Clonal Diversity of Acinetobacter baumannii Mediated by Carbapenem Resistance in Saudi Arabian Hospitals
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Allen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISSN: Volume 4 Number 5 (205) pp Original Research Article Clonal Diversity of Acinetobacter baumannii Mediated by Carbapenem Resistance in Saudi Arabian Hospitals Abdulrahman A. Alsultan* College of Medicine, King Faisal University, Alahsa 3982, PO Box 400, Saudi Arabia *Corresponding author A B S T R A C T K e y w o r d s Acinetobacter baumannii, Carbapenem resistance, Saudi Arabia, Prevalence To investigate the clonal diversity of multi-drug resistant A. baumannii associated with carbapenem resistance in hospitals of Saudi Arabia based in Riyadh city. Sixty-two non-repetitive strains of A. baumannii from different specimens, collected from King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre (KFSHRC) in Riyadh were included in the study. The isolates were identified by the Vitek compact II system. Multiplex PCR using primer for bla OXA-5 combined with primers for bla OXA-23, bla OXA-24/40 and bla OXA-58 was employed. The resistance pattern of the tested isolates was determined by Vitek 2 compact system and the minimum inhibitory concentrations of imipenem, meropenem, tigecycline and colistin were determined by Etest strips. The clonal diversity of the isolates was investigated by PFGE. Carbapenem resistance was considerably high. Sixty-one out of 62 (98.4%) and 58/62(93.5%) were resistant to imipenem and meropenem, respectively. All isolates were susceptible to colistin but resistance to tigecycline was observed in 9/62 (4.5%). The prevalence of bla OXA-23, bla OXA-24/40, bla VIM and bla SPM were 32 (5.6%), 5 (9.3%), 55 (89%) and 37 (60%), respectively. None of the isolates had bla OXA-58, bla IMP, bla SIM or bla GIM. ISAba and ISAba2, were 53 (85%) and (.6%) respectively, while ISAba3 and IS8 were not detected. PFGE results showed that the tested isolates were clustered in twenty two groups. Clone 0 and 7 were the dominants clones containing 7 and 9 isolates respectively were from six hospitals followed by clone 4 and 8 containing 5 and 6 isolates respectively were from 6 hospitals. It is concluded that bla OXA-23, bla OXA-24/40, bla VIM and bla SPM were the most prevalent genes in the carbapenem resistant A. baumannii isolates under investigation while ISAba was the most common insertion sequence with bla VIM emerging as the chief culprit. Early recognition of the epidemic clone is very helpful to prevent its dissemination by application of strict infection control measures. Introduction Acinetobacter baumannii, in recent years, has been emerged as an important pathogen associated with a wide range of infections causing significant health problems globally. 525
2 In immunocompromised patients Carbapenems are often used as the drugs of last resort for treating severe A. baumannii infections; however, their use is increasingly becoming challenged due to the emergence of -lactamase molecular classes B and D capable of hydrolysing carbapenems. 2 The emergence of carbapenem resistance in A. baumannii has been reported worldwide across different continents. 3 A variety of mechanisms have been conclusively proven to be responsible for carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter, that include modification or reduced expression of porins, over expression of efflux pump and production of carbapenemases. -lactamases with carbapenem hydrolysing activity produced by Acinetobacter include Class B metallo- -lactamase and Class D oxacillinase. 4 Several OXA carbapenemase genes in carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter have been reported so far. 2 The commonly found genetic lineages include OXA-23 like, OXA-24/40 like, OXA-58 like and OXA-5 like. The former three are acquired whereas the latter is a naturally occurring intrinsic gene that requires presence of insertion sequence ISAba upstream of the gene. Insertion sequence ISAba provides a promoter sequence that enhances expression of OXA-5 like gene. 5 A clone of A. baumannii with OXA-23 like gene was first reported from a clinical isolate in Scotland in 985, paradoxically even before the introduction of carbapenem itself, but since then this plasmid borne gene has disseminated across the globe. 6 Clonal outbreaks of carbapenem-resistant and OXA-23 producing A. baumannii have been reported in many countries, such as Bulgaria, People s Republic of China, Brazil, Iraq, Afghanistan and French Polynesia. 7 Other frequently detected carbapenem hydrolyzing oxacillinase enzymes among A. baumannii include the subgroups OXA24/40 and OXA-58. OXA-24/40 was first detected in a highly carbapenem resistant strain isolated in Spain. 8 OXA-58, which share <50% amino acid sequence with other oxacilinases, was first identified in France in There are reports of OXA-58-like enzyme from Argentina, Kuwait and Southern England. 0 Carbapenem resistance in A. baumannii in Saudi Arabia has been reported to be significantly high.,2 Multi drug resistant nosocomial A. baumannii has been reported in several hospitals in Saudi Arabia. 2 The aim of this study was to investigate the clonal diversity of carbapenem resistance in A. baumannii in a major Saudi Arabian Hospital and to establish the extent of dissemination of the common clonal lineages in Saudi Arabia. Material and Methods Bacteriological processing Sixty-two isolates of A. baumannii were collected from non-repetitive specimens from King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre (KFSHRC) in Riyadh between January 20 and April 20.The identity of A. baumannii was established by the Vitek Compact II system. Overall, the Vitek II GN kits for identification of Gram negative bacteria identifies more than 97% of isolates correctly up to the species level 3 and detection of bla OXA-5-like gene was done by PCR. 4 Susceptibility testing Disc diffusion method for testing antibiotic susceptibility was performed and minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were determined for imipenem, meropenem, tigecycline and colistin as per the British 526
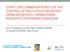
3 Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC) guidelines. 5 Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Multiplex PCR was performed using primer for bla OXA-5 combined with primers for bla OXA-23, bla OXA-24/40 and bla OXA-58. The former was used to confirm identity of the isolate as well, as this is an intrinsic gene. The amplification process was initial denaturation at 94 C for 5 minutes, 30 cycles of 94 C for 25s, 52 C for 40s and 72 C for 50s, and a final elongation at 72 C for 6 minutes. 4 The primers used were F- (5'-TAA TGC TTT GAT CGG CCT TG-'3) and R- (5'-TGG ATT GCA CTT CAT CTT GG-'3) to amplify a 353 bp fragment of the intrinsic OXA-5 like genes and these primers were combined with six new primers to amplify fragments of OXA-23- like 50bp F- (5'-GAT CGG ATT GGA GAA CCA GA-'3) and R- (5'-ATT TCT GAC CGC ATT TCC AT-'3), OXA-40/24- like 246 bp F- (5'-GGT TAG TTG GCC CCC TTA AA-'3) and R- (5'-AGTTGA GCG AAA AGG GGA TT-'3) and OXA-58- like 599 bp F- (5'-AAG TAT TGG GGC TTG TGC TG-'3) and R- (5'-CCC CTC TGC GCT CTA CAT AC-'3) genes. The primers were evaluated individually using control strains and then in a multiplex format. 4 Metallo -lactmases coding genes were amplified as previously described. 6 Molecular typing by PFGE Sixty two clinical isolates of A. baumannii were typed by PFGE analysis as previously described. DNA obtained from bacteria was digested using Apa restriction endonuclease (Promega, Southampton, UK), and DNA fragments were separated on % agarose gel in 0.5 TBE buffer using the CHEF-RDII apparatus (Bio-Rad, UK). The conditions used were the following: pulse time 5-35s at field strength of 6v/cm for 24h at 37C. The gel was stained by ethidium bromide and then the digital images were captured by Gel doc2000 (Bio-Rad, UK). All isolates were analyzed using Bionumerics software version 6.5. Isolates that clustered together with a similarity of >85% were considered to belong to the same PFGE type 7. Results and Discussion Sixty-two clinical isolates of A. baumannii were collected and identified using Vitek Compact II system. High level of carbapenem resistance was observed among the Acinetobacter isolates. Antibiotic sensitivity testing and MIC determination was performed by disc diffusion test as per BSAC guidelines. Sixty one isolates (98.4%) were resistant to imipenem. Of these, fifty-six (90.3%) were also resistant to meropenem as well (Table 2). Two strains were intermediate (MIC>4-8mg/L) and another two were sensitive (MIC 0.5mg/L) (Table and Figure ). All isolates were susceptible to colistin (MIC mg/l). Four isolates demonstrated resistance to tigecycline (6.5%) while six isolates were intermediate susceptible (Table and Figure ). Multiplex PCR was performed to detect OXA-like genes in order to find out genetic basis of carbapenem resistance. Thirty-two carbapenem resistant isolates possessed bla OXA-23 gene while OXA-40 gene was found in 5 isolates (Table 2). None of the organisms had OXA-58. An isolate was sensitive to imipenem, tigecycline and colistin while intermediate sensitive to meropenem was also found to be harbouring bla OXA-23 (Figure ). On the other hand, bla VIM and bla SPM were detected in 55 and 37 isolates, respectively, while bla SIM, bla IMP and bla GIM were absent (Table 2). Figure 527
4 showed the PFGE dendrogram of the 62 A. baumannii tested isolates. PFGE was applied to study the clonal diversity and relatedness of the tested isolates. The discrimination power of PFGE technique was express by dice coefficient via BioNumerics software version 6.5. Figure shows the clustering of Twenty-two clones of PFGE comprise the ID number (isolate code), sex, locations, -lactamase of OXA-23, OXA-40, insertion sequences (ISAba, ISAba2, ISAba3 and IS8) and MBLs (VIM, SIM, GIM, IMP and SPM). All detected PFGE patterns demonstrate the genetic similarity coefficient ranged from 65% to 00%. Epidemic isolates that clustered together with a similarity of more than 85% were considered to present the same PFGE type. Clone 0, 4, 7 and 8 included 7, 5, 9 and 6 PFGE types, respectively, with genetic similarity ranges from 85 to 00%, 88 to 00%, 89 to 00% and 87 to 00% respectively, and have shared 3, 2, 3 and 4 cities, respectively, as shown in Figure. The clonal diversity of the twenty-two clones and the mechanism of resistance in relation to the cities from which the isolates obtained were collected. Twelve, five and four different clones were detected in 2, 8 and 7 isolates from Riyadh, Breedah and Almadinah, respectively Table 5. The menace of multidrug resistant organisms including pan drug and carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter has thrown new challenges to medical fraternity. No part of the world is left untouched with this problem and Saudi Arabia is no exception to it. In fact, with a vibrant economic and raised standard of life, Saudi Arabia has been able to provide an excellent class healthcare delivery system. As a consequence of this, it has to face the aforementioned problem too. In this study, a considerably high level of carbapenem resistance among A. baumannii isolates was observed (96% against imipenem versus 93% against meropenem). Studies on carbapenem resistant A. baumannii in Saudi Arabia have also cited extremely high percentage resistance,2,8-23. Four strains (4%) were also resistant to tigecycline. Recent studies have reported an increased resistant to this antibiotic which has further narrowed down the therapeutic options. 24 The incidence of OXA type - lactamase mediated carbapenem resistance among A. baumannii has been rising and several different types of OXA-like genes have been identified until now. 2 The bla OXA- 23 gene, first characterized in Scotland, has been increasingly reported worldwide. A. radioresistens was recently identified as the progenitor of the bla OXA-23 -like genes. 6 Clonal outbreaks of carbapenem-resistant and OXA-23 producing A. baumannii have been reported in many countries, such as Brazil 25, China (GenBank accession number AY554200) 26, Korea 27, the United Kingdom 5 and Singapore (GenBank accession number AY795964). OXA-24/40 and OXA-58 are the other commonly occurring carbapenem hydrolyzing class D -lactamases. OXA-58, a plasmid-borne carbapenemase, has been seen in several countries including France, England, Argentina, Spain, Turkey, Romania, Austria, Greece, Scotland, and Kuwait. The intrinsic gene OXA-5 of A. baumannii, might also be responsible for carbapenem resistance, if it is accompanied with ISAba promoter gene upstream. 5 46% (3/28) of isolates tested by us harboredbla OXA-23, whereas 4% (/28) had bla OXA-24/40. bla OXA-58, the other common OXA-like gene was not detected in any isolate. We reviewed previous reports of bla OXA gene prevalence among carbapenem resistant A. baumanniiin Saudi Arabian hospitals. 528
5 Studies conducted on the genes responsible for carbapenem resistant A. baumannii in Saudi Arabia have shown that OXA-23 genes are the leading genes prevalent. The prevalence of bla OXA-23 gene in Saudi Arabia has been in the range of %. The genetic clone has disseminated considerably in this country as shown in Table 3. A. baumannii strains bearing OXA-23 gene has also been reported to be the chief cause of carbapenem resistant worldwide. bla OXA-23 geneis now endemic in several hospitals of England 28. In Greece, the bla OXA-23 gene mediated carbapenem resistance has been found to be 72.4% 29. Other parts of Middle East do have the presence of bla OXA-23 and bla OXA-24/40 carrying A. baumannii. Iraq, Bahrain, and United Arab Emirates have been found with such -lactamase producing A. baumannii strains 6. 26/44 (59.%) strains harboured bla OXA-23 gene in a study from Turkey 30. There are studies testifying to the occurrence of such strains of A. baumannii in South East Asia and Pacific region as well. Jeon et al. (2005) have reported that 36/52 or 69.2% of hospital isolates of A. baumannii in Republic of Korea had bla OXA Researcher in South Korea have found it to be 77%. 3 Very high prevalence of bla OXA-23 gene bearing A. baumannii - 28/32 (87.5%), was found in a study of clinical isolates from Sydney Hospital, Australia. 32 Similar higher prevalence has also been reported from Singapore (9%) 33 and Hong Kong (00%) 34. OXA-24/40 family of OXA genes could be seen in 4% isolates in this study. OXA- 24/40 in clinical isolates of A. baumannii has been reported in significant number. 3 Previous studies in Saudi Arabia have also documented the presence of A. baumannii strains carrying this gene as show in Table 4. No strains were positive for OXA-58 in our study. High prevalence of OXA-58 (47.8%) from different cities in Europe has been reported by Marque et al. (2005) 35. Much higher prevalence of bla OXA-58 (00%, n=9) has been reported from Turkey 36. However, bla OXA-58 is a less commonly found gene in comparison to the other genes 3. The remaining carbapenem resistant isolates (4% imipenem and % meropenem) had no OXA genes in them. Their resistance to carbapenem could be because of OXA-5 itself- an intrinsic OXA gene in A. baumannii over expression of which is known to be a reason for carbapenem resistance 2 or perhaps the presence of Class B metallo -lactamase which we didn t attempt to identify. Chi-square test was used to compare the locations and OXA-23 among them and the value of chi-square was with p-value 0.09, which had significant value. To determine which location made that difference, Post-hoc analysis was performed as follows: when converted to a z-score, the standardized residual (2.0) was greater than the critical value (.96), supporting a specific finding that among survey respondents who were in Breeda. There were more who had [OXA-23 (-)] than would be expected as shown in Table 4. The same test was used to compare the locations and OXA-40 among them, and the value of chi-square was with p-value 0.005, which had significant value. In addition, when converted to a z-score, the standardized residual (4.6) was greater than the critical value (.96), supporting a specific finding that among survey respondents who were in Breeda. There were more who had [OXA-23 (+)] than would be expected. 529
6 Table. MIC values and level of resistance among A. baumannii isolates Antibiotics No. of resistant MIC range % isolates (ml/l) Imipenem 6 > Meropenem 58 > Tigecycline Colistin Table.2 Prevalence of different carbapenemases in the tested isolates Gene Number of isolates (%) bla OXA (5.6) bla OXAcc 5 (24.2) bla VIM 55 (88.7) bla SPM 37 (59.6) bla SIM 0 (0) bla IMP 0 (0) bla GIM 0 (0) Table.3 Prevalence of bla OXA genes in Saudi Arabia Reference Number of isolates (%) harboring bla OXA-23 bla OXA-24/40 bla OXA-58 Al-Arfajet al. (20) 2 29/40 (72.5) 8/40 (45) 5/40 (37.5) Ribeiro et al. (202) 22 6/27 (46.3) /27 (3.7) ND Shehata et al. (202) 20 45/8 (38) ND ND Present study 32/62 (5.6) 5/62 (24.) 0/62 (0) ND: Not Determined Table.4 Relation between location and gender with the prevalence of different components Variables OXA-23 OXA-24/40 ISAba VIM SPM Imipenem resistance Meropenem resistance Tigecycline resistance Chi-square value Location df P-value Chi-square value Gender df 2 2 P-value
7 Table.5 Profiles of A. baumannii tested isolates Hospital location No. of isolates (%) Clone diversity Mechanism of resistant (Area) (n=62), 3, 6 RIYADH 9, 0, OXA-23, OXA-40, ISAba, 3, 4, 6 VIM and SPM 22 (3.6 %) 7, 8, 2 BREDAH 5, 5, 7 8, 22 OXA-40, ISAba, VIM and SPM 8 (5.0%) ALMADINAH 0, 4, 5, 20 OXA-23, ISAba, SPM and VIM 7 (4.4%) ARAR 2, 8, 20 OXA-40, ISAba, VIM and SPM 3 (.9%) HAIL 7, 8, 9 OXA-23, OXA-40, ISAba, VIM and SPM 3 (.9%) ENV 7, 8 OXA-40, ISAba, VIM and SPM 3 (.9%) NAJRAN 6, 7 OXA-23, ISAba, VIM and SPM 2 (.2%) ALJUBAIL 0 OXA-23, ISAba, VIM and SPM 2 (.2%) RANYA 2 OXA-23, ISAba, VIM and SPM 2 (.2%) ALJOUF 6, 2 OXA-23, ISAba, VIM and SPM 2 (.2%) K. MOSAIT 7, 22 OXA-40, VIM and SPM 2 (.2%) ALTAIF 4 OXA-23, ISAba, VIM and SPM (7.8) DAMMAM 4 OXA-23, ISAba and SPM (.6) ABHA 5 OXA-40, VIM and SPM (3.) ALMAJMAH 8 OXA-40, ISAba, VIM and SPM (.6) BISHAH 2 ISAba, VIM and SPM (.6) MACCA 5 VIM (.6) 53
8 Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (205) 4(5): Figure. PFGE patterns of A. baumannii. Abbreviations: R, resistance; S, susceptible; I, intermediate, IMIP, imipenem; MER, meropenem; TIG, tigecycline; COL, colistin 532
9 The same procedure was applied to compare the locations and meropenem resistance among them. Chi-square value was 47. with p-value 0.042, which had significant value and the standardized residual (5.2) was greater than the critical value (.96), supporting a specific finding that among survey respondents who were in Macca. There were more who had [Meropenem (I)] than would be expected. On the other hand, there was not any significant value between Gender and any other variable (Table 4). PFGE is one of the most important discriminatory methods of A. baumannii and many other pathogens It is an efficient tool for determining the genetic relationship between strains isolated and certain epidemiological situation 39. In the current work, the genetic similarity in PFGE among its own different types is very high (87 to 00%). The clonal diversity revealed two types of clones that cause an epidemic: monoclonal and polyclonal as mentioned in Table 5. The polyclonal model showed that it is the most common clone appears in 9 of 7 cities in the Kingdom. Two types of epidemic PFGE mainly caused these types of polyclonal outbreaks. In addition, Riyadh is the capital city of Saudi Arabia, which affected by 2 different clones of 7, and Bredah is the capital city of Al-Qaseem province had also affected by five different clones. Thus, it shows that both cities were affected an explosive outbreak however at different times. Whereas, the monoclonal model has affected eight cites (Jubail, Ranya, Altaif, Dammam, Abha, Almajmah, Bisha and K. Mosait), and each of these cities had only one clone. Therefore, it is depicted that it is present in the minority and that could reflect the coexistence of sporadic and epidemic clones 40 too. Indeed, it leads to a conclusion that all of these cities might have low levels of hospital infection control that may help in these outbreaks. Likewise, it appeared that clone 8 has been detected in hospitals of Riyadh, Bredah, Arar, Hail, and while clone 0 has been found from the environment in three cities Riyadh, Almadinah and Aljubail (Table 5). Henceforth, this study has pointed out that the transmission of an existing clone from one hospital to another could originate a new outbreak at these hospitals and that eventually affects health care workers. And during transmission, the possibility of A. baumannii transmission is highly recognized 4-43 that reflects the reappearance of certain clones within these hospitals. Consequently, it reinforces persistence of endemic from this pathogen in patients, hospital and environments, which, could be a major risk factor in future outbreaks. Thus, it is highly recommended that these isolates should to be compared with different strains on other countries through typing and -lactamase gene sequencing. The further research would establish whether there is a particular bacterial clone present and is associated with particularly to the kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The result of the current study revealed that bla OXA-23, bla OXA-24/40, bla VIM and bla SPM were the most common -lactamases conferring carbapenem resistance to A. baumannii. It is concluded that bla OXA-23, bla OXA-24/40, bla VIM and bla SPM were the most prevalent genes in the carbapenem resistant A. baumannii isolates under investigation while ISAba was the most common insertion sequence with bla VIM emerging as the chief culprit. Early recognition of the epidemic 533
10 clone is very helpful to prevent its dissemination by application of strict infection control measures. Moreover, the current study provided significant data regarding the clonal diversity of carbapenem resistant A. baumannii in different cities in Saudi Arabia. Detection of the certain clone in different cities reflects the horizontal transmission of carbapenem resistance. Strict infection control measures should be applied to prevent such type of transmission. Acknowledgements The authors wish to thank King Faisal University (KFU) for its support, Dr. Sayed Ibrahim, Hani Alrasasi, Hani Alfarhan, Hajar Al-dohilan, NofAlhomaini, AbdulqaderAbouli, and Fatemah Al Najar. Funding This study was funded by King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST). References. Perez, F., Hujer, A.M., Hujer, K.M., Decker, B.K., Rather, P.N., Bonomo, R.A Global challenge of Multidrug resistant A. baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother., 5: Brown, S., Amyes, S OXA - lactamases in Acinetobacter: the story so far. J Antimicrob. Chemother., 57: Durante-Mangoni, E., Zarilli, R. 20. Global spread of drug resistant A. baumannii: Molecular epidemiology and management of antimicrobial resistance. Future Microbial., 6: Poirel, L., Nordmann, P Carbapenem resistance in A. baumannii: Mechanisms and Epidemiology. Clin. Microbial. Infect., 2: Turton, J.F., Ward, M.E., Woodford, N., Kaufmann, M.E., Pike, R., Livermore, 534 D.M., et al The role of ISAba in expression of OXA carbapenemase genes in A. baumannii. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 258: Mugnier, P.D., Poirel, L., Naas, T., Nordmann, P Worldwide dissemination of the bla OXA- 23carbapenemase gene of Acinetobacter baumannii. Emerg. Infect. Dis., 6: Dijkshoorn, L., Nemec, A., Seifert, H An increasing threat in hospitals: multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 5: Bou, G., Oliver, A., Martínez-Beltrán, J OXA-24, a novel class D - lactamase with carbapenemase activity in an Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 44: Poirel, L., Marque, S., Heritier, C., Segonds, C., Chabanon, G., Nordmann, P OXA-58, a novel class D - lactamase involved in resistance to carbapenems in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 49: Coelho, J., Woodford, N., Afzal-Shah, M Detection of novel OXA-58-like carbapenemase in Acinetobacter spp. from three continents in: Abstracts of the 6th International Symposium on the Biology of Acinetobacter, Dublin, Ireland. Abstract pc7, p Al Johani, S.M., Akhter, J., Balkhy, H., El-Saed A, Younan M, Memish Z. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance among gram-negative isolates in an adult intensive care unit at a tertiary care center in Saudi Arabia. Ann Saudi Med 200;30: Al-Arfaj AA, Ibrahim ASS, Somily AM, Al-Salamah AA. Genetic basis of carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter clinical isolates in Saudi Arabia. African J Biotechnol 20;0: Funke G, Funke-Kissling P. Evaluation of new VITEK 2 card for identification of
11 clinically relevant Gram negative rods. J Clin Microbial 2004;42: Woodford N, Ellington M, Coelho JM, Turton JF, Ward ME, Brown S. Multiplex PCR for genes encoding prevalent OXA carbapenemases in Acinetobacter spp. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2006;27: BSAC (2007). Methods for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing.Version 6. February. ocuments/version_6..pdf. 6. Ellington MJ, Kistler J, Livermore DM, Woodford N. Multiplex PCR for rapid detection of genes encoding acquired metallo-beta-lactamases. J Antimicrob Chemother 2007;59: Miranda G, Kelly C, Solorzano F, Leanos B, Coria R, Patterson JE. Use of pulsedfield gel electrophoresis typing to study an outbreak of infection due to Serratia marcescens in a neonatal intensive care unit.j ClinMicrobiol996;34: Eltahawy AT, Khalaf RM. Antibiotic resistance among Gram negative nonfermenting bacteria at a teaching hospital in Saudi Arabia. J Chemother 200;3: Al Tawfiq A, Mohandas A, Hangiah T. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-baumannii complex in a Saudi Arabian hospital. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2007;28: Hanan AB, Kambal AM, Al-Anazy AR, Saidu AB, Aziz S. Acinetobacter blood stream infection in a teaching hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Kuwait Med J 2003;35: Shehata AI. Phenotypic and genotypic typing of multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii by plasmid profiles and Multiplex PCR typing.sci J Microbiol 202; Article ID SJMB- 274: AL-Sultan AA, Evans BA, Elsayed EA, Al-Thawadi SI, Al-Taher AY, Amyes SG. High frequency of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii in 535 patients with Diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia. J Med Microbial 203;62: Ribeiro A, Al Ghamy MH, Shibl AM, Tawfik AF, Courvalin P, Jeannot K. Molecular epidemiology and mechanisms of carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a Saudi Arabian hospital. 22 nd European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases Navon-Venezia S, Leavitt A, Carmeli Y. High tigecycline resistance in multidrug Acinetobacter baumannii. J Antimicrob Chemother 2007;59: Dalla-Costa, LM, Coelho JM, Souza HM, Castro ME, Stier CJ, Bragagnolo KL. Outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii producing the OXA-23 enzyme in Curitiba, Brazil.J ClinMicrobiol 2003;4: Yu YS, Yang Q, Xu XW, Kong HS, Xu GY, Zhong BY.Typing and characterization of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-baumannii complex in a Chinese hospital.j Med Microbiol 2004;53: Jeon BC, Jeong SH, Bae IK, Kwon SB, Lee K, Young D. Investigation of a nosocomial outbreak of imipenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii producing the OXA-23 -lactamase in Korea. J Clin Microbial 2005;43: Coelho JM, Woodford N, Warner M. Spread of two OXA-23-producing Acinetobacter baumannii clones in England. Abstracts of the 6 th International Symposium on the Biology of Acinetobacter, Dublin, Ireland.2004; Abstract C3.p Liakopoulos A, Miriagou V, Katsifas EA, Karagouni AD, Daikos GL, Tzouvelekis LS, et al. Identification of OXA-23- producing Acinetobacter baumannii in Greece, Euro surveill 202;7:pii Gur D, Korten V, Unal S, Deshpande LM, Castanheira M. Increasing carbapenem
12 resistance due to the clonal dissemination of oxacillinase (OXA-23 andoxa-58)-producing Acinetobacter baumannii: report from the Turkish SENTRY Program sites. J Med Microbiol 2008;57: Park YS, Lee H, Lee KS, Hwang SS, Cho YK, Kim HY. Extensively drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: risk factors for acquisition and prevalent OXA type carbapenemases- a multicentric study. Int J Antimicrob Agents 200;36: Mak JK, Kim MJ, Pham J, Tapsall J, White PA. Antibiotic resistant determinants in nosocomial strains of multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J Antimicrob Chemother 2009;63: Koh T, Sng L, Wang G, Hsu LY, Zhao Y. IMP-4 and OXA -lactamases in Acinetobacter baumannii from Singapore. J Antimicrob Chemother 2007;59: Ho PL, Ho AY, Chow KH, Lai EL, Ching P, Seto WH. Epidemiology and clonality of multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii from a health care region in Hong Kong. J Hosp Infect 200;74: Marque S, Poirel L, Heritier C, Brisse S, Blasco MD, Filip R, et al. Regional occurrence of plasmid- mediated carbapenem hydrolyzing oxacillinase OXA 58 in Acinetobacter spp. in Europe. J ClinMicrobiol 2005;43: Kulah C, Mooij MJ, Comerta F, Aktas E, Celebi G, Ozlu N, et al. Characterisation of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii outbreak strains producing OXA-58 in Turkey. Inter J Antimicrob Agents 200;36: Hunter PR, Gaston MA. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: an application of Simpson s index of diversity. J Clin Microbiol 998;26: Seifert H, Gerner-Smidt P. Comparison of ribotyping and pulsed-field gel 536 electrophoresis for molecular typing of Acinetobacter isolates. J ClinMicrobiol 995;33: Van Belkum A, Tassios PT, Dijkshoorn L, Haeggman S, Cookson B, Fry NK, et al. Guidelines for the validation and application of typing methods for use in bacterial epidemiology. Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2007;3: Rodríguez-Baño J, Cisneros JM, Fernández-Cuenca F, Ribera A, Vila J, Pascual A, et al. Clinical features and epidemiology of Acinetobacter baumannii colonization and infection in Spanish hospitals. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2004;25: Coelho JM, Turton JF, Kaufmann ME, Glover J, Woodford N, Warner M, et al. Occurrence of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clones at multiple hospitals in London and Southeast England. J Clin Microbiol 2006; 44: Dijkshoorn L, Aucken H, Gerner-Smidt P, Janssen P, Kaufmann ME, Garaizar J, et al. Comparison of outbreak and non outbreak Acinetobacter baumannii strains by genotypic and phenotypic methods. J Clin Microbiol 996; 34: Manikal VM, Landman D, Saurina G, Oydna E, Lal H, Quale J. Endemic carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter species in Brooklyn, New York: citywide prevalence, interinstitutional spread, and relation to antibiotic usage. Clin Infect Dis 2000;3:0-6.
Characterization of the Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter
 Ann Clin Microbiol Vol. 7, No. 2, June, 20 http://dx.doi.org/0.55/acm.20.7.2.29 pissn 2288-0585 eissn 2288-6850 Characterization of the Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter species Causing a Nosocomial Outbreak
Ann Clin Microbiol Vol. 7, No. 2, June, 20 http://dx.doi.org/0.55/acm.20.7.2.29 pissn 2288-0585 eissn 2288-6850 Characterization of the Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter species Causing a Nosocomial Outbreak
Diversity in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from paediatric cancer patients in Egypt
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Diversity in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from paediatric cancer patients in Egypt L. Al-Hassan 1, H. El Mehallawy 2 and S.G.B. Amyes 1 1) Medical Microbiology, University
ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Diversity in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from paediatric cancer patients in Egypt L. Al-Hassan 1, H. El Mehallawy 2 and S.G.B. Amyes 1 1) Medical Microbiology, University
Analysis of drug-resistant gene detection of blaoxa-like genes from Acinetobacter baumannii
 Analysis of drug-resistant gene detection of blaoxa-like genes from Acinetobacter baumannii D.K. Yang, H.J. Liang, H.L. Gao, X.W. Wang and Y. Wang Department of Infections, The First Affiliated Hospital
Analysis of drug-resistant gene detection of blaoxa-like genes from Acinetobacter baumannii D.K. Yang, H.J. Liang, H.L. Gao, X.W. Wang and Y. Wang Department of Infections, The First Affiliated Hospital
Molecular characterization of carbapenemase genes in Acinetobacter baumannii in China
 Molecular characterization of carbapenemase genes in Acinetobacter baumannii in China F. Fang 1 *, S. Wang 2 *, Y.X. Dang 3, X. Wang 3 and G.Q. Yu 3 1 The CT Room, Nanyang City Center Hospital, Nanyang,
Molecular characterization of carbapenemase genes in Acinetobacter baumannii in China F. Fang 1 *, S. Wang 2 *, Y.X. Dang 3, X. Wang 3 and G.Q. Yu 3 1 The CT Room, Nanyang City Center Hospital, Nanyang,
Department of Clinical Microbiology, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham, UK
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01911.x Genetic diversity of carbapenem-resistant isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii in Europe K. J. Towner, K. Levi and M. Vlassiadi, on behalf of the ARPAC
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01911.x Genetic diversity of carbapenem-resistant isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii in Europe K. J. Towner, K. Levi and M. Vlassiadi, on behalf of the ARPAC
Multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA) Surveillance and Control. Alison Holmes
 Multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA) Surveillance and Control Alison Holmes The organism and it s epidemiology Surveillance Control What is it? What is it? What is it? What is it? Acinetobacter :
Multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA) Surveillance and Control Alison Holmes The organism and it s epidemiology Surveillance Control What is it? What is it? What is it? What is it? Acinetobacter :
Acinetobacter Resistance in Turkish Tertiary Care Hospitals. Zeliha KOCAK TUFAN, MD, Assoc. Prof.
 Acinetobacter Resistance in Turkish Tertiary Care Hospitals Zeliha KOCAK TUFAN, MD, Assoc. Prof. Acinetobacter Problem Countries that have reported hospital outbreaks of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter
Acinetobacter Resistance in Turkish Tertiary Care Hospitals Zeliha KOCAK TUFAN, MD, Assoc. Prof. Acinetobacter Problem Countries that have reported hospital outbreaks of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter
Identification of Multidrug-Resistant Genes in Acinetobacter baumannii in Sulaimani City-Kurdistan Regional Government of Iraq
 Asian Journal of Medical Sciences 4(5): 179-183, 2012 ISSN: 2040-8773 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2012 Submitted: August 09, 2012 Accepted: September 17, 2012 Published: October 25, 2012 Identification
Asian Journal of Medical Sciences 4(5): 179-183, 2012 ISSN: 2040-8773 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2012 Submitted: August 09, 2012 Accepted: September 17, 2012 Published: October 25, 2012 Identification
RESEARCH NOTE. Molecular epidemiology of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii in New Caledonia
 Research tes 977 routine clinical testing. J Antimicrob Chemother 2002; 40: 2755 2759. 20. Galani I, Rekatsina PD, Hatzaki D et al. Evaluation of different laboratory tests for the detection of metallob-lactamase
Research tes 977 routine clinical testing. J Antimicrob Chemother 2002; 40: 2755 2759. 20. Galani I, Rekatsina PD, Hatzaki D et al. Evaluation of different laboratory tests for the detection of metallob-lactamase
Testing for antimicrobial activity against multi-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. For. Forbo Flooring B.V. Final Report. Work Carried Out By
 Technical Report Testing for antimicrobial activity against multi-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii For Forbo Flooring B.V. Final Report Work Carried Out By A. Smith Group Leader Peter Collins PRA Ref:
Technical Report Testing for antimicrobial activity against multi-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii For Forbo Flooring B.V. Final Report Work Carried Out By A. Smith Group Leader Peter Collins PRA Ref:
Molecular Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Five Proximal Hospitals in Taiwan
 Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 64, 222-227, 2011 Short Communication Molecular Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Five Proximal Hospitals in
Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 64, 222-227, 2011 Short Communication Molecular Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Five Proximal Hospitals in
ESBL Producers An Increasing Problem: An Overview Of An Underrated Threat
 ESBL Producers An Increasing Problem: An Overview Of An Underrated Threat Hicham Ezzat Professor of Microbiology and Immunology Cairo University Introduction 1 Since the 1980s there have been dramatic
ESBL Producers An Increasing Problem: An Overview Of An Underrated Threat Hicham Ezzat Professor of Microbiology and Immunology Cairo University Introduction 1 Since the 1980s there have been dramatic
Prevalence of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its antibiogram in a tertiary care centre
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 952-956 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 952-956 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase
Overnight identification of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii carriage in hospitalized patients
 TABLE 1. Origin and carbapenem resistance characteristics of the 64 Acinetobacter baumannii stock D-750 Overnight identification of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii carriage in hospitalized patients
TABLE 1. Origin and carbapenem resistance characteristics of the 64 Acinetobacter baumannii stock D-750 Overnight identification of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii carriage in hospitalized patients
Microbiology Unit, Hua Hin Hospital, Prachuap Khiri Khan, Thailand
 IDENTIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CARBAPENEMASE GENES IN CLINICAL ISOLATES OF CARBAPENEM-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII FROM A GENERAL HOSPITAL IN THAILAND Wichai Santimaleeworagun 1, Anukul Thathong
IDENTIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CARBAPENEMASE GENES IN CLINICAL ISOLATES OF CARBAPENEM-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII FROM A GENERAL HOSPITAL IN THAILAND Wichai Santimaleeworagun 1, Anukul Thathong
Supplemental Information. Discovery of Reactive Microbiota-Derived. Metabolites that Inhibit Host Proteases
 Cell, Volume 168 Supplemental Information Discovery of Reactive Microbiota-Derived Metabolites that Inhibit Host Proteases Chun-Jun Guo, Fang-Yuan Chang, Thomas P. Wyche, Keriann M. Backus, Timothy M.
Cell, Volume 168 Supplemental Information Discovery of Reactive Microbiota-Derived Metabolites that Inhibit Host Proteases Chun-Jun Guo, Fang-Yuan Chang, Thomas P. Wyche, Keriann M. Backus, Timothy M.
ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing microorganisms; state of the art. Laurent POIREL
 ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing microorganisms; state of the art Laurent POIREL Medical and Molecular Microbiology Unit Dept of Medicine University of Fribourg Switzerland INSERM U914 «Emerging Resistance
ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing microorganisms; state of the art Laurent POIREL Medical and Molecular Microbiology Unit Dept of Medicine University of Fribourg Switzerland INSERM U914 «Emerging Resistance
Differences in phenotypic and genotypic traits against antimicrobial agents between Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter genomic species 13TU
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2007) 59, 633 639 doi:10.1093/jac/dkm007 Advance Access publication 6 March 2007 Differences in phenotypic and genotypic traits against antimicrobial agents between
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2007) 59, 633 639 doi:10.1093/jac/dkm007 Advance Access publication 6 March 2007 Differences in phenotypic and genotypic traits against antimicrobial agents between
Antimicrobial Cycling. Donald E Low University of Toronto
 Antimicrobial Cycling Donald E Low University of Toronto Bad Bugs, No Drugs 1 The Antimicrobial Availability Task Force of the IDSA 1 identified as particularly problematic pathogens A. baumannii and
Antimicrobial Cycling Donald E Low University of Toronto Bad Bugs, No Drugs 1 The Antimicrobial Availability Task Force of the IDSA 1 identified as particularly problematic pathogens A. baumannii and
Molecular epidemiology of Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter nosocomialis in Germany over a 5-year period ( )
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/1469-0691.12026 Molecular epidemiology of Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter nosocomialis in Germany over a 5-year period (2005 2009) X. Schleicher 1, P. G. Higgins 1, H.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/1469-0691.12026 Molecular epidemiology of Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter nosocomialis in Germany over a 5-year period (2005 2009) X. Schleicher 1, P. G. Higgins 1, H.
REVIEW. Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: mechanisms and epidemiology L. Poirel and P. Nordmann /j
 REVIEW 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01456.x Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: mechanisms and epidemiology L. Poirel and P. Nordmann Service de Bactériologie-Virologie, Hôpital de Bicêtre, South-Paris
REVIEW 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01456.x Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: mechanisms and epidemiology L. Poirel and P. Nordmann Service de Bactériologie-Virologie, Hôpital de Bicêtre, South-Paris
ESCMID elibrary. Symposium: Acinetobacter Infections from East to West. Molecular Epidemiology Worldwide
 Symposium: Acinetobacter Infections from East to West Molecular Epidemiology Worldwide Harald Seifert Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie, Immunologie und Hygiene der Universität zu Köln 26 th ECCMID,
Symposium: Acinetobacter Infections from East to West Molecular Epidemiology Worldwide Harald Seifert Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie, Immunologie und Hygiene der Universität zu Köln 26 th ECCMID,
Georgios Meletis, Efstathios Oustas, Christina Botziori, Eleni Kakasi, Asimoula Koteli
 New Microbiologica, 38, 417-421, 2015 Containment of carbapenem resistance rates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Acinetobacter baumannii in a Greek hospital with a concomitant increase in colistin, gentamicin
New Microbiologica, 38, 417-421, 2015 Containment of carbapenem resistance rates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Acinetobacter baumannii in a Greek hospital with a concomitant increase in colistin, gentamicin
Outline. Antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrobial resistance in gram negative bacilli. % susceptibility 7/11/2010
 Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms Is Combination Therapy the Way to Go? Sutthiporn Pattharachayakul, PharmD Prince of Songkhla University, Thailand Outline Prevalence of anti-microbial resistance in Acinetobacter
Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms Is Combination Therapy the Way to Go? Sutthiporn Pattharachayakul, PharmD Prince of Songkhla University, Thailand Outline Prevalence of anti-microbial resistance in Acinetobacter
BLA-NDM-1 IN CLINICAL ISOLATES OF Acinetobacter baumannii FROM NORTH INDIA
 ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138(Online) BLA-NDM-1 IN CLINICAL ISOLATES OF Acinetobacter baumannii FROM NORTH INDIA NIDHI PAL a, R. SUJATHA b AND ANIL KUMAR 1c a Department of Microbiology, Rama
ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138(Online) BLA-NDM-1 IN CLINICAL ISOLATES OF Acinetobacter baumannii FROM NORTH INDIA NIDHI PAL a, R. SUJATHA b AND ANIL KUMAR 1c a Department of Microbiology, Rama
Comparative Assessment of b-lactamases Produced by Multidrug Resistant Bacteria
 Comparative Assessment of b-lactamases Produced by Multidrug Resistant Bacteria Juhee Ahn Department of Medical Biomaterials Engineering Kangwon National University October 23, 27 Antibiotic Development
Comparative Assessment of b-lactamases Produced by Multidrug Resistant Bacteria Juhee Ahn Department of Medical Biomaterials Engineering Kangwon National University October 23, 27 Antibiotic Development
Distribution of bla OXA genes among carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii nosocomial strains in Poland
 NEW MICROBIOLOGICA, 35, 317-325, 2012 Distribution of bla OXA genes among carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii nosocomial strains in Poland Paweł Nowak 1, Paulina Paluchowska 1, Alicja Budak 1,2
NEW MICROBIOLOGICA, 35, 317-325, 2012 Distribution of bla OXA genes among carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii nosocomial strains in Poland Paweł Nowak 1, Paulina Paluchowska 1, Alicja Budak 1,2
Clonal Diversity of Nosocomial Epidemic Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Isolated in Spain
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 2011, p. 875 882 Vol. 49, No. 3 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01026-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Clonal Diversity
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 2011, p. 875 882 Vol. 49, No. 3 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01026-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Clonal Diversity
Multicity Outbreak of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates Producing the Carbapenemase OXA-40
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Sept. 2006, p. 2941 2945 Vol. 50, No. 9 0066-4804/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.00116-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Multicity
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Sept. 2006, p. 2941 2945 Vol. 50, No. 9 0066-4804/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.00116-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Multicity
Antibiotic Reference Laboratory, Institute of Environmental Science and Research Limited (ESR); August 2017
 Antimicrobial susceptibility of Shigella, 2015 and 2016 Helen Heffernan and Rosemary Woodhouse Antibiotic Reference Laboratory, Institute of Environmental Science and Research Limited (ESR); August 2017
Antimicrobial susceptibility of Shigella, 2015 and 2016 Helen Heffernan and Rosemary Woodhouse Antibiotic Reference Laboratory, Institute of Environmental Science and Research Limited (ESR); August 2017
Activity of a novel aminoglycoside, ACHN-490, against clinical isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae from New York City
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published July 31, 2010 J Antimicrob Chemother doi:10.1093/jac/dkq278 Activity of a novel aminoglycoside, ACHN-490, against clinical isolates of Escherichia
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published July 31, 2010 J Antimicrob Chemother doi:10.1093/jac/dkq278 Activity of a novel aminoglycoside, ACHN-490, against clinical isolates of Escherichia
Presenter: Ombeva Malande. Red Cross Children's Hospital Paed ID /University of Cape Town Friday 6 November 2015: Session:- Paediatric ID Update
 Emergence of invasive Carbapenem Resistant Enterobacteriaceae CRE infection at RCWMCH Ombeva Oliver Malande, Annerie du Plessis, Colleen Bamford, Brian Eley Presenter: Ombeva Malande Red Cross Children's
Emergence of invasive Carbapenem Resistant Enterobacteriaceae CRE infection at RCWMCH Ombeva Oliver Malande, Annerie du Plessis, Colleen Bamford, Brian Eley Presenter: Ombeva Malande Red Cross Children's
Fighting MDR Pathogens in the ICU
 Fighting MDR Pathogens in the ICU Dr. Murat Akova Hacettepe University School of Medicine, Department of Infectious Diseases, Ankara, Turkey 1 50.000 deaths each year in US and Europe due to antimicrobial
Fighting MDR Pathogens in the ICU Dr. Murat Akova Hacettepe University School of Medicine, Department of Infectious Diseases, Ankara, Turkey 1 50.000 deaths each year in US and Europe due to antimicrobial
DR. MICHAEL A. BORG DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION & CONTROL MATER DEI HOSPITAL - MALTA
 DR. MICHAEL A. BORG DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION & CONTROL MATER DEI HOSPITAL - MALTA The good old days The dread (of) infections that used to rage through the whole communities is muted Their retreat
DR. MICHAEL A. BORG DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION & CONTROL MATER DEI HOSPITAL - MALTA The good old days The dread (of) infections that used to rage through the whole communities is muted Their retreat
Screening and deciphering antibiotic resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: a state of the art
 For reprint orders, please contact reprints@expert-reviews.com Screening and deciphering antibiotic resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: a state of the art Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 11(6), 571 583
For reprint orders, please contact reprints@expert-reviews.com Screening and deciphering antibiotic resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: a state of the art Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 11(6), 571 583
Florida Health Care Association District 2 January 13, 2015 A.C. Burke, MA, CIC
 Florida Health Care Association District 2 January 13, 2015 A.C. Burke, MA, CIC 11/20/2014 1 To describe carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. To identify laboratory detection standards for carbapenem-resistant
Florida Health Care Association District 2 January 13, 2015 A.C. Burke, MA, CIC 11/20/2014 1 To describe carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. To identify laboratory detection standards for carbapenem-resistant
β-lactams resistance among Enterobacteriaceae in Morocco 1 st ICREID Addis Ababa March 2018
 β-lactams resistance among Enterobacteriaceae in Morocco 1 st ICREID Addis Ababa 12-14 March 2018 Antibiotic resistance center Institut Pasteur du Maroc Enterobacteriaceae (E. coli, Salmonella, ) S. aureus
β-lactams resistance among Enterobacteriaceae in Morocco 1 st ICREID Addis Ababa 12-14 March 2018 Antibiotic resistance center Institut Pasteur du Maroc Enterobacteriaceae (E. coli, Salmonella, ) S. aureus
DRUG-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII A GROWING SUPERBUG POPULATION. Cara Wilder Ph.D. Technical Writer March 13 th 2014
 DRUG-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII A GROWING SUPERBUG POPULATION Cara Wilder Ph.D. Technical Writer March 13 th 2014 ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit organization with headquarters in Manassas,
DRUG-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII A GROWING SUPERBUG POPULATION Cara Wilder Ph.D. Technical Writer March 13 th 2014 ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit organization with headquarters in Manassas,
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times
 Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
Nosocomial Infections: What Are the Unmet Needs
 Nosocomial Infections: What Are the Unmet Needs Jean Chastre, MD Service de Réanimation Médicale Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, AP-HP, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris 6, France www.reamedpitie.com
Nosocomial Infections: What Are the Unmet Needs Jean Chastre, MD Service de Réanimation Médicale Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, AP-HP, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris 6, France www.reamedpitie.com
Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem non-susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii in France.
 Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem non-susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii in France. Katy Jeannot, Laure Diancourt, Sophie Vaux, Michelle Thouverez, Amandina Ribeiro, Bruno Coignard, Patrice Courvalin,
Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem non-susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii in France. Katy Jeannot, Laure Diancourt, Sophie Vaux, Michelle Thouverez, Amandina Ribeiro, Bruno Coignard, Patrice Courvalin,
Witchcraft for Gram negatives
 Witchcraft for Gram negatives Dr Subramanian S MD DNB MNAMS AB (Medicine, Infect Dis) Infectious Diseases Consultant Global Health City, Chennai www.asksubra.com Drug resistance follows the drug like a
Witchcraft for Gram negatives Dr Subramanian S MD DNB MNAMS AB (Medicine, Infect Dis) Infectious Diseases Consultant Global Health City, Chennai www.asksubra.com Drug resistance follows the drug like a
Polymerase chain reaction#$
 1393/2/2: 1393/6/24: 1393 "#!/31 / Polymerase chain reaction#$ "! 3 2 1 %&' " $'.' *+, ) '( & %"#$$! : % %5& 3 67 %54 ) 3 %"#$12 ) ' (Acinetobacter baumannii) PCR * ) $= %5)( "# #? Acinetobacter baumannii
1393/2/2: 1393/6/24: 1393 "#!/31 / Polymerase chain reaction#$ "! 3 2 1 %&' " $'.' *+, ) '( & %"#$$! : % %5& 3 67 %54 ) 3 %"#$12 ) ' (Acinetobacter baumannii) PCR * ) $= %5)( "# #? Acinetobacter baumannii
Other Enterobacteriaceae
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER NUMBER 50: Other Enterobacteriaceae Author Kalisvar Marimuthu, MD Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH Topic Outline Topic outline - Key Issues Known
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER NUMBER 50: Other Enterobacteriaceae Author Kalisvar Marimuthu, MD Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH Topic Outline Topic outline - Key Issues Known
In vitro Comparison of Anti-Biofilm Effects against
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3947/ic.2015.47.1.27 Infect Chemother 2015;47(1):27-32 ISSN 2093-2340 (Print) ISSN 2092-6448 (Online) Infection & Chemotherapy In vitro Comparison of Anti-Biofilm
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3947/ic.2015.47.1.27 Infect Chemother 2015;47(1):27-32 ISSN 2093-2340 (Print) ISSN 2092-6448 (Online) Infection & Chemotherapy In vitro Comparison of Anti-Biofilm
Molecular identification of tigecycline- and colistinresistant carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter baumannii from a Greek hospital from 2011 to 2013
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2015), 64, 993 997 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.000127 Molecular identification of tigecycline- and colistinresistant carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter baumannii from a Greek
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2015), 64, 993 997 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.000127 Molecular identification of tigecycline- and colistinresistant carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter baumannii from a Greek
PrevalenceofAntimicrobialResistanceamongGramNegativeIsolatesinanAdultIntensiveCareUnitataTertiaryCareCenterinSaudiArabia
 : K Interdisciplinary Volume 17 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2017 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618 & Print ISSN:
: K Interdisciplinary Volume 17 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2017 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618 & Print ISSN:
Pedro Martínez and Salim Mattar* ABSTRACT
 Brazilian Journal of Microbiology (2012): 1274-1280 ISSN 1517-8382 IMIPENEM-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII CARRYING THE ISABA1-BLA OXA-23, 51 AND ISABA1- BLA ADC-7 GENES IN MONTERIA, COLOMBIA Pedro
Brazilian Journal of Microbiology (2012): 1274-1280 ISSN 1517-8382 IMIPENEM-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII CARRYING THE ISABA1-BLA OXA-23, 51 AND ISABA1- BLA ADC-7 GENES IN MONTERIA, COLOMBIA Pedro
The Genetic Characteristics of Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Coproducing 16S rrna Methylase arma and Carbapenemase OXA-23
 Journal of Bacteriology and Virology 2013. Vol. 43, No. 1 p.27 36 http://dx.doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2013.43.1.27 Original Article The Genetic Characteristics of Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Journal of Bacteriology and Virology 2013. Vol. 43, No. 1 p.27 36 http://dx.doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2013.43.1.27 Original Article The Genetic Characteristics of Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Epidemiological Characteristics and Drug Resistance Analysis of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a China Hospital at a Certain Time
 Polish Journal of Microbiology 2014, Vol. 63, No 3, 275 281 ORIGINAL PAPER Epidemiological Characteristics and Drug Resistance Analysis of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a China Hospital
Polish Journal of Microbiology 2014, Vol. 63, No 3, 275 281 ORIGINAL PAPER Epidemiological Characteristics and Drug Resistance Analysis of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a China Hospital
Heteroresistance to Meropenem in Carbapenem-Susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 2009, p. 4055 4059 Vol. 47, No. 12 0095-1137/09/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.00959-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Heteroresistance
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 2009, p. 4055 4059 Vol. 47, No. 12 0095-1137/09/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.00959-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Heteroresistance
WHO laboratory-based global survey on multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) in health care interim analysis
 WHO laboratory-based global survey on multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) in health care interim analysis Aim: to estimate the burden of MDROs isolated among inpatients in a wide range of health-care
WHO laboratory-based global survey on multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) in health care interim analysis Aim: to estimate the burden of MDROs isolated among inpatients in a wide range of health-care
Acinetobacter Outbreaks: Experience from a Neurosurgery Critical Care Unit. Jumoke Sule Consultant Microbiologist 19 May 2010
 Acinetobacter Outbreaks: Experience from a Neurosurgery Critical Care Unit Jumoke Sule Consultant Microbiologist 19 May 2010 Epidemiology of Acinetobacter spp At least 32 different species Recovered from
Acinetobacter Outbreaks: Experience from a Neurosurgery Critical Care Unit Jumoke Sule Consultant Microbiologist 19 May 2010 Epidemiology of Acinetobacter spp At least 32 different species Recovered from
Isolation, molecular identification and antimicrobial susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from Baghdad hospitals
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 5, May 2016 351 Isolation, molecular identification and antimicrobial susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 5, May 2016 351 Isolation, molecular identification and antimicrobial susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from
Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version
 Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED 2018 Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY NO. IC-122 Policy Group Infection Control
Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED 2018 Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY NO. IC-122 Policy Group Infection Control
R. Uma Karthika, 1 R. Srinivasa Rao, 1 Suchismita Sahoo, 1 P. Shashikala, 2 Reba Kanungo, 2 S. Jayachandran 1 and K. Prashanth 1 INTRODUCTION
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2009), 58, 430 435 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.002105-0 Phenotypic and genotypic assays for detecting the prevalence of metallo-b-lactamases in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2009), 58, 430 435 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.002105-0 Phenotypic and genotypic assays for detecting the prevalence of metallo-b-lactamases in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter
Epidemiological characterization and distribution of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in Italy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Epidemiological characterization and distribution of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in Italy M. L. Mezzatesta 1, M. M. D Andrea 2, R. Migliavacca
ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Epidemiological characterization and distribution of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in Italy M. L. Mezzatesta 1, M. M. D Andrea 2, R. Migliavacca
Presence of extended spectrum β-lactamase producing Escherichia coli in
 1 2 Presence of extended spectrum β-lactamase producing Escherichia coli in wild geese 3 4 5 A. Garmyn* 1, F. Haesebrouck 1, T. Hellebuyck 1, A. Smet 1, F. Pasmans 1, P. Butaye 2, A. Martel 1 6 7 8 9 10
1 2 Presence of extended spectrum β-lactamase producing Escherichia coli in wild geese 3 4 5 A. Garmyn* 1, F. Haesebrouck 1, T. Hellebuyck 1, A. Smet 1, F. Pasmans 1, P. Butaye 2, A. Martel 1 6 7 8 9 10
Is biocide resistance already a clinical problem?
 Is biocide resistance already a clinical problem? Stephan Harbarth, MD MS University of Geneva Hospitals and Faculty of Medicine, Geneva, Switzerland Important points Biocide resistance exists Antibiotic
Is biocide resistance already a clinical problem? Stephan Harbarth, MD MS University of Geneva Hospitals and Faculty of Medicine, Geneva, Switzerland Important points Biocide resistance exists Antibiotic
Summary of the latest data on antibiotic consumption in the European Union
 Summary of the latest data on antibiotic consumption in the European Union ESAC-Net surveillance data November 2016 Provision of reliable and comparable national antimicrobial consumption data is a prerequisite
Summary of the latest data on antibiotic consumption in the European Union ESAC-Net surveillance data November 2016 Provision of reliable and comparable national antimicrobial consumption data is a prerequisite
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THE RISE OF CARBAPENEM-RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
 ENTEROBACTERIACEAE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
ENTEROBACTERIACEAE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria. Antimicrobial Resistance. Molecular Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance. Topics to be Covered
 Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased number of hospitalizations Increased length
Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased number of hospitalizations Increased length
MID 23. Antimicrobial Resistance. Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria. Molecular Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance
 Antimicrobial Resistance Molecular Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance Micro evolutionary change - point mutations Beta-lactamase mutation extends spectrum of the enzyme rpob gene (RNA polymerase) mutation
Antimicrobial Resistance Molecular Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance Micro evolutionary change - point mutations Beta-lactamase mutation extends spectrum of the enzyme rpob gene (RNA polymerase) mutation
Multi-drug resistant microorganisms
 Multi-drug resistant microorganisms Arzu TOPELI Director of MICU Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine, Ankara-Turkey Council Member of WFSICCM Deaths in the US declined by 220 per 100,000 with the
Multi-drug resistant microorganisms Arzu TOPELI Director of MICU Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine, Ankara-Turkey Council Member of WFSICCM Deaths in the US declined by 220 per 100,000 with the
MDR Acinetobacter baumannii. Has the post antibiotic era arrived? Dr. Michael A. Borg Infection Control Dept Mater Dei Hospital Malta
 MDR Acinetobacter baumannii Has the post antibiotic era arrived? Dr. Michael A. Borg Infection Control Dept Mater Dei Hospital Malta 1 The Armageddon recipe Transmissible organism with prolonged environmental
MDR Acinetobacter baumannii Has the post antibiotic era arrived? Dr. Michael A. Borg Infection Control Dept Mater Dei Hospital Malta 1 The Armageddon recipe Transmissible organism with prolonged environmental
Antimicrobial Resistance
 Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased number of hospitalizations Increased length
Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased number of hospitalizations Increased length
Antimicrobial Resistance Acquisition of Foreign DNA
 Antimicrobial Resistance Acquisition of Foreign DNA Levy, Scientific American Horizontal gene transfer is common, even between Gram positive and negative bacteria Plasmid - transfer of single or multiple
Antimicrobial Resistance Acquisition of Foreign DNA Levy, Scientific American Horizontal gene transfer is common, even between Gram positive and negative bacteria Plasmid - transfer of single or multiple
Mono- versus Bitherapy for Management of HAP/VAP in the ICU
 Mono- versus Bitherapy for Management of HAP/VAP in the ICU Jean Chastre, www.reamedpitie.com Conflicts of interest: Consulting or Lecture fees: Nektar-Bayer, Pfizer, Brahms, Sanofi- Aventis, Janssen-Cilag,
Mono- versus Bitherapy for Management of HAP/VAP in the ICU Jean Chastre, www.reamedpitie.com Conflicts of interest: Consulting or Lecture fees: Nektar-Bayer, Pfizer, Brahms, Sanofi- Aventis, Janssen-Cilag,
Mechanism of antibiotic resistance
 Mechanism of antibiotic resistance Dr.Siriwoot Sookkhee Ph.D (Biopharmaceutics) Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University Antibiotic resistance Cross-resistance : resistance
Mechanism of antibiotic resistance Dr.Siriwoot Sookkhee Ph.D (Biopharmaceutics) Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University Antibiotic resistance Cross-resistance : resistance
ETX2514SUL (sulbactam/etx2514) for the treatment of Acinetobacter baumannii infections
 ETX2514SUL (sulbactam/etx2514) for the treatment of Acinetobacter baumannii infections Robin Isaacs Chief Medical Officer, Entasis Therapeutics Dr. Isaacs is a full-time employee of Entasis Therapeutics.
ETX2514SUL (sulbactam/etx2514) for the treatment of Acinetobacter baumannii infections Robin Isaacs Chief Medical Officer, Entasis Therapeutics Dr. Isaacs is a full-time employee of Entasis Therapeutics.
Antimicrobial resistance (EARS-Net)
 SURVEILLANCE REPORT Annual Epidemiological Report for 2014 Antimicrobial resistance (EARS-Net) Key facts Over the last four years (2011 to 2014), the percentages of Klebsiella pneumoniae resistant to fluoroquinolones,
SURVEILLANCE REPORT Annual Epidemiological Report for 2014 Antimicrobial resistance (EARS-Net) Key facts Over the last four years (2011 to 2014), the percentages of Klebsiella pneumoniae resistant to fluoroquinolones,
A snapshot of polymyxin use around the world South America
 A snapshot of polymyxin use around the world South America Alexandre P. Zavascki Infectious Diseases Service, Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre Medical School, Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul
A snapshot of polymyxin use around the world South America Alexandre P. Zavascki Infectious Diseases Service, Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre Medical School, Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul
PCR detection of Leptospira in. stray cat and
 PCR detection of Leptospira in 1 Department of Pathology, School of Veterinary Medicine, Islamic Azad University, Shahrekord Branch, Shahrekord, Iran 2 Department of Microbiology, School of Veterinary
PCR detection of Leptospira in 1 Department of Pathology, School of Veterinary Medicine, Islamic Azad University, Shahrekord Branch, Shahrekord, Iran 2 Department of Microbiology, School of Veterinary
Bulletin of Pharmaceutical Sciences Assiut University
 Bull. Pharm. Sci., Assiut University, Vol. 35, Part 2, 212, pp. 99-17. Bulletin of Pharmaceutical Sciences Assiut University NOSOCOMIAL ACINETOBACTER INFECTION IN ASSIUT UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Isamil Seddek
Bull. Pharm. Sci., Assiut University, Vol. 35, Part 2, 212, pp. 99-17. Bulletin of Pharmaceutical Sciences Assiut University NOSOCOMIAL ACINETOBACTER INFECTION IN ASSIUT UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Isamil Seddek
ETX2514: Responding to the global threat of nosocomial multidrug and extremely drug resistant Gram-negative pathogens
 ETX2514: Responding to the global threat of nosocomial multidrug and extremely drug resistant Gram-negative pathogens Ruben Tommasi, PhD Chief Scientific Officer ECCMID 2017 April 24, 2017 Vienna, Austria
ETX2514: Responding to the global threat of nosocomial multidrug and extremely drug resistant Gram-negative pathogens Ruben Tommasi, PhD Chief Scientific Officer ECCMID 2017 April 24, 2017 Vienna, Austria
A novel variant of the β-lactamase ADC-61 gene in multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
 A novel variant of the β-lactamase ADC-61 gene in multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Y. Zhou, S.-J. Teng, L. Yang, S.-B. Li and Y. Xu Clinical Laboratory Department, The Second People s Hospital
A novel variant of the β-lactamase ADC-61 gene in multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Y. Zhou, S.-J. Teng, L. Yang, S.-B. Li and Y. Xu Clinical Laboratory Department, The Second People s Hospital
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Expert rules in susceptibility testing EUCAST-ESGARS-EPASG Educational Workshop Linz, 16 19 September, 2014 Dr. Rafael Cantón Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal SERVICIO DE MICROBIOLOGÍA Y PARASITOLOGÍA
Expert rules in susceptibility testing EUCAST-ESGARS-EPASG Educational Workshop Linz, 16 19 September, 2014 Dr. Rafael Cantón Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal SERVICIO DE MICROBIOLOGÍA Y PARASITOLOGÍA
Seasonal and Temperature-Associated Increase in Community-Onset Acinetobacter baumannii Complex Colonization or Infection
 Brief Communication Clinical Microbiology Ann Lab Med 18;38:266-27 https://doi.org/.3343/alm.18.38.3.266 ISSN 2234-386 eissn 2234-3814 Seasonal and Temperature-Associated Increase in Community-Onset Acinetobacter
Brief Communication Clinical Microbiology Ann Lab Med 18;38:266-27 https://doi.org/.3343/alm.18.38.3.266 ISSN 2234-386 eissn 2234-3814 Seasonal and Temperature-Associated Increase in Community-Onset Acinetobacter
MICRONAUT MICRONAUT-S Detection of Resistance Mechanisms. Innovation with Integrity BMD MIC
 MICRONAUT Detection of Resistance Mechanisms Innovation with Integrity BMD MIC Automated and Customized Susceptibility Testing For detection of resistance mechanisms and specific resistances of clinical
MICRONAUT Detection of Resistance Mechanisms Innovation with Integrity BMD MIC Automated and Customized Susceptibility Testing For detection of resistance mechanisms and specific resistances of clinical
Dissecting the epidemiology of resistant Enterobacteriaceae and non-fermenters
 Dissecting the epidemiology of resistant Enterobacteriaceae and non-fermenters Jon Otter, PhD Centre for Clinical Infection and Diagnostics Research (CIDR), King's College London & Guy's and St. Thomas'
Dissecting the epidemiology of resistant Enterobacteriaceae and non-fermenters Jon Otter, PhD Centre for Clinical Infection and Diagnostics Research (CIDR), King's College London & Guy's and St. Thomas'
Original Article. Suthan Srisangkaew, M.D. Malai Vorachit, D.Sc.
 Original Article Vol. 21 No.1 The optimum agent for ESBL screening and confirmatory tests:- Srisangkaew S & Vorachit M. 1 The Optimum Agent for Screening and Confirmatory Tests for Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases
Original Article Vol. 21 No.1 The optimum agent for ESBL screening and confirmatory tests:- Srisangkaew S & Vorachit M. 1 The Optimum Agent for Screening and Confirmatory Tests for Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases
Genotypes of Cornel Dorset and Dorset Crosses Compared with Romneys for Melatonin Receptor 1a
 Genotypes of Cornell Dorset and Dorset Crosses Compared with Romneys for Melatonin Receptor 1a By Christian Posbergh Cornell Undergraduate Honor Student, Dept. Animal Science Abstract: Sheep are known
Genotypes of Cornell Dorset and Dorset Crosses Compared with Romneys for Melatonin Receptor 1a By Christian Posbergh Cornell Undergraduate Honor Student, Dept. Animal Science Abstract: Sheep are known
Mechanisms and Pathways of AMR in the environment
 FMM/RAS/298: Strengthening capacities, policies and national action plans on prudent and responsible use of antimicrobials in fisheries Final Workshop in cooperation with AVA Singapore and INFOFISH 12-14
FMM/RAS/298: Strengthening capacities, policies and national action plans on prudent and responsible use of antimicrobials in fisheries Final Workshop in cooperation with AVA Singapore and INFOFISH 12-14
Geoffrey Coombs 1, Graeme Nimmo 2, Julie Pearson 1, Samantha Cramer 1 and Keryn Christiansen 1
 Community Onset MRSA Infections in Australia: A Tale of Two Clones Geoffrey Coombs 1, Graeme Nimmo 2, Julie Pearson 1, Samantha Cramer 1 and Keryn Christiansen 1 Community Associated MRSA First isolated
Community Onset MRSA Infections in Australia: A Tale of Two Clones Geoffrey Coombs 1, Graeme Nimmo 2, Julie Pearson 1, Samantha Cramer 1 and Keryn Christiansen 1 Community Associated MRSA First isolated
Originally published as:
 Originally published as: Yvonne Pfeifer, Gottfried Wilharm, Esther Zander, Thomas A. Wichelhaus, Stefan Göttig, Klaus- Peter Hunfeld, Harald Seifert, Wolfgang Witte and Paul G. Higgins Molecular characterization
Originally published as: Yvonne Pfeifer, Gottfried Wilharm, Esther Zander, Thomas A. Wichelhaus, Stefan Göttig, Klaus- Peter Hunfeld, Harald Seifert, Wolfgang Witte and Paul G. Higgins Molecular characterization
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN OF ESBL PRODUCING GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI ABSTRACT
 Research Article Microbiology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN OF ESBL PRODUCING GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI * PRABHAKAR C MAILAPUR, DEEPA
Research Article Microbiology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN OF ESBL PRODUCING GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI * PRABHAKAR C MAILAPUR, DEEPA
Antimicrobial Resistance
 Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased
Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased
Correspondence should be addressed to Rezvan Moniri;
 Pathogens Volume 2015, Article ID 957259, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/957259 Research Article Susceptibility Pattern and Distribution of Oxacillinases and bla PER-1 Genes among Multidrug Resistant
Pathogens Volume 2015, Article ID 957259, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/957259 Research Article Susceptibility Pattern and Distribution of Oxacillinases and bla PER-1 Genes among Multidrug Resistant
PHENOTYPIC AND GENOTYPIC CHARACTERIZATION OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE PATTERNS IN ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII STRAINS ISOLATED IN A ROMANIAN HOSPITAL
 362 FARMACIA, 2010, Vol.58, 3 PHENOTYPIC AND GENOTYPIC CHARACTERIZATION OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE PATTERNS IN ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII STRAINS ISOLATED IN A ROMANIAN HOSPITAL MANUELA-ANDA RADU-POPESCU 1*,
362 FARMACIA, 2010, Vol.58, 3 PHENOTYPIC AND GENOTYPIC CHARACTERIZATION OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE PATTERNS IN ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII STRAINS ISOLATED IN A ROMANIAN HOSPITAL MANUELA-ANDA RADU-POPESCU 1*,
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2018) 7(8):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 08 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.708.378
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 08 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.708.378
Wide dissemination of GES-type carbapenemases in Acinetobacter baumannii in. Kuwait
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 22 October 2012 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01384-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Wide dissemination
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 22 October 2012 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01384-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Wide dissemination
Clinical and microbiological characterization of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infections
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2011), 60, 605 611 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.029439-0 Clinical and microbiological characterization of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infections Joon
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2011), 60, 605 611 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.029439-0 Clinical and microbiological characterization of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infections Joon
(DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
 (DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE John Ferguson (Hunter New England, NSW) on behalf of MRGN Task Force Acknowledgement
(DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE John Ferguson (Hunter New England, NSW) on behalf of MRGN Task Force Acknowledgement
Dr Vivien CHUANG Associate Consultant Infection Control Branch, Centre for Health Protection/ Infectious Disease Control and Training Center,
 Dr Vivien CHUANG Associate Consultant Infection Control Branch, Centre for Health Protection/ Infectious Disease Control and Training Center, Hospital Authority NDM-1, which stands for New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase-1
Dr Vivien CHUANG Associate Consultant Infection Control Branch, Centre for Health Protection/ Infectious Disease Control and Training Center, Hospital Authority NDM-1, which stands for New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase-1
Neisseria meningitidis ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE:CURRENT SITUATION IN LATIN AMERICA AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE
 Neisseria meningitidis ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE:CURRENT SITUATION IN LATIN AMERICA AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE Dra. Silvia E. González Ayala Head Professor Cátedra Infectología, Facultad Ciencias Médicas,
Neisseria meningitidis ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE:CURRENT SITUATION IN LATIN AMERICA AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE Dra. Silvia E. González Ayala Head Professor Cátedra Infectología, Facultad Ciencias Médicas,
INCIDENCE OF BACTERIAL COLONISATION IN HOSPITALISED PATIENTS WITH DRUG-RESISTANT TUBERCULOSIS
 INCIDENCE OF BACTERIAL COLONISATION IN HOSPITALISED PATIENTS WITH DRUG-RESISTANT TUBERCULOSIS 1 Research Associate, Drug Utilisation Research Unit, Nelson Mandela University 2 Human Sciences Research Council,
INCIDENCE OF BACTERIAL COLONISATION IN HOSPITALISED PATIENTS WITH DRUG-RESISTANT TUBERCULOSIS 1 Research Associate, Drug Utilisation Research Unit, Nelson Mandela University 2 Human Sciences Research Council,
Detection of Inducible AmpC β-lactamase-producing Gram-Negative Bacteria in a Teaching Tertiary Care Hospital in North India
 Original Article Vol. 25 No. 3 Ampc β-lactamase Production in Gram-Negative Bacilli:-Chaudhary U, et al. 129 Detection of Inducible AmpC β-lactamase-producing Gram-Negative Bacteria in a Teaching Tertiary
Original Article Vol. 25 No. 3 Ampc β-lactamase Production in Gram-Negative Bacilli:-Chaudhary U, et al. 129 Detection of Inducible AmpC β-lactamase-producing Gram-Negative Bacteria in a Teaching Tertiary
AbaR7, a Genomic Resistance Island Found in Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates in Daejeon, Korea
 Original Article Clinical Microbiology Ann Lab Med 2012;32:324-330 ISSN 2234-3806 eissn 2234-3814 AbaR7, a Genomic Resistance Island Found in Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates in Daejeon,
Original Article Clinical Microbiology Ann Lab Med 2012;32:324-330 ISSN 2234-3806 eissn 2234-3814 AbaR7, a Genomic Resistance Island Found in Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates in Daejeon,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Isolated From Various Clinical
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Isolated From Various Clinical
Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance among Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Hospitalized Patients at Chiang Mai University Hospital,
 Original Article Vol. 28 No. 1 Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance:- Chaiwarith R, et al. 3 Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance among Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Hospitalized Patients at
Original Article Vol. 28 No. 1 Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance:- Chaiwarith R, et al. 3 Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance among Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Hospitalized Patients at
