Biology and Diseases of the Laboratory Ferret
|
|
|
- Milo Warner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology and Diseases of the Laboratory Ferret NCALAM Workshop in Laboratory Animal Medicine May 19, 2017 Slide credit: Chandra D. Williams, DVM, DACLAM, CPIA Who am I? Allison Rogala, DVM, DACLAM DISCLAIMER This is not an ACLAM sanctioned presentation All information is deemed reliable and correct No warranty for accuracy No information presented is known to be specifically included in the ACLAM Board examinations DISCLAIMER Photo credits are provided within the document. Product photos are from online vendor catalogs and DO NOT represent an endorsement of the product by the presenter. References Laboratory Animal Medicine, 3 rd Edition, Edited by Fox, Anderson, Otto, Pritchett Corning, Whary Biology and Diseases of the Ferret, 3 rd Edition, Edited by Fox and Marini Species Categories Based on mean importance ratings from the Role Delineation Study, the suggested species were classified as primary, secondary and tertiary. Below is the list by category. what level of detail do I need to know? Category Species Primary Mouse (Mus musculus) Primary Rat (Rattus norvegicus) Primary Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) Primary Macaques (Macaca spp). Primary Dog (Canis familiaris) Primary Pig (Sus scrofa) Secondary Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Secondary African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis and Xenopus tropicalis) Secondary Cat (Felis domestica) Secondary Guinea pig (Cavia porcellus) Secondary Ferret (Mustela putorius furo) Secondary Squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus) Secondary Sheep (Ovis aries) Secondary Syrian hamster (Mesocricetus auratus) Secondary Baboon (Papio spp.) Secondary Marmoset/tamarins (Callitrichidae) Secondary Gerbil (Meriones spp.) Secondary Goat (Capra hircus) Tertiary Other rodents Tertiary Chicken (Gallus domestica) Tertiary Other nonhuman primates Tertiary Other mammals Tertiary Pigeon (Columba livia) Tertiary Other amphibians Tertiary Other livestock species including cattle and horses Tertiary Other Fish Tertiary Reptiles Tertiary Other birds Tertiary Invertebrates Tertiary species Secondary species: Ferrets Primary species 1
2 Taxonomy Mustelidae Mustelinae is the subfamily Genus Mustela (weasels, mink, ferrets) 5 subgenera Mustela (weasels) Lutreola (European mink) Vison (American mink) Putorius (Ferrets) Grammogale (South American Weasels) Genus Martes (martens) Ancient family Dates back to the Eocene period, ~40 million years ago Primitive characteristics Small size, stocky legs, five toes/foot, elongated braincase, short rostrum Other Members Smallest member (25g): Least weasel, Mustela nivalis Largest member (45kg): Sea otter, Enhydra lutris Least Weasel, Photography on the Net Sea otter, Google images Mustela putorius furo Ferrets European polecat Domesticated over 2000 years ago; bred for rabbiting (rabbit hunting) in North Africa Mustela nigripes (North American black footed ferret) is closest relative Early use in England and the US was rodent control Also used for ferret legging or Put em Down Use in Research Human influenza Reye s syndrome SARS coronavirus Cystic fibrosis Helicobacter induced GI diseases Neural development Drug induced emesis Visual cortex development Use/Availability in Research Readily available commercially Coat colors include: albino, sable (fitch), Siamese, silver mitt, Siamesesilver mitt Fitch or wild coat color is most common Anecdotal from BB: 75% of US ferrets with a blaze or white head= Waardenburg syndrome & deafness Albino ferrets have impaired motion perception and contrast sensitivity Laboratory Management and Husbandry Housing Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animal Housing Standard (pg 59) Cat or rabbit caging widely used Cages with grid floor spacing must be less than 1 inch apart. Weight of Animal Floor Area/Animal Height (inches) (ft2) < 4 kg >4 kg
3 Housing and Husbandry of Ferrets Question Housing and Husbandry of Ferrets (Answer) Rabbits Temperature requirements for ferrets are similar to what other lab animal species? Housing and Husbandry of Ferrets Temperature requirements: F (Page 44 of the Guide) Blue book, page 578 recommends 4 18 C ( F) Ferrets < 6weeks should be housed at >15 C Kits under this age required a heat source if separated from the dam They tolerate low temperatures well and high temperatures poorly. Temps >30 C (86 F) cannot be tolerated. Study Table 14.1 on page 579 WHY are they heat intolerant? Light Cycles Non breeding: 12:12h Lighting can be altered to control breeding cycles Breeding/lactating: 16h of light daily Breeding or long term (beyond 6 months): winter light 6 weeks of year 14h of DARK Help maintain physiologic normalcy Air Circulation air changes per hour Use non recirculated air: Strong ferret odor Susceptibility of ferrets to human respiratory infections DO NOT overlap with rodents Rodents instinctive fear of ferrets Ferret scent can disrupt breeding & physiology Ferret Caging Females may be single or co housed but may become pseduopregnant Males >12 weeks should be single housed Enrichment program: Co housing Nesting material Extra paper for hiding 3
4 Ferret Caging Ferret Caging Ferret Caging Considerations of metal caging Avoid sharp edges > broken teeth Zinc toxicosis < metal leaching during steam sterilization Litter box Avoid clay litters > dust > upper respiratory infections Ferret Enrichment Isolation can result in hyperactivity Socially reared ferrets superior in maze learning Prefer prey like interactions Question Research with the black footed ferret has demonstrated that enrichment lowers in juvenile males. Answer Fecal glucocorticoid metabolites (FGM) Enrichment had NO effect on FGM in juvenile females and adult males. Page 580 in LAM 3 rd edition; Published by Poessel et. al.,
5 Ferret Biology Unique Anatomic/Physiologic Characteristics Ferret Biology Unique Anatomic/Physiologic Characteristics Image: Veterinary Practice News 1. Long, narrow thorax 2. Proportionately long trachea 3. Total lung capacity 3x that for an animal its size 4. High degree of bronchiolar branching and extensive bronchial submucosal glands 5. Paired common carotid arteries arise from brachiocephalic trunk (or innominate artery) 6. Simple monogastric stomach 7. SHORT alimentary tract (3h transit time) 8. Paired anal scent glands 9. No cecum 10.Heat intolerant Extramedullary hematopoesis common Splenomegaly (rule out: infectious, neoplastic, isoflurane administration No naturally occurring antibodies against unmatched erythrocyte antigens Ferret Biodata Question Table 14.2, LAM BB 3 rd edition, page 581 Life span is 6 8 years Weaning: 6 8 weeks Newborn kits: 6 12 g at birth; grow to ~400 g by weaning Length of breeding life: 2 5 years Litter size: 8 average Eyes open: 34 days Gestation: 42 days Sexually intact adults are subject to seasonal fluctuations of body fat of 30 40%. Dental formula: 2(I3/3, C1/2, P4/3, M1/2) What is a male ferret called and how much does it weigh? What is a female ferret called and how much does it weigh? Photo: imgur.com Answer A male ferret is called a hob and weighs 1 2 kg. A female ferret is called a jill and weighs 0.5 1kg. Young are called kits. 5
6 Ferret Nutrition Commercial diets available, featuring high protein (up to 50%) and low carbohydrate (<10%) Strict carnivores Short digestive tract and rapid GI transit time require that protein be readily digestible Adult ferrets drink ml of water daily. Ferret Reproduction Table 14.7, LAM BB 3 rd edition, page 585 Question Ferrets are breeders and ovulators. Photo: reddit.com Ferret Reproduction Answer: Ferrets are SEASONAL breeders and INDUCED ovulators. Page 584, LAM BB, 3 rd edition Ferret Reproduction Breeding facility practices range. One example: Jills breed 7 10 mos of age, average 3.7 litters per year and cycled out of reproduction after 6 litters Northern hemisphere breeding seasons: March to August for females December to July for males Ferrets born in late spring or early summer and maintained under natural lighting will not assume adult pattern of gonadal activity until the following season. Placentation: zonary and endotheliochorial Ferret Repro Data Minimum breeding age: 8 12 mos (M); 4 5 mos (F) Estrous cycle: Monoestrus, March August Induced ovulators Age at puberty Female ( g): 6 12 mos Male ( g): 6 12 mos Ferret Repro Data Question is the hallmark of estrus in jills. 6
7 Ferret Repro Data Answer VULVAR SWELLING is the hallmark of estrus in jills. LAM BB, 3 rd edition, pp 585 Females are brought to male ~14 D after vulvar enlargement. Left together ~2 days. Question Along with this species, the ferret has contributed extensively to an understanding of photoperiodic influences on the hypthalamicpituitary gonadal axis. Answer Along with the HAMSTER, ferret has contributed extensively to an understanding of photoperiodic influences on the hypthalamicpituitary gonadal axis. LAM BB, 3 rd edition, pag. 585 (Baum, 1998). Ferret Husbandry Pregnancy Jills within 2 weeks of parturition should be singly housed Rabbit nest boxes, cat litter pans work well and should have bedding. Should be at least 6 inches deep. Parturition occurs rapidly with few impending signs Jills that pass their due date without delivery should be palpated. Kits remaining beyond the 43 rd day typically die. Dystocia is common and jills tolerate C sections well. Oxytocin may be used. Crossfostering has been successful. Ferret Husbandry Pregnancy Nesting Box Ferret husbandry Newborns Altricial and covered in lanugo hair 3 days: albinos retain white hair; pigmented ferrets acquire gray coat Completely dependent upon jill for first 3 weeks of life. Sexing anogenital distance Developmental landmarks Hear: 32 days Open eyes: 34 days 1 st Teeth erupt: 14 days 7
8 Diseases of Ferrets Diseases of the Laboratory Ferret Infectious Diseases Metabolic and Nutritional Diseases Traumatic Disorders Iatrogenic Disorders Neoplastic Diseases Miscellaneous Diseases Legal Information Legal in 48 states other than CA and HI Classified as a pet in 1999 Rabies Compendium NASPHV Treatment after bite incidents may vary by locality Most enforce 10 day quarantine Some localities may enforce euthanasia and testing Case 1 Lesions Erythematous, pruritic rash on chin and ventral neck Additional lesions Histopathology Mucopurulent ocular discharge Hyperkeratosis of footpad Bladder with eosinophilic inclusions Both intracytoplasmic and intranuclear INIC and ICIC bodies in respiratory epithelial cells and macrophages. 8
9 What s Your Diagnosis? (WYD) Answer Distemper Canine Distemper Virus CD or CDV Paramyxoviridae Genus: Morbillivirus Related to measles and rinderpest Several strains, including ferret adapted CDV that differ in incubation, C/S and duration MOST SERIOUS VIRAL INFECTION OF FERRETS Almost 100% mortality Vaccine and husbandry are imperative Canine Distemper Virus Catarrhal phase 7 10 days post infection Fever, rash, footpad hyperkeratosis (inconsistent), serous to mucopurulent ocular/nasal discharge Erythematous, pruritic rash spreads from chin to inguinal region Cell mediated immunity response similar to measles in humans CNS phase Ataxia, tremors, paralysis Death in days (ferret strain) and within 35 days (canine strain) Canine Distemper Vaccine Transmission Unvaccinated dogs and other canids, mustelids, procyonids serve as reservoirs Virus shed from infected hosts from all orifices, urine, feces and sloughed skin. Viremia detectable 48 hours post infection and PERSISTS until ferret dies or mounts neutralizing antibody response. Canine Distemper Virus Necropsy and Diagnosis Eosinophilic inclusion bodies in tracheal, bronchial and bladder epithelium Presumptive DX based on C/S,? Vax history, exposure Fluorescent antibody test on peripheral blood on conjunctival scraping RT PCR used to detect experimental infection DDX: B. bronchiseptica, Influenza 9
10 Canine Distemper Virus Prevention Humane euthanasia of affected animals recommended due to lack of literature on animal survival. Modified Live Vaccine of chicken embryo tissue culture origin (CETCO) SQ or IM Vaccinate kits every 2 3 weeks starting at weeks of age until 14 weeks of age. Fervac D or Purevax Ferret Distemper Vaccine reactions have been noted INIC and ICIC bodies in respiratory epithelial cells and macrophages. Photo: Becker Animal Hospital Case 2 Clinical Signs Progressive weight loss Melena Ataxia Tremors Lesions Splenomegaly Glomerulonephritis Histopathology Non suppurative meningitis with plasma cell cuffing Clinical Pathology Hypergammaglobulinemia 10
11 WYD? Answer Aleutian Disease Aleutian Disease Aleutian Mink Disease (ADV) Parvovirus Genus: Amdoparvovirus Species: Carnivore amdoparvovirus 1 Mink derived strains are more virulent to mink than are ferret derived strains Most common strain in ferrets is ADV F. Transmission may be direct or via aerosol of urine, saliva, blood, feces and fomites. Aleutian Disease Lesions are typically immune mediated with elevation of gammaglobulins of >20% of the total proteins. C/S include: weight loss, malaise, cachexia, ataxia, tremors. DX: Presumptive based on HGG and chronic weight loss. Confirmed by IFA or CIEP (counterimmunoelectrophoresis). DDX: Neurotropic form of CD, chronic wasting diseases such as neoplasia, malabsorption/maldigestion, bacterial enteritis. Aleutian Disease Aleutian Disease Classic disease shows: glomerulonephritis, splenomegaly, hematuria, hypergammaglobulinemia, gastric ulcers, cachexia. Antigen antibody complexes are formed in large numbers which are deposited in vascular basement membranes throughout body. Widespread vasculitis including glomerulonephritis and Interstitial pneumonia. 11
12 Answer What human orthomyxovirus is zoonotic and pathogenic to ferrets? Human influenza viruses A and B Pathogenicity of type B is low. Ferrets are also susceptible to avian, phocine, equine and swine influenza. C/S appear 48 hours post infection and include anorexia, fever, sneezing and serous nasal discharge. Transmission is aerosol and direct contact. TX: Antibiotic, antivirals Since ferrets are warm blooded What other viral disease are they susceptible to? Rabies Rhabdovirus Genus: Lyssavirus Infrequently reported in ferrets. Treatment and Control: USDA approved, killed rabies vaccine given at SQ at ages 3 months, 1 year and annually thereafter. DDx: Neurotropic form of CD DX: IFA of brain tissue Answer What is the causative agent of green slime disease in ferrets? Coronavirus Or Epizootic Catarrhal Enteritis (ECE) Genus: Alphacoronavirus High morbidity and low mortality. Shed in feces and saliva. Highly infectious. C/S: Decreased appetite, diarrhea and vomiting; diarrhea is green and mucoid. DX: Hx, C/S; DDx: Intestinal biopsy and histopath; RT PCR on feces. 12
13 ECE Coronavirus particles Ferret Enteric Coronavirus Ferret Systemic Coronoviral Disease Diagnosis: Clinical signs and history Histology IHC Clinical pathology not specific Ferret Systemic Coronavirus Ferret Systemic Coronavirus 13
14 Ferret Systemic Coronavirus (FRSCV) Ferret Systemic Coronaviral Disease (FSCD) Systemic, granulomatous disease Behaves similar to Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP) Affects animals under 1 year of age C/S are non specific (lethargy, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss) Dx: Histology Predominant necropsy findings are enlarge mesenteric lymph nodes Pyogranulomatous inflammation Case 3 Chronic gastritis Histopathology Histopathology Special staining Normal pyloric junction in adult ferret, HE, 10X Pyloric junction in 4 year old ferret, HE, 10X Helicobacter mustelae What s the etiologic agent? What s the stain? Ubiquitous or not? Clinical signs: Typically asymptomatic Vomiting, melena, chronic weight loss, low hematocrit Diagnosis: Endoscopic visualization of gastric/duodenal ulcers Biopsy Treatment: Triple therapy: amoxicillin, metronidazole, bismuth subsalicylate Ranitidine bismuth and clarithromycin DDx: Gastric foreign body 14
15 Helicobacter mustelae Every ferret with chronic gastritis is H. mustelae positive Nearly 100% prevalence in exposed weanlings Ferret is the only domesticated animal to date that has naturally occurring helicobacter associated ulcer disease. Infected ferrets may also be susceptible to gastric cancer Case 4 Chronic diarrhea (green and/or bloody) Lethargy Anorexia Marked weight loss Dehydration Rectal prolapse Necropsy Segmented thickened colon Histopathology Special Staining What is the etiologic agent? Intracytoplasmic organisms in hyperplastic epithelial cells 15
16 Proliferative Bowel Disease Necropsy Findings: Segmented, thickened lower bowel Histo: marked mucosal proliferation and intracytoplasmic L. intracellularis w/ Silver Stain Proliferative Bowel Disease Lawsonia intracellularis Intracellular, gram negative, comma to spiral shaped bacteria Fecal oral transmission YOUNG ferrets Clinical signs: Large bowel diarrhea May be blood tinged, mucus, often green Rectal prolapse may occur Lethargy, anorexia, dehydration Case 5 Diarrhea, dehydration and lethargy in a four month old ferret Etiologies? Enteric Coccidiosis Isospora laidlawi Eimeria furonis Eimeria ictidea Infection occurs after ingestion of sporulated oocysts. Usually subclinical in ferrets. Dx: Fecal flotation or direct wet mount of feces Tx: Good husbandry, Sufadimethoxine, Coccidiostat Coccidiosis Schizonts and gametocytes of E. furonis Generally asymptomatic and minimal gross lesions 16
17 Tuberculosis Mycobacterium bovis, avium, tuberculosis, celatum Aerobic, gram positive, non branching, nonsporeforming, ACID FAST rods Ferrets may be more susceptible than other species Clostridium perfringens Clostridium perfringes type A (Clostridium welchii) Ubiquitous organism in intestines of all humans and animals. Acute abdominal distension, dyspnea, cyanosis in weaning ferrets. May be found dead and bloated. DX: Isolation of toxins from ingest; Mouse protection assay. Case 6 Additional clinical signs Bilaterally symmetrical alopecia Vulvar swelling Most likely diagnosis? Adrenal gland tumor or Adrenal associated Endocrinopathy Second most common type of neoplasia in ferrets Thought to be cause by early spay/neutering Artificially prolonged photoperiod (indoor housing) may also contribute In males, enlarged prostate may result in urinary blockage Animals are NOT cushingoid!!! 17
18 Adrenal associated Endocrinopathy Treatment Surgical excision or debulking Right adrenal difficult to remove (attached to vena cava) Medical management Palliative only Leuprolide acetate Deslorelin acetate Melatonin Case 7 Signs Necropsy/Histopath Vomiting Ataxia Weakness Pawing at mouth Posterior paresis Collapse WYD? Insulinoma Islet Cell Tumor Causes hypoglycemia Manage with prednisone and/or diazoxide Dietary modification Surgical debulking may reduce clinical signs transiently 18
19 Islet Cell Tumor Islet Cell Tumor Most common ferret tumor Arise from Islet of Langerhans Clinical signs: hypoglycemia, lethargy, stupor, ptyalism, ataxia, hindlimb paresis, salivation, seizures, coma, death Inappropriate secretion of insulin resulting in trances Most tumors secrete insulin Diagnosis: history, clinical signs, blood glucose test g/dl questionable, <60 positive Diagnosis based on histopathology? Lymphoma Most common in young animals (<2 years, very aggressive) Common forms are multicentric and gastrointestinal lymphoma Possibly retroviral involvement H. mustelae involved with specific gastric lymphoma Difficult to Dx; C/S include weight loss, anorexia, lethargy, splenic or liver enlargement. Treat with chemotherapy (L asparginase/cyclophosphamide/prednisone) Lymphoma Lymphoma Neoplastic lymphocytes 19
20 WYD? What is this common tumor of ferrets that typically occurs on the tail, but can also occur in the cervical region present like a lymphoma? Chordoma Notochord remnants Not epithelial Masses on tail that may cause ulceration of overlying skin. Slow growing. Metastasis has been documented. Chordoma Congenital Lesions Neural tube defects Gastroschisis Cleft palate Corneal dermoids Cataracts Supernumerary incisors Cataracts Cardiomyopathy Common cause of disease in aging ferrets. Dilatative form most common C/S: Lethargy, weight loss, anorexia and signs of CHF. DDx: Radiographs Tx: Medial therapy (support care, diuretics, inotropics) Long term prognosis is guarded/poor. 20
21 Cardiomyopathy Ectoparasites Ticks (Ixodes sp) Ear mites (Otodectes cyanotis) Fleas (Ctenocephalides sp.) Sarcoptic mange has been reported Very pruritic, whole body form Variable pruritic form localised to the feet Demodectic mange in old or immunosuppressed ferrets Biopsy moderate hyperkeratosis and mites Ectoparasites (Earmites: Otodectes cyanotes) Ectoparasites: Demodex sp. Dirofiliriasis Susceptible to natural and experimental infection with Dirofilaria immitis. Monthly heartworm preventative. In endemic areas, animals should be treated year round. Hyperestrogenism Induced ovulators May remain in persistent estrus if not bred or if estrus not terminated chemically or via OVH. >1 month may develop estrogen induced anemia. Also causes BM suppression. C/S: vulvar enlargement, bilaterally symmetrical alopecia of tail and abdomen, weakness, lethargy. Avoid by OVH of non breeders, use vasectomized hobs, Tx animal 10 days after estrus start. 21
22 Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis The End Eosinophilic gastroenteritis, idiopathic disorder Splendore Hoeppli material in inflamed lymph nodes Originates from Igs of host derived inflammatory cells. Named after Splendore, an Italian physician and Hoeppli, a German parasitologist. 22
Canine and Feline Distemper. Description. The following chart indicates the animals which are susceptible to infection by canine and feline distemp
 Canine and Feline Distemper Description Canine and feline distemper are diseases affecting many wild and domestic carnivo The following chart indicates the animals which are susceptible to infection by
Canine and Feline Distemper Description Canine and feline distemper are diseases affecting many wild and domestic carnivo The following chart indicates the animals which are susceptible to infection by
Canine Distemper Virus
 Photo: LE Carmichael, MJ Appel Photo: LE Carmichael, MJ Appel Photo: LE Carmichael, MJ Appel Canine Distemper Virus Canine Distemper (CD) is a highly contagious infectious disease of dogs worldwide caused
Photo: LE Carmichael, MJ Appel Photo: LE Carmichael, MJ Appel Photo: LE Carmichael, MJ Appel Canine Distemper Virus Canine Distemper (CD) is a highly contagious infectious disease of dogs worldwide caused
MSMR Enrichment Symposium, 15 April 2010 MSMR Enrichment Symposium, 15 April 2010
 Group Name: EE 1 Group Name: PS 1 Species: Pig, Sus scrofa domesticus Research: Heart Research. Research Protocol: Periodic surgery or non-invasive imaging, all require anaesthesia. Diet: Normal Pig Pellets.
Group Name: EE 1 Group Name: PS 1 Species: Pig, Sus scrofa domesticus Research: Heart Research. Research Protocol: Periodic surgery or non-invasive imaging, all require anaesthesia. Diet: Normal Pig Pellets.
Enteric Clostridia 10/27/2011. C. perfringens: general. C. perfringens: Types & toxins. C. perfringens: Types & toxins
 C. perfringens: general Enteric Clostridia Formerly called C. welchii Thick rods, forming spores Non motile Grow fast Habitats: Soil and sewage and in the intestines of animals and humans Double zone hemolysis
C. perfringens: general Enteric Clostridia Formerly called C. welchii Thick rods, forming spores Non motile Grow fast Habitats: Soil and sewage and in the intestines of animals and humans Double zone hemolysis
The Ones We All Know About. Infectious Diseases of Ferrets. The Odd Ones. Ferret Acute Hemorrhagic Syndrome IFC Symposium, Pittsburgh, PA
 The Ones We All Know About Infectious Diseases of Ferrets Karen Purcell DVM Canine Distemper (Morbillivirus) Aleutian Disease (Parvovirus) Rabies (Rhabdovirus) ECE (Coronavirus) Ringworm (Trichophyton
The Ones We All Know About Infectious Diseases of Ferrets Karen Purcell DVM Canine Distemper (Morbillivirus) Aleutian Disease (Parvovirus) Rabies (Rhabdovirus) ECE (Coronavirus) Ringworm (Trichophyton
COMMON CLINICAL CONDITIONS IN RATS AND MICE
 COMMON CLINICAL CONDITIONS IN RATS AND MICE Megan H. Nowland, DVM, Diplomate ACLAM Assistant Professor Unit for Laboratory Animal Medicine University of Michigan NCRC Building 10, Suite G90 2800 Plymouth
COMMON CLINICAL CONDITIONS IN RATS AND MICE Megan H. Nowland, DVM, Diplomate ACLAM Assistant Professor Unit for Laboratory Animal Medicine University of Michigan NCRC Building 10, Suite G90 2800 Plymouth
Enteric Clostridia. C. perfringens: general
 Enteric Clostridia C. perfringens: general Formerly called C. welchii Thick rods, forming spores Non motile Grow fast Habitats: Soil and sewage and in the intestines of animals and humans Toxins More than
Enteric Clostridia C. perfringens: general Formerly called C. welchii Thick rods, forming spores Non motile Grow fast Habitats: Soil and sewage and in the intestines of animals and humans Toxins More than
2007 BICHON FRISE BREEDERS HEALTH SURVEY Part 4: Prevalence of Health Conditions
 2007 BICHON FRISE BREEDERS HEALTH SURVEY Part 4: Prevalence of Health Conditions 25 Surveys reported the number of Bichons having no health problems Males 204 Females 221 11 surveys did not answer Temperament
2007 BICHON FRISE BREEDERS HEALTH SURVEY Part 4: Prevalence of Health Conditions 25 Surveys reported the number of Bichons having no health problems Males 204 Females 221 11 surveys did not answer Temperament
COMMON CLINICAL CONDITIONS IN RABBITS AND GUINEA PIGS
 COMMON CLINICAL CONDITIONS IN RABBITS AND GUINEA PIGS Megan H. Nowland, DVM, Diplomate ACLAM Assistant Professor Unit for Laboratory Animal Medicine University of Michigan NCRC Building 10, Suite G90 2800
COMMON CLINICAL CONDITIONS IN RABBITS AND GUINEA PIGS Megan H. Nowland, DVM, Diplomate ACLAM Assistant Professor Unit for Laboratory Animal Medicine University of Michigan NCRC Building 10, Suite G90 2800
DIVISION 056 IMPORTATION, POSSESSION, CONFINEMENT, TRANSPORTATION AND SALE OF NONNATIVE WILDLIFE
 DIVISION 056 IMPORTATION, POSSESSION, CONFINEMENT, TRANSPORTATION AND SALE OF NONNATIVE WILDLIFE 635 056 0010 Definitions For the purposes of these rules, the definitions in ORS 496.004 and OAR 635 045
DIVISION 056 IMPORTATION, POSSESSION, CONFINEMENT, TRANSPORTATION AND SALE OF NONNATIVE WILDLIFE 635 056 0010 Definitions For the purposes of these rules, the definitions in ORS 496.004 and OAR 635 045
TABLE 1: NUMBER OF ANIMALS USED IN RELATION TO THEIR PLACE OF ORIGIN
 XI/810/04rev3 TABLE 1: NUMBER OF ANIMALS USED IN RELATION TO THEIR PLACE OF ORIGIN Origin versus species 1.1 1.a. Mice (Mus musculus) 1.b. Rats (Rattus norvegicus) 1.c. Guinea-Pigs (Cavia porcellus) 1.d.
XI/810/04rev3 TABLE 1: NUMBER OF ANIMALS USED IN RELATION TO THEIR PLACE OF ORIGIN Origin versus species 1.1 1.a. Mice (Mus musculus) 1.b. Rats (Rattus norvegicus) 1.c. Guinea-Pigs (Cavia porcellus) 1.d.
Vaccines for Cats. 2. Feline viral rhinotracheitis, FVR caused by FVR virus, also known as herpes virus type 1, FHV-1
 Vaccines for Cats Recent advances in veterinary medical science have resulted in an increase in the number and type of vaccines that are available for use in cats, and improvements are continuously being
Vaccines for Cats Recent advances in veterinary medical science have resulted in an increase in the number and type of vaccines that are available for use in cats, and improvements are continuously being
04/02/2013. Parasites and breeding dogs: These parasites we don t hear so much about. Main internal parasites found in breeding kennels
 Parasites and breeding dogs: These parasites we don t hear so much about Main internal parasites found in breeding kennels Isospora sp. Giardia sp. Toxocara canis Something else? Breeders burden I m kind
Parasites and breeding dogs: These parasites we don t hear so much about Main internal parasites found in breeding kennels Isospora sp. Giardia sp. Toxocara canis Something else? Breeders burden I m kind
How to stop the snotty noses: Preventing feline upper respiratory infections. Staci Cannon, DVM, MPH, DACVPM, DABVP (Shelter Medicine Practice)
 How to stop the snotty noses: Preventing feline upper respiratory infections Staci Cannon, DVM, MPH, DACVPM, DABVP (Shelter Medicine Practice) Why is URI so hard to control? Multiple pathogens Chronic
How to stop the snotty noses: Preventing feline upper respiratory infections Staci Cannon, DVM, MPH, DACVPM, DABVP (Shelter Medicine Practice) Why is URI so hard to control? Multiple pathogens Chronic
LIFELONG CARE PLAN FELINE
 LIFELONG CARE PLAN FELINE Your pet is unique, and our veterinarian s treatment plan will be tailored to their specific needs. As your pet grows, however, there are certain health concerns associated with
LIFELONG CARE PLAN FELINE Your pet is unique, and our veterinarian s treatment plan will be tailored to their specific needs. As your pet grows, however, there are certain health concerns associated with
Ferret. Caring for your Pet Ferret. Basic Husbandry General Information
 Caring for your Pet Basic Husbandry General Information Vital Statistics Body Weight: Male 1000g 2000g; Female 500 1000g Life Span: 5 8 years Sexual Maturity: 4 8 months Behavior and Handling s have a
Caring for your Pet Basic Husbandry General Information Vital Statistics Body Weight: Male 1000g 2000g; Female 500 1000g Life Span: 5 8 years Sexual Maturity: 4 8 months Behavior and Handling s have a
Feline Vaccines: Benefits and Risks
 Feline Vaccines: Benefits and Risks Deciding which vaccines your cat should receive requires that you have a complete understanding of the benefits and risks of the procedure. For this reason, it is extremely
Feline Vaccines: Benefits and Risks Deciding which vaccines your cat should receive requires that you have a complete understanding of the benefits and risks of the procedure. For this reason, it is extremely
VACCINATION GUIDELINES
 WHY VACCINATE? VACCINATION GUIDELINES Vaccines help prepare the body's immune system to fight the invasion of disease-causing organisms. Vaccines contain antigens, which look like the disease-causing organism
WHY VACCINATE? VACCINATION GUIDELINES Vaccines help prepare the body's immune system to fight the invasion of disease-causing organisms. Vaccines contain antigens, which look like the disease-causing organism
Dondrae Coble, DVM, DACLAM January 8, 2014
 ALAT Chapter 32 Less Common Species Used in Research Dondrae Coble, DVM, DACLAM January 8, 2014 Outline Ferrets Horses Reptiles Other species Ferrets Research Uses Animal models Viral and respiratory diseases
ALAT Chapter 32 Less Common Species Used in Research Dondrae Coble, DVM, DACLAM January 8, 2014 Outline Ferrets Horses Reptiles Other species Ferrets Research Uses Animal models Viral and respiratory diseases
HEMATOPOETIC LAB. Heather Fenton/S. Martinson VPM 222 March, 2013
 HEMATOPOETIC LAB Heather Fenton/S. Martinson VPM 222 March, 2013 Diffuse Splenomegaly: Bloody vs Meaty Photos: Pathologic basis of veterinary disease Bloody Spleen: Swollen margins Dark red Oozes blood
HEMATOPOETIC LAB Heather Fenton/S. Martinson VPM 222 March, 2013 Diffuse Splenomegaly: Bloody vs Meaty Photos: Pathologic basis of veterinary disease Bloody Spleen: Swollen margins Dark red Oozes blood
There is no one correct way to describe a slide. Macroscopic Veterinary Pathology. Be concise. Look at the center of the slide.
 Macroscopic Veterinary Pathology There is no one correct way to describe a slide. Bruce Williams, DVM, DACVP Senior Pathologist, JPC Email: williams@cldavis.org Tissue from a sheep Tissue from a foal Be
Macroscopic Veterinary Pathology There is no one correct way to describe a slide. Bruce Williams, DVM, DACVP Senior Pathologist, JPC Email: williams@cldavis.org Tissue from a sheep Tissue from a foal Be
Update in Veterinary Medicine. Dr. Maria M. Crane Zoo Atlanta
 Update in Veterinary Medicine Dr. Maria M. Crane Zoo Atlanta Overview of Discussion Medical management of captive orangutans Preventative Medicine Anesthesia Protocols Vaccinations TB testing Current Health
Update in Veterinary Medicine Dr. Maria M. Crane Zoo Atlanta Overview of Discussion Medical management of captive orangutans Preventative Medicine Anesthesia Protocols Vaccinations TB testing Current Health
Hurricane Animal Hospital 2120 Mount Vernon Road Hurricane, WV or
 Hurricane Animal Hospital 2120 Mount Vernon Road Hurricane, WV 25526 304-757-5937 or 304-757-2287 www.hurricaneanimalhospital.com Feline Leukemia Virus (FELV) This information handout is designed as a
Hurricane Animal Hospital 2120 Mount Vernon Road Hurricane, WV 25526 304-757-5937 or 304-757-2287 www.hurricaneanimalhospital.com Feline Leukemia Virus (FELV) This information handout is designed as a
Panleuk Basics Understanding, preventing, and managing feline parvovirus infections in animal shelters
 Panleuk Basics Understanding, preventing, and managing feline parvovirus infections in animal shelters Your Presenter Stephanie Janeczko, DVM, MS, DABVP, CAWA Senior Director of Shelter Medical Programs
Panleuk Basics Understanding, preventing, and managing feline parvovirus infections in animal shelters Your Presenter Stephanie Janeczko, DVM, MS, DABVP, CAWA Senior Director of Shelter Medical Programs
KITTEN & ADULT HEALTH PROGRAM AND VACCINATION SCHEDULE
 OTTERKILL ANIMAL HOSPITAL 258 Maybrook Rd. Campbell Hall, NY 10916 Phone: (845)427-2854 Fax: (845)427-2344 www.otterkill.com KITTEN & ADULT HEALTH PROGRAM AND VACCINATION SCHEDULE Congratulations on the
OTTERKILL ANIMAL HOSPITAL 258 Maybrook Rd. Campbell Hall, NY 10916 Phone: (845)427-2854 Fax: (845)427-2344 www.otterkill.com KITTEN & ADULT HEALTH PROGRAM AND VACCINATION SCHEDULE Congratulations on the
PDP can be completed in the context of small animal, equine or farm animal practice, or any combination of these three.
 Clinical procedures checklists DRAFT REVISIONS PDP can be completed in the context of small animal, equine or farm animal practice, or any combination of these three. RCVS YEAR ONE CLINICAL PROCEDURES
Clinical procedures checklists DRAFT REVISIONS PDP can be completed in the context of small animal, equine or farm animal practice, or any combination of these three. RCVS YEAR ONE CLINICAL PROCEDURES
An Introduction To A Few Of The Most Common Diseases Found In Mammals
 An Introduction To A Few Of The Most Common Diseases Found In Mammals Introduction A disease can be considered something that causes a disturbance to the normal function or structure of an animal. Most
An Introduction To A Few Of The Most Common Diseases Found In Mammals Introduction A disease can be considered something that causes a disturbance to the normal function or structure of an animal. Most
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 14. Gram negative coccobacilli. Zoonosis. Brucella. Yersinia. Francesiella
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 14 Gram negative coccobacilli Zoonosis Brucella Yersinia Francesiella 1 Zoonosis: A disease, primarily of animals, which is transmitted to humans as a result of direct or
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 14 Gram negative coccobacilli Zoonosis Brucella Yersinia Francesiella 1 Zoonosis: A disease, primarily of animals, which is transmitted to humans as a result of direct or
FELINE CORONAVIRUS INFECTIONS. Dr. John R. August Texas A&M University
 FELINE CORONAVIRUS INFECTIONS Dr. John R. August Texas A&M University IX Curso Internacional de Medicina en Pequeños Animales Viña del Mar, 25 al 27 de Agosto, 2006 I. LEARNING OBJECTIVES A. Describe the
FELINE CORONAVIRUS INFECTIONS Dr. John R. August Texas A&M University IX Curso Internacional de Medicina en Pequeños Animales Viña del Mar, 25 al 27 de Agosto, 2006 I. LEARNING OBJECTIVES A. Describe the
Diagnosing intestinal parasites. Clinical reference guide for Fecal Dx antigen testing
 Diagnosing intestinal parasites Clinical reference guide for Fecal Dx antigen testing Screen every dog at least twice a year The Companion Animal Parasite Council (CAPC) guidelines recommend including
Diagnosing intestinal parasites Clinical reference guide for Fecal Dx antigen testing Screen every dog at least twice a year The Companion Animal Parasite Council (CAPC) guidelines recommend including
Above: life cycle of toxoplasma gondii. Below: transmission of this infection.
 Toxoplasmosis PDF This article is based on a paid for research paper dated 1972 of similar title and authored by J.K.Frenkel and J.P. Dubey. It was published by The Journal of Infectious Diseases Vol.
Toxoplasmosis PDF This article is based on a paid for research paper dated 1972 of similar title and authored by J.K.Frenkel and J.P. Dubey. It was published by The Journal of Infectious Diseases Vol.
Diagnosing intestinal parasites. Clinical reference guide for Fecal Dx antigen testing
 Diagnosing intestinal parasites Clinical reference guide for Fecal Dx antigen testing Screen every dog at least twice a year The Companion Animal Parasite Council (CAPC) guidelines recommend including
Diagnosing intestinal parasites Clinical reference guide for Fecal Dx antigen testing Screen every dog at least twice a year The Companion Animal Parasite Council (CAPC) guidelines recommend including
Systemic Apicomplexans. Toxoplasma
 Systemic Apicomplexans Toxoplasma Protozoan Groups Historically, protozoa have been grouped by mode of motility. Flagellates Hemoflagellates Trypanosoma cruzi Leishmania infantum Mucoflagellates Tritrichomonas
Systemic Apicomplexans Toxoplasma Protozoan Groups Historically, protozoa have been grouped by mode of motility. Flagellates Hemoflagellates Trypanosoma cruzi Leishmania infantum Mucoflagellates Tritrichomonas
Hair and Skin. Signs. Mass, swelling, tumor: size, ulceration, mobility
 PATHOLOGY Hair and Skin Signs Rough hair coat (unkempt, unthrifty, ungroomed) Alopecia (hair loss) Erythema (redness) Edema (swelling) Prutitis: Itching/scratching (scaling or flaking) Lesions: size and
PATHOLOGY Hair and Skin Signs Rough hair coat (unkempt, unthrifty, ungroomed) Alopecia (hair loss) Erythema (redness) Edema (swelling) Prutitis: Itching/scratching (scaling or flaking) Lesions: size and
What s Your Diagnosis?
 What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Maine Coone (8 month old, female intact) Presenting complaint: Lethargy, inappetence, serosanguinous vaginal discharge History: Lives with 11 other Maine Coone cats (males
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Maine Coone (8 month old, female intact) Presenting complaint: Lethargy, inappetence, serosanguinous vaginal discharge History: Lives with 11 other Maine Coone cats (males
Biology of rodents and lagomorphs Joanna Godawa Stormark. Taxonomy of rodents. Order: Rodentia (rodents) Class : Mammalia (mammals)
 Biology of rodents and lagomorphs Joanna Godawa Stormark Taxonomy of rodents Class : Mammalia (mammals) Order: Rodentia (rodents) Family: Muride (rats and mice) Sub-family: Murinae Genus: Mus Species:
Biology of rodents and lagomorphs Joanna Godawa Stormark Taxonomy of rodents Class : Mammalia (mammals) Order: Rodentia (rodents) Family: Muride (rats and mice) Sub-family: Murinae Genus: Mus Species:
Acute Vomiting & Diarrhea Overview & Presentation
 STEP 1: Comprehensive Overview Acute Vomiting & Diarrhea Overview & Presentation Craig Datz, DVM, MS, DABVP (Canine & Feline), DACVN University of Missouri Vomiting and diarrhea may indicate a primary
STEP 1: Comprehensive Overview Acute Vomiting & Diarrhea Overview & Presentation Craig Datz, DVM, MS, DABVP (Canine & Feline), DACVN University of Missouri Vomiting and diarrhea may indicate a primary
HEARTWORM DISEASE AND THE DAMAGE DONE
 HEARTWORM DISEASE AND THE DAMAGE DONE Stephen Jones, DVM There are now more months of the year where environmental conditions favor mosquito survival and reproduction. Warmer temperatures Indoor environments
HEARTWORM DISEASE AND THE DAMAGE DONE Stephen Jones, DVM There are now more months of the year where environmental conditions favor mosquito survival and reproduction. Warmer temperatures Indoor environments
Canine Distemper Virus
 Canine Distemper Virus Sandra Newbury, DVM National Shelter Medicine Extension Veterinarian Koret Shelter Medicine Program Center for Companion Animal Health U C Davis School of Veterinary Medicine www.sheltermedicine.com
Canine Distemper Virus Sandra Newbury, DVM National Shelter Medicine Extension Veterinarian Koret Shelter Medicine Program Center for Companion Animal Health U C Davis School of Veterinary Medicine www.sheltermedicine.com
Feline zoonoses. Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee 12/09
 Feline zoonoses Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee 12/09 Cat scratch disease Bacterial infection caused by Bartonella henselae Associated with a cat bite or scratch Infection at point of injury,
Feline zoonoses Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee 12/09 Cat scratch disease Bacterial infection caused by Bartonella henselae Associated with a cat bite or scratch Infection at point of injury,
Update on diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis (FIP)
 Update on diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) Séverine Tasker RCVS Specialist in Feline Medicine The Feline Centre Langford Veterinary Services University of Bristol http://www.felinecentre.co.uk/
Update on diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) Séverine Tasker RCVS Specialist in Feline Medicine The Feline Centre Langford Veterinary Services University of Bristol http://www.felinecentre.co.uk/
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Membership Examination. Small Animal Medicine Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2015 Small Animal Medicine Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal Answer
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2015 Small Animal Medicine Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal Answer
Acute Hemorrhagic Diarrhea Syndrome (AHDS) A Cause of Bloody Feces in Dogs
 Acute Hemorrhagic Diarrhea Syndrome (AHDS) A Cause of Bloody Feces in Dogs No dog parent wants to clean up diarrhea. Cleaning up bloody diarrhea is even more unpleasant. Unfortunately, the development
Acute Hemorrhagic Diarrhea Syndrome (AHDS) A Cause of Bloody Feces in Dogs No dog parent wants to clean up diarrhea. Cleaning up bloody diarrhea is even more unpleasant. Unfortunately, the development
Heartworm Disease in Dogs
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Heartworm Disease in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW Disease caused by infestation with heartworms
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Heartworm Disease in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW Disease caused by infestation with heartworms
Welcome to Pathogen Group 9
 Welcome to Pathogen Group 9 Yersinia pestis Francisella tularensis Borrelia burgdorferi Rickettsia rickettsii Rickettsia prowazekii Acinetobacter baumannii Yersinia pestis: Plague gram negative oval bacillus,
Welcome to Pathogen Group 9 Yersinia pestis Francisella tularensis Borrelia burgdorferi Rickettsia rickettsii Rickettsia prowazekii Acinetobacter baumannii Yersinia pestis: Plague gram negative oval bacillus,
What s Your Diagnosis? By Sohaila Jafarian, Class of 2018
 Signalment: Greeley, 3 yo MC DSH Presenting Complaint: ADR History: What s Your Diagnosis? By Sohaila Jafarian, Class of 2018 Patient is an indoor/outdoor cat. Previously healthy and up to date on vaccines
Signalment: Greeley, 3 yo MC DSH Presenting Complaint: ADR History: What s Your Diagnosis? By Sohaila Jafarian, Class of 2018 Patient is an indoor/outdoor cat. Previously healthy and up to date on vaccines
Understanding your pet s LIVER CONDITION
 Understanding your pet s LIVER CONDITION Why is the liver so important? What causes liver disease in dogs and cats? The liver is one of the largest organs in your pet s body, and it s vital for their good
Understanding your pet s LIVER CONDITION Why is the liver so important? What causes liver disease in dogs and cats? The liver is one of the largest organs in your pet s body, and it s vital for their good
Hamilton County General Health District Rabies Prevention Regulation
 Hamilton County General Health District Rabies Prevention Regulation 5 2014 HAMILTON COUNTY GENERAL HEALTH DISTRICT 250 William Howard Taft Road, 2 nd Floor Cincinnati, Ohio 45219 Effective June 1, 2014.
Hamilton County General Health District Rabies Prevention Regulation 5 2014 HAMILTON COUNTY GENERAL HEALTH DISTRICT 250 William Howard Taft Road, 2 nd Floor Cincinnati, Ohio 45219 Effective June 1, 2014.
Congratulations. on your new Puppy/Dog!
 Congratulations on your new Puppy/Dog! This handout is being provided to help you better understand the medical needs of your new pet. Hearing all this information at one time can be overwhelming. This
Congratulations on your new Puppy/Dog! This handout is being provided to help you better understand the medical needs of your new pet. Hearing all this information at one time can be overwhelming. This
Asilomar Definitions and Classification Guidelines
 Asilomar Definitions and Classification Guidelines STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE #E103.2 Written: July 2, 2008 Updated: February 12, 2009 By Emilia Gordon, DVM, Medical Director APPROVED: Emilia Gordon,
Asilomar Definitions and Classification Guidelines STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE #E103.2 Written: July 2, 2008 Updated: February 12, 2009 By Emilia Gordon, DVM, Medical Director APPROVED: Emilia Gordon,
Tick-borne Disease Testing in Shelters What Does that Blue Dot Really Mean?
 Tick-borne Disease Testing in Shelters What Does that Blue Dot Really Mean? 2017 ASPCA. All Rights Reserved. Your Presenter Stephanie Janeczko, DVM, MS, DABVP, CAWA Senior Director of Shelter Medical Programs
Tick-borne Disease Testing in Shelters What Does that Blue Dot Really Mean? 2017 ASPCA. All Rights Reserved. Your Presenter Stephanie Janeczko, DVM, MS, DABVP, CAWA Senior Director of Shelter Medical Programs
REGULATIONS OF THE BOARD OF HEALTH OF THE CLERMONT COUNTY GENERAL HEALTH DISTRICT. Rabies Prevention Regulation 425
 REGULATIONS OF THE BOARD OF HEALTH OF THE CLERMONT COUNTY GENERAL HEALTH DISTRICT Rabies Prevention Regulation 425 Effective April 1, 2018 Section I Definitions 1.1 Board of Health means the Board of Health
REGULATIONS OF THE BOARD OF HEALTH OF THE CLERMONT COUNTY GENERAL HEALTH DISTRICT Rabies Prevention Regulation 425 Effective April 1, 2018 Section I Definitions 1.1 Board of Health means the Board of Health
Care and Handling of Pets
 Communicable Disease Outreach Program 3020 Rucker Avenue, Suite 300 Everett, WA 98201-3900 425.339.5278 Care and Handling of Pets Name of facility: WIWS Pet restrictions 1. Pets will be inaccessible to
Communicable Disease Outreach Program 3020 Rucker Avenue, Suite 300 Everett, WA 98201-3900 425.339.5278 Care and Handling of Pets Name of facility: WIWS Pet restrictions 1. Pets will be inaccessible to
Care of Rats and Mice
 Care of Rats and Mice Ness Exotic Wellness Center 1007 Maple Avenue Lisle, IL 60532 People envision many different things when thinking about rats and mice. Some consider them as vermin or pests, many
Care of Rats and Mice Ness Exotic Wellness Center 1007 Maple Avenue Lisle, IL 60532 People envision many different things when thinking about rats and mice. Some consider them as vermin or pests, many
Taking the Teeth Out of Canine Distemper Virus July 21, 2016
 Taking the Teeth Out of Canine Distemper Virus Sandra Newbury, DVM Director University of Wisconsin-Madison Shelter Medicine Program UW School of Veterinary Medicine www.uwsheltermedicine.com Many thanks
Taking the Teeth Out of Canine Distemper Virus Sandra Newbury, DVM Director University of Wisconsin-Madison Shelter Medicine Program UW School of Veterinary Medicine www.uwsheltermedicine.com Many thanks
Feline Infectious Peritonitis: What Do We Know About This Disease?
 Feline Infectious Peritonitis: What Do We Know About This Disease? John R. August, BVetMed, MS, MRCVS, Dip ACVIM Dean of Faculties and Associate Provost Texas A&M University I. LEARNING OBJECTIVES A. Describe
Feline Infectious Peritonitis: What Do We Know About This Disease? John R. August, BVetMed, MS, MRCVS, Dip ACVIM Dean of Faculties and Associate Provost Texas A&M University I. LEARNING OBJECTIVES A. Describe
Adrenal Cortical Carcinomas with Myxoid Differentiation in Ferrets
 Adrenal Cortical Carcinomas with Myxoid Differentiation in Ferrets M. Kiupel,, R.A. Peterson II, C.C. Capen,, D.B. Wilson 4125 Beaumont Road Lansing, MI 48910 www.animalhealth.msu.edu Signalment 5-year-old
Adrenal Cortical Carcinomas with Myxoid Differentiation in Ferrets M. Kiupel,, R.A. Peterson II, C.C. Capen,, D.B. Wilson 4125 Beaumont Road Lansing, MI 48910 www.animalhealth.msu.edu Signalment 5-year-old
Beef... Beef Natural Contamination... Beef liver...
 Human... Human Natural Contamination... Human amniotic fluid... Human bile... Human blood... Human brain... Human breast... Human breast milk... Human cervix... Human colon... Human endometrium... Human
Human... Human Natural Contamination... Human amniotic fluid... Human bile... Human blood... Human brain... Human breast... Human breast milk... Human cervix... Human colon... Human endometrium... Human
Common Diseases of Small Animals
 Directions: Fill in the blanks. Introduction to Disease Segment 1. Disease Is a disorder or incorrect function of an organ, structure or system of an animal s body 2. Disease Is transmitted from infected
Directions: Fill in the blanks. Introduction to Disease Segment 1. Disease Is a disorder or incorrect function of an organ, structure or system of an animal s body 2. Disease Is transmitted from infected
Protozoan Parasites: Lecture 20 - Heteroxenous Coccidia - Part 1 Pages 39-51
 Protozoan Parasites: Lecture 20 - Heteroxenous Coccidia - Part 1 Pages 39-51 Tissue cyst -forming Coccidia General Taxonomy Apicomplexa Heteroxenous Two host life cycles Asexual & sexual reproduction Intestinal
Protozoan Parasites: Lecture 20 - Heteroxenous Coccidia - Part 1 Pages 39-51 Tissue cyst -forming Coccidia General Taxonomy Apicomplexa Heteroxenous Two host life cycles Asexual & sexual reproduction Intestinal
Lactation. Macroscopic Anatomy of the Mammary Gland. Anatomy AS 1124
 Lactation AS 1124 Macroscopic Anatomy of the Mammary Gland Species differences in numbers and locations of glands inguinal - caudal to the abdomen, between the hind legs (cow, mare, ewe) abdominal - along
Lactation AS 1124 Macroscopic Anatomy of the Mammary Gland Species differences in numbers and locations of glands inguinal - caudal to the abdomen, between the hind legs (cow, mare, ewe) abdominal - along
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Membership Examination. Medicine and Surgery of Unusual Pets Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2017 Medicine and Surgery of Unusual Pets Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2017 Medicine and Surgery of Unusual Pets Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours
Health Management. Pathology
 Health Management Pathology HEALTH MANAGEMENT Daily observation Food and water level Cage and room condition Animal condition BARH: Bright, alert, responsive, and hydrated QARD: Quiet, alert, responsive,
Health Management Pathology HEALTH MANAGEMENT Daily observation Food and water level Cage and room condition Animal condition BARH: Bright, alert, responsive, and hydrated QARD: Quiet, alert, responsive,
Having Puppies. Pregnancy Pregnancy normally lasts 9 weeks (63 days) but puppies may be delivered between 58 and 68 days.
 24- hour Emergency Service 01635 47170 Having Puppies Although a bitch is capable of having puppies at their first season (which will on average occur at about 9 months of age but may vary from 5 to 18
24- hour Emergency Service 01635 47170 Having Puppies Although a bitch is capable of having puppies at their first season (which will on average occur at about 9 months of age but may vary from 5 to 18
What you need to know to successfully live with your new Kitten-Cat
 What you need to know to successfully live with your new Kitten-Cat Basic information for owners A Publication of Sykesville Veterinary Clinic Table of Contents KITTEN PACKAGES BRONZE SILVER GOLD VACCINATIONS
What you need to know to successfully live with your new Kitten-Cat Basic information for owners A Publication of Sykesville Veterinary Clinic Table of Contents KITTEN PACKAGES BRONZE SILVER GOLD VACCINATIONS
ECHINOCOCCOSIS. By Dr. Ameer kadhim Hussein. M.B.Ch.B. FICMS (Community Medicine).
 ECHINOCOCCOSIS By Dr. Ameer kadhim Hussein. M.B.Ch.B. FICMS (Community Medicine). INTRODUCTION Species under genus Echinococcus are small tapeworms of carnivores with larval stages known as hydatids proliferating
ECHINOCOCCOSIS By Dr. Ameer kadhim Hussein. M.B.Ch.B. FICMS (Community Medicine). INTRODUCTION Species under genus Echinococcus are small tapeworms of carnivores with larval stages known as hydatids proliferating
Parvovirus Type 2c An Emerging Pathogen in Dogs. Sanjay Kapil, DVM, MS, PhD Professor Center for Veterinary Health Sciences OADDL Stillwater, OK
 Parvovirus Type 2c An Emerging Pathogen in Dogs Sanjay Kapil, DVM, MS, PhD Professor Center for Veterinary Health Sciences OADDL Stillwater, OK Properties of Canine Parvovirus Single-stranded DNA virus
Parvovirus Type 2c An Emerging Pathogen in Dogs Sanjay Kapil, DVM, MS, PhD Professor Center for Veterinary Health Sciences OADDL Stillwater, OK Properties of Canine Parvovirus Single-stranded DNA virus
DP.1. Control tables
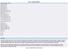 Data inclusion criteria Report year: 2015 Country: Croatia EU Submission: ALL Genetic status: ALL Animal Species: ALL Species grouping Level 1: ALL Species grouping Level 2: ALL Mammals: ALL Non-human
Data inclusion criteria Report year: 2015 Country: Croatia EU Submission: ALL Genetic status: ALL Animal Species: ALL Species grouping Level 1: ALL Species grouping Level 2: ALL Mammals: ALL Non-human
DP.1. Control tables
 Data inclusion criteria Report year: 2014 Country: Croatia EU Submission: ALL Genetic status: ALL Animal Species: ALL Species grouping Level 1: ALL Species grouping Level 2: ALL Mammals: ALL Non-human
Data inclusion criteria Report year: 2014 Country: Croatia EU Submission: ALL Genetic status: ALL Animal Species: ALL Species grouping Level 1: ALL Species grouping Level 2: ALL Mammals: ALL Non-human
European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals used for Experimental and Other Scientific Purposes *
 European Treaty Series - No. 123 European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals used for Experimental and Other Scientific Purposes * Strasbourg, 18.III.1986 Appendix B Statistical tables
European Treaty Series - No. 123 European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals used for Experimental and Other Scientific Purposes * Strasbourg, 18.III.1986 Appendix B Statistical tables
New Jersey Department of Health Rabies Background and Technical Information
 New Jersey Department of Health Rabies Background and Technical Information The History of Rabies Rabies is an ancient disease. It is well described in writings by Egyptians dating back to 2300 B.C. Rabies
New Jersey Department of Health Rabies Background and Technical Information The History of Rabies Rabies is an ancient disease. It is well described in writings by Egyptians dating back to 2300 B.C. Rabies
RARC: Animal Social Housing & Enrichment Requirements (ASHER)
 1) Social Housing a) Definitions: Single is defined as 1 animal in 1 primary enclosure; pair is 2 animals in 1 primary enclosure, and social is 3 or more animals in 1 primary enclosure. i) There are 2
1) Social Housing a) Definitions: Single is defined as 1 animal in 1 primary enclosure; pair is 2 animals in 1 primary enclosure, and social is 3 or more animals in 1 primary enclosure. i) There are 2
Bright Eyes & Bushy Tails
 Bright Eyes & Bushy Tails Housecall and Full-Service Veterinary Clinic 3005 Highway 1 NE Iowa City, IA 52240 (319) 351-4256 June 1, 2001 Newsletter Jennifer Berger, DVM Allan Berger DVM, PhD Dear friends
Bright Eyes & Bushy Tails Housecall and Full-Service Veterinary Clinic 3005 Highway 1 NE Iowa City, IA 52240 (319) 351-4256 June 1, 2001 Newsletter Jennifer Berger, DVM Allan Berger DVM, PhD Dear friends
Biology and Control of Insects and Rodents Workshop Vector Borne Diseases of Public Health Importance
 Vector-Borne Diseases of Public Health Importance Rudy Bueno, Jr., Ph.D. Director Components in the Disease Transmission Cycle Pathogen Agent that is responsible for disease Vector An arthropod that transmits
Vector-Borne Diseases of Public Health Importance Rudy Bueno, Jr., Ph.D. Director Components in the Disease Transmission Cycle Pathogen Agent that is responsible for disease Vector An arthropod that transmits
Feline Immunodefficiency Virus
 Feline Immunodefficiency Virus by Skye Patterson - Revised 1-Jun-15 Cats who are infected with feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) may not show symptoms until years after the initial infection occurred.
Feline Immunodefficiency Virus by Skye Patterson - Revised 1-Jun-15 Cats who are infected with feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) may not show symptoms until years after the initial infection occurred.
Bovine Viral Diarrhea (BVD)
 Bovine Viral Diarrhea (BVD) Why should you test your herd, or additions to your herd? Answer: BVD has been shown to cause lower pregnancy rates, increased abortions, higher calf morbidity and mortality;
Bovine Viral Diarrhea (BVD) Why should you test your herd, or additions to your herd? Answer: BVD has been shown to cause lower pregnancy rates, increased abortions, higher calf morbidity and mortality;
Washington State University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee
 1 Standard Operating Procedure #9 Title: Minor Medical Treatment of Rodents Washington State University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee Purpose: Currently, the Office of the Campus Veterinarian
1 Standard Operating Procedure #9 Title: Minor Medical Treatment of Rodents Washington State University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee Purpose: Currently, the Office of the Campus Veterinarian
Push flea protection forward
 Push flea protection forward Advantage Multi (imidacloprid + moxidectin) pushes protection forward The imidacloprid in prescription-only Advantage Multi starts working through contact fleas don t have
Push flea protection forward Advantage Multi (imidacloprid + moxidectin) pushes protection forward The imidacloprid in prescription-only Advantage Multi starts working through contact fleas don t have
Zoonotic Diseases. Risks of working with wildlife. Maria Baron Palamar, Wildlife Veterinarian
 Zoonotic Diseases Risks of working with wildlife www.cdc.gov Definition Zoonoses: infectious diseases of vertebrate animals that can be naturally transmitted to humans Health vs. Disease Transmission -
Zoonotic Diseases Risks of working with wildlife www.cdc.gov Definition Zoonoses: infectious diseases of vertebrate animals that can be naturally transmitted to humans Health vs. Disease Transmission -
FELINE INFECTIOUS PERITONITIS Visions Beyond the Tip of the Iceberg!
 FELINE INFECTIOUS PERITONITIS Visions Beyond the Tip of the Iceberg! Richard B. Ford, DVM, MS, Dipl. ACVIM Professor of Medicine North Carolina State University Richard_Ford@ncsu.edu As long as we've known
FELINE INFECTIOUS PERITONITIS Visions Beyond the Tip of the Iceberg! Richard B. Ford, DVM, MS, Dipl. ACVIM Professor of Medicine North Carolina State University Richard_Ford@ncsu.edu As long as we've known
Equine Diseases. Dr. Kashif Ishaq. Disease Management
 Equine Diseases Dr. Kashif Ishaq Disease Management Prevention is the singularly most important aspect Vaccinate regularly Keep horse areas cleaned up and sanitized Proper feeds and feeding management
Equine Diseases Dr. Kashif Ishaq Disease Management Prevention is the singularly most important aspect Vaccinate regularly Keep horse areas cleaned up and sanitized Proper feeds and feeding management
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV)
 Virus (FeLV) FIV and FeLV are both viruses within the same family of retroviruses, but they are in different groups within that family: FIV is in one group called lentiviruses these cause lifelong infections
Virus (FeLV) FIV and FeLV are both viruses within the same family of retroviruses, but they are in different groups within that family: FIV is in one group called lentiviruses these cause lifelong infections
On necropsy: petechial hemorrhages throughout small intestines 4+ Clostridium perfringes cultured from manure
 History: >2 lactation Jersey cow, 3 days fresh Late evening: blood in manure, slight diarrhea, normal TPR Next morning: found dead On necropsy: petechial hemorrhages throughout small intestines 4+ Clostridium
History: >2 lactation Jersey cow, 3 days fresh Late evening: blood in manure, slight diarrhea, normal TPR Next morning: found dead On necropsy: petechial hemorrhages throughout small intestines 4+ Clostridium
UPDATES IN DEMODICOSIS. Dr. Amelia G. White, DVM, MS, DACVD (Dermatology)
 UPDATES IN DEMODICOSIS Dr. Amelia G. White, DVM, MS, DACVD (Dermatology) Case 1 Gizmo 12 yo MC Beagle Case 1 Gizmo 12 yo MC Beagle Case 1 Gizmo 12 yo MC Beagle Case 1 Gizmo 12 yo MC Beagle Case 1 Gizmo
UPDATES IN DEMODICOSIS Dr. Amelia G. White, DVM, MS, DACVD (Dermatology) Case 1 Gizmo 12 yo MC Beagle Case 1 Gizmo 12 yo MC Beagle Case 1 Gizmo 12 yo MC Beagle Case 1 Gizmo 12 yo MC Beagle Case 1 Gizmo
My cat has kidney problems and food hypersensitivity what do I do now?
 TROVET Renal (Venison), complete, easily digestible, hypoallergenic dietary food for adult cats with an impaired kidney function My cat has kidney problems and food hypersensitivity what do I do now? reliable
TROVET Renal (Venison), complete, easily digestible, hypoallergenic dietary food for adult cats with an impaired kidney function My cat has kidney problems and food hypersensitivity what do I do now? reliable
Animals used under 7 (2) of the Animal Protection Act by species
 Animals used under 7 (2) of the Animal Protection Act by species 1. Animals used by species Table 1: In total animals used by species (excludes re-use) Animal Species Number of Animals % Mice 1.350.727
Animals used under 7 (2) of the Animal Protection Act by species 1. Animals used by species Table 1: In total animals used by species (excludes re-use) Animal Species Number of Animals % Mice 1.350.727
EU Statistical Data of all uses of animals
 Member State: Belgium Year: 2014 All uses of animals by species Animal Species Number of uses Percentage Mice 363,794 55.10% Rats 63,664 9.64% Guinea-Pigs 21,310 3.23% Hamsters (Syrian) 2,745 0.42% Hamsters
Member State: Belgium Year: 2014 All uses of animals by species Animal Species Number of uses Percentage Mice 363,794 55.10% Rats 63,664 9.64% Guinea-Pigs 21,310 3.23% Hamsters (Syrian) 2,745 0.42% Hamsters
EU Statistical Data of all uses of animals
 Member State: Slovakia Year: 2014 All uses of animals by species Animal Species Number of uses Percentage Mice 6,774 40.29% Rats 8,067 47.98% Guinea-Pigs 903 5.37% Hamsters (Syrian) Hamsters (Chinese)
Member State: Slovakia Year: 2014 All uses of animals by species Animal Species Number of uses Percentage Mice 6,774 40.29% Rats 8,067 47.98% Guinea-Pigs 903 5.37% Hamsters (Syrian) Hamsters (Chinese)
Rabies Postexposure Treatment Recommendations. Jennifer House, DVM, MPH, DACVPM Veterinary Epidemiologist
 Rabies Postexposure Treatment Recommendations Jennifer House, DVM, MPH, DACVPM Veterinary Epidemiologist Bite Treatment Clean wound Use a virucidal agent Evaluate the need for antibiotics 2 Incubation
Rabies Postexposure Treatment Recommendations Jennifer House, DVM, MPH, DACVPM Veterinary Epidemiologist Bite Treatment Clean wound Use a virucidal agent Evaluate the need for antibiotics 2 Incubation
General Health Care & Diseases
 General Health Care & Diseases 4-H Cats Unit 2: Chapter 6 I. Daily Health Check Health care for your cat begins with daily attention. Why daily grooming is important: Keeps coat shiny & tangle free Gets
General Health Care & Diseases 4-H Cats Unit 2: Chapter 6 I. Daily Health Check Health care for your cat begins with daily attention. Why daily grooming is important: Keeps coat shiny & tangle free Gets
Clinical Manifestations and Treatment of Plague Dr. Jacky Chan. Associate Consultant Infectious Disease Centre, PMH
 Clinical Manifestations and Treatment of Plague Dr. Jacky Chan Associate Consultant Infectious Disease Centre, PMH Update of plague outbreak situation in Madagascar A large outbreak since 1 Aug 2017 As
Clinical Manifestations and Treatment of Plague Dr. Jacky Chan Associate Consultant Infectious Disease Centre, PMH Update of plague outbreak situation in Madagascar A large outbreak since 1 Aug 2017 As
BOVINE RESPIRATORY DISEASE COMPLEX. Kristen Mierzwiak LCS 630
 BOVINE RESPIRATORY DISEASE COMPLEX Kristen Mierzwiak LCS 630 Ring... You are called out to the farm of one of your regular dairy clients because some of the replacement heifers they bought at a public
BOVINE RESPIRATORY DISEASE COMPLEX Kristen Mierzwiak LCS 630 Ring... You are called out to the farm of one of your regular dairy clients because some of the replacement heifers they bought at a public
Feline Idiopathic Cystitis (icatcare)
 Kingsbrook Animal Hospital 5322 New Design Road, Frederick, MD, 21703 Phone: (301) 631-6900 Website: KingsbrookVet.com Feline idiopathic cystitis (FIC) [1] Feline Idiopathic Cystitis (icatcare) Feline
Kingsbrook Animal Hospital 5322 New Design Road, Frederick, MD, 21703 Phone: (301) 631-6900 Website: KingsbrookVet.com Feline idiopathic cystitis (FIC) [1] Feline Idiopathic Cystitis (icatcare) Feline
Improved Cancer Surgery Imaging
 Feline Report 2017 ADVANCING HEALTH, SAVING LIVES Treatments for Upper Respiratory Disease Feline upper respiratory tract disease is expensive to treat and a leading cause of euthanasia in shelters. Two
Feline Report 2017 ADVANCING HEALTH, SAVING LIVES Treatments for Upper Respiratory Disease Feline upper respiratory tract disease is expensive to treat and a leading cause of euthanasia in shelters. Two
EYE CONDITIONS IN THE DOMESTIC FERRET
 EYE CONDITIONS IN THE DOMESTIC FERRET Several conditions can impact the eyes of domestic ferrets. The following conditions are the most common: cataracts, glaucoma, uveitis, infections, nutritional or
EYE CONDITIONS IN THE DOMESTIC FERRET Several conditions can impact the eyes of domestic ferrets. The following conditions are the most common: cataracts, glaucoma, uveitis, infections, nutritional or
Zoonoses in West Texas. Ken Waldrup, DVM, PhD Texas Department of State Health Services
 Zoonoses in West Texas Ken Waldrup, DVM, PhD Texas Department of State Health Services Notifiable Zoonotic Diseases Arboviruses* Anthrax Brucellosis Bovine Tuberculosis Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease (variant)
Zoonoses in West Texas Ken Waldrup, DVM, PhD Texas Department of State Health Services Notifiable Zoonotic Diseases Arboviruses* Anthrax Brucellosis Bovine Tuberculosis Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease (variant)
IACUC Policy on Humane Endpoints in Animal Use Proposals
 IACUC Policy on Humane Endpoints in Animal Use Proposals Definitions: moribund \MOR-uh-bund\, adjective: In a dying state; dying; at the point of death. morbid\ MOR-bid\, adjective: pertaining to, affected
IACUC Policy on Humane Endpoints in Animal Use Proposals Definitions: moribund \MOR-uh-bund\, adjective: In a dying state; dying; at the point of death. morbid\ MOR-bid\, adjective: pertaining to, affected
Feline Wellness Report
 Demo/Sample Clinic Feline Wellness Report 59 YOUR CAT'S AGE, IN HUMAN YEARS: Environment, genetics, nutrition and size are factors in determining a cat's age. Although this calculation is not exact, it
Demo/Sample Clinic Feline Wellness Report 59 YOUR CAT'S AGE, IN HUMAN YEARS: Environment, genetics, nutrition and size are factors in determining a cat's age. Although this calculation is not exact, it
Course 453. Dr. Soliman Mohammed Soliman Lecturer of Infectious Diseases Dept. of Medicine and Infectious Diseases
 Course 453 Dr. Soliman Mohammed Soliman Lecturer of Infectious Diseases Dept. of Medicine and Infectious Diseases COMMON VIRAL DISEASES OF DOGS & CATS 1. RABIES. 2. CANINE DISTEMPER. 1. RABIES 2. FELINE
Course 453 Dr. Soliman Mohammed Soliman Lecturer of Infectious Diseases Dept. of Medicine and Infectious Diseases COMMON VIRAL DISEASES OF DOGS & CATS 1. RABIES. 2. CANINE DISTEMPER. 1. RABIES 2. FELINE
Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference
 www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
