OCTOBER 2017 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN
|
|
|
- Elvin Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OCTOBER 2017 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement. The recommendations were developed using a systematic approach and are suppted by the scientific literature and the knowledge and experience of Quebec clinicians and experts. F me details, go to inesss.qc.ca. GENERAL INFORMATION IMPORTANT CONSIDERATIONS Cellulitis can be observed on all skin surfaces, but most cases are found on the legs. Cellulitis is typically caused by β-hemolytic streptococci Staphylococcus aureus, although a pathogen is isolated in less than 20 % of cases. The following risk facts f developing cellulitis may be found in children : Injury Skin problem (e.g., eczema, chickenpox, ingrown nail, tinea pedis, etc.) Immunosuppression Uncrected dental problem DIAGNOSIS SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS Cellulitis diagnosis is generally characterized by the acute appearance of a continuous erythematous area (without an area of healthy skin inside) that s edematous, warm and painful. The patient may also have systemic symptoms (fever, nausea, vomiting, chills, malaise, lack of appetite). Cellulitis generally does not cause any epidermal changes (scales, scabs, vesicles, etc.). If such changes are present, suspect a different related pathology (e.g., eczema, chickenpox, etc.). CLINICAL ASSESSMENT CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN Photos available to help with diagnosis Assess the general condition of the patient. Palpate the affected area to assess skin sensitivity, the depth of infection, tissue firmness and the presence of a fluctuant area. Determine the source of the infection. A dental, sinusal ophthalmic igin should always be suspected and investigated during the initial diagnosis of cervicofacial cellulitis. Look f the presence of special circumstances suggesting different pathogens. Make a differential diagnosis befe confirming the cellulitis diagnosis. Mark the outline photograph the infected area to follow its evolution. Stay up to date at inesss.qc.ca CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN
2 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Photos available to help with differential diagnosis General Stay up to date at inesss.qc.ca CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN Contact dermatitis : An edema that is often itchy, non-painful and afebrile. Presence of scaling microvesicles that can merge to fm bubbles. The shape of the affected area is very well defined and matches the point of contact. Acute eczema : An erythema that is often edematous, frequently observed in cases of allergic contact dermatitis and interspersed with very tight fmations of micropapules and/ superficial microvesicles. Insect bite : Edema and erythema with a central point. Itchy, afebrile, not very painful painless and sometimes accompanied by a vesicle a min subcutaneous ecchymosis. Cutaneous herpes shingles : Presence of vesicles a few millimetres in size grouped on an erythematous base. Shingles involves dermatomal distribution. Redness located in the upper and lower limbs Septic arthritis : Localized erythema on a joint with pain occurring during mobilization. Acute bursitis : Localized erythema around a joint. Vaccine reaction : Often occurs within the first 24 hours after vaccination. The absence of fever and the patient s good overall condition point to a vaccine reaction. The pain is often min compared to the extent of the erythematous zone. Redness located in the face Conjunctivitis : In some cases, manifests with a slight non-painful and afebrile palpebral peribital edema accompanied by purulent secretions. Often bilateral. Dacryocystitis : Localized edema and erythema in the internal angle (between the eye and nose) and often accompanied by tearing. Cold panniculitis : Circular induration with loss of sensation, usually localized on the cheeks and occurring after a few minutes of exposure to icy and windy weather. Other skin diseases Erythema migrans, erythema nodosum, acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis (Sweet syndrome), etc. : Erythema separated by areas of healthy skin ring-shaped erythema. Animal bite (cat dog) SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES Human bite (including injuries caused by contact with another person s teeth during a fight) Cellulitis of dental igin Peribital/bital cellulitis of sinusal igin Injury while immersed in water Neutropenic patient Main pathogens to suspect in addition to β-hemolytic streptococci and S. aureus Pasteurella multocida, Capnocytophaga spp. Viridans streptococci Buccal anaerobes (Fusobacterium, peptostreptococci) Eikenella crodens Viridans streptococci Buccal anaerobes (Fusobacterium, peptostreptococci) Viridans streptococci Buccal anaerobes (Fusobacterium, peptostreptococci) Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Aeromonas hydrophila (freshwater) Vibrio spp. (saltwater) Pseudomonas aeruginosa Fungal pathogens Cellulitis is rarely caused by methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). Meover, in Québec, these resistant strains are isolated in only 10 % of cases of purulent skin infections caused by S. aureus (2015). Community-associated MRSA should be suspected in the presence of an abscess and one of the following elements : Previous infection/colonization (in the patient their family) Recurrent furunculosis abscess Patient belongs to an Abiginal community Microbiological tests on skin samples (culture and antibiotic sensitivity) are recommended only in cases of cellulitis with purulent discharge.
3 SEVERITY The severity of the infection is assessed by clinical judgment and guides the choice of the antibiotic treatment s route of administration. If necessary, consult a specialist. Stay up to date at inesss.qc.ca CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN! WARNING SIGNS IN-HOSPITAL CONSULTATION GENERALLY REQUIRED General Impairment of general condition (persistent fever) Hemodynamic impairment Child < 3 months old Pain disproptionate to clinical signs! Rapid progression Vesicles with hemrhagic content Signs of dyspnea dysphagia (cervicofacial cellulitis) Significant edema/erythema of the external audity canal and auricle Suspected joint Suspected osteomyelitis Failure of antibiotic treatment after 72 hours Careful; when this symptom is present, suspect necrotizing fasciitis. TREATMENT PRINCIPLES Suspected bital Fever Severe pain Limited painful extraocular movements Difficulty inability to open eye Chemosis Proptosis Impaired vision Special circumstances Immunosuppressed patient Significant inflammation following the bite of an animal besides a cat dog Injury while immersed in water Treating the primary source of infection, when it can be identified, is essential in managing cellulitis : Treating the dental problem, wound sinusitis, excising the feign body, etc. Treating the associated risk facts (e.g., eczema, ingrown nail, tinea pedis, etc.). When there is an abscess, incision and drainage are essential aspects of initial treatment. In such cases, an antibiotic treatment can sometimes be added depending on the clinical context. Systemic antibiotic treatment is used to treat cellulitis. Topical antibiotic treatment is not indicated f this type of infection and provides no additional benefit.! In case of recurrent cellulitis, consider referring the patient to a specialized setting f a me in-depth assessment (diagnosis, source of infection, treatment). SUPPORTIVE TREATMENT Elevating the affected limb promotes the drainage of the edema by gravity. To relieve pain, you may consider adding an analgesic/antipyretic (acetaminophen ibuprofen*) to the antibiotic treatment. When a traumatic wound (including bites) is present, it is imptant to check the patient s tetanus vaccination schedule and consider rabies vaccination. F me infmation, refer to the protocole d immunisation du Québec (PIQ). F me infmation on human bites in childcare settings, refer to the Canadian Pediatric Society s position statement. * Ibuprofen is not recommended f children under 6 months of age. HISTORY OF ALLERGIC REACTION TO A PENICILLIN ANTIBIOTIC True penicillin allergy is uncommon. F 100 children with a histy of penicillin allergy, fewer than 6 will be CONFIRMED to have a true diagnosis of allergy and most of the reactions will be delayed non-severe rashes. It is therefe imptant to carefully assess the allergy status of a patient who repts a histy of allergic reaction to penicillins befe considering using alternatives to beta-lactams. F help, consult the decision-making tool in cases of allergy to penicillins.
4 Stay up to date at inesss.qc.ca CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN ANTIBIOTIC TREATMENT In vitro resistance of methicillin-sensitive S. aureus to clindamycin is about 25 % in Québec (2015). Response to this treatment should therefe be closely monited. If necessary, adjust the antibiotic treatment based on the results of culture and antibiotic sensitivity tests, when available. Persistence slight progression of redness may be observed within the first 24 to 48 hours despite proper treatment. In that case, decreased pain and a general improvement in the patient s condition are usually observed. During intravenous treatment, al relay should be considered when: The patient is afebrile after 48 hours of treatment. The infected area does not expand decreases. The diagnosis is well established and the patient is able to tolerate al treatment. Oral administration 1 If histy of allergic reaction to a penicillin antibiotic CELLULITIS WITH STRONG SUSPICION OF STREPTOCOCCI OR S. AUREUS Total recommended duration of treatment : 7 to 10 days Antibiotic Daily dosage Maximum dosage Cephalexin mg/kg/day PO TID mg / day Cefadroxil 2 30 mg/kg/day PO BID mg / day Cloxacillin mg/kg/day PO QID mg / day Click here to view the cellulitis with strong suspicion of streptococci S. aureus algithm f help in choosing an al antibiotic therapy Intravenous administration 4 Cefazolin mg/kg/day IV TID mg / day If histy of allergic reaction to a penicillin antibiotic Cloxacillin mg/kg/day IV QID mg / day Click here to view the cellulitis with strong suspicion of streptococci S. aureus algithm f help in choosing an intravenous antibiotic therapy Follow-up should be perfmed within 24 to 72 hours depending on the severity of the infection, the clinical evolution and the clinician s judgment. 1. Amoxicillin/clavulanate (45 60 mg/kg/day PO TID; maximum mg/day) may be a valid alternative when other treatment options cannot be used. In that case, the 7:1 fmulation (200 mg / 5 ml 400 mg / 5 ml) is preferred due to its higher digestive tolerance. 2. The pediatric suspension of cefadroxil is not marketed in Canada. 3. Cloxacillin as an al suspension is not widely used due to its unpleasant taste and interaction with food. 4. Ceftriaxone (50 75 mg/kg/day IV daily BID; maximum mg/day) may be a valid alternative when other treatment options cannot be used.
5 CELLULITIS ASSOCIATED WITH A COMMON ANIMAL BITE (CAT OR DOG) OR A HUMAN BITE 1 Total recommended duration of treatment : 7 to 10 days Antibiotic Daily dosage Maximum dosage Stay up to date at inesss.qc.ca CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN Oral administration Amoxicillin/Clavulanate mg/kg/day PO TID mg / day If histy of allergic reaction to a penicillin antibiotic Click here to view the cellulitis associated with a common animal bite a human bite algithm f help in choosing an antibiotic therapy It s imptant to check f tendon, bone joint. If there is, and f any other complicated case, consult a specialist refer the patient to a hospital. Usually, follow-up should be perfmed within 24 to 72 hours. However, follow-up within a maximum of 24 hours should be perfmed in cases involving a bite to the hand face. In cases involving a human bite that broke the skin, patient management in infectiology should be considered, when available, to assess the need f prophylaxis and follow-up f HIV, hepatitis B and hepatitis C. Early antibiotic prophylaxis lasting 3 to 5 days is recommended f : All cases of cat bite Dog bites in an asplenic immunosuppressed patient, in a patient with edema in the affected area a moderate severe injury (especially to the hand, face genitals) one that may have breached the periosteum joint capsule. CELLULITIS OF DENTAL ORIGIN Total recommended duration of treatment : 7 to 10 days Antibiotic Daily dosage Maximum dosage Oral administration Amoxicillin/Clavulanate mg/kg/day PO TID mg / day If histy of allergic reaction to a penicillin antibiotic Click here therapy to view the cellulitis of dental igin algithm f help in choosing an antibiotic When faced with an uncrected dental problem, a consultation with a dentist a maxillofacial specialist should be considered. It is essential to treat the dental source of these infections. In children, these infections can cause rapid deteriation of the patient s general condition. Perfm follow-up within 24 hours and consider treating the patient under observation in a hospital setting. In the absence of response to treatment and in me severe cases, consult a specialist refer the patient to a hospital. SIMPLE PERIORBITAL CELLULITIS OF SINUSAL ORIGIN 3 (If the skin is broken, treat like cellulitis with strong suspicion of streptococci S. aureus) Minimum total recommended duration of treatment : 10 to 14 days Antibiotic Daily dosage Maximum dosage Oral administration Amoxicillin/Clavulanate 2,4 90 mg/kg/daypo TID mg / day If histy of allergic reaction to a penicillin antibiotic Click here to view the simple peribital cellulitis of sinusal igin algithm f help in choosing an antibiotic therapy! Only simple cases of peribital cellulitis should be treated in the primary care setting. These are characterized by mild edema and erythema, the absence of severe pain, good eyelid opening, nmal and non-painful extraocular movements, nmal vision, the absence of proptosis and chemosis, and the patient being in good overall condition.! Follow-up on the evolution of these infections should be perfmed within 24 hours. In the absence of response to treatment, if bital is suspected, consult a specialist refer the patient to a hospital. 1. Including injuries caused by contact with another person s teeth during a fight. 2. The 7:1 fmulation (200 mg / 5 ml 400 mg / 5 ml) is preferred due to its higher digestive tolerance. 3. F the recommended supptive treatments to relieve sinus symptoms, see INESSS s optimal usage guide on acute rhinosinusitis. 4. Some clinicians use a combination of amoxicillin (45 mg/kg/day) and amoxicillin/clavulanate (7:1 fmulation) (45 mg/kg/day) to reduce adverse effects (total of 90 mg/kg/day, 14:1 equivalent). The quantities of amoxicillin and amoxicillin/clavulanate (ml) may be different.
6 CELLULITIS WITH SUSPICION OF CA-MRSA CELLULITIS IN CHILDREN Total recommended duration of treatment : 7 to 10 days Oral administration Intravenous administration Antibiotic Daily dosage Maximum dosage TMP/SMX1,2 TMP component : 8-12 mg/kg/day PO BID 320 mg of TMP / day Doxycycline1 (Child 8 years old) 20 to 25 kg : mg PO BID 25 to 40 kg : mg PO BID > 40 kg : 100 mg BID 200 mg / day Vancomycin3 60 mg/kg/day IV QID mg / day Follow-up should be perfmed within 24 to 72 hours depending on the severity of the infection, the clinical evolution and the clinician s judgment. 1. Note that doxycycline and TMP/SMX do not offer very good coverage against group A streptococcus. 2. TMP/SMX has not been approved by Health Canada f the treatment of cellulitis. However, it is frequently prescribed f this purpose, and experts agree that this antibiotic is an acceptable treatment option when CA-MRSA is suspected. 3. If necessary, consult a specialist f alternative treatment options to vancomycin. MAIN REFERENCES Health Prince Edward Island. Provincial Antibiotic Advisy Team Skin & Soft Tissue Infection Empiric Treatment Guidelines, Health PEI Liu, C. et al. Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America f the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2011; 52(3):e Nassisi, D. and Oishi, M. L. Evidence-based guidelines f evaluation and antimicrobial therapy f common emergency department infections. Emergency Medicine Practice 2012; 14(1):1 28. Stevens, D. L. et al. Practice guidelines f the diagnosis and management of skin and soft tissue infections: 2014 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2014; 59(2):e Wilson, L. and Caglar, D. Cellulitis and Abscess. Seattle Children s Hospital Stay up to date at inesss.qc.ca Please note that other references have been consulted. Any reproduction of this document in whole in part f non-commercial use is permitted on condition that the source is mentioned.
7 CELLULITIS WITH STRONG SUSPICION OF STREPTOCOCCI OR S. AUREUS IN CHILDREN ORAL ADMINISTRATION SEVERITY OF PREVIOUS ALLERGIC REACTION TO PENICILLIN ANTIBIOTICS F dosages see next page ASSESS THE SEVERITY OF THE INITIAL REACTION Vague histy Unconvincing histy repted by patient family Non-severe reaction 1 (urticaria and/ angioedema) (Rash and/ urticaria and/ angioedema) Severe reaction Anaphylaxis 4 Severe skin reaction (desquamation, pustules, vesicles, purpura with fever joint pain, but no DRESS, SJS/TEN AGEP) Serum sickness 3 Penicillin allergy CONFIRMED 5 Very severe reaction Anaphylactic shock (with without intubation) Hemolytic anemia Kidney damage Liver damage DRESS, SJS/TEN, AGEP (severe non-severe reaction only) THE FOLLOWING CAN BE PRESCRIBED SAFELY PRESCRIBE THE FOLLOWING WITH CAUTION AVOID PRESCRIBING SIMILAR cephalospins SIMILAR cephalospins Beta-lactams 6 Cephalexin OR Cefadroxil if histy of allergy does not suggest an immediate reaction Cephalexin OR Cefadroxil ONLY if serum sickness-like reactions occurred in childhood 3. Choose another class of antibiotics. PRESCRIBE THE FOLLOWING and DECISION-MAKING FOR CHOOSING A BETA-LACTAM AND THE CONDITIONS OF ADMINISTRATION If in doubt about the possibility of an immediate reaction A 1-hour observation period after the administration of the 1 st dose of Cephalexin OR Cefadroxil under the supervision of a health professional may be recommended accding to the clinician judgment. PRESCRIBE THE FOLLOWING WITH CAUTION Cloxacillin 7 The 1 st dose should always be administered under medical supervision. If histy of : s, a drug provocation test should be perfmed; Delayed reactions, the patient his/her family should be infmed of the possible risk of recurrence in the days following initiation of the antibiotic. The 1 st dose should always be administered under medical supervision. If histy of : s, a drug provocation test should be perfmed; Delayed reactions, the patient his/her family should be infmed of the possible risk of recurrence in the days following initiation of the antibiotic. and AVOID PRESCRIBING Cloxacillin SIMILAR cephalospins Cephalexin OR Cefadroxil f all other clinical situations (with the exception of children with a histy of serum sickness-like reactions 3, as described above).! IF A BETA-LACTAM 6 CANNOT BE ADMINISTERED, THE FOLLOWING CAN BE PRESCRIBED... Clindamycin 1. (type I IgE-mediated) : generally occurs within 1 hour following the first dose of an antibiotic. 2. Delayed reaction (type II, III and IV) : can occur at any time, starting 1 hour following the administration of an antibiotic. 3. The delayed skin reactions and serum sickness-like reactions that appear in children receiving antibiotic therapy are generally non-allergic and can be of viral igin. 4. Anaphylaxis without shock intubation : requires increased vigilance. 5. With no recommendations concerning other beta-lactams. 6., cephalospins and carbapenems. 7. Amoxicillin/Clavulanate may be a valid alternative when other treatment options cannot be used. F further infmation, see the interactive tool and the decision-making tool. AGEP : acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis; DRESS : drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms; SJS : Stevens Johnson syndrome; TEN : toxic epidermal necrolysis. Clindamycin
8 CELLULITIS WITH STRONG SUSPICION OF STREPTOCOCCI OR S. AUREUS IN CHILDREN ORAL ADMINISTRATION FIRST-LINE ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY FOR CELLULITIS WITH STRONG SUSPICION OF STREPTOCOCCI OR S. AUREUS IF HISTORY OF ALLERGIC REACTION TO A PENICILLIN ANTIBIOTIC Antibiotic Daily dosage Maximum dosage Recommended duration Beta-lactams recommended, accding to the clinical judgment suppt algithm 1 Cephalexin mg/kg/day PO TID mg / day Cefadroxil 2 30 mg/kg/day PO BID mg / day Cloxacillin mg/kg/day PO QID mg / day 7 to 10 days Alternative if a beta-lactam cannot be administered Clindamycin 4,5, mg/kg/day PO TID mg / day 1. Amoxicillin/clavulanate (45 60 mg/kg/day PO TID; maximum mg/day) may be a valid alternative when other treatment options cannot be used. In that case, the 7:1 fmulation (200 mg / 5 ml 400 mg / 5 ml) is preferred due to its higher digestive tolerance. 2. The pediatric suspension of cefadroxil is not marketed in Canada. 3. Cloxacillin as an al suspension is not widely used due to its unpleasant taste and interaction with food. 4. Taking this antibiotic can cause diarrhea and intestinal symptoms that may wsen and require consultation. It is imptant to infm the patient of this. 5. Clindamycin in suspension tastes bad. Consult a pharmacist f ways to improve the taste of this drug. 6. If necessary, consult a specialist f alternatives to clindamycin. Back to the optimal usage guide
9 CELLULITIS WITH STRONG SUSPICION OF STREPTOCOCCI OR S. AUREUS IN CHILDREN INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION SEVERITY OF PREVIOUS ALLERGIC REACTION TO PENICILLIN ANTIBIOTICS F dosages see next page ASSESS THE SEVERITY OF THE INITIAL REACTION Vague histy Unconvincing histy repted by patient family Non-severe reaction 1 (urticaria and/ angioedema) (Rash and/ urticaria and/ angioedema) Severe reaction Anaphylaxis 4 Severe skin reaction (desquamation, pustules, vesicles, purpura with fever joint pain, but no DRESS, SJS/TEN AGEP) Serum sickness 3 Penicillin allergy CONFIRMED 5 Very severe reaction Anaphylactic shock (with without intubation) Hemolytic anemia Kidney damage Liver damage DRESS, SJS/TEN, AGEP (severe non-severe reaction only) THE FOLLOWING CAN BE PRESCRIBED SAFELY DISSIMILAR cephalospins PRESCRIBE THE FOLLOWING WITH CAUTION DISSIMILAR cephalospins AVOID PRESCRIBING Beta-lactams 6 DECISION-MAKING FOR CHOOSING A BETA-LACTAM AND THE CONDITIONS OF ADMINISTRATION Cefazolin 7 PRESCRIBE THE FOLLOWING WITH CAUTION Cloxacillin The 1 st dose should always be administered under medical supervision. If histy of : s, a drug provocation test should be perfmed; Delayed reactions, the patient his/her family should be infmed of the possible risk of recurrence in the days following initiation of the antibiotic. Cefazolin 7 The 1 st dose should always be administered under medical supervision. If histy of : s, a drug provocation test should be perfmed; Delayed reactions, the patient his/her family should be infmed of the possible risk of recurrence in the days following initiation of the antibiotic. Clindamycin AVOID PRESCRIBING and Cloxacillin! IF A BETA-LACTAM 6 CANNOT BE ADMINISTERED, THE FOLLOWING CAN BE PRESCRIBED... Choose another class of antibiotics. PRESCRIBE THE FOLLOWING Clindamycin 1. (type I IgE-mediated) : generally occurs within 1 hour following the first dose of an antibiotic. 2. Delayed reaction (type II, III and IV) : can occur at any time, starting 1 hour following the administration of an antibiotic. 3. The delayed skin reactions and serum sickness-like reactions that appear in children receiving antibiotic therapy are generally non-allergic and can be of viral igin. 4. Anaphylaxis without shock intubation : requires increased vigilance. 5. With no recommendations concerning other beta-lactams. 6., cephalospins and carbapenems. 7. Ceftriaxone (50 75 mg/kg/day IV daily BID; maximum mg/day) may be a valid alternative when other treatment options cannot be used. F further infmation, see the interactive tool and the decision-making tool. AGEP : acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis; DRESS : drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms; SJS : Stevens Johnson syndrome; TEN : toxic epidermal necrolysis. and
10 CELLULITIS WITH STRONG SUSPICION OF STREPTOCOCCI OR S. AUREUS IN CHILDREN INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION FIRST-LINE ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY FOR CELLULITIS WITH STRONG SUSPICION OF STREPTOCOCCI OR S. AUREUS IF HISTORY OF ALLERGIC REACTION TO A PENICILLIN ANTIBIOTIC Antibiotic 1 Daily dosage Maximum dosage Recommended duration Beta-lactams recommended, accding to the clinical judgment suppt algithm 2 Cefazolin mg/kg/day IV TID mg / day Cloxacillin mg/kg/day IV QID mg / day 7 to 10 days Alternative if a beta-lactam cannot be administered Clindamycin 3,4 40 mg/kg/day IV TID mg / day 1. Antibiotics are usually listed in alphabetical der using their generic name. 2. Ceftriaxone (50 75 mg/kg/day IV daily BID; maximum mg/day) may be a valid alternative when other treatment options cannot be used. 3. Taking this antibiotic can cause diarrhea and intestinal symptoms that may wsen and require consultation. It is imptant to infm the patient of this. 4. If necessary, consult a specialist f alternatives to clindamycin. Back to the optimal usage guide
11 F dosages see next page CELLULITIS ASSOCIATED WITH A COMMON ANIMAL BITE (CAT OR DOG) OR A HUMAN BITE* IN CHILDREN * Including injuries caused by contact with another person s teeth during a fight. SEVERITY OF PREVIOUS ALLERGIC REACTION TO PENICILLIN ANTIBIOTICS ASSESS THE SEVERITY OF THE INITIAL REACTION Vague histy Unconvincing histy repted by patient family Non-severe reaction 1 (urticaria and/ angioedema) (Rash and/ urticaria and/ angioedema) Severe reaction Anaphylaxis 4 Severe skin reaction (desquamation, pustules, vesicles, purpura with fever joint pain, but no DRESS, SJS/TEN AGEP) Serum sickness 3 Penicillin allergy CONFIRMED 5 Very severe reaction Anaphylactic shock (with without intubation) Hemolytic anemia Kidney damage Liver damage DRESS, SJS/TEN, AGEP (severe non-severe reaction only) PRESCRIBE THE FOLLOWING WITH CAUTION AVOID PRESCRIBING DECISION-MAKING FOR CHOOSING A BETA-LACTAM AND THE CONDITIONS OF ADMINISTRATION Amoxicillin/Clavulanate The 1 st dose should always be administered under medical supervision. If histy of : s, a drug provocation test should be perfmed; Delayed reactions, the patient his/her family should be infmed of the possible risk of recurrence in the days following initiation of the antibiotic. Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Choose another class of antibiotics. Clindamycin + TMP/SMX OR Doxycycline (child 8 years old) 1. (type I IgE-mediated) : generally occurs within 1 hour following the first dose of an antibiotic. 2. Delayed reaction (type II, III and IV) : can occur at any time, starting 1 hour following the administration of an antibiotic. 3. The delayed skin reactions and serum sickness-like reactions that appear in children receiving antibiotic therapy are generally non-allergic and can be of viral igin. 4. Anaphylaxis without shock intubation : requires increased vigilance. 5. With no recommendations concerning other beta-lactams (penicillins, cephalospins and carbapenems). PRESCRIBE THE FOLLOWING F further infmation, see the interactive tool and the decision-making tool. AGEP : acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis; DRESS : drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms; SJS : Stevens Johnson syndrome; TEN : toxic epidermal necrolysis. and
12 CELLULITIS ASSOCIATED WITH A COMMON ANIMAL BITE (CAT OR DOG) OR A HUMAN BITE* IN CHILDREN * Including injuries caused by contact with another person s teeth during a fight. FIRST-LINE ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY FOR CELLULITIS ASSOCIATED WITH A COMMON ANIMAL BITE (CAT OR DOG) OR A HUMAN BITE IF HISTORY OF ALLERGIC REACTION TO A PENICILLIN ANTIBIOTIC Beta-lactams recommended, accding to the clinical judgment suppt algithm Antibiotic 1 Daily dosage Maximum dosage Amoxicillin/ Clavulanate mg/kg/day PO TID mg / day Recommended duration Alternative if a beta-lactam cannot be administered Clindamycin 3,4 + TMP/SMX 5 Doxycycline (Child 8 years old) mg/kg/day PO TID TMP component : 8-12 mg/kg/day PO BID 20 to 25 kg : mg PO BID 25 to 40 kg : mg PO BID > 40 kg : 100 mg BID mg / day 320 mg de TMP / day 200 mg / day 7 to 10 days 1. Antibiotics are usually listed in alphabetical der using their generic name. 2. The 7:1 fmulation (200 mg / 5 ml 400 mg / 5 ml) is preferred due to its higher digestive tolerance. 3. Taking this antibiotic can cause diarrhea and intestinal symptoms that may wsen and require consultation. It is imptant to infm the patient of this. 4. Clindamycin in suspension tastes bad. Consult a pharmacist f ways to improve the taste of this drug. 5. TMP/SMX has not been approved by Health Canada f the treatment of cellulitis. However, it is frequently prescribed f this purpose, and experts agree that this antibiotic is an acceptable treatment option in combination with clindamycin in bite cases in young children. Back to the optimal usage guide
13 F dosages see next page CELLULITIS OF DENTAL ORIGIN IN CHILDREN SEVERITY OF PREVIOUS ALLERGIC REACTION TO PENICILLIN ANTIBIOTICS ASSESS THE SEVERITY OF THE INITIAL REACTION Vague histy Unconvincing histy repted by patient family Non-severe reaction 1 (urticaria and/ angioedema) (Rash and/ urticaria and/ angioedema) Severe reaction Anaphylaxis 4 Severe skin reaction (desquamation, pustules, vesicles, purpura with fever joint pain, but no DRESS, SJS/TEN AGEP) Serum sickness 3 Penicillin allergy CONFIRMED 5 Very severe reaction Anaphylactic shock (with without intubation) Hemolytic anemia Kidney damage Liver damage DRESS, SJS/TEN, AGEP (severe non-severe reaction only) PRESCRIBE THE FOLLOWING WITH CAUTION AVOID PRESCRIBING DECISION-MAKING FOR CHOOSING A BETA-LACTAM AND THE CONDITIONS OF ADMINISTRATION Amoxicillin/Clavulanate The 1 st dose should always be administered under medical supervision. If histy of : s, a drug provocation test should be perfmed; Delayed reactions, the patient his/her family should be infmed of the possible risk of recurrence in the days following initiation of the antibiotic. Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Choose another class of antibiotics. Clindamycin 1. (type I IgE-mediated) : generally occurs within 1 hour following the first dose of an antibiotic. 2. Delayed reaction (type II, III and IV) : can occur at any time, starting 1 hour following the administration of an antibiotic. 3. The delayed skin reactions and serum sickness-like reactions that appear in children receiving antibiotic therapy are generally non-allergic and can be of viral igin. 4. Anaphylaxis without shock intubation : requires increased vigilance. 5. With no recommendations concerning other beta-lactams (penicillins, cephalospins and carbapenems). PRESCRIBE THE FOLLOWING F further infmation, see the interactive tool and the decision-making tool. AGEP : acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis; DRESS : drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms; SJS : Stevens Johnson syndrome; TEN : toxic epidermal necrolysis. and
14 CELLULITIS OF DENTAL ORIGIN IN CHILDREN FIRST-LINE ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY FOR CELLULITIS OF DENTAL ORIGIN IF HISTORY OF ALLERGIC REACTION TO A PENICILLIN ANTIBIOTIC Beta-lactams recommended, accding to the clinical judgment suppt algithm Alternative if a beta-lactam cannot be administered Antibiotic Daily dosage Maximum dosage Amoxicillin/ Clavulanate mg/kg/day PO TID mg / day Clindamycin 2,3, mg/kg/day PO TID mg / day Recommended duration 7 to 10 days 1. The 7:1 fmulation (200 mg / 5 ml 400 mg / 5 ml) is preferred due to its higher digestive tolerance. 2. Taking this antibiotic can cause diarrhea and intestinal symptoms that may wsen and require consultation. It is imptant to infm the patient of this. 3. Clindamycin in suspension tastes bad. Consult a pharmacist f ways to improve the taste of this drug. 4. If necessary, consult a specialist f alternatives to clindamycin. Back to the optimal usage guide
15 F dosages see next page SIMPLE PERIORBITAL CELLULITIS OF SINUSAL ORIGIN IN CHILDREN SEVERITY OF PREVIOUS ALLERGIC REACTION TO PENICILLIN ANTIBIOTICS ASSESS THE SEVERITY OF THE INITIAL REACTION Vague histy Unconvincing histy repted by patient family Non-severe reaction 1 (urticaria and/ angioedema) (Rash and/ urticaria and/ angioedema) Severe reaction Anaphylaxis 4 Severe skin reaction (desquamation, pustules, vesicles, purpura with fever joint pain, but no DRESS, SJS/TEN AGEP) Serum sickness 3 Penicillin allergy CONFIRMED 5 Very severe reaction Anaphylactic shock (with without intubation) Hemolytic anemia Kidney damage Liver damage DRESS, SJS/TEN, AGEP (severe non-severe reaction only) PRESCRIBE THE FOLLOWING WITH CAUTION AVOID PRESCRIBING DECISION-MAKING FOR CHOOSING A BETA-LACTAM AND THE CONDITIONS OF ADMINISTRATION Amoxicillin/Clavulanate The 1 st dose should always be administered under medical supervision. If histy of : s, a drug provocation test should be perfmed; Delayed reactions, the patient his/her family should be infmed of the possible risk of recurrence in the days following initiation of the antibiotic. Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Choose another class of antibiotics. CONSULT Refer to specialized services to learn about alternative treatment options. 1. (type I IgE-mediated) : generally occurs within 1 hour following the first dose of an antibiotic. 2. Delayed reaction (type II, III and IV) : can occur at any time, starting 1 hour following the administration of an antibiotic. 3. The delayed skin reactions and serum sickness-like reactions that appear in children receiving antibiotic therapy are generally non-allergic and can be of viral igin. 4. Anaphylaxis without shock intubation : requires increased vigilance. 5. With no recommendations concerning other beta-lactams (penicillins, cephalospins and carbapenems). F further infmation, see the interactive tool and the decision-making tool. AGEP : acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis; DRESS : drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms; SJS : Stevens Johnson syndrome; TEN : toxic epidermal necrolysis. and
16 SIMPLE PERIORBITAL CELLULITIS OF SINUSAL ORIGIN IN CHILDREN FIRST-LINE ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY FOR SIMPLE PERIORBITAL CELLULITIS OF SINUSAL ORIGIN IF HISTORY OF ALLERGIC REACTION TO A PENICILLIN ANTIBIOTIC Beta-lactams recommended, accding to the clinical judgment suppt algithm Alternative if a beta-lactam cannot be administered Antibiotic Daily dosage Maximum dosage Recommended duration Amoxicillin/ Clavulanate 1 90 mg/kg/day PO TID mg / day 10 to 14 days Seek a consultation with specialized services to learn about alternative treatment options. 1. The 7:1 fmulation (200 mg / 5 ml 400 mg / 5 ml) is preferred due to its higher digestive tolerance. Back to the optimal usage guide
ANTIBIOTICS ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA (AOM) IN CHILDREN 3 MONTHS OF AGE OR OLDER GENERAL INFORMATIONS PREVENTIVE MEASURES DIAGNOSIS
 MARCH 206 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement. The
MARCH 206 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement. The
ANTIBIOTICS. SCHOOL AGE AND ADOLESCENCE Respiratory viruses Respiratory viruses Respiratory viruses Streptococcus pneumoniae
 MARCH 2016 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
MARCH 2016 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
SEPTEMBER 2017 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA IN ADULTS
 SEPTEMBER 2017 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
SEPTEMBER 2017 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
Amoxicillin Introduction: Mechanism of action: Pharmacology: Indications: Dosage: 12 Weeks ( 3 Months):
 Amoxicillin Introduction: A semisynthetic antibiotic, an analog of ampicillin, with a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many gram-positive and gram-negative microganisms. Mechanism of action:
Amoxicillin Introduction: A semisynthetic antibiotic, an analog of ampicillin, with a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many gram-positive and gram-negative microganisms. Mechanism of action:
11/10/2016. Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. Disclosures. Educational Need/Practice Gap. Objectives. Case #1
 Disclosures Selecting Antimicrobials for Common Infections in Children FMR-Contemporary Pediatrics 11/2016 Sean McTigue, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical Director
Disclosures Selecting Antimicrobials for Common Infections in Children FMR-Contemporary Pediatrics 11/2016 Sean McTigue, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Pediatric Infectious Diseases Medical Director
Perichondritis: Source: UpToDate Ciprofloxacin 10 mg/kg/dose PO (max 500 mg/dose) BID Inpatient: Ceftazidime 50 mg/kg/dose q8 hours IV
 Empiric Antibiotics for Pediatric Infections Seen in ED NOTE: Choice of empiric antibiotic therapy must take into account local pathogen frequency and resistance patterns, individual patient characteristics,
Empiric Antibiotics for Pediatric Infections Seen in ED NOTE: Choice of empiric antibiotic therapy must take into account local pathogen frequency and resistance patterns, individual patient characteristics,
Similar to Penicillins: -Chemically. -Mechanism of action. -Toxicity.
 Similar to Penicillins: -Chemically. -Mechanism of action. -Toxicity. Cephalosporins are divided into Generations: -First generation have better activity against gram positive organisms. -Later compounds
Similar to Penicillins: -Chemically. -Mechanism of action. -Toxicity. Cephalosporins are divided into Generations: -First generation have better activity against gram positive organisms. -Later compounds
Prescribing Guidelines for Outpatient Antimicrobials in Otherwise Healthy Children
 Prescribing Guidelines for Outpatient Antimicrobials in Otherwise Healthy Children Prescribing Antimicrobials for Common Illnesses When treating common illnesses such as ear infections and strep throat,
Prescribing Guidelines for Outpatient Antimicrobials in Otherwise Healthy Children Prescribing Antimicrobials for Common Illnesses When treating common illnesses such as ear infections and strep throat,
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
Clinical Practice Standard
 Clinical Practice Standard 1-20-6-1-010 TITLE: INTRAVENOUS TO ORAL CONVERSION FOR ANTIMICROBIALS A printed copy of this document may not reflect the current, electronic version on OurNH. APPLICABILITY:
Clinical Practice Standard 1-20-6-1-010 TITLE: INTRAVENOUS TO ORAL CONVERSION FOR ANTIMICROBIALS A printed copy of this document may not reflect the current, electronic version on OurNH. APPLICABILITY:
CLINICAL USE OF BETA-LACTAMS
 CLINICAL USE OF BETA-LACTAMS Douglas Black, Pharm.D. Associate Professor School of Pharmacy University of Washington dblack@u.washington.edu WHY IS INFECTIOUS DISEASE PHARMACOTHERAPY SO CONFUSING? Microbial
CLINICAL USE OF BETA-LACTAMS Douglas Black, Pharm.D. Associate Professor School of Pharmacy University of Washington dblack@u.washington.edu WHY IS INFECTIOUS DISEASE PHARMACOTHERAPY SO CONFUSING? Microbial
Appropriate Management of Common Pediatric Infections. Blaise L. Congeni M.D. Akron Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases
 Appropriate Management of Common Pediatric Infections Blaise L. Congeni M.D. Akron Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases It s all about the microorganism The common pathogens Viruses
Appropriate Management of Common Pediatric Infections Blaise L. Congeni M.D. Akron Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases It s all about the microorganism The common pathogens Viruses
The β- Lactam Antibiotics. Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November 2018
 The β- Lactam Antibiotics Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November 2018 Penicillins. Cephalosporins. Carbapenems. Monobactams. The β- Lactam Antibiotics 2 3 How
The β- Lactam Antibiotics Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November 2018 Penicillins. Cephalosporins. Carbapenems. Monobactams. The β- Lactam Antibiotics 2 3 How
Invasive Group A Streptococcus (GAS)
 Invasive Group A Streptococcus (GAS) Cause caused by a bacterium commonly found on the skin and in the throat transmitted by direct, indirect or droplet contact with secretions from the nose, and throat
Invasive Group A Streptococcus (GAS) Cause caused by a bacterium commonly found on the skin and in the throat transmitted by direct, indirect or droplet contact with secretions from the nose, and throat
DRAFT DRAFT. Paediatric Antibiotic Prescribing Guideline. May
 Paediatric Antibiotic Prescribing Guideline www.oxfdahsn.g/children Magdalen Centre Nth, 1 Robert Robinson Avenue, Oxfd Science Park, OX4 4GA, United Kingdom t: +44(0) 1865 784944 e: info@oxfdahsn.g Follow
Paediatric Antibiotic Prescribing Guideline www.oxfdahsn.g/children Magdalen Centre Nth, 1 Robert Robinson Avenue, Oxfd Science Park, OX4 4GA, United Kingdom t: +44(0) 1865 784944 e: info@oxfdahsn.g Follow
Simplicef is Used to Treat Animals with Skin Infections
 Simplicef is Used to Treat Animals with Skin Infections PRODUCT INFO Simplicef tablets are a semi-synthetic cephalosporin antibiotic cefpodoxime proxetil used to cure infections caused by the susceptible
Simplicef is Used to Treat Animals with Skin Infections PRODUCT INFO Simplicef tablets are a semi-synthetic cephalosporin antibiotic cefpodoxime proxetil used to cure infections caused by the susceptible
Childrens Hospital Antibiogram for 2012 (Based on data from 2011)
 Childrens Hospital Antibiogram for 2012 (Based on data from 2011) Prepared by: Department of Clinical Microbiology, Health Sciences Centre For further information contact: Andrew Walkty, MD, FRCPC Medical
Childrens Hospital Antibiogram for 2012 (Based on data from 2011) Prepared by: Department of Clinical Microbiology, Health Sciences Centre For further information contact: Andrew Walkty, MD, FRCPC Medical
Approach to pediatric Antibiotics
 Approach to pediatric Antibiotics Gassem Gohal FAAP FRCPC Assistant professor of Pediatrics objectives To be familiar with common pediatric antibiotics o Classification o Action o Adverse effect To discus
Approach to pediatric Antibiotics Gassem Gohal FAAP FRCPC Assistant professor of Pediatrics objectives To be familiar with common pediatric antibiotics o Classification o Action o Adverse effect To discus
Optimizing Antibiotic Treatment of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
 Optimizing Antibiotic Treatment of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections 15th Annual Rocky Mountain Hospital Medicine Symposium November 6, 2017 Tim Jenkins, MD Director, Antibiotic Stewardship Program Denver
Optimizing Antibiotic Treatment of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections 15th Annual Rocky Mountain Hospital Medicine Symposium November 6, 2017 Tim Jenkins, MD Director, Antibiotic Stewardship Program Denver
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Emerging Therapies and 5 things to know
 2011 MFMER slide-1 Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Emerging Therapies and 5 things to know Aaron Tande, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine October 27, 2017 Division of INFECTIOUS DISEASES 2011 MFMER slide-2
2011 MFMER slide-1 Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Emerging Therapies and 5 things to know Aaron Tande, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine October 27, 2017 Division of INFECTIOUS DISEASES 2011 MFMER slide-2
Mrsa abscess and cellulitis
 Search Mrsa abscess and cellulitis An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The. Staph
Search Mrsa abscess and cellulitis An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The. Staph
Felipe N. Gutierrez MD, MPH Chief, Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare
 Felipe N. Gutierrez MD, MPH Chief, Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare 100% of all wounds will yield growth If you get a negative culture you something is wrong! Pseudomonas while ubiquitous does
Felipe N. Gutierrez MD, MPH Chief, Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare 100% of all wounds will yield growth If you get a negative culture you something is wrong! Pseudomonas while ubiquitous does
10/13/14. Low: not well absorbed. Good: [blood and tissue] < than if given IV. High: > 90% absorption orally
![10/13/14. Low: not well absorbed. Good: [blood and tissue] < than if given IV. High: > 90% absorption orally 10/13/14. Low: not well absorbed. Good: [blood and tissue] < than if given IV. High: > 90% absorption orally](/thumbs/79/80222162.jpg) Low: not well absorbed PO agent not for serious infection nitrofurantoin Good: [blood and tissue] < than if given IV [Therapeutic] in excess of [effective] eg. cephalexin High: > 90% absorption orally
Low: not well absorbed PO agent not for serious infection nitrofurantoin Good: [blood and tissue] < than if given IV [Therapeutic] in excess of [effective] eg. cephalexin High: > 90% absorption orally
AMOCLAN HIKMA PHARMACEUTICALS
 09-15 AMOCLAN HIKMA PHARMACEUTICALS (Amoxycillin and Clavulanic acid) ACTION Amoxicillin is a semisynthetic antibiotic with a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many gram-positive and gram-negative
09-15 AMOCLAN HIKMA PHARMACEUTICALS (Amoxycillin and Clavulanic acid) ACTION Amoxicillin is a semisynthetic antibiotic with a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many gram-positive and gram-negative
Author s: Clinical Standards Group and Effectiveness Sub-Board
 Trust Antibiotic Policy for the Management of Common Infections in Accident and Emergency and Cromer Minor Injuries Unit (Paediatrics) Accident and Emergency, Norfolk and Norwich and For Use in: Cromer
Trust Antibiotic Policy for the Management of Common Infections in Accident and Emergency and Cromer Minor Injuries Unit (Paediatrics) Accident and Emergency, Norfolk and Norwich and For Use in: Cromer
Amoxicillin dose for gum infection
 Amoxicillin dose for gum infection Learn about Prilosec (Omeprazole) may treat, uses, dosage, side effects, drug interactions, warnings, patient labeling, reviews, and related medications. 30-9-1990 Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin dose for gum infection Learn about Prilosec (Omeprazole) may treat, uses, dosage, side effects, drug interactions, warnings, patient labeling, reviews, and related medications. 30-9-1990 Amoxicillin
HEALTH SERVICES POLICY & PROCEDURE MANUAL
 PAGE 1 of 3 PURPOSE To assure that DOP inmates with Soft Tissue Infections are receiving high quality Primary Care for their infections and that the risk of infecting other inmates or staff is minimized.
PAGE 1 of 3 PURPOSE To assure that DOP inmates with Soft Tissue Infections are receiving high quality Primary Care for their infections and that the risk of infecting other inmates or staff is minimized.
Rational management of community acquired infections
 Rational management of community acquired infections Dr Tanu Singhal MD, MSc Consultant Pediatrics and Infectious Disease Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital, Mumbai Why is rational management needed?
Rational management of community acquired infections Dr Tanu Singhal MD, MSc Consultant Pediatrics and Infectious Disease Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital, Mumbai Why is rational management needed?
Antibiotic Abyss. Discussion Points. MRSA Treatment Guidelines
 Antibiotic Abyss Fredrick M. Abrahamian, D.O., FACEP, FIDSA Professor of Medicine UCLA School of Medicine Director of Education Department of Emergency Medicine Olive View-UCLA Medical Center Sylmar, California
Antibiotic Abyss Fredrick M. Abrahamian, D.O., FACEP, FIDSA Professor of Medicine UCLA School of Medicine Director of Education Department of Emergency Medicine Olive View-UCLA Medical Center Sylmar, California
Antibiotic Updates: Part II
 Antibiotic Updates: Part II Fredrick M. Abrahamian, DO, FACEP, FIDSA Health Sciences Clinical Professor of Emergency Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, California Financial Disclosures
Antibiotic Updates: Part II Fredrick M. Abrahamian, DO, FACEP, FIDSA Health Sciences Clinical Professor of Emergency Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, California Financial Disclosures
B. PACKAGE LEAFLET 1
 B. PACKAGE LEAFLET 1 PACKAGE LEAFLET NICILAN 400 mg/100 mg tablets for dogs 1. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER AND OF THE MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
B. PACKAGE LEAFLET 1 PACKAGE LEAFLET NICILAN 400 mg/100 mg tablets for dogs 1. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER AND OF THE MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION HOLDER RESPONSIBLE FOR BATCH
Pharmacology Week 6 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS
 Pharmacology Week 6 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS Mechanisms of antimicrobial action Mechanisms of antimicrobial action Bacteriostatic - Slow or stop bacterial growth, needs an immune system to finish off the microbe
Pharmacology Week 6 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS Mechanisms of antimicrobial action Mechanisms of antimicrobial action Bacteriostatic - Slow or stop bacterial growth, needs an immune system to finish off the microbe
S aureus infections: outpatient treatment. Dirk Vogelaers Dept of Infectious Diseases University Hospital Gent Belgium
 S aureus infections: outpatient treatment Dirk Vogelaers Dept of Infectious Diseases University Hospital Gent Belgium Intern Med J. 2005 Feb;36(2):142-3 Intern Med J. 2005 Feb;36(2):142-3 Treatment of
S aureus infections: outpatient treatment Dirk Vogelaers Dept of Infectious Diseases University Hospital Gent Belgium Intern Med J. 2005 Feb;36(2):142-3 Intern Med J. 2005 Feb;36(2):142-3 Treatment of
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr.Malik
 number 27 Done by Fatimah Farhan Corrected by Basil Al-Bakri Doctor Dr.Malik Note: anything in red is just extra info and you will not be asked about it in the exam. In this sheet we will continue talking
number 27 Done by Fatimah Farhan Corrected by Basil Al-Bakri Doctor Dr.Malik Note: anything in red is just extra info and you will not be asked about it in the exam. In this sheet we will continue talking
Safety of an Out-Patient Intravenous Antibiotics Programme
 Safety of an Out-Patient Intravenous Antibiotics Programme Chan VL, Tang ESK, Leung WS, Wong L, Cheung PS, Chu CM Department of Medicine & Geriatrics United Christian Hospital Outpatient Parental Antimicrobial
Safety of an Out-Patient Intravenous Antibiotics Programme Chan VL, Tang ESK, Leung WS, Wong L, Cheung PS, Chu CM Department of Medicine & Geriatrics United Christian Hospital Outpatient Parental Antimicrobial
Interactive session: adapting to antibiogram. Thong Phe Heng Vengchhun Felix Leclerc Erika Vlieghe
 Interactive session: adapting to antibiogram Thong Phe Heng Vengchhun Felix Leclerc Erika Vlieghe Case 1 63 y old woman Dx: urosepsis? After 2 d: intermediate result: Gram-negative bacilli Empiric antibiotic
Interactive session: adapting to antibiogram Thong Phe Heng Vengchhun Felix Leclerc Erika Vlieghe Case 1 63 y old woman Dx: urosepsis? After 2 d: intermediate result: Gram-negative bacilli Empiric antibiotic
Central Nervous System Infections
 Central Nervous System Infections Meningitis Treatment Bacterial meningitis is a MEDICAL EMERGENCY. ANTIBIOTICS SHOULD BE STARTED AS SOON AS THE POSSIBILITY OF BACTERIAL MENINGITIS BECOMES EVIDENT, IDEALLY
Central Nervous System Infections Meningitis Treatment Bacterial meningitis is a MEDICAL EMERGENCY. ANTIBIOTICS SHOULD BE STARTED AS SOON AS THE POSSIBILITY OF BACTERIAL MENINGITIS BECOMES EVIDENT, IDEALLY
Tropical infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus
 Tropical infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus Michael Ellis, MD Infectious Diseases Division Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences February 2015 Introduction Tropical Pyomyositis Cutaneous
Tropical infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus Michael Ellis, MD Infectious Diseases Division Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences February 2015 Introduction Tropical Pyomyositis Cutaneous
Duke University Hospital Guideline for Empiric Inpatient Treatment of Cancer- Related Neutropenic Fever in Adult Patients
 Duke University Hospital Guideline for Empiric Inpatient Treatment of Cancer- Related Neutropenic Fever in Adult Patients PURPOSE Fever among neutropenic patients is common and a significant cause of morbidity
Duke University Hospital Guideline for Empiric Inpatient Treatment of Cancer- Related Neutropenic Fever in Adult Patients PURPOSE Fever among neutropenic patients is common and a significant cause of morbidity
INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN-ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT
 INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN-ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT Name & Title Of Authors: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Dr N Rao,Consultant Paediatrician Dr V Desai Consultant Paediatrician Date Revised: DEC 2015
INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN-ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT Name & Title Of Authors: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Dr N Rao,Consultant Paediatrician Dr V Desai Consultant Paediatrician Date Revised: DEC 2015
Disclosures. Consider This Case. Objectives. Consequences of Bites. Animal Bites: What to Do and What to Avoid. Animal Bites: Epidemiology
 Animal Bites: What to Do and What to Avoid Meg Fisher, MD Medical Director Disclosures I have no disclosures I do not plan to discuss off label uses of drugs Objectives Manage a child who is bitten Discuss
Animal Bites: What to Do and What to Avoid Meg Fisher, MD Medical Director Disclosures I have no disclosures I do not plan to discuss off label uses of drugs Objectives Manage a child who is bitten Discuss
Cellulitis and Abscess: ED Phase v 1.1
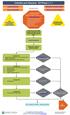 Cellulitis and Abscess: ED Phase v 1.1 Executive Summary Test Your Knowledge PHASE I (E.D.) Explanation of Evidence Ratings Summary of Version Changes! Labs if systemic illness or necrotizing fasciitis
Cellulitis and Abscess: ED Phase v 1.1 Executive Summary Test Your Knowledge PHASE I (E.D.) Explanation of Evidence Ratings Summary of Version Changes! Labs if systemic illness or necrotizing fasciitis
Provincial Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Memorandum Version 2
 Provincial Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Memorandum Version 2 16 Garfield Street 16, rue Garfield PO Box 2000, Charlottetown C.P. 2000, Charlottetown Prince Edward Island Île-du-Prince-Édouard Canada
Provincial Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Memorandum Version 2 16 Garfield Street 16, rue Garfield PO Box 2000, Charlottetown C.P. 2000, Charlottetown Prince Edward Island Île-du-Prince-Édouard Canada
Health PEI: Provincial Antibiotic Advisory Team Empiric Antibiotic Treatment Guidelines for Sepsis Syndromes in Adults
 Health PEI: Provincial Antibiotic Advisory Team Empiric Antibiotic Treatment Guidelines for Sepsis Syndromes in Adults COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED PNEUMONIA INTRA-ABDOMINAL INFECTION
Health PEI: Provincial Antibiotic Advisory Team Empiric Antibiotic Treatment Guidelines for Sepsis Syndromes in Adults COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED PNEUMONIA INTRA-ABDOMINAL INFECTION
Management of Native Valve
 Management of Native Valve Infective Endocarditis 2005 AHA 2015 Baddour LM, et al. Circulation. 2015;132(15):1435-86 2009 ESC 2015 Habib G, et al. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(44):3075-128 ESC 2015: Endocarditis
Management of Native Valve Infective Endocarditis 2005 AHA 2015 Baddour LM, et al. Circulation. 2015;132(15):1435-86 2009 ESC 2015 Habib G, et al. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(44):3075-128 ESC 2015: Endocarditis
Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections: Emerging Bacterial Resistance
 Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections: Emerging Bacterial Resistance Eileen M. Bulger, MD Professor of Surgery Harborview Medical Center University of Washington Objectives Review definition & diagnostic
Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections: Emerging Bacterial Resistance Eileen M. Bulger, MD Professor of Surgery Harborview Medical Center University of Washington Objectives Review definition & diagnostic
Staphylex Flucloxacillin (sodium)
 Staphylex Flucloxacillin (sodium) PRODUCT INFORMATION Name of the Medicine Flucloxacillin sodium is the sodium salt of 3-(2'-chloro-6'-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolylpenicillin monohydrate. Structural
Staphylex Flucloxacillin (sodium) PRODUCT INFORMATION Name of the Medicine Flucloxacillin sodium is the sodium salt of 3-(2'-chloro-6'-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolylpenicillin monohydrate. Structural
Bacterial skin and soft tissues infections (SSTI) are one of the most common 1. infections among different age groups
 Bacterial skin and soft tissues infections (SSTI) are one of the most common 1 infections among different age groups Gram-positive bacteria are the most frequently isolated pathogens from SSTI, with a
Bacterial skin and soft tissues infections (SSTI) are one of the most common 1 infections among different age groups Gram-positive bacteria are the most frequently isolated pathogens from SSTI, with a
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA IN ADULTS
 Version 3.1 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA IN ADULTS Date ratified June 2008 Updated March 2009 Review date June 2010 Ratified by Authors Consultation Evidence base Changes
Version 3.1 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA IN ADULTS Date ratified June 2008 Updated March 2009 Review date June 2010 Ratified by Authors Consultation Evidence base Changes
PRACTIC GUIDELINES for APPROPRIATE ANTIBIOTICS USE
 PRACTIC GUIDELINES for APPROPRIATE ANTIBIOTICS USE Global Alliance for Infection in Surgery World Society of Emergency Surgery (WSES) and not only!! Aims - 1 Rationalize the risk of antibiotics overuse
PRACTIC GUIDELINES for APPROPRIATE ANTIBIOTICS USE Global Alliance for Infection in Surgery World Society of Emergency Surgery (WSES) and not only!! Aims - 1 Rationalize the risk of antibiotics overuse
Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis
 Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis 1. Definition of Peritonitis: a. Cloudy effluent. b. WBC > 100 cells/mm3 with >50% polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells with minimum 2 hour dwell. c.
Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis 1. Definition of Peritonitis: a. Cloudy effluent. b. WBC > 100 cells/mm3 with >50% polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells with minimum 2 hour dwell. c.
Package leaflet: Information for the patient. Co-amoxiclav 500 mg/125 mg film-coated tablets. amoxicillin/ clavulanic acid
 Package leaflet: Information for the patient Co-amoxiclav 500 mg/125 mg film-coated tablets amoxicillin/ clavulanic acid Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine, because
Package leaflet: Information for the patient Co-amoxiclav 500 mg/125 mg film-coated tablets amoxicillin/ clavulanic acid Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine, because
Diabetic Foot Infection. Dr David Orr Consultant Microbiologist Lancashire Teaching Hospitals
 Diabetic Foot Infection Dr David Orr Consultant Microbiologist Lancashire Teaching Hospitals History of previous amputation [odds ratio (OR)=19.9, P=.01], Peripheral vascular disease (OR=5.5, P=.007)
Diabetic Foot Infection Dr David Orr Consultant Microbiologist Lancashire Teaching Hospitals History of previous amputation [odds ratio (OR)=19.9, P=.01], Peripheral vascular disease (OR=5.5, P=.007)
1. WHAT CO-AMOXICLAV TABLETS IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
 Package leaflet: Information for the patient Co-amoxiclav 250 mg/125 mg film-coated tablets amoxicillin/clavulanic acid Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine, because
Package leaflet: Information for the patient Co-amoxiclav 250 mg/125 mg film-coated tablets amoxicillin/clavulanic acid Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine, because
ANTIBIOTIC PRESCRIBING POLICY FOR DIABETIC FOOT DISEASE IN SECONDARY CARE
 ANTIBIOTIC PRESCRIBING POLICY FOR DIABETIC FOOT DISEASE IN SECONDARY CARE Version 1.0 Date ratified June 2009 Review date June 2011 Ratified by Authors Consultation Nottingham Antibiotic Guidelines Committee
ANTIBIOTIC PRESCRIBING POLICY FOR DIABETIC FOOT DISEASE IN SECONDARY CARE Version 1.0 Date ratified June 2009 Review date June 2011 Ratified by Authors Consultation Nottingham Antibiotic Guidelines Committee
Aberdeen Hospital. Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns For Commonly Isolated Organisms For 2015
 Aberdeen Hospital Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns For Commonly Isolated s For 2015 Services Laboratory Microbiology Department Aberdeen Hospital Nova Scotia Health Authority 835 East River Road New
Aberdeen Hospital Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns For Commonly Isolated s For 2015 Services Laboratory Microbiology Department Aberdeen Hospital Nova Scotia Health Authority 835 East River Road New
APPROVED PACKAGE INSERT. Each capsule contains clindamycin hydrochloride equivalent to 150 mg clindamycin base.
 APPROVED PACKAGE INSERT SCHEDULING STATUS: S4 PROPRIETARY NAMEAND DOSAGE FORM: DALACIN C TM 150 mg (Capsules) COMPOSITION: Each capsule contains clindamycin hydrochloride equivalent to 150 mg clindamycin
APPROVED PACKAGE INSERT SCHEDULING STATUS: S4 PROPRIETARY NAMEAND DOSAGE FORM: DALACIN C TM 150 mg (Capsules) COMPOSITION: Each capsule contains clindamycin hydrochloride equivalent to 150 mg clindamycin
Acute Pyelonephritis POAC Guideline
 Acute Pyelonephritis POAC Guideline Refer full regional pathway http://aucklandregion.healthpathways.org.nz/33444 EXCLUSION CRITERIA: COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS Discuss with relevant specialist for advice
Acute Pyelonephritis POAC Guideline Refer full regional pathway http://aucklandregion.healthpathways.org.nz/33444 EXCLUSION CRITERIA: COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS Discuss with relevant specialist for advice
CELLULITIS / SKIN INFECTIONS
 Skin Infections Assessment Investigations Cellulitis Management Abscess Management Infection Control Antibiotic Choice Education Recurrent Infections Referral to Community Nursing References Skin Infections
Skin Infections Assessment Investigations Cellulitis Management Abscess Management Infection Control Antibiotic Choice Education Recurrent Infections Referral to Community Nursing References Skin Infections
Chapter 61 Mammalian Bites
 Chapter 61 Mammalian Bites Episode Overview: 1. List 5 pathogens responsible for infection from dog bite 2. List 4 risk factors for overwhelming sepsis from dog bite 3. What first line antibiotic is a
Chapter 61 Mammalian Bites Episode Overview: 1. List 5 pathogens responsible for infection from dog bite 2. List 4 risk factors for overwhelming sepsis from dog bite 3. What first line antibiotic is a
Can levaquin treat group b strep
 Can levaquin treat group b strep The Borg System is 100 % Can levaquin treat group b strep IBS - Symptoms, Diet and Treatment. IBS, is the common slang term or abbreviation for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Can levaquin treat group b strep The Borg System is 100 % Can levaquin treat group b strep IBS - Symptoms, Diet and Treatment. IBS, is the common slang term or abbreviation for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Case 2 Synergy satellite event: Good morning pharmacists! Case studies on antimicrobial resistance
 Case 2 Synergy satellite event: Good morning pharmacists! Case studies on antimicrobial resistance 22nd Congress of the EAHP "Hospital pharmacists catalysts for change", 22-24 March 2017, Cannes Disclosure
Case 2 Synergy satellite event: Good morning pharmacists! Case studies on antimicrobial resistance 22nd Congress of the EAHP "Hospital pharmacists catalysts for change", 22-24 March 2017, Cannes Disclosure
Symptoms of cellulitis (n=396) %
 Cellulitis and lymphoedema Vaughan Keeley May 2012 What is cellulitis? - also called erysipelas, acute inflammatory episodes etc. - bacterial infection of skin + subcutaneous tissues - more common in people
Cellulitis and lymphoedema Vaughan Keeley May 2012 What is cellulitis? - also called erysipelas, acute inflammatory episodes etc. - bacterial infection of skin + subcutaneous tissues - more common in people
Northwestern Medicine Central DuPage Hospital Antimicrobial Criteria Updated 11/16/16
 Northwestern Medicine Central DuPage Hospital Antimicrobial Criteria Updated 11/16/16 These criteria are based on national and local susceptibility data as well as Infectious Disease Society of America
Northwestern Medicine Central DuPage Hospital Antimicrobial Criteria Updated 11/16/16 These criteria are based on national and local susceptibility data as well as Infectious Disease Society of America
Telephone Max dose amoxicillin pediatrics P.O. Box 189 Navan, ON, K4B 1J4 Canada. Sitemap
 Telephone 613-835-9490 Max dose amoxicillin pediatrics P.O. Box 189 Navan, ON, K4B 1J4 Canada Sitemap 25 mg/kg/ dose ( Max : 500 mg/ dose ) PO twice daily for 10 days is recommended by the Infectious Diseases
Telephone 613-835-9490 Max dose amoxicillin pediatrics P.O. Box 189 Navan, ON, K4B 1J4 Canada Sitemap 25 mg/kg/ dose ( Max : 500 mg/ dose ) PO twice daily for 10 days is recommended by the Infectious Diseases
Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis
 Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis 1. Definition of Peritonitis: a. Cloudy effluent. b. WBC > 100 cells/mm3 with >50% polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells with minimum 2 hour dwell. c.
Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis 1. Definition of Peritonitis: a. Cloudy effluent. b. WBC > 100 cells/mm3 with >50% polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells with minimum 2 hour dwell. c.
Rational use of antibiotic in upper respiratory tract infection (URI) and community acquired pneumonia รศ.จามร ธ รตก ลพ ศาล 23 พฤษภาคม 2550
 Rational use of antibiotic in upper respiratory tract infection (URI) and community acquired pneumonia รศ.จามร ธ รตก ลพ ศาล 23 พฤษภาคม 2550 Sinusitis Upper respiratory tract infections (URI) Common cold
Rational use of antibiotic in upper respiratory tract infection (URI) and community acquired pneumonia รศ.จามร ธ รตก ลพ ศาล 23 พฤษภาคม 2550 Sinusitis Upper respiratory tract infections (URI) Common cold
Advanced Practice Education Associates. Antibiotics
 Advanced Practice Education Associates Antibiotics Overview Difference between Gram Positive(+), Gram Negative(-) organisms Beta lactam ring, allergies Antimicrobial Spectra of Antibiotic Classes 78 Copyright
Advanced Practice Education Associates Antibiotics Overview Difference between Gram Positive(+), Gram Negative(-) organisms Beta lactam ring, allergies Antimicrobial Spectra of Antibiotic Classes 78 Copyright
Who should read this document? 2. Key practice points 2. Background/ Scope/ Definitions 2. What is new in this version? 3
 Neurosurgical infections (adult only) Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary
Neurosurgical infections (adult only) Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary
SASKATCHEWAN REGISTERED NURSES ASSOCIATION. RNs WITH ADDITIONAL AUTHORIZED PRACTICE CLINICAL DECISION TOOL DECEMBER 1, 2016 MASTITIS ADULT & PEDIATRIC
 DEFINITION An inflammatory condition of the breast, possibly accompanied by infection and usually associated with lactation. Can be seen in non-lactating clients. IMMEDIATE CONSULTATION REQUIRED IN THE
DEFINITION An inflammatory condition of the breast, possibly accompanied by infection and usually associated with lactation. Can be seen in non-lactating clients. IMMEDIATE CONSULTATION REQUIRED IN THE
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Fluclon 250 mg Capsules 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each capsule contains 250mg of flucloxacillin as flucloxacillin sodium.
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Fluclon 250 mg Capsules 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each capsule contains 250mg of flucloxacillin as flucloxacillin sodium.
Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Spinal Surgery Antibiotic Guidelines. Contents
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Spinal Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine Unique
Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Spinal Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine Unique
Misericordia Community Hospital (MCH) Antimicrobial Stewardship Report. July December 2013 Second and Third Quarters 2014
 H e a l i n g t h e B o d y E n r i c h i n g t h e M i n d N u r t u r i n g t h e S o u l Misericordia Community Hospital (MCH) Antimicrobial Stewardship Report July December 213 Second and Third Quarters
H e a l i n g t h e B o d y E n r i c h i n g t h e M i n d N u r t u r i n g t h e S o u l Misericordia Community Hospital (MCH) Antimicrobial Stewardship Report July December 213 Second and Third Quarters
Give the Right Antibiotics in Trauma Mitchell J Daley, PharmD, BCPS
 Give the Right Antibiotics in Trauma Mitchell J Daley, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Critical Care Dell Seton Medical Center at the University of Texas and Seton Healthcare Family Clinical
Give the Right Antibiotics in Trauma Mitchell J Daley, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Critical Care Dell Seton Medical Center at the University of Texas and Seton Healthcare Family Clinical
$100 $200 $300 $400 $500
 Skin is In Runny Noses Got to go! Hear no evil It s in the Lungs $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 Double Jeopardy
Skin is In Runny Noses Got to go! Hear no evil It s in the Lungs $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 Double Jeopardy
Author - Dr. Josie Traub-Dargatz
 Author - Dr. Josie Traub-Dargatz Dr. Josie Traub-Dargatz is a professor of equine medicine at Colorado State University (CSU) College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. She began her veterinary
Author - Dr. Josie Traub-Dargatz Dr. Josie Traub-Dargatz is a professor of equine medicine at Colorado State University (CSU) College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. She began her veterinary
Pocket Guide to Diagnosis & Treatment of Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Device (CIED) Infections
 Pocket Guide to Diagsis & Treatment of Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Device (CIED) Infections Draft Version : November 208 DEFINITION Pocket infection, if all 4 criteria are fulfilled: Investigation/sign
Pocket Guide to Diagsis & Treatment of Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Device (CIED) Infections Draft Version : November 208 DEFINITION Pocket infection, if all 4 criteria are fulfilled: Investigation/sign
Clindamycin coverage streptococcus
 Clindamycin coverage streptococcus Oct 12, 2017. While clindamycin and erythromycin were at one time uniformly active against group B streptococci, resistance has been increasing. One large. We assessed
Clindamycin coverage streptococcus Oct 12, 2017. While clindamycin and erythromycin were at one time uniformly active against group B streptococci, resistance has been increasing. One large. We assessed
USA Product Label CLINTABS TABLETS. Virbac. brand of clindamycin hydrochloride tablets. ANADA # , Approved by FDA DESCRIPTION
 VIRBAC CORPORATION USA Product Label http://www.vetdepot.com P.O. BOX 162059, FORT WORTH, TX, 76161 Telephone: 817-831-5030 Order Desk: 800-338-3659 Fax: 817-831-8327 Website: www.virbacvet.com CLINTABS
VIRBAC CORPORATION USA Product Label http://www.vetdepot.com P.O. BOX 162059, FORT WORTH, TX, 76161 Telephone: 817-831-5030 Order Desk: 800-338-3659 Fax: 817-831-8327 Website: www.virbacvet.com CLINTABS
APO-FLUCLOXACILLIN CAPSULES. sodium salt of 3-(2'-chloro-6'-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolylpenicillin monohydrate.
 APO-FLUCLOXACILLIN CAPSULES NAME OF THE MEDICINE Flucloxacillin sodium monohydrate. Chemical Name: sodium salt of 3-(2'-chloro-6'-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolylpenicillin monohydrate. Structural Formula:
APO-FLUCLOXACILLIN CAPSULES NAME OF THE MEDICINE Flucloxacillin sodium monohydrate. Chemical Name: sodium salt of 3-(2'-chloro-6'-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolylpenicillin monohydrate. Structural Formula:
Pneumonia Antibiotic Guidance for Adults PAGL Inclusion Approved at January 2017 PGC
 Pneumonia Antibiotic Guidance for Adults PAGL Inclusion Approved at January 2017 PGC APPROVED BY: Policy and Guidelines Committee TRUST REFERENCE: B9/2009 AWP Ref: AWP61 Date (approved): July 2008 REVIEW
Pneumonia Antibiotic Guidance for Adults PAGL Inclusion Approved at January 2017 PGC APPROVED BY: Policy and Guidelines Committee TRUST REFERENCE: B9/2009 AWP Ref: AWP61 Date (approved): July 2008 REVIEW
Le infezioni di cute e tessuti molli
 Le infezioni di cute e tessuti molli SCELTE e STRATEGIE TERAPEUTICHE Pierluigi Viale Clinica di Malattie Infettive Policlinico S. Orsola Malpighi Treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections
Le infezioni di cute e tessuti molli SCELTE e STRATEGIE TERAPEUTICHE Pierluigi Viale Clinica di Malattie Infettive Policlinico S. Orsola Malpighi Treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections
GP Small Group education April/May 2015 Antibiotics Resistance is futile
 GP Small Group education April/May 2015 Antibiotics Resistance is futile Acknowledgements This material was prepared by the Clinical Quality and Education team with help gratefully received from: Topic
GP Small Group education April/May 2015 Antibiotics Resistance is futile Acknowledgements This material was prepared by the Clinical Quality and Education team with help gratefully received from: Topic
notification of entry onto webpage Document Links
 Document Details Title Co-amoxiclav 250/125 tablets, co-amoxiclav 500/125 tablets, co-amoxiclav 125/31.25 oral suspension and co-amoxiclav 250/62 oral suspension Patient Group Direction (PGD) Trust Ref
Document Details Title Co-amoxiclav 250/125 tablets, co-amoxiclav 500/125 tablets, co-amoxiclav 125/31.25 oral suspension and co-amoxiclav 250/62 oral suspension Patient Group Direction (PGD) Trust Ref
Anaerobic and microaerophilic gram-positive cocci Peptococcus species, Peptostreptococcus species, Microaerophilic streptococci
 CLINDACIN Composition Each capsule contains Clindamycin (as hydrochloride) 150 mg Capsule Action Clindamycin bind exclusively to the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes and suppress protein synthesis. Clindamycin
CLINDACIN Composition Each capsule contains Clindamycin (as hydrochloride) 150 mg Capsule Action Clindamycin bind exclusively to the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes and suppress protein synthesis. Clindamycin
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid Amneal 500 mg/125 mg film-coated tablets Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid Amneal 875 mg/125 mg film-coated tablets (Amoxicillin/Clavulanic
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid Amneal 500 mg/125 mg film-coated tablets Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid Amneal 875 mg/125 mg film-coated tablets (Amoxicillin/Clavulanic
Replaces:04/14/16. Formulated: 1997 SKIN AND SOFT TISSUE INFECTION
 Effective Date: 04/13/17 Replaces:04/14/16 Page 1 of 7 POLICY To standardize the clinical management and housing of offenders with skin and soft tissue infections, thereby reducing the transmission and
Effective Date: 04/13/17 Replaces:04/14/16 Page 1 of 7 POLICY To standardize the clinical management and housing of offenders with skin and soft tissue infections, thereby reducing the transmission and
Bacterial skin infection
 D i v i s i o n o f P e d i a t r i c E m e r g e n c y M e d i c i n e P a g e 1 Bacterial skin infection Cellulitis w/o abscess Abscess Deep tissue involvement Multiple abscesses Perirectal Anterior
D i v i s i o n o f P e d i a t r i c E m e r g e n c y M e d i c i n e P a g e 1 Bacterial skin infection Cellulitis w/o abscess Abscess Deep tissue involvement Multiple abscesses Perirectal Anterior
IAEM Clinical Guideline 6 Bite Wound Management in Adults and Children Version 1 July 2016
 IAEM Clinical Guideline 6 Bite Wound Management in Adults and Children Version 1 July 2016 Authors: Dr Sinead Ni Bhraonain, Dr Jessica Pflipsen, Dr Éanna Mac Suibhne Guideline lead: Dr Termizi Hassan,
IAEM Clinical Guideline 6 Bite Wound Management in Adults and Children Version 1 July 2016 Authors: Dr Sinead Ni Bhraonain, Dr Jessica Pflipsen, Dr Éanna Mac Suibhne Guideline lead: Dr Termizi Hassan,
Treatment of Surgical Site Infection Meeting Quality Statement 6. Prof Peter Wilson University College London Hospitals
 Treatment of Surgical Site Infection Meeting Quality Statement 6 Prof Peter Wilson University College London Hospitals TEG Quality Standard 6 Treatment and effective antibiotic prescribing: People with
Treatment of Surgical Site Infection Meeting Quality Statement 6 Prof Peter Wilson University College London Hospitals TEG Quality Standard 6 Treatment and effective antibiotic prescribing: People with
Reduce the risk of recurrence Clear bacterial infections fast and thoroughly
 Reduce the risk of recurrence Clear bacterial infections fast and thoroughly Clearly advanced 140916_Print-Detailer_Englisch_V2_BAH-05-01-14-003_RZ.indd 1 23.09.14 16:59 In bacterial infections, bacteriological
Reduce the risk of recurrence Clear bacterial infections fast and thoroughly Clearly advanced 140916_Print-Detailer_Englisch_V2_BAH-05-01-14-003_RZ.indd 1 23.09.14 16:59 In bacterial infections, bacteriological
Amoxicillin 250mg Hard Capsules Amoxicillin 500mg Hard Capsules
 Package leaflet: Information for the user Amoxicillin 250mg Hard Capsules Amoxicillin 500mg Hard Capsules Amoxicillin Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it
Package leaflet: Information for the user Amoxicillin 250mg Hard Capsules Amoxicillin 500mg Hard Capsules Amoxicillin Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it
Copyright 2012 Diabetes In Control, Inc. For permission to reprint, please contact Heather Moran, Production Editor, at
 Malignant Otitis Externa Inflammation and damage at the base of the skull due to an untreated outer ear P. aeruginosa most common organism Yellow-green drainage from the ear Odor Fever Deep inner ear pain
Malignant Otitis Externa Inflammation and damage at the base of the skull due to an untreated outer ear P. aeruginosa most common organism Yellow-green drainage from the ear Odor Fever Deep inner ear pain
Remember: AIEs are painful: analgesics should be prescribed regularly and p.r.n. palliativedrugs.com November/December newsletter
 ACUTE INFLAMMATORY EPISODES IN A LYMPHOEDEMATOUS LIMB Acute inflammatory episodes (AIEs), often called cellulitis, are common in lymphoedema: mild: pain, increased swelling, erythema (well-defined or blotchy)
ACUTE INFLAMMATORY EPISODES IN A LYMPHOEDEMATOUS LIMB Acute inflammatory episodes (AIEs), often called cellulitis, are common in lymphoedema: mild: pain, increased swelling, erythema (well-defined or blotchy)
Other Beta - lactam Antibiotics
 Other Beta - lactam Antibiotics Assistant Professor Dr. Naza M. Ali Lec 5 8 Nov 2017 Lecture outlines Other beta lactam antibiotics Other inhibitors of cell wall synthesis Other beta-lactam Antibiotics
Other Beta - lactam Antibiotics Assistant Professor Dr. Naza M. Ali Lec 5 8 Nov 2017 Lecture outlines Other beta lactam antibiotics Other inhibitors of cell wall synthesis Other beta-lactam Antibiotics
Package leaflet: Information for the user
 Package leaflet: Information for the user Amoxicilline/Clavulaanzuur Devatis 250 mg/62,5 mg/5 ml poeder voor orale suspensie Amoxicilline/Clavulaanzuur Devatis 400 mg/57 mg/5 ml poeder voor orale suspensie
Package leaflet: Information for the user Amoxicilline/Clavulaanzuur Devatis 250 mg/62,5 mg/5 ml poeder voor orale suspensie Amoxicilline/Clavulaanzuur Devatis 400 mg/57 mg/5 ml poeder voor orale suspensie
InPHARMation. Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee Update May 23 rd, 2018 Meeting
 VOLUME FOUR; ISSUE 5 May 23, 2018 Edited by: Gregory K. Perry, PharmD, BCPS-AQID InPHARMation Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee Update May 23 rd, 2018 Meeting The Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee
VOLUME FOUR; ISSUE 5 May 23, 2018 Edited by: Gregory K. Perry, PharmD, BCPS-AQID InPHARMation Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee Update May 23 rd, 2018 Meeting The Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee
General Surgery Small Group Activity (Facilitator Notes) Curriculum for Antimicrobial Stewardship
 General Surgery Small Group Activity (Facilitator Notes) Curriculum for Antimicrobial Stewardship Facilitator instructions: Read through the facilitator notes and make note of discussion points for each
General Surgery Small Group Activity (Facilitator Notes) Curriculum for Antimicrobial Stewardship Facilitator instructions: Read through the facilitator notes and make note of discussion points for each
CLINICAL PROTOCOL FOR COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA. SCOPE: Western Australia. CORB score equal or above 1. All criteria must be met:
 CLINICAL PROTOCOL F COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA SCOPE: Western Australia All criteria must be met: Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria CB score equal or above 1. Mild/moderate pneumonia confirmed by
CLINICAL PROTOCOL F COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA SCOPE: Western Australia All criteria must be met: Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria CB score equal or above 1. Mild/moderate pneumonia confirmed by
2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY. MEASURE TYPE: Process
 Quality ID #407: Appropriate Treatment of Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus Aureus (MSSA) Bacteremia National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Quality ID #407: Appropriate Treatment of Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus Aureus (MSSA) Bacteremia National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
