Time Lapse. A glimpse into prehistoric genomics. DK Griffin University of Kent CoGen 2018 No conflict of interest
|
|
|
- Griselda Ray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Time Lapse A glimpse into prehistoric genomics DK Griffin University of Kent CoGen 2018 No conflict of interest
2 This is not a talk about time lapse imaging
3 Karyomapping
4 So, where do we start? Karyomapping works because We have characterized the human genome properly Every sequence mapped in order on each chromosome Chromosome level assembly
5 Cow-ryomapping Parental chromosomes Euploid (Chr 6) Monosomy (Chr 22) Trisomy (Chr 16)
6 Overview Every good genome needs a map assembling genomes Reconstructing ancestral karyotypes Dinosaurs Conclusions on a weird karyotype Will there be a "real" Jurassic Park? Parting thoughts
7 Overview Every good genome needs a map assembling genomes Reconstructing ancestral karyotypes Dinosaurs Conclusions on a weird karyotype Will there be a "real" Jurassic Park? Parting thoughts
8 Every good genome needs a map (Harris Lewin) Each sequence assigned to a specific locus on a chromosome Ultimate aim of any de-novo genome assembly is a representation of all the sequences, correctly ordered contiguously Study genome-phenome relationships, particularly of complex (e.g. quantitative) traits Mapping of Mendelian disorders Accurate identification of (e.g. cryptic) chromosome translocations Discovery and mapping of quantitative trait nucleotides (QTNs), expression quantitative trait loci (eqtls) Study of long-range regulatory interactions Significant economical impact, more efficient food production and improved global food security Agricultural species Relevance to conservation Understanding and preserving biodiversity Animals as models for human disease Retrace gross structural evolutionary changes across (extinct) species Dinosaurs!
9 Genome assembly In 2014 ~45 newly sequenced avian genomes - produced using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Around another (e.g. falcons) Many more genomes to come Bird 10k project all species by 2020 Only 5 avian genomes initially assembled to chromosomal level: Chicken Turkey Duck Zebra Finch Collared Flycatcher sub-sub- Usually we are left with chromosomal scaffolds Evolution Highway - interactive browser
10 Mapping Genomes + Bioinformatic methods = NGS scaffolds Predicted Chromosome Fragments + FISH = Assembled genome
11 Cross-Species Probe Development CH O22 CH261-50C15 CH K1 CH N3 CH N6 CH C19 CH C5 CH261-72A10 CH261-69D20 CH261-49P24 CH H14 TGMCBa-205N19 CH261-4M5 TGMCBa-342P15 CH261-95H20 Hybridisation Success: CH261-40G6 Based on degree of sequence conservation, repeat content and GC content CH J5 TGMCBa-305E19 Bioinformatic approach to identify highly conserved sequence elements in all birds Peregrine Pigeon Zebra Finch Chicken Turkey Universal BACs Scaffolds PCFs Zebra Finch Chicken selected 93%Chicken 92% 91% 100% 100% Chicken non-selected 47% 26% 21% 100% 89% GGA2 GGA28 GGA14 GGA12
12 Application of Selected Bird Probes Probes worked across all birds and both reptiles million Chicken Peregrine Falcon Budgerigar Anolis Lizard Turtle
13 Chicken Zebra Finch PCFs Peregrine Chromosome 5 GGA2 Scaffolds Universal BACs Combined Mapping Approach CH O22 CH261-50C15 CH261-40G6 GGA2 CH J5 CH K1 CH N3 CH N6 CH C19 CH C5 CH261-72A10 GGA28 CH261-69D20 GGA14 CH261-49P24 CH H14 TGMCBa-205N19 CH261-4M5 TGMCBa-342P15 CH261-95H20 Now mapped: Peregrine falcon Saker falcon Budgerigar Ostrich Pigeon GGA12 TGMCBa-305E19 (a) (b) (c) (d) O Connor R.E. et al. (2018) Chromosome-level assembly reveals extensive rearrangement in saker falcon, budgerigar but not ostrich genomes. Genome Biology. 19:171. Damas J., O Connor R.E. et al. (2017). Upgrading short read animal genome assemblies to chromosome level using comparative genomics and a universal probe set. Genome Research, pp.gr
14 Reconstructing scaffold-based genomes Chicken/turkey EBR Chicken EBR 8a Chicken/turkey EBR crow/mgfinch/finch/woodpecker EBR
15
16 Overview Every good genome needs a map assembling genomes Reconstructing ancestral karyotypes Dinosaurs Conclusions on a weird karyotype Will there be a "real" Jurassic Park? Parting thoughts
17 Chromosome changes in animals In patients Polyploidization Pregnancy loss Partial hyatidiform moles Translocation Infertility Inversion Infertility Aneuploidy Insertions and deletions CNVs In evolution Polyploidization More common in plants Some fish e.g. trout Translocation Species barrier Inversion Species barrier Fission and fusion Indels CNVs Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution Theodosius Dobzhansky
18 Turkey Chick ZF Turkey HSB Homologous synteny block EBR Evolutionary breakpoint region HSB HSB HSB HSB EBR EBR EBR Lithgow PE*, O'Connor R*, Smith D, Fonseka G, Al Mutery A, Rathje C, Frodsham R, O'Brien P, Kasai F, Ferguson-Smith MA, Skinner BM, Griffin DK (2014). Novel tools for characterising inter and intra chromosomal rearrangements in avian microchromosomes. Chromosome Res (1):85-97
19
20
21
22 ANCESTOR derived from MGRA Chicken Chromosome 5 Turkey Chromosome 5 Duck Chromosome 5 Zebra finch Chromosome 5 Ostrich Chromosome 5 (4 scaffolds) Budgerigar Chromosome 4q (9 scaffolds) Green Anole Lizard Chromosomes 1&2 (GGA 5 orthologue)
23 Multiple Genome Rearrangements and Ancestors reconstruction tools MGRA: Max Alekseyev and Pavel Pevzner (Genome Res May;19(5):943-57) MGRA2: Pavel Avdeyev, Shuai Jiang, Sergey Aganezov, Fei Hu, and Max Alekseyev
24 Romanov et al 2014
25 Overview Every good genome needs a map assembling genomes Reconstructing ancestral karyotypes Dinosaurs Conclusions on a weird karyotype Will there be a "real" Jurassic Park? Parting thoughts
26 Eulicosaurus regina Dinosaurs Captured the imagination of Scientists Creative arts General public Since earliest fossil discoveries Michael Crichton novel/ Steven Spielberg movie Jurassic Park And sequels Most recently in 2018 Not just the animals but also their genomics
27 Extinction events & climate change Permo-Triassic mass extinction event (PTME) ~251 mya Massive volcanic eruptions in Siberian Trapps prolonged global warming, anoxic conditions devastated synapsid species increasingly arid conditions Followed by period of extraordinary ecological change. ~10-15 my before ocean reefs, forests and vertebrate numbers were re-established Dinosaurs first appeared mya Low in biodiversity and abundance for ~30 million years by mid Jurassic, increase vastly in abundance, geographical spread, body size Dominant vertebrates and extraordinary biodiversity Dinosaurs survived Carnian-Norian Extinction event (CNEE) 228 mya Saw end of the rhynchosaurs and dicynodonts Dinosaurs survived End-Triassic mass extinction event (ETME) 201 mya Devastated the crocodilian ancestors leaving only 23 extant species. Steady increase in dinosaur biodiversity and abundance after this time Now >1000 dinosaur species in fossil record ~30 more being identified each year Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction event 66 mya Chicxulub impactor meteor strike Extreme reduction in temperature and daylight Wiped out all but one therapod lineage Emerged again as modern birds, with over 10,000 biodiverse representatives
28 Theropod Dinosaur Lineage Diapsid Ancestor Lepidosauromorpha Archelosauria Squamates (Snakes & Lizards) Sphenodontia (Tuatara) Testudines (Turtles) Archosauria Crurotarsi (Crocodiles) Avemetarsalia Pterosauria DINOSAURIA Saurischia Ornithoscelida Ornithischia Theropoda Maniraptora Avialae Aves 275mya 260mya 250mya 245mya 235mya 230mya 175mya 165mya Permian Triassic Jurassic
29 Some questions Can we reconstruct ancestral dinosaur genomes (karyotypes) by inference? Did dinosaurs have bird like karyotypes? Does this explain, in part, their biodiversity and resistance to climate change?
30 Dinosaur Genome Reconstruction Adapted bioinformatic approach taken by Romanov et al. (2014) to reconstruct avian ancestor Combined previous karyotype and chromosome painting data Highly conserved avian FISH probes tested on: Anole lizard (Anolis carolinensis) Red eared slider turtle (Trachemys scripta) Spiny soft-shelled turtle (Apalone spinifera) (Matsuda et al. 2005)
31 Chicken FISH in reptiles Chicken chromosome 26 - Protomicrochromosome - ancestral macrochromosome region that split in avian lineage to form a microchromosome Lizard Turtle
32 Crocs are bad Atypical reptilian karyotype 2n=44 ish No microchromosomes ~23 species that underwent wholesale chromosome fusion A shame because it might have given us Archosaurian ancestor ~240MYA
33 Diapsid Ancestor 275mya Archelosaur Ancestor 255mya Gallus gallus Diapsid Ancestor 275 mya Archelosaur Ancestor 255 mya Gallus gallus Z W a Ancestor to Avian Genome
34 Overview Every good genome needs a map assembling genomes Reconstructing ancestral karyotypes Dinosaurs Conclusions on a weird karyotype Will there be a "real" Jurassic Park? Parting thoughts
35 Conclusions 1 All aspects of avian cytogenetics combine to gain picture of Avian evolution (from avian ancestor) Dinosaur evolution (from the Diapsid ancestor to avian ancestor) Basic pattern of 2n = 80 (~30 pairs of microchromosomes) became fixed about the time the dinosaurs emerged 240mya Evolutionary advantage to retaining this configuration or lack of opportunity for change? Genome is constrained by size (related to flight?) Opportunity for interchromosomal change is reduced Doesn t preclude fission or intrachromosomal (e.g. inversion) Crocs not constrained by genome size Possible advantages of multiple chromosomes in a karyotype Generates BIODIVERSITY, the driver of natural selection. More chromosomes lead to more combinations of gametes Increase in recombination rate (at least one obligatory chiasma per chromosome) Configuration is successful AND absence of positive selection for change
36 Conclusions 2 Avian ancestor was probably a bipedal, feathered dinosaur Reconstruction of (mostly intra-chromosomal) rearrangements may give clues to evolution of phenotypic traits Dinosaurs DID NOT GO EXTINCT (BIRDS ARE DINOSAURS!!) On the contrary They survived 3-4 extinction events WITH INCREDIBCLE CLIMATE CHANGE Re-emerging more diverse each time (most recently as birds) Perhaps in part because of their amazing karyotype
37 THIS NOT ONLY LEADS TO THIS
38 BUT ALSO THIS
39 Overview Every good genome needs a map assembling genomes Reconstructing ancestral karyotypes Dinosaurs Conclusions on a weird karyotype Will there be a "real" Jurassic Park? Parting thoughts
40
41 Why there will be no Jurassic Park DNA will not survive that long This is a well described field Neanderthal men and wooly mammoths, yes Cave bears are particularly well studied The DNA would be fragmented Unclear of organization or gaps Developmental biology don t work like that Recreating the molecular cues that the eggs gives the developing embryo would be nigh on impossible Theoretical possibility for recreating recently extinct species Some gene function studies looking at dino genes by manipulating chick embryos
42 Overview Every good genome needs a map assembling genomes Reconstructing ancestral karyotypes Dinosaurs Conclusions on a weird karyotype Will there be a "real" Jurassic Park? Parting thoughts
43 Extinction events & climate change Permo-Triassic mass extinction event (PTME) ~251 mya Volcanoes in the Siberian Trapps Dinosaurs first appeared mya They have been biodiverse almost from the outset Perhaps because of their karyotype Dinosaurs survived Carnian-Norian Extinction event (CNEE) 228 mya Dinosaurs survived End-Triassic mass extinction event (ETME) 201 mya Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction event 66 mya Chicxulub impactor meteor strike WE ARE THE METEOR We are living a great extinction event and we caused it And dinosaurs (birds) will probably survive it Perhaps because of their chromosomes But we might not
44 For the first time in 66 million years The karyotype of a Velociraptor
45 Acknowledgments Digital Scientific UK Griffin lab (University of Kent past and present) Becky O Connor, Mike Romanov, Ben Skinner, Claudia Rathje, Gothami Fonseka, Katie Fowler, Becca Jennings, Lucas Kiazim, Kat Sanders, Giuseppe Silvestri, RVC London. Denis Larkin, Marta Farre, Joana Damas Kornsorn Srikulnath, Worrapong Singchat, Bal-Jing Ballsackz - Thailand Michael Schmid lab, Ferguson-Smith Lab Dave Burt, Roslin Institute Peter Houde NMSU Yoichi Matsuda, Shibusawa - Hokkaido, Japan BBSRC, Cytocell Martin Lawrie, John Anson Central Veterinary Research Laboratory Dubai (CVRL) Ullrich Wernery, Suntiha Joseph, Abdullah Al Mutery Nicole Valenzuela Iowa 45 genome consortium Tom Gilbert, Erich Jarvis, Guojie Zhang Paul Barrett - Natural History Museum Digital Scientific UK Michael Ellis
The Triassic Transition
 The Triassic Transition The Age of Reptiles Begins As the Paleozoic drew to a close through the Carboniferous and Permian several important processes were at work. Assembly of Pangea Evolutionary radiation
The Triassic Transition The Age of Reptiles Begins As the Paleozoic drew to a close through the Carboniferous and Permian several important processes were at work. Assembly of Pangea Evolutionary radiation
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs. LAB 7: Dinosaur diversity- Saurischians
 Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 7: Dinosaur diversity- Saurischians Last lab you were presented with a review of major ornithischian clades. You also were presented with some of the kinds of plants that
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 7: Dinosaur diversity- Saurischians Last lab you were presented with a review of major ornithischian clades. You also were presented with some of the kinds of plants that
Video Assignments. Microraptor PBS The Four-winged Dinosaur Mark Davis SUNY Cortland Library Online
 Video Assignments Microraptor PBS The Four-winged Dinosaur Mark Davis SUNY Cortland Library Online Radiolab Apocalyptical http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k52vd4wbdlw&feature=youtu.be Minute 13 through minute
Video Assignments Microraptor PBS The Four-winged Dinosaur Mark Davis SUNY Cortland Library Online Radiolab Apocalyptical http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k52vd4wbdlw&feature=youtu.be Minute 13 through minute
Evolution as Fact. The figure below shows transitional fossils in the whale lineage.
 Evolution as Fact Evolution is a fact. Organisms descend from others with modification. Phylogeny, the lineage of ancestors and descendants, is the scientific term to Darwin's phrase "descent with modification."
Evolution as Fact Evolution is a fact. Organisms descend from others with modification. Phylogeny, the lineage of ancestors and descendants, is the scientific term to Darwin's phrase "descent with modification."
Evolution of Birds. Summary:
 Oregon State Standards OR Science 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.3S.1, 7.3S.2 8.1, 8.2, 8.2L.1, 8.3, 8.3S.1, 8.3S.2 H.1, H.2, H.2L.4, H.2L.5, H.3, H.3S.1, H.3S.2, H.3S.3 Summary: Students create phylogenetic trees to
Oregon State Standards OR Science 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.3S.1, 7.3S.2 8.1, 8.2, 8.2L.1, 8.3, 8.3S.1, 8.3S.2 H.1, H.2, H.2L.4, H.2L.5, H.3, H.3S.1, H.3S.2, H.3S.3 Summary: Students create phylogenetic trees to
Red Eared Slider Secrets. Although Most Red-Eared Sliders Can Live Up to Years, Most WILL NOT Survive Two Years!
 Although Most Red-Eared Sliders Can Live Up to 45-60 Years, Most WILL NOT Survive Two Years! Chris Johnson 2014 2 Red Eared Slider Secrets Although Most Red-Eared Sliders Can Live Up to 45-60 Years, Most
Although Most Red-Eared Sliders Can Live Up to 45-60 Years, Most WILL NOT Survive Two Years! Chris Johnson 2014 2 Red Eared Slider Secrets Although Most Red-Eared Sliders Can Live Up to 45-60 Years, Most
Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection. Hunting for evolution clues Elementary, my dear, Darwin!
 Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection Hunting for evolution clues Elementary, my dear, Darwin! 2006-2007 Evidence supporting evolution Fossil record shows change over time Anatomical record comparing
Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection Hunting for evolution clues Elementary, my dear, Darwin! 2006-2007 Evidence supporting evolution Fossil record shows change over time Anatomical record comparing
1 Describe the anatomy and function of the turtle shell. 2 Describe respiration in turtles. How does the shell affect respiration?
 GVZ 2017 Practice Questions Set 1 Test 3 1 Describe the anatomy and function of the turtle shell. 2 Describe respiration in turtles. How does the shell affect respiration? 3 According to the most recent
GVZ 2017 Practice Questions Set 1 Test 3 1 Describe the anatomy and function of the turtle shell. 2 Describe respiration in turtles. How does the shell affect respiration? 3 According to the most recent
Tuesday, December 6, 11. Mesozoic Life
 Mesozoic Life Review of Paleozoic Transgression/regressions and Mountain building events during the paleoozoic act as driving force of evolution. regression of seas and continental uplift create variety
Mesozoic Life Review of Paleozoic Transgression/regressions and Mountain building events during the paleoozoic act as driving force of evolution. regression of seas and continental uplift create variety
Living Dinosaurs (3-5) Animal Demonstrations
 Living Dinosaurs (3-5) Animal Demonstrations At a glance Students visiting the zoo will be introduced to live animals and understand their connection to a common ancestor, dinosaurs. Time requirement One
Living Dinosaurs (3-5) Animal Demonstrations At a glance Students visiting the zoo will be introduced to live animals and understand their connection to a common ancestor, dinosaurs. Time requirement One
REPTILES. Scientific Classification of Reptiles To creep. Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Reptilia
 Scientific Classification of Reptiles To creep Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Reptilia REPTILES tetrapods - 4 legs adapted for land, hip/girdle Amniotes - animals whose
Scientific Classification of Reptiles To creep Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Reptilia REPTILES tetrapods - 4 legs adapted for land, hip/girdle Amniotes - animals whose
6. The lifetime Darwinian fitness of one organism is greater than that of another organism if: A. it lives longer than the other B. it is able to outc
 1. The money in the kingdom of Florin consists of bills with the value written on the front, and pictures of members of the royal family on the back. To test the hypothesis that all of the Florinese $5
1. The money in the kingdom of Florin consists of bills with the value written on the front, and pictures of members of the royal family on the back. To test the hypothesis that all of the Florinese $5
The Fossil Record of Vertebrate Transitions
 The Fossil Record of Vertebrate Transitions The Fossil Evidence of Evolution 1. Fossils show a pattern of change through geologic time of new species appearing in the fossil record that are similar to
The Fossil Record of Vertebrate Transitions The Fossil Evidence of Evolution 1. Fossils show a pattern of change through geologic time of new species appearing in the fossil record that are similar to
Evolution of Tetrapods
 Evolution of Tetrapods Amphibian-like creatures: The earliest tracks of a four-legged animal were found in Poland in 2010; they are Middle Devonian in age. Amphibians arose from sarcopterygians sometime
Evolution of Tetrapods Amphibian-like creatures: The earliest tracks of a four-legged animal were found in Poland in 2010; they are Middle Devonian in age. Amphibians arose from sarcopterygians sometime
Outline 17: Reptiles and Dinosaurs
 Outline 17: Reptiles and Dinosaurs Evolution of Reptiles The first reptiles appeared in the Mississippian. They evolved from amphibians, which first appeared in the Devonian. The evolutionary jump was
Outline 17: Reptiles and Dinosaurs Evolution of Reptiles The first reptiles appeared in the Mississippian. They evolved from amphibians, which first appeared in the Devonian. The evolutionary jump was
Biology 1B Evolution Lecture 11 (March 19, 2010), Insights from the Fossil Record and Evo-Devo
 Biology 1B Evolution Lecture 11 (March 19, 2010), Insights from the Fossil Record and Evo-Devo Extinction Important points on extinction rates: Background rate of extinctions per million species per year:
Biology 1B Evolution Lecture 11 (March 19, 2010), Insights from the Fossil Record and Evo-Devo Extinction Important points on extinction rates: Background rate of extinctions per million species per year:
Modern Evolutionary Classification. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview Modern Evolutionary Classification
 Lesson Overview 18.2 Modern Evolutionary Classification THINK ABOUT IT Darwin s ideas about a tree of life suggested a new way to classify organisms not just based on similarities and differences, but
Lesson Overview 18.2 Modern Evolutionary Classification THINK ABOUT IT Darwin s ideas about a tree of life suggested a new way to classify organisms not just based on similarities and differences, but
May 10, SWBAT analyze and evaluate the scientific evidence provided by the fossil record.
 May 10, 2017 Aims: SWBAT analyze and evaluate the scientific evidence provided by the fossil record. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing our AIMS: E.3-Examining
May 10, 2017 Aims: SWBAT analyze and evaluate the scientific evidence provided by the fossil record. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing our AIMS: E.3-Examining
CLADISTICS Student Packet SUMMARY Phylogeny Phylogenetic trees/cladograms
 CLADISTICS Student Packet SUMMARY PHYLOGENETIC TREES AND CLADOGRAMS ARE MODELS OF EVOLUTIONARY HISTORY THAT CAN BE TESTED Phylogeny is the history of descent of organisms from their common ancestor. Phylogenetic
CLADISTICS Student Packet SUMMARY PHYLOGENETIC TREES AND CLADOGRAMS ARE MODELS OF EVOLUTIONARY HISTORY THAT CAN BE TESTED Phylogeny is the history of descent of organisms from their common ancestor. Phylogenetic
What is the evidence for evolution?
 What is the evidence for evolution? 1. Geographic Distribution 2. Fossil Evidence & Transitional Species 3. Comparative Anatomy 1. Homologous Structures 2. Analogous Structures 3. Vestigial Structures
What is the evidence for evolution? 1. Geographic Distribution 2. Fossil Evidence & Transitional Species 3. Comparative Anatomy 1. Homologous Structures 2. Analogous Structures 3. Vestigial Structures
Evolution by Natural Selection
 Evolution by Natural Selection 2006-2007 DOCTRINE But the Fossil record OBSERVATION Quaternary 1.5 Tertiary 63 Cretaceous 135 Jurassic 180 Triassic 225 Permian 280 Carboniferous 350 Devonian 400 Silurian
Evolution by Natural Selection 2006-2007 DOCTRINE But the Fossil record OBSERVATION Quaternary 1.5 Tertiary 63 Cretaceous 135 Jurassic 180 Triassic 225 Permian 280 Carboniferous 350 Devonian 400 Silurian
UNIT III A. Descent with Modification(Ch19) B. Phylogeny (Ch20) C. Evolution of Populations (Ch21) D. Origin of Species or Speciation (Ch22)
 UNIT III A. Descent with Modification(Ch9) B. Phylogeny (Ch2) C. Evolution of Populations (Ch2) D. Origin of Species or Speciation (Ch22) Classification in broad term simply means putting things in classes
UNIT III A. Descent with Modification(Ch9) B. Phylogeny (Ch2) C. Evolution of Populations (Ch2) D. Origin of Species or Speciation (Ch22) Classification in broad term simply means putting things in classes
Crocs and Birds as Dino models Crocs and birds united with dinos by morphology Both also have parental care and vocal communication between offspring
 Chapter 16. Mesozoic Diapsids Phylogenetic relationships Earliest from late carboniferous stem diapsids Petrolacosaurus Lineage split into two: Archosauromorpha Crocs, birds, dinos, pterosaurs Lepidosauromorpha
Chapter 16. Mesozoic Diapsids Phylogenetic relationships Earliest from late carboniferous stem diapsids Petrolacosaurus Lineage split into two: Archosauromorpha Crocs, birds, dinos, pterosaurs Lepidosauromorpha
Name: Per. Date: 1. How many different species of living things exist today?
 Name: Per. Date: Life Has a History We will be using this website for the activity: http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/explorations/tours/intro/index.html Procedure: A. Open the above website and click
Name: Per. Date: Life Has a History We will be using this website for the activity: http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/explorations/tours/intro/index.html Procedure: A. Open the above website and click
Natural Selection. What is natural selection?
 Natural Selection Natural Selection What is natural selection? In 1858, Darwin and Alfred Russell proposed the same explanation for how evolution occurs In his book, Origin of the Species, Darwin proposed
Natural Selection Natural Selection What is natural selection? In 1858, Darwin and Alfred Russell proposed the same explanation for how evolution occurs In his book, Origin of the Species, Darwin proposed
Carnivore An animal that feeds chiefly on the flesh of other animals.
 Name: School: Date: Bipedalism A form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs, or legs. An animal that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped, meaning
Name: School: Date: Bipedalism A form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs, or legs. An animal that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped, meaning
Origin and Evolution of Birds. Read: Chapters 1-3 in Gill but limited review of systematics
 Origin and Evolution of Birds Read: Chapters 1-3 in Gill but limited review of systematics Review of Taxonomy Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Aves Characteristics: wings,
Origin and Evolution of Birds Read: Chapters 1-3 in Gill but limited review of systematics Review of Taxonomy Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Aves Characteristics: wings,
Evolution by Natural Selection
 Evolution by Natural Selection 2006-2007 DOCTRINE TINTORETTO The Creation of the Animals 1550 But the Fossil record OBSERVATION Anaerobic Bacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria Dinosaurs Green Algae Multicellular
Evolution by Natural Selection 2006-2007 DOCTRINE TINTORETTO The Creation of the Animals 1550 But the Fossil record OBSERVATION Anaerobic Bacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria Dinosaurs Green Algae Multicellular
Characteristics of a Reptile. Vertebrate animals Lungs Scaly skin Amniotic egg
 Reptiles Characteristics of a Reptile Vertebrate animals Lungs Scaly skin Amniotic egg Characteristics of Reptiles Adaptations to life on land More efficient lungs and a better circulator system were develope
Reptiles Characteristics of a Reptile Vertebrate animals Lungs Scaly skin Amniotic egg Characteristics of Reptiles Adaptations to life on land More efficient lungs and a better circulator system were develope
Species: Panthera pardus Genus: Panthera Family: Felidae Order: Carnivora Class: Mammalia Phylum: Chordata
 CHAPTER 6: PHYLOGENY AND THE TREE OF LIFE AP Biology 3 PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS Phylogeny - evolutionary history of a species or group of related species Systematics - analytical approach to understanding
CHAPTER 6: PHYLOGENY AND THE TREE OF LIFE AP Biology 3 PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS Phylogeny - evolutionary history of a species or group of related species Systematics - analytical approach to understanding
Biology Slide 1 of 50
 Biology 1 of 50 2 of 50 What Is a Reptile? What are the characteristics of reptiles? 3 of 50 What Is a Reptile? What Is a Reptile? A reptile is a vertebrate that has dry, scaly skin, lungs, and terrestrial
Biology 1 of 50 2 of 50 What Is a Reptile? What are the characteristics of reptiles? 3 of 50 What Is a Reptile? What Is a Reptile? A reptile is a vertebrate that has dry, scaly skin, lungs, and terrestrial
8/19/2013. Topic 5: The Origin of Amniotes. What are some stem Amniotes? What are some stem Amniotes? The Amniotic Egg. What is an Amniote?
 Topic 5: The Origin of Amniotes Where do amniotes fall out on the vertebrate phylogeny? What are some stem Amniotes? What is an Amniote? What changes were involved with the transition to dry habitats?
Topic 5: The Origin of Amniotes Where do amniotes fall out on the vertebrate phylogeny? What are some stem Amniotes? What is an Amniote? What changes were involved with the transition to dry habitats?
Chapter 22 Darwin and Evolution by Natural Selection
 Anaerobic Bacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria Dinosaurs Green Algae Multicellular Animals Flowering Molluscs Arthropods Chordates Jawless Fish Teleost Fish Amphibians Insects Reptiles Mammals Birds Land Plants
Anaerobic Bacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria Dinosaurs Green Algae Multicellular Animals Flowering Molluscs Arthropods Chordates Jawless Fish Teleost Fish Amphibians Insects Reptiles Mammals Birds Land Plants
Comparing DNA Sequence to Understand
 Comparing DNA Sequence to Understand Evolutionary Relationships with BLAST Name: Big Idea 1: Evolution Pre-Reading In order to understand the purposes and learning objectives of this investigation, you
Comparing DNA Sequence to Understand Evolutionary Relationships with BLAST Name: Big Idea 1: Evolution Pre-Reading In order to understand the purposes and learning objectives of this investigation, you
AP Biology. AP Biology
 Evolution by Natural Selection 2006-2007 DOCTRINE TINTORETTO The Creation of the Animals 1550 But the Fossil record OBSERVATION mya Quaternary 1.5 Tertiary 63 Cretaceous 135 Jurassic 180 Triassic 225 Permian
Evolution by Natural Selection 2006-2007 DOCTRINE TINTORETTO The Creation of the Animals 1550 But the Fossil record OBSERVATION mya Quaternary 1.5 Tertiary 63 Cretaceous 135 Jurassic 180 Triassic 225 Permian
Vertebrate Evolution
 Vertebrate Evolution Torsten Bernhardt Redpath Museum, McGill University This teaching resource was made possible with funding from the PromoScience programme of NSERC. McGill University 2010 History of
Vertebrate Evolution Torsten Bernhardt Redpath Museum, McGill University This teaching resource was made possible with funding from the PromoScience programme of NSERC. McGill University 2010 History of
Modern taxonomy. Building family trees 10/10/2011. Knowing a lot about lots of creatures. Tom Hartman. Systematics includes: 1.
 Modern taxonomy Building family trees Tom Hartman www.tuatara9.co.uk Classification has moved away from the simple grouping of organisms according to their similarities (phenetics) and has become the study
Modern taxonomy Building family trees Tom Hartman www.tuatara9.co.uk Classification has moved away from the simple grouping of organisms according to their similarities (phenetics) and has become the study
The Origin of Species: Lizards in an Evolutionary Tree
 The Origin of Species: Lizards in an Evolutionary Tree Cara Larracas, Stacy Lopez, Takara Yaegashi Period 4 Background Information Throughout the Caribbean Islands there is a species of anole lizards that
The Origin of Species: Lizards in an Evolutionary Tree Cara Larracas, Stacy Lopez, Takara Yaegashi Period 4 Background Information Throughout the Caribbean Islands there is a species of anole lizards that
LABORATORY EXERCISE 7: CLADISTICS I
 Biology 4415/5415 Evolution LABORATORY EXERCISE 7: CLADISTICS I Take a group of organisms. Let s use five: a lungfish, a frog, a crocodile, a flamingo, and a human. How to reconstruct their relationships?
Biology 4415/5415 Evolution LABORATORY EXERCISE 7: CLADISTICS I Take a group of organisms. Let s use five: a lungfish, a frog, a crocodile, a flamingo, and a human. How to reconstruct their relationships?
S7L2_Genetics and S7L5_Theory of Evolution (Thrower)
 Name: Date: 1. Single-celled organisms can reproduce and create cells exactly like themselves without combining genes from two different parent cells. When they do this, they use a type of A. asexual reproduction.
Name: Date: 1. Single-celled organisms can reproduce and create cells exactly like themselves without combining genes from two different parent cells. When they do this, they use a type of A. asexual reproduction.
Yr 11 Evolution of Australian Biota Workshop Students Notes. Welcome to the Australian Biota Workshop!! Some of the main points to have in mind are:
 Yr 11 Evolution of Australian Biota Workshop Students Notes Welcome to the Australian Biota Workshop!! Some of the main points to have in mind are: A) Humans only live a short amount of time - lots of
Yr 11 Evolution of Australian Biota Workshop Students Notes Welcome to the Australian Biota Workshop!! Some of the main points to have in mind are: A) Humans only live a short amount of time - lots of
Origin and Evolution of Birds. Read: Chapters 1-3 in Gill but limited review of systematics
 Origin and Evolution of Birds Read: Chapters 1-3 in Gill but limited review of systematics Review of Taxonomy Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Aves Characteristics: wings,
Origin and Evolution of Birds Read: Chapters 1-3 in Gill but limited review of systematics Review of Taxonomy Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Aves Characteristics: wings,
Mesozoic reptiles. Benton: Chapters 6 & 8. G404 Geobiology. Department of Geological Sciences Indiana University
 Mesozoic reptiles Benton: Chapters 6 & 8 Gait of Plateosaurus (Mallison, 2010, Palaeontologia Electronica 13.2.8A) Lab Tomorrow: Please bring laptop computers if you have them. Lab assignment will use
Mesozoic reptiles Benton: Chapters 6 & 8 Gait of Plateosaurus (Mallison, 2010, Palaeontologia Electronica 13.2.8A) Lab Tomorrow: Please bring laptop computers if you have them. Lab assignment will use
Sec KEY CONCEPT Reptiles, birds, and mammals are amniotes.
 Thu 4/27 Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Activities Students will describe the evolutionary significance of amniotic
Thu 4/27 Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Activities Students will describe the evolutionary significance of amniotic
Stuart S. Sumida Biology 342. (Simplified)Phylogeny of Archosauria
 Stuart S. Sumida Biology 342 (Simplified)Phylogeny of Archosauria Remember, we re studying AMNIOTES. Defined by: EMBRYOLOGICAL FEATURES: amnion, chorion, allantois, yolk sac. ANATOMICAL FEATURES: lack
Stuart S. Sumida Biology 342 (Simplified)Phylogeny of Archosauria Remember, we re studying AMNIOTES. Defined by: EMBRYOLOGICAL FEATURES: amnion, chorion, allantois, yolk sac. ANATOMICAL FEATURES: lack
Fossilized remains of cat-sized flying reptile found in British Columbia
 Fossilized remains of cat-sized flying reptile found in British Columbia By Washington Post, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.06.16 Word Count 768 An artist's impression of the small-bodied, Late Cretaceous
Fossilized remains of cat-sized flying reptile found in British Columbia By Washington Post, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.06.16 Word Count 768 An artist's impression of the small-bodied, Late Cretaceous
When Dinosaurs Ruled the Earth
 Buffalo Geosciences Program: Lesson Plan #2 When Dinosaurs Ruled the Earth Objectives: By the end of the program, the participants should be able to understand the earth and its creatures during the Triassic,
Buffalo Geosciences Program: Lesson Plan #2 When Dinosaurs Ruled the Earth Objectives: By the end of the program, the participants should be able to understand the earth and its creatures during the Triassic,
Lecture 11 Wednesday, September 19, 2012
 Lecture 11 Wednesday, September 19, 2012 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean
Lecture 11 Wednesday, September 19, 2012 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 4: Systematics Part 1
 Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 4: Systematics Part 1 Systematics is the comparative study of biological diversity with the intent of determining the relationships between organisms. Humankind has always
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 4: Systematics Part 1 Systematics is the comparative study of biological diversity with the intent of determining the relationships between organisms. Humankind has always
Fish 2/26/13. Chordates 2. Sharks and Rays (about 470 species) Sharks etc Bony fish. Tetrapods. Osteichthans Lobe fins and lungfish
 Chordates 2 Sharks etc Bony fish Osteichthans Lobe fins and lungfish Tetrapods ns Reptiles Birds Feb 27, 2013 Chordates ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME Notochord Common ancestor of chordates Head Vertebral column
Chordates 2 Sharks etc Bony fish Osteichthans Lobe fins and lungfish Tetrapods ns Reptiles Birds Feb 27, 2013 Chordates ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME Notochord Common ancestor of chordates Head Vertebral column
 Context Attributes Diving? Rough Furry Furry Rough Son of Man, Magritte What is this man doing? What is this man doing? Two birds with funny blue feet. Two professors converse in front of a blackboard.
Context Attributes Diving? Rough Furry Furry Rough Son of Man, Magritte What is this man doing? What is this man doing? Two birds with funny blue feet. Two professors converse in front of a blackboard.
NAME: DATE: SECTION:
 NAME: DATE: SECTION: MCAS PREP PACKET EVOLUTION AND BIODIVERSITY 1. Which of the following observations best supports the conclusion that dolphins and sharks do not have a recent common ancestor? A. Dolphins
NAME: DATE: SECTION: MCAS PREP PACKET EVOLUTION AND BIODIVERSITY 1. Which of the following observations best supports the conclusion that dolphins and sharks do not have a recent common ancestor? A. Dolphins
What are taxonomy, classification, and systematics?
 Topic 2: Comparative Method o Taxonomy, classification, systematics o Importance of phylogenies o A closer look at systematics o Some key concepts o Parts of a cladogram o Groups and characters o Homology
Topic 2: Comparative Method o Taxonomy, classification, systematics o Importance of phylogenies o A closer look at systematics o Some key concepts o Parts of a cladogram o Groups and characters o Homology
Bi156 Lecture 1/13/12. Dog Genetics
 Bi156 Lecture 1/13/12 Dog Genetics The radiation of the family Canidae occurred about 100 million years ago. Dogs are most closely related to wolves, from which they diverged through domestication about
Bi156 Lecture 1/13/12 Dog Genetics The radiation of the family Canidae occurred about 100 million years ago. Dogs are most closely related to wolves, from which they diverged through domestication about
Resources. Visual Concepts. Chapter Presentation. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Vertebrates Table of Contents Section 1 Vertebrates in the Sea and on Land Section 2 Terrestrial Vertebrates Section
Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Vertebrates Table of Contents Section 1 Vertebrates in the Sea and on Land Section 2 Terrestrial Vertebrates Section
Evolution of Biodiversity
 Long term patterns Evolution of Biodiversity Chapter 7 Changes in biodiversity caused by originations and extinctions of taxa over geologic time Analyses of diversity in the fossil record requires procedures
Long term patterns Evolution of Biodiversity Chapter 7 Changes in biodiversity caused by originations and extinctions of taxa over geologic time Analyses of diversity in the fossil record requires procedures
7. Describe the following with words and give an example: Heterozygous, homozygous recessive, homozygous dominant
 Name: Genetics UNIT EXAM Review Below are review questions for each of the 5 learning goals we have addressed during this unit. This is the majority of the science content we covered. However, as a disclaimer
Name: Genetics UNIT EXAM Review Below are review questions for each of the 5 learning goals we have addressed during this unit. This is the majority of the science content we covered. However, as a disclaimer
Non-Dinosaurians of the Mesozoic
 Non-Dinosaurians of the Mesozoic Calling the Mesozoic the Age of Dinosaurs is actually not quite correct Not all reptiles of the Mesozoic were dinosaurs. Many reptiles (and other amniotes) have returned
Non-Dinosaurians of the Mesozoic Calling the Mesozoic the Age of Dinosaurs is actually not quite correct Not all reptiles of the Mesozoic were dinosaurs. Many reptiles (and other amniotes) have returned
GEOL 104 Dinosaurs: A Natural History Homework 6: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Extinction. DUE: Fri. Dec. 8
 GEOL 104 Dinosaurs: A Natural History Homework 6: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Extinction DUE: Fri. Dec. 8 Part I: Victims and Survivors Below is a list of various taxa. Indicate (by letter) if the taxon: A.
GEOL 104 Dinosaurs: A Natural History Homework 6: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Extinction DUE: Fri. Dec. 8 Part I: Victims and Survivors Below is a list of various taxa. Indicate (by letter) if the taxon: A.
LABORATORY EXERCISE 6: CLADISTICS I
 Biology 4415/5415 Evolution LABORATORY EXERCISE 6: CLADISTICS I Take a group of organisms. Let s use five: a lungfish, a frog, a crocodile, a flamingo, and a human. How to reconstruct their relationships?
Biology 4415/5415 Evolution LABORATORY EXERCISE 6: CLADISTICS I Take a group of organisms. Let s use five: a lungfish, a frog, a crocodile, a flamingo, and a human. How to reconstruct their relationships?
Giant croc with T. rex teeth roamed Madagascar
 Giant croc with T. rex teeth roamed Madagascar www.scimex.org/newsfeed/giant-croc-with-t.-rex-teeth-used-to-roam-in-madagascar Embargoed until: Publicly released: PeerJ A fossil of the largest and oldest
Giant croc with T. rex teeth roamed Madagascar www.scimex.org/newsfeed/giant-croc-with-t.-rex-teeth-used-to-roam-in-madagascar Embargoed until: Publicly released: PeerJ A fossil of the largest and oldest
Ch 1.2 Determining How Species Are Related.notebook February 06, 2018
 Name 3 "Big Ideas" from our last notebook lecture: * * * 1 WDYR? Of the following organisms, which is the closest relative of the "Snowy Owl" (Bubo scandiacus)? a) barn owl (Tyto alba) b) saw whet owl
Name 3 "Big Ideas" from our last notebook lecture: * * * 1 WDYR? Of the following organisms, which is the closest relative of the "Snowy Owl" (Bubo scandiacus)? a) barn owl (Tyto alba) b) saw whet owl
The Cretaceous Period
 The Cretaceous Period By Doug and Claudia Mann Illustrated by David Cobb Copyright 2007 www.fossils-facts-and-finds.com Mesozoic Era Triassic Jurassic Cretaceous The Cretaceous Period: Flowers Bloom For
The Cretaceous Period By Doug and Claudia Mann Illustrated by David Cobb Copyright 2007 www.fossils-facts-and-finds.com Mesozoic Era Triassic Jurassic Cretaceous The Cretaceous Period: Flowers Bloom For
B D. C D) Devonian E F. A) Cambrian. B) Ordovician. C) Silurian. E) Carboniferous. F) Permian. Paleozoic Era
 Paleozoic Era A) Cambrian A B) Ordovician B D C) Silurian C D) Devonian E) Carboniferous F) Permian E F The Cambrian explosion refers to the sudden appearance of many species of animals in the fossil record.
Paleozoic Era A) Cambrian A B) Ordovician B D C) Silurian C D) Devonian E) Carboniferous F) Permian E F The Cambrian explosion refers to the sudden appearance of many species of animals in the fossil record.
Supplementary Figure 1 Cartilaginous stages in non-avian amniotes. (a) Drawing of early ankle development of Alligator mississippiensis, as reported
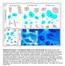 Supplementary Figure 1 Cartilaginous stages in non-avian amniotes. (a) Drawing of early ankle development of Alligator mississippiensis, as reported by a previous study 1. The intermedium is formed at
Supplementary Figure 1 Cartilaginous stages in non-avian amniotes. (a) Drawing of early ankle development of Alligator mississippiensis, as reported by a previous study 1. The intermedium is formed at
Animal Diversity wrap-up Lecture 9 Winter 2014
 Animal Diversity wrap-up Lecture 9 Winter 2014 1 Animal phylogeny based on morphology & development Fig. 32.10 2 Animal phylogeny based on molecular data Fig. 32.11 New Clades 3 Lophotrochozoa Lophophore:
Animal Diversity wrap-up Lecture 9 Winter 2014 1 Animal phylogeny based on morphology & development Fig. 32.10 2 Animal phylogeny based on molecular data Fig. 32.11 New Clades 3 Lophotrochozoa Lophophore:
Evolution by Natural Selection
 Evolution by Natural Selection 225 Permian Seed Plants Flowering Plants Birds Land Plants Mammals Insects Reptiles Teleost Fish Amphibians Chordates Molluscs Arthropods Dinosaurs 180 Triassic Jawless Fish
Evolution by Natural Selection 225 Permian Seed Plants Flowering Plants Birds Land Plants Mammals Insects Reptiles Teleost Fish Amphibians Chordates Molluscs Arthropods Dinosaurs 180 Triassic Jawless Fish
Differences between Reptiles and Mammals. Reptiles. Mammals. No milk. Milk. Small brain case Jaw contains more than one bone Simple teeth
 Differences between Reptiles and Mammals Reptiles No milk Mammals Milk The Advantage of Being a Furball: Diversification of Mammals Small brain case Jaw contains more than one bone Simple teeth One ear
Differences between Reptiles and Mammals Reptiles No milk Mammals Milk The Advantage of Being a Furball: Diversification of Mammals Small brain case Jaw contains more than one bone Simple teeth One ear
CHAPTER 26. Animal Evolution The Vertebrates
 CHAPTER 26 Animal Evolution The Vertebrates Impacts, Issues: Interpreting and Misinterpreting the Past No one was around to witness the transitions in the history of life Fossils allow us glimpses into
CHAPTER 26 Animal Evolution The Vertebrates Impacts, Issues: Interpreting and Misinterpreting the Past No one was around to witness the transitions in the history of life Fossils allow us glimpses into
Animal Evolution The Chordates. Chapter 26 Part 2
 Animal Evolution The Chordates Chapter 26 Part 2 26.10 Birds The Feathered Ones Birds are the only animals with feathers Descendants of flying dinosaurs in which scales became modified as feathers Long
Animal Evolution The Chordates Chapter 26 Part 2 26.10 Birds The Feathered Ones Birds are the only animals with feathers Descendants of flying dinosaurs in which scales became modified as feathers Long
Introduction to phylogenetic trees and tree-thinking Copyright 2005, D. A. Baum (Free use for non-commercial educational pruposes)
 Introduction to phylogenetic trees and tree-thinking Copyright 2005, D. A. Baum (Free use for non-commercial educational pruposes) Phylogenetics is the study of the relationships of organisms to each other.
Introduction to phylogenetic trees and tree-thinking Copyright 2005, D. A. Baum (Free use for non-commercial educational pruposes) Phylogenetics is the study of the relationships of organisms to each other.
Evolution on Exhibit Hints for Teachers
 1 Evolution on Exhibit Hints for Teachers This gallery activity explores a variety of evolution themes that are well illustrated by gallery specimens and exhibits. Each activity is aligned with the NGSS
1 Evolution on Exhibit Hints for Teachers This gallery activity explores a variety of evolution themes that are well illustrated by gallery specimens and exhibits. Each activity is aligned with the NGSS
BioSci 110, Fall 08 Exam 2
 1. is the cell division process that results in the production of a. mitosis; 2 gametes b. meiosis; 2 gametes c. meiosis; 2 somatic (body) cells d. mitosis; 4 somatic (body) cells e. *meiosis; 4 gametes
1. is the cell division process that results in the production of a. mitosis; 2 gametes b. meiosis; 2 gametes c. meiosis; 2 somatic (body) cells d. mitosis; 4 somatic (body) cells e. *meiosis; 4 gametes
Do the traits of organisms provide evidence for evolution?
 PhyloStrat Tutorial Do the traits of organisms provide evidence for evolution? Consider two hypotheses about where Earth s organisms came from. The first hypothesis is from John Ray, an influential British
PhyloStrat Tutorial Do the traits of organisms provide evidence for evolution? Consider two hypotheses about where Earth s organisms came from. The first hypothesis is from John Ray, an influential British
Adaptations: Changes Through Time
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and Activitydevelop the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Adaptations: Changes Through Time How do adaptations
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and Activitydevelop the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Adaptations: Changes Through Time How do adaptations
17.2 Classification Based on Evolutionary Relationships Organization of all that speciation!
 Organization of all that speciation! Patterns of evolution.. Taxonomy gets an over haul! Using more than morphology! 3 domains, 6 kingdoms KEY CONCEPT Modern classification is based on evolutionary relationships.
Organization of all that speciation! Patterns of evolution.. Taxonomy gets an over haul! Using more than morphology! 3 domains, 6 kingdoms KEY CONCEPT Modern classification is based on evolutionary relationships.
Title: Phylogenetic Methods and Vertebrate Phylogeny
 Title: Phylogenetic Methods and Vertebrate Phylogeny Central Question: How can evolutionary relationships be determined objectively? Sub-questions: 1. What affect does the selection of the outgroup have
Title: Phylogenetic Methods and Vertebrate Phylogeny Central Question: How can evolutionary relationships be determined objectively? Sub-questions: 1. What affect does the selection of the outgroup have
Unit 5 Guided Notes Genetics
 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named documented inheritance in peas Medel s Work What is inheritance: used good experimental design used analysis
Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named documented inheritance in peas Medel s Work What is inheritance: used good experimental design used analysis
You have 254 Neanderthal variants.
 1 of 5 1/3/2018 1:21 PM Joseph Roberts Neanderthal Ancestry Neanderthal Ancestry Neanderthals were ancient humans who interbred with modern humans before becoming extinct 40,000 years ago. This report
1 of 5 1/3/2018 1:21 PM Joseph Roberts Neanderthal Ancestry Neanderthal Ancestry Neanderthals were ancient humans who interbred with modern humans before becoming extinct 40,000 years ago. This report
Barney to Big Bird: The Origin of Birds. Caudipteryx. The fuzzy raptor. Solnhofen Limestone, cont d
 Barney to Big Bird: The Origin of Birds Caudipteryx The fuzzy raptor The discovery of feathered dinosaurs in Liaoning, China, has excited the many paleontologists who suspected a direct link between dinosaurs
Barney to Big Bird: The Origin of Birds Caudipteryx The fuzzy raptor The discovery of feathered dinosaurs in Liaoning, China, has excited the many paleontologists who suspected a direct link between dinosaurs
What is a dinosaur? Reading Practice
 Reading Practice What is a dinosaur? A. Although the name dinosaur is derived from the Greek for "terrible lizard", dinosaurs were not, in fact, lizards at all. Like lizards, dinosaurs are included in
Reading Practice What is a dinosaur? A. Although the name dinosaur is derived from the Greek for "terrible lizard", dinosaurs were not, in fact, lizards at all. Like lizards, dinosaurs are included in
When a species can t stand the heat
 When a species can t stand the heat Featured scientists: Kristine Grayson from University of Richmond, Nicola Mitchell from University of Western Australia, & Nicola Nelson from Victoria University of
When a species can t stand the heat Featured scientists: Kristine Grayson from University of Richmond, Nicola Mitchell from University of Western Australia, & Nicola Nelson from Victoria University of
Definition of Homologous Synteny Blocks (HSBs)
 Definition of Homologous Synteny Blocks (HSBs) The gene mapping data were derived from the following publications: mouse and rat GRIMM synteny blocks (Bourque et al. 2004), cat radiation hybrid map (Menotti-
Definition of Homologous Synteny Blocks (HSBs) The gene mapping data were derived from the following publications: mouse and rat GRIMM synteny blocks (Bourque et al. 2004), cat radiation hybrid map (Menotti-
d. Wrist bones. Pacific salmon life cycle. Atlantic salmon (different genus) can spawn more than once.
 Lecture III.5b Answers to HW 1. (2 pts). Tiktaalik bridges the gap between fish and tetrapods by virtue of possessing which of the following? a. Humerus. b. Radius. c. Ulna. d. Wrist bones. 2. (2 pts)
Lecture III.5b Answers to HW 1. (2 pts). Tiktaalik bridges the gap between fish and tetrapods by virtue of possessing which of the following? a. Humerus. b. Radius. c. Ulna. d. Wrist bones. 2. (2 pts)
Evolution. Evolution is change in organisms over time. Evolution does not have a goal; it is often shaped by natural selection (see below).
 Evolution Evolution is change in organisms over time. Evolution does not have a goal; it is often shaped by natural selection (see below). Species an interbreeding population of organisms that can produce
Evolution Evolution is change in organisms over time. Evolution does not have a goal; it is often shaped by natural selection (see below). Species an interbreeding population of organisms that can produce
Unit 7: Adaptation STUDY GUIDE Name: SCORE:
 Unit 7: Adaptation STUDY GUIDE Name: SCORE: 1. Which is an adaptation that makes it possible for the animal to survive in a cold climate? A. tail on a lizard B. scales on a fish C. stripes on a tiger D.
Unit 7: Adaptation STUDY GUIDE Name: SCORE: 1. Which is an adaptation that makes it possible for the animal to survive in a cold climate? A. tail on a lizard B. scales on a fish C. stripes on a tiger D.
In North America 1. the Triassic is represented by the thick Newark Group along the east coast, 2. by widespread red-bed and fluvial sediments in the
 The Triassic System The name Triassic derives from the three parts into which the Triassic is divided on the European platform: 3. Keuper (highest) 2. Muschelkalk 1. Bunter (lowest) In North America 1.
The Triassic System The name Triassic derives from the three parts into which the Triassic is divided on the European platform: 3. Keuper (highest) 2. Muschelkalk 1. Bunter (lowest) In North America 1.
Ch 34: Vertebrate Objective Questions & Diagrams
 Ch 34: Vertebrate Objective Questions & Diagrams Invertebrate Chordates and the Origin of Vertebrates 1. Distinguish between the two subgroups of deuterostomes. 2. Describe the four unique characteristics
Ch 34: Vertebrate Objective Questions & Diagrams Invertebrate Chordates and the Origin of Vertebrates 1. Distinguish between the two subgroups of deuterostomes. 2. Describe the four unique characteristics
Deakin et al. BMC Genomics (2016) 17:447 DOI /s
 Deakin et al. BMC Genomics (2016) 17:447 DOI 10.1186/s12864-016-2774-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Anchoring genome sequence to chromosomes of the central bearded dragon (Pogona vitticeps) enables reconstruction
Deakin et al. BMC Genomics (2016) 17:447 DOI 10.1186/s12864-016-2774-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Anchoring genome sequence to chromosomes of the central bearded dragon (Pogona vitticeps) enables reconstruction
These small issues are easily addressed by small changes in wording, and should in no way delay publication of this first- rate paper.
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): This paper reports on a highly significant discovery and associated analysis that are likely to be of broad interest to the scientific community.
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): This paper reports on a highly significant discovery and associated analysis that are likely to be of broad interest to the scientific community.
PHYSICAL MAP OF THE AUSTRALIAN CENTRAL BEARDED DRAGON. (Pogona vitticeps) AND COMPARATIVE MAPPING AMONG DRAGONS. (Squamata, Agamidae) AND AMNIOTES
 PHYSICAL MAP OF THE AUSTRALIAN CENTRAL BEARDED DRAGON (Pogona vitticeps) AND COMPARATIVE MAPPING AMONG DRAGONS (Squamata, Agamidae) AND AMNIOTES By MATTHEW JOHN YOUNG B. Environmental Science Institute
PHYSICAL MAP OF THE AUSTRALIAN CENTRAL BEARDED DRAGON (Pogona vitticeps) AND COMPARATIVE MAPPING AMONG DRAGONS (Squamata, Agamidae) AND AMNIOTES By MATTHEW JOHN YOUNG B. Environmental Science Institute
Get the other MEGA courses!
 www.thesimplehomeschool.com Simple Schooling BUGS MEGA course is ten weeks of all about bugs! This course grabs your student s attention and never lets go! Grades K-3 Get the other MEGA courses! Simple
www.thesimplehomeschool.com Simple Schooling BUGS MEGA course is ten weeks of all about bugs! This course grabs your student s attention and never lets go! Grades K-3 Get the other MEGA courses! Simple
KINGDOM ANIMALIA Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Class Reptilia
 KINGDOM ANIMALIA Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Class Reptilia Vertebrate Classes Reptiles are the evolutionary base for the rest of the tetrapods. Early divergence of mammals from reptilian ancestor.
KINGDOM ANIMALIA Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Class Reptilia Vertebrate Classes Reptiles are the evolutionary base for the rest of the tetrapods. Early divergence of mammals from reptilian ancestor.
Interpreting Evolutionary Trees Honors Integrated Science 4 Name Per.
 Interpreting Evolutionary Trees Honors Integrated Science 4 Name Per. Introduction Imagine a single diagram representing the evolutionary relationships between everything that has ever lived. If life evolved
Interpreting Evolutionary Trees Honors Integrated Science 4 Name Per. Introduction Imagine a single diagram representing the evolutionary relationships between everything that has ever lived. If life evolved
Anatomy. Name Section. The Vertebrate Skeleton
 Name Section Anatomy The Vertebrate Skeleton Vertebrate paleontologists get most of their knowledge about past organisms from skeletal remains. Skeletons are useful for gleaning information about an organism
Name Section Anatomy The Vertebrate Skeleton Vertebrate paleontologists get most of their knowledge about past organisms from skeletal remains. Skeletons are useful for gleaning information about an organism
From Reptiles to Aves
 First Vertebrates From Reptiles to Aves Evolutions of Fish to Amphibians Evolution of Amphibians to Reptiles Evolution of Reptiles to Dinosaurs to Birds Common Ancestor of Birds and Reptiles: Thecodonts
First Vertebrates From Reptiles to Aves Evolutions of Fish to Amphibians Evolution of Amphibians to Reptiles Evolution of Reptiles to Dinosaurs to Birds Common Ancestor of Birds and Reptiles: Thecodonts
Welcome to Darwin Day!
 Welcome to Darwin Day! Considered to be the father of evolutionary ideas Sailed upon the HMS Beagle for 5 years around the world Gathered data and specimens from South America Galapagos Islands, as well
Welcome to Darwin Day! Considered to be the father of evolutionary ideas Sailed upon the HMS Beagle for 5 years around the world Gathered data and specimens from South America Galapagos Islands, as well
TAXONOMIC HIERARCHY. science of classification and naming of organisms
 TAXONOMIC HIERARCHY Taxonomy - science of classification and naming of organisms Taxonomic Level Kingdom Phylum subphylum Class subclass superorder Order Family Genus Species Example Animalae Chordata
TAXONOMIC HIERARCHY Taxonomy - science of classification and naming of organisms Taxonomic Level Kingdom Phylum subphylum Class subclass superorder Order Family Genus Species Example Animalae Chordata
13. Swim bladder function: A. What happens to the density of a fish if the volume of its swim bladder increases?
 Ch 11 Review - Use this worksheet as practice and as an addition to your Chapter 11 Study Guide. Test will only be over Ch 11.1-11.4. (Ch 11.5 Fossil and Paleontology section will not be on your test)
Ch 11 Review - Use this worksheet as practice and as an addition to your Chapter 11 Study Guide. Test will only be over Ch 11.1-11.4. (Ch 11.5 Fossil and Paleontology section will not be on your test)
From Slime to Scales: Evolution of Reptiles. Review: Disadvantages of Being an Amphibian
 From Slime to Scales: Evolution of Reptiles Review: Disadvantages of Being an Amphibian Gelatinous eggs of amphibians cannot survive out of water, so amphibians are limited in terms of the environments
From Slime to Scales: Evolution of Reptiles Review: Disadvantages of Being an Amphibian Gelatinous eggs of amphibians cannot survive out of water, so amphibians are limited in terms of the environments
