Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: the molecular epidemic features of an emerging problem in health care facilities
|
|
|
- Debra Sullivan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Article Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: the molecular epidemic features of an emerging problem in health care facilities Raffaele Zarrilli 1,2, Maria Giannouli 1, Federica Tomasone 1, Maria Triassi 1, and Athanassios Tsakris 3 1 Department of Preventive Medical Sciences, Hygiene Section, University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy 2 CEINGE Advanced Biotechnologies, Naples, Italy 3 Department of Microbiology, Medical School, University of Athens, Athens, Greece Abstract Acinetobacter baumannii is an opportunistic gram-negative pathogen with increasing relevance in a variety of nosocomial infections especially among intensive-care-unit (ICU) patients. Carbapenems have been widely used to treat serious multidrug-resistant A. baumannii infections; however, incidences of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii are rising in several parts of the world and large and sustained outbreaks caused by such bacteria have been described. Carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii epidemics are sustained by clusters of highly similar strains that successfully spread among different cities and countries; their resistance phenotype is mainly due to the acquisition of carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D β-lactamase (CHDL) genes flanked by insertion sequence (IS) elements. Multi-facility outbreaks can be also sustained by inter-hospital transfer of colonized patients. Here, we review the global epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii, with the emphasis on the molecular epidemiology and genetic characterization of carbapenem resistance in epidemic strains. Key words: Acinetobacter baumannii, nosocomial outbreaks, genotyping, carbapenemases J Infect Dev Ctries 2009; 3(5): Received 25 March Accepted 17 May 2009 Copyright 2009 Zarrilli et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Introduction Acinetobacter spp. are glucose-non fermentative gram-negative coccobacilli that have emerged in recent years as a cause of healthcare-associated infections [1,2]. Considered to be commensals of low-grade pathogenicity, i.e. opportunistic microorganisms, Acinetobacter were frequently ignored in the 1970s whenever isolated from clinical specimens [1]. The genus Acinetobacter currently contains up to 32 described named and unnamed (genomic) species [1]. Acinetobacter baumannii, genomic species 3 and 13TU, three of the most clinically relevant species, are genetically and phenotypically very similar to an environmental species, A. calcoaceticus, and are therefore grouped together into the so-called A. calcoaceticus-a. baumannii (Acb) complex [1]. Because phenotypic identification of Acinetobacter isolates to the species level has proven to be insufficient, several genotypic methods have been developed for genomic species identification, that include amplified 16S rrna gene restriction analysis (ARDRA), high-resolution fingerprint analysis by amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP), or sequence analysis of the 16S-23S rrna gene spacer region [1,3,4]. However, genotypic methods for species identification are often unavailable in developing countries, where Acinetobacter are frequently isolated but identified only at genus level. The species that is most commonly involved in hospital infections is A. baumannii, which causes a variety of health-care associated infections, comprising bacteremia, urinary tract infection, surgical-site infection, and nosocomial and ventilator-associated pneumonia, especially in intensive-care-unit (ICU) patients [1,2,5-7]. The rates of recovery of A. baumannii from natural environments and its incidence in the community are low, while its rate of carriage by hospitalized patients is high and its occurrence in the hospital setting is frequent [1]. A. baumannii has simple growth requirements and can survive in dry conditions. This might contribute to the fitness of A. baumannii in the hospital environment, which represents the main reservoir of the bacterium [1].
2 Carbapenem resistance mechanisms in A. baumannii Resistance to antimicrobial agents may be the main advantage of A. baumannii in the nosocomial environment. Multidrug-resistant isolates of A. baumannii have been reported increasingly during the last decade, probably as a consequence of extensive use of antimicrobial agents in western countries [2,8]. Also, as recently demonstrated by a retrospective, matched cohort study, patients with infection by multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter show higher mortality rate and length of hospitalization than patients with infection by susceptible Acinetobacter [5]. Mounting evidence indicates that A. baumannii possesses a broad range of mechanisms of resistance to all existing antibiotic classes as well as a prodigious capacity to acquire new determinants of resistance [1,2] Genome sequence analysis of six A. baumannii clinical strains has shown the presence of a resistance island with a variable composition of resistance genes interspersed with transposons, integrons, and other mobile genetic elements in three of them [9-11]. Also, plasmids carrying resistance genes and/or resistance determinants involved in horizontal gene transfer have been described in several A. baumannii strains [12-19]. The broad-spectrum β-lactam antibiotics, carbapenems, were introduced by 1985 and have been for years the most important agents for the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant A. baumannii. Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter is now observed increasingly worldwide, and constitutes a sentinel event for emerging antimicrobial resistance [2,12]. Carbapenem-resistant isolates of A. baumannii are usually resistant to all classes of antimicrobials, and show intermediate resistance to rifampin, while usually retaining susceptibility to tigecycline and colistin [2,12,20]. Resistance against carbapenems is, in itself, considered sufficient to define an isolate of A. baumannii as highly resistant [12]. The resistance of A. baumannii to carbapenems can be mediated by one of the resistance mechanisms that are known to occur in bacteria, including enzymatic inactivation, active efflux of drugs, and modification of target sites (Table 1). The production of carbapenem-hydrolizing beta-lactamases is the most common mechanism responsible for carbapenem resistance in A. baumannii. Several carbapenem-hydrolyzing β- lactamases have been identified so far in A. baumannii. These include metallo-β-lactamases (VIM-, IMP- and SIM-types), which have been sporadically reported in some parts of the world and have been associated with class 1 integrons [2,7,12]. Nevertheless, the most widespread carbapenemases in A. baumannii are class D β-lactamases. Three main acquired carbapenem-hydrolysing class D oxacillinase (CHDL) gene clusters have been identified either in the chromosome or in plasmids of A. baumannii strains, represented by the bla OXA-23 -, bla OXA-24/40 -, and bla OXA-58 -like genes [12]. Different insertion sequence (IS) elements at the 5 and/or the 3 end of bla OXA-23 -, and bla OXA-58 -like genes, such as ISAba1, ISAba2, ISAba3, or IS18, have been demonstrated to regulate their expression [12,13,15-17]. Also, it has been recently demonstrated that the ISAba1 element is capable of transposition in E. coli and of mobilizing an antibiotic resistance gene [18]. In addition to these CHDL genes, the chromosomal bla OXA-51-like gene, intrinsic to A. baumannii species, has been demonstrated to confer carbapenem resistance when an ISAba1 element is inserted upstream of the gene [19]. Reduced susceptibility to carbapenems has also been associated with the modification of penicillin-binding proteins and porins or with upregulation of the AdeABC efflux system, and it has been suggested that the interplay of different mechanisms might result in high-level carbapenem resistance in A. baumannii (Table 1) [21-23]. Global epidemiology of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii Carbapenem resistance in A. baumannii is now an emerging issue worldwide [2]. Surveillance studies indicate that the percentage of carbapenemresistant isolates gradually increased over the last ten years in Europe, North America, and Latin America [2]. Numerous outbreaks of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii were reported from hospitals in Northern Europe (Spain, Portugal, France, the United Kingdom (UK), the Netherlands, Czech Republic, Poland) [1,2, 24-29], Southern Europe and the Middle East (Bulgaria, Greece, Italy, Turkey, Lebanon, Israel, Iran, Iraq and United Arab Emirates) [2,6-8,10,12,14,16,17,30-35], North America and Latin America (Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Colombia) [2,36,37], Tunisia and South Africa [38,39], China, Taiwan, Singapore, Hong Kong, Japan, South Korea [2,40,41], and Australia [42] and from areas as remote as French Polynesia [43]. In the majority of cases, one or two epidemic strains were detected in a given hospital. Transmission of such strains was 336
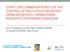
3 Table 1. Carbapenem resistance mechanisms in A. baumannii. Mechanism or responsible structure -lactam hydrolysis IMP-1, -2, -4, -5, -6, -11 VIM-2, SIM-1 Note Class B metallo beta-lactamases. Class 1 integronassociated genes. References OXA-23 cluster Class D beta-lactamases. Chromosomal or plasmid genes 2,12,13,17 flanked by IS elements. OXA-24/40 cluster Class D beta-lactamases. Chromosomal or plasmid genes. 2,12 OXA-58 cluster Class D beta-lactamases. Plasmid or chromosomal genes flanked by IS elements. OXA-51cluster Chromosomal class D beta-lactamase intrinsic to A. 2,19 baumannii. Confers carbapenem resistances if IS elements are inserted upstream of the gene Changes in outer-membrane proteins (OMPs) CarO 26 kda OMP implicated in drug influx to 36-kDa OMP OprD-like OMP Other OMPs associated with carbapenem resistance 2,12 Target alteration Altered penicillin-binding proteins Reduced PBP-2 expression 22 2,12 observed between hospitals in the same city and also on a national scale [1,2,6,12,24-27,29,30,3,38,42,44-46] and a direct epidemiological link was established in several cases [6,25,28,29,38,42,44-46]. The inter-hospital transfer of colonised patients was demonstrated during multifacility outbreaks that occurred in the Netherlands [25], Italy [6], South Africa [38], and Tunisia [39]. The international transfer of patients colonised by carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii was also reported [28, 29, 42]. More recently, several cases of United Kingdom and US military and nonmilitary personnel returning from operations in Iraq and Afghanistan and harbouring infections caused by carbapenemresistant A. baumannii were reported [44-46] (Figure 1). Outbreaks caused by carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii have also been observed in developing countries such as Morocco, Thailand, India, and Indonesia [47,41]. Furthermore, infections caused by Acinetobacter spp. without specifying whether they are caused by carbapenem-resistant strains have been reported in Africa (Lagos, Nigeria) and several Asian countries including Nepal [48-50]. Molecular epidemiology of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii Genotypic characterization of carbapenemresistant A. baumannii strains showed the occurrence of bla OXA-23 -, bla OXA-24/40 -, or bla OXA-58 -like genes in multiple isolates from the same hospital or among different hospitals worldwide [2,12,13,33,34,43,52]. bla OXA-23 was mostly detected in isolates from Asian countries [41], but was also reported in South America [36,37] and Europe [12,17,31,51]; bla OXA-58 was frequently found in Europe [6,7,10,14,30,33,16,30-35,51]. bla OXA-24/40 was mostly found in the Iberian peninsula and Asia, but also detected in Iran, Belgium, Czech Republic and the United States of America (USA) [2,26,27,41,44,51,52] (Figure 1). Molecular epidemiology of A. baumannii strains responsible for outbreaks that occurred in several European hospitals revealed clusters of highly similar strains, which were defined as European clones I and II [1,2] and corresponded to sequence type (ST) groups 2 and 1, respectively, identified by sequence-based typing [53]. A recent study on a collection of 96 carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii strains collected in 17 European countries assigned 85% of them to sequence type (ST) groups 1 and 2 by multiple PCRs [51]. The prevalence of carbapenem-resistant epidemic A. baumannii strains belonging to ST group 1 was also demonstrated in Italy and Greece [30,33] along with the spread of a prevalent clone isolated with identical pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) profiles in two hospitals in Naples, Italy, and in three hospitals in three distinct Greek cities [33]. The circulation of distinct carbapenem-resistant A. 337
4 Figure 1 Geographic distribution and genetic characterization of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii. Countries reporting carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii outbreaks producing OXA-23-, OXA-24/40-, and/or OXA-58-type enzymes are indicated by yellow, blue, and red colours, respectively. Countries reporting carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii outbreaks in which the OXA-type enzyme has not been identified are indicated by green colour. Green arrows indicate hospital transfer of colonized/infected patients by carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii between different countries. baumannii genotypes belonging to ST group 2 in Greece and in Lebanon, and to two novel ST groups 4 and 5 in different Greek and Turkish cities, was also shown in the same study [33]. The bla OXA-58 gene flanked by IS elements was present in all carbapenem-resistant genotypes analyzed from hospitals in Greece, Italy, Lebanon, and Turkey [7,16,33] (Figure 1). Of note, each of the IS elements flanking the 5 end of bla OXA-58 occurred in strains of distinct ST groups and PFGE profiles isolated in the same geographic region. Thus, ISAba2 element was detected in Greece and Italy, IS18 in Lebanon and Turkey, and ISAba1 in Turkey and Italy, suggesting that they might have been acquired through horizontal gene transfer [33]. In further support of this hypothesis, plasmid-borne bla OXA-58 has been found in the majority of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii strains isolated in Europe [6,7,10,13,14,16,33]. The spread of carbapenemresistant A. baumannii carrying the bla OXA-58 gene might had also been contributed by international transfer of colonised patients, as recently demonstrated from Greece to Belgium [28], Greece to Australia [42], and Iraq to USA military services [44] (Figure 1). Conclusions Outbreaks of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii are increasingly reported in several parts of the world that also include developing countries. They are sustained by clusters of highly similar strains that successfully spread among different cities and countries and are selected because of the acquisition of CHDLs genes flanked by IS elements. Multifacility A. baumannii outbreaks can be also sustained by inter-hospital transfer of colonized patients. This emphasizes the need to adopt surveillance and infection control programmes to prevent colonisation and infection by multidrug-resistant A. baumannii in the hospital setting. These programmes would include the study of global epidemiology of multidrug-resistant A. baumannii using molecular typing of bacterial isolates and characterization of antibiotic resistance in order to control the spread of A. baumannii infections over a wide geographic region. Acknowledgments Work performed in the authors laboratories is supported in part by a grant from Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco (AIFA2007 contract no. FARM7X9F8K). Restriction placed on the number of references that could be cited in this review mean that, in many cases, either a single paper or a review is cited. We apologize to those authors whose work has not been cited. References 1. Dijkshoorn L, Nemec A, Seifert H (2007) An increasing threat in hospitals: multidrugresistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat Rev Microbiol 5: Peleg ΑΥ, Seifert Η, Paterson DL (2008) Acinetobacter baumannii: emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev 21:
5 3. Dijkshoorn L, van Harsselaar B, Tjernberg I, Bouvet PJ, Vaneechoutte M (1998) Evaluation of amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis for identification of Acinetobacter genomic species. Syst Appl Microbiol 21: Chang HC, Wei YF, Dijkshoorn L, Vaneechoutte M, Tang CT, Chang TC (2005) Species-level identification of isolates of the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-acinetobacter baumannii complex by sequence analysis of the 16S-23S rrna gene spacer region. J Clin Microbiol 43: Sunenshine RH, Wright M-O, Maragakis LL, Haris AD, Song X, Hebden J, Cosgrove SE, Anderson A, Carnell J, Jernigan DB, Kleinbaum DG, Perl TM, Standiford HC, Srinivasan A (2007) Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter infection mortality rate and length of hospitalization. Emerg Infect Dis 13: Zarrilli R, Casillo R, Di Popolo A, Tripodi MF, Bagattini M, Cuccurullo S, Crivaro V, Ragone E, Mattei A, Galdieri N, Triassi M, Utili R (2007) Molecular epidemiology of a clonal outbreak of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a university hospital in Italy. Clin Microbiol Infect 13: Tsakris A, Ikonomidis A, Poulou A, Spanakis N, Vrizas D, Diomidous M, Pournaras S, Markou F (2008) Clusters of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clones producing different carbapenemases in an intensive care unit. Clin Microbiol Infect 14: Zarrilli R, Crispino M, Bagattini M, Barretta E, Di Popolo A, Triassi M, Villari P (2004) Molecular epidemiology of sequential outbreaks of Acinetobacter baumannii in an intensive care unit shows the emergence of carbapenem resistance. J Clin Microbiol 42: Vallenet D, Nordmann P, Barbe V, Poirel L, Mangenot S, Bataille E, Dossat C, Gas S, Kreimeyer A, Lenoble P, Oztas S, Poulain J, Segurens B, Robert C, Abergel C, Claverie JM, Raoult D, Médigue C, Weissenbach J, Cruveiller S (2005) Comparative analysis of Acinetobacters: three genomes for three lifestyles. PLos ONE 3: e Iacono M., Villa L, Fortini D, Bordoni R, Imperi F, Bonnal RJ, Sicheritz-Ponten T, De Bellis G, Visca P, Cassone A, Carattoli A (2008) Whole genome pyrosequencing of an epidemic multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii of the European clone II. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52: Adams MA, Goglin K, Molyneaux N, Hujer KM, Lavender H, Jamison JJ, MacDonald IJ, Martin KM, Russo T, Campagnari AA, Hujer AM, Bonomo RA, Gill SR (2009) Comparative genome sequence analysis of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J Bacteriol 190: Poirel L, Nordmann P (2006) Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: mechanisms and epidemiology. Clin Microbiol Infect 12: Poirel L, Nordmann P (2006) Genetic structure at the origin of acquisition and expression of the carbapenemhydrolyzing oxacillinase gene bla OXA-58 in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50: Pournaras S, Markogiannakis A, Ikonomidis A, Kondyli L, Bethimouti K, Maniatis AN, Legakis NJ, Tsakris A (2006) Outbreak of multiple clones of imipenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates expressing OXA-58 carbapenemase in an intensive care unit. J Antimicrob Chemother 57: Chen T-L, Wu RC-C, Shaio M-F, Fung C-P, Cho W-L (2008) Acquisition of a plasmid-borne blaoxa-58 gene with an upstream IS1008 insertion conferring a high level of carbapenem resistance to Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52: Zarrilli R, Vitale D, Di Popolo A, Bagattini M, Daoud Z, Khan AU, Afif C, Triassi M (2008) A plasmid-borne bla OXA-58 gene confers imipenem resistance to Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from a Lebanese hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52: Meric M, Kasap M, Gacar G, Budak F, Dundar D, Kolayli F, Eroglu C, Vahaboglu H (2008) Emergence and spread of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a tertiary care hospital in Turkey. FEMS Microbiol Lett 282: Mugnier PD, Poirel L, Nordmann P (2009) Functional Analysis of Insertion Sequence ISAba1, Responsible for Genomic Plasticity of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Bacteriol 191: Turton J F, Ward ME, Woodford N, Kaufmann ME, Pike R, Livermore DM, Pitt TL (2006) The role of ISAba1 in expression of OXA carbapenemase genes in Acinetobacter baumannii. FEMS Microbiol Lett 258: Tripodi M-F, Durante-Mangoni E, Fortunato R, Utili R, Zarrilli R (2007) Comparative activities of colistin, rifampicin, imipenem, sulbactam/ampicillin alone or in combination against epidemic multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates producing OXA-58 carbapenemases. Int J Antimicrob Agents 30: Mussi MA, Limansky AS, Viale AM (2005) Acquisition of resistance to carbapenems in multidrug-resistant clinical strains of Acinetobacter baumannii: natural insertional inactivation of a gene encoding a member of a novel family of β-barrel outer membrane proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49: Fernandez-Cuenca F, Martínez-Martínez L, Conejo MC, Ayala JA, Perea EJ, Pascual A (2003) Relationship between beta-lactamase production, outer membrane protein and penicillin-binding protein profiles on the activity of carbapenems against clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Antimicrob Chemother 51: Heritier C, Poirel L, Lambert T, Nordmann P (2005) Contribution of acquired carbapenem-hydrolyzing oxacillinases to carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49: Coelho JM, Turton JF, Kaufmann ME, Glover J, Woodford N, Warner M, Palepou MF, Pike R, Pitt TL, Patel BC, Livermore DM (2006) Occurrence of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clones at multiple hospitals in London and Southeast England. J Clin Microbiol 44: van den Broek PJ, Arends J, Bernards AT, De Brauwer E, Mascini EM, van der Reijden TJ, Spanjaard L, Thewessen EA, van der Zee A, van Zeijl JH, Dijkshoorn L (2006) Epidemiology of multiple Acinetobacter outbreaks in The Netherlands during the period Clin Microbiol Infect 12: Nemec A, Krizova L, Maixnerova M, Diancourt L, van der Reijden TJ, Brisse S, van den Broek P, Dijkshoorn L (2008) Emergence of carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii in the Czech Republic is associated with the spread of multidrug resistant strains of European clone II. J Antimicrob Chemother 62: Da Silva GJ, Quintera S, Bertolo E, Sousa JC, Gallego L, Duarte A, Peixe L; Portugese Resistance Study Group 339
6 (2004) Long-term dissemination of an OXA-40 carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter baumannii clone in the Iberian Peninsula. J Antimicrob Chemother 54: Wybo I, Blommaert L, De Beer T, Soetens O, De Regt J, Lacor P, Piérard D, Lauwers S (2007) Outbreak of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a Belgian university hospital after transfer of patients from Greece. J Hosp Infect 67: Schulte B, Goerke C, Weyrich P, Gröbner S, Bahrs C, Wolz C, Autenrieth IB, Borgmann S (2005) Clonal spread of meropenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains in hospitals in the Mediterranean region and transmission to south-west Germany. J Hosp Infect 61: D Arezzo S, Capone A, Petrosillo N, Visca P, on behalf of GRAB (2009) Epidemic multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii related to European clonal types I and II in Rome (Italy). Clin Microbiol Infect 15: Stoeva T, Higgins PG, Savov E, Markovska R, Mitov I, Seifert H (2009) Nosocomial spread of OXA-23 and OXA- 58 beta-lactamase-producing Acinetobacter baumannii in a Bulgarian hospital J Antimicrob Chemother 63: Marchaim D, Navon-Venezia S, Leavitt A, Chmelnitsky I, Schwaber MJ, Carmeli Y (2007) Molecular and epidemiologic study of polyclonal outbreaks of multidrugresistant Acinetobacter baumannii infection in an Israeli hospital. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 28: Giannouli M, Tomasone F, Agodi A, Vahaboglu H, Daoud Z, Triassi M, Tsakris A, Zarrilli R (2009) Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains in intensive care units of multiple Mediterranean hospitals. J Antimicrob Chemother 63: Mugnier P, Poirel L, Pitout M, Nordmann P (2008) Carbapenem-resistant and OXA-23-producing Acinetobacter baumannii isolates in the United Arab Emirates. Clin Microbiol Infect 14: Feizabadi MM et al. (2008) Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns and distribution of bla OXA genes among Acinetobacter spp. isolated from patients at Tehran hospitals. Jpn J Infect Dis 61: Villegas MV, Kattan JN, Correa A, Lolans K, Guzman AM, Woodford N, Livermore D, Quinn JP, and the Colombian Nosocomial Bacterial Resistance Study Group (2007) Dissemination of Acinetobacter baumannii clones with OXA-23 carbapenemase in Colombian hospitals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51: Merkier AK, Catalano M, Ramirez MS, Quiroga C, Orman B, Ratier L, Famiglietti A, Vay C, Di Martino A, Kaufman S, Centron D (2008) Polyclonal spread of blaoxa-23 and blaoxa-58 in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from Argentina. J Infect Developing Countries 2: Marais E, de Jong G, Ferraz V, Maloba B, Dusé AG (2004) Interhospital transfer of pan-resistant Acinetobacter strains in Johannesburg, South Africa. Am J Infect Control 32: Poirel L, Mansour W, Bouallegue O, Nordmann P (2008) Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from Tunisia producing the OXA-58-like carbapenemhydrolyzing oxacillinase OXA-97. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52: Hsueh P-R et al. (2002) Pandrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii causing nosocomial infections in a university hospital, Taiwan. Emerg Infect Dis 8: Mendes RE, Bell JM, Turnidge JD, Castanheira M, Jones RN. (2009) Emergence and widespread dissemination of OXA-23, -24/40 and -58 carbapenemases among Acinetobacter spp. in Asia-Pacific nations: report from the SENTRY surveillance program. J Antimicrob Chemother 63: Peleg AY, Bell JM, Hofmeyr A, Wiese P (2006) Intercountry transfer of Gram-negative organisms carrying the VIM-4 and OXA-58 carbapenem-hydrolysing enzymes. J Antimicrob Chemother 57: Naas T, Levy M, Hirschauer C, Marchandin H, Nordmann P (2005) Outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii producing the carbapenemase OXA-23 in a tertiary care hospital of Papeete, French Polynesia. J Clin Microbiol 43: Hujer KM, Hujer AM, Bajaksouzian S, Adams JM, Donskey CJ, Ecker DJ, Massire C, Eshoo MW, Sampath R, Thomson JM, Rather PN, Craft DW, Fishbain JT, Ewell AJ, Jacobs MR, Paterson DL, Bonomo RA (2006) Analysis of antibiotic resistance genes in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter sp. isolates from military and civilian patients treated at the Walter Reed Army Medical Center. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50: Hawley JS, Murray CK, Griffith ME, McElmeel ME, Fulcher LC, Hospenthal DR, Jorgensen JH (2007) Susceptibility of Acinetobacter strains isolated from deployed U.S. military personnel. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51: Scott P, Deye G, Srinivasan A, Murray C, Moran K, Hulten E, Fishbain J, Craft D, Riddell S, Lindler L, Mancuso J, Milstrey E, Bautista CT, Patel J, Ewell A, Hamilton T, Gaddy C, Tenney M, Christofer G, Petersen K, Endy T, Petruccelli B (2007) An outbreak of multidrugresistant Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex infection in the US military health care system associated with military operations in Iraq. Clin Infect Dis 44: Motaouakkil S, Charra B, Hachimi A, Nejmi H, Benslama A, Elmdaghri N, Belabbes H, Benbachir M Colistin and rifampicin in the treatment of nosocomial infections from multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii. (2006) J Infect 53: Shankar P R, Upadhyay D K, Subish P, Dubey A K, Mishra P (2006) Prescribing patterns among paediatric inpatients in a teaching hospital in western Nepal. Singapore Med J 47: Iregbu KC, Ogunsola FT, Odugbemi TO (2002) Infections caused by Acinetobacter species and their susceptibility to 14 antibiotics in Lagos University Teaching Hospital, Lagos, West Afr J Med 21: Chawla R. (2008) Epidemiology, etiology, and diagnosis of hospital-acquired pneumonia and ventilator-associated pneumonia in Asian countries. Am J Infect Control 36:S Towner KJ, Levi K, Vlassiadi M; ARPAC Steering Group (2008) Genetic diversity of carbapenem-resistant isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii in Europe. Clin Microbiol Infect 14: Lolans K, Rice TW, Munoz-Price LS, Quinn JP (2006) Multicity outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates producing the carbapenemase OXA-40. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50: Turton JF, Gabriel SN, Valderrey C, Kaufmann ME, Pitt TL (2007) Use of sequence-based typing and multiplex 340
7 PCR to identify clonal lineages of outbreak strains of Acinetobacter baumannii. Clin Microbiol Infect 13: Corresponding Author Raffaele Zarrilli Department of Preventive Medical Sciences, Hygiene Section University of Naples Federico II Via Pansini nr. 5, Napoli, Italy Conflict of interest: No conflict of interest is declared. 341
Multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA) Surveillance and Control. Alison Holmes
 Multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA) Surveillance and Control Alison Holmes The organism and it s epidemiology Surveillance Control What is it? What is it? What is it? What is it? Acinetobacter :
Multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA) Surveillance and Control Alison Holmes The organism and it s epidemiology Surveillance Control What is it? What is it? What is it? What is it? Acinetobacter :
Department of Clinical Microbiology, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham, UK
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01911.x Genetic diversity of carbapenem-resistant isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii in Europe K. J. Towner, K. Levi and M. Vlassiadi, on behalf of the ARPAC
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01911.x Genetic diversity of carbapenem-resistant isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii in Europe K. J. Towner, K. Levi and M. Vlassiadi, on behalf of the ARPAC
classification of Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates to international clones
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 12 March 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.03565-13 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 Single locus sequence-based
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 12 March 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.03565-13 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 Single locus sequence-based
Received 19 November 2009/Returned for modification 14 January 2010/Accepted 12 February 2010
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2010, p. 1223 1230 Vol. 48, No. 4 0095-1137/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.02263-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Molecular Epidemiology
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2010, p. 1223 1230 Vol. 48, No. 4 0095-1137/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.02263-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Molecular Epidemiology
Analysis of drug-resistant gene detection of blaoxa-like genes from Acinetobacter baumannii
 Analysis of drug-resistant gene detection of blaoxa-like genes from Acinetobacter baumannii D.K. Yang, H.J. Liang, H.L. Gao, X.W. Wang and Y. Wang Department of Infections, The First Affiliated Hospital
Analysis of drug-resistant gene detection of blaoxa-like genes from Acinetobacter baumannii D.K. Yang, H.J. Liang, H.L. Gao, X.W. Wang and Y. Wang Department of Infections, The First Affiliated Hospital
A Plasmid-Borne bla OXA-58 Gene Confers Imipenem Resistance to Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates from a Lebanese Hospital
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Nov. 2008, p. 4115 4120 Vol. 52, No. 11 0066-4804/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.00366-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. A Plasmid-Borne
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Nov. 2008, p. 4115 4120 Vol. 52, No. 11 0066-4804/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.00366-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. A Plasmid-Borne
Diversity in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from paediatric cancer patients in Egypt
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Diversity in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from paediatric cancer patients in Egypt L. Al-Hassan 1, H. El Mehallawy 2 and S.G.B. Amyes 1 1) Medical Microbiology, University
ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Diversity in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from paediatric cancer patients in Egypt L. Al-Hassan 1, H. El Mehallawy 2 and S.G.B. Amyes 1 1) Medical Microbiology, University
Epidemiological characterization and distribution of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in Italy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Epidemiological characterization and distribution of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in Italy M. L. Mezzatesta 1, M. M. D Andrea 2, R. Migliavacca
ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Epidemiological characterization and distribution of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in Italy M. L. Mezzatesta 1, M. M. D Andrea 2, R. Migliavacca
Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria. Antimicrobial Resistance. Molecular Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance. Topics to be Covered
 Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased number of hospitalizations Increased length
Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased number of hospitalizations Increased length
Antimicrobial Resistance
 Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased number of hospitalizations Increased length
Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased number of hospitalizations Increased length
Antimicrobial Resistance Acquisition of Foreign DNA
 Antimicrobial Resistance Acquisition of Foreign DNA Levy, Scientific American Horizontal gene transfer is common, even between Gram positive and negative bacteria Plasmid - transfer of single or multiple
Antimicrobial Resistance Acquisition of Foreign DNA Levy, Scientific American Horizontal gene transfer is common, even between Gram positive and negative bacteria Plasmid - transfer of single or multiple
Heteroresistance to Meropenem in Carbapenem-Susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 2009, p. 4055 4059 Vol. 47, No. 12 0095-1137/09/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.00959-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Heteroresistance
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 2009, p. 4055 4059 Vol. 47, No. 12 0095-1137/09/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.00959-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Heteroresistance
MID 23. Antimicrobial Resistance. Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria. Molecular Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance
 Antimicrobial Resistance Molecular Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance Micro evolutionary change - point mutations Beta-lactamase mutation extends spectrum of the enzyme rpob gene (RNA polymerase) mutation
Antimicrobial Resistance Molecular Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance Micro evolutionary change - point mutations Beta-lactamase mutation extends spectrum of the enzyme rpob gene (RNA polymerase) mutation
Acinetobacter Resistance in Turkish Tertiary Care Hospitals. Zeliha KOCAK TUFAN, MD, Assoc. Prof.
 Acinetobacter Resistance in Turkish Tertiary Care Hospitals Zeliha KOCAK TUFAN, MD, Assoc. Prof. Acinetobacter Problem Countries that have reported hospital outbreaks of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter
Acinetobacter Resistance in Turkish Tertiary Care Hospitals Zeliha KOCAK TUFAN, MD, Assoc. Prof. Acinetobacter Problem Countries that have reported hospital outbreaks of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter
Acinetobacter baumannii producing OXA-23 detected in the Czech Republic
 Senkyrikova et al. SpringerPlus 2013, 2:296 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Acinetobacter baumannii producing OXA-23 detected in the Czech Republic Marketa Senkyrikova 1*, Vendula Husickova
Senkyrikova et al. SpringerPlus 2013, 2:296 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Acinetobacter baumannii producing OXA-23 detected in the Czech Republic Marketa Senkyrikova 1*, Vendula Husickova
Antimicrobial Resistance
 Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased
Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased
ESCMID elibrary. Symposium: Acinetobacter Infections from East to West. Molecular Epidemiology Worldwide
 Symposium: Acinetobacter Infections from East to West Molecular Epidemiology Worldwide Harald Seifert Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie, Immunologie und Hygiene der Universität zu Köln 26 th ECCMID,
Symposium: Acinetobacter Infections from East to West Molecular Epidemiology Worldwide Harald Seifert Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie, Immunologie und Hygiene der Universität zu Köln 26 th ECCMID,
DRUG-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII A GROWING SUPERBUG POPULATION. Cara Wilder Ph.D. Technical Writer March 13 th 2014
 DRUG-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII A GROWING SUPERBUG POPULATION Cara Wilder Ph.D. Technical Writer March 13 th 2014 ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit organization with headquarters in Manassas,
DRUG-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII A GROWING SUPERBUG POPULATION Cara Wilder Ph.D. Technical Writer March 13 th 2014 ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit organization with headquarters in Manassas,
Antimicrobial Cycling. Donald E Low University of Toronto
 Antimicrobial Cycling Donald E Low University of Toronto Bad Bugs, No Drugs 1 The Antimicrobial Availability Task Force of the IDSA 1 identified as particularly problematic pathogens A. baumannii and
Antimicrobial Cycling Donald E Low University of Toronto Bad Bugs, No Drugs 1 The Antimicrobial Availability Task Force of the IDSA 1 identified as particularly problematic pathogens A. baumannii and
Acinetobacter Outbreaks: Experience from a Neurosurgery Critical Care Unit. Jumoke Sule Consultant Microbiologist 19 May 2010
 Acinetobacter Outbreaks: Experience from a Neurosurgery Critical Care Unit Jumoke Sule Consultant Microbiologist 19 May 2010 Epidemiology of Acinetobacter spp At least 32 different species Recovered from
Acinetobacter Outbreaks: Experience from a Neurosurgery Critical Care Unit Jumoke Sule Consultant Microbiologist 19 May 2010 Epidemiology of Acinetobacter spp At least 32 different species Recovered from
ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing microorganisms; state of the art. Laurent POIREL
 ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing microorganisms; state of the art Laurent POIREL Medical and Molecular Microbiology Unit Dept of Medicine University of Fribourg Switzerland INSERM U914 «Emerging Resistance
ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing microorganisms; state of the art Laurent POIREL Medical and Molecular Microbiology Unit Dept of Medicine University of Fribourg Switzerland INSERM U914 «Emerging Resistance
Other Enterobacteriaceae
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER NUMBER 50: Other Enterobacteriaceae Author Kalisvar Marimuthu, MD Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH Topic Outline Topic outline - Key Issues Known
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER NUMBER 50: Other Enterobacteriaceae Author Kalisvar Marimuthu, MD Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH Topic Outline Topic outline - Key Issues Known
Molecular characterization of carbapenemase genes in Acinetobacter baumannii in China
 Molecular characterization of carbapenemase genes in Acinetobacter baumannii in China F. Fang 1 *, S. Wang 2 *, Y.X. Dang 3, X. Wang 3 and G.Q. Yu 3 1 The CT Room, Nanyang City Center Hospital, Nanyang,
Molecular characterization of carbapenemase genes in Acinetobacter baumannii in China F. Fang 1 *, S. Wang 2 *, Y.X. Dang 3, X. Wang 3 and G.Q. Yu 3 1 The CT Room, Nanyang City Center Hospital, Nanyang,
Summary of the latest data on antibiotic consumption in the European Union
 Summary of the latest data on antibiotic consumption in the European Union ESAC-Net surveillance data November 2016 Provision of reliable and comparable national antimicrobial consumption data is a prerequisite
Summary of the latest data on antibiotic consumption in the European Union ESAC-Net surveillance data November 2016 Provision of reliable and comparable national antimicrobial consumption data is a prerequisite
Multi-drug resistant microorganisms
 Multi-drug resistant microorganisms Arzu TOPELI Director of MICU Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine, Ankara-Turkey Council Member of WFSICCM Deaths in the US declined by 220 per 100,000 with the
Multi-drug resistant microorganisms Arzu TOPELI Director of MICU Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine, Ankara-Turkey Council Member of WFSICCM Deaths in the US declined by 220 per 100,000 with the
Testing for antimicrobial activity against multi-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. For. Forbo Flooring B.V. Final Report. Work Carried Out By
 Technical Report Testing for antimicrobial activity against multi-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii For Forbo Flooring B.V. Final Report Work Carried Out By A. Smith Group Leader Peter Collins PRA Ref:
Technical Report Testing for antimicrobial activity against multi-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii For Forbo Flooring B.V. Final Report Work Carried Out By A. Smith Group Leader Peter Collins PRA Ref:
Mechanism of antibiotic resistance
 Mechanism of antibiotic resistance Dr.Siriwoot Sookkhee Ph.D (Biopharmaceutics) Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University Antibiotic resistance Cross-resistance : resistance
Mechanism of antibiotic resistance Dr.Siriwoot Sookkhee Ph.D (Biopharmaceutics) Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University Antibiotic resistance Cross-resistance : resistance
β-lactams resistance among Enterobacteriaceae in Morocco 1 st ICREID Addis Ababa March 2018
 β-lactams resistance among Enterobacteriaceae in Morocco 1 st ICREID Addis Ababa 12-14 March 2018 Antibiotic resistance center Institut Pasteur du Maroc Enterobacteriaceae (E. coli, Salmonella, ) S. aureus
β-lactams resistance among Enterobacteriaceae in Morocco 1 st ICREID Addis Ababa 12-14 March 2018 Antibiotic resistance center Institut Pasteur du Maroc Enterobacteriaceae (E. coli, Salmonella, ) S. aureus
RESEARCH NOTE. Molecular epidemiology of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii in New Caledonia
 Research tes 977 routine clinical testing. J Antimicrob Chemother 2002; 40: 2755 2759. 20. Galani I, Rekatsina PD, Hatzaki D et al. Evaluation of different laboratory tests for the detection of metallob-lactamase
Research tes 977 routine clinical testing. J Antimicrob Chemother 2002; 40: 2755 2759. 20. Galani I, Rekatsina PD, Hatzaki D et al. Evaluation of different laboratory tests for the detection of metallob-lactamase
Distribution of bla OXA genes among carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii nosocomial strains in Poland
 NEW MICROBIOLOGICA, 35, 317-325, 2012 Distribution of bla OXA genes among carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii nosocomial strains in Poland Paweł Nowak 1, Paulina Paluchowska 1, Alicja Budak 1,2
NEW MICROBIOLOGICA, 35, 317-325, 2012 Distribution of bla OXA genes among carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii nosocomial strains in Poland Paweł Nowak 1, Paulina Paluchowska 1, Alicja Budak 1,2
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times
 Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
Georgios Meletis, Efstathios Oustas, Christina Botziori, Eleni Kakasi, Asimoula Koteli
 New Microbiologica, 38, 417-421, 2015 Containment of carbapenem resistance rates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Acinetobacter baumannii in a Greek hospital with a concomitant increase in colistin, gentamicin
New Microbiologica, 38, 417-421, 2015 Containment of carbapenem resistance rates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Acinetobacter baumannii in a Greek hospital with a concomitant increase in colistin, gentamicin
WHO laboratory-based global survey on multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) in health care interim analysis
 WHO laboratory-based global survey on multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) in health care interim analysis Aim: to estimate the burden of MDROs isolated among inpatients in a wide range of health-care
WHO laboratory-based global survey on multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) in health care interim analysis Aim: to estimate the burden of MDROs isolated among inpatients in a wide range of health-care
A review on multidrug - resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 2 (2014) pp. 9-13 http://www.ijcmas.com Review Article A review on multidrug - resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Pavani Gandham* Department of Microbiology, Apollo Institute
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 2 (2014) pp. 9-13 http://www.ijcmas.com Review Article A review on multidrug - resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Pavani Gandham* Department of Microbiology, Apollo Institute
Prevalence of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its antibiogram in a tertiary care centre
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 952-956 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 952-956 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase
REVIEW. Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: mechanisms and epidemiology L. Poirel and P. Nordmann /j
 REVIEW 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01456.x Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: mechanisms and epidemiology L. Poirel and P. Nordmann Service de Bactériologie-Virologie, Hôpital de Bicêtre, South-Paris
REVIEW 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01456.x Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: mechanisms and epidemiology L. Poirel and P. Nordmann Service de Bactériologie-Virologie, Hôpital de Bicêtre, South-Paris
Molecular epidemiology of Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter nosocomialis in Germany over a 5-year period ( )
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/1469-0691.12026 Molecular epidemiology of Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter nosocomialis in Germany over a 5-year period (2005 2009) X. Schleicher 1, P. G. Higgins 1, H.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/1469-0691.12026 Molecular epidemiology of Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter nosocomialis in Germany over a 5-year period (2005 2009) X. Schleicher 1, P. G. Higgins 1, H.
Presenter: Ombeva Malande. Red Cross Children's Hospital Paed ID /University of Cape Town Friday 6 November 2015: Session:- Paediatric ID Update
 Emergence of invasive Carbapenem Resistant Enterobacteriaceae CRE infection at RCWMCH Ombeva Oliver Malande, Annerie du Plessis, Colleen Bamford, Brian Eley Presenter: Ombeva Malande Red Cross Children's
Emergence of invasive Carbapenem Resistant Enterobacteriaceae CRE infection at RCWMCH Ombeva Oliver Malande, Annerie du Plessis, Colleen Bamford, Brian Eley Presenter: Ombeva Malande Red Cross Children's
Summary of the latest data on antibiotic consumption in the European Union
 Summary of the latest data on antibiotic consumption in the European Union November 2012 Highlights on antibiotic consumption Antibiotic use is one of the main factors responsible for the development and
Summary of the latest data on antibiotic consumption in the European Union November 2012 Highlights on antibiotic consumption Antibiotic use is one of the main factors responsible for the development and
Microbiology Unit, Hua Hin Hospital, Prachuap Khiri Khan, Thailand
 IDENTIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CARBAPENEMASE GENES IN CLINICAL ISOLATES OF CARBAPENEM-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII FROM A GENERAL HOSPITAL IN THAILAND Wichai Santimaleeworagun 1, Anukul Thathong
IDENTIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CARBAPENEMASE GENES IN CLINICAL ISOLATES OF CARBAPENEM-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII FROM A GENERAL HOSPITAL IN THAILAND Wichai Santimaleeworagun 1, Anukul Thathong
Florida Health Care Association District 2 January 13, 2015 A.C. Burke, MA, CIC
 Florida Health Care Association District 2 January 13, 2015 A.C. Burke, MA, CIC 11/20/2014 1 To describe carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. To identify laboratory detection standards for carbapenem-resistant
Florida Health Care Association District 2 January 13, 2015 A.C. Burke, MA, CIC 11/20/2014 1 To describe carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. To identify laboratory detection standards for carbapenem-resistant
OXA-type carbapenemases in Acinetobacter baumannii in South America
 Review Article OXA-type carbapenemases in Acinetobacter baumannii in South America Andres Opazo 1,2, Mariana Domínguez 1, Helia Bello 1, Sebastian G. B. Amyes 2, Gerardo González-Rocha 1 1 Laboratorio
Review Article OXA-type carbapenemases in Acinetobacter baumannii in South America Andres Opazo 1,2, Mariana Domínguez 1, Helia Bello 1, Sebastian G. B. Amyes 2, Gerardo González-Rocha 1 1 Laboratorio
DR. MICHAEL A. BORG DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION & CONTROL MATER DEI HOSPITAL - MALTA
 DR. MICHAEL A. BORG DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION & CONTROL MATER DEI HOSPITAL - MALTA The good old days The dread (of) infections that used to rage through the whole communities is muted Their retreat
DR. MICHAEL A. BORG DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION & CONTROL MATER DEI HOSPITAL - MALTA The good old days The dread (of) infections that used to rage through the whole communities is muted Their retreat
Longitudinal Analysis of the Temporal Evolution of Acinetobacter baumannii Strains in Ohio, USA, by Using Rapid Automated Typing Methods
 Longitudinal Analysis of the Temporal Evolution of Acinetobacter baumannii Strains in Ohio, USA, by Using Rapid Automated Typing Methods Brooke K. Decker, Case Western Reserve University Federico Perez,
Longitudinal Analysis of the Temporal Evolution of Acinetobacter baumannii Strains in Ohio, USA, by Using Rapid Automated Typing Methods Brooke K. Decker, Case Western Reserve University Federico Perez,
RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI ISOLATES AMONG DIFFERENT CLINICAL SAMPLES FROM A DIAGNOSTIC CENTER OF KANPUR
 Original article RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI ISOLATES AMONG DIFFERENT CLINICAL SAMPLES FROM A DIAGNOSTIC CENTER OF KANPUR R.Sujatha 1,Nidhi Pal 2, Deepak S 3 1. Professor & Head, Department
Original article RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI ISOLATES AMONG DIFFERENT CLINICAL SAMPLES FROM A DIAGNOSTIC CENTER OF KANPUR R.Sujatha 1,Nidhi Pal 2, Deepak S 3 1. Professor & Head, Department
Differences in phenotypic and genotypic traits against antimicrobial agents between Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter genomic species 13TU
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2007) 59, 633 639 doi:10.1093/jac/dkm007 Advance Access publication 6 March 2007 Differences in phenotypic and genotypic traits against antimicrobial agents between
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2007) 59, 633 639 doi:10.1093/jac/dkm007 Advance Access publication 6 March 2007 Differences in phenotypic and genotypic traits against antimicrobial agents between
Witchcraft for Gram negatives
 Witchcraft for Gram negatives Dr Subramanian S MD DNB MNAMS AB (Medicine, Infect Dis) Infectious Diseases Consultant Global Health City, Chennai www.asksubra.com Drug resistance follows the drug like a
Witchcraft for Gram negatives Dr Subramanian S MD DNB MNAMS AB (Medicine, Infect Dis) Infectious Diseases Consultant Global Health City, Chennai www.asksubra.com Drug resistance follows the drug like a
ESBL Producers An Increasing Problem: An Overview Of An Underrated Threat
 ESBL Producers An Increasing Problem: An Overview Of An Underrated Threat Hicham Ezzat Professor of Microbiology and Immunology Cairo University Introduction 1 Since the 1980s there have been dramatic
ESBL Producers An Increasing Problem: An Overview Of An Underrated Threat Hicham Ezzat Professor of Microbiology and Immunology Cairo University Introduction 1 Since the 1980s there have been dramatic
ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY ADDRESSING ACCURATE TESTING OF MULTIDRUG- RESISTANT ACINETOBACTERS
 RESISTANT ACINETOBACTERS Sample ES-01 was a simulated blood culture and a duplicate of a strain used in 2009 (ES-03). Participants were instructed to perform organism isolation, identification of the pathogen,
RESISTANT ACINETOBACTERS Sample ES-01 was a simulated blood culture and a duplicate of a strain used in 2009 (ES-03). Participants were instructed to perform organism isolation, identification of the pathogen,
Overnight identification of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii carriage in hospitalized patients
 TABLE 1. Origin and carbapenem resistance characteristics of the 64 Acinetobacter baumannii stock D-750 Overnight identification of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii carriage in hospitalized patients
TABLE 1. Origin and carbapenem resistance characteristics of the 64 Acinetobacter baumannii stock D-750 Overnight identification of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii carriage in hospitalized patients
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THE RISE OF CARBAPENEM-RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
 ENTEROBACTERIACEAE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
ENTEROBACTERIACEAE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
Comparative Assessment of b-lactamases Produced by Multidrug Resistant Bacteria
 Comparative Assessment of b-lactamases Produced by Multidrug Resistant Bacteria Juhee Ahn Department of Medical Biomaterials Engineering Kangwon National University October 23, 27 Antibiotic Development
Comparative Assessment of b-lactamases Produced by Multidrug Resistant Bacteria Juhee Ahn Department of Medical Biomaterials Engineering Kangwon National University October 23, 27 Antibiotic Development
Multicity Outbreak of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates Producing the Carbapenemase OXA-40
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Sept. 2006, p. 2941 2945 Vol. 50, No. 9 0066-4804/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.00116-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Multicity
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Sept. 2006, p. 2941 2945 Vol. 50, No. 9 0066-4804/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.00116-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Multicity
Prevalence of Acinetobacter infections among Intensive Care Unit's patients in Najran
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 5-2017 Prevalence of Acinetobacter
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 5-2017 Prevalence of Acinetobacter
What does multiresistance actually mean? Yohei Doi, MD, PhD University of Pittsburgh
 What does multiresistance actually mean? Yohei Doi, MD, PhD University of Pittsburgh Disclosures Merck Research grant Clinical context of multiresistance Resistance to more classes of agents Less options
What does multiresistance actually mean? Yohei Doi, MD, PhD University of Pittsburgh Disclosures Merck Research grant Clinical context of multiresistance Resistance to more classes of agents Less options
Dr Vivien CHUANG Associate Consultant Infection Control Branch, Centre for Health Protection/ Infectious Disease Control and Training Center,
 Dr Vivien CHUANG Associate Consultant Infection Control Branch, Centre for Health Protection/ Infectious Disease Control and Training Center, Hospital Authority NDM-1, which stands for New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase-1
Dr Vivien CHUANG Associate Consultant Infection Control Branch, Centre for Health Protection/ Infectious Disease Control and Training Center, Hospital Authority NDM-1, which stands for New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase-1
Antimicrobial resistance (EARS-Net)
 SURVEILLANCE REPORT Annual Epidemiological Report for 2014 Antimicrobial resistance (EARS-Net) Key facts Over the last four years (2011 to 2014), the percentages of Klebsiella pneumoniae resistant to fluoroquinolones,
SURVEILLANCE REPORT Annual Epidemiological Report for 2014 Antimicrobial resistance (EARS-Net) Key facts Over the last four years (2011 to 2014), the percentages of Klebsiella pneumoniae resistant to fluoroquinolones,
Originally published as:
 Originally published as: Yvonne Pfeifer, Gottfried Wilharm, Esther Zander, Thomas A. Wichelhaus, Stefan Göttig, Klaus- Peter Hunfeld, Harald Seifert, Wolfgang Witte and Paul G. Higgins Molecular characterization
Originally published as: Yvonne Pfeifer, Gottfried Wilharm, Esther Zander, Thomas A. Wichelhaus, Stefan Göttig, Klaus- Peter Hunfeld, Harald Seifert, Wolfgang Witte and Paul G. Higgins Molecular characterization
Mechanisms and Pathways of AMR in the environment
 FMM/RAS/298: Strengthening capacities, policies and national action plans on prudent and responsible use of antimicrobials in fisheries Final Workshop in cooperation with AVA Singapore and INFOFISH 12-14
FMM/RAS/298: Strengthening capacities, policies and national action plans on prudent and responsible use of antimicrobials in fisheries Final Workshop in cooperation with AVA Singapore and INFOFISH 12-14
Rise of Resistance: From MRSA to CRE
 Rise of Resistance: From MRSA to CRE Paul D. Holtom, MD Professor of Medicine and Orthopaedics USC Keck School of Medicine SUPERBUGS (AKA MDROs) MRSA Methicillin-resistant S. aureus Evolution of Drug Resistance
Rise of Resistance: From MRSA to CRE Paul D. Holtom, MD Professor of Medicine and Orthopaedics USC Keck School of Medicine SUPERBUGS (AKA MDROs) MRSA Methicillin-resistant S. aureus Evolution of Drug Resistance
Identification of Multidrug-Resistant Genes in Acinetobacter baumannii in Sulaimani City-Kurdistan Regional Government of Iraq
 Asian Journal of Medical Sciences 4(5): 179-183, 2012 ISSN: 2040-8773 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2012 Submitted: August 09, 2012 Accepted: September 17, 2012 Published: October 25, 2012 Identification
Asian Journal of Medical Sciences 4(5): 179-183, 2012 ISSN: 2040-8773 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2012 Submitted: August 09, 2012 Accepted: September 17, 2012 Published: October 25, 2012 Identification
Pedro Martínez and Salim Mattar* ABSTRACT
 Brazilian Journal of Microbiology (2012): 1274-1280 ISSN 1517-8382 IMIPENEM-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII CARRYING THE ISABA1-BLA OXA-23, 51 AND ISABA1- BLA ADC-7 GENES IN MONTERIA, COLOMBIA Pedro
Brazilian Journal of Microbiology (2012): 1274-1280 ISSN 1517-8382 IMIPENEM-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII CARRYING THE ISABA1-BLA OXA-23, 51 AND ISABA1- BLA ADC-7 GENES IN MONTERIA, COLOMBIA Pedro
Neisseria meningitidis ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE:CURRENT SITUATION IN LATIN AMERICA AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE
 Neisseria meningitidis ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE:CURRENT SITUATION IN LATIN AMERICA AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE Dra. Silvia E. González Ayala Head Professor Cátedra Infectología, Facultad Ciencias Médicas,
Neisseria meningitidis ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE:CURRENT SITUATION IN LATIN AMERICA AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE Dra. Silvia E. González Ayala Head Professor Cátedra Infectología, Facultad Ciencias Médicas,
Clinical and microbiological characterization of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infections
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2011), 60, 605 611 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.029439-0 Clinical and microbiological characterization of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infections Joon
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2011), 60, 605 611 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.029439-0 Clinical and microbiological characterization of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infections Joon
Nosocomial Infections: What Are the Unmet Needs
 Nosocomial Infections: What Are the Unmet Needs Jean Chastre, MD Service de Réanimation Médicale Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, AP-HP, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris 6, France www.reamedpitie.com
Nosocomial Infections: What Are the Unmet Needs Jean Chastre, MD Service de Réanimation Médicale Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, AP-HP, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris 6, France www.reamedpitie.com
Endemic and Epidemic Acinetobacter Species in a University Hospital: an 8-Year Survey
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2009, p. 3593 3599 Vol. 47, No. 11 0095-1137/09/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.00967-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Endemic and
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2009, p. 3593 3599 Vol. 47, No. 11 0095-1137/09/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.00967-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Endemic and
Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance among Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Hospitalized Patients at Chiang Mai University Hospital,
 Original Article Vol. 28 No. 1 Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance:- Chaiwarith R, et al. 3 Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance among Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Hospitalized Patients at
Original Article Vol. 28 No. 1 Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance:- Chaiwarith R, et al. 3 Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance among Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Hospitalized Patients at
Antimicrobial Resistance and Prescribing
 Antimicrobial Resistance and Prescribing John Ferguson, Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, John Hunter Hospital, University of Newcastle, NSW, Australia M Med Part 1 updates UPNG 2017 Tw @mdjkf http://idmic.net
Antimicrobial Resistance and Prescribing John Ferguson, Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, John Hunter Hospital, University of Newcastle, NSW, Australia M Med Part 1 updates UPNG 2017 Tw @mdjkf http://idmic.net
(DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
 (DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE John Ferguson (Hunter New England, NSW) on behalf of MRGN Task Force Acknowledgement
(DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE John Ferguson (Hunter New England, NSW) on behalf of MRGN Task Force Acknowledgement
Fighting MDR Pathogens in the ICU
 Fighting MDR Pathogens in the ICU Dr. Murat Akova Hacettepe University School of Medicine, Department of Infectious Diseases, Ankara, Turkey 1 50.000 deaths each year in US and Europe due to antimicrobial
Fighting MDR Pathogens in the ICU Dr. Murat Akova Hacettepe University School of Medicine, Department of Infectious Diseases, Ankara, Turkey 1 50.000 deaths each year in US and Europe due to antimicrobial
Chart showing the average height of males and females in various world countries.
 Chart showing the average height of males and females in various world countries. Country/Region Average male height Average female height Sampled Age Range Albania 174.0 cm (5 ft 8 1/2 in) 161.8 cm (5
Chart showing the average height of males and females in various world countries. Country/Region Average male height Average female height Sampled Age Range Albania 174.0 cm (5 ft 8 1/2 in) 161.8 cm (5
Antibiotic resistance a mechanistic overview Neil Woodford
 Antibiotic Resistance a Mechanistic verview BSc PhD FRCPath Consultant Clinical Scientist 1 Polymyxin Colistin Daptomycin Mechanisms of antibiotic action Quinolones Mupirocin Nitrofurans Nitroimidazoles
Antibiotic Resistance a Mechanistic verview BSc PhD FRCPath Consultant Clinical Scientist 1 Polymyxin Colistin Daptomycin Mechanisms of antibiotic action Quinolones Mupirocin Nitrofurans Nitroimidazoles
ORIGINAL ARTICLE /j x. Mallorca, Spain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01251.x Contribution of clonal dissemination and selection of mutants during therapy to Pseudomonas aeruginosa antimicrobial resistance in an intensive care unit
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01251.x Contribution of clonal dissemination and selection of mutants during therapy to Pseudomonas aeruginosa antimicrobial resistance in an intensive care unit
MDR Acinetobacter baumannii. Has the post antibiotic era arrived? Dr. Michael A. Borg Infection Control Dept Mater Dei Hospital Malta
 MDR Acinetobacter baumannii Has the post antibiotic era arrived? Dr. Michael A. Borg Infection Control Dept Mater Dei Hospital Malta 1 The Armageddon recipe Transmissible organism with prolonged environmental
MDR Acinetobacter baumannii Has the post antibiotic era arrived? Dr. Michael A. Borg Infection Control Dept Mater Dei Hospital Malta 1 The Armageddon recipe Transmissible organism with prolonged environmental
A novel variant of the β-lactamase ADC-61 gene in multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
 A novel variant of the β-lactamase ADC-61 gene in multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Y. Zhou, S.-J. Teng, L. Yang, S.-B. Li and Y. Xu Clinical Laboratory Department, The Second People s Hospital
A novel variant of the β-lactamase ADC-61 gene in multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Y. Zhou, S.-J. Teng, L. Yang, S.-B. Li and Y. Xu Clinical Laboratory Department, The Second People s Hospital
Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem non-susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii in France.
 Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem non-susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii in France. Katy Jeannot, Laure Diancourt, Sophie Vaux, Michelle Thouverez, Amandina Ribeiro, Bruno Coignard, Patrice Courvalin,
Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem non-susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii in France. Katy Jeannot, Laure Diancourt, Sophie Vaux, Michelle Thouverez, Amandina Ribeiro, Bruno Coignard, Patrice Courvalin,
Molecular Epidemiology and Insights into the Genomes of. Acinetobacter calcoaceticus - Acinetobacter baumannii complex
 Molecular Epidemiology and Insights into the Genomes of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus - Acinetobacter baumannii complex Witchuda Kamolvit MD A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy at The
Molecular Epidemiology and Insights into the Genomes of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus - Acinetobacter baumannii complex Witchuda Kamolvit MD A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy at The
Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Concern for Healthcare Security and Resilience
 Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Concern for Healthcare Security and Resilience Neil Woodford HPA AMRHAI - Colindale Resistance is entirely natural...and is ancient Permafrost samples Late Pleistocene
Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Concern for Healthcare Security and Resilience Neil Woodford HPA AMRHAI - Colindale Resistance is entirely natural...and is ancient Permafrost samples Late Pleistocene
First Identification of OXA-72 Carbapenemase from Acinetobacter pittii in Colombia.
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 16 April 2012 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.05628-11 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 16 April 2012 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.05628-11 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6
Mono- versus Bitherapy for Management of HAP/VAP in the ICU
 Mono- versus Bitherapy for Management of HAP/VAP in the ICU Jean Chastre, www.reamedpitie.com Conflicts of interest: Consulting or Lecture fees: Nektar-Bayer, Pfizer, Brahms, Sanofi- Aventis, Janssen-Cilag,
Mono- versus Bitherapy for Management of HAP/VAP in the ICU Jean Chastre, www.reamedpitie.com Conflicts of interest: Consulting or Lecture fees: Nektar-Bayer, Pfizer, Brahms, Sanofi- Aventis, Janssen-Cilag,
Amoxicillin trihydrate. Amoxicillin trihydrate. Amoxicillin trihydrate. Amoxicillin trihydrate. Amoxicillin trihydrate. Amoxicillin trihydrate
 Annex I List of the names, pharmaceutical form, strength of the veterinary medicinal product, animal species, route of administration, applicant in the Member States Member State EU/EEA Applicant Name
Annex I List of the names, pharmaceutical form, strength of the veterinary medicinal product, animal species, route of administration, applicant in the Member States Member State EU/EEA Applicant Name
BLA-NDM-1 IN CLINICAL ISOLATES OF Acinetobacter baumannii FROM NORTH INDIA
 ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138(Online) BLA-NDM-1 IN CLINICAL ISOLATES OF Acinetobacter baumannii FROM NORTH INDIA NIDHI PAL a, R. SUJATHA b AND ANIL KUMAR 1c a Department of Microbiology, Rama
ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138(Online) BLA-NDM-1 IN CLINICAL ISOLATES OF Acinetobacter baumannii FROM NORTH INDIA NIDHI PAL a, R. SUJATHA b AND ANIL KUMAR 1c a Department of Microbiology, Rama
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN OF ESBL PRODUCING GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI ABSTRACT
 Research Article Microbiology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN OF ESBL PRODUCING GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI * PRABHAKAR C MAILAPUR, DEEPA
Research Article Microbiology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN OF ESBL PRODUCING GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI * PRABHAKAR C MAILAPUR, DEEPA
Molecular Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Five Proximal Hospitals in Taiwan
 Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 64, 222-227, 2011 Short Communication Molecular Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Five Proximal Hospitals in
Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 64, 222-227, 2011 Short Communication Molecular Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Five Proximal Hospitals in
Pneumococcus: Antibiotic Resistance in the Region
 Pneumococcus: Antibiotic Resistance in the Region Çiğdem Bal Kayacan Istanbul University Istanbul Faculty of Medicine Department of Microbiology & Clinical Microbiology Drug Resistance in S.pneumoniae
Pneumococcus: Antibiotic Resistance in the Region Çiğdem Bal Kayacan Istanbul University Istanbul Faculty of Medicine Department of Microbiology & Clinical Microbiology Drug Resistance in S.pneumoniae
Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version
 Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED 2018 Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY NO. IC-122 Policy Group Infection Control
Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED 2018 Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY NO. IC-122 Policy Group Infection Control
Epidemic multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii related to European clonal types I and II in Rome (Italy)
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02668.x Epidemic multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii related to European clonal types I and II in Rome (Italy) S. D Arezzo 1, A. Capone 1, N. Petrosillo
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02668.x Epidemic multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii related to European clonal types I and II in Rome (Italy) S. D Arezzo 1, A. Capone 1, N. Petrosillo
Geoffrey Coombs 1, Graeme Nimmo 2, Julie Pearson 1, Samantha Cramer 1 and Keryn Christiansen 1
 Community Onset MRSA Infections in Australia: A Tale of Two Clones Geoffrey Coombs 1, Graeme Nimmo 2, Julie Pearson 1, Samantha Cramer 1 and Keryn Christiansen 1 Community Associated MRSA First isolated
Community Onset MRSA Infections in Australia: A Tale of Two Clones Geoffrey Coombs 1, Graeme Nimmo 2, Julie Pearson 1, Samantha Cramer 1 and Keryn Christiansen 1 Community Associated MRSA First isolated
Epidemiology and Burden of Antimicrobial-Resistant P. aeruginosa Infections
 Epidemiology and Burden of Antimicrobial-Resistant P. aeruginosa Infections Keith S. Kaye, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases Department of Internal Medicine University of Michigan
Epidemiology and Burden of Antimicrobial-Resistant P. aeruginosa Infections Keith S. Kaye, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases Department of Internal Medicine University of Michigan
Assessment of antibiotic resistance pattern in Acinetobacter baumannii carrying bla oxa type genes isolated from hospitalized patients
 Novelty in Biomedicine Original Article Assessment of antibiotic resistance pattern in Acinetobacter baumannii carrying bla oxa type genes isolated from hospitalized patients Hossein Goudarzi 1*, Masoumeh
Novelty in Biomedicine Original Article Assessment of antibiotic resistance pattern in Acinetobacter baumannii carrying bla oxa type genes isolated from hospitalized patients Hossein Goudarzi 1*, Masoumeh
HEALTHCARE-ACQUIRED INFECTIONS AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE
 Universidade de São Paulo Departamento de Moléstias Infecciosas e Parasitárias HEALTHCARE-ACQUIRED INFECTIONS AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE Anna S. Levin 4 main lines! Epidemiology of HAS and resistance!
Universidade de São Paulo Departamento de Moléstias Infecciosas e Parasitárias HEALTHCARE-ACQUIRED INFECTIONS AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE Anna S. Levin 4 main lines! Epidemiology of HAS and resistance!
Decrease of vancomycin resistance in Enterococcus faecium from bloodstream infections in
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 30 March 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00513-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Decrease of vancomycin
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 30 March 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00513-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Decrease of vancomycin
Clonal Diversity of Nosocomial Epidemic Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Isolated in Spain
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 2011, p. 875 882 Vol. 49, No. 3 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01026-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Clonal Diversity
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 2011, p. 875 882 Vol. 49, No. 3 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01026-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Clonal Diversity
Global Alliance for Infections in Surgery. Better understanding of the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance
 Better understanding of the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance Antibiotic prescribing practices in surgery Contents Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance 4 Antibiotic resistance in Enterobacteriaceae 9
Better understanding of the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance Antibiotic prescribing practices in surgery Contents Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance 4 Antibiotic resistance in Enterobacteriaceae 9
Global response to antibiotic access and resistance: Stuart B. Levy, M.D. Tufts University School of Medicine Alliance for Prudent Use of Antibiotics
 Global response to antibiotic access and resistance: Stuart B. Levy, M.D. Tufts University School of Medicine Alliance for Prudent Use of Antibiotics Established in 1981 APUA s Mission To improve control
Global response to antibiotic access and resistance: Stuart B. Levy, M.D. Tufts University School of Medicine Alliance for Prudent Use of Antibiotics Established in 1981 APUA s Mission To improve control
Activity of a novel aminoglycoside, ACHN-490, against clinical isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae from New York City
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published July 31, 2010 J Antimicrob Chemother doi:10.1093/jac/dkq278 Activity of a novel aminoglycoside, ACHN-490, against clinical isolates of Escherichia
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published July 31, 2010 J Antimicrob Chemother doi:10.1093/jac/dkq278 Activity of a novel aminoglycoside, ACHN-490, against clinical isolates of Escherichia
METHODS. Imipenem Meropenem Colistin Polymyxin B Ampicillinsulbactam. Downloaded from by IP:
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (01), 1, 353 30 DOI.99/jmm.0.03939-0 In vitro time-kill studies of antimicrobial agents against blood isolates of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, including colistin-
Journal of Medical Microbiology (01), 1, 353 30 DOI.99/jmm.0.03939-0 In vitro time-kill studies of antimicrobial agents against blood isolates of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, including colistin-
Increasing trends in mcr-1 prevalence among ESBL-producing E. coli in French calves
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 8 August 2016 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01147-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Increasing trends
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 8 August 2016 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01147-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Increasing trends
Intrinsic, implied and default resistance
 Appendix A Intrinsic, implied and default resistance Magiorakos et al. [1] and CLSI [2] are our primary sources of information on intrinsic resistance. Sanford et al. [3] and Gilbert et al. [4] have been
Appendix A Intrinsic, implied and default resistance Magiorakos et al. [1] and CLSI [2] are our primary sources of information on intrinsic resistance. Sanford et al. [3] and Gilbert et al. [4] have been
Prevalence of Extended-spectrum β-lactamase Producing Enterobacteriaceae Strains in Latvia
 Prevalence of Extended-spectrum β-lactamase Producing Enterobacteriaceae Strains in Latvia Ruta Paberza 1, Solvita Selderiņa 1, Sandra Leja 1, Jelena Storoženko 1, Lilija Lužbinska 1, Aija Žileviča 2*
Prevalence of Extended-spectrum β-lactamase Producing Enterobacteriaceae Strains in Latvia Ruta Paberza 1, Solvita Selderiņa 1, Sandra Leja 1, Jelena Storoženko 1, Lilija Lužbinska 1, Aija Žileviča 2*
