Epidemiology of MRSA in Australia
|
|
|
- Anabel Hunt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
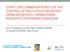
1 Epidemiology of MRSA in Australia Graeme R Nimmo Director, Division of Microbiology Pathology Queensland Central Laboratory, Herston QLD 429 Tel: (7) Fax: (7) Graeme_Nimmo@health. qld.gov.au Geoffrey W Coombs Chief Scientist, Dept Microbiology and Infectious Diseases PathWest Laboratory Medicine WA Royal Perth Hospital, Perth WA 6 Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has presented challenges to laboratories and clinicians since it first appeared in Australia in the mid-196s. However, in spite of its long presence and familiarity, a clear understanding of its epidemiology has only been possible with the recent advent of sequence-based typing methods (see the article by O Brien and Giffard, page 131). Archaic MRSA Staphylococcus aureus resistant to methicillin were reported soon after its introduction in 196. The initial reports were from the United Kingdom 1 and it was not until 1968 that MRSA was reported in Australia by Rountree and Beard 2. These archaic MRSA were limited to relatively few institutions, were not associated with widespread epidemics and appear to have been less virulent than later healthcare-associated MRSA 3. They were generally streptomycin-, tetracycline- and erythromycin-resistant but were susceptible to gentamicin. Using multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) and SCCmec typing, archaic MRSA have been characterised as ST-MRSA-I 4. Epidemic multi-resistant MRSA in our hospitals Gentamicin-resistant MRSA were first reported in Melbourne in 1976 by Perceval et al. and in Sydney soon thereafter 3. Subsequently, major epidemics of multi-resistant (including gentamicin-resistant) MRSA beginning in the late 197s were reported in Melbourne and Sydney hospitals 6, 7. It was associated with considerable morbidity and mortality and spread easily between institutions. Once established in an institution, MRSA were difficult to control and consequently usually became endemic. Similar epidemics occurred in the other Australian capital cities in the 198s. Vickery et al. found that these new MRSA formed a distinct group by phage typing compared to earlier strains 8. Similarly, Warren Grubb s group was able to demonstrate that this new eastern Australian MRSA (EA-MRSA) was genetically different from MRSA previously isolated in Australia and Europe 9. Early surveys by the Australian Group for Antimicrobial Resistance (AGAR) showed EA-MRSA was endemic in New South Wales/ACT, Victoria, Queensland and South Australia by the mid-198s but not in Western Australia (WA) 1, 11. The control of EA-MRSA in WA is a remarkable feat given the history of MRSA in the remainder of the country. In 198, Pearman et al. reported control of an outbreak of EA-MRSA at Royal Perth Hospital 12. They were able to contain the spread of the outbreak by an exhaustive programme of screening of patients and staff and by transfer of patients to a dedicated isolation facility (after isolation in the ward in which MRSA was detected had failed to control the outbreak). Establishment of stringent infection control procedures based on extensive screening of patients and staff and on notification of MRSA has allowed WA to maintain consistently low rates of healthcare-associated MRSA infection (see also the article by Coombs, van Gessel and Christiansen, page 14). MLST/SCCmec typing of EA-MRSA and its progeny AUS-2 and AUS- 3 have characterised these strains as ST239-MRSA-III. It appears that this clone was first reported in Australia 13 and subsequently spread to the United Kingdom and beyond. It is now found on all inhabited continents and goes by a variety of names including EMRSA-1, the Hungarian strain and the Brazilian strain 14. As EA-MRSA is unique among MRSA strains in Australia in being uniformly resistant to multiple classes of antimicrobials, it is possible to follow trends using multi-resistant MRSA as a surrogate as shown in Figure 1. It can be seen that Brisbane has had a generally downward trend in prevalence since 1989, while Melbourne, Adelaide and Darwin have seen reduced prevalence in recent years. Community MRSA appears Community-acquired MRSA (CA-MRSA) was first reported in WA 126 MICROBIOLOGY AUSTRALIA SEPTEMBER 8
2 in the early 199s from indigenous people living in different communities in the Kimberley region, 16. Colloquially known as WA-MRSA, CA-MRSA in WA was subsequently identified throughout the State and now accounts for up to 1% of the State s community S. aureus infections. CA-MRSA notification rates per 1, population continue to increase dramatically throughout WA, particularly in the remote country health regions. In 1983, the overall rate of MRSA notifications was 1/1, in the country health regions and 7/1, in the metropolitan health regions. By 6, the State s MRSA notification rate increased to 179/1,, of which 144/1, were CA-MRSA. In the metropolitan heath regions the CA-MRSA notification rate was 134/1,, while in the Kimberley health region the CA- MRSA notification rate had increased 4-fold to 391/1, 17. Molecular analysis of the early strains of CA-MRSA in WA showed these strains were different from MRSA isolated from hospitals in eastern Australia. Most of the CA-MRSA isolates had a similar pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) pattern and have subsequently been characterised as ST8-MRSA-IV 18. In the mid 199s a number of laboratories in eastern States noticed the appearance of non-multi-resistant MRSA causing furunculosis in outpatients with an apparent association with Polynesian ethnicity 19. Further studies showed that this epidemic was due to a southwest Pacific (SWP) MRSA strain (ST3-MRSA- IV) identical to that characterised by the Western Samoan phage pattern (WSPP) in New Zealand. This strain carries the genes for Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL), an exotoxin that has been associated with furunculosis and necrotising staphylococcal pneumonia. PVL has also been found in numerous other CA- MRSA strains around the world 21. Infection due to the SWP strain in Caucasians were unusual, but in a cluster of cases of CA-MRSA in Caucasians occurred in Ipswich, Queensland. An observational study revealed that these cases were due to a new strain, initially identified as the R pulsotype by PFGE and subsequently known as the Queensland Clone (QLD) (ST93-MRSA-IV) 21, 22. Like the SWP strain, it carried the genes for PVL and has been associated not only with furunculosis but also fatal necrotising pneumonia 23, 24. It has since spread throughout Australia to become one of the dominant epidemic strains of CA-MRSA. Unwelcome arrivals EMRSA- (ST22-MRSA-IV) is an epidemic strain described in the UK and Germany that appears to be very well adapted to the healthcare environment. In Australia it was first reported in WA where it was thought to have been introduced by healthcare workers from the UK. It is characterised phenotypically by non-ß-lactam resistance to ciprofloxacin or to ciprofloxacin and % MRSA Brisbane Sydney Melbourne mmrsa nmmrsa Figure 1. Prevalence of multi-resistant MRSA and non-multi-resistant MRSA in selected Australian cities based on AGAR surveys, MICROBIOLOGY AUSTRALIA SEPTEMBER Adelaide Perth Darwin
3 erythromycin and by the lack of urease production. It is now found throughout Australia and is a major healthcare-associated strain in New South Wales 26, 27. In the United States USA3 MRSA (ST8-MRSA-IV), has not only become the predominant cause of community-acquired infection but has also rapidly emerged as a major cause of healthcare-acquired infection. Sporadic reports of this strain have been reported in Australia, Canada, Denmark, Germany, Japan, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. In addition to carrying the PVL genes, USA3 has also acquired an arginine catabolic mobile element (ACME) which does not normally occur in S. aureus but has been detected in Staphylococcus epidermidis 28. It has been hypothesised that the presence of ACME may contribute to the coagulase-negative staphylococci-like traits found in USA3 such as its ability to metabolically alter the local ph on the skin of the host. This change in ph may increase the ability of USA3 to persist on intact skin and consequently facilitate spread by skin contact. Furthermore, USA3 carries a unique PVL sequence variant resulting in an amino acid substitution on the interactive surface of the LukF-PV component and, as a consequence, may enhance PVL function 29. In WA, the number of USA3 MRSA isolated per year since 3 has increased several-fold. Overall, 89 USA3 strains from 78 patients have been characterised, with 92% of these isolates causing skin and soft tissue infections predominantly with abscess formation. Over 6% of patients were younger than 4 years. A total of 76 (8%) isolates were erythromycin-resistant, 3 (39%) ciprofloxacin-resistant, nine (1%) tetracycline-resistant and five (6%) mupirocin-resistant. Of the erythromycin-resistant strains, 88% were clindamycin susceptible (inducible resistance not detected). To prevent USA3 MRSA from becoming established in both the WA community and its hospitals, the WA Health Department has recently commenced a search and destroy policy for all PVL-positive MRSA strains isolated in WA. In addition, in some acute care hospitals, screening has been extended to all high risk and surgical unit admissions. New York Japan (NY-Japan) (ST-MRSA-II) MRSA is a major EMRSA clone that has been reported in several USA States, Canada, Brazil, Mexico, China and Korea. Although infrequently reported in Europe, this clone has been described in Hungary. An outbreak of NY-Japan was recently reported in the south west of WA which involved the area s regional hospital, several community hospitals and long-term care facilities, as well as two teaching hospitals located in the Perth metropolitan area 3. This strain is typically resistant to ciprofloxacin and erythromycin and is urease positive. Sporadic isolates throughout Australia have been reported in recent AGAR surveys. Several other imported MRSA clones have also been isolated in Australia including the healthcare-associated strains EMRSA- 16 (ST36-MRSA-II), EMRSA-17 (ST247-MRSA-I), Irish-1 EMRSA (ST8-MRSA-II) and Irish-2 EMRSA (ST8-MRSA-VI); and several PVL-positive CA-MRSA strains including Taiwan CA-MRSA (ST9- MRSA-V T ), European CA-MRSA (ST8-MRSA-IV) and USA4 (ST1-MRSA-IV). Current trends The MRSA epidemic in Australia can be viewed as a series of concurrent epidemics due to a variety of clones associated with distinct clinical and epidemiological characteristics. There is evidence that the major healthcare-associated epidemic clones, EA-MRSA and EMRSA-, are waning at least in some regions. A recent study in Queensland showed a reduction in EA-MRSA phenotype from 19% of inpatient pus, tissue and fluid S. aureus isolates to 9% between and 6, with a similar decrease for blood culture isolates 31. AGAR data from the hospital survey showed that an increasing proportion of healthcare-associated MRSA infections was due to clones previously associated with community infection particularly in WA, South Australia and Queensland (Figure 2 AGAR, unpublished data) 32. However, MRSA remains the major cause of healthcare-associated infection in Australia and continued efforts in screening and isolation and heightened hand hygiene are warranted. The situation in the community is also changing with the overall prevalence of MRSA increasing while the proportion of clones continues to change. The Queensland clone is now dominant in community MRSA infections in Australia (Figure 3 AGAR, unpublished data). This is of concern as the Queensland clone is PVL positive and has been associated with severe and fatal infections in healthy young adults. These rapid changes in the community have put MRSA on the public health agenda, with WA once again leading the way with a major public health intervention. References 1. Jevons, M.P. (1961) Celbenin-resistant staphylococci. Brit. Med. J. 1, Rountree, P.M. and Beard, M.A. (1968) Hospital strains of Staphylococcus aureus with particular reference to methicillin-resistant strains. Med. J. Aust. 2, Rountree, P.M. (1978) History of staphylococcal infection in Australia. Med. J. Aust. 2, Robinson, D.A. and Enright, M.C. (3) Evolutionary models of the emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47, Perceval, A. et al. (1976) Emergence of gentamicin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Med. J. Aust. 2, King, K. et al. (1981) Gentamicin-resistant staphylococci. Lancet 2, Pavillard, R. et al. (1982) Epidemic of hospital-acquired infection due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in major Victorian hospitals. Med. J. Aust. 1, Vickery, A.M. (1993) Strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated in Australian hospitals from 1986 to 199. Australian Group for Antimicrobial Resistance. J. Hosp. Infect. 24, Townsend, D.E. et al. (198) Evolution of Australian isolates of methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus: a problem of plasmid incompatibility? J. Med. Microbiol., Nimmo, G.R. et al. (3) Antimicrobial resistance in Staphylococcus aureus in Australian teaching hospitals Microb. Drug Resist. 9, MICROBIOLOGY AUSTRALIA SEPTEMBER 8
4 cmrsa National:.7% of MRSA ST93-MRSA-IV* ST1-MRSA-IV ST3-MRSA-IV* ST-MRSA-IV ST78-MRSA-IV ST4-MRSA-IV OTHER *PVL positive clones Queensland: 36 isolates % South Australia: 31 isolates New South Wales: 39 isolates 62% 37% 12% Western Australia: 1 isolates ACT: 2 isolates 6% 12% AGAR Tasmania: 1 isolate 3% Victoria: 23 isolates Figure 2. Proportion of CA-MRSA clones among MRSA isolated in the AGAR survey of hospital-acquired S. aureus infection. cmrsa National: 6.1% of MRSA ST93-MRSA-IV* ST1-MRSA-IV ST3-MRSA-IV* ST-MRSA-IV ST78-MRSA-IV ST4-MRSA-IV Northern Territory: 16 isolates 84% Queensland: 46 isolates 7% ST7-MRSA-IV OTHER *PVL positive clones 89% South Australia: 27 isolates 7% New South Wales: 8 isolates 44% Western Australia: 39 isolates ACT: 3 isolates 6% 46% AGAR Tasmania: 3 isolates 23% Victoria: 4 isolates Figure 3. Proportion of CA-MRSA clones among MRSA isolated in the 6 AGAR survey of outpatient S. aureus infection. MICROBIOLOGY AUSTRALIA SEPTEMBER 8 129
5 11. Turnidge, J. et al. (1989) A national survey of antimicrobial resistance in Staphylococcus aureus in Australian teaching hospitals. Med. J. Aust., Pearman, J.W. et al. (198) Control of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in an Australian metropolitan teaching hospital complex. Med. J. Aust. 142, Townsend, D.E. et al. (1987) The international spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Hosp. Infect. 9, Enright, M.C. et al. (2) The evolutionary history of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, Riley, T.V. et al. (199) Changing epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Western Australia. Med. J. Aust. 163: Udo, E.E. et al. (1993) Genetic analysis of community isolates of methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus in Western Australia. J. Hosp. Infect., Nimmo, G.R. and Coombs, G.W. (8) Community-associated methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Australia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 31, Coombs, G.W. et al. (6) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones, Western Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis.12, Collignon, P. et al. (1998) Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Australia. Lancet 32, Riley, D. et al. (1998) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the suburbs. NZ. J. Med, 111, Vandenesch, F. et al. (3) Community-acquired methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying Panton-Valentine Leukocidin genes: worldwide emergence. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 9, Munckhof, W.J. et al. (3) Emergence of community-acquired methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection in Queensland, Australia. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 7, Peleg, A.Y. et al. () Life-threatening community-acquired methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in Australia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 24, Risson, D.C. et al. (7) A rapidly fatal case of necrotising pneumonia due to community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Med. J. Aust. 186, Pearman, J.W. et al. (1) A British epidemic strain of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (UK EMRSA-) has become established in Australia. Med. J. Aust. 174, Coombs, G.W. et al. (4) Community methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Australia: genetic diversity in strains causing outpatient infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42, Nimmo, G.R. et al. (6) MRSA in the Australian community: an evolving epidemic. Med. J. Aust. 184, Diep, B.A. et al. (8) The arginine catabolic mobile element and Staphylococcal chromosomal cassette mec linkage: convergence of virulence and resistance in the USA3 Clone of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Dis. Apr 21. [Epub ahead of print]. 29. O Hara, F.P. et al. (8) A geographic variant of the Staphylococcus aureus Panton-Valentine leukocidin toxin and the origin of community-associated methicillin-resistant S. aureus USA3. J. Infect. Dis. 197, Coombs, G.W. et al. (7) Controlling a multicenter outbreak involving the New York/Japan methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clone. Infect. Cont. Hosp. Epidemiol. 28, Nimmo, G.R. et al. (8) Changing prevalence of methicillin-resistant S. aureus phenotypes in inpatient infections in Queensland Health areas, - 6, as measured by passive susceptibility surveillance. Antimicrobials 8; February 8; Sydney, abstract O Coombs, G. et al. (7) Staphylococcus aureus Programme (SAP ): Hospital Survey: MRSA Epidemiology and Typing Report. Canberra: Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance. Graeme Nimmo is Director of Microbiology for Pathology Queensland and Associate Professor of Molecular Pathology at the University of Queensland. He is currently President of the Australian Society for Antimicrobials, Chair of the Australian Group for Antimicrobial Resistance, and a member of the National Pathology Accreditation Advisory Council and of the Public Health Laboratory Network. His major research interest is the epidemiology of MRSA and he is Chair of the Organising Committee for the 13th International Symposium on Staphylococci and Staphylococcal Infection. Geoffrey Coombs (Please see details on page 114). Food Microbiology Seminar Series: Tales from the Green Book The AIFST, in conjunction with the ASM Food Microbiology SIG, is proud to present a world class, bi-monthly, food microbiology seminar series presented solely by authors of AIFST s award winning Foodborne Microorganisms of Public Health Significance (Green Book). Dates still current are listed below. Wed 1 September 8 Peter Sutherland (NSW-FA) on Ch.13 Listeria Wed 12 November 8 Gary Grohman (Enviro Path) on Ch.22 Viruses Venue Food Science Australia, cnr Creek & Wynnum Roads, Cannon Hill, Brisbane, QLD Who should attend Microbiologists from food industry and consulting laboratories Current / future NATA food microbiology signatories Food industry technical / QA / research staff Food microbiology students wishing to gain further skills and meet future employers Contacts Sofroni Eglezos, Series Co-ordinator & ASM Food Micro SIG Tel: (7) sofroni@eml.com.au David Pickup, AIFST QLD Branch Chair Tel: (7) dp@gchahn.com.au Registrations Fax or Vicki Wallace, AIFST National Tel: (2) Fax: (2) aifst@aifst.asn.au 13 MICROBIOLOGY AUSTRALIA SEPTEMBER 8
Geoffrey Coombs 1, Graeme Nimmo 2, Julie Pearson 1, Samantha Cramer 1 and Keryn Christiansen 1
 Community Onset MRSA Infections in Australia: A Tale of Two Clones Geoffrey Coombs 1, Graeme Nimmo 2, Julie Pearson 1, Samantha Cramer 1 and Keryn Christiansen 1 Community Associated MRSA First isolated
Community Onset MRSA Infections in Australia: A Tale of Two Clones Geoffrey Coombs 1, Graeme Nimmo 2, Julie Pearson 1, Samantha Cramer 1 and Keryn Christiansen 1 Community Associated MRSA First isolated
Staphylococcus aureus Programme 2007 (SAP 2007) Hospital Survey MRSA Epidemiology and Typing Report
 AGAR The Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance http://antimicrobial-resistance.com Staphylococcus aureus Programme 2007 (SAP 2007) Hospital Survey MRSA Epidemiology and Typing Report PREPARED BY:
AGAR The Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance http://antimicrobial-resistance.com Staphylococcus aureus Programme 2007 (SAP 2007) Hospital Survey MRSA Epidemiology and Typing Report PREPARED BY:
Staphylococcus aureus Programme 2008 (SAP 2008) Community Survey Antimicrobial Susceptibility Report
 AGAR The Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance http://antimicrobial-resistance.com Staphylococcus aureus Programme 2008 (SAP 2008) Community Survey Antimicrobial Susceptibility Report PREPARED BY:
AGAR The Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance http://antimicrobial-resistance.com Staphylococcus aureus Programme 2008 (SAP 2008) Community Survey Antimicrobial Susceptibility Report PREPARED BY:
Staphylococcus aureus Programme 2012 (SAP 2012) Community Survey MRSA Epidemiology and Typing Report
 Staphylococcus aureus Programme 2012 (SAP 2012) Community Survey MRSA Epidemiology and Typing Report PREPARED BY: Dr Geoffrey Coombs Department of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, PathWest Laboratory
Staphylococcus aureus Programme 2012 (SAP 2012) Community Survey MRSA Epidemiology and Typing Report PREPARED BY: Dr Geoffrey Coombs Department of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, PathWest Laboratory
Surveillance Programme annual report, Abstract
 Community-onset Staphylococcus aureus Surveillance Programme, 2012 Community-onset Staphylococcus aureus Surveillance Programme annual report, 2012 Geoffrey W Coombs, Denise A Daley, Julie C Pearson, Graeme
Community-onset Staphylococcus aureus Surveillance Programme, 2012 Community-onset Staphylococcus aureus Surveillance Programme annual report, 2012 Geoffrey W Coombs, Denise A Daley, Julie C Pearson, Graeme
Community-onset Staphylococcus aureus infections presenting to general practices in South-eastern Australia
 Epidemiol. Infect. (2014), 142, 501 511. Cambridge University Press 2013 doi:10.1017/s0950268813001581 Community-onset Staphylococcus aureus infections presenting to general practices in South-eastern
Epidemiol. Infect. (2014), 142, 501 511. Cambridge University Press 2013 doi:10.1017/s0950268813001581 Community-onset Staphylococcus aureus infections presenting to general practices in South-eastern
Annual survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), 2008
 Annual survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), 2008 Each year ESR conducts a one-month survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) to provide ongoing information
Annual survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), 2008 Each year ESR conducts a one-month survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) to provide ongoing information
aureus isolated from hospital inpatients, 2009:
 Antibiotic susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus, 2009 Antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from hospital inpatients, 2009: Report from the Australian Group on Antimicrobial
Antibiotic susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus, 2009 Antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from hospital inpatients, 2009: Report from the Australian Group on Antimicrobial
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the Australian community: an evolving epidemic
 Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the Australian community: an evolving epidemic Graeme R Nimmo, Geoffrey W Coombs, Julie C Pearson, Francis G O'Brien, Keryn J Christiansen, John D Turnidge,
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the Australian community: an evolving epidemic Graeme R Nimmo, Geoffrey W Coombs, Julie C Pearson, Francis G O'Brien, Keryn J Christiansen, John D Turnidge,
Staphylococcus aureus Programme 2006 (SAP 2006) Community Survey Antimicrobial Susceptibility Report
 AGAR The tralian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance ://antimicrobial-resistance.com Staphylococcus aureus Programme 2006 (P 2006) Community Survey Antimicrobial Susceptibility Report PREPARED BY: Associate
AGAR The tralian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance ://antimicrobial-resistance.com Staphylococcus aureus Programme 2006 (P 2006) Community Survey Antimicrobial Susceptibility Report PREPARED BY: Associate
National MRSA Reference Laboratory
 Author: Gráinne Brennan Date: 23/02/2017 Date of Issue: 23/02/2017 National MRSA Reference Laboratory User s Manual NMRSARL Users Manual Page 1 of 12 Table of Contents Page 1. Location... 3 2. Contact
Author: Gráinne Brennan Date: 23/02/2017 Date of Issue: 23/02/2017 National MRSA Reference Laboratory User s Manual NMRSARL Users Manual Page 1 of 12 Table of Contents Page 1. Location... 3 2. Contact
Annual reports AGAR Hospital-onset Staphylococcus aureus Surveillance Programme, 2011
 Annual reports AGAR -onset Staphylococcus aureus Surveillance Programme, 2011 AGAR -onset Staphylococcus aureus Surveillance Programme, 2011 Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance -onset Staphylococcus
Annual reports AGAR -onset Staphylococcus aureus Surveillance Programme, 2011 AGAR -onset Staphylococcus aureus Surveillance Programme, 2011 Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance -onset Staphylococcus
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION The Staphylococci are a group of Gram-positive bacteria, 14 species are known to cause human infections but the vast majority of infections are caused by only three of them. They
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION The Staphylococci are a group of Gram-positive bacteria, 14 species are known to cause human infections but the vast majority of infections are caused by only three of them. They
Staphylococcus aureus
 Staphylococcus aureus Significant human pathogen. SSTI Biomaterial related infections Osteomyelitis Endocarditis Toxin mediated diseases TSST Staphylococcal enterotoxins Quintessential Pathogen? Nizet
Staphylococcus aureus Significant human pathogen. SSTI Biomaterial related infections Osteomyelitis Endocarditis Toxin mediated diseases TSST Staphylococcal enterotoxins Quintessential Pathogen? Nizet
Staphylococcus aureus Down Under : contemporary epidemiology of S. aureus in Australia, New Zealand, and the South West Pacific
 REVIEW 10.1111/1469-0691.12702 Staphylococcus aureus Down Under : contemporary epidemiology of S. aureus in Australia, New Zealand, and the South West Pacific D. A. Williamson 1,2, G. W. Coombs 3,4 and
REVIEW 10.1111/1469-0691.12702 Staphylococcus aureus Down Under : contemporary epidemiology of S. aureus in Australia, New Zealand, and the South West Pacific D. A. Williamson 1,2, G. W. Coombs 3,4 and
Significant human pathogen. SSTI Biomaterial related infections Osteomyelitis Endocarditis Toxin mediated diseases TSST Staphylococcal enterotoxins
 Staphylococcus aureus Significant human pathogen. SSTI Biomaterial related infections Osteomyelitis Endocarditis Toxin mediated diseases TSST Staphylococcal enterotoxins Quintessential Pathogen? Nizet
Staphylococcus aureus Significant human pathogen. SSTI Biomaterial related infections Osteomyelitis Endocarditis Toxin mediated diseases TSST Staphylococcal enterotoxins Quintessential Pathogen? Nizet
Annual survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), 2015
 Annual survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), 2015 Helen Heffernan and Sarah Bakker Nosocomial Infections Laboratory, Institute of Environmental Science and Research Limited (ESR);
Annual survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), 2015 Helen Heffernan and Sarah Bakker Nosocomial Infections Laboratory, Institute of Environmental Science and Research Limited (ESR);
Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus in Ghana
 Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus in Ghana Beverly Egyir, PhD Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research Bacteriology Department, University of Ghana Background
Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus in Ghana Beverly Egyir, PhD Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research Bacteriology Department, University of Ghana Background
Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia, Australia
 RESEARCH Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia, Australia Peter Collignon,* Graeme R. Nimmo, Thomas Gottlieb, and Iain B. Gosbell, on behalf of the Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance 1 Staphylococcus
RESEARCH Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia, Australia Peter Collignon,* Graeme R. Nimmo, Thomas Gottlieb, and Iain B. Gosbell, on behalf of the Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance 1 Staphylococcus
SCOTTISH MRSA REFERENCE LABORATORY
 Title SCOTTISH MRSA REFERENCE LABORATORY LABORATORY PROCEDURE NUMBER / VERSION User Manual DATE OF ISSUE 17/05/2014 REVIEW INTERVAL AUTHORISED BY AUTHOR 2 Years Dr. B. Jones B. Cosgrove COPY 1 of 1 Master
Title SCOTTISH MRSA REFERENCE LABORATORY LABORATORY PROCEDURE NUMBER / VERSION User Manual DATE OF ISSUE 17/05/2014 REVIEW INTERVAL AUTHORISED BY AUTHOR 2 Years Dr. B. Jones B. Cosgrove COPY 1 of 1 Master
Annual survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), 2014
 Annual survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), 2014 Helen Heffernan, Sarah Bakker, Kristin Dyet, Deborah Williamson Nosocomial Infections Laboratory, Institute of Environmental Science
Annual survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), 2014 Helen Heffernan, Sarah Bakker, Kristin Dyet, Deborah Williamson Nosocomial Infections Laboratory, Institute of Environmental Science
SCOTTISH MRSA REFERENCE LABORATORY
 Title SCOTTISH MRSA REFERENCE LABORATORY LABORATORY PROCEDURE NUMBER / VERSION User Manual DATE OF ISSUE 20/01/2017 REVIEW INTERVAL AUTHORISED BY AUTHOR 1 Year Dr. B. Jones Dr E. Dickson COPY 1 of 1 Master
Title SCOTTISH MRSA REFERENCE LABORATORY LABORATORY PROCEDURE NUMBER / VERSION User Manual DATE OF ISSUE 20/01/2017 REVIEW INTERVAL AUTHORISED BY AUTHOR 1 Year Dr. B. Jones Dr E. Dickson COPY 1 of 1 Master
MRSA Control : Belgian policy
 MRSA Control : Belgian policy PEN ERY CLI DOT GEN KAN SXT CIP MIN RIF FUC MUP OXA Marc Struelens Service de microbiologie & unité d épidémiologie des maladies infectieuses Université Libre de Bruxelles
MRSA Control : Belgian policy PEN ERY CLI DOT GEN KAN SXT CIP MIN RIF FUC MUP OXA Marc Struelens Service de microbiologie & unité d épidémiologie des maladies infectieuses Université Libre de Bruxelles
Abstract. Australian Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis Outcome Programme, 2013 Australian Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis. Introduction
 Australian Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis Outcome Programme, 2013 Australian Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis Outcome Programme annual report, 2013 Geoffrey W Coombs, Graeme R Nimmo, Denise A Daley, Tam T Le,
Australian Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis Outcome Programme, 2013 Australian Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis Outcome Programme annual report, 2013 Geoffrey W Coombs, Graeme R Nimmo, Denise A Daley, Tam T Le,
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus By Karla Givens Means of Transmission and Usual Reservoirs Staphylococcus aureus is part of normal flora and can be found on the skin and in the noses of one
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus By Karla Givens Means of Transmission and Usual Reservoirs Staphylococcus aureus is part of normal flora and can be found on the skin and in the noses of one
Ca-MRSA Update- Hand Infections. Washington Hand Society September 19, 2007
 Ca-MRSA Update- Hand Infections Washington Hand Society September 19, 2007 Resistant Staph. Aureus Late 1940 s -50% S.Aureus resistant to PCN 1957-80/81 strain- of S.A. highly virulent and easily transmissible
Ca-MRSA Update- Hand Infections Washington Hand Society September 19, 2007 Resistant Staph. Aureus Late 1940 s -50% S.Aureus resistant to PCN 1957-80/81 strain- of S.A. highly virulent and easily transmissible
Epidemiology of community MRSA obtained from the UK West Midlands region.
 Epidemiology of community MRSA obtained from the UK West Midlands region. J. Rollason a, L. Bastin b, A. C. Hilton a, D. G. Pillay c, T. Worthington a, C. Mckeon c, P. De c, K. Burrows c and P. A. Lambert
Epidemiology of community MRSA obtained from the UK West Midlands region. J. Rollason a, L. Bastin b, A. C. Hilton a, D. G. Pillay c, T. Worthington a, C. Mckeon c, P. De c, K. Burrows c and P. A. Lambert
MRSA in the United Kingdom status quo and future developments
 MRSA in the United Kingdom status quo and future developments Dietrich Mack Chair of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases The School of Medicine - University of Wales Swansea P R I F Y S G O L
MRSA in the United Kingdom status quo and future developments Dietrich Mack Chair of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases The School of Medicine - University of Wales Swansea P R I F Y S G O L
Helen Heffernan and Sarah Bakker Nosocomial Infections Laboratory, Institute of Environmental Science and Research Limited (ESR); October 2018
 2017 survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Helen Heffernan and Sarah Bakker Nosocomial Infections Laboratory, Institute of Environmental Science and Research Limited (ESR); October
2017 survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Helen Heffernan and Sarah Bakker Nosocomial Infections Laboratory, Institute of Environmental Science and Research Limited (ESR); October
Prevalence & Risk Factors For MRSA. For Vets
 For Vets General Information Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive, aerobic commensal bacterium of humans that is carried in the anterior nares of approximately 30% of the general population. It is
For Vets General Information Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive, aerobic commensal bacterium of humans that is carried in the anterior nares of approximately 30% of the general population. It is
CA-MRSA a new problem in Indonesia?
 CA-MRSA a new problem in Indonesia? Latre Buntaran Clinical Microbiologist Consultant Indonesia Coordinator of ANSORP Study Secretary General of INASIC Community Associated MRSA Papua New Guinea Asia Europe
CA-MRSA a new problem in Indonesia? Latre Buntaran Clinical Microbiologist Consultant Indonesia Coordinator of ANSORP Study Secretary General of INASIC Community Associated MRSA Papua New Guinea Asia Europe
Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Epidemiology and Clinical Consequences of an Emerging Epidemic
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, July 2010, p. 616 687 Vol. 23, No. 3 0893-8512/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cmr.00081-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Community-Associated
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, July 2010, p. 616 687 Vol. 23, No. 3 0893-8512/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cmr.00081-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Community-Associated
Impact of a Standardized Protocol to Address Outbreak of Methicillin-resistant
 Impact of a Standardized Protocol to Address Outbreak of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Skin Infections at a large, urban County Jail System Earl J. Goldstein, MD* Gladys Hradecky, RN* Gary
Impact of a Standardized Protocol to Address Outbreak of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Skin Infections at a large, urban County Jail System Earl J. Goldstein, MD* Gladys Hradecky, RN* Gary
Annual reports Australian Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis Outcome Programme, 2014
 Australian Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis Outcome Programme, 2014 Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance Australian Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis Outcome Programme annual report, 2014 Geoffrey W Coombs,
Australian Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis Outcome Programme, 2014 Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance Australian Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis Outcome Programme annual report, 2014 Geoffrey W Coombs,
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times
 Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria. Antimicrobial Resistance. Molecular Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance. Topics to be Covered
 Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased number of hospitalizations Increased length
Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased number of hospitalizations Increased length
MID 23. Antimicrobial Resistance. Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria. Molecular Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance
 Antimicrobial Resistance Molecular Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance Micro evolutionary change - point mutations Beta-lactamase mutation extends spectrum of the enzyme rpob gene (RNA polymerase) mutation
Antimicrobial Resistance Molecular Genetics of Antimicrobial Resistance Micro evolutionary change - point mutations Beta-lactamase mutation extends spectrum of the enzyme rpob gene (RNA polymerase) mutation
Does Screening for MRSA Colonization Have A Role In Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevention Programs?
 Does Screening for MRSA Colonization Have A Role In Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevention Programs? John A. Jernigan, MD, MS Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Centers for Disease Control and
Does Screening for MRSA Colonization Have A Role In Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevention Programs? John A. Jernigan, MD, MS Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Centers for Disease Control and
Changing epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization in paediatric intensive-care units
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2012 Changing epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization in paediatric intensive-care
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2012 Changing epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization in paediatric intensive-care
Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections
 British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published April 1, 2010 Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections Fiona J. Cooke and Nicholas M. Brown * Clinical Microbiology
British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published April 1, 2010 Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections Fiona J. Cooke and Nicholas M. Brown * Clinical Microbiology
Microbiological Surveillance of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Belgian Hospitals in 2003
 Microbiological Surveillance of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Belgian Hospitals in 3 Final report Olivier Denis and Marc J. Struelens Reference Laboratory for Staphylococci Department
Microbiological Surveillance of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Belgian Hospitals in 3 Final report Olivier Denis and Marc J. Struelens Reference Laboratory for Staphylococci Department
Antimicrobial Resistance
 Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased number of hospitalizations Increased length
Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased number of hospitalizations Increased length
Antimicrobial Resistance Acquisition of Foreign DNA
 Antimicrobial Resistance Acquisition of Foreign DNA Levy, Scientific American Horizontal gene transfer is common, even between Gram positive and negative bacteria Plasmid - transfer of single or multiple
Antimicrobial Resistance Acquisition of Foreign DNA Levy, Scientific American Horizontal gene transfer is common, even between Gram positive and negative bacteria Plasmid - transfer of single or multiple
LA-MRSA in the Netherlands: the past, presence and future.
 LA-MRSA in the Netherlands: the past, presence and future. Prof. Jaap Wagenaar DVM, PhD With input from Prof. Jan Kluytmans MD, PhD Department of Infectious Diseases and Immunology, Faculty of Veterinary
LA-MRSA in the Netherlands: the past, presence and future. Prof. Jaap Wagenaar DVM, PhD With input from Prof. Jan Kluytmans MD, PhD Department of Infectious Diseases and Immunology, Faculty of Veterinary
Population dynamics of methicillin-susceptible and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus in remote communities
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2009) 64, 684 693 doi:10.1093/jac/dkp285 Advance Access publication 27 August 2009 Population dynamics of methicillin-susceptible and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2009) 64, 684 693 doi:10.1093/jac/dkp285 Advance Access publication 27 August 2009 Population dynamics of methicillin-susceptible and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Hong-Kai Wang 1, Chun-Yen Huang 1 and Yhu-Chering Huang 1,2*
 Wang et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2017) 17:470 DOI 10.1186/s12879-017-2560-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Clinical features and molecular characteristics of childhood communityassociated methicillin-resistant
Wang et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2017) 17:470 DOI 10.1186/s12879-017-2560-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Clinical features and molecular characteristics of childhood communityassociated methicillin-resistant
Nosocomial Infections: What Are the Unmet Needs
 Nosocomial Infections: What Are the Unmet Needs Jean Chastre, MD Service de Réanimation Médicale Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, AP-HP, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris 6, France www.reamedpitie.com
Nosocomial Infections: What Are the Unmet Needs Jean Chastre, MD Service de Réanimation Médicale Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, AP-HP, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris 6, France www.reamedpitie.com
 This is an author version of the contribution published on: Corcione S,Motta I,Fossati L,Campanile F,Stefani S,Cavallo R,Di Perri G,Ranieri VM,De Rosa FG Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant
This is an author version of the contribution published on: Corcione S,Motta I,Fossati L,Campanile F,Stefani S,Cavallo R,Di Perri G,Ranieri VM,De Rosa FG Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant
Dr Nata Menabde Executive Director World Health Organization Office at the United Nations Global action plan on antimicrobial resistance
 Global action plan on antimicrobial resistance Dr Nata Menabde Executive Director World Health Organization Office at the United Nations Proportion of MDR among previously treated TB cases, 1994-2010 0-
Global action plan on antimicrobial resistance Dr Nata Menabde Executive Director World Health Organization Office at the United Nations Proportion of MDR among previously treated TB cases, 1994-2010 0-
PREVALENCE OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE IN ENTEROCOCCUS ISOLATES IN AUSTRALIA, 2005:
 PREVALENCE OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE IN ENTEROCOCCUS ISOLATES IN AUSTRALIA, 25: REPORT FROM THE AUSTRALIAN GROUP ON ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE Keryn J Christiansen, John D Turnidge, Jan M Bell, Narelle
PREVALENCE OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE IN ENTEROCOCCUS ISOLATES IN AUSTRALIA, 25: REPORT FROM THE AUSTRALIAN GROUP ON ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE Keryn J Christiansen, John D Turnidge, Jan M Bell, Narelle
The molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in the major countries of East Asia
 Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2017 The molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in the
Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2017 The molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in the
Absence of LA-MRSA CC398 as nasal colonizer of pigs raised
 AEM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 9 December 2011 Appl. Environ. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/aem.07260-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
AEM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 9 December 2011 Appl. Environ. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/aem.07260-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
Spread of a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST80 strain in the community of the northern Netherlands
 Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2007) 26:723 727 DOI 10.1007/s10096-007-0352-y CONCISE ARTICLE Spread of a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST80 strain in the community of the northern Netherlands
Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2007) 26:723 727 DOI 10.1007/s10096-007-0352-y CONCISE ARTICLE Spread of a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST80 strain in the community of the northern Netherlands
The Australian Gonococcal Surveillance Programme
 The Australian Gonococcal Surveillance Programme 1979 2017 Monica M Lahra A,B,F, CR Robert George A,C and David M Whiley D,E A WHO Collaborating Centre for STD, Microbiology Department, New South Wales
The Australian Gonococcal Surveillance Programme 1979 2017 Monica M Lahra A,B,F, CR Robert George A,C and David M Whiley D,E A WHO Collaborating Centre for STD, Microbiology Department, New South Wales
Staphylococcus aureus
 The National Reference Centre (NRC) for S. aureus of Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB) provides the following tasks: - Identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Staphylococcus sp. strains
The National Reference Centre (NRC) for S. aureus of Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB) provides the following tasks: - Identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Staphylococcus sp. strains
Deborah A. Williamson 1,2,3 *, Sally A. Roberts 2, Stephen R. Ritchie 1, Geoffrey W. Coombs 4,5, John D. Fraser 1, Helen Heffernan 3.
 Clinical and Molecular Epidemiology of Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in New Zealand: Rapid Emergence of Sequence Type 5 (ST5)-SCCmec-IV as the Dominant Community-Associated MRSA Clone Deborah
Clinical and Molecular Epidemiology of Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in New Zealand: Rapid Emergence of Sequence Type 5 (ST5)-SCCmec-IV as the Dominant Community-Associated MRSA Clone Deborah
Community Strain of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Involved in a Hospital Outbreak
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1999, p. 2858 2862 Vol. 37, No. 9 0095-1137/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Community Strain of Methicillin-Resistant
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1999, p. 2858 2862 Vol. 37, No. 9 0095-1137/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Community Strain of Methicillin-Resistant
Research Article Genotyping of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Hospitalized Children
 International Pediatrics, Article ID 314316, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/314316 Research Article Genotyping of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Hospitalized
International Pediatrics, Article ID 314316, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/314316 Research Article Genotyping of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Hospitalized
Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Lina Cavaco
 Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Lina Cavaco licav@food.dtu.dk 1 DTU Food, Technical University of Denmark Staphylococcus aureus Gram positive cocci Catalase positive Coagulase postive
Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Lina Cavaco licav@food.dtu.dk 1 DTU Food, Technical University of Denmark Staphylococcus aureus Gram positive cocci Catalase positive Coagulase postive
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2016) 5(12):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 12 (2016) pp. 644-649 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.512.071
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 12 (2016) pp. 644-649 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.512.071
Annual Surveillance Summary: Methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections in the Military Health System (MHS), 2017
 Annual Surveillance Summary: Methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections in the Military Health System (MHS), 2017 Jessica R. Spencer and Uzo Chukwuma Approved for public release. Distribution
Annual Surveillance Summary: Methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections in the Military Health System (MHS), 2017 Jessica R. Spencer and Uzo Chukwuma Approved for public release. Distribution
Clinical Guideline. District Infectious Diseases Management. Go to Guideline. District Infectious Diseases Management CG 18_24
 Clinical Guideline District Infectious Diseases Management Sites where Clinical Guideline applies All facilities This Clinical Guideline applies to: 1. Adults Yes 2. Children up to 16 years Yes 3. Neonates
Clinical Guideline District Infectious Diseases Management Sites where Clinical Guideline applies All facilities This Clinical Guideline applies to: 1. Adults Yes 2. Children up to 16 years Yes 3. Neonates
Multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA) Surveillance and Control. Alison Holmes
 Multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA) Surveillance and Control Alison Holmes The organism and it s epidemiology Surveillance Control What is it? What is it? What is it? What is it? Acinetobacter :
Multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA) Surveillance and Control Alison Holmes The organism and it s epidemiology Surveillance Control What is it? What is it? What is it? What is it? Acinetobacter :
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2018) 7(8):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 08 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.708.378
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 08 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.708.378
FM - Male, 38YO. MRSA nasal swab (+) Due to positive MRSA nasal swab test, patient will be continued on Vancomycin 1500mg IV q12 for MRSA treatment...
 Jillian O Keefe Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate 2016 September 15, 2015 FM - Male, 38YO HPI: Previously healthy male presents to ED febrile (102F) and in moderate distress ~2 weeks after getting a tattoo
Jillian O Keefe Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate 2016 September 15, 2015 FM - Male, 38YO HPI: Previously healthy male presents to ED febrile (102F) and in moderate distress ~2 weeks after getting a tattoo
Susan A.J. Harch 1,4*, Eleanor MacMorran 1, Steven Y.C. Tong 2,5, Deborah C. Holt 2, Judith Wilson 2, Eugene Athan 3 and Saliya Hewagama 1
 Harch et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2017) 17:405 DOI 10.1186/s12879-017-2460-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE High burden of complicated skin and soft tissue infections in the Indigenous population of Central Australia
Harch et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2017) 17:405 DOI 10.1186/s12879-017-2460-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE High burden of complicated skin and soft tissue infections in the Indigenous population of Central Australia
Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy
 Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy Doo Ryeon Chung, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases Director, Infection Control Office SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE CASE 1
Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy Doo Ryeon Chung, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases Director, Infection Control Office SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE CASE 1
Success for a MRSA Reduction Program: Role of Surveillance and Testing
 Success for a MRSA Reduction Program: Role of Surveillance and Testing Singapore July 13, 2009 Lance R. Peterson, MD Director of Microbiology and Infectious Disease Research Associate Epidemiologist, NorthShore
Success for a MRSA Reduction Program: Role of Surveillance and Testing Singapore July 13, 2009 Lance R. Peterson, MD Director of Microbiology and Infectious Disease Research Associate Epidemiologist, NorthShore
Antimicrobial Resistance and Papua New Guinea WHY is it important? HOW has the problem arisen? WHAT can we do?
 Antimicrobial Resistance and Papua New Guinea WHY is it important? HOW has the problem arisen? WHAT can we do? John Ferguson, John Hunter Hospital, University of Newcastle, NSW, Australia Infectious Diseases
Antimicrobial Resistance and Papua New Guinea WHY is it important? HOW has the problem arisen? WHAT can we do? John Ferguson, John Hunter Hospital, University of Newcastle, NSW, Australia Infectious Diseases
TACKLING THE MRSA EPIDEMIC
 TACKLING THE MRSA EPIDEMIC Paul D. Holtom, MD Associate Professor of Medicine and Orthopaedics USC Keck School of Medicine MRSA Trend (HA + CA) in US TSN Database USA (1993-2003) % of MRSA among S. aureus
TACKLING THE MRSA EPIDEMIC Paul D. Holtom, MD Associate Professor of Medicine and Orthopaedics USC Keck School of Medicine MRSA Trend (HA + CA) in US TSN Database USA (1993-2003) % of MRSA among S. aureus
MRSA Outbreak in Firefighters
 MRSA Outbreak in Firefighters Angie Carranza Munger, MD Resident, Occupational and Environmental Medicine The University of Colorado, Denver and National Jewish Health Candidate, Masters of Public Health
MRSA Outbreak in Firefighters Angie Carranza Munger, MD Resident, Occupational and Environmental Medicine The University of Colorado, Denver and National Jewish Health Candidate, Masters of Public Health
Community Acquisition of Gentamicin-Sensitive Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Southeast Queensland, Australia
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2000, p. 3926 3931 Vol. 38, No. 11 0095-1137/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Community Acquisition of Gentamicin-Sensitive
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2000, p. 3926 3931 Vol. 38, No. 11 0095-1137/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Community Acquisition of Gentamicin-Sensitive
PVL Staph aureusjust a skin/soft tissue problem? Layla Mohammadi Lead Pharmacist, Antimicrobials Lewisham Healthcare NHS Trust
 PVL Staph aureusjust a skin/soft tissue problem? Layla Mohammadi Lead Pharmacist, Antimicrobials Lewisham Healthcare NHS Trust Neonatal Case History Neonate born at 26 +2 gestation Spontaneous onset of
PVL Staph aureusjust a skin/soft tissue problem? Layla Mohammadi Lead Pharmacist, Antimicrobials Lewisham Healthcare NHS Trust Neonatal Case History Neonate born at 26 +2 gestation Spontaneous onset of
North West Neonatal Operational Delivery Network Working together to provide the highest standard of care for babies and families
 Document Title and Reference : Guideline for the management of multi-drug resistant organisms (MDRO) Main Author (s) Simon Power Ratified by: GM NSG Date Ratified: February 2012 Review Date: March 2017
Document Title and Reference : Guideline for the management of multi-drug resistant organisms (MDRO) Main Author (s) Simon Power Ratified by: GM NSG Date Ratified: February 2012 Review Date: March 2017
MRSA control strategies in Europekeeping up with epidemiology?
 MRSA 15 years in Belgium MRSA control strategies in Europekeeping up with epidemiology? Marc J. Struelens, MD, PhD Senior Expert, Scientific Advice Unit European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control,
MRSA 15 years in Belgium MRSA control strategies in Europekeeping up with epidemiology? Marc J. Struelens, MD, PhD Senior Expert, Scientific Advice Unit European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control,
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus:
 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Action-Oriented Guidance for Community-Based Prevention Jackie Dawson, PhD Public Health Epidemiologist Chelan, Douglas, Grant, Kittitas, & Okanogan Counties
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Action-Oriented Guidance for Community-Based Prevention Jackie Dawson, PhD Public Health Epidemiologist Chelan, Douglas, Grant, Kittitas, & Okanogan Counties
Prevalence and Molecular Characteristics of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolates in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
 Journal of Bacteriology and Virology 2016. Vol. 46, No. 2 p.99 103 http://dx.doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2016.46.2.99 Communication Prevalence and Molecular Characteristics of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
Journal of Bacteriology and Virology 2016. Vol. 46, No. 2 p.99 103 http://dx.doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2016.46.2.99 Communication Prevalence and Molecular Characteristics of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
Evaluating the Role of MRSA Nasal Swabs
 Evaluating the Role of MRSA Nasal Swabs Josh Arnold, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Pharmacy Grand Rounds February 28, 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Identify the pathophysiology of MRSA nasal colonization
Evaluating the Role of MRSA Nasal Swabs Josh Arnold, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Pharmacy Grand Rounds February 28, 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Identify the pathophysiology of MRSA nasal colonization
European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (EARSS) in Scotland: 2004
 European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (EARSS) in Scotland: 2004 SECOND ANNUAL REPORT MJ Coyne 1, SJ Dancer 1, G Edwards 2, 3, D Morrison 2. 1 Health Protection Scotland, 2 Scottish MRSA
European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (EARSS) in Scotland: 2004 SECOND ANNUAL REPORT MJ Coyne 1, SJ Dancer 1, G Edwards 2, 3, D Morrison 2. 1 Health Protection Scotland, 2 Scottish MRSA
DR. MICHAEL A. BORG DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION & CONTROL MATER DEI HOSPITAL - MALTA
 DR. MICHAEL A. BORG DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION & CONTROL MATER DEI HOSPITAL - MALTA The good old days The dread (of) infections that used to rage through the whole communities is muted Their retreat
DR. MICHAEL A. BORG DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION & CONTROL MATER DEI HOSPITAL - MALTA The good old days The dread (of) infections that used to rage through the whole communities is muted Their retreat
Tel: Fax:
 CONCISE COMMUNICATION Bactericidal activity and synergy studies of BAL,a novel pyrrolidinone--ylidenemethyl cephem,tested against streptococci, enterococci and methicillin-resistant staphylococci L. M.
CONCISE COMMUNICATION Bactericidal activity and synergy studies of BAL,a novel pyrrolidinone--ylidenemethyl cephem,tested against streptococci, enterococci and methicillin-resistant staphylococci L. M.
Doxycycline staph aureus
 Search Search Doxycycline staph aureus Mercer infection is the one of the colloquial terms given for MRSA (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus ) infection. Initially, Staphylococcal resistance
Search Search Doxycycline staph aureus Mercer infection is the one of the colloquial terms given for MRSA (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus ) infection. Initially, Staphylococcal resistance
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE. S114 CID 2001:32 (Suppl 2) Diekema et al.
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Survey of Infections Due to Staphylococcus Species: Frequency of Occurrence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Isolates Collected in the United States, Canada, Latin America, Europe,
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Survey of Infections Due to Staphylococcus Species: Frequency of Occurrence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Isolates Collected in the United States, Canada, Latin America, Europe,
Infection Control Priorities for Antibiotics Resistance - The Search and Destroy Strategy. WH Seto Hong Kong China
 Infection Control Priorities for Antibiotics Resistance - The Search and Destroy Strategy WH Seto Hong Kong China WHD 2011 slogan Tier 1 Education Surveillance Environment Administration Usage IC isolation
Infection Control Priorities for Antibiotics Resistance - The Search and Destroy Strategy WH Seto Hong Kong China WHD 2011 slogan Tier 1 Education Surveillance Environment Administration Usage IC isolation
(DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
 (DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE John Ferguson (Hunter New England, NSW) on behalf of MRGN Task Force Acknowledgement
(DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE John Ferguson (Hunter New England, NSW) on behalf of MRGN Task Force Acknowledgement
Antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in dermatology and burn wards
 J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 40-44 Antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in dermatology and burn wards G. A. J. AYLIFFE, WENDA GREEN, R. LIVINGSTON, AND E. J. L. LOWBURY From the Hospital Infection Research
J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 40-44 Antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in dermatology and burn wards G. A. J. AYLIFFE, WENDA GREEN, R. LIVINGSTON, AND E. J. L. LOWBURY From the Hospital Infection Research
Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Review of an Emerging Public Health Concern
 Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Review of an Emerging Public Health Concern Timothy D. Drews, MD; Jonathan L. Temte, MD, PhD; Barry C. Fox, MD ABSTRACT Methicillin-resistant
Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Review of an Emerging Public Health Concern Timothy D. Drews, MD; Jonathan L. Temte, MD, PhD; Barry C. Fox, MD ABSTRACT Methicillin-resistant
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An Update
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An Update Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An Update Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain
J M e d A l l i e d S c i ; 6 ( 2 ) : w w w. j m a s. i n. P r i n t I S S N : O n l i n e I S S N : X
 J M e d A l l i e d S c i 2 0 1 6 ; 6 ( 2 ) : 5 6-6 0 w w w. j m a s. i n P r i n t I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 6 9 6 O n l i n e I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 7 0 X Journal of M e d i cal & Allied Sciences Original article
J M e d A l l i e d S c i 2 0 1 6 ; 6 ( 2 ) : 5 6-6 0 w w w. j m a s. i n P r i n t I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 6 9 6 O n l i n e I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 7 0 X Journal of M e d i cal & Allied Sciences Original article
Source: Portland State University Population Research Center (
 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Surveillance Report 2010 Oregon Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Office of Disease Prevention & Epidemiology Oregon Health Authority Updated:
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Surveillance Report 2010 Oregon Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Office of Disease Prevention & Epidemiology Oregon Health Authority Updated:
Monitoring gonococcal antimicrobial susceptibility
 Monitoring gonococcal antimicrobial susceptibility The rapidly changing antimicrobial susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae has created an important public health problem. Because of widespread resistance
Monitoring gonococcal antimicrobial susceptibility The rapidly changing antimicrobial susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae has created an important public health problem. Because of widespread resistance
ORIGINAL ARTICLE /j x
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01718.x Clonal spread of SCCmec type IV methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus between community and hospital Y. H. Huang 1, S. P. Tseng 1,J.M.Hu 1, J. C.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01718.x Clonal spread of SCCmec type IV methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus between community and hospital Y. H. Huang 1, S. P. Tseng 1,J.M.Hu 1, J. C.
OIE Collaborating Centres Reports Activities
 OIE Collaborating Centres Reports Activities Activities in 2017 This report has been submitted : 2018-01-13 02:04:00 Title of collaborating centre: Diagnosis and Vaccine Evaluation in the Address of Collaborating
OIE Collaborating Centres Reports Activities Activities in 2017 This report has been submitted : 2018-01-13 02:04:00 Title of collaborating centre: Diagnosis and Vaccine Evaluation in the Address of Collaborating
Detection of inducible clindamycin resistance among clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus in a tertiary care hospital
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 9 (2014) pp. 689-694 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Detection of inducible clindamycin resistance among clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus in a
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 9 (2014) pp. 689-694 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Detection of inducible clindamycin resistance among clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus in a
Typing of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Using DNA Fingerprints by Pulsed-field Gel Electrophoresis
 Published online: 16/07/2016 Published print:08/2016 ORIGINAL PAPER Typing of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Using DNA Fingerprints by Pulsed-field Gel Electrophoresis Velma Rebic 1, Ana Budimir
Published online: 16/07/2016 Published print:08/2016 ORIGINAL PAPER Typing of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Using DNA Fingerprints by Pulsed-field Gel Electrophoresis Velma Rebic 1, Ana Budimir
Antimicrobial Resistance
 Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased
Antimicrobial Resistance Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Change in the approach to the administration of Change in the approach to the administration of empiric antimicrobial therapy Increased
03/09/2014. Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course. Talk outline
 Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course 2014 What is healthcare-associated infection (HCAI), antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs)? Why we should be worried?
Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course 2014 What is healthcare-associated infection (HCAI), antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs)? Why we should be worried?
Annual Surveillance Summary: Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections in the Military Health System (MHS), 2016
 Annual Surveillance Summary: Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections in the Military Health System (MHS), 2016 Jessica Spencer and Uzo Chukwuma Approved for public release. Distribution
Annual Surveillance Summary: Methicillin- Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections in the Military Health System (MHS), 2016 Jessica Spencer and Uzo Chukwuma Approved for public release. Distribution
Campylobacter infections in EU/EEA and related AMR
 Campylobacter infections in EU/EEA and related AMR Therese Westrell, ECDC EURL Campylobacter workshop, Uppsala, Sweden, 9 October 2018 Zoonoses Zoonotic infections in the EU, 2016 Campylobacteriosis (N
Campylobacter infections in EU/EEA and related AMR Therese Westrell, ECDC EURL Campylobacter workshop, Uppsala, Sweden, 9 October 2018 Zoonoses Zoonotic infections in the EU, 2016 Campylobacteriosis (N
