Staying Alive. Strand Achievement Aim Achievement Objective. Learning Area
|
|
|
- Catherine Howard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Teachers This unit of work has been designed to support your class visit for the Staying Alive programme at the National Aquarium of New Zealand. Students will participate in a range of level-specific interactive activities. The primary focus of this programme is the Living World Strand of the Science Curriculum, however when planning your unit of work, links can be made to other essential learning areas. Similarly, different essential skills can be emphasised depending on the needs of your students. Programme Overview The staying alive programme teaches students about the different adaptations found in a variety of animals, including fish. Students will examine and discover what special features the animals have to successfully live in certain environments and why each animal has adapted to live in its environment. Essential Learning Area: Science Strand: Living World Achievement Aim 2 and 3: Investigate and understand relationships between structure and function in living organisms. Investigate and understand how organisms grow, reproduce and change over generations. Level Essential Learning Area Strand Achievement Aim Achievement Objective 1 Science Living World Structure and Function Interdependence of living organisms 2 Science Living World Structure and Function Interdependence of living organisms 3 Science Living World Structure and Function Interdependence of living organisms 4 Science Living World Structure and Function Scientific Skills and Attitudes Focusing and Planning Information Gathering Processing and Interpreting Reporting Staying Alive Interdependence of living organisms Observe and identify parts of common animals. Investigate and understand the general functions of the main parts of animals and plants. Investigate special features of common animals and describe how these help them to stay alive. Investigate and describe special features of animals or plants which help survival into the next generation.
2 The Staying Alive programme at the National Aquarium of New Zealand lays the foundations for developing the above investigative skills and attitudes. Specific Learning Outcomes To understand why a particular type of animal lives in certain habitats. To understand, describe and identify examples of structural, functional and behavioural adaptations which help animals survive into the next generation. To become aware of the environmental factors affecting aquatic organisms and discuss how certain factors affect their survival. Major topics covered by this booklet: 1) Patterns, colours and shapes 2) Teeth, jaws and guts 3) Survival on the land Fabulous Facts. What do you know about evolution? The theory of evolution discusses how certain characteristics of organisms have come about using the ideas of natural selection and mutation. Darwin and Wallace in the 19th Century both* came up with an idea to explain why there are so many different animals in the world and how organisms change over time. Natural selection and survival of the fittest Darwin suggested that certain organisms have characteristics that better suited them to their environment. These organisms would tend to reproduce more prolifically than other organisms. Therefore their characteristics could be passed on in higher proportion to future generations. In some cases, new characteristics formed due to a mutation. If this mutation was beneficial to the organism in its environment, the mutation would be passed on to future generations. Over time, populations could continually improve their adaptations to the environment to which they were subjected, and those with inadequate adaptations would become extinct. *Charles Darwin is usually recognised as the first person to come up with a generally accepted scientific explanation for evolution. However, Alfred Wallace who also carried out large voyages around the world came up with an explanation for evolution, possibly even before Darwin but his theory was not published before Darwin s theory of evolution (Origin of Species) and therefore is not well recognised.
3 Staying Alive Pre and post-visit activities Pre - visit activities Many features of animals and plants can help them to adapt to their surrounding environment, some are more obvious than others. Adaptations of animals can be divided into structural or behavioural adaptations both are addressed in this booklet. Patterns, colours and shapes Spot the difference? Look at the pictures of adaptations in a variety of animals (see pictures provided at the back of the booklet). Discuss with the class how the patterns differ on the animals, what do the shapes and patterns on the animals look like? Could the patterns, spots and shapes be useful? Fabulous Facts. What do you know about mimicry? Mimicry is used by some animals as a way of protecting themselves. The animal mimics/resembles another animal which is usually poisonous or has some nasty habits when being attacked (e.g. skunks)! Monarch and viceroy butterflies By eating and storing toxic compounds that are found in milkweed, the monarch caterpillar and butterfly are poisonous to many birds. The bright orange and black colours of the butterfly wings are a warning to birds. The viceroy butterfly mimics the monarch butterfly in wing shape and colouring and so escapes being preyed upon by many birds! Can you tell the difference between the butterfly species? Eye-spots and mimicry? Brainstorm the words eye-spots, camouflage and mimicry what do they mean? Check the class definitions with dictionary definitions. Your own adapted animal Draw a picture of an animal (use the sheet found at the back of the booklet) with different patterns, colours and shapes. Once the students have drawn the adapted animal ask the students to present their drawing, explaining what features the animal has and how it is adapted to a particular environment. For example, does it have eyespots? Does it have spines or spikes? Is it camouflaged?
4 Camouflage mural Create sheets with different patterns (e.g. zebra stripes or leaf patterns). Ask the students to design an animal which uses camouflage. Cut and paste the different camouflage animals to the mural. Tall tails and fins Have a class discussion about the different shaped tails (see picture at back of the booklet). What are the different tail shapes likely to be used for? Balance, speed or manoeuvrability? Fabulous Facts. Are all tails and fins the same? Tails depending on their shape and size have very different uses Kangaroo and kangaroo rats have very long tails which are used for balance while they are hopping along at high speed. Can you think of any other animals that use their tails for balance while running? New world monkeys (e.g. howler monkeys and spider monkeys) use their tails as a 5 th prehensile limb (used for hanging in trees, or moving from tree to tree). Old world monkeys (e.g. rhesus monkeys and baboons) use their tails for balance rather than as a prehensile organ. Fishes have many different fins that are used in many different ways Pelvic fins are often found on the bottom side (ventral) of fish. Pelvic fins are usually used as stabilisers and in bottom dwelling fish the pelvic fin is modified to help hold onto substrates. Pectoral fins are usually located high up on the sides of fishes. The shape of the fins will be long and pointed in fast swimming fish (e.g. Tuna) and rounded in slower moving fish (e.g. Groper). Dorsal and anal fins are used for stability in fish which need to manoeuvre quickly and are shaped as small finlets in fast swimming fish. The finlets are often folded up when swimming fast. The caudal fin is often a very good indicator of a fish s ability to swim fast. Fast swimming fish have a stiff quarter moon shaped tail whereas fish that swim at a constant speed over long distances have forked shaped tails. Fish that swim slowly but need to manoeuvre quickly have square or rounded tails.
5 Teeth, jaws and guts Small teeth and large teeth Look at pictures of carnivore and herbivore teeth or bring along animal skulls (with teeth) to aid your class discussions. Discuss with the class the function of teeth. What do we use teeth for? What type/shape of teeth do carnivores have? What type/shape teeth do herbivores have? Do humans have both carnivore and herbivore type teeth? Hint: You may need to do a prior brainstorm about the words carnivore, herbivore and omnivore. Definitions and associated tasks can be found in the Rocky Shore pre- and post - visit activity booklet, in the food web section. The basic pattern of teeth in mammals (upper jaw, from front to back) is four incisors, two canines, eight premolars and six molars. However there are modifications to the basic teeth pattern which often reflect the dietary habits of the animal. Large predatory carnivores (e.g. lions) have canines adapted for stabbing and slicing and large sharp molars which can crush bones. Herbivores have incisors and canines modified for clipping grass and large flat molars for grinding tough fibrous food. Elephant tusks are a form of modified incisors and in the case of a walrus, modified canines! Invite a tooth authority Invite the dental nurse or a dentist to come along to the school to talk about human teeth. Fabulous Facts. What do you know about your teeth? Humans are usually omnivores (eat both meat and veggies) and therefore we need a range of teeth for different jobs. Humans have four different types of teeth; canines, incisors, premolars and molars. The teeth in the front of the mouth are flat chisel like teeth (incisors) used for nipping and cutting. Back from the incisors is a set of canines (four in total). Canines are sharp pointed teeth used for stabbing and tearing. Carnivores have many canine-like teeth. Behind the canines are the pre-molars, and further back again are molars (molars don t usually grow through until humans are in their late teens). Pre-molars and molars are used for grinding. incisors canine premolars molars
6 The tooth rap Make a song or rap about teeth, jaws and guts. For example. Jiggle, jiggle Chatter, chatter the teeth go It s a bit chillllly out there Gnaw, grind, chew Use those jaws Chomp, champ, chip the teeth go on a bit of old steak Tear, shread, pull these are the actions your teeth make When you are chewing your food. Say cheese Make a classroom tooth poster. Put a characteristic shaped tooth beside pictures of different animals. Can you identify the type of animal (i.e. carnivore or herbivore) by the shape of the tooth? Fabulous Facts. What do you know about specialised teeth? Most sharks are predators and have very sharp teeth. However, different sharks eat different prey and used different methods of attack and biting so the tooth shape does vary slightly. For example mako shark teeth are designed to hold, pierce and rip flesh (a bit like a set of very sharp needles) whereas the seven gill shark and spiny dogfish teeth are designed to cut flesh (a bit like a serrated knife!). Mako Shark Tooth Sevengill Shark Tooth Spiny Dogfish Tooth Survival on the land What helps this animal survive? Look at the different animal pictures (see pictures in the back of the booklet) with the class. Discuss with the class if there are any features that the animals may have that might help its survival on land. Hint: For most animals, the move to land was associated with ways of combating desiccation (i.e. drying out). Feathers, scales and efficient water retaining devices such as kidneys all helped animals make the move to land. What would you do if.? Role-play behavioural adaptations with the class. Ask the class to act, mime or discuss what they would do under different scenarios. Ask the children to identify the different behavioural adaptations in each of the scenarios. Here are some examples of scenarios to role-play; make up some of your own too!
7 Pretend you are a slug or a snail and you are on a footpath and the sun has just come out! What would you do? You are outside and it is cold and windy! What would you do? Pretend you are a small bird pecking at food on the lawn. Out of the corner of your eye you see a cat! What would you do? Pretend you are a hedgehog out in broad daylight and some children come along! What would you do? After the role-plays, sit the class down and discuss the difference between behavioural adaptations and structural adaptations. For example a hedgehog curls into a ball when frightened (behavioural adaptation) and has spines (structural adaptation). Fabulous Facts. Did you know? Herbivores can only give limited protection to their newly born offspring. As a behavioural adaptation to avoid predation, many newly born herbivores (e.g. zebra, sheep and goats) are able to get to their feet and run with their parents less than an hour after their birth.
8 Post visit activities Bill shapes and guts Bird bills are a good example of a structural adaptation for collecting food. Take a class trip to an estuary, the beach or wildlife sanctuary. Observe the different birds, their bill shape and feeding habits. Fill in the provided field sheet (see back of booklet) or adapt your own for the field trip. Make sure you take binoculars along with you! Have a class discussion about the different bill types (see provided pictures at back of booklet). Can you suggest what food the birds may eat by looking at their bill shape? Do a class research project on the differences between herbivore and carnivore stomachs. How many stomachs does a herbivore have? Why? Hint: The functional adaptation may have something to do with the type of food they eat! Discuss with the class why humans have an appendix?? Note most biology text books will have diagrams of animal anatomy. Styles of running There are many different running styles found in two or four legged animals. Here are a few to give you an appreciation of what they are and why the different running styles are useful: Most mammals show examples of cursorial locomotion (running design). A full cycle of running motion is called a stride. Animals are able to increase their speed by increasing the length of the stride or the number of times they complete a stride in a set time (i.e. the rate of the stride). The length of the stride can be maximised by increasing the gait (time in which the animal s feet are off the ground). The gait is increased in a number of ways; 1) Lengthening of limbs, many herbivores such as horses and giraffes have long leg bones. 2) Running on your toes! The bone structure, particularly in herbivores (e.g. horses) has been modified in such a way that these animals are really only running on a single digit. 3) Flexing of the spine, many carnivores such as cats and dogs are able to flex their spines while running. Cheetahs are an extreme example of spine flexing! Animals can be grouped into weakly cursorial, highly developed cursors or richochetal animals. Weakly cursorial animals usually have at least one foot on the ground at any one time. Highly developed cursors have extended periods in their stride where they are unsupported. Richochetal animals spend most of the time off the ground during their stride! Richochetal locomotion is used by smaller animals as an escape mechanism (e.g. kangaroo mouse). Cursorial locomotion can also be grouped according to speed and distance covered. Animals that use spring - like movements can move very fast but only for short durations (e.g. antelope and cheetahs). Animals that use pendulum - like movements can move quickly over long distances (e.g. wolves and horses). Discuss different running styles (use the above information or the web sites: Animal diversity (look up special topics, mammal anatomy) and anatomical adaptation for cursorial locomotion). Once you have discussed different running styles, look at videos of animals (e.g. wildlife documentaries, big game animals in Africa) see if you can identify the different running styles or specialisation in running styles. Discuss why different animals have different running styles. Is it for catching prey? To avoid being caught? For speed (running short distances)? For endurance (running long distances)? An extension task may be to look at some athletics sports, e.g. the 2016 Olympics. Is there a difference in running style between sprinters and long distance runners?
9 Eye position Get the children to bring in a picture of their favourite animal (the picture must show the head clearly) to class. Discuss with the class differences in eye position (see fact box). Ask the children to discuss the eye position of their favourite animal. Can you tell whether it is likely to be a herbivore or carnivore? Fabulous Facts. Did you know? The position of eyes can often indicate whether the animal is a predator or prey. Predatory animals tend to have eyes positioned in the front of the head. This leads to stereoscopic vision which allows distances ahead to be judged while moving. Animals which are preyed upon (e.g. rabbits and other herbivores) have eyes positioned on the side of the head, giving a wide total visual field both in front of them and behind them. The size of the eye can also give clues as to whether an animal is nocturnal (night dwelling) or not. For example owls and possums have large eyes.
10 Some useful references: Discovering Life on Earth. David Attenborough. (1981), Collins, London. Biology, 5th Edition. Curtis and Barnes. (1989), Worth Publishers, New York. Evolution a New Zealand perspective. Secondary Education programmes, National Aquarium of New Zealand. The Life of Birds. David Attenborough (1998). BBC Books, London. Videos: Survival: A Wild South Video Mutation: Science of Survival: A Wild South Video
Animal Adaptations. EQ: How do animals adapt to survive?
 Animal Adaptations EQ: How do animals adapt to survive? What is adaptation? An adaptation is any special characteristic or skill that helps an animal to survive in its habitat. Examples: The shape of a
Animal Adaptations EQ: How do animals adapt to survive? What is adaptation? An adaptation is any special characteristic or skill that helps an animal to survive in its habitat. Examples: The shape of a
Inferring SKILLS INTRODUCTION
 SKILLS INTRODUCTION Inferring Have you ever come home, smelled fish cooking, and thought, We re having fish for dinner? You made an observation using your sense of smell and used past experience to conclude
SKILLS INTRODUCTION Inferring Have you ever come home, smelled fish cooking, and thought, We re having fish for dinner? You made an observation using your sense of smell and used past experience to conclude
SKELETONS: Museum of Osteology Tooth and Eye Dentification Teacher Resource
 SKELETONS: Museum of Osteology Tooth and Eye Dentification Teacher Resource Grade Levels: 3 rd 5 th Grade 3 rd Grade: SC.3.N.1.1 - Raise questions about the natural world, investigate them individually
SKELETONS: Museum of Osteology Tooth and Eye Dentification Teacher Resource Grade Levels: 3 rd 5 th Grade 3 rd Grade: SC.3.N.1.1 - Raise questions about the natural world, investigate them individually
Species must be adapted to their habitat.
 Species must be adapted to their habitat. Species must protect themselves from the heat, cold, move around, feed themselves, communicate and reproduce. These are the types of adaptations which we will
Species must be adapted to their habitat. Species must protect themselves from the heat, cold, move around, feed themselves, communicate and reproduce. These are the types of adaptations which we will
Is That Mammal a Carnivore, Herbivore or Omnivore?
 Name: Is That Mammal a Carnivore, by Guy Belleranti A mammal can be a carnivore (meat eater), herbivore (plant eater) or omnivore (meat and plant eater). By looking at the teeth, eye position and feet
Name: Is That Mammal a Carnivore, by Guy Belleranti A mammal can be a carnivore (meat eater), herbivore (plant eater) or omnivore (meat and plant eater). By looking at the teeth, eye position and feet
Inferring #1 This diagram shows the beak of several different species of birds. Make observations about the beaks and answer the questions.
 Observing #1 1. Record a qualitative observation of the scene in the illustration. 2. Record a quantitative observation of the scene in the illustration. 3. Observation or inference? The house collapsed.
Observing #1 1. Record a qualitative observation of the scene in the illustration. 2. Record a quantitative observation of the scene in the illustration. 3. Observation or inference? The house collapsed.
ASSESSMENT. Assessment
 ASSESSMENT Assessment This section provides some possible questions that could be incorporated into a pre and/or postassessment of student learning regarding concepts covered with the Bone Box Resource
ASSESSMENT Assessment This section provides some possible questions that could be incorporated into a pre and/or postassessment of student learning regarding concepts covered with the Bone Box Resource
Adaptation. Survival of the Fittest
 Adaptation Survival of the Fittest It s all about traits Acquired Traits Happen After Birth Scars Pierced Ears Learning a Skill Changing Appearance It s all about traits Inherited Traits Programmed at
Adaptation Survival of the Fittest It s all about traits Acquired Traits Happen After Birth Scars Pierced Ears Learning a Skill Changing Appearance It s all about traits Inherited Traits Programmed at
MAMMAL LESSON PLAN. Understanding (s)/goals Students will understand that mammals are a unique group within the animal kingdom.
 MAMMAL LESSON PLAN Lesson Topic: Mammals Grade level: Elementary Grades Length of lesson: Approximately 5 days; will vary based on age and ability Curriculum Developer: Jennifer Mooney, M.Ed. Stage 1 Desired
MAMMAL LESSON PLAN Lesson Topic: Mammals Grade level: Elementary Grades Length of lesson: Approximately 5 days; will vary based on age and ability Curriculum Developer: Jennifer Mooney, M.Ed. Stage 1 Desired
Bones and Bellies Clue Card 1
 Bones and Bellies Clue Card 1 Land Animals to the land food web. Animal A I am a carnivorous marsupial. My upper canine teeth are slightly larger than the lower canines. My molar teeth are sharp and pointy
Bones and Bellies Clue Card 1 Land Animals to the land food web. Animal A I am a carnivorous marsupial. My upper canine teeth are slightly larger than the lower canines. My molar teeth are sharp and pointy
ADAPTATION IN ANIMALS. 1. Which body feature of a frog MAINLY helps it to capture a flying insect? Ans
 Name : Subject : Science Class : V Roll No. : Date : SECTION A Choose the correct alternative ADAPTATION IN ANIMALS 1. Which body feature of a frog MAINLY helps it to capture a flying insect? a. Long,
Name : Subject : Science Class : V Roll No. : Date : SECTION A Choose the correct alternative ADAPTATION IN ANIMALS 1. Which body feature of a frog MAINLY helps it to capture a flying insect? a. Long,
HUMAN APPENDIX BATS & TROPICAL FLOWERS
 HUMAN APPENDIX In humans, the appendix is a short piece of tissue off the large intestine. It is not used by humans for digestive functions. In other mammals, like rabbits and deer, the cecum is a large
HUMAN APPENDIX In humans, the appendix is a short piece of tissue off the large intestine. It is not used by humans for digestive functions. In other mammals, like rabbits and deer, the cecum is a large
Station #4. All information Adapted from:http://school.discoveryeducation.com/lessonplans/activities/makeitahabitat/adaptations.html and other sites
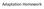 Adaptation Homework Station #1 GOAL: Avoid the Sun s heat and keep themselves cool. Animals spend the daylight hours hiding in burrows or behind boulders. They come out at night to hunt and forage for
Adaptation Homework Station #1 GOAL: Avoid the Sun s heat and keep themselves cool. Animals spend the daylight hours hiding in burrows or behind boulders. They come out at night to hunt and forage for
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and. the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and Activityengage the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Big Cats, Big Teeth How does the shape and size of
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and Activityengage the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Big Cats, Big Teeth How does the shape and size of
Adaptations 4. Adaptations 1 Adaptations 2
 Adaptations 1 Adaptations 2 Describe Charles Darwin s Theory of Natural Selection. Charles Darwin studied many new species and their adaptations. On which group of islands did he complete most of his research?
Adaptations 1 Adaptations 2 Describe Charles Darwin s Theory of Natural Selection. Charles Darwin studied many new species and their adaptations. On which group of islands did he complete most of his research?
Examples of herbivorous animals: rabbits, deer and beaver
 Mammal Adaptations Mammals are a group of animals that fit together because they all 1)have fur or hair 2) bear live young 3) feed their young with milk from specialized mammary glands. We are going to
Mammal Adaptations Mammals are a group of animals that fit together because they all 1)have fur or hair 2) bear live young 3) feed their young with milk from specialized mammary glands. We are going to
KS3 Adaptation. KS3 Adaptation. Adaptation dominoes Trail
 KS3 Adaptation KS3 Adaptation Adaptation dominoes Trail Adaptation Trail The Adaptation Trail is a journey of discovery through Marwell which allows students to develop and apply their knowledge and understanding
KS3 Adaptation KS3 Adaptation Adaptation dominoes Trail Adaptation Trail The Adaptation Trail is a journey of discovery through Marwell which allows students to develop and apply their knowledge and understanding
Let s learn about ANIMALS. Level : School:.
 Let s learn about ANIMALS Name: Level : School:. 1. CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS There are many different animals and we can classify them according to: Their skeleton: Vertebrates have a skeleton but Invertebrates
Let s learn about ANIMALS Name: Level : School:. 1. CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS There are many different animals and we can classify them according to: Their skeleton: Vertebrates have a skeleton but Invertebrates
Reptilian Requirements Created by the North Carolina Aquarium at Fort Fisher Education Section
 Essential Question: North Carolina Aquariums Education Section Reptilian Requirements Created by the North Carolina Aquarium at Fort Fisher Education Section What physical and behavioral adaptations do
Essential Question: North Carolina Aquariums Education Section Reptilian Requirements Created by the North Carolina Aquarium at Fort Fisher Education Section What physical and behavioral adaptations do
What Can I Learn From a Skull?
 What Can I Learn From a Skull? Pennsylvania Envirothon 2018 Skulls- Herbivores, Omnivores, and Carnivores Lesson Overview Grade level(s): Elementary School (K-5), Middle School Subjects(s): Biology/Life
What Can I Learn From a Skull? Pennsylvania Envirothon 2018 Skulls- Herbivores, Omnivores, and Carnivores Lesson Overview Grade level(s): Elementary School (K-5), Middle School Subjects(s): Biology/Life
Use your Fact Files to circle the correct lion facts. Which food would the lion rather eat? About how many years does a lion live?
 Use your Fact Files to circle the correct lion facts. Which food would the lion rather eat? About how many years does a lion live? 25 50 1 16 GRADE ONE ZOO ANIMALS SCIENCE 001 Which lion would typically
Use your Fact Files to circle the correct lion facts. Which food would the lion rather eat? About how many years does a lion live? 25 50 1 16 GRADE ONE ZOO ANIMALS SCIENCE 001 Which lion would typically
KS3 Adaptation. KS3 Adaptation. Adaptation dominoes Trail
 KS3 Adaptation KS3 Adaptation Adaptation dominoes Trail Adaptation Trail The Adaptation Trail is a journey of discovery through Marwell which allows students to develop and apply their knowledge and understanding
KS3 Adaptation KS3 Adaptation Adaptation dominoes Trail Adaptation Trail The Adaptation Trail is a journey of discovery through Marwell which allows students to develop and apply their knowledge and understanding
Teacher s Guide. All About Baby Animals series
 Teacher s Guide All About Baby Animals series Introduction This teacher s guide helps educate young children about baby animals. Animals live in many different habitats. Some live in grasslands, rainforests,
Teacher s Guide All About Baby Animals series Introduction This teacher s guide helps educate young children about baby animals. Animals live in many different habitats. Some live in grasslands, rainforests,
Lab 9: Inventing Life Forms
 Name: Section: Date: Lab 9: Inventing Life Forms 1 Instructions The purpose of this lab is to create a life form that may have evolved on a planet other than Earth. Follow the instructions below detailing
Name: Section: Date: Lab 9: Inventing Life Forms 1 Instructions The purpose of this lab is to create a life form that may have evolved on a planet other than Earth. Follow the instructions below detailing
Class Reptilia Testudines Squamata Crocodilia Sphenodontia
 Class Reptilia Testudines (around 300 species Tortoises and Turtles) Squamata (around 7,900 species Snakes, Lizards and amphisbaenids) Crocodilia (around 23 species Alligators, Crocodiles, Caimans and
Class Reptilia Testudines (around 300 species Tortoises and Turtles) Squamata (around 7,900 species Snakes, Lizards and amphisbaenids) Crocodilia (around 23 species Alligators, Crocodiles, Caimans and
Reproduction in Seed Plants (pp )
 Structure and Function of Plants Reading/Notetaking Guide Reproduction in Seed Plants (pp. 388 397) This section gives examples of the group of seed plants known as gymnosperms and angiosperms and describes
Structure and Function of Plants Reading/Notetaking Guide Reproduction in Seed Plants (pp. 388 397) This section gives examples of the group of seed plants known as gymnosperms and angiosperms and describes
Unit 7: Adaptation STUDY GUIDE Name: SCORE:
 Unit 7: Adaptation STUDY GUIDE Name: SCORE: 1. Which is an adaptation that makes it possible for the animal to survive in a cold climate? A. tail on a lizard B. scales on a fish C. stripes on a tiger D.
Unit 7: Adaptation STUDY GUIDE Name: SCORE: 1. Which is an adaptation that makes it possible for the animal to survive in a cold climate? A. tail on a lizard B. scales on a fish C. stripes on a tiger D.
Slide 1. Birds & Mammals. Chapter 15
 Slide 1 Birds & Mammals Chapter 15 Slide 2 What is a Bird? Vertebrate Endothermic Feathered 4 chambered heart Egg laying Fore-limbs adapted for flight Bones nearly hollow (allow for lighter weight) Slide
Slide 1 Birds & Mammals Chapter 15 Slide 2 What is a Bird? Vertebrate Endothermic Feathered 4 chambered heart Egg laying Fore-limbs adapted for flight Bones nearly hollow (allow for lighter weight) Slide
Skulls & Evolution. 14,000 ya cro-magnon. 300,000 ya Homo sapiens. 2 Ma Homo habilis A. boisei A. robustus A. africanus
 Skulls & Evolution Purpose To illustrate trends in the evolution of humans. To demonstrate what you can learn from bones & fossils. To show the adaptations of various mammals to different habitats and
Skulls & Evolution Purpose To illustrate trends in the evolution of humans. To demonstrate what you can learn from bones & fossils. To show the adaptations of various mammals to different habitats and
Animal Adaptations Woodland Animal Fact Sheet
 Post Visit Resource 5 Animal Adaptations Woodland Animal Fact Sheet Fox Food: Foxes will eat almost anything they can get hold of. They eat small mammals such as rabbits and voles, insects and invertebrates,
Post Visit Resource 5 Animal Adaptations Woodland Animal Fact Sheet Fox Food: Foxes will eat almost anything they can get hold of. They eat small mammals such as rabbits and voles, insects and invertebrates,
YOU! THANK. Connect with us: Facebook Pinterest Instagram Blog
 THANK YOU! Thank you for checking out our store. We use these products in our classrooms and feel they benefit students greatly. We appreciate your interest and hope you enjoy using our creations in your
THANK YOU! Thank you for checking out our store. We use these products in our classrooms and feel they benefit students greatly. We appreciate your interest and hope you enjoy using our creations in your
Survivor: A Game of Traits and Natural Selection VINSE/VSVS Rural
 Survivor: A Game of Traits and Natural Selection 2018-2019 VINSE/VSVS Rural IA. Introduction Why is Charles Darwin so important? Concluded that organisms changed over time to better survive in their specific
Survivor: A Game of Traits and Natural Selection 2018-2019 VINSE/VSVS Rural IA. Introduction Why is Charles Darwin so important? Concluded that organisms changed over time to better survive in their specific
How Animals Live. Chapter 2 Review
 How Animals Live Chapter 2 Review What do animals need to survive? Water Food Air (oxygen) Shelter Butterfly life cycle During the larva stage, the butterfly is called a caterpillar. During the pupa stage,
How Animals Live Chapter 2 Review What do animals need to survive? Water Food Air (oxygen) Shelter Butterfly life cycle During the larva stage, the butterfly is called a caterpillar. During the pupa stage,
Birds & Mammals. Chapter 15
 Birds & Mammals Chapter 15 What is a Bird? Vertebrate Endothermic Feathered 4 chambered heart Egg laying Fore-limbs adapted for flight Bones nearly hollow (allow for lighter weight) Bird Internal Anatomy
Birds & Mammals Chapter 15 What is a Bird? Vertebrate Endothermic Feathered 4 chambered heart Egg laying Fore-limbs adapted for flight Bones nearly hollow (allow for lighter weight) Bird Internal Anatomy
You are about to go on a journey of discovery around the zoo to find out more about how different animals are suited to their environment.
 Name: Adaptation Trail Welcome to Marwell Zoo! You are about to go on a journey of discovery around the zoo to find out more about how different animals are suited to their environment. First, let s remind
Name: Adaptation Trail Welcome to Marwell Zoo! You are about to go on a journey of discovery around the zoo to find out more about how different animals are suited to their environment. First, let s remind
AN2.3 Curriculum: Animal Growth and Change (grade 2)
 AN2.3 Curriculum: Animal Growth and Change (grade 2) Overview: This lesson will introduce elementary level students to snakes. Its goal is to have the students understand that all creatures have a role
AN2.3 Curriculum: Animal Growth and Change (grade 2) Overview: This lesson will introduce elementary level students to snakes. Its goal is to have the students understand that all creatures have a role
ì<(sk$m)=bdibci< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Labels Diagram Glossary Animals Scott Foresman Science 3.2 ì
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Labels Diagram Glossary Animals Scott Foresman Science 3.2 ì
Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy
 Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy Presented by BIOBUGS: Biology Inquiry and Outreach with Boston University Graduate Students In association with LERNet and The BU Biology Teaching Laboratory Designed and
Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy Presented by BIOBUGS: Biology Inquiry and Outreach with Boston University Graduate Students In association with LERNet and The BU Biology Teaching Laboratory Designed and
CORE LESSON: Adaptation Rooms
 CORE LESSON: Adaptation Rooms Objectives and Summary: Students explore the concept of animal adaptation by modeling the benefit of an adaptation in the introduction (teacher led), and by observing and
CORE LESSON: Adaptation Rooms Objectives and Summary: Students explore the concept of animal adaptation by modeling the benefit of an adaptation in the introduction (teacher led), and by observing and
Curriculum connections: Science: grade 2 Life Science Animal Growth and Change Art: grades 1-4 Patterns, Animal Portraits
 First Nations F.O.F. Elementary Years Lesson Plan Overview: This lesson will introduce Elementary level students to snakes. Its goal is to have the students understand that all creatures have a role and
First Nations F.O.F. Elementary Years Lesson Plan Overview: This lesson will introduce Elementary level students to snakes. Its goal is to have the students understand that all creatures have a role and
Owl Pellet Dissection A Study of Food Chains & Food Webs
 NAME Owl Pellet Dissection A Study of Food Chains & Food Webs INTRODUCTION: Owl pellets are masses of bone, teeth, hair, feathers and exoskeletons of various animals preyed upon by raptors, or birds of
NAME Owl Pellet Dissection A Study of Food Chains & Food Webs INTRODUCTION: Owl pellets are masses of bone, teeth, hair, feathers and exoskeletons of various animals preyed upon by raptors, or birds of
Let s begin by learning a little more about rays, in general. First, an anatomy lesson!
 Let s begin by learning a little more about rays, in general. First, an anatomy lesson! Eyes Rays, in general, do not have very good eyesight. What they lack in eyesight, they make up for using electroreceptors,
Let s begin by learning a little more about rays, in general. First, an anatomy lesson! Eyes Rays, in general, do not have very good eyesight. What they lack in eyesight, they make up for using electroreceptors,
Animal Adaptations. Structure and Function
 Name period date assigned date due date returned 1. What is a variation 2. What is an adaptation omplete the chart with the examples from the power point. List adaptations that help animals do the following:
Name period date assigned date due date returned 1. What is a variation 2. What is an adaptation omplete the chart with the examples from the power point. List adaptations that help animals do the following:
discover more! Follow Up Activities and Questions Kindy - Pre Primary Curriculum Reference Key Concepts Follow Up Questions Follow Up Activities
 Science - Understanding Concepts Life and living Students understand the biology of other living things and recognise the interdependence of life. Kindy - Pre Primary Students understand the relationship
Science - Understanding Concepts Life and living Students understand the biology of other living things and recognise the interdependence of life. Kindy - Pre Primary Students understand the relationship
Science Class 4 Topic: Habitats Reinforcement Worksheet. Name: Sec: Date:
 Science Class 4 Topic: Habitats Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the correct answer. 1. Which of these things are you NOT likely to find in a park or a garden? A. An earthworm B. An
Science Class 4 Topic: Habitats Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the correct answer. 1. Which of these things are you NOT likely to find in a park or a garden? A. An earthworm B. An
Beaver. Mammal Rodent
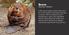 Beaver Rodent Is the second largest rodent in the world. It is a semi-aquatic rodent that is primarily nocturnal. They are mainly known for building dams, canals, and lodges(their homes). Large sharp front
Beaver Rodent Is the second largest rodent in the world. It is a semi-aquatic rodent that is primarily nocturnal. They are mainly known for building dams, canals, and lodges(their homes). Large sharp front
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore SCAVENGER For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore SCAVENGER For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Science10 (AdaptationsMulberry4th)
 Name: Date: 1. Which bird's foot below is best for grasping prey? A. B. C. D. This online assessment item contains material that has been released to the public by the Massachusetts Department of Education.
Name: Date: 1. Which bird's foot below is best for grasping prey? A. B. C. D. This online assessment item contains material that has been released to the public by the Massachusetts Department of Education.
Teacher: Read directions only. Students read passage and answer questions 1-6 independently.
 2 nd Grade ELA Benchmark #2 Teacher Assessment [22 points] Teacher: Read directions only. Students read passage and answer questions 1-6 independently. Student Directions: Read both texts and answer questions
2 nd Grade ELA Benchmark #2 Teacher Assessment [22 points] Teacher: Read directions only. Students read passage and answer questions 1-6 independently. Student Directions: Read both texts and answer questions
A. Body Temperature Control Form and Function in Mammals
 Taxonomy Chapter 22 Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Mammals Characteristics Evolution of Mammals Have hair and First appear in the mammary glands Breathe air, 4chambered heart, endotherms
Taxonomy Chapter 22 Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Mammals Characteristics Evolution of Mammals Have hair and First appear in the mammary glands Breathe air, 4chambered heart, endotherms
4th Grade Bite into Structure and Function Activity
 Slide 1 / 22 Slide 2 / 22 4th Grade Bite into Structure and Function Activity 2015-08-27 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 22 Animal Teeth Animal teeth are a good example of how structure fits function. Below is
Slide 1 / 22 Slide 2 / 22 4th Grade Bite into Structure and Function Activity 2015-08-27 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 22 Animal Teeth Animal teeth are a good example of how structure fits function. Below is
You are about to go on a journey of discovery around the park to find out more about how different animals are suited to their environment.
 Name: Adaptation Trail Welcome to Marwell Wildlife! You are about to go on a journey of discovery around the park to find out more about how different animals are suited to their environment. First, let
Name: Adaptation Trail Welcome to Marwell Wildlife! You are about to go on a journey of discovery around the park to find out more about how different animals are suited to their environment. First, let
Monarchs: Metamorphosis, Migration, Mimicry and More
 Monarchs: Metamorphosis, Migration, Mimicry and More Middle School Life Science TEKS Sixth Grade: 6.12E, 6.12F Seventh Grade: 7.10A, 7.10B, 7.10C, 7.11A, 7.11B, 7.11C, 7.12A, 7.13A, 7.13B, 7.14A Eighth
Monarchs: Metamorphosis, Migration, Mimicry and More Middle School Life Science TEKS Sixth Grade: 6.12E, 6.12F Seventh Grade: 7.10A, 7.10B, 7.10C, 7.11A, 7.11B, 7.11C, 7.12A, 7.13A, 7.13B, 7.14A Eighth
Pre-lab Homework Lab 9: Food Webs in the Wild
 Lab Section: Name: Pre-lab Homework Put your field hat on and complete the questions below before coming to lab! As always, it is expected that you have supplemented your understanding by reading about
Lab Section: Name: Pre-lab Homework Put your field hat on and complete the questions below before coming to lab! As always, it is expected that you have supplemented your understanding by reading about
Effects of Natural Selection
 Effects of Natural Selection Lesson Plan for Secondary Science Teachers Created by Christine Taylor And Mark Urban University of Connecticut Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology Funded by the
Effects of Natural Selection Lesson Plan for Secondary Science Teachers Created by Christine Taylor And Mark Urban University of Connecticut Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology Funded by the
I will learn to talk about. groups of animals animal characteristics animal habitats. Unit Unit 7
 I am a mammal with both fur and wings. I sleep during the day, and I hunt for food at night. I use high-pitched sounds to find my way around. What am I? I will learn to talk about groups of animals animal
I am a mammal with both fur and wings. I sleep during the day, and I hunt for food at night. I use high-pitched sounds to find my way around. What am I? I will learn to talk about groups of animals animal
Copyright Yan Li. All rights reserved.
 Copyright Yan Li All rights reserved. Without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a database and retrieval system
Copyright Yan Li All rights reserved. Without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a database and retrieval system
Animal Evolution The Chordates. Chapter 26 Part 2
 Animal Evolution The Chordates Chapter 26 Part 2 26.10 Birds The Feathered Ones Birds are the only animals with feathers Descendants of flying dinosaurs in which scales became modified as feathers Long
Animal Evolution The Chordates Chapter 26 Part 2 26.10 Birds The Feathered Ones Birds are the only animals with feathers Descendants of flying dinosaurs in which scales became modified as feathers Long
Equipment and Room Requirements. Three large tables (or desks moved to create three stations) with adequate space for students to move around.
 FROM MICE TO MOOSE MAMMALS OF MAINE From Mice to Moose is an activity-based program where students participate in hands-on activities to develop an understanding of the mammals of Maine. Through the use
FROM MICE TO MOOSE MAMMALS OF MAINE From Mice to Moose is an activity-based program where students participate in hands-on activities to develop an understanding of the mammals of Maine. Through the use
Unterrichtsmaterialien in digitaler und in gedruckter Form. Auszug aus: Cross Curriculum Creativity - Biology - Book 2: Mammals
 Unterrichtsmaterialien in digitaler und in gedruckter Form Auszug aus: Cross Curriculum Creativity - Biology - Das komplette Material finden Sie hier: School-Scout.de Contents Introduction 6 Mammals Mammals
Unterrichtsmaterialien in digitaler und in gedruckter Form Auszug aus: Cross Curriculum Creativity - Biology - Das komplette Material finden Sie hier: School-Scout.de Contents Introduction 6 Mammals Mammals
distance north or south from the equator Learned behavior: actions or mannerisms that are not instinctive but are taught through experience
 Glossary Adaptation: a trait that helps an animal or plant survive in its environment Alpha: the highest ranking individual in a group Amino acid: the building blocks of proteins; found within DNA Bear-proof:
Glossary Adaptation: a trait that helps an animal or plant survive in its environment Alpha: the highest ranking individual in a group Amino acid: the building blocks of proteins; found within DNA Bear-proof:
Mimicry Scientific Background
 Mimicry Scientific Background The adult Monarch butterfly advertises the fact that it is bitter tasting and toxic to its predators by its bright orange, black, and white wing color pattern. This pattern
Mimicry Scientific Background The adult Monarch butterfly advertises the fact that it is bitter tasting and toxic to its predators by its bright orange, black, and white wing color pattern. This pattern
RCPS7-Science-Evolution (RCPS7-Science-Evolution) 1. Which is an adaptation that makes it possible for the animal to survive in a cold climate?
 Name: Date: 1. Which is an adaptation that makes it possible for the animal to survive in a cold climate? A. tail on a lizard B. scales on a fish C. stripes on a tiger D. fur on a bear 2. Use the picture
Name: Date: 1. Which is an adaptation that makes it possible for the animal to survive in a cold climate? A. tail on a lizard B. scales on a fish C. stripes on a tiger D. fur on a bear 2. Use the picture
Mammal Scavenger Hunt Activity
 Mammal Scavenger Hunt Activity Materials: Mammal questions worksheet (pages 2-3) 18 Mammal fact cards (pages 4-8) Tape and scissors Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper
Mammal Scavenger Hunt Activity Materials: Mammal questions worksheet (pages 2-3) 18 Mammal fact cards (pages 4-8) Tape and scissors Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper
Identifying Plant and Animal Adaptations Answer Key
 Identifying Plant and Animal Adaptations Answer Key Instructions: Review the provided photos on the ipad. Try to identify as many adaptations for each plant or animal and determine how each adaptation
Identifying Plant and Animal Adaptations Answer Key Instructions: Review the provided photos on the ipad. Try to identify as many adaptations for each plant or animal and determine how each adaptation
Fishes, Amphibians, Reptiles
 Fishes, Amphibians, Reptiles Section 1: What is a Vertebrate? Characteristics of CHORDATES Most are Vertebrates (have a spinal cord) Some point in life cycle all chordates have: Notochord Nerve cord that
Fishes, Amphibians, Reptiles Section 1: What is a Vertebrate? Characteristics of CHORDATES Most are Vertebrates (have a spinal cord) Some point in life cycle all chordates have: Notochord Nerve cord that
The platypus lives in streams, ponds, and rivers in Australia. It closes its eyes under water and uses its bill to dig in the mud to find its food.
 The platypus lives in streams, ponds, and rivers in Australia. It closes its eyes under water and uses its bill to dig in the mud to find its food. The hyena, found in Africa and parts of Asia, weighs
The platypus lives in streams, ponds, and rivers in Australia. It closes its eyes under water and uses its bill to dig in the mud to find its food. The hyena, found in Africa and parts of Asia, weighs
God s Amazing World. from apples to zebras. Sample. Illustrated by Kristi Davis. My Father s World. Used by Permission
 God s Amazing World from apples to zebras Illustrated by Kristi Davis My Father s World Illustrations by Kristi Davis Text and Creative Design Team: Katerina Hazell, Kristi Davis, Judy Cureton, Marie Hazell
God s Amazing World from apples to zebras Illustrated by Kristi Davis My Father s World Illustrations by Kristi Davis Text and Creative Design Team: Katerina Hazell, Kristi Davis, Judy Cureton, Marie Hazell
Overall structure is similar to humans, but again there are differences. Some features that are unique to mammals: Found in eutherian mammals.
 Mammalian anatomy and physiology (part II): Nervous system: Brain: Sensory input: Overall structure is similar to humans, but again there are differences. Some features that are unique to mammals: Smell:
Mammalian anatomy and physiology (part II): Nervous system: Brain: Sensory input: Overall structure is similar to humans, but again there are differences. Some features that are unique to mammals: Smell:
Balmandir Bhavnagar, 13 April, 1936
 Balmandir Bhavnagar, 13 April, 1936 Dear Children, It is 3 o clock in the afternoon. There are no clouds in the sky. The sun is burning hot. The sparrows, doves and sunbirds have started working in pairs
Balmandir Bhavnagar, 13 April, 1936 Dear Children, It is 3 o clock in the afternoon. There are no clouds in the sky. The sun is burning hot. The sparrows, doves and sunbirds have started working in pairs
Photocopiable Resources
 Photocopiable Resources Macmillan Children s Readers Worksheets and Teacher s Notes Contents Big and Little Cats Worksheet 1 Big and Little Cats Worksheet 2 Big and Little Cats Worksheet 3 Big and Little
Photocopiable Resources Macmillan Children s Readers Worksheets and Teacher s Notes Contents Big and Little Cats Worksheet 1 Big and Little Cats Worksheet 2 Big and Little Cats Worksheet 3 Big and Little
Talks generally last minutes and take place in one of our classrooms.
 Key Stage 1 & Key Stage 2 REPTILES General points about this talk: Talks generally last 30-40 minutes and take place in one of our classrooms. Talks are generally lead by the keepers on this section so
Key Stage 1 & Key Stage 2 REPTILES General points about this talk: Talks generally last 30-40 minutes and take place in one of our classrooms. Talks are generally lead by the keepers on this section so
Pre-lab homework Lab 8: Food chains in the wild.
 Pre-lab homework Lab 8: Food chains in the wild. Lab Section: Name: Put your field hat on and complete the questions below before coming to lab! The bits of information you and your classmates collect
Pre-lab homework Lab 8: Food chains in the wild. Lab Section: Name: Put your field hat on and complete the questions below before coming to lab! The bits of information you and your classmates collect
Reptile Round Up. An Educator s Guide to the Program
 Reptile Round Up An Educator s Guide to the Program GRADES: K-3 PROGRAM DESCRIPTION: This guide provided by the Oklahoma Aquarium explores reptiles and their unique characteristics. The Reptile Round Up
Reptile Round Up An Educator s Guide to the Program GRADES: K-3 PROGRAM DESCRIPTION: This guide provided by the Oklahoma Aquarium explores reptiles and their unique characteristics. The Reptile Round Up
Charles Darwin s Theory that Shapes the Scientific Study of Life
 Charles Darwin s Theory that Shapes the Scientific Study of Life Understand the basics: = change in a species over time ONLY HAPPENS IN POPULATIONS NOT IN INDIVIDUALS! And understand how this happens:
Charles Darwin s Theory that Shapes the Scientific Study of Life Understand the basics: = change in a species over time ONLY HAPPENS IN POPULATIONS NOT IN INDIVIDUALS! And understand how this happens:
Animals WORKSHEET 3.1 Animals
 Animals WORKSHEET 3.1 Animals 1. Are these sentences true or false? Correct the false ones. a) A butterfly is a non-living thing. b) Water is a non-living thing. c) Living things are born, die, reproduce
Animals WORKSHEET 3.1 Animals 1. Are these sentences true or false? Correct the false ones. a) A butterfly is a non-living thing. b) Water is a non-living thing. c) Living things are born, die, reproduce
Characteristics of Tetrapods
 Marine Tetrapods Characteristics of Tetrapods Tetrapod = four-footed Reptiles, Birds, & Mammals No marine species of amphibian Air-breathing lungs Class Reptilia Saltwater Crocodiles, Sea turtles, sea
Marine Tetrapods Characteristics of Tetrapods Tetrapod = four-footed Reptiles, Birds, & Mammals No marine species of amphibian Air-breathing lungs Class Reptilia Saltwater Crocodiles, Sea turtles, sea
Amazing oceans. Age 3-5 years. Contents
 SEA LIFE for Early Years Amazing oceans Age 3-5 years Self-guided learning This guide provides exciting and inspiring information linked to key displays throughout Brighton SEA LIFE to help young children
SEA LIFE for Early Years Amazing oceans Age 3-5 years Self-guided learning This guide provides exciting and inspiring information linked to key displays throughout Brighton SEA LIFE to help young children
Chinese New Year ACTIVITY 1: Animals (all levels) - WORKSHEET 1
 ACTIVITY 1: Animals (all levels) - WORKSHEET 1 The animals below are all from the Chinese horoscope. Find them in the wordsearch: RAT RABBIT HORSE ROOSTER OX DRAGON GOAT DOG TIGER SNAKE MONKEY PIG A C
ACTIVITY 1: Animals (all levels) - WORKSHEET 1 The animals below are all from the Chinese horoscope. Find them in the wordsearch: RAT RABBIT HORSE ROOSTER OX DRAGON GOAT DOG TIGER SNAKE MONKEY PIG A C
T. 6. THE VERTEBRATES
 T. 6. THE VERTEBRATES 1.- Relate the following concepts to their definition. Later, relate each concept to one of the pictures you are going to see. 1.- FIN a.- mammals with their babies 2.- GILLS b.-
T. 6. THE VERTEBRATES 1.- Relate the following concepts to their definition. Later, relate each concept to one of the pictures you are going to see. 1.- FIN a.- mammals with their babies 2.- GILLS b.-
KS2 Wild Explorers Whose tracks? Which cheetah?
 KS2 Wild Explorers Whose tracks? Which cheetah? KS2 Wild Explorers - Whose tracks? This classroom based activity consists of 30 different cards to print out; 10 animal picture cards, 10 animal track cards
KS2 Wild Explorers Whose tracks? Which cheetah? KS2 Wild Explorers - Whose tracks? This classroom based activity consists of 30 different cards to print out; 10 animal picture cards, 10 animal track cards
Life Cycle of a Leopard
 Text Structures Life Cycle of a Leopard A Sequence and Order Text Contents For teachers' What is a Leopard?...4 What Does a Leopard Look Like?...6 What is a Life Cycle?...8 Mating and Reproduction... 10
Text Structures Life Cycle of a Leopard A Sequence and Order Text Contents For teachers' What is a Leopard?...4 What Does a Leopard Look Like?...6 What is a Life Cycle?...8 Mating and Reproduction... 10
Mammals. Introduction (page 821) Evolution of Mammals (page 821) Form and Function in Mammals (pages ) Chapter 32.
 Chapter 32 Mammals Section 32 1 Introduction to the Mammals (pages 821 827) This section describes the characteristics common to all mammals, as well as how mammals carry out life functions. It also briefly
Chapter 32 Mammals Section 32 1 Introduction to the Mammals (pages 821 827) This section describes the characteristics common to all mammals, as well as how mammals carry out life functions. It also briefly
May 10, SWBAT analyze and evaluate the scientific evidence provided by the fossil record.
 May 10, 2017 Aims: SWBAT analyze and evaluate the scientific evidence provided by the fossil record. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing our AIMS: E.3-Examining
May 10, 2017 Aims: SWBAT analyze and evaluate the scientific evidence provided by the fossil record. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing our AIMS: E.3-Examining
Animal Traits and Behaviors that Enhance Survival. Copyright 2010:PEER.tamu.edu
 Animal Traits and Behaviors that Enhance Survival Copyright 2010:PEER.tamu.edu What We Are Going To Learn: What are traits? Inherited vs. Learned Response to stimuli Evolutionary Adaptations Natural Selection
Animal Traits and Behaviors that Enhance Survival Copyright 2010:PEER.tamu.edu What We Are Going To Learn: What are traits? Inherited vs. Learned Response to stimuli Evolutionary Adaptations Natural Selection
NAME: DATE: SECTION:
 NAME: DATE: SECTION: MCAS PREP PACKET EVOLUTION AND BIODIVERSITY 1. Which of the following observations best supports the conclusion that dolphins and sharks do not have a recent common ancestor? A. Dolphins
NAME: DATE: SECTION: MCAS PREP PACKET EVOLUTION AND BIODIVERSITY 1. Which of the following observations best supports the conclusion that dolphins and sharks do not have a recent common ancestor? A. Dolphins
Great Science Adventures Lesson 12
 Great Science Adventures Lesson 12 What are turtles and tortoises? Vertebrate Concepts: Turtles and tortoises are vertebrates and their backbone consists of a shell. Most of them can tuck their head inside
Great Science Adventures Lesson 12 What are turtles and tortoises? Vertebrate Concepts: Turtles and tortoises are vertebrates and their backbone consists of a shell. Most of them can tuck their head inside
Special Educational Needs (SEN) CARING FOR ANIMALS
 Special Educational Needs (SEN) CARING FOR ANIMALS General points about this talk: This talk generally lasts 30 minutes and will take place out in the Park in all weathers; please ensure that your pupils
Special Educational Needs (SEN) CARING FOR ANIMALS General points about this talk: This talk generally lasts 30 minutes and will take place out in the Park in all weathers; please ensure that your pupils
Orpheus. see how we live. First published in 2009 by Orpheus Books Ltd., 6 Church Green, Witney, Oxfordshire, OX28 4AW
 First published in 2009 by Orpheus Books Ltd., 6 Church Green, Witney, Oxfordshire, OX28 4AW Copyright 2009 Orpheus Books Ltd. Created and produced by Julia Bruce, Rachel Coombs, Nicholas Harris, Sarah
First published in 2009 by Orpheus Books Ltd., 6 Church Green, Witney, Oxfordshire, OX28 4AW Copyright 2009 Orpheus Books Ltd. Created and produced by Julia Bruce, Rachel Coombs, Nicholas Harris, Sarah
Evolution. Evolution is change in organisms over time. Evolution does not have a goal; it is often shaped by natural selection (see below).
 Evolution Evolution is change in organisms over time. Evolution does not have a goal; it is often shaped by natural selection (see below). Species an interbreeding population of organisms that can produce
Evolution Evolution is change in organisms over time. Evolution does not have a goal; it is often shaped by natural selection (see below). Species an interbreeding population of organisms that can produce
ANTHR 1L Biological Anthropology Lab
 ANTHR 1L Biological Anthropology Lab Name: DEFINING THE ORDER PRIMATES Humans belong to the zoological Order Primates, which is one of the 18 Orders of the Class Mammalia. Today we will review some of
ANTHR 1L Biological Anthropology Lab Name: DEFINING THE ORDER PRIMATES Humans belong to the zoological Order Primates, which is one of the 18 Orders of the Class Mammalia. Today we will review some of
NATURAL SELECTION SIMULATION
 ANTHR 1-L BioAnthro Lab Name: NATURAL SELECTION SIMULATION INTRODUCTION Natural selection is an important process underlying the theory of evolution as proposed by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russell Wallace.
ANTHR 1-L BioAnthro Lab Name: NATURAL SELECTION SIMULATION INTRODUCTION Natural selection is an important process underlying the theory of evolution as proposed by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russell Wallace.
THE CHILDREN S ZOO. Scavenger Hunt GRADES K-3
 THE CHILDREN S ZOO Scavenger Hunt GRADES K-3 Scavenger Hunt The Children s Zoo (K-3) Teacher s Guide Updated Summer 2011 APPROXIMATE TIME: 60 Minutes Suggestions for Teachers: 1. Allow your children about
THE CHILDREN S ZOO Scavenger Hunt GRADES K-3 Scavenger Hunt The Children s Zoo (K-3) Teacher s Guide Updated Summer 2011 APPROXIMATE TIME: 60 Minutes Suggestions for Teachers: 1. Allow your children about
GOLDILOCKS AND THE THREE HARES by Heidi Petach, in consultation with Joan Farabee
 GOLDILOCKS AND THE THREE HARES by Heidi Petach, in consultation with Joan Farabee INTRODUCTION Goldilocks and the Three Hares can be successfully integrated into a cross-curriculum program for grades 1-4.
GOLDILOCKS AND THE THREE HARES by Heidi Petach, in consultation with Joan Farabee INTRODUCTION Goldilocks and the Three Hares can be successfully integrated into a cross-curriculum program for grades 1-4.
Introduction to the Cheetah
 Lesson Plan 1 Introduction to the Cheetah CRITICAL OUTCOMES CO #1: Identify and solve problems and make decisions using critical and creative thinking. CO #2: Work effectively with others as members of
Lesson Plan 1 Introduction to the Cheetah CRITICAL OUTCOMES CO #1: Identify and solve problems and make decisions using critical and creative thinking. CO #2: Work effectively with others as members of
1. Examine the specimens of sponges on the lab table. Which of these are true sponges? Explain your answers.
 Station #1 - Porifera 1. Examine the specimens of sponges on the lab table. Which of these are true sponges? Explain your answers. 2. Sponges are said to have an internal special skeleton. Examine the
Station #1 - Porifera 1. Examine the specimens of sponges on the lab table. Which of these are true sponges? Explain your answers. 2. Sponges are said to have an internal special skeleton. Examine the
Key Stage 2 Adaptation Resource Pack
 Key Stage 2 Adaptation Resource Pack Contents Page Introduction 3 Summary of resources 3 Preparation before your visit 4 Adaptation trail Student booklet 5-11 Map (last page of booklet) 11 Cold Blooded
Key Stage 2 Adaptation Resource Pack Contents Page Introduction 3 Summary of resources 3 Preparation before your visit 4 Adaptation trail Student booklet 5-11 Map (last page of booklet) 11 Cold Blooded
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL- RIYADH HALF YEARLY WORKSHEET CLASS: III. SUBJECT: EVS LESSONS: 3,4,5,6,7,12,17
 INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL- RIYADH HALF YEARLY WORKSHEET- 2018-2019 CLASS: III. SUBJECT: EVS LESSONS: 3,4,5,6,7,12,17 LESSON: 3- ANIMAL WORLD FILL IN THE BLANKS 1. A lives in the shade of trees. 2. A
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL- RIYADH HALF YEARLY WORKSHEET- 2018-2019 CLASS: III. SUBJECT: EVS LESSONS: 3,4,5,6,7,12,17 LESSON: 3- ANIMAL WORLD FILL IN THE BLANKS 1. A lives in the shade of trees. 2. A
Nat Geo Notes for: How do Living Things Survive and Change?
 Nat Geo Notes for: How do Living Things Survive and Change? I. Physical characteristics of living things A. Animal Adaptations 1. adaptations are characteristics that help organisms survive or reproduce
Nat Geo Notes for: How do Living Things Survive and Change? I. Physical characteristics of living things A. Animal Adaptations 1. adaptations are characteristics that help organisms survive or reproduce
Animal Study: Adelaide Zoo
 Animal Study: Adelaide Zoo Name: Animal: 16 1 Is this animal a social animal? Give reasons for your answer. Reflect on what you have learned about the animal you studied. If you were designing an enclosure
Animal Study: Adelaide Zoo Name: Animal: 16 1 Is this animal a social animal? Give reasons for your answer. Reflect on what you have learned about the animal you studied. If you were designing an enclosure
