The life cycle of Myxobolus lentisuturalis (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae), from goldfish (Carassius auratus auratus), involves a Raabeia-type actinospore
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Gilmore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FOLIA PARASITOLOGICA 56[1]: 6 12, 2009 ISSN (print), ISSN (online) Institute of Parasitology, Biology Centre ASCR The life cycle of Myxobolus lentisuturalis (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae), from goldfish (Carassius auratus auratus), involves a Raabeia-type actinospore Monica Caffara 1, Elena Raimondi 1, Daniela Florio 1, Federica Marcer 2, Francesco Quaglio 3 and Maria Letizia Fioravanti 1 1 Department of Veterinary Public Health and Animal Pathology, Alma Mater Studiorum University of Bologna, via Tolara di Sopra 50, Ozzano Emila (Bologna), Italy; 2 Department of Experimental and Veterinary Sciences, University of Padova, Agripolis Viale dell Università 16, Padova, Italy; 3 Department of Public Health, Comparative Pathology and Veterinary Hygiene, University of Padova, Agripolis Viale dell Università 16, Padova, Italy Abstract: We studied a natural infection of the oligochaete Branchiura sowerbyi Beddard, 1892 with the Raabeia-type actinosporean stage of Myxobolus lentisuturalis Dyková, Fiala et Nie, 2002 which infected goldfish Carassius auratus auratus (L.) in Italy, using molecular analysis of the SSU rrna gene. The existence of intraoligochaete development shows that this parasite follows the lifecycle pattern described by Wolf and Markiw (1984) for Myxobolus cerebralis. Histological examinations of the goldfish infected by M. lentisuturalis showed at low magnification the presence of two bilateral crescent-shaped masses in the dorsal epaxial muscle. These lesions were not circumscribed, presented irregular edges and infiltrated the underlying bundles of skeletal muscle and interstitial tissue. At higher magnification, disappearance of muscle fibres and substitution of the muscle tissue with Myxobolus spores and plasmodia were observed. Key words: Myxosporea, Myxobolus lentisuturalis, actinospore, Raabeia-type, life cycle, Carassius auratus auratus, Branchiura sowerbyi, Italy Table 1. Myxobolus species with completely known developmental cycles (Lom and Dyková 2006). Myxosporean stage Actinosporean stage Authority Myxobolus cerebralis Triactinomyxon Wolf and Markiw 1984 M. cotti Triactinomyxon El-Matbouli and Hoffmann 1989 M. carassii Triactinomyxon El-Matbouli and Hoffmann 1993 M. arcticus Triactinomyxon Kent et al. 1993, Urawa 1994 M. drjagini Triactinomyxon El-Mansy and Molnár 1997a M. hungaricus Triactinomyxon El-Mansy and Molnár 1997b M. portucalensis Triactinomyxon El-Mansy et al M. bramae Triactinomyxon Eszterbauer et al M. pseudodispar Triactinomyxon Székely et al M. macrocapsularis Triactinomyxon Székely et al M. parviformis Triactinomyxon Kallert et al M. pavlovskii Hexactinomyxon Ruidisch et al M. cultus Raabeia Yokoyama et al M. dispar Raabeia Molnár et al. 1999, Holzer et al Myxobolus lentisuturalis Dyková, Fiala et Nie, 2002 was first described by Dyková et al. (2002) as a highly pathogenic myxozoan infecting the muscles of Prussian carp, Carassius gibelio Bloch in China. Some aspects of its development within the fish host were studied by the above-mentioned authors but they provided no data on putative extrapiscine developmental stage. Since the intraoligochaete developmental phase of Myxobolus cerebralis Hofer, 1903 was first described by Wolf and Markiw (1984), several other authors have supported the hypothesis that the development of other myxosporeans is also accomplished through oligochaete and fish alternate hosts. Thus far, complete developmental cycles have been described for 14 Myxobolus species (Table 1). Recent studies have shown that, besides oligochaetes, polychaetes (Bartholomew et al. 1997, 2006, Køie et al. 2004, 2007, 2008) and bryozoans (Longshaw et al. 1999, Kent et al. 2000) can also serve as alternate hosts for fish myxozoans. The alternate actinospore and myxospore life cycle stage of a given myxozoan species can be identified by experimental infection studies in both fish and invertebrate hosts or by analysis of DNA sequences from both stages. Several authors recommend the inclusion of DNA sequences in the identification of actinospores (El-Mansy Address for correspondence: M. Caffara, Department of Veterinary Public Health and Animal Pathology, University of Bologna, via Tolara di Sopra 50, Ozzano Emilia (Bologna), Italy. Phone: ; Fax: ; monica.caffara@unibo.it 6
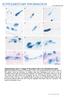
2 Caffara et al.: Life cycle of Myxobolus lentisuturalis et al. 1998, Hallett et al. 1999, Negredo et al. 2003), and SSU rrna sequences have been used successfully for the confirmation of heteroxenous life cycles in several studies (Andree et al. 1997, Bartholomew et al. 1997, 2006, Anderson et al. 1999, 2000, Lin et al. 1999, Køie et al. 2004, 2007, 2008, Atkinson et al. 2007). In Italy, goldfish Carassius auratus auratus (L.) farming has been a traditional activity since the end of the 1800 s, with a current production of more than 25 million fish per year. Myxozoan parasites described in farmed goldfish in Italy include Sphaerospora renicola, S. molnari and Zschokkella sp. (Marcer et al. 2000) but, until now, no Myxobolus infection has been reported. In this paper, we report a muscle infection caused by Myxobolus lentisuturalis in goldfish farmed in Italy. Morphological and molecular analyses of this species, as well as data on the histopathological damage in goldfish and on its extrapiscine development in the oligochaete, Branchiura sowerbyi Beddard, 1892, is provided. MATERIALS AND METHODS Fish. Twenty-eight goldfish (C. auratus auratus), displaying dorsolateral humps (2 1 cm), from a pond farm in the province of Bologna (Italy) underwent parasitological examination. The contents of the humps were collected with a sterile syringe and examined microscopically, both fresh and stained with May- Grünwald-Giemsa. The humps were excised and fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin along with the gills, gut and kidney. Tissue samples were embedded in paraffin and the sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E), Giemsa, Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS), Ziehl-Neelsen and Crossmonn s trichrome stain. Spore measurements were taken from the fresh material (n = 50) under the light microscope with the aid of a camera lucida, and are given in micrometres (μm) as the mean followed by the range and standard deviation (SD) in parentheses. Species description followed the criteria established by Lom and Arthur (1989). DNA extraction and PCR. Total spore DNA was extracted with a spin column purification procedure (DNeasy Tissue Kit, Qiagen, Valencia, CA) following the manufacturer s protocol. The SSU rrna gene was amplified with the universal eukaryotic primer pair (forward 5 -AYCTGGTTGATYYTGCCAG-3 and reverse 5 -TGATCCATCTGCAGGTTCACCT-3 ) (Embley et al. 1992). The total volume of the PCR reaction was 50 μl, containing 10 PCR buffer (Invitrogen), 25 mm dntps (Invitrogen), 50 pmol/μl of each primer, 1.5 mm MgCl 2 and 1.25 U Taq DNA Polymerase (Invitrogen). A Tpersonal (Biometra) thermocycler was used for the amplification. The reactions consisted of 35 cycles of 30 sec at 94 C, 30 sec at 55 C and 1.5 min at 72 C, preceded by a denaturation step at 94 C for 2 min and followed by an extended elongation step at 72 C for 10 min. The PCR products were electrophoresed in 1% agarose gel (Sigma) and stained with Sybr Safe DNA Gel Stain 0.5 TBE (Molecular Probes, Invitrogen). PCR products were cloned into the pcr 2.1 TOPO Cloning vector using the TOPO TA Cloning Kit (Invitrogen). Plasmid DNA was isolated from each clone using a Quantum Prep-Plasmid Miniprep Kit (BioRad) following the manufacturer s procedure. The presence of the insert of the expected size was confirmed by restriction digestion analysis with the EcoRI enzyme. Ten positive clones were sequenced (PRIMM, Milano, Italy) in both directions using M13 Forward ( 20) (5 -GTAAAACGACGGCCAG-3 ) and M13 Reverse (5 -CAG- GAAACAGCTATGAC-3 ) primers (Invitrogen) in an ABI 3730 DNA Analyzer. Sequence assembling was carried out using Vector NTI Advance TM 10 software (Invitrogen), and underwent a database search using BLAST (Altschul et al. 1990). Oligochaetes. To define the life cycle of this parasite and identify the possible alternate hosts, a survey of invertebrates at the goldfish farm was carried out. Mud samples were collected in mid-october both from the bottom of the pond and from the decantation tank, and transported to the laboratory. The oligochaetes were washed from the mud, sorted by size and placed in small aerated aquaria with dechlorinated tap water and sterile sand. They were kept at room temperature and fed with dried spirulina. The water covering the worms was filtered once a week through 20 μm mesh and the filtrate collected in a drop of water and examined for the presence of actinospores. Once spores were seen in the main sample of water, one-hundred oligochaetes were isolated and kept individually in the wells of cell-well plates according to Yokoyama et al. (1991). Each well was examined for the presence of released actinospores every 3 d for two months, using an inverted microscope. Actinospores released were studied by microscopy and PCR, and the SSU rrna products were cloned and sequenced as described above. The oligochaetes releasing actinospores were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin, embedded in paraffin and stained with H&E and Giemsa. The oligochaetes were identified morphologically according to the key of Brinkhurst and Jamieson (1971). RESULTS Morphology of myxospore Fig. 1 The mature spores collected from the goldfish were ellipsoidal with symmetrical shell valves, an indistinct sutural ridge, a conspicuous intercapsular process and the sporoplasm occupying the posterior half of the spore body. The average length of fresh spores was 10.5 ( ), the width was 6.6 ( ) and the thickness was 3.9 ( ) (n = 50 from one host). Two equal anteriorly-tapered pyriform polar capsules were located at the anterior part of the spore. The anterior ends of the polar capsules were separated from each other; polar filaments were coiled 4 5 times. The average length of the polar capsule was 3.7 ( ) and the width was 2.2 ( ) (n = 100). Pseudocysts, composed of several plasmodia measuring up to 70 and filled with developing spores, were observed subcutaneously in the superficial lateral muscle. The spores were identified as Myxobolus lentisuturalis on the basis of morphometry and morphology. Morphology of actinospore Fig. 2 Actinospores were released from only one of the worm biotypes (18 subjects), later identified as Branchiura 7
3 Figs Myxobolus lentisuturalis infection of the goldfish Carassius auratus auratus and of the oligochaete Branchiura sowerbyi. Fig. 1. Myxospores, frontal view; phase contrast (scale bar = 6 μm). Fig. 2. Raabeia-type actinospore; fresh mount (scale bar = 14 μm). Fig. 3. Cross-section through the intestine of an infected B. sowerbyi. Pansporocysts in the intestinal epithelium. H&E, 250. Fig. 4. Goldfish infected by M. lentisuturalis. Note the dorsolateral humps. Fig. 5. Cross-section through the dorsal epaxial muscle of goldfish infected by M. lentisuturalis. Arrow muscle fibres containing spores. PAS, 60. Fig. 6. Higher magnification of the same. Pseudocyst filled with M. lentisuturalis plasmodium. Crossmon s trichrome,
4 Caffara et al.: Life cycle of Myxobolus lentisuturalis sowerbyi, commencing 15 days post-collection from the farm and continuing for almost 60 days. The spore had a slightly elongated body and 3 relatively long, pointed and curved caudal processes without a style. The caudal processes were 196 ( ) long, the spore body length was 22.1 ( ) and the width was 10.8 ( ). Three pyriform polar capsules situated at the top of spore body were 4.7 ( ) in length and 2.9 ( ) in width. The polar filaments were coiled 3 4 times. The morphology and morphometry (n = 20 from one worm) of the actinospores collected are consistent with Raabeia type Janiszewska, Histological examination of the Raabeia-infected B. sowerbyi disclosed pansporocysts in the intestinal epithelium (Fig. 3). SSU rrna analysis The SSU rrna from all 10 myxospore clones amplified with the universal primers resulted in a 2090 bp fragment. The consensus sequence fragment analyzed by BLAST search gave 99.8% identity with M. lentisuturalis from China (AY Dyková et al. 2002). Eight out of the 10 actinospore clones sequenced showed 100% identity with M. lentisuturalis from Italy (AY ) while 2 clones showed 99.7% identity with M. cultus (AB121146). Table 2 shows the percentage of identical base pairs of the approximately 850 bp of the SSU rrna sequence from all Raabeia-type actinospores available in GenBank. Table 2. Percentage of identical base pairs in the Raabeia-type actinospore sequences available, comparing an approximate 840 bp fragment of 18S rdna [1] Raabeia EE 2005 (DQ Eszterbauer et al. 2006); [2] Raabeia type 3 (AJ Holzer et al. 2004); [3] Raabeia type 4 (AJ Holzer et al. 2004); [4] Raabeia type 1 (AJ Holzer et al. 2004); [5] Raabeia type 1 (AY Hallet et al. 2006); [6] Raabeia (M. lentisuturalis type, present study); [7] Raabeia (M. cultus type, present study); [8] Raabeia (M. cultus AB Iwashita and Yokoyama, unpubl.). Histology The 28 fish with conspicuous humps on the dorsolateral side, just behind the head (Fig. 4), showed no other clinical signs of infection. Histological examination at low magnification showed the presence, in cross-section, of two bilateral crescent-shaped masses, in the dorsal epaxial muscle (Fig. 5). These lesions were not circumscribed, presented irregular edges and infiltrated the underlying bundles of skeletal muscle and interstitial tissue. The muscle fibres within the masses were strongly altered. At higher magnification, disappearance of muscle fibres and substitution of the muscle tissue with Myxobolus spores and plasmodia, grouped in pseudocysts, were observed (Fig. 6). In advanced infections, the muscle cells were necrotic with pycnotic and hypertrophic nuclei, and the tissue was infiltrated with scattered lymphocytes and macrophages as described by Dyková et al. (2002). In some cases, at the border of the lesion, the muscular tissue appeared atrophic with hyaline necrosis and slight inflammation with the presence of lymphocytes and macrophages. Some Ziehl-Neelsen negative granulomatous lesions, of unclear etiology, with necrotic foci were also observed scattered between the muscle fibres. In other cases, also the dermis was filled with parasites at various stages of development as well as lymphocytes and plasma cells. In a few cases, spores at different stages of differentiation were evident within the collagen tissue of the dermis under the scales. Mature spores and melanomacrophages were noticed in contact with the vertebrae, within the loose collagenous tissue next to the blood vessels and spinal nerves. Rodlet cells were detected in the vessel walls. Other groups of mature spores embedded in melanomacrophage centres were found outside the head kidney, adjacent to the vertebrae. No spores were observed in the melanomacrophage centres of parenchymatous organs or in gills, intestine, brain or gall bladder, unlike the findings of Dyková et al. (2002). DISCUSSION Myxobolus lentisuturalis is a little known myxozoan parasite that infects piscine skeletal muscles. It was described for the first time by Dyková et al. (2002) in Prussian carp (Carassius gibelio) from China. These authors gave no information on this myxosporean s extrapiscine development. The Myxobolus species found in goldfish (Carassius auratus auratus), farmed in Italy, is most consistent morphologically and molecularly with M. lentisuturalis described by Dyková et al. (2002). The myxospores are identical except for some minor morphometric discrepancies; the spores described by Dyková et al. (2002) are bigger in all dimensions. The sequence obtained by the amplification of the SSU rrna (AY ) showed 99.8% identity with M. lentisuturalis (AY119688), confirming the previously reported variability of spores collected from different fish hosts sharing the genotype but showing differences in the phenotype (Holzer et al. 2004). The actinospore stages released by the oligochaete, Branchiura sowerbyi, were phenotypically compatible with Raabeia-type spores described by other authors, but possessed at least one different characteristic. The morphology and morphometry of the Italian Raabeia type are consistent with: Raabeia type 4 of El-Mansy et al. (1998) 9
5 except that the polar capsules of the former are smaller (5.7 4 vs ); Raabeia described by Eszterbauer et al. (2006) in which, however, the caudal processes are slightly shorter (190 vs 204); Raabeia type B-C-D reported by Xiao and Desser (1998) and, in particular, type D which is very similar morphologically except for its longer caudal process (290 vs 204); Raabeia type 3 of Özer et al. (2002) which was larger and showed 100% genetic identity with Myxobolus truttae (Holzer et al. 2004) on DNA; and Raabeia type 2 of Oumouna et al. (2002) which has a smaller spore body (18 15 vs ) and a shorter caudal process (80 vs 204). The morphometry of our Raabeia and that of the Raabeia reported by Yokoyama et al. (1995) is very similar except for the shape of the spore body which is more cylindrical than rounded in the latter. This Raabeia from Japan was collected from B. sowerbyi and has been identified from an experimental infection of goldfish as the actinospore stage of Myxobolus cultus (Yokoyama et al. 1995). In a later study, Eszterbauer et al. (2006) identified similar actinospores at the DNA level and found out their 99.4% similarity with M. cultus (AB121146). The SSU rrna sequence of the Raabeia-type actinospores from Italy reveals 100% identity with M. lentisuturalis (AY ) myxospores from goldfish farmed in Italy, indicating the involvement of B. sowerbyi in the life cycle of this Myxobolus species. Based on the SSU rrna sequences, we were able to demonstrate that the life cycle of M. lentisuturalis involves two distinct types of spore stages: Myxobolus myxospores from hump lesions on the dorsolateral side of the head in goldfish, and Raabeia actinospores released by the oligochaete Branchiura sowerbyi. In 2 of the 10 SSU rrna clones obtained from the actinospore DNA sample, the sequence had 99.7% identical base pairs to that of the Raabeia type identified by Eszterbauer et al. (2006) as the actinosporean stage of M. cultus (AB121146). This suggests that the oligochaete population in the goldfish pond was naturally infected with more than one type of actinospore. The identification of the actinospores should not be based only on morphology, as already suggested by several authors (El-Mansy et al. 1998, Hallett et al. 1999, Kent et al. 2001, Negredo et al. 2003, Eszterbauer et al. 2006), for the possibility of multiple infections in oligochaetes and the similarity of the actinospores of different myxosporeans (as pointed out in the differential diagnosis above). In our survey, the morphology and morphometry of the Raabeia-type spore detected and measured were referable to a single type, identified as the actinosporean stage of M. lentisuturalis and morphologically different from the Raabeia-type spore described by Yokoyama et al. (1995) as the actinosporean stage of M. cultus. This latter type was detected only after cloning the PCR product from a pool of spores from the same worm. This points out the importance of approaching the diagnosis by combining traditional parasitological methods with molecular techniques and, in particular, the advantages of cloning the PCR product and then sequencing rather than obtaining direct sequences from the PCR products. None of the goldfish examined had cysts in their cartilage tissue, the primary site of infection by M. cultus, but the finding of the actinospore stage of this myxozoan indicates that this species is present in ponds, despite never been detected in goldfish farmed in Italy. In this study, a natural infection of the oligochaete, Branchiura sowerbyi, by the Raabeia-type actinosporean stage of M. lentisuturalis was detected by molecular analysis, showing that this parasite s life-cycle follows the same pattern as that described for M. cerebralis by Wolf and Markiw (1984). Although the entire developmental cycle was not followed because no experimental infections were performed, comparison of the SSU rrna sequence of the myxospore stage from goldfish with that of the actinospore stage from B. sowerbyi demonstrates that they are, in fact, the same species. This approach has also been used for linking the life-cycle stages for other freshwater myxozoans (Andree et al. 1997, Bartholomew et al. 1997, Lin et al. 1999, Longshaw et al. 1999, Pote et al. 2000). The goldfish examined originate from a farm where no new fish have been introduced for several years and where a similar syndrome had not previously been observed. We could only hypothesize the introduction of actinospores by way of water inasmuch as the goldfish farm is fed by a channel where wild cyprinids live and into which other fish farms discharge. Further experiments are required in order to complete the life cycle of M. lentisuturalis to demonstrate that Raabeia actinospores transform into M. lentisuturalis myxospores in goldfish. However, the current study suggests that these are alternating stages of the same myxozoan species. This species is reported for the first time from goldfish and from Italy. In addition, although M. cultus was not found in goldfish in our surveys, the identification of the rdna of this species in actinospores released from oligochaetes provides evidence of its presence in the Italian farm surveyed. Acknowledgements. We wish to thank Dr. Oswaldo Palenzuela, Instituto de Acuicultura de Torre de la Sal, Castellon, Spain for his valuable contribution to this paper. 10
6 Caffara et al.: Life cycle of Myxobolus lentisuturalis REFERENCES ALTSCHUL S.F., GISH W., MILLER W., MYERS E.W., LIPMAN D.J. 1990: Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: ANDERSON C.L., CANNING E.U., OKAMURA B. 1999: Molecular data implicate bryozoans as hosts for PKX (phylum Myxozoa) and identify a clade of bryozoan parasites within the Myxozoa. Parasitology 119: ANDERSON C.L., CANNING E.U., SCHAEFER S.M., YOKOYAMA H., OKAMURA B. 2000: Molecular confirmation of the life cycle of Thelohanellus hovorkai Achmerov, 1960 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea). Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 20: ANDREE K.B., GRESOVIAC S.J., HEDRICK R.P. 1997: Small subunit ribosomal sequences unite actinosporean and myxosporean stages of Myxobolus cerebralis, the causative agent of whirling disease in salmonid fishes. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 44: ATKINSON S.D., HALLETT S.L., BARTHOLOMEW J.L. 2007: The life cycle of Chloromyxum auratum (Myxozoa) from goldfish, Carassius auratus (L.), involves an antonactinomyxon actinospore. J. Fish Dis. 30: BARTHOLOMEW J.L., ATKINSON S.D., HALLETT S.L. 2006: Involvement of Manayunkia speciosa (Annelida: Polychaeta: Sabellidae) in the life cycle of Parvicapsula minibicornis, a myxozoan parasite of pacific salmon. J. Parasitol. 92: BARTHOLOMEW J.L., WHIPPLE M.J., STEVENS D.G., FRYER J.L. 1997: The life cycle of Ceratomyxa shasta, a myxosporean parasite of salmonids, requires a freshwater polychaete as an alternate host. J. Parasitol. 83: BRINKHURST R.O., JAMIESON B.G.M. 1971: Aquatic Oligochaeta of the World. Oliver & Boyd, Edinburgh, 860 pp. DYKOVÁ I., FIALA I., NIE P. 2002: Myxobolus lentisuturalis sp. n. (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae), a new muscle-infecting species from the Prussian carp, Carassius gibelio from China. Folia Parasitol. 49: EL-MANSY A., MOLNÁR K. 1997a: Extrapiscine development of Myxobolus drjagini Akhmerov, 1954 (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) in oligochaete alternate hosts. Acta Vet. Hung. 45: EL-MANSY A., MOLNÁR K. 1997b: Development of Myxobolus hungaricus (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) in oligochaete alternate hosts. Dis. Aquat. Org. 31: EL-MANSY A., MOLNÁR K., SZÉKELY C. 1998: Development of Myxobolus portucalensis Saraiva & Molnár, 1990 (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) in the oligochaete Tubifex tubifex (Müller). Syst. Parasitol. 41: EL-MANSY A., SZÉKELY C., MOLNÁR K. 1998: Studies on the occurrence of actinosporean stages of fish myxosporeans in a fish farm of Hungary, with the description of triactinomyxon, raabeia, aurantiactinomyxon and neoactinomyxum types. Acta Vet. Hung. 46: EL-MATBOULI M., HOFFMANN R.W. 1989: Experimental transmission of two Myxobolus spp. developing bisporogeny via tubificid worm. Parasitol. Res. 75: EL-MATBOULI M., HOFFMANN R.W. 1993: Myxobolus carassii Klokaceva, 1914 also requires an oligochaete, Tubifex tubifex, as intermediate host in its life cycle. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 13: EMBLEY T.M., FINLAY B.J., THOMAS R.H., DYAL P.L. 1992: The use of rrna sequences and fluorescent probes to investigate the phylogenetic position of the anaerobic ciliate Metopus palaeformis and its archaeobacteria endosymbiont. J. Gen. Microbiol. 138: ESZTERBAUER E., MARTON S., RÁCZ O.Z., LETENYEI M., MOLNÁR K. 2006: Morphological and genetic differences among actinosporean stages of fish-parasitic myxosporeans (Myxozoa): difficulties of species identification. Syst. Parasitol. 65: ESZTERBAUER E., SZÉKELY C., MOLNÁR K., BASKA F. 2000: Development of Myxobolus bramae (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) in an oligochaete alternate host, Tubifex tubifex. J. Fish Dis. 23: HALLETT S.L., ATKINSON S.D., ERSÉUS C., EL-MATBOULI M. 2006: Myxozoan parasites disseminated via oligochaete worms as live food for aquarium fishes: descriptions of aurantiactinomyxon and raabeia actinospore types. Dis. Aquat. Org. 69: HALLETT S.L., ERSÉUS C., LESTER R.J.G. 1999: Actinosporeans (Myxozoa) from marine oligochaetes of the Great Barrier Reef. Syst. Parasitol. 44: HOLZER A.S., SOMMERVILLE C., WOOTTEN R. 2004: Molecular relationship and phylogeny in a community of myxosporean and actinosporean based on their 18S rdna sequences. Int. J. Parasitol. 34: KALLERT D.M., ESZTERBAUER E., ERSÉUS C., EL-MATBOULI M., HAAS W. 2005: Life cycle studies of Myxobolus parviformis sp. n. (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) from bream. Dis. Aquat. Org. 66: KENT M.L., ANDREE K.B., BARTHOLOMEW J.L., EL-MATBOULI M., DESSER S.S., DEVLIN R.H., FEIST S.W., HEDRICK R.P., HOFF- MAN R.W., KHATTRA J., HALLETT S.L., LESTER R.J.G., LONG- SHAW M., PALENZUELA O., SIDDALL M.E., XIAO C. 2001: Recent advances in our knowledge of the Myxozoa. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 48: KENT M.L., KHATTRA J., HEDRICK R.P. DEVLIN R.H. 2000: Tetracapsula renicola n. sp. (Myxozoa: Saccosporidae); the PKD myxozoan the cause of proliferative kidney disease of salmonid fishes. J. Parasitol. 86: KENT M.L., WHITAKER D.J., MARGOLIS L. 1993: Transmission of Myxobolus arcticus Pugachev and Khokhlov, 1979, a myxosporean parasite of Pacific salmon, via a triactinomyxon from the aquatic oligochaete Stylodrilus heringianus (Lumbriculidae). Can. J. Zool. 71: KØIE M., KARLSBAKK E., NYLUND A. 2007: A new genus Gadimyxa with three new species (Myxozoa, Parvicapsulidae) parasitic in marine fish (Gadidae) and the two-host life cycle of Gadimyxa atlantica n. sp. J. Parasitol. 93: KØIE M., KARLSBAKK E., NYLUND A. 2008: The marine herring myxozoan Ceratomyxa auerbachi (Myxozoa: Ceratomyxidae) uses Chone infundibuliformis (Annelida: Polychaeta: Sabellidae) as invertebrate host. Folia Parasitol. 55: KØIE M., WHIPPS C.M., KENT M.L. 2004: Ellipsomyxa gobii (Myxozoa: Ceratomyxidae) in the common goby Pomatoschistus microps (Teleostei: Gobiidae) uses Nereis spp. (Annelida: Polychaeta) as invertebrate hosts. Folia Parasitol. 51: LIN D., HANSON L.A., POTE L.M. 1999: Small subunit ribosomal RNA sequence of Henneguya exilis (class Myxosporea) identifies the actinosporean stage from an oligochaete host. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 46: LOM J., ARTHUR J.R. 1989: A guideline for the preparation of species description in Myxosporea. J. Fish Dis. 12: LOM J., DYKOVÁ I. 2006: Myxozoan genera: definition and notes on taxonomy, life-cycle terminology and pathogenic species. Folia Parasitol. 53: LONGSHAW M., FEIST S.W., CANNING E.U., OKAMURA B. 1999: First identification of PKD in bryozoans from the United King- 11
7 dom molecular evidence. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 19: MARCER F., FIORAVANTI M.L., CAFFARA M., DELGADO M.L., FLO- RIO D., RESTANI R. 2000: Ricerche parassitologiche in pesci rossi (Carassius auratus) allevati in Emilia-Romagna. Boll. Soc. It. Patol. Ittica 32: MOLNÁR K., EL-MANSY A., SZÉKELY C., BASKA F. 1999: Development of Myxobolus dispar (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) in an oligochaete alternate host, Tubifex tubifex. Folia Parasitol. 46: NEGREDO C., DILLANE E., MULCAHY M.F. 2003: Small subunit ribosomal DNA characterization of an unidentified aurantiactinomyxon form and its oligochaete host Tubifex ignotus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 54: OUMOUNA M., HALLETT S.L., HOFFMANN R.W., EL-MATBOULI M. 2002: Early developmental stages of two actinosporean, Raabeia and Aurantiactinomyxon (Myxozoa), as detected by light and electron microscopy. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 79: ÖZER A., WOOTTEN R., SHINN A.P. 2002: Survey of actinosporean types (Myxozoa) belonging to seven collective groups found in a freshwater salmon farm in Northern Scotland. Folia Parasitol. 49: POTE L.M., HANSON L.A., SHIVAJI R. 2000: Small subunit ribosomal RNA sequences link the cause of proliferative gill disease in channel catfish to Henneguya ictaluri (Myxozoa: Myxosporea). J. Aquat. Anim. Health 12: RUIDISCH S., EL-MATBOULI M., HOFFMAN R.W. 1991: The role of tubificid worms as an intermediate host in the life cycle of Myxobolus pavlovskii (Achmerov, 1954). Parasitol. Res. 77: SZÉKELY C., MOLNÁR K., RÁCZ O. 2001: Complete developmental cycle of Myxobolus pseudodispar (Gorbunova) (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae). J. Fish Dis. 24: SZÉKELY C., RÁCZ O. MOLNÁR K., ESZTERBAUER E. 2002: Development of Myxobolus macrocapsularis (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) in an oligochaete alternate host, Tubifex tubifex. Dis. Aquat. Org. 48: URAWA S. 1994: Life cycle of Myxobolus arcticus, a myxosporean parasite of salmonid fishes. Int. Symp. Aquat. Anim. Health, Seattle 4 8 Sept. 1994, Program and Abstracts, p. W WOLF K., MARKIW M.E. 1984: Biology contravenes taxonomy in the Myxozoa: new discoveries show alternation of invertebrate and vertebrate hosts. Science 225: XIAO C.X., DESSER S.S. 1998: Actinosporean stages of myxozoan parasites of oligochaetes from Lake Sasajewun, Algonquin Park, Ontario: new forms of triactinomyxon and raabeia. J. Parasitol. 84: YOKOYAMA H., OGAWA K., WAKABAYASHI H. 1991: A new collection method of actinosporeans a probable infective stage of myxosporeans to fishes from tubificids and experimental infection of goldfish with the actinosporean Raabeia sp. Fish Pathol. 26: YOKOYAMA H., OGAWA K., WAKABAYASHI H. 1995: Myxobolus cultus n. sp. (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) in the goldfish Carassius auratus transformed from the actinosporean stage in the oligochaete Branchiura sowerbyi. J. Parasitol. 81: Received 17 June 2008 Accepted 11 November
BORKHANUDDIN Hafiz, CECH Gábor, OSTOROS Györgyi, MOLNÁR Kálmán, SZÉKELY Csaba
 BORKHANUDDIN Hafiz, CECH Gábor, OSTOROS Györgyi, MOLNÁR Kálmán, SZÉKELY Csaba Veterinary Medical Research Institute of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, 1143. Budapest. Hungária krt. 21. Introduction
BORKHANUDDIN Hafiz, CECH Gábor, OSTOROS Györgyi, MOLNÁR Kálmán, SZÉKELY Csaba Veterinary Medical Research Institute of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, 1143. Budapest. Hungária krt. 21. Introduction
Ahead of print online version
 Folia Parasitologica 58[2]: 157 163, 2011 ISSN 0015-5683 (print), ISSN 1803-6465 (online) Institute of Parasitology, Biology Centre ASCR http://www.paru.cas.cz/folia/ The development of Myxobolus pavlovskii
Folia Parasitologica 58[2]: 157 163, 2011 ISSN 0015-5683 (print), ISSN 1803-6465 (online) Institute of Parasitology, Biology Centre ASCR http://www.paru.cas.cz/folia/ The development of Myxobolus pavlovskii
Myxosporeans and myxosporidiosis of allogynogenetic gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio Bloch) in China
 Myxosporeans and myxosporidiosis of allogynogenetic gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio Bloch) in China Zhang Jinyong zhangjy@ihb.ac.cn Laboratory of Fish Diseases; Institute of Hydrobiology (IHB), Chinese
Myxosporeans and myxosporidiosis of allogynogenetic gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio Bloch) in China Zhang Jinyong zhangjy@ihb.ac.cn Laboratory of Fish Diseases; Institute of Hydrobiology (IHB), Chinese
Myxosporeans and myxosporidiosis of common carp and gibel carp in China
 Myxosporeans and myxosporidiosis of common carp and gibel carp in China Zhang Jinyong, Liu Xinhua, Xi Bingwen, Kálmán Molnár zhangjy@ihb.ac.cn Hungary 2015 June.3 Laboratory of Fish Diseases; Institute
Myxosporeans and myxosporidiosis of common carp and gibel carp in China Zhang Jinyong, Liu Xinhua, Xi Bingwen, Kálmán Molnár zhangjy@ihb.ac.cn Hungary 2015 June.3 Laboratory of Fish Diseases; Institute
Ahead of print online version
 FOLIA PARASITOLOGICA 61 [6]: 505 511, 2014 ISSN 0015-5683 (print), ISSN 1803-6465 (online) doi: 10.14411/fp.2014.052 Institute of Parasitology, Biology Centre ASCR http://folia.paru.cas.cz/ Myxobolus oralis
FOLIA PARASITOLOGICA 61 [6]: 505 511, 2014 ISSN 0015-5683 (print), ISSN 1803-6465 (online) doi: 10.14411/fp.2014.052 Institute of Parasitology, Biology Centre ASCR http://folia.paru.cas.cz/ Myxobolus oralis
Thomas G. Rosser. Wes A. Baumgartner. Michael A. Barger. Matt J. Griffin
 DOI 10.1007/s10-017-9719-3 Myxobolus lepomis n. sp. (Cnidaria: Myxobolidae), a gill myxozoan infecting Lepomis marginatus Holbrook and Lepomis miniatus Jordan (Perciformes: Centrarchidae), in the Big Thicket
DOI 10.1007/s10-017-9719-3 Myxobolus lepomis n. sp. (Cnidaria: Myxobolidae), a gill myxozoan infecting Lepomis marginatus Holbrook and Lepomis miniatus Jordan (Perciformes: Centrarchidae), in the Big Thicket
The role of the fish parasite Myxobolus inornatus in young-of-year Smallmouth Bass Micropterus dolomieu mortality in Pennsylvania
 The role of the fish parasite Myxobolus inornatus in young-of-year Smallmouth Bass Micropterus dolomieu mortality in Pennsylvania Identifying parasite distribution, intermediate host, and distribution
The role of the fish parasite Myxobolus inornatus in young-of-year Smallmouth Bass Micropterus dolomieu mortality in Pennsylvania Identifying parasite distribution, intermediate host, and distribution
Prevention of experimentally induced whirling disease in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss by Fumagillin
 Vol. 10: 109-113, 1991 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Dis. aquat. Org. Published April 4 Prevention of experimentally induced whirling disease in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss by Fumagillin M. El-Matbouli,
Vol. 10: 109-113, 1991 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Dis. aquat. Org. Published April 4 Prevention of experimentally induced whirling disease in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss by Fumagillin M. El-Matbouli,
A novel myxozoan parasite of terrestrial mammals: description of Soricimyxum minuti sp. n. (Myxosporea) in pygmy shrew Sorex minutus from Hungary
 Institute of Parasitology, Biology Centre CAS Folia Parasitologica 2015, 62: 045 http://folia.paru.cas.cz Research Article A novel myxozoan parasite of terrestrial mammals: description of Soricimyxum minuti
Institute of Parasitology, Biology Centre CAS Folia Parasitologica 2015, 62: 045 http://folia.paru.cas.cz Research Article A novel myxozoan parasite of terrestrial mammals: description of Soricimyxum minuti
Myxobolus albi infection in cartilage of captive lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus)
 440990JVDXXX10.1177/1040638712440990Ca vin et al.myxobolus albi in lumpfish cartilage Myxobolus albi infection in cartilage of captive lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation
440990JVDXXX10.1177/1040638712440990Ca vin et al.myxobolus albi in lumpfish cartilage Myxobolus albi infection in cartilage of captive lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation
First Record of Myxobolus Species (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) in Grey Mullet Mugil cephalus (Teleostei, Mugilidae) from Syria
 First Record of Myxobolus Species (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) in Grey Mullet Mugil cephalus (Teleostei, Mugilidae) from Syria Hassan M Salman*,Amal I Dayoub**, Paolo Merella***,Nasreen M Kurhaily* *Department
First Record of Myxobolus Species (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) in Grey Mullet Mugil cephalus (Teleostei, Mugilidae) from Syria Hassan M Salman*,Amal I Dayoub**, Paolo Merella***,Nasreen M Kurhaily* *Department
PCR detection of Leptospira in. stray cat and
 PCR detection of Leptospira in 1 Department of Pathology, School of Veterinary Medicine, Islamic Azad University, Shahrekord Branch, Shahrekord, Iran 2 Department of Microbiology, School of Veterinary
PCR detection of Leptospira in 1 Department of Pathology, School of Veterinary Medicine, Islamic Azad University, Shahrekord Branch, Shahrekord, Iran 2 Department of Microbiology, School of Veterinary
A Lymphosarcoma in an Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar)
 A Lymphosarcoma in an Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Authors: Paul R. Bowser, Marilyn J. Wolfe, and Timothy Wallbridge Source: Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 23(4) : 698-701 Published By: Wildlife Disease
A Lymphosarcoma in an Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Authors: Paul R. Bowser, Marilyn J. Wolfe, and Timothy Wallbridge Source: Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 23(4) : 698-701 Published By: Wildlife Disease
Zoology Department, College of Science, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia 3
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 106(5): 557-561, August 2011 557 Myxidium volitans sp. nov., a parasite of the gallbladder of the fish, Dactylopterus volitans (Teleostei: Triglidae) from the
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 106(5): 557-561, August 2011 557 Myxidium volitans sp. nov., a parasite of the gallbladder of the fish, Dactylopterus volitans (Teleostei: Triglidae) from the
*Corresponding author:
 American Journal of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 4, 137-142 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajidm/5/4/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajidm-5-4-3
American Journal of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 4, 137-142 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajidm/5/4/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajidm-5-4-3
The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture Bamidgeh 58(3), 2006,
 The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture Bamidgeh 58(3), 26, 157-169. 157 Efficacy and Toxicity of Orally Administrated Anti-Coccidial Drug Treatment on Enteromyxum leei Infections in Sharpsnout Seabream (Diplodus
The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture Bamidgeh 58(3), 26, 157-169. 157 Efficacy and Toxicity of Orally Administrated Anti-Coccidial Drug Treatment on Enteromyxum leei Infections in Sharpsnout Seabream (Diplodus
4-year-old neutered male American domestic shorthair cat with a locally extensive area of swelling ulceration and crusting over the nasal planum.
 4-year-old neutered male American domestic shorthair cat with a locally extensive area of swelling ulceration and crusting over the nasal planum. Which of the following is the most likely disease? 1. Squamous
4-year-old neutered male American domestic shorthair cat with a locally extensive area of swelling ulceration and crusting over the nasal planum. Which of the following is the most likely disease? 1. Squamous
Vertebrates. Vertebrate Characteristics. 444 Chapter 14
 4 Vertebrates Key Concept All vertebrates have a backbone, which supports other specialized body structures and functions. What You Will Learn Vertebrates have an endoskeleton that provides support and
4 Vertebrates Key Concept All vertebrates have a backbone, which supports other specialized body structures and functions. What You Will Learn Vertebrates have an endoskeleton that provides support and
PLASMODIUM MODULE 39.1 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 39.2 MALARIAL PARASITE. Notes
 Plasmodium MODULE 39 PLASMODIUM 39.1 INTRODUCTION Malaria is characterized by intermittent fever associated with chills and rigors in the patient. There may be enlargement of the liver and spleen in the
Plasmodium MODULE 39 PLASMODIUM 39.1 INTRODUCTION Malaria is characterized by intermittent fever associated with chills and rigors in the patient. There may be enlargement of the liver and spleen in the
Myxidium leei (Myxozoa) infections in aquarium-reared Mediterranean fish species
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 47: 57 62, 2001 Published October 29 Dis Aquat Org Myxidium leei (Myxozoa) infections in aquarium-reared Mediterranean fish species F. Padrós 1, *, O. Palenzuela 2, C.
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 47: 57 62, 2001 Published October 29 Dis Aquat Org Myxidium leei (Myxozoa) infections in aquarium-reared Mediterranean fish species F. Padrós 1, *, O. Palenzuela 2, C.
Myxozoans Exploiting Homeotherms
 Myxozoans Exploiting Homeotherms Sascha L. Hallett, Stephen D. Atkinson, Jerri L. Bartholomew, and Csaba Székely 7 Abstract Discoveries published in 2007 and 2008 expanded the known host range of myxozoans
Myxozoans Exploiting Homeotherms Sascha L. Hallett, Stephen D. Atkinson, Jerri L. Bartholomew, and Csaba Székely 7 Abstract Discoveries published in 2007 and 2008 expanded the known host range of myxozoans
Article.
 Zootaxa 3887 (2): 157 190 www.mapress.com/zootaxa/ Copyright 2014 Magnolia Press Article http://dx.doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3887.2.3 http://zoobank.org/urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:b697d6ba-836b-44e2-a8d9-07661554fe59
Zootaxa 3887 (2): 157 190 www.mapress.com/zootaxa/ Copyright 2014 Magnolia Press Article http://dx.doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3887.2.3 http://zoobank.org/urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:b697d6ba-836b-44e2-a8d9-07661554fe59
The detection of Cytauxzoon felis in apparently healthy free-roaming cats in the USA
 Veterinary Parasitology 146 (2007) 316 320 www.elsevier.com/locate/vetpar The detection of Cytauxzoon felis in apparently healthy free-roaming cats in the USA Marion D. Haber a, Melissa D. Tucker a, Henry
Veterinary Parasitology 146 (2007) 316 320 www.elsevier.com/locate/vetpar The detection of Cytauxzoon felis in apparently healthy free-roaming cats in the USA Marion D. Haber a, Melissa D. Tucker a, Henry
NA 100 R. Multi-functional electrophoresis device
 NA 100 R Multi-functional electrophoresis device No need for UV transilluminator and darkroom You can see DNA bands after 2 or 3 minutes of electrophoresis You can check 80 PCR products at a time. No need
NA 100 R Multi-functional electrophoresis device No need for UV transilluminator and darkroom You can see DNA bands after 2 or 3 minutes of electrophoresis You can check 80 PCR products at a time. No need
A Unique Approach to Managing the Problem of Antibiotic Resistance
 A Unique Approach to Managing the Problem of Antibiotic Resistance By: Heather Storteboom and Sung-Chul Kim Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Colorado State University A Quick Review The
A Unique Approach to Managing the Problem of Antibiotic Resistance By: Heather Storteboom and Sung-Chul Kim Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Colorado State University A Quick Review The
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Introduction:
 Introduction: HISTOPATHOLOGY Goats and sheep are the major domestic animal species in India. Much of the economy of the country has been depend upon the domestication of these animals. Especially economy
Introduction: HISTOPATHOLOGY Goats and sheep are the major domestic animal species in India. Much of the economy of the country has been depend upon the domestication of these animals. Especially economy
CERTIFIED REFERENCE MATERIAL IRMM 313
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements (Geel) CERTIFIED REFERENCE MATERIAL IRMM 313 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS PFGE AGAROSE PLUGS Certified value 2) SmaI
EUROPEAN COMMISSION JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements (Geel) CERTIFIED REFERENCE MATERIAL IRMM 313 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS PFGE AGAROSE PLUGS Certified value 2) SmaI
Name Class Date. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 14 4 Vertebrates SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are vertebrates different from invertebrates? How
CHAPTER 14 4 Vertebrates SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are vertebrates different from invertebrates? How
THE STRUCTURE OF ECHINOCOCCAL CYSTS AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN LIVER
 THE STRUCTURE OF ECHINOCOCCAL CYSTS AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN LIVER Michal Juszynski Helena Palenga, Danuta Cielecka PhD Department of General Biology and Parasitology Medical University of Warsaw
THE STRUCTURE OF ECHINOCOCCAL CYSTS AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN LIVER Michal Juszynski Helena Palenga, Danuta Cielecka PhD Department of General Biology and Parasitology Medical University of Warsaw
Center for Fish Disease Research, Department of Microbiology, 220 Nash Hall, Oregon State University, Corvallis, Oregon , USA
 Journal of Aquatic Animal Health 16:116 129, 24 Copyright by the American Fisheries Society 24 A Digenean Metacercaria (Apophallus sp.) and a Myxozoan (Myxobolus sp.) Associated with Vertebral Deformities
Journal of Aquatic Animal Health 16:116 129, 24 Copyright by the American Fisheries Society 24 A Digenean Metacercaria (Apophallus sp.) and a Myxozoan (Myxobolus sp.) Associated with Vertebral Deformities
International Journal of Multidisciplinary and Current Research ISSN: Research Article. Available at:
 International Journal of Multidisciplinary and Current Research ISSN: - Research Article Available at: http://ijmcr.com, parasites of Barbus callipterus Boulenger, (Cyprinidae) in the Soudano-guinean zone
International Journal of Multidisciplinary and Current Research ISSN: - Research Article Available at: http://ijmcr.com, parasites of Barbus callipterus Boulenger, (Cyprinidae) in the Soudano-guinean zone
Sarcocystis heydorni, n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Protozoa) with cattle (Bos taurus) and human
 1 Sarcocystis heydorni, n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Protozoa) with cattle (Bos taurus) and human (Homo sapiens) cycle Jitender P. Dubey 1, Erna van Wilpe 2, Rafael Calero-Bernal 1, Shiv Kumar Verma 1, Ronald
1 Sarcocystis heydorni, n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Protozoa) with cattle (Bos taurus) and human (Homo sapiens) cycle Jitender P. Dubey 1, Erna van Wilpe 2, Rafael Calero-Bernal 1, Shiv Kumar Verma 1, Ronald
The surveillance programme for bovine tuberculosis in Norway 2017
 Annual Report The surveillance programme for bovine tuberculosis in Norway 2017 Norwegian Veterinary Institute The surveillance programme for bovine tuberculosis in Norway in 2017 Content Summary... 3
Annual Report The surveillance programme for bovine tuberculosis in Norway 2017 Norwegian Veterinary Institute The surveillance programme for bovine tuberculosis in Norway in 2017 Content Summary... 3
Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus of Camel (Camelus dromedarius) Skin Origin
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.410
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.410
Cystic echinococcosis in a domestic cat: an Italian case report
 13th NRL Workshop, Rome, 24-25 May, 2018 Cystic echinococcosis in a domestic cat: an Italian case report Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale (IZS) of Sardinia National Reference Laboratory for Cistic
13th NRL Workshop, Rome, 24-25 May, 2018 Cystic echinococcosis in a domestic cat: an Italian case report Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale (IZS) of Sardinia National Reference Laboratory for Cistic
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and
 Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Medical Genetics and Diagnosis Lab #3. Gel electrophoresis
 Medical Genetics and Diagnosis Lab #3 Gel electrophoresis Background Information Gel electrophoresis is the standard lab procedure for separating DNA by size (e.g. length in base pairs) for visualization
Medical Genetics and Diagnosis Lab #3 Gel electrophoresis Background Information Gel electrophoresis is the standard lab procedure for separating DNA by size (e.g. length in base pairs) for visualization
Follow-up meeting 2 GENBAS
 Follow-up meeting 2 GENBAS Location: Liége November 4, 2014 Authored by: Sofie Derycke, Loïc Kéver and Maarten Van Steenberghe Follow-up meeting 2 GENBAS 04/11/2014 Present: Maarten Van Steenberge, Loic
Follow-up meeting 2 GENBAS Location: Liége November 4, 2014 Authored by: Sofie Derycke, Loïc Kéver and Maarten Van Steenberghe Follow-up meeting 2 GENBAS 04/11/2014 Present: Maarten Van Steenberge, Loic
A comparison of placental tissue in the skinks Eulamprus tympanum and E. quoyii. Yates, Lauren A.
 A comparison of placental tissue in the skinks Eulamprus tympanum and E. quoyii Yates, Lauren A. Abstract: The species Eulamprus tympanum and Eulamprus quoyii are viviparous skinks that are said to have
A comparison of placental tissue in the skinks Eulamprus tympanum and E. quoyii Yates, Lauren A. Abstract: The species Eulamprus tympanum and Eulamprus quoyii are viviparous skinks that are said to have
Proteocephalus filicollis (Rud. 1810) in the Netherlands
 Proteocephalus filicollis (Rud. 1810) in the Netherlands by J.J. Willemse AND A.L.M. Veltman Zoological Laboratory, University of Amsterdam INTRODUCTION in another glass dish containing about 50 specimens
Proteocephalus filicollis (Rud. 1810) in the Netherlands by J.J. Willemse AND A.L.M. Veltman Zoological Laboratory, University of Amsterdam INTRODUCTION in another glass dish containing about 50 specimens
The Identification of the Cryptosporidium ubiquitum in Pre weaned Ovines from Aba Tibetan and Qiang Autonomous Prefecture in China*
 Biomed Environ Sci, 2011; 24(3): 315 320 315 Original Article The Identification of the Cryptosporidium ubiquitum in Pre weaned Ovines from Aba Tibetan and Qiang Autonomous Prefecture in China* SHEN YuJuan
Biomed Environ Sci, 2011; 24(3): 315 320 315 Original Article The Identification of the Cryptosporidium ubiquitum in Pre weaned Ovines from Aba Tibetan and Qiang Autonomous Prefecture in China* SHEN YuJuan
Ectoparasites Myobia musculi Radfordia affinis Radfordia ensifera
 Ectoparasites Fleas, ticks, and lice are uncommon in modern laboratory facilities, but may be seen on wild or feral rodents. Most ectoparasite infestations seen in rats and mice used for research are various
Ectoparasites Fleas, ticks, and lice are uncommon in modern laboratory facilities, but may be seen on wild or feral rodents. Most ectoparasite infestations seen in rats and mice used for research are various
InternationalJournalofAgricultural
 www.ijasvm.com IJASVM InternationalJournalofAgricultural SciencesandVeterinaryMedicine ISSN:2320-3730 Vol.5,No.1,February2017 E-Mail:editorijasvm@gmail.com oreditor@ijasvm.comm@gmail.com Int. J. Agric.Sc
www.ijasvm.com IJASVM InternationalJournalofAgricultural SciencesandVeterinaryMedicine ISSN:2320-3730 Vol.5,No.1,February2017 E-Mail:editorijasvm@gmail.com oreditor@ijasvm.comm@gmail.com Int. J. Agric.Sc
AXOLOTLS C A R E. P & K Pets Info Sheet #12 19 Magill Rd Stepney SA 5069 P: F:
 P & K Pets AXOLOTLS C A R E INTRODUCTION Axolotls (ambystoma mexicanum) originate in Mexico from lake Xochimilco and Lake Chalco. Both of these lakes have almost disappeared now due to development of the
P & K Pets AXOLOTLS C A R E INTRODUCTION Axolotls (ambystoma mexicanum) originate in Mexico from lake Xochimilco and Lake Chalco. Both of these lakes have almost disappeared now due to development of the
Hydatid Cyst Dr. Nora L. El-Tantawy
 Hydatid Cyst Dr. Nora L. El-Tantawy Ass. Prof. of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura university, Egypt Echinococcus granulosus Geographical Distribution: cosmopolitan especially in sheep raising
Hydatid Cyst Dr. Nora L. El-Tantawy Ass. Prof. of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura university, Egypt Echinococcus granulosus Geographical Distribution: cosmopolitan especially in sheep raising
Efficacy and toxicity of orally administrated anti-coccidial drugs for innovative treatments of Myxobolus sp. infection in Puntazzo puntazzo
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 62: 217 226, 2004 Published December 13 Dis Aquat Org Efficacy and toxicity of orally administrated anti-coccidial drugs for innovative treatments of Myxobolus sp. infection
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 62: 217 226, 2004 Published December 13 Dis Aquat Org Efficacy and toxicity of orally administrated anti-coccidial drugs for innovative treatments of Myxobolus sp. infection
HISTOPHYSIOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE HYPOPHYSIO- MAMMARY AXIS IN SHEEP (Ovis aries) - MAMMOTROPHS
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 912 917 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOPHYSIOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE HYPOPHYSIO- MAMMARY AXIS IN SHEEP (Ovis aries)
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 912 917 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOPHYSIOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE HYPOPHYSIO- MAMMARY AXIS IN SHEEP (Ovis aries)
Current information about teaching and research in veterinary parasitology in Hungary.
 Current information about teaching and research in veterinary parasitology in Hungary. The department was established in 1929 by the world-famous parasitologist, Sándor Kotlán, who led education and
Current information about teaching and research in veterinary parasitology in Hungary. The department was established in 1929 by the world-famous parasitologist, Sándor Kotlán, who led education and
Technique for microdissection and measurement in biopsies of human small intestine
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1977, 30, 1068-1073 Technique for microdissection and measurement in biopsies of human small intestine ANNE FERGUSON, A. SUTHERLAND, T. T. MAcDONALD, AND FRANCES ALLAN From
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1977, 30, 1068-1073 Technique for microdissection and measurement in biopsies of human small intestine ANNE FERGUSON, A. SUTHERLAND, T. T. MAcDONALD, AND FRANCES ALLAN From
Surveillance programmes for terrestrial and aquatic animals in Norway. The surveillance and control programme for bovine tuberculosis in Norway 2013
 Annual Report 2013 Surveillance programmes for terrestrial and aquatic animals in Norway The surveillance and control programme for bovine tuberculosis in Norway 2013 Ståle Sviland Tone Bjordal Johansen
Annual Report 2013 Surveillance programmes for terrestrial and aquatic animals in Norway The surveillance and control programme for bovine tuberculosis in Norway 2013 Ståle Sviland Tone Bjordal Johansen
Molecular study for the sex identification in Japanese quails (Coturnix Japonica) Iran.
 Molecular study for the sex identification in Japanese quails (Coturnix Japonica) Nasrollah Vali1 1 and Abbas Doosti 2 1 Department of Animal Sciences, Faculty of Agriculture, Islamic Azad University,
Molecular study for the sex identification in Japanese quails (Coturnix Japonica) Nasrollah Vali1 1 and Abbas Doosti 2 1 Department of Animal Sciences, Faculty of Agriculture, Islamic Azad University,
Drd. OBADĂ MIHAI DORU. PhD THESIS ABSTRACT
 UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AND VETERINARY MEDICINE ION IONESCU DE LA BRAD IAŞI FACULTY OF VETERINARY MEDICINE SPECIALIZATION MICROBIOLOGY- IMUNOLOGY Drd. OBADĂ MIHAI DORU PhD THESIS ABSTRACT RESEARCHES
UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AND VETERINARY MEDICINE ION IONESCU DE LA BRAD IAŞI FACULTY OF VETERINARY MEDICINE SPECIALIZATION MICROBIOLOGY- IMUNOLOGY Drd. OBADĂ MIHAI DORU PhD THESIS ABSTRACT RESEARCHES
HYDATID CYST DISEASE
 HYDATID CYST DISEASE Hydatid disease, also called hydatidosis or echinococcosis, is a cystforming disease resulting from an infection with the metacestode, or larval form, of parasitic dog tapeworms from
HYDATID CYST DISEASE Hydatid disease, also called hydatidosis or echinococcosis, is a cystforming disease resulting from an infection with the metacestode, or larval form, of parasitic dog tapeworms from
Flatworms Flatworms Platyhelminthes dorsoventrally free-living planarian parasitic fluke tapeworm label three body layers ectoderm mesoderm
 Flatworms Flatworms are in the phylum Platyhelminthes. Flatworms are flattened dorsoventrally (top to bottom). The group includes the freshwater, free-living planarian and the parasitic fluke and tapeworm.
Flatworms Flatworms are in the phylum Platyhelminthes. Flatworms are flattened dorsoventrally (top to bottom). The group includes the freshwater, free-living planarian and the parasitic fluke and tapeworm.
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/319/5870/1679/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Drosophila Egg-Laying Site Selection as a System to Study Simple Decision-Making Processes Chung-hui Yang, Priyanka
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/319/5870/1679/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Drosophila Egg-Laying Site Selection as a System to Study Simple Decision-Making Processes Chung-hui Yang, Priyanka
Epidemiology of Opisthorchis felineus in the European Union
 Epidemiology of Opisthorchis felineus in the European Union Edoardo Pozio European Union Reference Laboratory for Parasites Istituto Superiore di Sanità Rome, Italy World distribution and human prevalence
Epidemiology of Opisthorchis felineus in the European Union Edoardo Pozio European Union Reference Laboratory for Parasites Istituto Superiore di Sanità Rome, Italy World distribution and human prevalence
How to load and run an Agarose gel PSR
 How to load and run an Agarose gel PSR Agarose gel electrophoresis is the most effective way of separating DNA fragments of varying sizes ranging from100 bp to 25 kb. This protocol divided into three stages:
How to load and run an Agarose gel PSR Agarose gel electrophoresis is the most effective way of separating DNA fragments of varying sizes ranging from100 bp to 25 kb. This protocol divided into three stages:
The epidemiology of infections with Giardia species and genotypes in well cared for dogs and cats in Germany
 Pallant et al. Parasites & Vectors (2015) 8:2 DOI 10.1186/s13071-014-0615-2 RESEARCH The epidemiology of infections with Giardia species and genotypes in well cared for dogs and cats in Germany Louise
Pallant et al. Parasites & Vectors (2015) 8:2 DOI 10.1186/s13071-014-0615-2 RESEARCH The epidemiology of infections with Giardia species and genotypes in well cared for dogs and cats in Germany Louise
The Rufford Foundation Final Report
 The Rufford Foundation Final Report Congratulations on the completion of your project that was supported by The Rufford Foundation. We ask all grant recipients to complete a Final Report Form that helps
The Rufford Foundation Final Report Congratulations on the completion of your project that was supported by The Rufford Foundation. We ask all grant recipients to complete a Final Report Form that helps
Fish Farms. DATCP Fish Health 4/21/2009. Myron Kebus, MS, DVM. State Aquaculture Veterinary Epidemiologist
 Fish Farms Myron Kebus, MS, DVM State Aquaculture Veterinary Epidemiologist DATCP Fish Health National model for fish health programs Requirements: Import permits Health certificates Record-keeping Reportable
Fish Farms Myron Kebus, MS, DVM State Aquaculture Veterinary Epidemiologist DATCP Fish Health National model for fish health programs Requirements: Import permits Health certificates Record-keeping Reportable
Biology 120 Lab Exam 2 Review
 Biology 120 Lab Exam 2 Review Student Learning Services and Biology 120 Peer Mentors Sunday, November 26 th, 2017 4:00 pm Arts 263 Important note: This review was written by your Biology Peer Mentors (not
Biology 120 Lab Exam 2 Review Student Learning Services and Biology 120 Peer Mentors Sunday, November 26 th, 2017 4:00 pm Arts 263 Important note: This review was written by your Biology Peer Mentors (not
*: Corresponding author : E. Nezan, address :
 Please note that this is an author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication following peer review. The definitive publisher-authenticated version is available on the publisher Web site Harmful
Please note that this is an author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication following peer review. The definitive publisher-authenticated version is available on the publisher Web site Harmful
EXOSTOSIS OF THE MANDIBLE OF THE CHICKEN
 EXOSTOSIS OF THE MANDIBLE OF THE CHICKEN COMPLICATING EDEMA OF THE WATTLES GEORGE MILTON SMITH, M.D.1 (AnutomioaZ Laboratory, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut) During the past year opportunity
EXOSTOSIS OF THE MANDIBLE OF THE CHICKEN COMPLICATING EDEMA OF THE WATTLES GEORGE MILTON SMITH, M.D.1 (AnutomioaZ Laboratory, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut) During the past year opportunity
JUNE Yorkshire Goldfish a Ryukin gets a First
 JUNE 2016 Yorkshire Goldfish a Ryukin gets a First Traditionally the Bradford & District Aquarist Society starts the club show scene in Yorkshire with a Springtime Open Show and Auction. This year (and
JUNE 2016 Yorkshire Goldfish a Ryukin gets a First Traditionally the Bradford & District Aquarist Society starts the club show scene in Yorkshire with a Springtime Open Show and Auction. This year (and
Chapter 7. Marine Animals Without a Backbone
 Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Echinoderms Characteristics of Phylum: Name means "Spiny Skin" Endoskeleton Skeleton on inside of body Covered by tissue All 7000 species exclusively marine
Chapter 7 Marine Animals Without a Backbone Echinoderms Characteristics of Phylum: Name means "Spiny Skin" Endoskeleton Skeleton on inside of body Covered by tissue All 7000 species exclusively marine
Phylum Mollusca (mollis, soft)
 Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca (mollis, soft) Body usually an anterior head, ventral foot and a dorsal visceral mass. Covered by a fleshy outgrowth of the body wall called a mantle. Shell if present is
Phylum Mollusca Phylum Mollusca (mollis, soft) Body usually an anterior head, ventral foot and a dorsal visceral mass. Covered by a fleshy outgrowth of the body wall called a mantle. Shell if present is
Cryptosporidium spp. Oocysts
 Sampling and Source Tracking of Cryptosporidium spp. Oocysts June 28, 2005 Kristen L. Jellison, Ph.D. Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Lehigh University Bethlehem, Pennsylvania Ultimate
Sampling and Source Tracking of Cryptosporidium spp. Oocysts June 28, 2005 Kristen L. Jellison, Ph.D. Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Lehigh University Bethlehem, Pennsylvania Ultimate
Veterinary Diagnostics Portfolio Overview. Complete solutions for veterinary testing and pathogen research
 Veterinary Diagnostics Portfolio Overview Complete solutions for veterinary testing and pathogen research Sample preparation products Cat. no. (number of preps) Target analyte Product Short description
Veterinary Diagnostics Portfolio Overview Complete solutions for veterinary testing and pathogen research Sample preparation products Cat. no. (number of preps) Target analyte Product Short description
BEAK AND FEATHER DYSTROPHY IN WILD SULPHUR-CRESTED COCKATOOS (CACATUA GALERITA)
 BEAK AND FEATHER DYSTROPHY IN WILD SULPHUR-CRESTED COCKATOOS (CACATUA GALERITA) Author(s): Steven McOrist, Douglas G. Black, David A. Pass, Peter C. Scott, and John Marshall Source: Journal of Wildlife
BEAK AND FEATHER DYSTROPHY IN WILD SULPHUR-CRESTED COCKATOOS (CACATUA GALERITA) Author(s): Steven McOrist, Douglas G. Black, David A. Pass, Peter C. Scott, and John Marshall Source: Journal of Wildlife
AP Lab Three: Comparing DNA Sequences to Understand Evolutionary Relationships with BLAST
 AP Biology Name AP Lab Three: Comparing DNA Sequences to Understand Evolutionary Relationships with BLAST In the 1990 s when scientists began to compile a list of genes and DNA sequences in the human genome
AP Biology Name AP Lab Three: Comparing DNA Sequences to Understand Evolutionary Relationships with BLAST In the 1990 s when scientists began to compile a list of genes and DNA sequences in the human genome
HISTOLOGY OF MAMMARY GLAND DURING LACTATING AND NON-LACTATING PHASES OF MADRAS RED SHEEP WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO INVOLUTION
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 991 996 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOLOGY OF MAMMARY GLAND DURING LACTATING AND NON-LACTATING PHASES OF MADRAS
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 991 996 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOLOGY OF MAMMARY GLAND DURING LACTATING AND NON-LACTATING PHASES OF MADRAS
RICKETTSIA SPECIES AMONG TICKS IN AN AREA OF JAPAN ENDEMIC FOR JAPANESE SPOTTED FEVER
 RICKETTSIA SPECIES AMONG TICKS IN AN AREA OF JAPAN ENDEMIC FOR JAPANESE SPOTTED FEVER Makoto Kondo 1, Katsuhiko Ando 2, Keiichi Yamanaka 1 and Hitoshi Mizutani 1 1 Department of Dermatology, 2 Department
RICKETTSIA SPECIES AMONG TICKS IN AN AREA OF JAPAN ENDEMIC FOR JAPANESE SPOTTED FEVER Makoto Kondo 1, Katsuhiko Ando 2, Keiichi Yamanaka 1 and Hitoshi Mizutani 1 1 Department of Dermatology, 2 Department
Seasonal Variations of yeso sika Deer Skin and its Vegetable Tanned Leather
 Seasonal Variations of yeso sika Deer Skin and its Vegetable Tanned Leather Shigeharu Fukunaga, Akihiko Yoshie, Ikuo Yamakawa, Fumio Nakamura Laboratory of Animal By-product Science, Graduate School of
Seasonal Variations of yeso sika Deer Skin and its Vegetable Tanned Leather Shigeharu Fukunaga, Akihiko Yoshie, Ikuo Yamakawa, Fumio Nakamura Laboratory of Animal By-product Science, Graduate School of
Scientific background concerning Echinococcus multilocularis. Muza Kirjušina, Daugavpils University, Latvia
 Scientific background concerning Echinococcus multilocularis Muza Kirjušina, Daugavpils University, Latvia Echinococcus multilocularis Infection with the larval form causes alveolar echinococcosis (AE).
Scientific background concerning Echinococcus multilocularis Muza Kirjušina, Daugavpils University, Latvia Echinococcus multilocularis Infection with the larval form causes alveolar echinococcosis (AE).
Cestodes. Tapeworms from man and animals
 Cestodes Tapeworms from man and animals Taenia sp. The common (beef) tapeworm is several meters long. Courtesy Peters W. & Gilles H. Courtesy CDC Courtesy CDC Taenia sp. Unstained egg with four (visible)
Cestodes Tapeworms from man and animals Taenia sp. The common (beef) tapeworm is several meters long. Courtesy Peters W. & Gilles H. Courtesy CDC Courtesy CDC Taenia sp. Unstained egg with four (visible)
Research Note. A novel method for sexing day-old chicks using endoscope system
 Research Note A novel method for sexing day-old chicks using endoscope system Makoto Otsuka,,1 Osamu Miyashita,,1 Mitsuru Shibata,,1 Fujiyuki Sato,,1 and Mitsuru Naito,2,3 NARO Institute of Livestock and
Research Note A novel method for sexing day-old chicks using endoscope system Makoto Otsuka,,1 Osamu Miyashita,,1 Mitsuru Shibata,,1 Fujiyuki Sato,,1 and Mitsuru Naito,2,3 NARO Institute of Livestock and
Objectives. Antibiotics uses in food animals 3/25/2018. California Dairy Productions. Antimicrobial Resistance in the Animal Production Environment
 Antimicrobial Resistance in the Animal Production Environment Xunde Li Western Institute for Food Safety and Security Department of Population Health and Reproduction University of California Davis Objectives
Antimicrobial Resistance in the Animal Production Environment Xunde Li Western Institute for Food Safety and Security Department of Population Health and Reproduction University of California Davis Objectives
Gulf and Caribbean Research
 Gulf and Caribbean Research Volume 16 Issue 1 January 4 Morphological Characteristics of the Carapace of the Hawksbill Turtle, Eretmochelys imbricata, from n Waters Mari Kobayashi Hokkaido University DOI:
Gulf and Caribbean Research Volume 16 Issue 1 January 4 Morphological Characteristics of the Carapace of the Hawksbill Turtle, Eretmochelys imbricata, from n Waters Mari Kobayashi Hokkaido University DOI:
DESCRIPTIONS OF THREE NEW SPECIES OF PETALOCEPHALA STÅL, 1853 FROM CHINA (HEMIPTERA: CICADELLIDAE: LEDRINAE) Yu-Jian Li* and Zi-Zhong Li**
 499 DESCRIPTIONS OF THREE NEW SPECIES OF PETALOCEPHALA STÅL, 1853 FROM CHINA (HEMIPTERA: CICADELLIDAE: LEDRINAE) Yu-Jian Li* and Zi-Zhong Li** * Institute of Entomology, Guizhou University, Guiyang, Guizhou
499 DESCRIPTIONS OF THREE NEW SPECIES OF PETALOCEPHALA STÅL, 1853 FROM CHINA (HEMIPTERA: CICADELLIDAE: LEDRINAE) Yu-Jian Li* and Zi-Zhong Li** * Institute of Entomology, Guizhou University, Guiyang, Guizhou
Echinoderms. Copyright 2011 LessonSnips
 Echinoderms The ocean is home to different creatures from animals that are found on land and the phylum of echinoderms is a prime example. The phylum Echinodermata is a scientific classification of simple
Echinoderms The ocean is home to different creatures from animals that are found on land and the phylum of echinoderms is a prime example. The phylum Echinodermata is a scientific classification of simple
Cerebrospinal Nematodiasis in a Moose in Norway
 Cerebrospinal Nematodiasis in a Moose in Norway Author: Kjell Handeland Source: Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 38(4) : 817-821 Published By: Wildlife Disease Association URL: https://doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-38.4.817
Cerebrospinal Nematodiasis in a Moose in Norway Author: Kjell Handeland Source: Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 38(4) : 817-821 Published By: Wildlife Disease Association URL: https://doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-38.4.817
MOLECULAR AND PHYLOGENETIC CHARACTERISATION OF FASCIOLA SPP. ISOLATED FROM CATTLE AND SHEEP IN SOUTHEASTERN IRAN
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 21, No 1, 86 93 ISSN 1311-1477; DOI: 10.15547/bjvm.1043 Original article MOLECULAR AND PHYLOGENETIC CHARACTERISATION OF FASCIOLA SPP. ISOLATED FROM CATTLE
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 21, No 1, 86 93 ISSN 1311-1477; DOI: 10.15547/bjvm.1043 Original article MOLECULAR AND PHYLOGENETIC CHARACTERISATION OF FASCIOLA SPP. ISOLATED FROM CATTLE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11046 Supplementary Figure 1: Images of PB-positive cells in the subepidermal region (a-i) Representative images of PB positive cells in the subepidermis of the upper beak of the pigeon.
doi:10.1038/nature11046 Supplementary Figure 1: Images of PB-positive cells in the subepidermal region (a-i) Representative images of PB positive cells in the subepidermis of the upper beak of the pigeon.
Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Clinically Relevant Gram-Positive Anaerobic Cocci Collected over a Three-Year Period in the Netherlands
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Mar. 2011, p. 1199 1203 Vol. 55, No. 3 0066-4804/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aac.01771-09 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Antimicrobial
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Mar. 2011, p. 1199 1203 Vol. 55, No. 3 0066-4804/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aac.01771-09 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Antimicrobial
The Search For Antibiotics BY: ASLEY, ELIANA, ISABELLA AND LUNISCHA BSC1005 LAB 4/18/2018
 The Search For Antibiotics BY: ASLEY, ELIANA, ISABELLA AND LUNISCHA BSC1005 LAB 4/18/2018 The Need for New Antibiotics Antibiotic crisis An antibiotic is a chemical that kills bacteria. Since the 1980s,
The Search For Antibiotics BY: ASLEY, ELIANA, ISABELLA AND LUNISCHA BSC1005 LAB 4/18/2018 The Need for New Antibiotics Antibiotic crisis An antibiotic is a chemical that kills bacteria. Since the 1980s,
Formation of Proximal and Anterior Limb Skeleton Requires Early Function of Irx3 and Irx5 and Is Negatively Regulated by Shh Signaling
 Developmental Cell, Volume 29 Supplemental Information Formation of Proximal and Anterior Limb Skeleton Requires Early Function of Irx3 and Irx5 and Is Negatively Regulated by Shh Signaling Danyi Li, Rui
Developmental Cell, Volume 29 Supplemental Information Formation of Proximal and Anterior Limb Skeleton Requires Early Function of Irx3 and Irx5 and Is Negatively Regulated by Shh Signaling Danyi Li, Rui
In the first half of the 20th century, Dr. Guido Fanconi published detailed clinical descriptions of several heritable human diseases.
 In the first half of the 20th century, Dr. Guido Fanconi published detailed clinical descriptions of several heritable human diseases. Two disease syndromes were named after him: Fanconi Anemia and Fanconi
In the first half of the 20th century, Dr. Guido Fanconi published detailed clinical descriptions of several heritable human diseases. Two disease syndromes were named after him: Fanconi Anemia and Fanconi
A Scanning Electron Microscopic Study of Eggshell Surface Topography of Leidynema portentosae and L. appendiculatum (Nematoda: Oxyuroidea)
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 88, Issue 5 (December, 1988) 1988-12 A Scanning Electron Microscopic
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 88, Issue 5 (December, 1988) 1988-12 A Scanning Electron Microscopic
Dirofilaria. Dirofilaria immitis and D. repens in dog and cat and human infections. Editors Claudio Genchi, Laura Rinaldi, Giuseppe Cringoli
 Close window to return to IVIS Dirofilaria Dirofilaria immitis and D. repens in dog and cat and human infections Editors Claudio Genchi, Laura Rinaldi, Giuseppe Cringoli Reprinted in the IVIS website with
Close window to return to IVIS Dirofilaria Dirofilaria immitis and D. repens in dog and cat and human infections Editors Claudio Genchi, Laura Rinaldi, Giuseppe Cringoli Reprinted in the IVIS website with
cyst&' appeared to be of two kinds-one smaller and Smnith "is inclined to regard these epithelial cell parasites as
 COCCIDIA IN SUBEPITHELIAL INFECTIONS OF THE INTESTINES OF BIRDS PHILIP B. HADLEY From the Agricultural Experiment Station of the Rhode Island State College' Received for publication, July 10, 1916 In an
COCCIDIA IN SUBEPITHELIAL INFECTIONS OF THE INTESTINES OF BIRDS PHILIP B. HADLEY From the Agricultural Experiment Station of the Rhode Island State College' Received for publication, July 10, 1916 In an
Outline 1/13/15. Range is mostly surrounding Puerto Rico Important for Tourism and ecological balance
 1/13/15 Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Antillean manatees (Trichechus manatus manatus) and investigating transmission from feral cat feces in Puerto Rico Heidi Wyrosdick M.S. Candidate University of
1/13/15 Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Antillean manatees (Trichechus manatus manatus) and investigating transmission from feral cat feces in Puerto Rico Heidi Wyrosdick M.S. Candidate University of
Morphological characterization of Haemonchus contortus in goats (Capra hircus) and sheep (Ovis aries) in Penang, Malaysia
 Tropical Biomedicine 24(1): 23 27 (2007) Morphological characterization of Haemonchus contortus in goats (Capra hircus) and sheep (Ovis aries) in Penang, Malaysia Wahab A. Rahman and Suhaila Abd. Hamid
Tropical Biomedicine 24(1): 23 27 (2007) Morphological characterization of Haemonchus contortus in goats (Capra hircus) and sheep (Ovis aries) in Penang, Malaysia Wahab A. Rahman and Suhaila Abd. Hamid
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12234 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic naked mole-rat fibroblasts do not undergo ECI. Embryonic naked mole-rat fibroblasts ( EF) were isolated from eight mid-gestation embryos. All the
doi:10.1038/nature12234 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic naked mole-rat fibroblasts do not undergo ECI. Embryonic naked mole-rat fibroblasts ( EF) were isolated from eight mid-gestation embryos. All the
Title: Phylogenetic Methods and Vertebrate Phylogeny
 Title: Phylogenetic Methods and Vertebrate Phylogeny Central Question: How can evolutionary relationships be determined objectively? Sub-questions: 1. What affect does the selection of the outgroup have
Title: Phylogenetic Methods and Vertebrate Phylogeny Central Question: How can evolutionary relationships be determined objectively? Sub-questions: 1. What affect does the selection of the outgroup have
Study of pathological effects of an organic germicide bathing on rainbow trout
 Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences 12(3) 500-510 2013 Study of pathological effects of an organic germicide bathing on rainbow trout Afzali F. 1 ; Sharifpour I. 2, *; Soltani M. 3 Received: July 2011
Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences 12(3) 500-510 2013 Study of pathological effects of an organic germicide bathing on rainbow trout Afzali F. 1 ; Sharifpour I. 2, *; Soltani M. 3 Received: July 2011
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 1, 2018,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 1, 2018, 116 120 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) A SLAUGHTER HOUSE REPORT OF OESOPHAGOSTOMOSIS IN GOAT Amit Gamit Navsari Agricultural
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 1, 2018, 116 120 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) A SLAUGHTER HOUSE REPORT OF OESOPHAGOSTOMOSIS IN GOAT Amit Gamit Navsari Agricultural
ESCHERICHIA COLI RESISTANCE AND GUT MICROBIOTA PROFILE IN PIGS RAISED WITH DIFFERENT ANTIMICROBIAL ADMINISTRATION IN FEED
 ESCHERICHIA COLI RESISTANCE AND GUT MICROBIOTA PROFILE IN PIGS RAISED WITH DIFFERENT ANTIMICROBIAL ADMINISTRATION IN FEED Caroline Pissetti 1, Jalusa Deon Kich 2, Heather K. Allen 3, Claudia Navarrete
ESCHERICHIA COLI RESISTANCE AND GUT MICROBIOTA PROFILE IN PIGS RAISED WITH DIFFERENT ANTIMICROBIAL ADMINISTRATION IN FEED Caroline Pissetti 1, Jalusa Deon Kich 2, Heather K. Allen 3, Claudia Navarrete
Co-transfer of bla NDM-5 and mcr-1 by an IncX3 X4 hybrid plasmid in Escherichia coli 4
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ARTICLE NUMBER: 16176 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.2016.176 Co-transfer of bla NDM-5 and mcr-1 by an IncX3 X4 hybrid plasmid in Escherichia coli 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ARTICLE NUMBER: 16176 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.2016.176 Co-transfer of bla NDM-5 and mcr-1 by an IncX3 X4 hybrid plasmid in Escherichia coli 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
Bioinformatics: Investigating Molecular/Biochemical Evidence for Evolution
 Bioinformatics: Investigating Molecular/Biochemical Evidence for Evolution Background How does an evolutionary biologist decide how closely related two different species are? The simplest way is to compare
Bioinformatics: Investigating Molecular/Biochemical Evidence for Evolution Background How does an evolutionary biologist decide how closely related two different species are? The simplest way is to compare
Name Class Date. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 14 2 The Animal Kingdom SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is diversity? What are vertebrates? What
CHAPTER 14 2 The Animal Kingdom SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is diversity? What are vertebrates? What
