The impact of the recognizing evolution on systematics
|
|
|
- Miranda Karen Matthews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The impact of the recognizing evolution on systematics 1. Genealogical relationships between species could serve as the basis for taxonomy 2. Two sources of similarity: (a) similarity from descent (b) similarity caused by convergence (driven by natural selection for the same function).
2 Phylogeny as the basis of Taxonomy Before the acceptance of evolutionary theory, related and naturalness where used with a variety of meanings. After Darwin genealogically related when we say related and we could define naturalness of taxa by whether or not they recognize clades. clade a branch of a phylogenetic tree including an ancestral species and all of its descendants. monophyletic the adjective form (from the Greek words mono for one and phylon for race, class or tribe). A clade is a monophyletic group.
3 Darwin s largest contributions to systematics 1. provided a theoretical base for understanding the existence of the Linnean hierarchy and relatedness among organisms. 2. provided the expectation for a historical continuity among organisms led to an emphasis on phylogeny reconstruction that underpins current systematics.
4 The impact of the recognizing evolution on systematics 1. Genealogical relationships between species could serve as the basis for taxonomy 2. Two sources of similarity: (a) similarity from descent (b) similarity caused by convergence (driven by natural selection for the same function).
5 Phylogeny as the basis of Taxonomy clade a branch of a phylogenetic tree including an ancestral species and all of its descendants. monophyletic the adjective form (from the Greek words mono for one and phylon for race, class or tribe). A clade is a monophyletic group.
6 Pisces Amphibia Mammalia Testudines Lepidosauria Crocodylia Aves Archosauria Diapsida Reptilia Amniota Tetrapoda Vertebrata Monophyly image from
7 The impact of the recognizing evolution on systematics 1. Genealogical relationships between species could serve as the basis for taxonomy 2. Two sources of similarity: (a) similarity from descent (b) similarity caused by convergence (driven by natural selection for the same function).
8 Similarities from common descent homologous characters may exhibit anatomical correspondences coupled with functional difference co-opting of existing structures. similarity in seemingly arbitrary features frozen accidents Convergent ( analogous ) characters tend to: have similar function, and similar in form on a gross level differ in details. present problems when we try to imagine a continuum of descent (final structure made by different parts, or significant devolopmental differences). have obvious fitness implications. These rules of thumb too vague to provide an error-proof means of distinguishing from homology, but they capture a key insight of evolutionary thinking.
9 Taxonomy after Darwin A burst of interest in phylogeny reconstruction, e.g., tree like constructions of Haeckel( s). But in the late 1800 s and early 1900 s there was a decline in systematics: 1. uncertainty about the reliability of phylogeny reconstruction and how to separate this from classification (conceptual problems) 2. disappointment in failure to resolve higher level phylogeny. 3. practical procedure for inferring phylogenies were lacking 4. growing competition from other emerging branches of biology (embryology, cytology, Mendelian genetics, physiology, biochemistry, etc.)
10 5. Development of the codes of nomenclature became a focus of some researchers 6. Rise of population thinking became a focus of systematists. With the growth of the field of genetics and an understanding of the structure of populations, a new direction was forged for systematics.
11 International codes of nomenclature Zoology (1901) Botany (1930) Bacteriology (1947) The codes provided for: 1. rules for choosing among competing names 2. rules for how names must be proposed to be valid.
12 The New Systematics book of that title by Huxley, J. (1940) gave its name to the movement blended into the Modern Synthesis of evolutionary biology. a merger of evolutionary taxonomy, genetics, and theory of populations Concentrated on microtaxonomy species, subspecies and populations.
13 Phylogenetics before the 1960 s 1. Many systematists conceded that phylogeny should be the basis of taxonomy but were very pessimistic about the prospects of inferring phylogenies. 2. Phylogeny estimates were the results of ad hoc, inscrutable analyses by experts rather than clear protocols. 3. There was debate on whether or not phylogenetic information should be the only information affecting taxonomy.
14 Three schools of Systematics We can estimate phyologenies for most groups? Taxonomic procedures must be standardized? Taxonomy should reflect phylogeny only? Evolutionary Phenetics Phylogenetic Systematics Systematics? No Yes? Yes Yes No No Yes
15 Evolutionary Systematics Different types of evolutionary change 1. cladogenesis - speciation, splitting of a lineage into 2 or more descendants 2. anagenesis - change within a lineage. Evolutionary systematists felt that both types of changes must be reflected in classification so that classification reflected both major components of evolution.
16 Pisces Amphibia Mammalia Testudines Lepidosauria Crocodylia Aves Archosauria Diapsida Reptilia Amniota Tetrapoda Vertebrata Paraphyly image from
17 Pisces Amphibia Mammalia Testudines Lepidosauria Crocodylia Aves Archosauria Diapsida Reptilia Amniota Tetrapoda Vertebrata Polyphyletic image from
18 Criteria for Delimitation and Ranking of a group Quoted (or paraphrased) from page 267 Mayr and Ashlock (1991) 1. Distinctness (size of gap between groups) 2. Degree of difference (within a group - tight clusters argue for ranking). 3. Evolutionary role (uniqueness of adaptive zone) 4. Grade characteristics. grades are similar in general level of organization (Simpson, 1961). E.g. prokaryotes. 5. Size of taxon 6. Equivalence of ranking in related taxa (balance) 7. Stability
19 Classic examples of the evolutionary systematics approach 1. Aves and Reptilia as classes despite the fact that some Reptiles (e.g. crocodylomporhs) are more closely related to birds than they are to lizards. 2. Huxley (1940) suggested that humans should be in their own phylum Psychozoa because reasoning and rational thought were particularly important innovations.
20 d I '{To", b ee.o sleuuela spr!g \----\-----J e!t!jorlloujoh \% ir, I I I e1;[dou / e-0r sunch ('886/ ilurec leuv)'eprsderoql : 'Bunesoc^lod I = 'eunesoqcjv d : v'ert'uleqlouoh uoxet cledqd^lod Illue6io^uoc prle^ur or]l pue 'sleuiujey\ pue spr!g sdnor6-xo cllallqdolot.l oiv$ or.ll '!ll[dau (cuel,{qdercd q6noq1) crle;iqdouour aql qllm 'Btoruuv lo sosselc luoooh sr.1l 1o Iue6ollqd y From Mayr and Ashlock, 1991
21 Numerical taxonomy phenetics 1. choose the specimens OTU s: operational taxonomic units 2. choose and measure characters (largest number possible). 3. treat characters equally 4. code the characters in a matrix 5. produces a similarity matrix. 6. use clustering methods to group OTU s
22 References Mayr, E. and Ashlock, P. D. (1991). Principles of Systematics Zoology. McGraw-Hill, New York, 2nd edition.
Modern Evolutionary Classification. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview Modern Evolutionary Classification
 Lesson Overview 18.2 Modern Evolutionary Classification THINK ABOUT IT Darwin s ideas about a tree of life suggested a new way to classify organisms not just based on similarities and differences, but
Lesson Overview 18.2 Modern Evolutionary Classification THINK ABOUT IT Darwin s ideas about a tree of life suggested a new way to classify organisms not just based on similarities and differences, but
Cladistics (reading and making of cladograms)
 Cladistics (reading and making of cladograms) Definitions Systematics The branch of biological sciences concerned with classifying organisms Taxon (pl: taxa) Any unit of biological diversity (eg. Animalia,
Cladistics (reading and making of cladograms) Definitions Systematics The branch of biological sciences concerned with classifying organisms Taxon (pl: taxa) Any unit of biological diversity (eg. Animalia,
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2006
 Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2006 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #4 -- Phylogenetic Analysis (Cladistics) -- Oct.
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2006 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #4 -- Phylogenetic Analysis (Cladistics) -- Oct.
Taxonomy and Pylogenetics
 Taxonomy and Pylogenetics Taxonomy - Biological Classification First invented in 1700 s by Carolus Linneaus for organizing plant and animal species. Based on overall anatomical similarity. Similarity due
Taxonomy and Pylogenetics Taxonomy - Biological Classification First invented in 1700 s by Carolus Linneaus for organizing plant and animal species. Based on overall anatomical similarity. Similarity due
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 4: Systematics Part 1
 Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 4: Systematics Part 1 Systematics is the comparative study of biological diversity with the intent of determining the relationships between organisms. Humankind has always
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 4: Systematics Part 1 Systematics is the comparative study of biological diversity with the intent of determining the relationships between organisms. Humankind has always
17.2 Classification Based on Evolutionary Relationships Organization of all that speciation!
 Organization of all that speciation! Patterns of evolution.. Taxonomy gets an over haul! Using more than morphology! 3 domains, 6 kingdoms KEY CONCEPT Modern classification is based on evolutionary relationships.
Organization of all that speciation! Patterns of evolution.. Taxonomy gets an over haul! Using more than morphology! 3 domains, 6 kingdoms KEY CONCEPT Modern classification is based on evolutionary relationships.
What are taxonomy, classification, and systematics?
 Topic 2: Comparative Method o Taxonomy, classification, systematics o Importance of phylogenies o A closer look at systematics o Some key concepts o Parts of a cladogram o Groups and characters o Homology
Topic 2: Comparative Method o Taxonomy, classification, systematics o Importance of phylogenies o A closer look at systematics o Some key concepts o Parts of a cladogram o Groups and characters o Homology
INQUIRY & INVESTIGATION
 INQUIRY & INVESTIGTION Phylogenies & Tree-Thinking D VID. UM SUSN OFFNER character a trait or feature that varies among a set of taxa (e.g., hair color) character-state a variant of a character that occurs
INQUIRY & INVESTIGTION Phylogenies & Tree-Thinking D VID. UM SUSN OFFNER character a trait or feature that varies among a set of taxa (e.g., hair color) character-state a variant of a character that occurs
Systematics, Taxonomy and Conservation. Part I: Build a phylogenetic tree Part II: Apply a phylogenetic tree to a conservation problem
 Systematics, Taxonomy and Conservation Part I: Build a phylogenetic tree Part II: Apply a phylogenetic tree to a conservation problem What is expected of you? Part I: develop and print the cladogram there
Systematics, Taxonomy and Conservation Part I: Build a phylogenetic tree Part II: Apply a phylogenetic tree to a conservation problem What is expected of you? Part I: develop and print the cladogram there
Introduction to phylogenetic trees and tree-thinking Copyright 2005, D. A. Baum (Free use for non-commercial educational pruposes)
 Introduction to phylogenetic trees and tree-thinking Copyright 2005, D. A. Baum (Free use for non-commercial educational pruposes) Phylogenetics is the study of the relationships of organisms to each other.
Introduction to phylogenetic trees and tree-thinking Copyright 2005, D. A. Baum (Free use for non-commercial educational pruposes) Phylogenetics is the study of the relationships of organisms to each other.
Lecture 11 Wednesday, September 19, 2012
 Lecture 11 Wednesday, September 19, 2012 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean
Lecture 11 Wednesday, September 19, 2012 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean
Species: Panthera pardus Genus: Panthera Family: Felidae Order: Carnivora Class: Mammalia Phylum: Chordata
 CHAPTER 6: PHYLOGENY AND THE TREE OF LIFE AP Biology 3 PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS Phylogeny - evolutionary history of a species or group of related species Systematics - analytical approach to understanding
CHAPTER 6: PHYLOGENY AND THE TREE OF LIFE AP Biology 3 PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS Phylogeny - evolutionary history of a species or group of related species Systematics - analytical approach to understanding
Title: Phylogenetic Methods and Vertebrate Phylogeny
 Title: Phylogenetic Methods and Vertebrate Phylogeny Central Question: How can evolutionary relationships be determined objectively? Sub-questions: 1. What affect does the selection of the outgroup have
Title: Phylogenetic Methods and Vertebrate Phylogeny Central Question: How can evolutionary relationships be determined objectively? Sub-questions: 1. What affect does the selection of the outgroup have
Interpreting Evolutionary Trees Honors Integrated Science 4 Name Per.
 Interpreting Evolutionary Trees Honors Integrated Science 4 Name Per. Introduction Imagine a single diagram representing the evolutionary relationships between everything that has ever lived. If life evolved
Interpreting Evolutionary Trees Honors Integrated Science 4 Name Per. Introduction Imagine a single diagram representing the evolutionary relationships between everything that has ever lived. If life evolved
8/19/2013. Topic 5: The Origin of Amniotes. What are some stem Amniotes? What are some stem Amniotes? The Amniotic Egg. What is an Amniote?
 Topic 5: The Origin of Amniotes Where do amniotes fall out on the vertebrate phylogeny? What are some stem Amniotes? What is an Amniote? What changes were involved with the transition to dry habitats?
Topic 5: The Origin of Amniotes Where do amniotes fall out on the vertebrate phylogeny? What are some stem Amniotes? What is an Amniote? What changes were involved with the transition to dry habitats?
Ch. 17: Classification
 Ch. 17: Classification Who is Carolus Linnaeus? Linnaeus developed the scientific naming system still used today. Taxonomy What is? the science of naming and classifying organisms. A taxon group of organisms
Ch. 17: Classification Who is Carolus Linnaeus? Linnaeus developed the scientific naming system still used today. Taxonomy What is? the science of naming and classifying organisms. A taxon group of organisms
Modern taxonomy. Building family trees 10/10/2011. Knowing a lot about lots of creatures. Tom Hartman. Systematics includes: 1.
 Modern taxonomy Building family trees Tom Hartman www.tuatara9.co.uk Classification has moved away from the simple grouping of organisms according to their similarities (phenetics) and has become the study
Modern taxonomy Building family trees Tom Hartman www.tuatara9.co.uk Classification has moved away from the simple grouping of organisms according to their similarities (phenetics) and has become the study
CLADISTICS Student Packet SUMMARY Phylogeny Phylogenetic trees/cladograms
 CLADISTICS Student Packet SUMMARY PHYLOGENETIC TREES AND CLADOGRAMS ARE MODELS OF EVOLUTIONARY HISTORY THAT CAN BE TESTED Phylogeny is the history of descent of organisms from their common ancestor. Phylogenetic
CLADISTICS Student Packet SUMMARY PHYLOGENETIC TREES AND CLADOGRAMS ARE MODELS OF EVOLUTIONARY HISTORY THAT CAN BE TESTED Phylogeny is the history of descent of organisms from their common ancestor. Phylogenetic
Ch 1.2 Determining How Species Are Related.notebook February 06, 2018
 Name 3 "Big Ideas" from our last notebook lecture: * * * 1 WDYR? Of the following organisms, which is the closest relative of the "Snowy Owl" (Bubo scandiacus)? a) barn owl (Tyto alba) b) saw whet owl
Name 3 "Big Ideas" from our last notebook lecture: * * * 1 WDYR? Of the following organisms, which is the closest relative of the "Snowy Owl" (Bubo scandiacus)? a) barn owl (Tyto alba) b) saw whet owl
Are node-based and stem-based clades equivalent? Insights from graph theory
 Are node-based and stem-based clades equivalent? Insights from graph theory November 18, 2010 Tree of Life 1 2 Jeremy Martin, David Blackburn, E. O. Wiley 1 Associate Professor of Mathematics, San Francisco,
Are node-based and stem-based clades equivalent? Insights from graph theory November 18, 2010 Tree of Life 1 2 Jeremy Martin, David Blackburn, E. O. Wiley 1 Associate Professor of Mathematics, San Francisco,
Introduction to Cladistic Analysis
 3.0 Copyright 2008 by Department of Integrative Biology, University of California-Berkeley Introduction to Cladistic Analysis tunicate lamprey Cladoselache trout lungfish frog four jaws swimbladder or
3.0 Copyright 2008 by Department of Integrative Biology, University of California-Berkeley Introduction to Cladistic Analysis tunicate lamprey Cladoselache trout lungfish frog four jaws swimbladder or
Phylogenetics. Phylogenetic Trees. 1. Represent presumed patterns. 2. Analogous to family trees.
 Phylogenetics. Phylogenetic Trees. 1. Represent presumed patterns of descent. 2. Analogous to family trees. 3. Resolve taxa, e.g., species, into clades each of which includes an ancestral taxon and all
Phylogenetics. Phylogenetic Trees. 1. Represent presumed patterns of descent. 2. Analogous to family trees. 3. Resolve taxa, e.g., species, into clades each of which includes an ancestral taxon and all
Animal Diversity wrap-up Lecture 9 Winter 2014
 Animal Diversity wrap-up Lecture 9 Winter 2014 1 Animal phylogeny based on morphology & development Fig. 32.10 2 Animal phylogeny based on molecular data Fig. 32.11 New Clades 3 Lophotrochozoa Lophophore:
Animal Diversity wrap-up Lecture 9 Winter 2014 1 Animal phylogeny based on morphology & development Fig. 32.10 2 Animal phylogeny based on molecular data Fig. 32.11 New Clades 3 Lophotrochozoa Lophophore:
History of Lineages. Chapter 11. Jamie Oaks 1. April 11, Kincaid Hall 524. c 2007 Boris Kulikov boris-kulikov.blogspot.
 History of Lineages Chapter 11 Jamie Oaks 1 1 Kincaid Hall 524 joaks1@gmail.com April 11, 2014 c 2007 Boris Kulikov boris-kulikov.blogspot.com History of Lineages J. Oaks, University of Washington 1/46
History of Lineages Chapter 11 Jamie Oaks 1 1 Kincaid Hall 524 joaks1@gmail.com April 11, 2014 c 2007 Boris Kulikov boris-kulikov.blogspot.com History of Lineages J. Oaks, University of Washington 1/46
UNIT III A. Descent with Modification(Ch19) B. Phylogeny (Ch20) C. Evolution of Populations (Ch21) D. Origin of Species or Speciation (Ch22)
 UNIT III A. Descent with Modification(Ch9) B. Phylogeny (Ch2) C. Evolution of Populations (Ch2) D. Origin of Species or Speciation (Ch22) Classification in broad term simply means putting things in classes
UNIT III A. Descent with Modification(Ch9) B. Phylogeny (Ch2) C. Evolution of Populations (Ch2) D. Origin of Species or Speciation (Ch22) Classification in broad term simply means putting things in classes
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 2 Dr. Stuart Sumida. Phylogenetic Perspective and the Evolution of Development.
 Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 2 Dr. Stuart Sumida Phylogenetic Perspective and the Evolution of Development Evo-Devo So, what is all the fuss about phylogeny? PHYLOGENETIC SYSTEMATICS allows
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 2 Dr. Stuart Sumida Phylogenetic Perspective and the Evolution of Development Evo-Devo So, what is all the fuss about phylogeny? PHYLOGENETIC SYSTEMATICS allows
Classification. Chapter 17. Classification. Classification. Classification
 Classification Chapter 17 Classification Classification is the arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities. Classification shows how organisms are related and different. Classification
Classification Chapter 17 Classification Classification is the arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities. Classification shows how organisms are related and different. Classification
What is Classification?
 Classification Diversity of Life Biologists have identified over 1.5 million different species of living organisms so far... Estimates = between 2-100 million species yet to be discovered What is Classification?
Classification Diversity of Life Biologists have identified over 1.5 million different species of living organisms so far... Estimates = between 2-100 million species yet to be discovered What is Classification?
Evolution and Biodiversity Laboratory Systematics and Taxonomy I. Taxonomy taxonomy taxa taxon taxonomist natural artificial systematics
 Evolution and Biodiversity Laboratory Systematics and Taxonomy by Dana Krempels and Julian Lee Recent estimates of our planet's biological diversity suggest that the species number between 5 and 50 million,
Evolution and Biodiversity Laboratory Systematics and Taxonomy by Dana Krempels and Julian Lee Recent estimates of our planet's biological diversity suggest that the species number between 5 and 50 million,
Origin and Evolution of Birds. Read: Chapters 1-3 in Gill but limited review of systematics
 Origin and Evolution of Birds Read: Chapters 1-3 in Gill but limited review of systematics Review of Taxonomy Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Aves Characteristics: wings,
Origin and Evolution of Birds Read: Chapters 1-3 in Gill but limited review of systematics Review of Taxonomy Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Aves Characteristics: wings,
Understanding Evolutionary History: An Introduction to Tree Thinking
 1 Understanding Evolutionary History: An Introduction to Tree Thinking Laura R. Novick Kefyn M. Catley Emily G. Schreiber Vanderbilt University Western Carolina University Vanderbilt University Version
1 Understanding Evolutionary History: An Introduction to Tree Thinking Laura R. Novick Kefyn M. Catley Emily G. Schreiber Vanderbilt University Western Carolina University Vanderbilt University Version
Warm-Up: Fill in the Blank
 Warm-Up: Fill in the Blank 1. For natural selection to happen, there must be variation in the population. 2. The preserved remains of organisms, called provides evidence for evolution. 3. By using and
Warm-Up: Fill in the Blank 1. For natural selection to happen, there must be variation in the population. 2. The preserved remains of organisms, called provides evidence for evolution. 3. By using and
Using the Appendices Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora
 www.cites.org 1 Using the Appendices Copyright CITES Secretariat 2005 Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora Overview 2 In this session we will: Look at how the
www.cites.org 1 Using the Appendices Copyright CITES Secretariat 2005 Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora Overview 2 In this session we will: Look at how the
PHYLOGENETIC TAXONOMY*
 Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1992.23:449~0 PHYLOGENETIC TAXONOMY* Kevin dd Queiroz Division of Amphibians and Reptiles, United States National Museum of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, Washington,
Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1992.23:449~0 PHYLOGENETIC TAXONOMY* Kevin dd Queiroz Division of Amphibians and Reptiles, United States National Museum of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, Washington,
1 Describe the anatomy and function of the turtle shell. 2 Describe respiration in turtles. How does the shell affect respiration?
 GVZ 2017 Practice Questions Set 1 Test 3 1 Describe the anatomy and function of the turtle shell. 2 Describe respiration in turtles. How does the shell affect respiration? 3 According to the most recent
GVZ 2017 Practice Questions Set 1 Test 3 1 Describe the anatomy and function of the turtle shell. 2 Describe respiration in turtles. How does the shell affect respiration? 3 According to the most recent
Toward an Integrated System of Clade Names
 Syst. Biol. 56(6):956 974, 2007 Copyright c Society of Systematic Biologists ISSN: 1063-5157 print / 1076-836X online DOI: 10.1080/10635150701656378 Toward an Integrated System of Clade Names KEVIN DE
Syst. Biol. 56(6):956 974, 2007 Copyright c Society of Systematic Biologists ISSN: 1063-5157 print / 1076-836X online DOI: 10.1080/10635150701656378 Toward an Integrated System of Clade Names KEVIN DE
Fig Phylogeny & Systematics
 Fig. 26- Phylogeny & Systematics Tree of Life phylogenetic relationship for 3 clades (http://evolution.berkeley.edu Fig. 26-2 Phylogenetic tree Figure 26.3 Taxonomy Taxon Carolus Linnaeus Species: Panthera
Fig. 26- Phylogeny & Systematics Tree of Life phylogenetic relationship for 3 clades (http://evolution.berkeley.edu Fig. 26-2 Phylogenetic tree Figure 26.3 Taxonomy Taxon Carolus Linnaeus Species: Panthera
Natural Sciences 360 Legacy of Life Lecture 3 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Phylogeny (and Its Rules) Biogeography
 Natural Sciences 360 Legacy of Life Lecture 3 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Phylogeny (and Its Rules) Biogeography So, what is all the fuss about phylogeny? PHYLOGENETIC SYSTEMATICS allows us both define groups
Natural Sciences 360 Legacy of Life Lecture 3 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Phylogeny (and Its Rules) Biogeography So, what is all the fuss about phylogeny? PHYLOGENETIC SYSTEMATICS allows us both define groups
Origin and Evolution of Birds. Read: Chapters 1-3 in Gill but limited review of systematics
 Origin and Evolution of Birds Read: Chapters 1-3 in Gill but limited review of systematics Review of Taxonomy Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Aves Characteristics: wings,
Origin and Evolution of Birds Read: Chapters 1-3 in Gill but limited review of systematics Review of Taxonomy Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Aves Characteristics: wings,
Phylogeny Reconstruction
 Phylogeny Reconstruction Trees, Methods and Characters Reading: Gregory, 2008. Understanding Evolutionary Trees (Polly, 2006) Lab tomorrow Meet in Geology GY522 Bring computers if you have them (they will
Phylogeny Reconstruction Trees, Methods and Characters Reading: Gregory, 2008. Understanding Evolutionary Trees (Polly, 2006) Lab tomorrow Meet in Geology GY522 Bring computers if you have them (they will
Chapter 13 Death by Decree
 Chapter 13 Death by Decree In the same paper in which Richard Owen coined their name, he also claimed that dinosaurs are extinct, in an effort to disprove the idea of evolution 1,2. But with so much evidence
Chapter 13 Death by Decree In the same paper in which Richard Owen coined their name, he also claimed that dinosaurs are extinct, in an effort to disprove the idea of evolution 1,2. But with so much evidence
Animal Diversity III: Mollusca and Deuterostomes
 Animal Diversity III: Mollusca and Deuterostomes Objectives: Be able to identify specimens from the main groups of Mollusca and Echinodermata. Be able to distinguish between the bilateral symmetry on a
Animal Diversity III: Mollusca and Deuterostomes Objectives: Be able to identify specimens from the main groups of Mollusca and Echinodermata. Be able to distinguish between the bilateral symmetry on a
Comparative Zoology Portfolio Project Assignment
 Comparative Zoology Portfolio Project Assignment Using your knowledge from the in class activities, your notes, you Integrated Science text, or the internet, you will look at the major trends in the evolution
Comparative Zoology Portfolio Project Assignment Using your knowledge from the in class activities, your notes, you Integrated Science text, or the internet, you will look at the major trends in the evolution
Evolution of Birds. Summary:
 Oregon State Standards OR Science 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.3S.1, 7.3S.2 8.1, 8.2, 8.2L.1, 8.3, 8.3S.1, 8.3S.2 H.1, H.2, H.2L.4, H.2L.5, H.3, H.3S.1, H.3S.2, H.3S.3 Summary: Students create phylogenetic trees to
Oregon State Standards OR Science 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.3S.1, 7.3S.2 8.1, 8.2, 8.2L.1, 8.3, 8.3S.1, 8.3S.2 H.1, H.2, H.2L.4, H.2L.5, H.3, H.3S.1, H.3S.2, H.3S.3 Summary: Students create phylogenetic trees to
Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection. Hunting for evolution clues Elementary, my dear, Darwin!
 Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection Hunting for evolution clues Elementary, my dear, Darwin! 2006-2007 Evidence supporting evolution Fossil record shows change over time Anatomical record comparing
Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection Hunting for evolution clues Elementary, my dear, Darwin! 2006-2007 Evidence supporting evolution Fossil record shows change over time Anatomical record comparing
Classification &Taxa. Primate Classification. Adaptive Radiation
 Memorize for Exam Primate Classification 1 Adaptive Radiation Definition: the relatively rapid expansion and diversification of an evolving group of organisms as they adapt to new ecological niches. Classification
Memorize for Exam Primate Classification 1 Adaptive Radiation Definition: the relatively rapid expansion and diversification of an evolving group of organisms as they adapt to new ecological niches. Classification
muscles (enhancing biting strength). Possible states: none, one, or two.
 Reconstructing Evolutionary Relationships S-1 Practice Exercise: Phylogeny of Terrestrial Vertebrates In this example we will construct a phylogenetic hypothesis of the relationships between seven taxa
Reconstructing Evolutionary Relationships S-1 Practice Exercise: Phylogeny of Terrestrial Vertebrates In this example we will construct a phylogenetic hypothesis of the relationships between seven taxa
Subphylum Vertebrata
 Subphylum Vertebrata Superclass Agnatha (jawless vertebrates) Class Myxini Class Cephalaspidomorphi Superclass Gnathostomata (jawed vertebrates) Class Chondrichthyes Class Osteichthyes Class Amphibia Class
Subphylum Vertebrata Superclass Agnatha (jawless vertebrates) Class Myxini Class Cephalaspidomorphi Superclass Gnathostomata (jawed vertebrates) Class Chondrichthyes Class Osteichthyes Class Amphibia Class
Required and Recommended Supporting Information for IUCN Red List Assessments
 Required and Recommended Supporting Information for IUCN Red List Assessments This is Annex 1 of the Rules of Procedure for IUCN Red List Assessments 2017 2020 as approved by the IUCN SSC Steering Committee
Required and Recommended Supporting Information for IUCN Red List Assessments This is Annex 1 of the Rules of Procedure for IUCN Red List Assessments 2017 2020 as approved by the IUCN SSC Steering Committee
Defining and redefining monophyly: Haeckel, Hennig, Ashlock, Nelson and the proliferation of definitions
 CSIRO PUBLISHING Australian Systematic Botany, 2013, 26, 347 355 http://dx.doi.org/10.1071/sb13031 Review Defining and redefining monophyly: Haeckel, Hennig, Ashlock, Nelson and the proliferation of definitions
CSIRO PUBLISHING Australian Systematic Botany, 2013, 26, 347 355 http://dx.doi.org/10.1071/sb13031 Review Defining and redefining monophyly: Haeckel, Hennig, Ashlock, Nelson and the proliferation of definitions
Herpetology Biol 119. Herpetology Introduction. Philip Bergmann. Philip Bergmann - Research. TA: Allegra Mitchell. Philip Bergmann - Personal
 Herpetology Biol 119 Clark University Fall 2011 Lecture: Tuesday, Thursday 9:00-10:15 in Lasry 124 Lab: Tuesday 13:25-16:10 in Lasry 150 Office hours: T 10:15-11:15 in Lasry 331 Contact: pbergmann@clarku.edu
Herpetology Biol 119 Clark University Fall 2011 Lecture: Tuesday, Thursday 9:00-10:15 in Lasry 124 Lab: Tuesday 13:25-16:10 in Lasry 150 Office hours: T 10:15-11:15 in Lasry 331 Contact: pbergmann@clarku.edu
Pacing Guide for 7-12 Curriculum
 Pacing Guide for 7-12 Curriculum Course Title: Zoology Length of Course: 36 Weeks Week Number Week 1 Week 2 Chapter COS Objectives Student Will Be Able To: Biology COS 1- Select Successfully follow appropriate
Pacing Guide for 7-12 Curriculum Course Title: Zoology Length of Course: 36 Weeks Week Number Week 1 Week 2 Chapter COS Objectives Student Will Be Able To: Biology COS 1- Select Successfully follow appropriate
INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL AND VETERINARY SCIENCE CURRICULUM. Unit 1: Animals in Society/Global Perspective
 Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL AND VETERINARY SCIENCE CURRICULUM Unit 1: Animals in Society/Global Perspective Students will gain an understanding
Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL AND VETERINARY SCIENCE CURRICULUM Unit 1: Animals in Society/Global Perspective Students will gain an understanding
What is the evidence for evolution?
 What is the evidence for evolution? 1. Geographic Distribution 2. Fossil Evidence & Transitional Species 3. Comparative Anatomy 1. Homologous Structures 2. Analogous Structures 3. Vestigial Structures
What is the evidence for evolution? 1. Geographic Distribution 2. Fossil Evidence & Transitional Species 3. Comparative Anatomy 1. Homologous Structures 2. Analogous Structures 3. Vestigial Structures
Ichthyology Lecture # 3 Systematics, taxonomy and classification schemes
 In all probability more paper has been consumed on the questions of the nature and definition of the species than any other subject in evolutionary and systematic biology. E. O. Wiley 1978 http://www.iczn.org/
In all probability more paper has been consumed on the questions of the nature and definition of the species than any other subject in evolutionary and systematic biology. E. O. Wiley 1978 http://www.iczn.org/
Prof. Neil. J.L. Heideman
 Prof. Neil. J.L. Heideman Position Office Mailing address E-mail : Vice-dean (Professor of Zoology) : No. 10, Biology Building : P.O. Box 339 (Internal Box 44), Bloemfontein 9300, South Africa : heidemannj.sci@mail.uovs.ac.za
Prof. Neil. J.L. Heideman Position Office Mailing address E-mail : Vice-dean (Professor of Zoology) : No. 10, Biology Building : P.O. Box 339 (Internal Box 44), Bloemfontein 9300, South Africa : heidemannj.sci@mail.uovs.ac.za
14 February th class meeting (Miller Chapter 3) Environmental Biology ECOL 206 University of Arizona spring 2005
 14 February 2005 14th class meeting (Miller Chapter 3) Environmental Biology ECOL 206 University of Arizona spring 2005 Kevin Bonine, Ph.D. Alona Bachi, Matthew Herron, Graduate TAs 1 Hawaiian Vegetation
14 February 2005 14th class meeting (Miller Chapter 3) Environmental Biology ECOL 206 University of Arizona spring 2005 Kevin Bonine, Ph.D. Alona Bachi, Matthew Herron, Graduate TAs 1 Hawaiian Vegetation
Learning Goals: 1. I can list the traditional classification hierarchy in order.
 Learning Goals: 1. I can list the traditional classification hierarchy in order. 2. I can explain what binomial nomenclature is, and where an organism gets its first and last name. 3. I can read and create
Learning Goals: 1. I can list the traditional classification hierarchy in order. 2. I can explain what binomial nomenclature is, and where an organism gets its first and last name. 3. I can read and create
HAWAIIAN BIOGEOGRAPHY EVOLUTION ON A HOT SPOT ARCHIPELAGO EDITED BY WARREN L. WAGNER AND V. A. FUNK SMITHSONIAN INSTITUTION PRESS
 HAWAIIAN BIOGEOGRAPHY EVOLUTION ON A HOT SPOT ARCHIPELAGO EDITED BY WARREN L. WAGNER AND V. A. FUNK SMITHSONIAN INSTITUTION PRESS WASHINGTON AND LONDON 995 by the Smithsonian Institution All rights reserved
HAWAIIAN BIOGEOGRAPHY EVOLUTION ON A HOT SPOT ARCHIPELAGO EDITED BY WARREN L. WAGNER AND V. A. FUNK SMITHSONIAN INSTITUTION PRESS WASHINGTON AND LONDON 995 by the Smithsonian Institution All rights reserved
The extant amphibians and reptiles are a diverse collection
 2 Phylogenetic Systematics and the Origins of Amphibians and Reptiles The extant amphibians and reptiles are a diverse collection of animals with evolutionary histories dating back to the Early Carboniferous
2 Phylogenetic Systematics and the Origins of Amphibians and Reptiles The extant amphibians and reptiles are a diverse collection of animals with evolutionary histories dating back to the Early Carboniferous
Mammalogy: Biology 5370 Syllabus for Fall 2005
 Mammalogy: Biology 5370 Syllabus for Fall 2005 Objective: This lecture course provides an overview of the evolution, diversity, structure and function and ecology of mammals. It will introduce you to the
Mammalogy: Biology 5370 Syllabus for Fall 2005 Objective: This lecture course provides an overview of the evolution, diversity, structure and function and ecology of mammals. It will introduce you to the
14 February th class meeting (Miller Chapter 3) Environmental Biology ECOL 206 University of Arizona spring 2005
 1 14 February 2005 14th class meeting (Miller Chapter 3) Environmental Biology ECOL 206 University of Arizona spring 2005 Kevin Bonine, Ph.D. Alona Bachi, Matthew Herron, Graduate TAs Hawaiian Vegetation
1 14 February 2005 14th class meeting (Miller Chapter 3) Environmental Biology ECOL 206 University of Arizona spring 2005 Kevin Bonine, Ph.D. Alona Bachi, Matthew Herron, Graduate TAs Hawaiian Vegetation
Do the traits of organisms provide evidence for evolution?
 PhyloStrat Tutorial Do the traits of organisms provide evidence for evolution? Consider two hypotheses about where Earth s organisms came from. The first hypothesis is from John Ray, an influential British
PhyloStrat Tutorial Do the traits of organisms provide evidence for evolution? Consider two hypotheses about where Earth s organisms came from. The first hypothesis is from John Ray, an influential British
LABORATORY EXERCISE 6: CLADISTICS I
 Biology 4415/5415 Evolution LABORATORY EXERCISE 6: CLADISTICS I Take a group of organisms. Let s use five: a lungfish, a frog, a crocodile, a flamingo, and a human. How to reconstruct their relationships?
Biology 4415/5415 Evolution LABORATORY EXERCISE 6: CLADISTICS I Take a group of organisms. Let s use five: a lungfish, a frog, a crocodile, a flamingo, and a human. How to reconstruct their relationships?
Classification and Taxonomy
 NAME: DATE: PERIOD: Taxonomy: the science of classifying organisms Classification and Taxonomy Common names of organisms: Spider monkey Clown fish Mud puppy Black bear Ringworm Sea horse Sea monkey Firefly
NAME: DATE: PERIOD: Taxonomy: the science of classifying organisms Classification and Taxonomy Common names of organisms: Spider monkey Clown fish Mud puppy Black bear Ringworm Sea horse Sea monkey Firefly
Darwin and the Family Tree of Animals
 Darwin and the Family Tree of Animals Note: These links do not work. Use the links within the outline to access the images in the popup windows. This text is the same as the scrolling text in the popup
Darwin and the Family Tree of Animals Note: These links do not work. Use the links within the outline to access the images in the popup windows. This text is the same as the scrolling text in the popup
Classification systems help us to understand where humans fit into the history of life on earth Organizing the great diversity of life into
 You are here Classification systems help us to understand where humans fit into the history of life on earth Organizing the great diversity of life into categories (groups based on shared characteristics)
You are here Classification systems help us to understand where humans fit into the history of life on earth Organizing the great diversity of life into categories (groups based on shared characteristics)
388 NOTES AND COMMENTS
 388 NOTES AND COMMENTS DIAGNOSIS OF THE CLASSES REPTILIA AND MAMMALIA GEORGE GAYLORD SIMPSON Museiun of Comparative Zoology, Harvard University, Cambridge The editor has asked me to comment on two papers
388 NOTES AND COMMENTS DIAGNOSIS OF THE CLASSES REPTILIA AND MAMMALIA GEORGE GAYLORD SIMPSON Museiun of Comparative Zoology, Harvard University, Cambridge The editor has asked me to comment on two papers
Chapter 13. Phylogenetic Systematics: Developing an Hypothesis of Amniote Relationships
 Chapter 3 Phylogenetic Systematics: Developing an Hypothesis of Amniote Relationships Daniel R. Brooks, Deborah A. McLennan, Joseph P. Carney Michael D. Dennison, and Corey A. Goldman Department of Zoology
Chapter 3 Phylogenetic Systematics: Developing an Hypothesis of Amniote Relationships Daniel R. Brooks, Deborah A. McLennan, Joseph P. Carney Michael D. Dennison, and Corey A. Goldman Department of Zoology
Bio 312, Spring 2017 Exam 1 ( 1 ) Name:
 Bio 312, Spring 2017 Exam 1 ( 1 ) Name: Please write the first letter of your last name in the box; 5 points will be deducted if your name is hard to read or the box does not contain the correct letter.
Bio 312, Spring 2017 Exam 1 ( 1 ) Name: Please write the first letter of your last name in the box; 5 points will be deducted if your name is hard to read or the box does not contain the correct letter.
6. The lifetime Darwinian fitness of one organism is greater than that of another organism if: A. it lives longer than the other B. it is able to outc
 1. The money in the kingdom of Florin consists of bills with the value written on the front, and pictures of members of the royal family on the back. To test the hypothesis that all of the Florinese $5
1. The money in the kingdom of Florin consists of bills with the value written on the front, and pictures of members of the royal family on the back. To test the hypothesis that all of the Florinese $5
Inferring Ancestor-Descendant Relationships in the Fossil Record
 Inferring Ancestor-Descendant Relationships in the Fossil Record (With Statistics) David Bapst, Melanie Hopkins, April Wright, Nick Matzke & Graeme Lloyd GSA 2016 T151 Wednesday Sept 28 th, 9:15 AM Feel
Inferring Ancestor-Descendant Relationships in the Fossil Record (With Statistics) David Bapst, Melanie Hopkins, April Wright, Nick Matzke & Graeme Lloyd GSA 2016 T151 Wednesday Sept 28 th, 9:15 AM Feel
TOPIC CLADISTICS
 TOPIC 5.4 - CLADISTICS 5.4 A Clades & Cladograms https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/46/clade-grade_ii.svg IB BIO 5.4 3 U1: A clade is a group of organisms that have evolved from a common
TOPIC 5.4 - CLADISTICS 5.4 A Clades & Cladograms https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/46/clade-grade_ii.svg IB BIO 5.4 3 U1: A clade is a group of organisms that have evolved from a common
Testing Phylogenetic Hypotheses with Molecular Data 1
 Testing Phylogenetic Hypotheses with Molecular Data 1 How does an evolutionary biologist quantify the timing and pathways for diversification (speciation)? If we observe diversification today, the processes
Testing Phylogenetic Hypotheses with Molecular Data 1 How does an evolutionary biologist quantify the timing and pathways for diversification (speciation)? If we observe diversification today, the processes
No limbs Eastern glass lizard. Monitor lizard. Iguanas. ANCESTRAL LIZARD (with limbs) Snakes. No limbs. Geckos Pearson Education, Inc.
 No limbs Eastern glass lizard Monitor lizard guanas ANCESTRAL LZARD (with limbs) No limbs Snakes Geckos Species: Panthera pardus Genus: Panthera Family: Felidae Order: Carnivora Class: Mammalia Phylum:
No limbs Eastern glass lizard Monitor lizard guanas ANCESTRAL LZARD (with limbs) No limbs Snakes Geckos Species: Panthera pardus Genus: Panthera Family: Felidae Order: Carnivora Class: Mammalia Phylum:
This is a series of skulls and front leg fossils of organisms believed to be ancestors of the modern-day horse.
 Evidence of Evolution Background When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide as much evidence as
Evidence of Evolution Background When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide as much evidence as
HENNIG'S PARASITOLOGICAL METHOD: A PROPOSED SOLUTION
 Syst. Zool., 3(3), 98, pp. 229-249 HENNIG'S PARASITOLOGICAL METHOD: A PROPOSED SOLUTION DANIEL R. BROOKS Abstract Brooks, ID. R. (Department of Zoology, University of British Columbia, 275 Wesbrook Mall,
Syst. Zool., 3(3), 98, pp. 229-249 HENNIG'S PARASITOLOGICAL METHOD: A PROPOSED SOLUTION DANIEL R. BROOKS Abstract Brooks, ID. R. (Department of Zoology, University of British Columbia, 275 Wesbrook Mall,
1 EEB 2245/2245W Spring 2014: exercises working with phylogenetic trees and characters
 1 EEB 2245/2245W Spring 2014: exercises working with phylogenetic trees and characters 1. Answer questions a through i below using the tree provided below. a. The sister group of J. K b. The sister group
1 EEB 2245/2245W Spring 2014: exercises working with phylogenetic trees and characters 1. Answer questions a through i below using the tree provided below. a. The sister group of J. K b. The sister group
Course Offerings: Associate of Applied Science Veterinary Technology. Course Number Name Credits
 Course Offerings: Associate of Applied Science Veterinary Technology Course Number Name Credits Required Courses in Major: Fall Semester, First Year *VETT-101 Animal Health Careers 1-0-1 *VETT-102 Veterinary
Course Offerings: Associate of Applied Science Veterinary Technology Course Number Name Credits Required Courses in Major: Fall Semester, First Year *VETT-101 Animal Health Careers 1-0-1 *VETT-102 Veterinary
LABORATORY EXERCISE 7: CLADISTICS I
 Biology 4415/5415 Evolution LABORATORY EXERCISE 7: CLADISTICS I Take a group of organisms. Let s use five: a lungfish, a frog, a crocodile, a flamingo, and a human. How to reconstruct their relationships?
Biology 4415/5415 Evolution LABORATORY EXERCISE 7: CLADISTICS I Take a group of organisms. Let s use five: a lungfish, a frog, a crocodile, a flamingo, and a human. How to reconstruct their relationships?
Evolution as Fact. The figure below shows transitional fossils in the whale lineage.
 Evolution as Fact Evolution is a fact. Organisms descend from others with modification. Phylogeny, the lineage of ancestors and descendants, is the scientific term to Darwin's phrase "descent with modification."
Evolution as Fact Evolution is a fact. Organisms descend from others with modification. Phylogeny, the lineage of ancestors and descendants, is the scientific term to Darwin's phrase "descent with modification."
Mr. Bouchard Summer Assignment AP Biology. Name: Block: Score: / 20. Topic: Chemistry Review and Evolution Intro Packet Due: 9/4/18
 Name: Block: Score: / 20 Topic: Chemistry Review and Evolution Intro Packet Due: 9/4/18 Week Schedule Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday In class discussion/activity NONE NONE NONE Syllabus and Course
Name: Block: Score: / 20 Topic: Chemistry Review and Evolution Intro Packet Due: 9/4/18 Week Schedule Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday In class discussion/activity NONE NONE NONE Syllabus and Course
Evolution. Evolution is change in organisms over time. Evolution does not have a goal; it is often shaped by natural selection (see below).
 Evolution Evolution is change in organisms over time. Evolution does not have a goal; it is often shaped by natural selection (see below). Species an interbreeding population of organisms that can produce
Evolution Evolution is change in organisms over time. Evolution does not have a goal; it is often shaped by natural selection (see below). Species an interbreeding population of organisms that can produce
Cladistics, evolution and the fossils
 Cladistics, evolution and the fossils Shaun Doyle Cladistics is the premier method used for determining evolutionary relationships in biology. The results of cladistics analyses, tree diagrams called cladograms,
Cladistics, evolution and the fossils Shaun Doyle Cladistics is the premier method used for determining evolutionary relationships in biology. The results of cladistics analyses, tree diagrams called cladograms,
8/19/2013. What is convergence? Topic 11: Convergence. What is convergence? What is convergence? What is convergence? What is convergence?
 Topic 11: Convergence What are the classic herp examples? Have they been formally studied? Emerald Tree Boas and Green Tree Pythons show a remarkable level of convergence Photos KP Bergmann, Philadelphia
Topic 11: Convergence What are the classic herp examples? Have they been formally studied? Emerald Tree Boas and Green Tree Pythons show a remarkable level of convergence Photos KP Bergmann, Philadelphia
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activitydevelop EXPLO RING VERTEBRATE CL ASSIFICATIO N What criteria
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activitydevelop EXPLO RING VERTEBRATE CL ASSIFICATIO N What criteria
Phylogeographic assessment of Acanthodactylus boskianus (Reptilia: Lacertidae) based on phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial DNA.
 Zoology Department Phylogeographic assessment of Acanthodactylus boskianus (Reptilia: Lacertidae) based on phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial DNA By HAGAR IBRAHIM HOSNI BAYOUMI A thesis submitted in
Zoology Department Phylogeographic assessment of Acanthodactylus boskianus (Reptilia: Lacertidae) based on phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial DNA By HAGAR IBRAHIM HOSNI BAYOUMI A thesis submitted in
Ch 34: Vertebrate Objective Questions & Diagrams
 Ch 34: Vertebrate Objective Questions & Diagrams Invertebrate Chordates and the Origin of Vertebrates 1. Distinguish between the two subgroups of deuterostomes. 2. Describe the four unique characteristics
Ch 34: Vertebrate Objective Questions & Diagrams Invertebrate Chordates and the Origin of Vertebrates 1. Distinguish between the two subgroups of deuterostomes. 2. Describe the four unique characteristics
HETEROCHRONY OF CRANIAL BONES IN AMNIOTA AND THE PHYLOGENETIC PLACEMENT OF TESTUDINES
 John Carroll University Carroll Collected Masters Theses Theses, Essays, and Senior Honors Projects Summer 2016 HETEROCHRONY OF CRANIAL BONES IN AMNIOTA AND THE PHYLOGENETIC PLACEMENT OF TESTUDINES Kathleen
John Carroll University Carroll Collected Masters Theses Theses, Essays, and Senior Honors Projects Summer 2016 HETEROCHRONY OF CRANIAL BONES IN AMNIOTA AND THE PHYLOGENETIC PLACEMENT OF TESTUDINES Kathleen
Systematics and taxonomy of the genus Culicoides what is coming next?
 Systematics and taxonomy of the genus Culicoides what is coming next? Claire Garros 1, Bruno Mathieu 2, Thomas Balenghien 1, Jean-Claude Delécolle 2 1 CIRAD, Montpellier, France 2 IPPTS, Strasbourg, France
Systematics and taxonomy of the genus Culicoides what is coming next? Claire Garros 1, Bruno Mathieu 2, Thomas Balenghien 1, Jean-Claude Delécolle 2 1 CIRAD, Montpellier, France 2 IPPTS, Strasbourg, France
Sample Questions: EXAMINATION I Form A Mammalogy -EEOB 625. Name Composite of previous Examinations
 Sample Questions: EXAMINATION I Form A Mammalogy -EEOB 625 Name Composite of previous Examinations Part I. Define or describe only 5 of the following 6 words - 15 points (3 each). If you define all 6,
Sample Questions: EXAMINATION I Form A Mammalogy -EEOB 625 Name Composite of previous Examinations Part I. Define or describe only 5 of the following 6 words - 15 points (3 each). If you define all 6,
LABORATORY #10 -- BIOL 111 Taxonomy, Phylogeny & Diversity
 LABORATORY #10 -- BIOL 111 Taxonomy, Phylogeny & Diversity Scientific Names ( Taxonomy ) Most organisms have familiar names, such as the red maple or the brown-headed cowbird. However, these familiar names
LABORATORY #10 -- BIOL 111 Taxonomy, Phylogeny & Diversity Scientific Names ( Taxonomy ) Most organisms have familiar names, such as the red maple or the brown-headed cowbird. However, these familiar names
Let s Build a Cladogram!
 Name Let s Build a Cladogram! Date Introduction: Cladistics is one of the newest trends in the modern classification of organisms. This method shows the relationship between different organisms based on
Name Let s Build a Cladogram! Date Introduction: Cladistics is one of the newest trends in the modern classification of organisms. This method shows the relationship between different organisms based on
Supplementary Figure 1 Cartilaginous stages in non-avian amniotes. (a) Drawing of early ankle development of Alligator mississippiensis, as reported
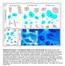 Supplementary Figure 1 Cartilaginous stages in non-avian amniotes. (a) Drawing of early ankle development of Alligator mississippiensis, as reported by a previous study 1. The intermedium is formed at
Supplementary Figure 1 Cartilaginous stages in non-avian amniotes. (a) Drawing of early ankle development of Alligator mississippiensis, as reported by a previous study 1. The intermedium is formed at
These small issues are easily addressed by small changes in wording, and should in no way delay publication of this first- rate paper.
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): This paper reports on a highly significant discovery and associated analysis that are likely to be of broad interest to the scientific community.
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): This paper reports on a highly significant discovery and associated analysis that are likely to be of broad interest to the scientific community.
f35 Cladistics < derived characters >
 THE SYNTHETIC THEORY OF EVOLUTION 381 f35 Cladistics < derived characters > Taxa once touted as ancestral are really not ancestral, for a variety of empirical reasons. To learn [this] proves sometimes
THE SYNTHETIC THEORY OF EVOLUTION 381 f35 Cladistics < derived characters > Taxa once touted as ancestral are really not ancestral, for a variety of empirical reasons. To learn [this] proves sometimes
Amniote Relationships. Reptilian Ancestor. Reptilia. Mesosuarus freshwater dwelling reptile
 Amniote Relationships mammals Synapsida turtles lizards,? Anapsida snakes, birds, crocs Diapsida Reptilia Amniota Reptilian Ancestor Mesosuarus freshwater dwelling reptile Reptilia General characteristics
Amniote Relationships mammals Synapsida turtles lizards,? Anapsida snakes, birds, crocs Diapsida Reptilia Amniota Reptilian Ancestor Mesosuarus freshwater dwelling reptile Reptilia General characteristics
May 10, SWBAT analyze and evaluate the scientific evidence provided by the fossil record.
 May 10, 2017 Aims: SWBAT analyze and evaluate the scientific evidence provided by the fossil record. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing our AIMS: E.3-Examining
May 10, 2017 Aims: SWBAT analyze and evaluate the scientific evidence provided by the fossil record. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing our AIMS: E.3-Examining
Name: Date: Hour: Fill out the following character matrix. Mark an X if an organism has the trait.
 Name: Date: Hour: CLADOGRAM ANALYSIS What is a cladogram? It is a diagram that depicts evolutionary relationships among groups. It is based on PHYLOGENY, which is the study of evolutionary relationships.
Name: Date: Hour: CLADOGRAM ANALYSIS What is a cladogram? It is a diagram that depicts evolutionary relationships among groups. It is based on PHYLOGENY, which is the study of evolutionary relationships.
Chapter 11. Dinosaurs and the Hierarchy of Life
 Chapter 11 Dinosaurs and the Hierarchy of Life Are birds related to dinosaurs or not? Deinonychus carried the question full circle. First Huxley and then Ostrom argued that small dinosaurs are closely
Chapter 11 Dinosaurs and the Hierarchy of Life Are birds related to dinosaurs or not? Deinonychus carried the question full circle. First Huxley and then Ostrom argued that small dinosaurs are closely
