PUBLIC HEALTH LABORATORY DUBLIN, HSE, DML. USERS MANUAL
|
|
|
- Marjorie Shonda Berry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 , Page 1 of 21 PUBLIC HEALTH LABORATORY DUBLIN, HSE, DML. USERS MANUAL Issue date March 2017 Review March 2019, Dublin HSE Dublin Mid Leinster, Cherry Orchard Hospital, Dublin 10. Tel: /6 Fax: phl.dublin@hse.ie
2 , Page 2 of 21 CONTENTS General Information...4 Opening Hours...4 Out of Hours service..4 Clinical Advice..5 User satisfaction. 5 PHL Staff Contact Numbers....6 Sample Submission...7 VTEC and Clinical Samples...7 Completion of PHL, HSE, DML Request Forms..7 Specimen/Sample Identification...8 Transport of Clinical Specimens/Samples to the Laboratory....9 Food, Water and environmental swabs sample Submission 11 Sample Rejection...13 Sample Retention and Further Test Requests...13 Complaints Procedure..14 Turnaround Time..14 PHL Protocol for Phoning Results PHL Policy on Faxing and ing Reports.14 Summary of VTEC and Clinical Microbiology Service..15 Summary of the Food Testing Service...19 Summary of the Water Testing Service...21
3 , Page 3 of 21 FOREWORD We hope that the production of this manual will help all users of the Public Health Laboratory to get the best value from the PHL service. In particular, we hope that it will aid in selecting and obtaining the most appropriate specimen, submitting appropriate information for test selection, transporting the sample to the laboratory without delay and aid interpretation of results. The value of a particular bacteriology test is still greatly dependant on this process. If you have any comments, corrections or suggestions on this manual we would like to hear from you. Document control: All changes made to a new issue of this document are highlighted. Authors: Dr. Eleanor McNamara Ms. Mary Linehan March 2017
4 , Page 4 of 21 GENERAL INFORMATION This user manual provides information on the activities and structure of the Public Health Laboratory Dublin. The is a Health Service Executive laboratory, located within the grounds of Cherry Orchard Hospital, Ballyfermot, Dublin 10. The laboratory provides a microbiology scope for: 1. A National VTEC (verocytotoxin E.coli) Reference service. Clinical and environmental samples are analyzed for VTEC utilizing molecular and culture techniques. The VTEC service is accredited to ISO for clinical enteric specimens and ISO for food, water and environmental samples. 2. A detailed gastro-enteric clinical microbiology diagnostic service accredited to ISO to support and advise on the investigation of gastro-enteric outbreaks both nationally and regionally. 3. A clinical diagnostic microbiology service for long-term care facilities and local general practices. 4. An ISO accredited Regional Public Health food and water microbiology service. This is accessed by the Environmental Health Service (EHS), Public Health Doctors and Acute Hospital Facilities. Clinical samples, isolates and food and water samples are tested for microbiological analysis only. OPENING HOURS: Routine service is provided from 9.00 a.m. to 5.00 p.m. Monday-Friday, a limited service on Saturday morning from 9.30 a.m. to pm and Sunday from to mid-day. Outside of these hours, please contact the laboratory to arrange the receipt of specimens or specimens may be delivered to the gate lodge of COH and refrigerated until collected by laboratory staff. Clerical staff are available for results or enquiries etc. from 9.00 a.m. to 5 p.m. Monday to Friday at OUT OF HOUR S SERVICE: A consultant microbiologist approved emergency out of hours service is available between 5 p.m. and 9 a.m. Monday to Friday and between p.m. on Saturday to 9.00 a.m. on Monday. This service is accessed by contacting the Laboratory Director or the designated locum. Contact details are available via the Cherry Orchard Hospital switchboard ( ).
5 , Page 5 of 21 Note that the Consultant Microbiologist must be telephoned for urgent specimens to be processed out of hours, users should not telephone the laboratory as telephones are not staffed out of routine hours. CLINICAL ADVICE: Advice regarding diagnosis and treatment of infection is available at all times. Contact numbers are given overleaf. For out of hours advice including infection control advice, please contact the on-call Consultant Microbiologist via switchboard ( ) or on-call Medical Scientist. Advice regarding the designation of environmental results on the final report is available at all times. Contact numbers are given overleaf. USER SATISFACTION: The operates an on-going process of service evaluation and improvement to meet the needs and requirements of users. Laboratory management regularly assesses contributions and complaints received in the laboratory from users of the Microbiology service.
6 , Page 6 of 21 PHL STAFF CONTACT NUMBERS ( ) Name Ext. E mail General secretarial office phl.dublin@hse.ie General enquiries/results Consultant Microbiologists Dr. Eleanor McNamara eleanor.mcnamara@hse.ie Dr. Brian O Connell boconnell@stjames.ie Chief Medical Scientist Ms. Mary Linehan mary.linehan2@hse.ie VTEC Service Anne Carroll Clinical Laboratory Senior Medical Scientist Donal Lanigan Food Laboratory Senior Medical Scientist Aidan Gibson Water Laboratory Senior Medical Scientist Paul Larkin Quality Manager Lucy Devlin eleanor.mcnamara@hse.ie anne.carroll@hse.ie mary.linehan2@hse.ie donal.lanigan@hse.ie aidan.gibson@hse.ie paul.larkin@hse.ie lucy.devlin@hse.ie Infection Control Nurse Specialist Muthu Saba
7 , Page 7 of 21 SAMPLE SUBMISSION GENERAL GUIDELINES All samples submitted to PHL should be in the appropriate sterile container along with the relevant completed PHL request form. Samples should be transported to the laboratory as soon as possible under the appropriate transport conditions. VTEC AND CLINICAL SAMPLES: Faecal specimens or bacterial isolates are tested for verocytotoxin producing E. coli. See details for gastrointestinal tract specimens below. Collect specimens in sterile containers before commencement of antimicrobial therapy. This is usually possible for most mild infections. For more serious infections, antimicrobial therapy should not be withheld pending collection of a specific specimen. However, blood cultures can be obtained in nearly all cases prior to antimicrobial treatment of serious infection. If in any doubt as to the appropriate container, please contact the laboratory for advice. Please send an adequate amount of specimen. As a general rule the more specimen the better. If pus is present, send pus rather than a swab and remember to send enough specimen if a whole series of tests are required. Please ensure that relevant clinical details are included on the request form. All of the above may influence the type of test that the laboratory performs. COMPLETION OF PHL CLINICAL REQUEST FORMS: Adequate identification of patient samples is essential for patient safety. The following details must be recorded on the request form: Full Patient Name DOB Patients Address External laboratory number/mrn (where available) Gender
8 , Page 8 of 21 Date of Collection Ward/Source Requesting Clinician Specimen Type Tests requested Those highlighted in bold are essential patient identifiers. Please ensure that relevant clinical details are included on the request form. For example, include details if the specimen is sent during an outbreak (outbreak code) or if there is a history of foreign travel or a specific diagnosis is being considered. All of the above may influence the type of test that the laboratory performs. Bacterial isolates for identification, serotyping or toxin testing must be accompanied by a current VTEC request form. This form is available from: blic_health_laboratory_dublin/ SPECIMEN/SAMPLE IDENTIFICATION The following details should be recorded on all specimens: Full Patient Name DOB MRN (where available) Date of collection Those highlighted in bold are essential patient identifiers. Specimens cannot be processed unless there is a minimum of two patient identifiers on the specimen which match those on the request form, one of which must be the full patient name. If the sample does not have the two patient identifiers or is unsuitable (i.e. leaking) the client will be informed by telephone and a repeat sample requested. The sample is still logged in and it is recorded as an unsuitable sample on our Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) and a telephone comment is also recorded. It is laboratory policy NOT to process unlabelled or mislabeled specimens.
9 , Page 9 of 21 TRANSPORT OF CLINICAL SPECIMENS/SAMPLES TO THE LABORATORY. Specimens should be transported and processed as soon as possible; individual test requirements may invalidate the test request if the samples is too old (48-72h). All sample containers must be tightly closed and placed in a transport hazard bag. All VTEC samples must be packaged appropriately. Clinical specimens/bacterial isolates for identification, serotyping or toxin testing must be transported to the laboratory in suitable packaging (Ref: UN 3373 Category B Infectious Substances and UN 2814 Infectious Substances by road). It is the responsibility of the person dispatching the sample to the laboratory to ensure that it is packaged correctly and does not pose a risk to anyone coming in contact with it during transport or on receipt in the laboratory (Ref: S.I. No.617 of 2010 Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road Regulations 2010). Faeces samples are held at room temperature if they are to be processed on the day of arrival in the laboratory. Other sample types (e.g. urines) are refrigerated at 2-8º C. If processing is delayed sample should be refrigerated at 2-8º C for a maximum of 72 hours. Urgent samples will be processed upon receipt or discussed with Consultant Microbiologist if received out of hours. Clients sending urgent samples should notify the laboratory in advance as outlined in the PHL. 1-2g is sufficient for culture of faeces. As multiple samples are rarely indicated for detection of faecal pathogens, if more than one sample is taken on the same day they may be pooled. Isolates received for VTEC analysis before 11a.m. will be processed directly from the slope/plate on the day of receipt. For ova and parasite analysis, ideally three stool samples should be collected over no more than a 10-day period. It is usually recommended that samples are collected every other day. Unless the patient has severe diarrhoea or dysentery, no more than one sample should be examined within a single 24 hour period, as shedding of cysts and ova tends to be intermittent. If E. histolytica or G. duodenalis are suspected and the first 3 samples are negative, ideally 3 additional samples should be submitted at weekly intervals. There are no prescribed limits for the size of sample required, but some laboratory procedures will require larger quantities than others. For Sellotape slides/perianal swabs suspecting E. vermicularis ova, the sample should be taken between 10pm and midnight, or early in the morning, before defecation or bathing. To prevent deterioration, refrigeration or storage of sample
10 , Page 10 of 21 at room temperature for up to 48hrs is advised. It is recommended that samples should be taken for at least 4 to 6 consecutive days. If the results of all these are negative the patient can be considered free from infection. In practice, more than one sample is rarely received. Samples requesting detection of S. haematobium, it is preferable to obtain total urine collected over the time period between 10am and 2pm. A minimum of 10ml is required. In patients with haematuria, eggs may be found trapped in the blood and mucus in the terminal portion of the urine sample. If the urine cannot be examined within an hour of collection, it is advisable to add 1mL of undiluted formalin to preserve any eggs that may be present. For duodenal/jejunal aspirates, a minimum volume of 1mL is required. Fresh faeces samples are essential for the examination of trophozoites ideally within 30 minutes from the time of collection. SWABS/CONTAINERS USED IN THE PHL DUBLIN 1. Universal container two types with different apertures are used for collection of bodily fluids stools, pus, urine, etc. 2. Amies Transport Swabs for routine collection of swab specimens of skin, wounds etc. 3. Blood culture bottles: Oxoid SIGNAL blood culture BC100M 4. Viral transport medium and viral swabs: Please consult the Laboratory Diagnosis of Viral infections handbook for further details, or contact the Microbiology Medical Staff.
11 , Page 11 of 21 FOOD AND WATER SAMPLE SUBMISSION: FOOD SAMPLES: Foods should be sampled and transported to the laboratory as per FSAI/HSE Guidance on Sampling of Food for Microbiological Testing Issue 1 Revision 3, Official Food Sample Under the terms of the Official Control of foodstuffs Directive 93/99/EEC an official food sample is a sample that is examined in an official Food Control Laboratory. Formal Food Sample A formal sample is a sample taken for which formal action and/or legal proceedings may ensue or for which formal action may be considered. Specimen Request Form for Food samples. A specimen request form (National Sample Submission Form (NSSF)) should accompany each sample of food to be tested. The receiving PHL staff member must record the following details on the requisition form: By the EHO: Sample Size 1. Date and time of receipt of sample. 2. Temperature of sample on receipt if appropriate 3. Receivers name 4. Storage condition on receipt 5. Tick box once sample and form information has been crosschecked. 1. Name of the EHO delivering sample 2. Name of EHO collecting sample 3. Food type and code 4. Packaging conditions etc 5. Reason for sampling 6. Supplementary information if food poisoning outbreak 7. Premises name and sample description. 8. Any other comments about the sample The standard minimum routine food sample size for the PHL is 100g (25g x 4). WATER SAMPLES:
12 , Page 12 of 21 Water samples must be submitted in sterile containers. The sample container must contain sodium thiosulphate if the water sample has been treated with a biocide (e.g. chlorine). If in any doubt as to the appropriate container or transport conditions, please contact the laboratory for advice. Specimen Request Form for Water samples A specimen request form should accompany each sample of water sample to be tested. The receiving PHL staff member will record the temperature of the container that was used to transport the sample. See Table 1 for the minimum volume of sample required and the type of container required. TABLE 1 Sample type Min. Vol. required Sodium Thiosulphate Mains/ Drinking Water 500ml Required YES Endoscopy water 500ml Required(If YES biocide) Heater cooler water 300ml Required(If YES biocide) Swimming Pools 500ml Required YES Hydrotherapy pools 500ml Required YES Sterile Container Well Water (microbiologically treated) 500ml Required(If biocide) YES Well water untreated 500ml Not Required YES Group Scheme (treated) 500ml Required(If YES biocide) Group Scheme (untreated) 500ml Not Required YES Seawater 500ml/1000ml/2000ml Not Required YES Surface water 500ml Not Required YES Water for pathogens At least 1 litre If biocide present YES Bottled water At least 1 litre YES Pre bottled water At least 1 litre If biocide present YES
13 , Page 13 of 21 Water for dialysis 500ml If biocide present YES Please ensure that relevant details are included on the request form. All of the above may influence the type of tests that the laboratory performs. The current food and water sample request forms are available to download from the website: _Health_Laboratory_Dublin/ SAMPLE REJECTION: Referred samples that don t meet the required acceptance criteria will be registered and discussed with a Senior Scientist or Consultant staff. If the decision is to reject the sample, it will be discarded and the reason for rejection noted and informed to the referring doctor/laboratory. It is laboratory policy NOT to process unlabelled or mislabelled samples. Where deviating samples are chosen to be processed, this will be recorded as such and, if applicable, an interpretation will be applied cautiously. SAMPLE RETENTION AND FURTHER TESTING REQUESTS: Clinical Specimens: Following testing, routine clinical samples are stored at 2-8º C for a week or until the final report has been authorised. Samples processed in the CL3 laboratory are stored at 2-8º C for a minimum of a week. Requests for further testing on samples may be possible on a case-by-case basis, up to 72 hours after receipt. Please contact the Laboratory as soon as possible if the need for further testing is identified. If a client/user requests additional testing verbally, it must be followed up by a written confirmation. Food and Water Samples; Where practicable, food samples are frozen at -30ºC on the day of testing and retained in the laboratory for up to three weeks.
14 , Page 14 of 21 Water samples are stored in the fridge for up to a week. A sample will be held for longer than a week should further testing be required and/or until the final confirmed results are obtained. VTEC Isolates: VTEC isolates that are toxin positive are logged and stored indefinitely on freezer beads at -70ºC. COMPLAINTS PROCEDURE: A complaints procedure is in place in the. Initial complaints may be received by phone. All complaints will be fully investigated in accordance with our quality management system documented protocols (See File 8). TURNAROUND TIME: Turnaround times vary depending on the sample type and the tests requested. When sending a culture to PHL for VTEC testing, please pick from a non-selective medium or check the purity of the isolate before sending. Submitting a pure culture ensures that results are available within 24 hours. PHL PROTOCOL FOR PHONING RESULTS: Clinical results All preliminary positive results, of clinical significance are phoned to the relevant client. All results If a significant pathogen is detected, a preliminary result will be phoned to the client and then a final hard copy result dispatched. Such phone calls are documented on LIMS and the final report/cert of analysis. PHL POLICY ON FAXING AND ING REPORTS: The public health laboratory complies with the Health Service Executive s policies on electronic transmission of results.
15 , Page 15 of 21 A. SUMMARY OF VTEC AND CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY SERVICE. The PHL provides a National VTEC Reference service for clinical and environmental samples. This service is accessed by Directors of regional and primary clinical laboratories, the Environmental Health Service and Public Health Doctors who submit samples or presumptive isolates for confirmatory VTEC studies and detailed molecular strain characterization. Isolates for Verocytotoxin producing E. coli (VTEC) The range of services includes: Identification to genus and species level Phenotypic and molecular typing. A serodiagnostic service for E. coli O157, O26, O104,O145,O111 and O103 Clinical diagnostic specimens are submitted by Clinicians for general microbiology studies from long-term care facility patients or from community patients attending local general practices. The following are some recommended samples to be sent from patients with particular clinical syndromes - 1. GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT INFECTION Gastroenteritis Please note that this laboratory employs a cost-effective approach to the diagnosis of infectious diarrhoea. Not all specimens are examined for every pathogen. It is therefore important that clinical details or suspected diagnoses are included on the request form. Information that is of use when processing specimens includes: travel history, relationship to a particular food, prolonged diarrhoea, antibiotic use, suspected outbreak. The laboratory examines all stool samples routinely for: Salmonella sp. Shigella sp. VTEC (Verotoxigenic E. coli) Campylobacter sp. Clostridium difficile toxin detection and culture is performed on all specimens from patients over 2 years of age. Other pathogens e.g. Cryptosporidium, Yersinia, Vibrio, Aeromonas, ova and parasites etc. are only examined if the clinical details suggest that possibility or if specifically requested.
16 , Page 16 of 21 Ova and Parasite testing may be requested if the patient has had chronic unexplained diarrhoea, if the patient is immunocompromised or if there is a history of foreign travel. Rotavirus/Adenovirus detection is performed on patients under 5 years of age. Accreditation to ISO is pending for the detection of norovirus and other enteric viruses. If typhoid fever is suspected, please send a blood culture in addition to a faecal sample. When to send a stool specimen: Send a stool specimen to the laboratory when there are 3 liquid or very loose stools per day. There may be other symptoms suggestive of infectious diarrhoea e.g. abdominal pain or discomfort, nausea, faecal urgency, tenesmus, fever, blood or mucus in stools. Asymptomatic patients may be requested to submit samples in outbreak investigations. Within the hospital specimens must be sent to the laboratory immediately. In General Practice, please refrigerate if there is to be a delay in transporting the specimen. How many samples to send: One stool specimen is normally all that is required for culture. As microscopy for parasites is less sensitive, please send 3 specimens (but no more than 3) on different days as some parasites are excreted intermittently. If a worm is excreted, please send the worm and faeces sample. How much to send: Please fill the specimen container to between ¼ and ½ full. Please do not fill to the brim. 2. SUSPECTED BACTERAEMIA, SYSTEMIC INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE SYNDROME (SIRS), SEPSIS, SEPTIC SHOCK Blood cultures - For optimum sensitivity, two sets of blood cultures should be collected from separate sites within a 24 h period. These should be taken at least 20 min apart. For patients with suspected endocarditis, three sets should be collected. Method: Observe standard precautions, wash hands, carefully disinfect the skin with alcohol, allow to dry, wear sterile gloves, insert vacutainer into vein, collect 10 ml of blood into Oxoid SIGNAL blood culture BC100M and 10 ml into Haemoline Perf. diphas blood culture bottles Yeasts and fungi may be detected in the normal blood culture system.
17 , Page 17 of RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTION Tonsillopharyngitis: Send a throat swab. Please contact the laboratory if diphtheria or pertussis is suspected. Sinusitis: Using a syringe aspiration technique, a specially trained physician or an ENT surgeon can obtain material from maxillary, frontal, or other sinuses. Place the contents of the syringe into a sterile universal container. Otitis media: Usually no specimens are forwarded to the laboratory. Bronchitis: A good quality purulent or mucopurulent sputum specimen should be obtained, preferably before antimicrobial therapy. Pneumonia: It is not necessary to perform a full range of microbiological investigations on all patients with community-acquired pneumonia. The extent of investigation should be determined by the severity and clinical course. Specimens that should/may be sent include: Blood cultures should be obtained from all patients. Sputum: A good quality purulent or mucopurulent sputum specimen should be obtained, preferably before antimicrobial therapy although antimicrobial therapy should not be delayed unnecessarily while awaiting a sputum specimen. The specimen should be transported to the laboratory within 2 h. Salivary or mucosalivary specimens are unsuitable and as such are not processed. 4. URINE SPECIMENS When should you send a sample of urine? It is probably reasonable to treat a young sexually active female with symptoms of simple cystitis empirically but a urine specimen should be sent for microbiological examination from all other cases. In severe or complicated UTI, a follow-up specimen should be taken 5 days post completion of antibiotic therapy. Persistence of bacteriuria implies a structural abnormality.
18 , Page 18 of 21 A specimen should be sent from patients with symptoms as asymptomatic bacteriuria is generally not a cause for concern except in pregnant women and patients undergoing surgery on the g-u tract. The role of asymptomatic bacteriuria in children is controversial. The same applies to patients with in-dwelling urinary catheters. Bacteriuria occurs in the vast majority of patients who are catheterised for more than 5 days, a urine specimen should only be sent if there are symptoms or signs suggestive of a urinary or a systemic infection. What type of specimen should you send? Send a mid-stream specimen of urine (MSU) where possible. Patients should be instructed to pass a little urine into the toilet first, then pass enough urine into the specimen container to half fill it and finish urinating into the toilet. Never obtain urine from a bedpan or commode. Obtain about 10 ml of urine in a sterile universal container tighten the lid and transport to the laboratory without delay. Specimens should be processed within 4 h. In General Practice if transport to the laboratory has to be delayed, the specimen can be stored at 4 C for up to 48 h. A clean catch urine may also be obtained if the patient cannot co-operate. A catheter specimen of urine (CSU) may also be sent to the laboratory. Urine should be obtained from an already catheterised patient by a syringe and needle from the catheter before it enters the collection bag. Clean the access point with a swab saturated with 70% isopropyl alcohol and allow time to dry. Using a sterile syringe and needle (if necessary), aspirate the required amount of urine from the access point. Re-clean access point with a swab saturated with 70% isopropyl alcohol. 5. RECTAL SWABS Rectal swabs are used to detect rectal carriage of resistant organism s e.g. vancomycin resistant Enterococci or carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE). The tip of a sterile swab is passed approximately 2.5 cm beyond the anal sphincter. Rotate the swab gently and withdraw it into the appropriate transport medium.
19 , Page 19 of SKIN AND SUPERFICIAL WOUND SWABS Note that routine sampling of skin lesions that do not appear clinically infected should generally not be performed. If there is a clinically infected lesion, please send a sample of pus in a universal container wherever possible. Pus is always preferable to a swab. If there is insufficient specimen, then use Amies Transport swab, sample the infected area and send to the laboratory. 7. DEEP-SEATED WOUNDS/ABSCESSES/ POST-OPERATIVE WOUND INFECTION Please send a sample of pus in a universal container wherever possible. Pus is always preferable to a swab. If there is insufficient specimen, then use an Amies Transport Swab, sample the infected area and send to the laboratory. Clean the surface of the wound with sterile saline or water before taking the swab.
20 , Page 20 of 21 B. A SUMMARY OF THE FOOD TESTING SERVICE: The is designated an Official Laboratory approved for Microbiological testing under Statutory Instrument (SI) 117/2010: European Communities (Official Control of Foodstuffs) Regulations ISO ACCREDITATION: The is accredited to ISO by the Irish National Accreditation Board. ISO section 4.5 requires laboratories to review the competency of referral laboratories. A competent referral laboratory is one that complies with this International Standard. For information: The current scope of accreditation for the Laboratory is freely available as a pdf download from the INAB web site at: 101T.pdf Food samples are tested as per the FSAI/HSE service contract in addition to samples analysed from hospitals. A schedule of testing is agreed locally on an annual basis with the environmental health service (EHS) and hospital catering managers. National surveys are agreed annually with the Food Safety Authority of Ireland (FSAI). FOOD TESTING AVAILABLE: The following tests are available: Aerobic Colony Count Enumeration of Escherichia coli Enumeration of Staphylococcus aureus Enumeration of Bacillus species including presumptive Bacillus cereus Enumeration of Clostridium perfringens Detection of Salmonella species including S.enteritidis and S.typhimurium Detection and Enumeration of L.monocytogenes and Other Listeria species Detection of Campylobacter species including C.jejuni and C.coli Enumeration of Enterobacteriaceae Detection of Escherichia coli O157 using Immuno Magnetic Separation (IMS)
21 , Page 21 of 21 Detection of Escherichia coli O26 using Immuno Magnetic Separation (IMS) Detection of Salmonella species by VIDAS including S.enteritidis and S.typhimurium Verocytotoxin E. coli (VTEC) detection by PCR C. A SUMMARY OF THE WATER TESTING SERVICE. A local schedule of water testing is reviewed and agreed annually with the HSE, EHS and hospital clients. WATER TESTING AVAILABLE: Enumeration of Coliform Bacteria and E. coli by Membrane Filtration Enumeration and confirmation of Enterococci Enumeration and confirmation of Clostridium perfringens Enumeration of Total Plate Counts Enumeration and confirmation of Ps. aeruginosa Detection and enumeration of Coliform Bacteria and E. coli by IDEXX Quantitray Detection of E coli O157 using IMS Detection of E. coli O26 using IMS Detection of Salmonella spp. by VIDAS and/or by culture Detection and enumeration of Legionella species by membrane filtration Total Viable Count for Environmental/Endoscopy water Detection of mycobacterium species by membrane filtration Enumeration of S. aureus by Membrane Filtration (Non-Accredited) Verocytotoxin E. coli (VTEC) detection by PCR
National MRSA Reference Laboratory
 Author: Gráinne Brennan Date: 23/02/2017 Date of Issue: 23/02/2017 National MRSA Reference Laboratory User s Manual NMRSARL Users Manual Page 1 of 12 Table of Contents Page 1. Location... 3 2. Contact
Author: Gráinne Brennan Date: 23/02/2017 Date of Issue: 23/02/2017 National MRSA Reference Laboratory User s Manual NMRSARL Users Manual Page 1 of 12 Table of Contents Page 1. Location... 3 2. Contact
Role of the nurse in diagnosing infection: The right sample, every time
 BROUGHT TO YOU BY Role of the nurse in diagnosing infection: The right sample, every time The module has been written by Shanika Anne-Marie Crusz and Amelia Joseph Authors affiliation: Department of Clinical
BROUGHT TO YOU BY Role of the nurse in diagnosing infection: The right sample, every time The module has been written by Shanika Anne-Marie Crusz and Amelia Joseph Authors affiliation: Department of Clinical
Department Of Pathology MIC Collection Guidelines - Gastrointestinal (GI) Specimens Version#4 POLICY NO.
 1.1. Department Of Pathology MIC.20200.04 Collection Guidelines - Gastrointestinal (GI) Specimens Version#4 Department Microbiology POLICY NO. 839 PAGE NO. 1 OF 5 Printed copies are for reference only.
1.1. Department Of Pathology MIC.20200.04 Collection Guidelines - Gastrointestinal (GI) Specimens Version#4 Department Microbiology POLICY NO. 839 PAGE NO. 1 OF 5 Printed copies are for reference only.
SOFT Movement Survey of FMT Programs
 Appendix 1 (as supplied by the authors): Survey SOFT Movement Survey of FMT Programs Part 1: General Information about your Fecal Microbiota Transplant (FMT) Program 1) Please fill out the information
Appendix 1 (as supplied by the authors): Survey SOFT Movement Survey of FMT Programs Part 1: General Information about your Fecal Microbiota Transplant (FMT) Program 1) Please fill out the information
SPECIMEN COLLECTION FOR CULTURE OF BACTERIAL PATHOLOGENS QUICK REFERENCE
 1 Policy #: Subject: 611 (PLH-611-02) Effective Date: NA Reviewed Date: 2/1/2008 SPECIMEN COLLECTION FOR CULTURE OF BACTERIAL PATHOGENS QUICK REFERENCE Approved by: Laboratory Executive Director, Ed Hughes
1 Policy #: Subject: 611 (PLH-611-02) Effective Date: NA Reviewed Date: 2/1/2008 SPECIMEN COLLECTION FOR CULTURE OF BACTERIAL PATHOGENS QUICK REFERENCE Approved by: Laboratory Executive Director, Ed Hughes
Approval Signature: Original signed by Dr. Michel Tetreault Date of Approval: July Review Date: July 2017
 WRHA Infection Prevention and Control Program Operational Directives Admission Screening for Antibiotic Resistant Organisms (AROs): Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Vancomycin Resistant
WRHA Infection Prevention and Control Program Operational Directives Admission Screening for Antibiotic Resistant Organisms (AROs): Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Vancomycin Resistant
Policy # MI_ENT Department of Microbiology. Page Quality Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Quality Manual Version: 2.0 CURRENT 1 of 15 Prepared by QA Committee Issued by: Laboratory Manager Revision Date: 1/2/2018 Approved by Laboratory Director: Annual Review Date: 5/1/2018 Microbiologist-in-Chief
Quality Manual Version: 2.0 CURRENT 1 of 15 Prepared by QA Committee Issued by: Laboratory Manager Revision Date: 1/2/2018 Approved by Laboratory Director: Annual Review Date: 5/1/2018 Microbiologist-in-Chief
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Continuing Care. Urinary Tract Infections Clinical Checklist
 Antimicrobial Stewardship in Continuing Care Urinary Tract Infections Clinical Checklist December 2014 What is Antimicrobial Stewardship? Using the: right antimicrobial agent for a given diagnosis at the
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Continuing Care Urinary Tract Infections Clinical Checklist December 2014 What is Antimicrobial Stewardship? Using the: right antimicrobial agent for a given diagnosis at the
Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms (MDRO)
 Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms (MDRO) 2016 What are MDROs? Multi-drug resistant organisms, or MDROs, are bacteria resistant to current antibiotic therapy and therefore difficult to treat. MDROs can cause
Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms (MDRO) 2016 What are MDROs? Multi-drug resistant organisms, or MDROs, are bacteria resistant to current antibiotic therapy and therefore difficult to treat. MDROs can cause
Volume. December Infection. Notes. length of. cases as 90% 1 week. tonsillitis. First Line. sore throat / daily for 5 days. quinsy >4000.
 Volume 8; Number 22 LINCOLNSHIRE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT OF COMMONLYY OCCURRING INFECTIONS IN PRIMARY CARE: WINTER 2014/15 In this issue of the PACE Bulletin we present an update of our Guidelines
Volume 8; Number 22 LINCOLNSHIRE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT OF COMMONLYY OCCURRING INFECTIONS IN PRIMARY CARE: WINTER 2014/15 In this issue of the PACE Bulletin we present an update of our Guidelines
GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT INFECTIONS - ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT
 GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT INFECTIONS - ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT DRAFT AS CURRENTLY OUT FOR CONSULTATION BUT CAN BE UTILISED IN PRESENT FORMAT Name & Title Of Author: Date Revised: Approved by Committee/Group:
GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT INFECTIONS - ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT DRAFT AS CURRENTLY OUT FOR CONSULTATION BUT CAN BE UTILISED IN PRESENT FORMAT Name & Title Of Author: Date Revised: Approved by Committee/Group:
Schedule of Accreditation
 Schedule of Accreditation Organisation Name INAB Reg No Contact Name Address Saolta University Health Care Group Sligo University Hospital Microbiology Department 321MT Anne O'Toole Contact Phone No 071
Schedule of Accreditation Organisation Name INAB Reg No Contact Name Address Saolta University Health Care Group Sligo University Hospital Microbiology Department 321MT Anne O'Toole Contact Phone No 071
Campylobacter species
 ISSUE NO. 1 SEPTEMBER 2011 1. What are Campylobacter spp.? Campylobacter spp. are microaerophilic, Gram-negative, spiral shaped cells with corkscrew-like motility. They are the most common cause of bacterial
ISSUE NO. 1 SEPTEMBER 2011 1. What are Campylobacter spp.? Campylobacter spp. are microaerophilic, Gram-negative, spiral shaped cells with corkscrew-like motility. They are the most common cause of bacterial
Prevention & Management of Infection post Trans Rectal Ultrasound (TRUS) biopsy
 Prevention & Management of Infection post Trans Rectal Ultrasound (TRUS) biopsy Dr. Fidelma Fitzpatrick Consultant Microbiologist, Co-chair, NCCP Prostate Bx Infection Project Board Fidelma.fitzpatrick@hse.ie
Prevention & Management of Infection post Trans Rectal Ultrasound (TRUS) biopsy Dr. Fidelma Fitzpatrick Consultant Microbiologist, Co-chair, NCCP Prostate Bx Infection Project Board Fidelma.fitzpatrick@hse.ie
SCOTTISH MRSA REFERENCE LABORATORY
 Title SCOTTISH MRSA REFERENCE LABORATORY LABORATORY PROCEDURE NUMBER / VERSION User Manual DATE OF ISSUE 20/01/2017 REVIEW INTERVAL AUTHORISED BY AUTHOR 1 Year Dr. B. Jones Dr E. Dickson COPY 1 of 1 Master
Title SCOTTISH MRSA REFERENCE LABORATORY LABORATORY PROCEDURE NUMBER / VERSION User Manual DATE OF ISSUE 20/01/2017 REVIEW INTERVAL AUTHORISED BY AUTHOR 1 Year Dr. B. Jones Dr E. Dickson COPY 1 of 1 Master
Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae Multi Drug Resistant Organism Management Procedure. (IPC Manual)
 Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae Multi Drug Resistant Organism Management Procedure (IPC Manual) DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 1 Ratified by: Clinical Policies Review and Approval Group Date ratified:
Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae Multi Drug Resistant Organism Management Procedure (IPC Manual) DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 1 Ratified by: Clinical Policies Review and Approval Group Date ratified:
Antibiotic stewardship in long term care
 Antibiotic stewardship in long term care Shira Doron, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Geographic Medicine and Infectious Diseases Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA Consultant to Massachusetts
Antibiotic stewardship in long term care Shira Doron, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Geographic Medicine and Infectious Diseases Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA Consultant to Massachusetts
Your Guide to Managing. Multi Drug-resistant Organisms (MDROs)
 Agency for Integrated Care 5 Maxwell Road #10-00 Tower Block MND Complex Singapore 069110 Singapore Silver Line: 1800-650-6060 Email: enquiries@aic.sg Website: www.silverpages.sg Facebook: www.facebook.com/carerssg
Agency for Integrated Care 5 Maxwell Road #10-00 Tower Block MND Complex Singapore 069110 Singapore Silver Line: 1800-650-6060 Email: enquiries@aic.sg Website: www.silverpages.sg Facebook: www.facebook.com/carerssg
CLINICAL PROTOCOL FOR COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA. SCOPE: Western Australia. CORB score equal or above 1. All criteria must be met:
 CLINICAL PROTOCOL F COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA SCOPE: Western Australia All criteria must be met: Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria CB score equal or above 1. Mild/moderate pneumonia confirmed by
CLINICAL PROTOCOL F COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA SCOPE: Western Australia All criteria must be met: Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria CB score equal or above 1. Mild/moderate pneumonia confirmed by
Protocol for Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Urinary Isolates in Scotland
 Protocol for Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Urinary Isolates in Scotland Version 1.0 23 December 2011 General enquiries and contact details This is the first version (1.0) of the Protocol
Protocol for Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Urinary Isolates in Scotland Version 1.0 23 December 2011 General enquiries and contact details This is the first version (1.0) of the Protocol
Originally posted February 13, Update: March 26, 2018
 UPDATED: FDA Investigates Pattern of Contamination in Certain Raw Pet Foods Made by Arrow Reliance Inc., Including Darwin s Natural Pet Products and ZooLogics Pet Food Originally posted February 13, 2018
UPDATED: FDA Investigates Pattern of Contamination in Certain Raw Pet Foods Made by Arrow Reliance Inc., Including Darwin s Natural Pet Products and ZooLogics Pet Food Originally posted February 13, 2018
B. PACKAGE LEAFLET 1
 B. PACKAGE LEAFLET 1 PACKAGE LEAFLET FOR: Cadorex 300 mg/ml solution for injection for cattle, sheep and pigs 1. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER AND OF THE MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION
B. PACKAGE LEAFLET 1 PACKAGE LEAFLET FOR: Cadorex 300 mg/ml solution for injection for cattle, sheep and pigs 1. NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER AND OF THE MANUFACTURING AUTHORISATION
SCOTTISH MRSA REFERENCE LABORATORY
 Title SCOTTISH MRSA REFERENCE LABORATORY LABORATORY PROCEDURE NUMBER / VERSION User Manual DATE OF ISSUE 17/05/2014 REVIEW INTERVAL AUTHORISED BY AUTHOR 2 Years Dr. B. Jones B. Cosgrove COPY 1 of 1 Master
Title SCOTTISH MRSA REFERENCE LABORATORY LABORATORY PROCEDURE NUMBER / VERSION User Manual DATE OF ISSUE 17/05/2014 REVIEW INTERVAL AUTHORISED BY AUTHOR 2 Years Dr. B. Jones B. Cosgrove COPY 1 of 1 Master
Infection Control and Standard Precautions
 Home Care Aide Training Guide Infection Control and Standard Precautions Pre-Service Training Course #1 Home Care Aide Orientation Training Manual: Infection Control & Standard Precautions Page 2 Table
Home Care Aide Training Guide Infection Control and Standard Precautions Pre-Service Training Course #1 Home Care Aide Orientation Training Manual: Infection Control & Standard Precautions Page 2 Table
Overview of Infection Control and Prevention
 Overview of Infection Control and Prevention Review of the Cesarean-section Antibiotic Prophylaxis Program in Jordan and Workshop on Rational Medicine Use and Infection Control Terry Green and Salah Gammouh
Overview of Infection Control and Prevention Review of the Cesarean-section Antibiotic Prophylaxis Program in Jordan and Workshop on Rational Medicine Use and Infection Control Terry Green and Salah Gammouh
Antimicrobial Resistance, Everyone s Fight. Charlotte Makanga Consultant Antimicrobial Pharmacist Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board
 Antimicrobial Resistance, Everyone s Fight Charlotte Makanga Consultant Antimicrobial Pharmacist Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board Antimicrobial Resistance Antimicrobial resistance happens when microorganisms
Antimicrobial Resistance, Everyone s Fight Charlotte Makanga Consultant Antimicrobial Pharmacist Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board Antimicrobial Resistance Antimicrobial resistance happens when microorganisms
Swab Sampling Policy & Procedures
 Swab Sampling Policy & Procedures G. Fish Chief Steward G. Fish - Chief Steward Effective 3 rd April 2014 Table of Contents Policy Objectives... 3 Overview of the Procedures... 3 Security Measures Pre
Swab Sampling Policy & Procedures G. Fish Chief Steward G. Fish - Chief Steward Effective 3 rd April 2014 Table of Contents Policy Objectives... 3 Overview of the Procedures... 3 Security Measures Pre
Please distribute a copy of this information to each provider in your organization.
 HEALTH ADVISORY TO: Physicians and other Healthcare Providers Please distribute a copy of this information to each provider in your organization. Questions regarding this information may be directed to
HEALTH ADVISORY TO: Physicians and other Healthcare Providers Please distribute a copy of this information to each provider in your organization. Questions regarding this information may be directed to
Delayed Prescribing for Minor Infections Resource Pack for Prescribers
 Delayed Prescribing for Minor Infections Resource Pack for Prescribers Background: Antibiotic resistance is an alarming threat to modern healthcare, and infectious illness remains a major global threat
Delayed Prescribing for Minor Infections Resource Pack for Prescribers Background: Antibiotic resistance is an alarming threat to modern healthcare, and infectious illness remains a major global threat
03/09/2014. Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course. Talk outline
 Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course 2014 What is healthcare-associated infection (HCAI), antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs)? Why we should be worried?
Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course 2014 What is healthcare-associated infection (HCAI), antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs)? Why we should be worried?
Liofilchem Chromatic Chromogenic culture media for microbial identification and for the screening of antimicrobial resistance mechanisms
 Liofilchem Chromatic Chromogenic culture media for microbial identification and for the screening of antimicrobial resistance mechanisms Microbiology Products since 1983 Liofilchem Chromatic ESBL Selective
Liofilchem Chromatic Chromogenic culture media for microbial identification and for the screening of antimicrobial resistance mechanisms Microbiology Products since 1983 Liofilchem Chromatic ESBL Selective
Dr Eleri Davies. Consultant Microbiologist and Infection Control Doctor, Public Health Wales NHS Trust
 Dr Eleri Davies Consultant Microbiologist and Infection Control Doctor, Public Health Wales NHS Trust Antimicrobial stewardship What is it? Why is it important? Treatment and management of catheter-associated
Dr Eleri Davies Consultant Microbiologist and Infection Control Doctor, Public Health Wales NHS Trust Antimicrobial stewardship What is it? Why is it important? Treatment and management of catheter-associated
Course: Microbiology in Health and Disease
 SYLLABUS BIOL 2900 SECTION D SPRING 2012 Course: Microbiology in Health and Disease BIPIN PATEL Office Hours: Before or after Class or by appointment Semester Begins JANUARY 09 TO MAY 04 2012 2900 D 4.00
SYLLABUS BIOL 2900 SECTION D SPRING 2012 Course: Microbiology in Health and Disease BIPIN PATEL Office Hours: Before or after Class or by appointment Semester Begins JANUARY 09 TO MAY 04 2012 2900 D 4.00
Course: Microbiology in Health and Disease Office Hours: Before or after Class or by appointment
 SYLLABUS BIOL 2900 SECTIONS C AND D Spring, 2011 Course: Microbiology in Health and Disease Office Hours: Before or after Class or by appointment Semester Begins on January 10, 2011 and ends on May 2,
SYLLABUS BIOL 2900 SECTIONS C AND D Spring, 2011 Course: Microbiology in Health and Disease Office Hours: Before or after Class or by appointment Semester Begins on January 10, 2011 and ends on May 2,
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA IN ADULTS
 Version 3.1 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA IN ADULTS Date ratified June 2008 Updated March 2009 Review date June 2010 Ratified by Authors Consultation Evidence base Changes
Version 3.1 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA IN ADULTS Date ratified June 2008 Updated March 2009 Review date June 2010 Ratified by Authors Consultation Evidence base Changes
Biological Threat Fact Sheets
 Biological Threat Fact Sheets Anthrax Agent: Bacillus anthracis There are three clinical forms of B. anthracis which are determined by route of entry: Pulmonary or Inhalation BT implications Cutaneous
Biological Threat Fact Sheets Anthrax Agent: Bacillus anthracis There are three clinical forms of B. anthracis which are determined by route of entry: Pulmonary or Inhalation BT implications Cutaneous
Antibiotics in the trenches: An ER Doc s Perspective
 Antibiotics in the trenches: An ER Doc s Perspective Peter Currie, MD Medical Director for Quality Emergency Physicians Professional Association (EPPA) Agenda Emergency Medicine Specific Disease Processes
Antibiotics in the trenches: An ER Doc s Perspective Peter Currie, MD Medical Director for Quality Emergency Physicians Professional Association (EPPA) Agenda Emergency Medicine Specific Disease Processes
An Approach to Appropriate Antibiotic Prescribing in Outpatient and LTC Settings?
 An Approach to Appropriate Antibiotic Prescribing in Outpatient and LTC Settings? Dr. Andrew Morris Antimicrobial Stewardship ProgramMt. Sinai Hospital University Health Network amorris@mtsinai.on.ca andrew.morris@uhn.ca
An Approach to Appropriate Antibiotic Prescribing in Outpatient and LTC Settings? Dr. Andrew Morris Antimicrobial Stewardship ProgramMt. Sinai Hospital University Health Network amorris@mtsinai.on.ca andrew.morris@uhn.ca
NATIONAL REFERENCE LABORATORY FOR Escherichia coli (VTEC) ROMANIA
 NATIONAL REFERENCE LABORATORY FOR Escherichia coli (VTEC) ROMANIA INSTITUTE FOR HYGIENE AND VETERINARY PUBLIC HEALTH BUCHAREST NATIONAL REFERENCE INSTITUTE IN ANIMAL ORIGIN PRODUCTS AND CERTAIN FOODSTUFFS
NATIONAL REFERENCE LABORATORY FOR Escherichia coli (VTEC) ROMANIA INSTITUTE FOR HYGIENE AND VETERINARY PUBLIC HEALTH BUCHAREST NATIONAL REFERENCE INSTITUTE IN ANIMAL ORIGIN PRODUCTS AND CERTAIN FOODSTUFFS
Hand washing/hand hygiene reduces the number of microorganisms on the hands and is the most important practice to prevent the spread of infection.
 1. Hand Hygiene Quick Reference Chart Hand washing/hand hygiene reduces the number of microorganisms on the hands and is the most important practice to prevent the spread of infection. WHEN Before: Direct
1. Hand Hygiene Quick Reference Chart Hand washing/hand hygiene reduces the number of microorganisms on the hands and is the most important practice to prevent the spread of infection. WHEN Before: Direct
The Rise of Antibiotic Resistance: Is It Too Late?
 The Rise of Antibiotic Resistance: Is It Too Late? Paul D. Holtom, MD Professor of Medicine and Orthopaedics USC Keck School of Medicine None DISCLOSURES THE PROBLEM Antibiotic resistance is one of the
The Rise of Antibiotic Resistance: Is It Too Late? Paul D. Holtom, MD Professor of Medicine and Orthopaedics USC Keck School of Medicine None DISCLOSURES THE PROBLEM Antibiotic resistance is one of the
Objectives. Basic Microbiology. Patient related. Environment related. Organism related 10/12/2017
 Basic Microbiology Vaneet Arora, MD MPH D(ABMM) FCCM Associate Director of Clinical Microbiology, UK HealthCare Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Kentucky
Basic Microbiology Vaneet Arora, MD MPH D(ABMM) FCCM Associate Director of Clinical Microbiology, UK HealthCare Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Kentucky
Cork and Kerry SARI Newsletter; Vol. 2 (2), December 2006
 Cork and SARI Newsletter; Vol. 2 (2), December 6 Item Type Newsletter Authors Murray, Deirdre;O'Connor, Nuala;Condon, Rosalind Download date 31/1/18 15:27:31 Link to Item http://hdl.handle.net/1147/67296
Cork and SARI Newsletter; Vol. 2 (2), December 6 Item Type Newsletter Authors Murray, Deirdre;O'Connor, Nuala;Condon, Rosalind Download date 31/1/18 15:27:31 Link to Item http://hdl.handle.net/1147/67296
Infection Comments First Line Agents Penicillin Allergy History of multiresistant. line treatment: persist for >7 days they may be
 Gastrointestinal Infections Infection Comments First Line Agents Penicillin Allergy History of multiresistant Campylobacter Antibiotics not recommended. Erythromycin 250mg PO 6 Alternative to first N/A
Gastrointestinal Infections Infection Comments First Line Agents Penicillin Allergy History of multiresistant Campylobacter Antibiotics not recommended. Erythromycin 250mg PO 6 Alternative to first N/A
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL. NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 705. Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 705 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF WOUNDS (FIRST AID) 1. PURPOSE: Proper
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 705 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF WOUNDS (FIRST AID) 1. PURPOSE: Proper
9/30/2016. Dr. Janell Mayer, Pharm.D., CGP, BCPS Dr. Lindsey Votaw, Pharm.D., CGP, BCPS
 Dr. Janell Mayer, Pharm.D., CGP, BCPS Dr. Lindsey Votaw, Pharm.D., CGP, BCPS 1 2 Untoward Effects of Antibiotics Antibiotic resistance Adverse drug events (ADEs) Hypersensitivity/allergy Drug side effects
Dr. Janell Mayer, Pharm.D., CGP, BCPS Dr. Lindsey Votaw, Pharm.D., CGP, BCPS 1 2 Untoward Effects of Antibiotics Antibiotic resistance Adverse drug events (ADEs) Hypersensitivity/allergy Drug side effects
INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN-ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT
 INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN-ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT Name & Title Of Authors: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Dr N Rao,Consultant Paediatrician Dr V Desai Consultant Paediatrician Date Revised: DEC 2015
INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN-ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT Name & Title Of Authors: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Dr N Rao,Consultant Paediatrician Dr V Desai Consultant Paediatrician Date Revised: DEC 2015
A patient s guide to. MRSA - Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
 A patient s guide to MRSA - Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus 1 What is MRSA? There are lots of micro-organisms (germs) on our skin. They are in the air we breathe, the water we drink, and the
A patient s guide to MRSA - Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus 1 What is MRSA? There are lots of micro-organisms (germs) on our skin. They are in the air we breathe, the water we drink, and the
Septicaemia Definitions 1
 Septicaemia Definitions 1 Term Definition Bacteraemia Systemic Inflammatory response (SIRS) Sepsis Bacteria that can be cultured from the blood stream The systemic response to a wide range of stresses.
Septicaemia Definitions 1 Term Definition Bacteraemia Systemic Inflammatory response (SIRS) Sepsis Bacteria that can be cultured from the blood stream The systemic response to a wide range of stresses.
Rules 26: Compulsory Veterinary Community Service Facilities & Regulatory Service Facilities
 Veterinary Facility Evaluated: Rule 26: Compulsory Veterinary Community Service (CCS) Facilities & Regulatory Service Facilities NAME OF THE FACILITY: BY TICKING YES TO ANY RULE ON THIS CHECKLIST YOU AGREE
Veterinary Facility Evaluated: Rule 26: Compulsory Veterinary Community Service (CCS) Facilities & Regulatory Service Facilities NAME OF THE FACILITY: BY TICKING YES TO ANY RULE ON THIS CHECKLIST YOU AGREE
THIS PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION HAS BEEN APPROVED on behalf of NHS Fife by:
 Patient Group Direction for Named Community Pharmacists to Supply CHLORAMPHENICOL EYE DROPS 0.5% To patients aged 1 year and older Under the Minor Ailments Service. Number 114 Issued October 2016 Issue
Patient Group Direction for Named Community Pharmacists to Supply CHLORAMPHENICOL EYE DROPS 0.5% To patients aged 1 year and older Under the Minor Ailments Service. Number 114 Issued October 2016 Issue
A solution for current veterinary challenges
 A solution for current veterinary challenges 2 www.jakmarketing.co.uk Introduction The current disease challenge in veterinary practices is increasingly coming from pathogens that are resistant to both
A solution for current veterinary challenges 2 www.jakmarketing.co.uk Introduction The current disease challenge in veterinary practices is increasingly coming from pathogens that are resistant to both
BIOL 2900 D 4.00 Microbiology in Health/Disease
 SYLLABUS BIOL 2900 - D Spring, 2017 Course: Microbiology in Health and Disease Instructor: Prafull C. Shah Office Hours: Before or after classes, or by appointment by Email to pcshah@valdosta.edu. Semester
SYLLABUS BIOL 2900 - D Spring, 2017 Course: Microbiology in Health and Disease Instructor: Prafull C. Shah Office Hours: Before or after classes, or by appointment by Email to pcshah@valdosta.edu. Semester
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times
 Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
Multidrug Resistant Organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff)
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Multidrug Resistant Organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff) This information explains multidrug resistant organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff),
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Multidrug Resistant Organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff) This information explains multidrug resistant organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff),
Wildlife DNA Sampling Guide. Instructions for the Wildlife DNA Sampling Kit
 Wildlife DNA Sampling Guide Instructions for the Wildlife DNA Sampling Kit Wildlife DNA Sampling Guide This guide has been produced by the PAW Forensic Working Group (FWG) and is designed to accompany
Wildlife DNA Sampling Guide Instructions for the Wildlife DNA Sampling Kit Wildlife DNA Sampling Guide This guide has been produced by the PAW Forensic Working Group (FWG) and is designed to accompany
Prescribing Guidelines for Outpatient Antimicrobials in Otherwise Healthy Children
 Prescribing Guidelines for Outpatient Antimicrobials in Otherwise Healthy Children Prescribing Antimicrobials for Common Illnesses When treating common illnesses such as ear infections and strep throat,
Prescribing Guidelines for Outpatient Antimicrobials in Otherwise Healthy Children Prescribing Antimicrobials for Common Illnesses When treating common illnesses such as ear infections and strep throat,
Infection Prevention Highlights for the Medical Staff. Pamela Rohrbach MSN, RN, CIC Director of Infection Prevention
 Highlights for the Medical Staff Pamela Rohrbach MSN, RN, CIC Director of Infection Prevention Standard Precautions every patient every time a. Hand Hygiene b. Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Highlights for the Medical Staff Pamela Rohrbach MSN, RN, CIC Director of Infection Prevention Standard Precautions every patient every time a. Hand Hygiene b. Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
MRSA Screening Programme National Targeted Rollout. MRSA Screening
 National Targeted Rollout. MRSA Screening A resource pack to support the training of healthcare staff 5th February 2010 Xxxx Learning Outcomes Xxxx On completion of this course you should be able to: Give
National Targeted Rollout. MRSA Screening A resource pack to support the training of healthcare staff 5th February 2010 Xxxx Learning Outcomes Xxxx On completion of this course you should be able to: Give
To guide safe and appropriate selection of antibiotic therapy for Peritoneal Dialysis patients.
 Nephrology Directorate Subject: Objective: Prepared by: Aintree Antibiotic Guidelines for Peritoneal Dialysis (PD): Catheter Insertion, and the Diagnosis and Treatment of PD Peritonitis and Exit-Site Infections.
Nephrology Directorate Subject: Objective: Prepared by: Aintree Antibiotic Guidelines for Peritoneal Dialysis (PD): Catheter Insertion, and the Diagnosis and Treatment of PD Peritonitis and Exit-Site Infections.
Volume 2; Number 16 October 2008
 Volume 2; Number 16 October 2008 What s new this month NHS Lincolnshire have launched a public information campaign designed to raise public awareness of the risks associated with the inappropriate use
Volume 2; Number 16 October 2008 What s new this month NHS Lincolnshire have launched a public information campaign designed to raise public awareness of the risks associated with the inappropriate use
BY TICKING YES TO ANY RULE ON THIS CHECKLIST YOU AGREE THAT THE FACILITY ALREADY COMPLIES WITH THAT STANDARD.
 Veterinary Facility Evaluated: Rule 34: Facilities for Consultants in Industry and other Consultancies NAME OF THE FACILITY: BY TICKING YES TO ANY RULE ON THIS CHECKLIST YOU AGREE THAT THE FACILITY ALREADY
Veterinary Facility Evaluated: Rule 34: Facilities for Consultants in Industry and other Consultancies NAME OF THE FACILITY: BY TICKING YES TO ANY RULE ON THIS CHECKLIST YOU AGREE THAT THE FACILITY ALREADY
Recommendations on Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Ireland
 Recommendations on Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Ireland Background This discussion document was prepared by the Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Surveillance Working Group, one of a number
Recommendations on Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Ireland Background This discussion document was prepared by the Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Surveillance Working Group, one of a number
E-BOOK # BACTERIAL DISEASES IN HUMANS EBOOK
 15 November, 2017 E-BOOK # BACTERIAL DISEASES IN HUMANS EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 475.49 KB 0 E-BOOK # BACTERIAL DISEASES IN HUMANS EBOOK Communicable diseases, also known as infectious diseases or
15 November, 2017 E-BOOK # BACTERIAL DISEASES IN HUMANS EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 475.49 KB 0 E-BOOK # BACTERIAL DISEASES IN HUMANS EBOOK Communicable diseases, also known as infectious diseases or
Treatment of peritonitis in patients receiving peritoneal dialysis Antibiotic Guidelines. Contents
 Treatment of peritonitis in patients receiving Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Jude Allen (Pharmacist) Additional author(s): Dr David Lewis, Dr Dimitrios Poulikakos,
Treatment of peritonitis in patients receiving Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Jude Allen (Pharmacist) Additional author(s): Dr David Lewis, Dr Dimitrios Poulikakos,
CANINE PARVO VIRUS HEALTHY HINTS I S S U E 1 GET THE BEST FOR YOUR BEST FRIENDS!
 CANINE PARVO VIRUS I S S U E 1 HEALTHY HINTS GET THE BEST FOR YOUR BEST FRIENDS! WHAT IS CANINE PARVO VIRUS? Parvovirus is a HIGHLY CONTAGIOUS virus that attacks the intestines and causes sloughing of
CANINE PARVO VIRUS I S S U E 1 HEALTHY HINTS GET THE BEST FOR YOUR BEST FRIENDS! WHAT IS CANINE PARVO VIRUS? Parvovirus is a HIGHLY CONTAGIOUS virus that attacks the intestines and causes sloughing of
Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version
 Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED 2018 Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY NO. IC-122 Policy Group Infection Control
Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED 2018 Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY NO. IC-122 Policy Group Infection Control
Meropenem for all? Midge Asogan ICU Fellow (also ID AT)
 Meropenem for all? Midge Asogan ICU Fellow (also ID AT) Infections Common reason for presentation to ICU Community acquired - vs nosocomial - new infection acquired within hospital environment Treatment
Meropenem for all? Midge Asogan ICU Fellow (also ID AT) Infections Common reason for presentation to ICU Community acquired - vs nosocomial - new infection acquired within hospital environment Treatment
Mastitis and On-Farm Milk Cultures - A Field Study - Part 1
 Mastitis and On-Farm Milk Cultures - A Field Study - Part 1 This two-part article discusses the results of a research project undertaken by Dr. Tim Olchowy, Senior Lecturer in Livestock Medicine, School
Mastitis and On-Farm Milk Cultures - A Field Study - Part 1 This two-part article discusses the results of a research project undertaken by Dr. Tim Olchowy, Senior Lecturer in Livestock Medicine, School
Treatment of septic peritonitis
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Treatment of septic peritonitis Author : Andrew Linklater Categories : Companion animal, Vets Date : November 2, 2016 Septic
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Treatment of septic peritonitis Author : Andrew Linklater Categories : Companion animal, Vets Date : November 2, 2016 Septic
BreenLab - Molecular Cytogenetic Investigation of Soft Tissue Sarcoma General information and sample submission requirements
 PARTICIPANTS NEEDED FOR RESEARCH ON CANINE CANCER THE STUDY The research project Cellular Genomics- A molecular cytogenetics investigation of canine soft tissue sarcoma is part of Dr. Matthew Breen s laboratory
PARTICIPANTS NEEDED FOR RESEARCH ON CANINE CANCER THE STUDY The research project Cellular Genomics- A molecular cytogenetics investigation of canine soft tissue sarcoma is part of Dr. Matthew Breen s laboratory
Guidelines on prescribing antibiotics. For physicians and others in Denmark
 Guidelines on prescribing antibiotics 2013 For physicians and others in Denmark Guidelines on prescribing antibiotics For physicians and others in Denmark 2013 by the Danish Health and Medicines Authority.
Guidelines on prescribing antibiotics 2013 For physicians and others in Denmark Guidelines on prescribing antibiotics For physicians and others in Denmark 2013 by the Danish Health and Medicines Authority.
Commonwealth of Kentucky Antibiotic Stewardship Practice Assessment For Long-Term Care Facilities
 Commonwealth of Kentucky Antibiotic Stewardship Practice Assessment For Long-Term Care Facilities Introduction As the problem of antibiotic resistance continues to worsen in all healthcare setting, we
Commonwealth of Kentucky Antibiotic Stewardship Practice Assessment For Long-Term Care Facilities Introduction As the problem of antibiotic resistance continues to worsen in all healthcare setting, we
Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections. For National Patient Safety Goal
 Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections For National Patient Safety Goal 07.03.01 2009 Methicillin Resistant Staphlococcus aureus (MRSA) About 3-8% of the population at large is a carrier
Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections For National Patient Safety Goal 07.03.01 2009 Methicillin Resistant Staphlococcus aureus (MRSA) About 3-8% of the population at large is a carrier
The Disinfecting Effect of Electrolyzed Water Produced by GEN-X-3. Laboratory of Diagnostic Medicine, College of Medicine, Soonchunhyang University
 The Disinfecting Effect of Electrolyzed Water Produced by GEN-X-3 Laboratory of Diagnostic Medicine, College of Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Tae-yoon Choi ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: The use of disinfectants
The Disinfecting Effect of Electrolyzed Water Produced by GEN-X-3 Laboratory of Diagnostic Medicine, College of Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Tae-yoon Choi ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: The use of disinfectants
EASTER BUSH PATHOLOGY, R(D)SVS POST MORTEM ROOM CODE OF PRACTICE CONTENTS
 EASTER BUSH PATHOLOGY, R(D)SVS POST MORTEM ROOM CODE OF PRACTICE 2015 CONTENTS Introduction 2 General 2 Routine diagnostic service 2 Working in the PM room 4 Research Work 5 Disposal 5 Excluded necropsies
EASTER BUSH PATHOLOGY, R(D)SVS POST MORTEM ROOM CODE OF PRACTICE 2015 CONTENTS Introduction 2 General 2 Routine diagnostic service 2 Working in the PM room 4 Research Work 5 Disposal 5 Excluded necropsies
DRAFT DRAFT. Paediatric Antibiotic Prescribing Guideline. May
 Paediatric Antibiotic Prescribing Guideline www.oxfdahsn.g/children Magdalen Centre Nth, 1 Robert Robinson Avenue, Oxfd Science Park, OX4 4GA, United Kingdom t: +44(0) 1865 784944 e: info@oxfdahsn.g Follow
Paediatric Antibiotic Prescribing Guideline www.oxfdahsn.g/children Magdalen Centre Nth, 1 Robert Robinson Avenue, Oxfd Science Park, OX4 4GA, United Kingdom t: +44(0) 1865 784944 e: info@oxfdahsn.g Follow
Dr Steve Holden Consultant Microbiologist Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust
 Dr Steve Holden Consultant Microbiologist Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Clinical Case 38 yrold man Renal replacement (CAPD) since 2011 Unexplained ESRF Visited Pakistan for 3 months end of
Dr Steve Holden Consultant Microbiologist Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Clinical Case 38 yrold man Renal replacement (CAPD) since 2011 Unexplained ESRF Visited Pakistan for 3 months end of
Summary of the latest data on antibiotic resistance in the European Union
 Summary of the latest data on antibiotic resistance in the European Union EARS-Net surveillance data November 2017 For most bacteria reported to the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network
Summary of the latest data on antibiotic resistance in the European Union EARS-Net surveillance data November 2017 For most bacteria reported to the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network
FDA Announcement. For Immediate Release. Contact. Announcement. February 13, Consumers
 FDA Announcement FDA Investigates Pattern of Contamination in Certain Raw Pet Foods Made by Arrow Reliance Inc., Including Darwin s Natural Pet Products and ZooLogics Pet Food For Immediate Release February
FDA Announcement FDA Investigates Pattern of Contamination in Certain Raw Pet Foods Made by Arrow Reliance Inc., Including Darwin s Natural Pet Products and ZooLogics Pet Food For Immediate Release February
Running head: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE 1
 Running head: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE 1 Clostridium difficile Infection Christy Lee Fenton Mountainland Applied Technology College CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE 2 Clostridium difficile Infection Approximately 200,000
Running head: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE 1 Clostridium difficile Infection Christy Lee Fenton Mountainland Applied Technology College CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE 2 Clostridium difficile Infection Approximately 200,000
MICRO-ORGANISMS by COMPANY PROFILE
 MICRO-ORGANISMS by COMPANY PROFILE 2017 1 SAPROPHYTES AND PATHOGENES SAPROPHYTES Not dangerous PATHOGENES Inducing diseases Have to be eradicated WHERE ARE THERE? EVERYWHERE COMPANY PROFILE 2017 3 MICROORGANISMS
MICRO-ORGANISMS by COMPANY PROFILE 2017 1 SAPROPHYTES AND PATHOGENES SAPROPHYTES Not dangerous PATHOGENES Inducing diseases Have to be eradicated WHERE ARE THERE? EVERYWHERE COMPANY PROFILE 2017 3 MICROORGANISMS
This information is intended to give guidance for vets and CP staff and volunteers in the treatment of a CP cat with diarrhoea.
 Diarrhoea Procedures This information is intended to give guidance for vets and CP staff and volunteers in the treatment of a CP cat with diarrhoea. In the shelter environment acute (sudden onset) diarrhoea
Diarrhoea Procedures This information is intended to give guidance for vets and CP staff and volunteers in the treatment of a CP cat with diarrhoea. In the shelter environment acute (sudden onset) diarrhoea
Sites of IM injections : 1. Ventrogluteal site: site is in the gluteus medius muscle, which lies over the gluteus minimus. 2. Vastus lateralis site:
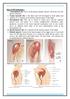 Sites of IM injections : 1. Ventrogluteal site: site is in the gluteus medius muscle, which lies over the gluteus minimus. 2. Vastus lateralis site: is the thick and well developed in both adults and children.
Sites of IM injections : 1. Ventrogluteal site: site is in the gluteus medius muscle, which lies over the gluteus minimus. 2. Vastus lateralis site: is the thick and well developed in both adults and children.
ANTIBIOTIC USE GUIDELINES FOR URINARY TRACT AND RESPIRATORY DISEASE
 ANTIBIOTIC USE GUIDELINES FOR URINARY TRACT AND RESPIRATORY DISEASE Jane Sykes, BVSc(Hons), PhD, DACVIM (SAIM) School of Veterinary Medicine Dept. of Medicine & Epidemiology University of California Davis,
ANTIBIOTIC USE GUIDELINES FOR URINARY TRACT AND RESPIRATORY DISEASE Jane Sykes, BVSc(Hons), PhD, DACVIM (SAIM) School of Veterinary Medicine Dept. of Medicine & Epidemiology University of California Davis,
FELINE LOWER URINARY TRACT DISEASE (Sometimes known as feline urological syndrome)
 FELINE LOWER URINARY TRACT DISEASE (Sometimes known as feline urological syndrome) Introduction Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) is sometimes still referred to as feline urological syndrome or
FELINE LOWER URINARY TRACT DISEASE (Sometimes known as feline urological syndrome) Introduction Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) is sometimes still referred to as feline urological syndrome or
Gynaecological Surgery in Adults Surgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis
 Gynaecological Surgery in Adults Surgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date
Gynaecological Surgery in Adults Surgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date
A retrospective analysis of urine culture results issued by the microbiology department, Teaching Hospital, Karapitiya
 A retrospective analysis of urine culture results issued by the microbiology department, Teaching Hospital, Karapitiya LU Edirisinghe 1, D Vidanagama 2 1 Senior Registrar in Medicine, 2 Consultant Microbiologist,
A retrospective analysis of urine culture results issued by the microbiology department, Teaching Hospital, Karapitiya LU Edirisinghe 1, D Vidanagama 2 1 Senior Registrar in Medicine, 2 Consultant Microbiologist,
Author of PGD: Adrian MacKenzie, Lead Pharmacist, Community Pharmacy.
 Patient Group Direction for the supply of Chloramphenicol 0.5% eye drops to named patients registered with the Minor Ailment Service attending Community Pharmacies in NHS Borders This document authorises
Patient Group Direction for the supply of Chloramphenicol 0.5% eye drops to named patients registered with the Minor Ailment Service attending Community Pharmacies in NHS Borders This document authorises
Terry Talks Nutrition: Infectious microbes
 Terry Talks Nutrition: Infectious microbes Meet the Microbes Microbes = very tiny living things that can only be seen under a microscope 4 types of disease-causing microbes Bacteria Viruses Yeast (fungi)
Terry Talks Nutrition: Infectious microbes Meet the Microbes Microbes = very tiny living things that can only be seen under a microscope 4 types of disease-causing microbes Bacteria Viruses Yeast (fungi)
11-ID-10. Committee: Infectious Disease. Title: Creation of a National Campylobacteriosis Case Definition
 11-ID-10 Committee: Infectious Disease Title: Creation of a National Campylobacteriosis Case Definition I. Statement of the Problem Although campylobacteriosis is not nationally-notifiable, it is a disease
11-ID-10 Committee: Infectious Disease Title: Creation of a National Campylobacteriosis Case Definition I. Statement of the Problem Although campylobacteriosis is not nationally-notifiable, it is a disease
Summary of Product Characteristics
 Summary of Product Characteristics 1 NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT Selectan 300 mg/ml solution for injection for cattle and swine. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml contains:
Summary of Product Characteristics 1 NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT Selectan 300 mg/ml solution for injection for cattle and swine. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml contains:
Glycopeptide Resistant Enterococci (GRE) Policy IC/292/10
 BASINGSTOKE AND NORTH HAMPSHIRE NHS FOUNDATION TRUST Glycopeptide Resistant Enterococci (GRE) Policy IC/292/10 Supersedes: IC/292/07 Owner Name Dr Nicki Hutchinson Job Title Consultant Microbiologist,
BASINGSTOKE AND NORTH HAMPSHIRE NHS FOUNDATION TRUST Glycopeptide Resistant Enterococci (GRE) Policy IC/292/10 Supersedes: IC/292/07 Owner Name Dr Nicki Hutchinson Job Title Consultant Microbiologist,
Acute Hemorrhagic Diarrhea Syndrome (AHDS) A Cause of Bloody Feces in Dogs
 Acute Hemorrhagic Diarrhea Syndrome (AHDS) A Cause of Bloody Feces in Dogs No dog parent wants to clean up diarrhea. Cleaning up bloody diarrhea is even more unpleasant. Unfortunately, the development
Acute Hemorrhagic Diarrhea Syndrome (AHDS) A Cause of Bloody Feces in Dogs No dog parent wants to clean up diarrhea. Cleaning up bloody diarrhea is even more unpleasant. Unfortunately, the development
Breastfeeding Challenges - Mastitis & Breast Abscess -
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Breastfeeding Challenges - Mastitis & Breast Abscess - SCOPE (Area): Maternity Unit, Emergency Department, Paediatrics SCOPE (Staff): Medical, Midwifery & Nursing DESIRED OUTCOME/OBJECTIVE
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Breastfeeding Challenges - Mastitis & Breast Abscess - SCOPE (Area): Maternity Unit, Emergency Department, Paediatrics SCOPE (Staff): Medical, Midwifery & Nursing DESIRED OUTCOME/OBJECTIVE
These recommendations were approved for use by the Pharmaceutical and Therapeutics Committee, RCWMCH on 1 February 2017.
 Antibiotic regimens for suspected hospital-acquired infection (HAI) outside the Paediatric Intensive Care Unit at Red Cross War Memorial Children s Hospital (RCWMCH) Lead author: Brian Eley Contributing
Antibiotic regimens for suspected hospital-acquired infection (HAI) outside the Paediatric Intensive Care Unit at Red Cross War Memorial Children s Hospital (RCWMCH) Lead author: Brian Eley Contributing
Prepared: August Review: July Common Infections. A Medicines Optimisation Antibiotic Prescribing Guide.
 Prepared: August 2013 Review: July 2014 Common Infections. A Medicines Optimisation Antibiotic Prescribing Guide. Contents Page: Page No Why do we want to review antibiotics? 2 What do NICE say? 3 Acute
Prepared: August 2013 Review: July 2014 Common Infections. A Medicines Optimisation Antibiotic Prescribing Guide. Contents Page: Page No Why do we want to review antibiotics? 2 What do NICE say? 3 Acute
31.0 Pathology Unit. Indian Health Facility Guidelines Introduction Planning
 31.0 Pathology Unit 31.1 Introduction 31.1.1 General The Pathology Unit provides facilities and equipment for the examination of body tissues and fluids, involving receipt of patient specimens, testing
31.0 Pathology Unit 31.1 Introduction 31.1.1 General The Pathology Unit provides facilities and equipment for the examination of body tissues and fluids, involving receipt of patient specimens, testing
Surveillance of AMR in PHE: a multidisciplinary,
 Surveillance of AMR in PHE: a multidisciplinary, integrated approach Professor Neil Woodford Antimicrobial Resistance & Healthcare Associated Infections (AMRHAI) Reference Unit Crown copyright International
Surveillance of AMR in PHE: a multidisciplinary, integrated approach Professor Neil Woodford Antimicrobial Resistance & Healthcare Associated Infections (AMRHAI) Reference Unit Crown copyright International
Cephalosporins, Quinolones and Co-amoxiclav Prescribing Audit
 Cephalosporins, Quinolones and Co-amoxiclav Prescribing Audit Executive Summary Background Antibiotic resistance poses a significant threat to public health, as antibiotics underpin routine medical practice.
Cephalosporins, Quinolones and Co-amoxiclav Prescribing Audit Executive Summary Background Antibiotic resistance poses a significant threat to public health, as antibiotics underpin routine medical practice.
