CA-MRSA infections should not compete unless the wound can be completely covered with a dry dressing. Recommend to those in charge of school or commercial facilities that, in cases of confirmed MRSA infection, they routinely clean locker rooms and sports equipment with either a 10% bleach solution or commercial disinfectant. There is no evidence, however, that more widespread or vigorous cleaning such as dismantling a training room and all its cardio-fitness equipment for disinfecting prevents the spread of MRSA. Encourage athletes to wash their hands properly. Communal towels should be washed in hot water (>140ºF) with bleach before reuse. Personal equipment should be cleaned per the instructions of the manufacturer. Athletes should use a clean towel to provide a barrier between their skin and the surfaces of weight-room or cardio-fitness equipment. They should also clean equipment before and after use with an appropriate cleanser, such as a disinfectant hand-wipe. Unproductive efforts you can avoid. Screening household contacts for MRSA is not useful, and attempts to eliminate colonization are generally ineffective. In a large military study, use of intranasal mupirocin failed to decrease nasal carriage of MRSA and the incidence of MRSA infections. 11 The MRSA nasal colonization rate was 3.9%; 121 individuals with MRSA colonization needed to be treated with nasal mupirocin to prevent 1 MRSA infection in the total study population. More complex antibiotic regimens are sometimes used in an attempt to eradicate MRSA carriage, though they also have limited effectiveness and carry the general risks of antibiotic use (gastrointestinal disturbance, allergic reaction, etc). If your office is considering an eradication FAST TRACK If incision and drainage fail to promote healing within 7 days, start the patient on trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole or tetracycline VOL 57, NO 9 / SEPTEMBER
5 WE ARE WITNESSING S I N A HISTORIC EVOLUTION IN THE C OF MEDICINE Ë CAN WE COUNT YOU IN? Biology evolves slowly, but medical practice is changing every day. As physicians, our challenge is to continually refocus our core values and demonstrate the true meaning and value of healthcare. Current Clinical Practice brings you the kind of timely articles from key opinion leaders that will keep you in step with the rapid changes in modern medical practice. READ THE OCTOBER ISSUE IN PRINT OR ONLINE TO FIND OUT ABOUT: The hospitalist model: How it benefits you and your patients How one medical specialty society s use of measures and reporting dramatically improved patient care The ABCs of training the doctors of the future CURRENT CLINICAL An indexed, peer-reviewed supplement to The Journal of Family Practice FAMILY attempt, consult with an infectious disease clinician first. References 1. Moran GJ, Krishnadasan A, Gorwitz RJ, et al, Methicillin-resistant S. aureus infections among patients in the emergency department. N Engl J Med. 2006;355: Cohen PR. The skin in the gym: a comprehensive review of the cutaneous manifestations of communityacquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in athletes. Clin Dermatol. 2008; 26: Cohen PR. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin infections: implications for patients and practitioners. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2007;8: Miller LG, Perdreau-Remington F, Bayer AS, et al. Clinical and epidemiologic characteristics cannot distinguish community associated methicillin resistant Staph aureus infection from methicillin susceptible S aureus infection: a prospective investigation. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44: Lee MC, Rios AM, Aten MF, et al. Management and outcome of children with skin and soft tissue abscesses caused by community-acquired methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004;23: Eron LJ, Lipsky BA, Low DE, et al. Managing skin and soft tissue infections: expert panel recommendations on key decision points. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003;52(suppl S1):i3 i CDC, AMA, IDSA, Outpatient management of skin and soft tissue infections in the era of community-associated MRSA. Available at: ama1/pub/upload/mm/36/ca_mrsa_desk_ pdf. Accessed June 8, Rajendran PM, Young D, Maurer T, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of cephalexin for treatment of uncomplicated skin abscesses in a population at risk for community-acquired methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51: Stevens DL, Bisno AL, Chambers HF, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft-tissue infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41: Dellit TH, Ducin J. Guidelines for Evaluation and Management of Community-Associated Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Skin and Soft Tissue Infections in Outpatient Settings. Available at: http: // /MRSA-guidelines.pdf. Accessed August 6, Ellis MW, Griffith ME, Dooley DP, et al. Targeted intranasal mupirocin to prevent colonization and infection by community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in soldiers: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Healthcare-associated methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Available at: ncidod/dhqp/ar_mrsa.html. Accessed April 14, Fridkin SK, Hageman JC, Morrison M, et al. Methicillin-reistant Staphylococcus aureus disease in three communities. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2362-a. 14. Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Report, Emerging Infections Program Network, methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus, Available at: mrsa06.pdf. Accessed May 5, Holmes A, Ganner M, McGuane S, et al. Staphylococcus aureus isolates carrying panton-valentine leucocidin genes in England and Wales: frequency, characterization, and association with clinical disease. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43: Davis SL, Perri MB, Donabedian SM, et al. Epidemiology and outcomes of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45: currentclinicalpractice.com
Management of Skin and Soft-Tissue Infection
 Clinical Decisions Interactive at www.nejm.org Management of Skin and Soft-Tissue Infection This interactive feature addresses the diagnosis or management of a clinical case. A case vignette is followed
Clinical Decisions Interactive at www.nejm.org Management of Skin and Soft-Tissue Infection This interactive feature addresses the diagnosis or management of a clinical case. A case vignette is followed
Replaces:04/14/16. Formulated: 1997 SKIN AND SOFT TISSUE INFECTION
 Effective Date: 04/13/17 Replaces:04/14/16 Page 1 of 7 POLICY To standardize the clinical management and housing of offenders with skin and soft tissue infections, thereby reducing the transmission and
Effective Date: 04/13/17 Replaces:04/14/16 Page 1 of 7 POLICY To standardize the clinical management and housing of offenders with skin and soft tissue infections, thereby reducing the transmission and
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus:
 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Action-Oriented Guidance for Community-Based Prevention Jackie Dawson, PhD Public Health Epidemiologist Chelan, Douglas, Grant, Kittitas, & Okanogan Counties
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Action-Oriented Guidance for Community-Based Prevention Jackie Dawson, PhD Public Health Epidemiologist Chelan, Douglas, Grant, Kittitas, & Okanogan Counties
HEALTH SERVICES POLICY & PROCEDURE MANUAL
 PAGE 1 of 3 PURPOSE To assure that DOP inmates with Soft Tissue Infections are receiving high quality Primary Care for their infections and that the risk of infecting other inmates or staff is minimized.
PAGE 1 of 3 PURPOSE To assure that DOP inmates with Soft Tissue Infections are receiving high quality Primary Care for their infections and that the risk of infecting other inmates or staff is minimized.
Infections caused by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus
 MRSA infections are no longer limited to hospitals. An infectious disease specialist offers insight on what this means for dermatologists. By Robert S. Jones, DO, Reading, PA Infections caused by Methicillin-Resistant
MRSA infections are no longer limited to hospitals. An infectious disease specialist offers insight on what this means for dermatologists. By Robert S. Jones, DO, Reading, PA Infections caused by Methicillin-Resistant
Staph and MRSA Skin Infections Fact Sheet for Schools
 Cape May County Department of Health 4 Moore Road, Cape May Court House, NJ 08210 Staph and MRSA Skin Infections Fact Sheet for Schools What is a staph/mrsa skin infection? Staphylococcus or staph bacteria
Cape May County Department of Health 4 Moore Road, Cape May Court House, NJ 08210 Staph and MRSA Skin Infections Fact Sheet for Schools What is a staph/mrsa skin infection? Staphylococcus or staph bacteria
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
S aureus infections: outpatient treatment. Dirk Vogelaers Dept of Infectious Diseases University Hospital Gent Belgium
 S aureus infections: outpatient treatment Dirk Vogelaers Dept of Infectious Diseases University Hospital Gent Belgium Intern Med J. 2005 Feb;36(2):142-3 Intern Med J. 2005 Feb;36(2):142-3 Treatment of
S aureus infections: outpatient treatment Dirk Vogelaers Dept of Infectious Diseases University Hospital Gent Belgium Intern Med J. 2005 Feb;36(2):142-3 Intern Med J. 2005 Feb;36(2):142-3 Treatment of
Mrsa abscess and cellulitis
 Search Mrsa abscess and cellulitis An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The. Staph
Search Mrsa abscess and cellulitis An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The. Staph
5/17/2012 DISCLOSURES OBJECTIVES CONTEMPORARY PEDIATRICS
 CONTEMPORARY PEDIATRICS Surgical Management of MRSA Soft Tissue Infections John M. Draus, Jr., M.D. Assistant Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics Kentucky Children s Hospital University of Kentucky DISCLOSURES
CONTEMPORARY PEDIATRICS Surgical Management of MRSA Soft Tissue Infections John M. Draus, Jr., M.D. Assistant Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics Kentucky Children s Hospital University of Kentucky DISCLOSURES
Ca-MRSA Update- Hand Infections. Washington Hand Society September 19, 2007
 Ca-MRSA Update- Hand Infections Washington Hand Society September 19, 2007 Resistant Staph. Aureus Late 1940 s -50% S.Aureus resistant to PCN 1957-80/81 strain- of S.A. highly virulent and easily transmissible
Ca-MRSA Update- Hand Infections Washington Hand Society September 19, 2007 Resistant Staph. Aureus Late 1940 s -50% S.Aureus resistant to PCN 1957-80/81 strain- of S.A. highly virulent and easily transmissible
M R S A. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. The Facts
 M R S A Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus The Facts Michael Parry, M.D. Director of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology Stamford Hospital January 24, 2008 Introduction to Staph aureus Staphylococcus
M R S A Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus The Facts Michael Parry, M.D. Director of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology Stamford Hospital January 24, 2008 Introduction to Staph aureus Staphylococcus
COMMUNITY ASSOCIATED METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHLOCOCCUS AUREUS A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PRIMARY CARE PRACTITIONERS
 COMMUNITY ASSOCIATED METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHLOCOCCUS AUREUS A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PRIMARY CARE PRACTITIONERS December 21, 2010 Background Since it was first described in 1961 methicillin resistant
COMMUNITY ASSOCIATED METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHLOCOCCUS AUREUS A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PRIMARY CARE PRACTITIONERS December 21, 2010 Background Since it was first described in 1961 methicillin resistant
Today s Agenda: 9/30/14
 Today s Agenda: 9/30/14 1. Students will take C List Medical Abbreviation Quiz. 2. TO: Discuss MRSA. MRSA MRSA Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus What
Today s Agenda: 9/30/14 1. Students will take C List Medical Abbreviation Quiz. 2. TO: Discuss MRSA. MRSA MRSA Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus What
Living with MRSA Learning how to control the spread of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
 Living with MRSA Learning how to control the spread of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) IMPORTANT MRSA is a serious infection that can become life-threatening if left untreated. If you
Living with MRSA Learning how to control the spread of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) IMPORTANT MRSA is a serious infection that can become life-threatening if left untreated. If you
Skin & Soft Tissue Infections (SSTI) Skin & Soft Tissue Infections. Skin & Soft Tissue Infections (SSTI)
 Skin & Soft Tissue Infections (SSTI) Skin & Soft Tissue Infections 2007 Abscess Cellulitis Bradley W Frazee, MD, FACEP Dept of Emergency Medicine Alameda County Medical Center - Highland Hospital Associate
Skin & Soft Tissue Infections (SSTI) Skin & Soft Tissue Infections 2007 Abscess Cellulitis Bradley W Frazee, MD, FACEP Dept of Emergency Medicine Alameda County Medical Center - Highland Hospital Associate
MRSA Outbreak in Firefighters
 MRSA Outbreak in Firefighters Angie Carranza Munger, MD Resident, Occupational and Environmental Medicine The University of Colorado, Denver and National Jewish Health Candidate, Masters of Public Health
MRSA Outbreak in Firefighters Angie Carranza Munger, MD Resident, Occupational and Environmental Medicine The University of Colorado, Denver and National Jewish Health Candidate, Masters of Public Health
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus By Karla Givens Means of Transmission and Usual Reservoirs Staphylococcus aureus is part of normal flora and can be found on the skin and in the noses of one
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus By Karla Givens Means of Transmission and Usual Reservoirs Staphylococcus aureus is part of normal flora and can be found on the skin and in the noses of one
Bacterial skin infection
 D i v i s i o n o f P e d i a t r i c E m e r g e n c y M e d i c i n e P a g e 1 Bacterial skin infection Cellulitis w/o abscess Abscess Deep tissue involvement Multiple abscesses Perirectal Anterior
D i v i s i o n o f P e d i a t r i c E m e r g e n c y M e d i c i n e P a g e 1 Bacterial skin infection Cellulitis w/o abscess Abscess Deep tissue involvement Multiple abscesses Perirectal Anterior
Risk factors? Insect bites? Hygiene? Household crowding Health literacy
 Recurrent boils Commonest sites face, neck, armpits, shoulders, and buttocks (bottom) infection of the hair root or sweat pore Occur in otherwise healthy people (higher rates in diabetics, eczema, iron
Recurrent boils Commonest sites face, neck, armpits, shoulders, and buttocks (bottom) infection of the hair root or sweat pore Occur in otherwise healthy people (higher rates in diabetics, eczema, iron
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Emerging Therapies and 5 things to know
 2011 MFMER slide-1 Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Emerging Therapies and 5 things to know Aaron Tande, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine October 27, 2017 Division of INFECTIOUS DISEASES 2011 MFMER slide-2
2011 MFMER slide-1 Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Emerging Therapies and 5 things to know Aaron Tande, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine October 27, 2017 Division of INFECTIOUS DISEASES 2011 MFMER slide-2
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 43: Staphylococcus Aureus Authors J. Pierce, MD M. Edmond, MD, MPH, MPA M.P. Stevens, MD, MPH Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH) Topic Outline Key
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 43: Staphylococcus Aureus Authors J. Pierce, MD M. Edmond, MD, MPH, MPA M.P. Stevens, MD, MPH Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH) Topic Outline Key
FM - Male, 38YO. MRSA nasal swab (+) Due to positive MRSA nasal swab test, patient will be continued on Vancomycin 1500mg IV q12 for MRSA treatment...
 Jillian O Keefe Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate 2016 September 15, 2015 FM - Male, 38YO HPI: Previously healthy male presents to ED febrile (102F) and in moderate distress ~2 weeks after getting a tattoo
Jillian O Keefe Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate 2016 September 15, 2015 FM - Male, 38YO HPI: Previously healthy male presents to ED febrile (102F) and in moderate distress ~2 weeks after getting a tattoo
Sixth Plague of Egypt. Community MRSA. Epidemiology. Basic Features of Community MRSA. Populations with CA-MRSA
 Community MRSA Henry F. Chambers, M.D. University of California San Francisco San Francisco General Hospital Sixth Plague of Egypt (~ 1200 BCE) So they took soot from a kiln, and stood before Pharaoh;
Community MRSA Henry F. Chambers, M.D. University of California San Francisco San Francisco General Hospital Sixth Plague of Egypt (~ 1200 BCE) So they took soot from a kiln, and stood before Pharaoh;
MRSA Background. New Challenges From an Old Foe. MRSA Demographics. Comparison of Types of MRSA CA-MRSA HA-MRSA
 Winter Clinical 2017 : MRSA Update Whitney A. High, MD, JD, Meng whitney.high@ucdenver.edu Associate Professor, Dermatology & Pathology Director of Dermatopathology University of Colorado School of Medicine
Winter Clinical 2017 : MRSA Update Whitney A. High, MD, JD, Meng whitney.high@ucdenver.edu Associate Professor, Dermatology & Pathology Director of Dermatopathology University of Colorado School of Medicine
Cellulitis and Abscess: ED Phase v 1.1
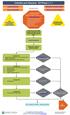 Cellulitis and Abscess: ED Phase v 1.1 Executive Summary Test Your Knowledge PHASE I (E.D.) Explanation of Evidence Ratings Summary of Version Changes! Labs if systemic illness or necrotizing fasciitis
Cellulitis and Abscess: ED Phase v 1.1 Executive Summary Test Your Knowledge PHASE I (E.D.) Explanation of Evidence Ratings Summary of Version Changes! Labs if systemic illness or necrotizing fasciitis
Impact of a Standardized Protocol to Address Outbreak of Methicillin-resistant
 Impact of a Standardized Protocol to Address Outbreak of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Skin Infections at a large, urban County Jail System Earl J. Goldstein, MD* Gladys Hradecky, RN* Gary
Impact of a Standardized Protocol to Address Outbreak of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Skin Infections at a large, urban County Jail System Earl J. Goldstein, MD* Gladys Hradecky, RN* Gary
MRSA What We Need to Know Sharon Pearce, CRNA, MSN Carolina Anesthesia Associates
 MRSA What We Need to Know Sharon Pearce, CRNA, MSN Carolina Anesthesia Associates What is MRSA? Methicillin-resistant Staphylococus aureus This hardy bacterium has developed resistance to every antibiotic
MRSA What We Need to Know Sharon Pearce, CRNA, MSN Carolina Anesthesia Associates What is MRSA? Methicillin-resistant Staphylococus aureus This hardy bacterium has developed resistance to every antibiotic
Community Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Sixth Plague of Egypt. Epidemiology
 Community Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Henry F. Chambers, M.D. University of California San Francisco San Francisco General Hospital Sixth Plague of Egypt (~ 1200 BCE) So they took soot
Community Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Henry F. Chambers, M.D. University of California San Francisco San Francisco General Hospital Sixth Plague of Egypt (~ 1200 BCE) So they took soot
Staphylococcus Aureus
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 43: Staphylococcus Aureus Authors J. Pierce, MD M. Edmond, MD, MPH, MPA M.P. Stevens, MD, MPH Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH) Topic Outline Key
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 43: Staphylococcus Aureus Authors J. Pierce, MD M. Edmond, MD, MPH, MPA M.P. Stevens, MD, MPH Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH) Topic Outline Key
Randomized, Controlled Trial of Antibiotics in the Management of Community-Acquired Skin Abscesses in the Pediatric Patient
 PEDIATRICS/ORIGINAL RESEARCH Randomized, Controlled Trial of Antibiotics in the Management of Community-Acquired Skin Abscesses in the Pediatric Patient Myto Duong, MD, MS Stephen Markwell, MA John Peter,
PEDIATRICS/ORIGINAL RESEARCH Randomized, Controlled Trial of Antibiotics in the Management of Community-Acquired Skin Abscesses in the Pediatric Patient Myto Duong, MD, MS Stephen Markwell, MA John Peter,
Invasive Group A Streptococcus (GAS)
 Invasive Group A Streptococcus (GAS) Cause caused by a bacterium commonly found on the skin and in the throat transmitted by direct, indirect or droplet contact with secretions from the nose, and throat
Invasive Group A Streptococcus (GAS) Cause caused by a bacterium commonly found on the skin and in the throat transmitted by direct, indirect or droplet contact with secretions from the nose, and throat
Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Review of an Emerging Public Health Concern
 Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Review of an Emerging Public Health Concern Timothy D. Drews, MD; Jonathan L. Temte, MD, PhD; Barry C. Fox, MD ABSTRACT Methicillin-resistant
Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Review of an Emerging Public Health Concern Timothy D. Drews, MD; Jonathan L. Temte, MD, PhD; Barry C. Fox, MD ABSTRACT Methicillin-resistant
Treatment of Surgical Site Infection Meeting Quality Statement 6. Prof Peter Wilson University College London Hospitals
 Treatment of Surgical Site Infection Meeting Quality Statement 6 Prof Peter Wilson University College London Hospitals TEG Quality Standard 6 Treatment and effective antibiotic prescribing: People with
Treatment of Surgical Site Infection Meeting Quality Statement 6 Prof Peter Wilson University College London Hospitals TEG Quality Standard 6 Treatment and effective antibiotic prescribing: People with
Perichondritis: Source: UpToDate Ciprofloxacin 10 mg/kg/dose PO (max 500 mg/dose) BID Inpatient: Ceftazidime 50 mg/kg/dose q8 hours IV
 Empiric Antibiotics for Pediatric Infections Seen in ED NOTE: Choice of empiric antibiotic therapy must take into account local pathogen frequency and resistance patterns, individual patient characteristics,
Empiric Antibiotics for Pediatric Infections Seen in ED NOTE: Choice of empiric antibiotic therapy must take into account local pathogen frequency and resistance patterns, individual patient characteristics,
Bacterial skin and soft tissues infections (SSTI) are one of the most common 1. infections among different age groups
 Bacterial skin and soft tissues infections (SSTI) are one of the most common 1 infections among different age groups Gram-positive bacteria are the most frequently isolated pathogens from SSTI, with a
Bacterial skin and soft tissues infections (SSTI) are one of the most common 1 infections among different age groups Gram-positive bacteria are the most frequently isolated pathogens from SSTI, with a
11/10/2016. Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. Disclosures. Educational Need/Practice Gap. Objectives. Case #1
 Disclosures Selecting Antimicrobials for Common Infections in Children FMR-Contemporary Pediatrics 11/2016 Sean McTigue, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical Director
Disclosures Selecting Antimicrobials for Common Infections in Children FMR-Contemporary Pediatrics 11/2016 Sean McTigue, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical Director
CA-MRSA. The New Sports Pathogen
 10763-11_ON2605-Kurkowski.qxd 9/13/07 2:25 PM Page 310 CA-MRSA The New Sports Pathogen Christina Kurkowski Skin infections in athletes caused by community-associated (CA-MRSA) have been observed within
10763-11_ON2605-Kurkowski.qxd 9/13/07 2:25 PM Page 310 CA-MRSA The New Sports Pathogen Christina Kurkowski Skin infections in athletes caused by community-associated (CA-MRSA) have been observed within
Summary Report Relating to a Pilot Program to Require Reporting of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
 Summary Report Relating to a Pilot Program to Require Reporting of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Prepared by the Texas Department of State Health Services as required by House Bill 1082,
Summary Report Relating to a Pilot Program to Require Reporting of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Prepared by the Texas Department of State Health Services as required by House Bill 1082,
UPDATE ON ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP REGULATIONS AND IMPLEMENTATION OF AN AMS PROGRAM
 UPDATE ON ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP REGULATIONS AND IMPLEMENTATION OF AN AMS PROGRAM Diane Rhee, Pharm.D. Associate Professor of Pharmacy Practice Roseman University of Health Sciences Chair, Valley Health
UPDATE ON ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP REGULATIONS AND IMPLEMENTATION OF AN AMS PROGRAM Diane Rhee, Pharm.D. Associate Professor of Pharmacy Practice Roseman University of Health Sciences Chair, Valley Health
Tropical infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus
 Tropical infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus Michael Ellis, MD Infectious Diseases Division Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences February 2015 Introduction Tropical Pyomyositis Cutaneous
Tropical infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus Michael Ellis, MD Infectious Diseases Division Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences February 2015 Introduction Tropical Pyomyositis Cutaneous
Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms (MDRO)
 Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms (MDRO) 2016 What are MDROs? Multi-drug resistant organisms, or MDROs, are bacteria resistant to current antibiotic therapy and therefore difficult to treat. MDROs can cause
Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms (MDRO) 2016 What are MDROs? Multi-drug resistant organisms, or MDROs, are bacteria resistant to current antibiotic therapy and therefore difficult to treat. MDROs can cause
Source: Portland State University Population Research Center (
 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Surveillance Report 2010 Oregon Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Office of Disease Prevention & Epidemiology Oregon Health Authority Updated:
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Surveillance Report 2010 Oregon Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Office of Disease Prevention & Epidemiology Oregon Health Authority Updated:
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An Update
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An Update Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An Update Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain
Prevalence & Risk Factors For MRSA. For Vets
 For Vets General Information Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive, aerobic commensal bacterium of humans that is carried in the anterior nares of approximately 30% of the general population. It is
For Vets General Information Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive, aerobic commensal bacterium of humans that is carried in the anterior nares of approximately 30% of the general population. It is
PVL Staph aureusjust a skin/soft tissue problem? Layla Mohammadi Lead Pharmacist, Antimicrobials Lewisham Healthcare NHS Trust
 PVL Staph aureusjust a skin/soft tissue problem? Layla Mohammadi Lead Pharmacist, Antimicrobials Lewisham Healthcare NHS Trust Neonatal Case History Neonate born at 26 +2 gestation Spontaneous onset of
PVL Staph aureusjust a skin/soft tissue problem? Layla Mohammadi Lead Pharmacist, Antimicrobials Lewisham Healthcare NHS Trust Neonatal Case History Neonate born at 26 +2 gestation Spontaneous onset of
In This Issue: Community-Associated MRSA Infection Surveillance in Washoe County Final Report For Health Care Providers
 EPI - NEWS Page 1 of 6 In This Issue: Community-Associated MRSA Infection Surveillance in Washoe County Final Report For Health Care Providers Please share this document with all physicians & staff in
EPI - NEWS Page 1 of 6 In This Issue: Community-Associated MRSA Infection Surveillance in Washoe County Final Report For Health Care Providers Please share this document with all physicians & staff in
Responders as percent of overall members in each category: Practice: Adult 490 (49% of 1009 members) 57 (54% of 106 members)
 Infectious Diseases Society of America Emerging Infections Network 6/2/10 Report for Query: Perioperative Staphylococcus aureus Screening and Decolonization Overall response rate: 674/1339 (50.3%) physicians
Infectious Diseases Society of America Emerging Infections Network 6/2/10 Report for Query: Perioperative Staphylococcus aureus Screening and Decolonization Overall response rate: 674/1339 (50.3%) physicians
Clostridium difficile Colitis
 Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Fredrick M. Abrahamian, D.O., FACEP Associate Professor of Medicine UCLA School of Medicine Director of Education Department of Emergency Medicine Olive View-UCLA
Update on Clostridium difficile Colitis Fredrick M. Abrahamian, D.O., FACEP Associate Professor of Medicine UCLA School of Medicine Director of Education Department of Emergency Medicine Olive View-UCLA
Optimizing Antibiotic Treatment of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
 Optimizing Antibiotic Treatment of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections 15th Annual Rocky Mountain Hospital Medicine Symposium November 6, 2017 Tim Jenkins, MD Director, Antibiotic Stewardship Program Denver
Optimizing Antibiotic Treatment of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections 15th Annual Rocky Mountain Hospital Medicine Symposium November 6, 2017 Tim Jenkins, MD Director, Antibiotic Stewardship Program Denver
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) The drug resistant `Superbug that won t die
 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) The drug resistant `Superbug that won t die Michael A. Miller, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics -Jacksonville OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the basic microbiology
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) The drug resistant `Superbug that won t die Michael A. Miller, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics -Jacksonville OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the basic microbiology
INFECTIOUS DISEASE/ORIGINAL RESEARCH
 INFECTIOUS DISEASE/ORIGINAL RESEARCH Randomized Controlled Trial of Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole for Uncomplicated Skin Abscesses in Patients at Risk for Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus
INFECTIOUS DISEASE/ORIGINAL RESEARCH Randomized Controlled Trial of Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole for Uncomplicated Skin Abscesses in Patients at Risk for Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus
Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Spinal Surgery Antibiotic Guidelines. Contents
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Spinal Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine Unique
Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Spinal Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine Unique
MEMORANDUM. Re: New guidelines for the Management of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections where MRSA is prevalent
 Athabasca Health Authority Keewatin Yatthé Health Region Mamawetan Churchill River Health Region Box 6000 La Ronge, SK S0J 1L0 Ph: 306-425-8588 Fax: 306-425-8530 MEMORANDUM To: Physicians and Primary Care
Athabasca Health Authority Keewatin Yatthé Health Region Mamawetan Churchill River Health Region Box 6000 La Ronge, SK S0J 1L0 Ph: 306-425-8588 Fax: 306-425-8530 MEMORANDUM To: Physicians and Primary Care
Appropriate Management of Common Pediatric Infections. Blaise L. Congeni M.D. Akron Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases
 Appropriate Management of Common Pediatric Infections Blaise L. Congeni M.D. Akron Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases It s all about the microorganism The common pathogens Viruses
Appropriate Management of Common Pediatric Infections Blaise L. Congeni M.D. Akron Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases It s all about the microorganism The common pathogens Viruses
Duke University Hospital Guideline for Empiric Inpatient Treatment of Cancer- Related Neutropenic Fever in Adult Patients
 Duke University Hospital Guideline for Empiric Inpatient Treatment of Cancer- Related Neutropenic Fever in Adult Patients PURPOSE Fever among neutropenic patients is common and a significant cause of morbidity
Duke University Hospital Guideline for Empiric Inpatient Treatment of Cancer- Related Neutropenic Fever in Adult Patients PURPOSE Fever among neutropenic patients is common and a significant cause of morbidity
Healthcare-associated infections surveillance report
 Healthcare-associated infections surveillance report Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Update, Q3 of 2017/18 Summary Table Q3 2017/18 Previous quarter (Q2 2017/18) Same quarter of previous
Healthcare-associated infections surveillance report Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Update, Q3 of 2017/18 Summary Table Q3 2017/18 Previous quarter (Q2 2017/18) Same quarter of previous
Felipe N. Gutierrez MD, MPH Chief, Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare
 Felipe N. Gutierrez MD, MPH Chief, Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare 100% of all wounds will yield growth If you get a negative culture you something is wrong! Pseudomonas while ubiquitous does
Felipe N. Gutierrez MD, MPH Chief, Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare 100% of all wounds will yield growth If you get a negative culture you something is wrong! Pseudomonas while ubiquitous does
Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections: Emerging Bacterial Resistance
 Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections: Emerging Bacterial Resistance Eileen M. Bulger, MD Professor of Surgery Harborview Medical Center University of Washington Objectives Review definition & diagnostic
Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections: Emerging Bacterial Resistance Eileen M. Bulger, MD Professor of Surgery Harborview Medical Center University of Washington Objectives Review definition & diagnostic
Pneumonia considerations Galia Rahav Infectious diseases unit Sheba medical center
 Pneumonia considerations 2017 Galia Rahav Infectious diseases unit Sheba medical center Sir William Osler (1849 1919) "Father of modern medicine Pneumonia: The old man's friend The captain of the men of
Pneumonia considerations 2017 Galia Rahav Infectious diseases unit Sheba medical center Sir William Osler (1849 1919) "Father of modern medicine Pneumonia: The old man's friend The captain of the men of
Evaluating the Role of MRSA Nasal Swabs
 Evaluating the Role of MRSA Nasal Swabs Josh Arnold, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Pharmacy Grand Rounds February 28, 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Identify the pathophysiology of MRSA nasal colonization
Evaluating the Role of MRSA Nasal Swabs Josh Arnold, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Pharmacy Grand Rounds February 28, 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Identify the pathophysiology of MRSA nasal colonization
New Antibiotics for MRSA
 New Antibiotics for MRSA Faculty Warren S. Joseph, DPM, FIDSA Consultant, Lower Extremity Infectious Diseases Roxborough Memorial Hospital Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Faculty Disclosure Dr. Joseph: Speaker
New Antibiotics for MRSA Faculty Warren S. Joseph, DPM, FIDSA Consultant, Lower Extremity Infectious Diseases Roxborough Memorial Hospital Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Faculty Disclosure Dr. Joseph: Speaker
A Prospective Investigation of Nasal Mupirocin, Hexachlorophene Body Wash, and Systemic
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 14 November 2011 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01608-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 14 November 2011 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01608-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
Skin Infections and Antibiotic Stewardship: Analysis of Emergency Department Prescribing Practices,
 Original Research Skin Infections and Antibiotic Stewardship: Analysis of Emergency Department Prescribing Practices, 2007-2010 Daniel J. Pallin, MD, MPH Carlos A. Camargo Jr, MD, DrPH Jeremiah D. Schuur,
Original Research Skin Infections and Antibiotic Stewardship: Analysis of Emergency Department Prescribing Practices, 2007-2010 Daniel J. Pallin, MD, MPH Carlos A. Camargo Jr, MD, DrPH Jeremiah D. Schuur,
Le infezioni di cute e tessuti molli
 Le infezioni di cute e tessuti molli SCELTE e STRATEGIE TERAPEUTICHE Pierluigi Viale Clinica di Malattie Infettive Policlinico S. Orsola Malpighi Treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections
Le infezioni di cute e tessuti molli SCELTE e STRATEGIE TERAPEUTICHE Pierluigi Viale Clinica di Malattie Infettive Policlinico S. Orsola Malpighi Treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections
Horizontal vs Vertical Infection Control Strategies
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL Chapter 14 Horizontal vs Vertical Infection Control Strategies Author Salma Abbas, MBBS Michael Stevens, MD, MPH Chapter Editor Shaheen Mehtar, MBBS. FRC Path,
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL Chapter 14 Horizontal vs Vertical Infection Control Strategies Author Salma Abbas, MBBS Michael Stevens, MD, MPH Chapter Editor Shaheen Mehtar, MBBS. FRC Path,
CELLULITIS / SKIN INFECTIONS
 Skin Infections Assessment Investigations Cellulitis Management Abscess Management Infection Control Antibiotic Choice Education Recurrent Infections Referral to Community Nursing References Skin Infections
Skin Infections Assessment Investigations Cellulitis Management Abscess Management Infection Control Antibiotic Choice Education Recurrent Infections Referral to Community Nursing References Skin Infections
CA-MRSA: How Should We Respond to Outbreaks?
 CA-MRSA: How Should We Respond to Outbreaks? Robert B. Stroube, MD, MPH Medscape Infectious Diseases. 2008; 2008 Medscape Posted 11/05/2008 Introduction to MRSA Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
CA-MRSA: How Should We Respond to Outbreaks? Robert B. Stroube, MD, MPH Medscape Infectious Diseases. 2008; 2008 Medscape Posted 11/05/2008 Introduction to MRSA Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Appropriate Antimicrobial Therapy for Treatment of
 Appropriate Antimicrobial Therapy for Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infections ( MRSA ) By : A. Bojdi MD Assistant Professor Inf. Dis. Dep. Imam Reza Hosp. MUMS Antibiotics Still Miracle Drugs Paul
Appropriate Antimicrobial Therapy for Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infections ( MRSA ) By : A. Bojdi MD Assistant Professor Inf. Dis. Dep. Imam Reza Hosp. MUMS Antibiotics Still Miracle Drugs Paul
Overview of C. difficile infections. Kurt B. Stevenson, MD MPH Professor Division of Infectious Diseases
 Overview of C. difficile infections Kurt B. Stevenson, MD MPH Professor Division of Infectious Diseases Conflicts of Interest I have no financial conflicts of interest related to this topic and presentation.
Overview of C. difficile infections Kurt B. Stevenson, MD MPH Professor Division of Infectious Diseases Conflicts of Interest I have no financial conflicts of interest related to this topic and presentation.
11/22/2016. Antimicrobial Stewardship Update Disclosures. Outline. No conflicts of interest to disclose
 Antimicrobial Stewardship Update 2016 APIC-CI Conference November 17 th, 2016 Jay R. McDonald, MD Chief, ID Section VA St. Louis Health Care System Assistant Professor of medicine Washington University
Antimicrobial Stewardship Update 2016 APIC-CI Conference November 17 th, 2016 Jay R. McDonald, MD Chief, ID Section VA St. Louis Health Care System Assistant Professor of medicine Washington University
Implementing Antibiotic Stewardship in Rural and Critical Access Hospitals
 National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases Implementing Antibiotic Stewardship in Rural and Critical Access Hospitals Denise Cardo, MD Director, Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion,
National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases Implementing Antibiotic Stewardship in Rural and Critical Access Hospitals Denise Cardo, MD Director, Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion,
Community Acquired Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
 Community Acquired Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus John S. Hammes, M.D. ABSTRACT Community acquired Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (ca-mrsa) is an important cause of illness among
Community Acquired Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus John S. Hammes, M.D. ABSTRACT Community acquired Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (ca-mrsa) is an important cause of illness among
Optimizing Antimicrobial Stewardship Activities Based on Institutional Resources
 Optimizing Antimicrobial Stewardship Activities Based on Institutional Resources Andrew Hunter, PharmD, BCPS Infectious Diseases Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center Andrew.hunter@va.gov
Optimizing Antimicrobial Stewardship Activities Based on Institutional Resources Andrew Hunter, PharmD, BCPS Infectious Diseases Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center Andrew.hunter@va.gov
Inappropriate Use of Antibiotics and Clostridium difficile Infection. Jocelyn Srigley, MD, FRCPC November 1, 2012
 Inappropriate Use of Antibiotics and Clostridium difficile Infection Jocelyn Srigley, MD, FRCPC November 1, 2012 Financial Disclosures } No conflicts of interest } The study was supported by a Hamilton
Inappropriate Use of Antibiotics and Clostridium difficile Infection Jocelyn Srigley, MD, FRCPC November 1, 2012 Financial Disclosures } No conflicts of interest } The study was supported by a Hamilton
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium tigecycline 50mg vial of powder for intravenous infusion (Tygacil ) (277/06) Wyeth 9 June 2006 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
Scottish Medicines Consortium tigecycline 50mg vial of powder for intravenous infusion (Tygacil ) (277/06) Wyeth 9 June 2006 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
Antimicrobial Stewardship in the Long Term Care and Outpatient Settings. Carlos Reyes Sacin, MD, AAHIVS
 Antimicrobial Stewardship in the Long Term Care and Outpatient Settings Carlos Reyes Sacin, MD, AAHIVS Disclosure Speaker and consultant in HIV medicine for Gilead and Jansen Pharmaceuticals Objectives
Antimicrobial Stewardship in the Long Term Care and Outpatient Settings Carlos Reyes Sacin, MD, AAHIVS Disclosure Speaker and consultant in HIV medicine for Gilead and Jansen Pharmaceuticals Objectives
Antibiotic Abyss. Discussion Points. MRSA Treatment Guidelines
 Antibiotic Abyss Fredrick M. Abrahamian, D.O., FACEP, FIDSA Professor of Medicine UCLA School of Medicine Director of Education Department of Emergency Medicine Olive View-UCLA Medical Center Sylmar, California
Antibiotic Abyss Fredrick M. Abrahamian, D.O., FACEP, FIDSA Professor of Medicine UCLA School of Medicine Director of Education Department of Emergency Medicine Olive View-UCLA Medical Center Sylmar, California
Since its discovery in the 1960s, methicillinresistant
 CME Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Diagnosis and Treatment Update for Plastic Surgeons D. Heath Stacey, M.D. Barry C. Fox, M.D. Samuel O. Poore, M.D., Ph.D. Michael L.
CME Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Diagnosis and Treatment Update for Plastic Surgeons D. Heath Stacey, M.D. Barry C. Fox, M.D. Samuel O. Poore, M.D., Ph.D. Michael L.
Preventing Surgical Site Infections. Edward L. Goodman, MD September 16, 2013
 Preventing Surgical Site Infections Edward L. Goodman, MD September 16, 2013 Outline NHSN Reporting and Definitions Magnitude of the Problem Risk Factors Non Pharmacologic Interventions Pharmacologic Interventions
Preventing Surgical Site Infections Edward L. Goodman, MD September 16, 2013 Outline NHSN Reporting and Definitions Magnitude of the Problem Risk Factors Non Pharmacologic Interventions Pharmacologic Interventions
Multidrug Resistant Organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff)
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Multidrug Resistant Organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff) This information explains multidrug resistant organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff),
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Multidrug Resistant Organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff) This information explains multidrug resistant organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff),
Protocol for exit-site care and treatment of exit-site infections in peritoneal dialysis CONTROLLED DOCUMENT
 CONTROLLED DOCUMENT Protocol for exit-site care and treatment of exit-site infections in peritoneal dialysis CATEGORY: CLASSIFICATION: PURPOSE Controlled Document Number: Guideline Clinical The purpose
CONTROLLED DOCUMENT Protocol for exit-site care and treatment of exit-site infections in peritoneal dialysis CATEGORY: CLASSIFICATION: PURPOSE Controlled Document Number: Guideline Clinical The purpose
Antimicrobial Stewardship in the Hospital Setting
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 12 Antimicrobial Stewardship in the Hospital Setting Authors Dan Markley, DO, MPH, Amy L. Pakyz, PharmD, PhD, Michael Stevens, MD, MPH Chapter Editor
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 12 Antimicrobial Stewardship in the Hospital Setting Authors Dan Markley, DO, MPH, Amy L. Pakyz, PharmD, PhD, Michael Stevens, MD, MPH Chapter Editor
Isolation of MRSA from the Oral Cavity of Companion Dogs
 InfectionControl.tips Join. Contribute. Make A Difference. https://infectioncontrol.tips Isolation of MRSA from the Oral Cavity of Companion Dogs By: Thomas L. Patterson, Alberto Lopez, Pham B Reviewed
InfectionControl.tips Join. Contribute. Make A Difference. https://infectioncontrol.tips Isolation of MRSA from the Oral Cavity of Companion Dogs By: Thomas L. Patterson, Alberto Lopez, Pham B Reviewed
Antimicrobial Update. Alison MacDonald Area Antimicrobial Pharmacist NHS Highland April 2018
 Antimicrobial Update Alison MacDonald Area Antimicrobial Pharmacist NHS Highland alisonc.macdonald@nhs.net April 2018 Starter Questions Setting the scene... What if antibiotics were no longer effective?
Antimicrobial Update Alison MacDonald Area Antimicrobial Pharmacist NHS Highland alisonc.macdonald@nhs.net April 2018 Starter Questions Setting the scene... What if antibiotics were no longer effective?
Host, Syndrome, Bug, Drug: Introducing 2 Frameworks to Approach Infectious Diseases Cases with an Antimicrobial Stewardship Focus
 Host, Syndrome, Bug, Drug: Introducing 2 Frameworks to Approach Infectious Diseases Cases with an Antimicrobial Stewardship Focus Montana ACP Meeting 2018 September 8, 2018 Staci Lee, MD, MEHP Billings
Host, Syndrome, Bug, Drug: Introducing 2 Frameworks to Approach Infectious Diseases Cases with an Antimicrobial Stewardship Focus Montana ACP Meeting 2018 September 8, 2018 Staci Lee, MD, MEHP Billings
Antibiotic Stewardship in the LTC Setting
 Antibiotic Stewardship in the LTC Setting Joe Litsey, Director of Consulting Services Pharm.D., Board Certified Geriatric Pharmacist Thrifty White Pharmacy Objectives Describe the Antibiotic Stewardship
Antibiotic Stewardship in the LTC Setting Joe Litsey, Director of Consulting Services Pharm.D., Board Certified Geriatric Pharmacist Thrifty White Pharmacy Objectives Describe the Antibiotic Stewardship
Antimicrobial Stewardship:
 Antimicrobial Stewardship: Inpatient and Outpatient Elements Angela Perhac, PharmD afperhac@carilionclinic.org Disclosure I have no relevant finances to disclose. Objectives Review the core elements of
Antimicrobial Stewardship: Inpatient and Outpatient Elements Angela Perhac, PharmD afperhac@carilionclinic.org Disclosure I have no relevant finances to disclose. Objectives Review the core elements of
Can you treat mrsa with amoxicillin
 Can you treat mrsa with amoxicillin 15-8-2017 Community-associated MRSA You can pick up MRSA outside the hospital, especially if you :. (a related drug developed to treat these germs). Amoxicillin and
Can you treat mrsa with amoxicillin 15-8-2017 Community-associated MRSA You can pick up MRSA outside the hospital, especially if you :. (a related drug developed to treat these germs). Amoxicillin and
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium daptomycin 350mg powder for concentrate for solution for infusion (Cubicin ) Chiron Corporation Limited No. (248/06) 10 March 2006 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC)
Scottish Medicines Consortium daptomycin 350mg powder for concentrate for solution for infusion (Cubicin ) Chiron Corporation Limited No. (248/06) 10 March 2006 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC)
Hosted by Dr. Jon Otter, Guys & St. Thomas Hospital, King s College, London A Webber Training Teleclass 1
 Andreas Voss, MD, PhD Professor of Infection Control Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre & Canisius-Wilhelmina Hospital Nijmegen, Netherlands Hosted by Dr. Jon O0er Guys & St. Thomas NHS Founda
Andreas Voss, MD, PhD Professor of Infection Control Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre & Canisius-Wilhelmina Hospital Nijmegen, Netherlands Hosted by Dr. Jon O0er Guys & St. Thomas NHS Founda
INTERIM GUIDELINES FOR EVALUATION & MANAGEMENT OF COMMUNITY-ASSOCIATED METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS
 INTERIM GUIDELINES FOR EVALUATION & MANAGEMENT OF COMMUNITY-ASSOCIATED METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS SKIN AND SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONS IN OUTPATIENT SETTINGS AUGUST 10, 2004 Prepared by: Tim
INTERIM GUIDELINES FOR EVALUATION & MANAGEMENT OF COMMUNITY-ASSOCIATED METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS SKIN AND SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONS IN OUTPATIENT SETTINGS AUGUST 10, 2004 Prepared by: Tim
Prophylactic antibiotic timing and dosage. Dr. Sanjeev Singh AIMS, Kochi
 Prophylactic antibiotic timing and dosage Dr. Sanjeev Singh AIMS, Kochi Meaning - Webster Medical Definition of prophylaxis plural pro phy lax es \-ˈlak-ˌsēz\play : measures designed to preserve health
Prophylactic antibiotic timing and dosage Dr. Sanjeev Singh AIMS, Kochi Meaning - Webster Medical Definition of prophylaxis plural pro phy lax es \-ˈlak-ˌsēz\play : measures designed to preserve health
Advice for those affected by MRSA outside of hospital If you have MRSA this booklet provides information to help manage your day-to-day life
 Registered Charity No 1115672 raising public awareness - campaigning for safe standards supporting sufferers and dependants Patron: Edwina Currie President: Professor Hugh Pennington Advice for those affected
Registered Charity No 1115672 raising public awareness - campaigning for safe standards supporting sufferers and dependants Patron: Edwina Currie President: Professor Hugh Pennington Advice for those affected
Cellulitis. Assoc Prof Mark Thomas. Conference for General Practice Auckland Saturday 28 July 2018
 Cellulitis Assoc Prof Mark Thomas Conference for General Practice Auckland Saturday 28 July 2018 Summary Cellulitis Usual treatment flucloxacillin for 5 days Frequent recurrences consider penicillin 250mg
Cellulitis Assoc Prof Mark Thomas Conference for General Practice Auckland Saturday 28 July 2018 Summary Cellulitis Usual treatment flucloxacillin for 5 days Frequent recurrences consider penicillin 250mg
Clinical Management of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections in the U.S. Emergency Departments
 Original Research Clinical Management of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections in the U.S. Emergency Departments Rakesh D. Mistry, MD, MS* Daniel J. Shapiro, BA Monika K. Goyal, MD Theoklis E. Zaoutis Jeffrey
Original Research Clinical Management of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections in the U.S. Emergency Departments Rakesh D. Mistry, MD, MS* Daniel J. Shapiro, BA Monika K. Goyal, MD Theoklis E. Zaoutis Jeffrey
Antimicrobial stewardship: Quick, don t just do something! Stand there!
 Antimicrobial stewardship: Quick, don t just do something! Stand there! Stanley I. Martin, MD, FACP, FIDSA Director, Division of Infectious Diseases Director, Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Geisinger
Antimicrobial stewardship: Quick, don t just do something! Stand there! Stanley I. Martin, MD, FACP, FIDSA Director, Division of Infectious Diseases Director, Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Geisinger
SIVEXTRO (tedizolid phosphate) oral tablet ZYVOX (linezolid) oral suspension and tablet
 ZYVOX (linezolid) oral suspension and tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
ZYVOX (linezolid) oral suspension and tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
Author - Dr. Josie Traub-Dargatz
 Author - Dr. Josie Traub-Dargatz Dr. Josie Traub-Dargatz is a professor of equine medicine at Colorado State University (CSU) College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. She began her veterinary
Author - Dr. Josie Traub-Dargatz Dr. Josie Traub-Dargatz is a professor of equine medicine at Colorado State University (CSU) College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. She began her veterinary
