Wildlife Prairie State Park Feathered Friends Teacher s Packet
|
|
|
- Maurice Spencer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Teacher s Packet Grades 3-4 Abstract Birds play an important role in the environment, as do all organisms. They help pollinate flowers, spread seeds in their droppings, and eat pest insects. They are also an important indicator of the quality of a habitat. Although they have many common characteristics, birds are a very diverse group of animals. Addresses State Goal Requirements Goal 1: Read with understanding and fluency. Goal 11A: Know and apply the concepts, principles and processes of scientific inquiry. Goal 12A: Know and apply concepts that explain how living things function, adapt and change. Goal 12B: Know and apply concepts that describe how living things interact with each other and with their environment. Objectives Students will learn the characteristics of birds, and will be able to distinguish the type of food it eats by its bill, different uses for different types of feet, and distinguish between different nests. Students will learn about the family lives of birds including singing, finding a mate, nest building and raising the young. Students will learn how birds affect our lives and the ways we affect theirs. The goal of all environmental education programs at Wildlife Prairie State Park is to help students become environmentally knowledgeable, skilled, dedicated citizens who are willing to work individually and collectively toward achieving and maintaining a dynamic equilibrium between the quality of life and the quality of the environment.
2 Student Preparation Before coming to Wildlife Prairie State Park, please familiarize your class with the following vocabulary words. In addition, students should participate in at least one pre-trip activity. 1) Organism: any living creature. 2) Properties: identifiable characteristics (color, size, texture, warm blooded, etc.). 3) Habitat: the place where an organism usually lives. 4) Bird: an egg laying organism with feathers and has a beak and claws. 5) Field Marks: marks on a bird s body that help us identify it species (colors, body shape, stripes, leg type and beak type). 6) Predator: An animal that hunts and eats other animals. 7) Prey: an animal that is caught and eaten by another animal. 8) Adaptation: a behavior, physical feature, or other characteristic that helps an animal survive and make the most of its habitat. For example, ducks have webbed feet that help them swim. 9) Down: soft feathers next to the body that provide insulation. 10) Migration: seasonal movement from one region to another to take advantage of some situation (warmth, food supply, etc.). For example, a hawk may migrate from southern Canada to Central America for the winter. 11) Preen: to clean, straighten, and fluff the feathers.
3 Pre-Trip Activity Fill the Bill It would be impossible for a hummingbird to gobble up a mouse. And it would be just as impossible for a hawk to slurp up some nectar from a flower. Each type of bird has a special beak and tongue adapted to eating a certain type of food. In this demonstration your group can find out which beaks are best for tearing, scooping, cracking and picking by going to different stations you ve set up and trying to find out which tools go with which types of food. First talk about some different bird beaks to get the students thinking about how beaks help birds survive. Here are some examples of birds and beaks you can talk about: Hummingbirds have long hollow beaks that they use to probe flowers for nectar. The beak protects the tongue, which slurps up the nectar. Woodcocks, Cranes, and Snipes have long beaks that they use to probe for worms, crustaceans and other small creatures in mud and water. Cardinals, Sparrows, Grosbeaks, and Finches have very short, conical beaks. These beaks are very strong and can crack open tough seeds. Pelicans have long sharp beaks they use to scoop up fish and other aquatic creatures, Herons and Egrets have long sharp beaks that they use to spear fish, frogs, crayfish and other small aquatic creatures. Nighthawks, Whip-poor-wills, Swifts, and Swallows have large, gaping mouths that act like nets to trap insects. These birds catch insects on the wing. Warblers and Vireos have small, sharp, pointed beaks for picking insects from leaves, logs, twigs and in flight. Hawks, Owls, Eagles and Vultures have strong hooked beaks that they use to tear meat into bite-size chunks. Flamingos have a large grooved beak that allows them to filter small crustaceans from the water. After having tested the food samples, test the students by asking them to match the beak adaptation to the drawings by comparing bill and descriptions. Adapted with permission of National Wildlife Federation form the Birds, Birds, Birds, issue of Nature Scope, Adapted with permission from Nature Discovery I: Illinois Birds. Developed by the Wildlife Prairie State Park Education Department, 1994
4 Pre-trip Activity Fill the Bill 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) BEAK ADAPTATIONS Fish-eating beak: long, slim, strong, and pointed to reach into the water and to grasp slippery creatures. Insect-catching beak: small sized beak that can open wide to grab insects in flight. Water and Mud-sifting beak: wide and shallow; comb-like strainers on edges filter out bits of food in water. Chisel beak: sturdy and sharply pointed to chisel into wood; accompanied by an extremely long, barb-tipped tongue to pull insects and insect eggs out of tunnels in bark or wood. Insect and Fruit-eating beak: narrow and pointed to grab insects or reach fruits, and slightly arched to crack seeds; larger than an insect-eating beak but shorter than a fish-eating beak; sleeker and longer than a seed-eating beak. Preying beak: stout, sharp and sharply hooked to tear the flesh of animals. Probing beak: thin and long to reach insects and other small animals buried in sand or mud. Filter beak: large and curved with grooves and comb-like filter for sifting out crustaceans from water.
5 Pre-trip Activity Fill the Bill: TEACHER S COPY 1) Probing beak (Woodcock) 2) Insect/Fruit-eating beak (Meadowlark) 3) Fish-eating beak (Great Blue Heron) 4) Preying beak (Bald Eagle) 5) Water/Mud-sifting beak (Wood Duck) 6) Chisel beak (Nuthatch) 7) Seed-eating beak (Cardinal) 8) Fish-eating beak (Kingfisher) 9) Filter beak (Flamingo) BEAK ADAPTATIONS Fish-eating beak: long, slim, strong, and pointed to reach into the water and to grasp slippery creatures. Insect-catching beak: small sized beak that can open wide to grab insects in flight. Water and Mud-sifting beak: wide and shallow; comb-like strainers on edges filter out bits of food in water. Chisel beak: sturdy and sharply pointed to chisel into wood; accompanied by an extremely long, barb-tipped tongue to pull insects and insect eggs out of tunnels in bark or wood. Insect and Fruit-eating beak: narrow and pointed to grab insects or reach fruits, and slightly arched to crack seeds; larger than an insect-eating beak but shorter than a fish-eating beak; sleeker and longer than a seed-eating beak. Preying beak: stout, sharp and sharply hooked to tear the flesh of animals. Probing beak: thin and long to reach insects and other small animals buried in sand or mud. Filter beak: large and curved with grooves and comb-like filter for sifting out crustaceans from water.
6 Pre-trip activity Feet Are Neat One good way for students to understand how birds are adapted to live in their habitats is for them to take a look at bird feet. In different ways, bird feet come in a lot of different shapes and sizes. Ask your group to think of some of the ways birds use their feet. They use them for walking, perching, swimming, running, climbing and grabbing. Then talk about some of the different kinds of feet different birds have. Here are some examples: Climbers: Woodpeckers have two toes in front and two toes in back for climbing up and down tree trunks. Graspers: Hawks, Owls and other birds of prey have large curved claws, called talons, which dig into their prey and help them hold onto it in flight. Perchers: Robins, Mourning Doves, and most songbirds have three toes that face forward and one long hind toe that helps them grip their perches tightly. Runners: Killdeer have three toes (instead of four, and all their toes point forward for fast running. Scratchers: Chickens, Pheasants and other larger land birds have rake-like toes for scratching in the soil. Some have fringes for easy snow walking. Swimmers: Ducks, Coots, and other swimmers use their feet as paddles. Next pass out copies of the next page to the group and have them try to figure out which birds go with which feet. Then pass out lumps of clay or modeling dough and have everyone make a model of bird feet. When they re finished, have each person draw a picture of his or her bird on a piece of white cardboard or stiff white paper, color it and tape pip cleaner legs to the cardboard. (To make each leg, have them twist two pipe cleaners together). Then they can push the legs, with the bodies attached, down into the feet. Adopted with permission of National Wildlife Federation from the Birds, Birds, Birds! issue of NatureScope, copyright 1989.
7 Pre-trip Activity Match The Feet
8 Pre-trip Activity Match The Feet: TEACHER S COPY
9 Pre-trip Activity Feather Features Birds are the only animals in the world with feathers. In this demonstration, your students can learn the parts of a feather and how feathers help a bird fly and stay warm. Explain that there are two main types of feather: contour feathers, which are found on the bird s body, wings, and tail; and down feathers, which are fluffier and lie close to the bird s body, under the contour feathers. It is illegal to collect most feathers in the wild, so the best bet for obtaining feathers may be a poultry farm or a craft store. Down feathers and contour feathers along with magnifying glasses, a little baby oil, and some water will be needed in the feather section of the center. Remind students to wash their hands after touching feathers. 1) Ask the students to separate the feathers into the two main types of feathers: Down feathers, the soft, fluffy feathers found close to the bird s body. Contour feathers, found on the bird s body, wings and tail. Children can tell the difference between a wing feather, where the shaft is to one side of the vane, and a tail feather, which has the shaft in the middle 2) Examining a contour feather with a magnifying glass and identify: Shaft: the stiff center tube. Quill: the hollow end of the shaft. Vane: the rest of the feather. Barbs: hundreds of skinny hairs coming off the shaft. Barbules: tiny hooks and rolled edges found on the barbs that zip together. 3) Feathers damage easily and birds must repair them so they are able to fly well. To repair a feather, a bird pulls the feather gently through its beak to zip up any barbules that have pulled apart. Students can repair or preen a contour feather like a bird does by holding the shaft in one hand and rubbing a finger and thumb of the other hand up the feather. 4) Preening or feather care is very important for birds. Preen glands found on most birds backs provide oil to rub over their feathers. This keeps the feathers waterproof, flexible, and in good condition. Test to see if a feather is waterproof by spraying a few drops of water on the feather. If the water does not run right off, rub a little baby oil on the feather. Spray again and see how the water runs off when the feather has a coating of oil. The oil makes it waterproof. 5) Down feathers keep a bird warm... just like thermal underwear! Demonstrate this fact by filling two small jars with warm water. Wrap one of the jars in a feather pillow and place the other jar on the table. After one hour feel the jars. The water in the far wrapped in the feather pillow stays warmer just as a bird stays warmer when covered with downy feathers. Adapted with permission from Copycat Press. P.O. Box , Racine, WI
10 Pre-trip Activity Classroom Aviary Plan your own colorful classroom aviary using the reproducible birds found on the next page. Place a small dead tree branch in a large flowerpot filled with sand. Ask the students to color and cut out one of the birds reproduced on tag board. Use books from the library to show correct coloration when coloring the birds. Attach the birds to the branch by sliding the branch through the slit in the birds feet. Write the name of each bird on a small piece of paper and place it next to the bird on the branch. A great way to learn the names of birds! Name That Bird! Have fun using the birds in the classroom aviary. Remove the labels from each bird and replace the name with a number. Add a few fictional or fun birds like Tweetie, Heckle, and Jeckle, Woodstock, Woody Woodpecker, Little Bird, etc. Ask the students to write the name of each bird next to the corresponding number on a sheet of paper name that bird! State Birds What is your state bird? Introduce your students to their state bird by writing a group story. Research the bird and give as much information as possible. What does it eat? Does it migrate? Where does it live and nest? What are their behaviors? What habitat does it prefer? Information will not be difficult to find because it will be a familiar bird. Adapted with permission from Copycat Press, P.O. Box , Racine Wisconsin
11
12
13 Post-trip Activity House Hunting Birds build their nests in all kinds of places. Some nest high in trees while others nest on the ground. Some plaster their nests on the sides of buildings or rocky cliffs and others build floating nests in marshy areas. Many birds also nest in tree cavities, stream banks, fields, and swamps. Birds also use a variety of nesting materials to build their nests, including sticks, mud, stones, lichens, grass, spider webs, snakeskins and thistledown. Some birds are adaptable nest builders. It seems they ll build their nests wherever they can find a spot and use whatever materials they can find. But other birds are much pickier and will build their nests only in certain places and use only certain materials. In this activity, your students can pick the perfect site to build a nest and then try to build one themselves. First, write down on slips of paper the names of five common birds that live in your area. (Choose birds that nest in your schoolyard or in a nearby park). Divide the group into five teams and have each team pick one slip. Then explain that each team is a real estate agent hired by the bird on their slip of paper to find the perfect nest site. Pass out copies of the next page to each person. Explain to the group that each person in the team must research their bird out fill out the nesting information sheet. (You can have them work in teams too). After everyone has filled out the information, take the group to a schoolyard that has several different ty0pes of habitats. Have the students in each team search for the perfect spot to build a nest. Remind them that most birds build their nests near a food source and that the nests are usually sheltered from rain, hot sun, and other types of weather. Also tell them that many birds hide their nest so predators can t spot them. Give everyone 15 minutes to find the perfect spot and then have everyone gather back together. Start with one team and have the students in the team describe their bird and its requirements for a home. Then visit the nest site and talk about the pros and cons of the location. (This one s too exposed, this one s too far from water, this one would get run over by a lawnmower, and so on). After visiting all the nest sites, for one type of bird, take a vote on which team found the best site. Afterward, have each group work together to try to build the nest of their bird, using the same materials the bird would use. Each nest should also be the correct size and shape. Have everyone on the team pitch in to help gather the materials and shape the nest. (Warn the children not to pick flowers or pull living plants). Then line up the nests and talk about each one. Encourage the children to look out for nests when they take walks with their parents or friends. But remind them that it s against the law to remove or damage a nest in the wild, even if it is old or abandoned. Adapted with permission of National Wildlife Federation from the Birds, Birds, Birds! issue of Nature Scope, copyright 1989.
14 Post-trip Activity House Hunting 1) Name your bird. 2) Draw a picture of your bird on the back of this sheet. 3) Describe your bird s habitat. 4) What does your bird eat? 5) What kind of nest does it build or use? 6) Draw a picture of the nest. 7) Where does your bird usually build its nest(s)? 8) What time of year does your bird nest? 9) About how many eggs does it lay? 10) Draw and color what their eggs look like below. Adapted with permission of National Wildlife Federation from the Birds, Birds, Birds!
15 Post-trip Activity issue of Nature Scope, copyright, Nest Guide On the next page there are 11 kinds of bird nests. Your job is to use the nest descriptions below to label the nest drawings. Cavity Nest: a hollow pocket in a tree. Large Stick Nest: a mass of sticks and leaves in the crotch of a tree. Small Stick Nest: a small, loose collection of sticks resting on a fork of branches. Shrub Cup Nest: a rounded nest of grasses, bark strips, leaves, and stems woven around the branches of a shrub or small tree. Grassy Cup Nest: a rounded nest of grass stems woven into a stand of grasses. Bank Nest: a tunnel in a bank, the actual nest is an enlarged chamber at the end of the tunnel. Leafy Ground Nest: a bed of leaves on the ground in a wooded area. Grass Ground Nest: a bed of grasses on the ground in a grassy area. Bare Ground Nest: a shallow scratched-out hollow in the bare ground, often on a sandy or rocky surface. Hanging Nest: a hanging basket of plant fibers, moss, leaves, twigs, and feathers. Floating Nest: a mass of reeds floating on the surface of water. Reprinted with permission from Nature Discovery I: Illinois Birds
16
17
18
19 Post-trip Activity Take a Bird to Lunch Soda Bottle Thistle Feeder Materials: o Large plastic soft drink bottle (liter size) o 3 or 4 wooden dowels, each 3/16 (5 mm) wide and about 8 (20 cm) long o X-acto knife o Nail or other sharp object for punching holes in the bottle o Wire clothes hanger o Wire cutters Procedures: 1. Wash the bottle and remove the label and colored base. 2. To make a perch, use a nail to punch two holes, opposite each other. Insert a dowel so that it passes through one hole on the other side. Make three or four such perches, alternating the positions so that all sides of the bottle are used. 3. Now you re ready to cut the feeding holes. (Remember that the finished feeder will hang with the bottle s neck facing down). With the neck facing toward you, use an X-acto knife to cut a ¼ long by 1/8 wide (6 x 3 mm) hole about 2 (5 cm) above each perch. Keep in mind that the seeds will fall out if the holes are too big. 4. Cut a clothes hanger in two places with the wire cutters (see diagram A). Each cut should be at least 4 (10 cm) from the base of the hook. Bend the hanger so it looks like diagram B. 5. Use the nail to poke a hole in the bottle, about 2½ (6.3 cm) from the bottle s base (not its neck). Do the same on the other side of the bottle, opposite the first hole. 6. Push the ends of the clothes hanger into the holes. Adjust the hanger so that the feeder hangs evenly and the ends of the hanger don t slip out of the holes. 7. Fill the feeder with niger (thistle) seeds, replace the cap, invert it and hang it from a tree. Adapted with permission of National Wildlife Federation from the Birds, Birds, Birds! issue of Nature Scope, copyright 1989.
20 Post-trip Activity Bird Search Reading up, down, forward, backward and diagonally, can you find the names of these birds? When you have found all of them, the left over letters will give you a secret message. BLUE JAY BLUEBIRD CANADA GOOSE CARDINAL CHICKADEE CROW DOVE DUCK EAGLE EGRET FINCH GRACKLE GROSBEAK GULL HAWK HERON HUMMINGBIRD KESTREL KILLDEER NUTHATCH OWL PEWEE ROBIN SPARROW TEAL TITMOUSE TURKEY VULTURE VIREO WOODPECKER WREN Developed by the Wildlife Prairie State Park Education Department, 1994.
Examining Bird Adaptations
 Biology I Unit V: Zoology Chapter 25-28 & DOL: Vertebrates Examining Bird Adaptations Lab Name: Date: Hour: Examining Bird Adaptations Pre-Lab Discussion There are many different types of birds. Each type
Biology I Unit V: Zoology Chapter 25-28 & DOL: Vertebrates Examining Bird Adaptations Lab Name: Date: Hour: Examining Bird Adaptations Pre-Lab Discussion There are many different types of birds. Each type
Bird Beaks and Feet Activity Beak Type Adaptation:
 Bird Beaks and Feet Activity Beak Type Adaptation: The beaks of birds have their job or function based on their shape and size. Study the beak types information below. Beak Type Adaptation Questions: Answer
Bird Beaks and Feet Activity Beak Type Adaptation: The beaks of birds have their job or function based on their shape and size. Study the beak types information below. Beak Type Adaptation Questions: Answer
Birds THE BODY. attract =to pull towards. avoid =to keep away from. backbone =the row of connected bones that go down the middle of your back
 attract =to pull towards avoid =to keep away from backbone =the row of connected bones that go down the middle of your back beak = the hard, pointed mouth of a bird bore = to make a hole breeding season
attract =to pull towards avoid =to keep away from backbone =the row of connected bones that go down the middle of your back beak = the hard, pointed mouth of a bird bore = to make a hole breeding season
Comparing Adaptations of Birds
 Name Class Date Comparing Adaptations of Birds Introduction When Charles Darwin explored the Galápagos Islands, he noted the great variety of beak shapes on the finches there. It was later determined that
Name Class Date Comparing Adaptations of Birds Introduction When Charles Darwin explored the Galápagos Islands, he noted the great variety of beak shapes on the finches there. It was later determined that
Activity 4 Building Bird Nests
 Activity 4 Building Bird Nests Created By Point Reyes Bird Observatory Education Program Building Bird Nests Activity 4 Objective: To teach students about songbird nests, the different types, placement
Activity 4 Building Bird Nests Created By Point Reyes Bird Observatory Education Program Building Bird Nests Activity 4 Objective: To teach students about songbird nests, the different types, placement
The Hills Checklist of Birds That Have Been Seen as of
 The Hills Checklist of Birds That Have Been Seen as of 3.6.18 1 2 3 4 COMMON NAME SEASON AND ABUNDANCE Date Date Date Date Geese and Ducks o o o o Greater White-fronted Goose Winter, rare o o o o Snow
The Hills Checklist of Birds That Have Been Seen as of 3.6.18 1 2 3 4 COMMON NAME SEASON AND ABUNDANCE Date Date Date Date Geese and Ducks o o o o Greater White-fronted Goose Winter, rare o o o o Snow
Post-Activity. (Bird Beaks) Pre-K Guidelines/Examples of Child Behavior. Learning Objectives
 Pre-K Guidelines/Examples of Child Behavior Learning Objectives VI.B.1. Child observes, investigates, describes and discusses the characteristics of organisms. Describes color, size, and shape of organisms.
Pre-K Guidelines/Examples of Child Behavior Learning Objectives VI.B.1. Child observes, investigates, describes and discusses the characteristics of organisms. Describes color, size, and shape of organisms.
What Makes a Bird a Bird?
 What Makes a Bird a Bird? Overview Students will compare types of feathers by examining structure and function of each. California Science Standards Grade 5: 6.g.-I&E Grade 6: 7.b.-I&E Grade 7: 7.a.-I&E
What Makes a Bird a Bird? Overview Students will compare types of feathers by examining structure and function of each. California Science Standards Grade 5: 6.g.-I&E Grade 6: 7.b.-I&E Grade 7: 7.a.-I&E
Kingdom: Animalia. Phylum: Chordata. Class: Aves. Order: 28 orders Passeriformes- most. Strigiformes- owls. Piciformes- woodpeckers
 Snowball 3:54 1 2 Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Aves Order: 28 orders Passeriformes- most Strigiformes- owls Piciformes- woodpeckers Anseriformes- ducks & geese Osprey-Gone Fishin 1:58 3 Similar
Snowball 3:54 1 2 Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Aves Order: 28 orders Passeriformes- most Strigiformes- owls Piciformes- woodpeckers Anseriformes- ducks & geese Osprey-Gone Fishin 1:58 3 Similar
Balmandir Bhavnagar, 13 April, 1936
 Balmandir Bhavnagar, 13 April, 1936 Dear Children, It is 3 o clock in the afternoon. There are no clouds in the sky. The sun is burning hot. The sparrows, doves and sunbirds have started working in pairs
Balmandir Bhavnagar, 13 April, 1936 Dear Children, It is 3 o clock in the afternoon. There are no clouds in the sky. The sun is burning hot. The sparrows, doves and sunbirds have started working in pairs
K-5a Images: Mystery Animal Cards
 Clues for American Crow: I have wings made of black feathers. I have a strong black beak. I eat many things including seeds, and insects, and left over lunches. I am very smart and sometimes tricky. I
Clues for American Crow: I have wings made of black feathers. I have a strong black beak. I eat many things including seeds, and insects, and left over lunches. I am very smart and sometimes tricky. I
BUILDING A HOME (NESTS) VOLUNTEER DIRECTIONS
 BUILDING A HOME (NESTS) VOLUNTEER DIRECTIONS 1. Your station, Building a Home (Nests), will explore a collection of different nests, how each is made, where they can be found, what shape it is, and what
BUILDING A HOME (NESTS) VOLUNTEER DIRECTIONS 1. Your station, Building a Home (Nests), will explore a collection of different nests, how each is made, where they can be found, what shape it is, and what
Birds & Mammals. Chapter 15
 Birds & Mammals Chapter 15 What is a Bird? Vertebrate Endothermic Feathered 4 chambered heart Egg laying Fore-limbs adapted for flight Bones nearly hollow (allow for lighter weight) Bird Internal Anatomy
Birds & Mammals Chapter 15 What is a Bird? Vertebrate Endothermic Feathered 4 chambered heart Egg laying Fore-limbs adapted for flight Bones nearly hollow (allow for lighter weight) Bird Internal Anatomy
Slide 1. Birds & Mammals. Chapter 15
 Slide 1 Birds & Mammals Chapter 15 Slide 2 What is a Bird? Vertebrate Endothermic Feathered 4 chambered heart Egg laying Fore-limbs adapted for flight Bones nearly hollow (allow for lighter weight) Slide
Slide 1 Birds & Mammals Chapter 15 Slide 2 What is a Bird? Vertebrate Endothermic Feathered 4 chambered heart Egg laying Fore-limbs adapted for flight Bones nearly hollow (allow for lighter weight) Slide
This Coloring Book has been adapted for the Wildlife of the Table Rocks
 This Coloring Book has been adapted for the Wildlife of the Table Rocks All images and some writing belong to: Additional writing by: The Table Rocks Environmental Education Program I became the national
This Coloring Book has been adapted for the Wildlife of the Table Rocks All images and some writing belong to: Additional writing by: The Table Rocks Environmental Education Program I became the national
2. Using an appropriate illustration and words, describe the physics of flight.
 1. Besides the obvious, like feathers and wings, birds have many special features that allow them to fly. Explain how each of the characteristics are specialized to help birds fly. A. Skeletal System-
1. Besides the obvious, like feathers and wings, birds have many special features that allow them to fly. Explain how each of the characteristics are specialized to help birds fly. A. Skeletal System-
Brook Trout. Wood Turtle. Shelter: Lives near the river
 Wood Turtle Brook Trout Shelter: Lives near the river in wet areas, winters underground in river bottoms or river banks, builds nests for eggs in sandy or gravelly open areas near water Food: Eats plants
Wood Turtle Brook Trout Shelter: Lives near the river in wet areas, winters underground in river bottoms or river banks, builds nests for eggs in sandy or gravelly open areas near water Food: Eats plants
Learning Objectives: Students will explain why animals must move, adapt or die when an environment changes.
 Lesson Plan: Bird Beak Buffet Author: Betsy Rivera Subject: Evolution Topic: Extinction of a Species Grade Level: 4 th 9 th Academic Content Standards: 7th grade Science Standard 4c: Extinction of a species
Lesson Plan: Bird Beak Buffet Author: Betsy Rivera Subject: Evolution Topic: Extinction of a Species Grade Level: 4 th 9 th Academic Content Standards: 7th grade Science Standard 4c: Extinction of a species
It s All About Birds!
 I. Introduction to Birds It s All About Birds! Grade 8 Science Birds are warm-blooded, have distinctive beaks, and their young hatch from hardshelled eggs. A characteristic unique to birds is the presence
I. Introduction to Birds It s All About Birds! Grade 8 Science Birds are warm-blooded, have distinctive beaks, and their young hatch from hardshelled eggs. A characteristic unique to birds is the presence
Birds Birds are vertebrates (animals with backbones) with wings and feathers. Most birds can fly, using powerful muscles to flap their wings.
 Birds Birds are vertebrates (animals with backbones) with wings and feathers. Most birds can fly, using powerful muscles to flap their wings. But a few bird speces do not have strong enough wings to fly,
Birds Birds are vertebrates (animals with backbones) with wings and feathers. Most birds can fly, using powerful muscles to flap their wings. But a few bird speces do not have strong enough wings to fly,
Science10 (AdaptationsMulberry4th)
 Name: Date: 1. Which bird's foot below is best for grasping prey? A. B. C. D. This online assessment item contains material that has been released to the public by the Massachusetts Department of Education.
Name: Date: 1. Which bird's foot below is best for grasping prey? A. B. C. D. This online assessment item contains material that has been released to the public by the Massachusetts Department of Education.
Bird Cards and Scenario Cards
 Bird Cards and Scenario Cards The following bird cards and scenario cards have been adapted from the Flying Wild Home is Where the Forest Is (page 95) cards to more accurately represent birds that breed
Bird Cards and Scenario Cards The following bird cards and scenario cards have been adapted from the Flying Wild Home is Where the Forest Is (page 95) cards to more accurately represent birds that breed
Common Birds Around Denver. Seen in All Seasons Depending on the Habitat
 Common Birds Around Denver Seen in All Seasons Depending on the Habitat Near and Around Water Canada Goose (golf courses) Mallard Ring-billed Gull (parking lots) American Coot Killdeer Canada Goose Canada
Common Birds Around Denver Seen in All Seasons Depending on the Habitat Near and Around Water Canada Goose (golf courses) Mallard Ring-billed Gull (parking lots) American Coot Killdeer Canada Goose Canada
The platypus lives in streams, ponds, and rivers in Australia. It closes its eyes under water and uses its bill to dig in the mud to find its food.
 The platypus lives in streams, ponds, and rivers in Australia. It closes its eyes under water and uses its bill to dig in the mud to find its food. The hyena, found in Africa and parts of Asia, weighs
The platypus lives in streams, ponds, and rivers in Australia. It closes its eyes under water and uses its bill to dig in the mud to find its food. The hyena, found in Africa and parts of Asia, weighs
Animal Behavior OBJECTIVES PREPARATION SCHEDULE VOCABULARY BACKGROUND INFORMATION MATERIALS. For the class. The students.
 activity 7 Animal Behavior OBJECTIVES Students observe the animals in the terrariums and draw conclusions about their typical behavior. The students continue to observe and record the behavior of the animals
activity 7 Animal Behavior OBJECTIVES Students observe the animals in the terrariums and draw conclusions about their typical behavior. The students continue to observe and record the behavior of the animals
Exercise 4: Animal Adaptations
 Exercise 4: Animal Adaptations Introduction There are approximately 1.5 million species of organisms that have been described and named today. But, some scientists estimate that we may have as many as
Exercise 4: Animal Adaptations Introduction There are approximately 1.5 million species of organisms that have been described and named today. But, some scientists estimate that we may have as many as
Precocial Birds. (Ducks, geese, quail, rails and shorebirds, etc.)
 Precocial Birds (Ducks, geese, quail, rails and shorebirds, etc.) Precocial Birds are "self-sufficient" because most of these babies can find and eat food on their own often within minutes or hours of
Precocial Birds (Ducks, geese, quail, rails and shorebirds, etc.) Precocial Birds are "self-sufficient" because most of these babies can find and eat food on their own often within minutes or hours of
Atlantic Puffins By Guy Belleranti
 Flying over my head are plump seabirds with brightly colored beaks and feet. Each bird's pigeonsized body looks a little like a football with wings. The wings are too small for gliding. However, by flapping
Flying over my head are plump seabirds with brightly colored beaks and feet. Each bird's pigeonsized body looks a little like a football with wings. The wings are too small for gliding. However, by flapping
Which is the smallest bird? Which one is the largest? Why do birds migrate? What are vertebrates? What do birds use their beaks for?
 QU! hich is the smallest bird? hich one is the largest? hy do birds migrate? hat are vertebrates? hat do birds use their beaks for? hy do birds have light skeletons? hat is so special about their bones?
QU! hich is the smallest bird? hich one is the largest? hy do birds migrate? hat are vertebrates? hat do birds use their beaks for? hy do birds have light skeletons? hat is so special about their bones?
CHAPTER 3 EATING HABIT OF ANIMALS
 JABAL FARASAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL, RABEGH KSA Affiliated to CBSE New Delhi SCIENCE-CLASS III-CHAPTER-WISE WORKSHEET-2 STUDENT NAME... ROLL NO. DATE CHAPTER 3 EATING HABIT OF ANIMALS I. FILL IN THE BLANKS
JABAL FARASAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL, RABEGH KSA Affiliated to CBSE New Delhi SCIENCE-CLASS III-CHAPTER-WISE WORKSHEET-2 STUDENT NAME... ROLL NO. DATE CHAPTER 3 EATING HABIT OF ANIMALS I. FILL IN THE BLANKS
Animal Adaptations Woodland Animal Fact Sheet
 Post Visit Resource 5 Animal Adaptations Woodland Animal Fact Sheet Fox Food: Foxes will eat almost anything they can get hold of. They eat small mammals such as rabbits and voles, insects and invertebrates,
Post Visit Resource 5 Animal Adaptations Woodland Animal Fact Sheet Fox Food: Foxes will eat almost anything they can get hold of. They eat small mammals such as rabbits and voles, insects and invertebrates,
patch. The egg will be as snug and warm there as if it were in a sleeping bag. Penguin Chick By Betty Tatham Illustrated by Helen K.
 Penguin Chick By Betty Tatham Illustrated by Helen K. Davis A fierce wind howls. It whips across the ice. Here, a female emperor penguin has just laid an egg. It is the only egg she will lay this year.
Penguin Chick By Betty Tatham Illustrated by Helen K. Davis A fierce wind howls. It whips across the ice. Here, a female emperor penguin has just laid an egg. It is the only egg she will lay this year.
Great Horned Owls. Rob & Ann Simpson
 Lesson 3 Great Horned Owl Great Horned Owls Hoo, hoo-oo, hoo, hoo! A great horned owl hoots in the night. Maybe it is hunting for a rabbit to eat. The great horned owl is one of the largest owls of North
Lesson 3 Great Horned Owl Great Horned Owls Hoo, hoo-oo, hoo, hoo! A great horned owl hoots in the night. Maybe it is hunting for a rabbit to eat. The great horned owl is one of the largest owls of North
Adaptation Creature Creation Addison Swenson, Cora Glass, Alexander Young: Lesson for 3rd-5th graders: Green and Health Schools Focus Areas:
 Adaptation Creature Creation Addison Swenson, Cora Glass, Alexander Young: Lesson for 3rd-5th graders: Green and Health Schools Focus Areas: Environmental & Sustainability Education Possible Subject areas
Adaptation Creature Creation Addison Swenson, Cora Glass, Alexander Young: Lesson for 3rd-5th graders: Green and Health Schools Focus Areas: Environmental & Sustainability Education Possible Subject areas
Stony Point Elementary School
 Written and illustrated by Ms. Pyle s kindergartners Stony Point Elementary School November 2013 We dedicate this book to our teacher, Ms. Pyle, Mr. Rush, and all the animals and people who share the world
Written and illustrated by Ms. Pyle s kindergartners Stony Point Elementary School November 2013 We dedicate this book to our teacher, Ms. Pyle, Mr. Rush, and all the animals and people who share the world
Commonly kept birds in Australia
 Learning topic: Provide advice on animal breeds and species Commonly kept birds in Australia Features of the different orders of birds There are two groups of birds: ratites flightless carinates birds
Learning topic: Provide advice on animal breeds and species Commonly kept birds in Australia Features of the different orders of birds There are two groups of birds: ratites flightless carinates birds
2009 Eagle Nest News from Duke Farms eagle nest Written by Larissa Smith, Assistant Biologist
 2009 Eagle Nest News from Duke Farms eagle nest Written by Larissa Smith, Assistant Biologist July 7 - The youngest chick was gone from the nest this morning but has returned to the nest several times
2009 Eagle Nest News from Duke Farms eagle nest Written by Larissa Smith, Assistant Biologist July 7 - The youngest chick was gone from the nest this morning but has returned to the nest several times
Identifying Plant and Animal Adaptations Answer Key
 Identifying Plant and Animal Adaptations Answer Key Instructions: Review the provided photos on the ipad. Try to identify as many adaptations for each plant or animal and determine how each adaptation
Identifying Plant and Animal Adaptations Answer Key Instructions: Review the provided photos on the ipad. Try to identify as many adaptations for each plant or animal and determine how each adaptation
Mother Nature Visits Preschool: Teaching Science Standards and Having Fun!
 Mother Nature Visits Preschool: Teaching Science Standards and Having Fun! ELIZABETH MCLAREN MOREHEAD STATE UNIVERSITY E.MCLAREN@ MOREHEADSTATE.EDU READY KIDS REGIONAL CONFERENCE MOREHEAD, KY JUNE 18-19,
Mother Nature Visits Preschool: Teaching Science Standards and Having Fun! ELIZABETH MCLAREN MOREHEAD STATE UNIVERSITY E.MCLAREN@ MOREHEADSTATE.EDU READY KIDS REGIONAL CONFERENCE MOREHEAD, KY JUNE 18-19,
They arguably have the most beautiful song of all the birds. They especially like to sing after rain. Buzzard
 To borrow... Feel free to borrow this guide for your visit today, but do return it so that others can enjoy it too. Stowe's bird guide Which birds can you spot when you're out and about? You might want
To borrow... Feel free to borrow this guide for your visit today, but do return it so that others can enjoy it too. Stowe's bird guide Which birds can you spot when you're out and about? You might want
A. Write the words under the picture.
 Before Reading Practice A. Write the words under the picture. swallow gull hawk owl goose duck crane gull goose crane duck roadrunner chicken hawk swallow chicken roadrunner owl ostrich ostrich Dance My
Before Reading Practice A. Write the words under the picture. swallow gull hawk owl goose duck crane gull goose crane duck roadrunner chicken hawk swallow chicken roadrunner owl ostrich ostrich Dance My
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * For Judges Use Only
 Welcome to the Wildlife O-Rama! JUNIOR KEY NAME: COUNTY: * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * For Judges Use Only Score Wildlife ID (30 pts) Wildlife Foods (15 pts) Wildlife Concepts (15 pts) Total RANK: Wildlife
Welcome to the Wildlife O-Rama! JUNIOR KEY NAME: COUNTY: * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * For Judges Use Only Score Wildlife ID (30 pts) Wildlife Foods (15 pts) Wildlife Concepts (15 pts) Total RANK: Wildlife
EUROPEAN STARLING HOUSE FINCH
 EUROPEAN STARLING Scientific Name: Sturnus vulgaris Size: 7.5-8.5 " (19-21 cm) Shape: Short tail; plump body Color: Blackbird with shiny feathers; yellow bill in springtime. Habitat: Cities, parks, farms,
EUROPEAN STARLING Scientific Name: Sturnus vulgaris Size: 7.5-8.5 " (19-21 cm) Shape: Short tail; plump body Color: Blackbird with shiny feathers; yellow bill in springtime. Habitat: Cities, parks, farms,
Animals of Maryland. By Mrs. Clubbs Kindergarten Class March 2013
 Animals of Maryland By Mrs. Clubbs Kindergarten Class March 2013 Our class made an informational book about animals that live in Maryland. In science, we studied mealworms and learned about how the external
Animals of Maryland By Mrs. Clubbs Kindergarten Class March 2013 Our class made an informational book about animals that live in Maryland. In science, we studied mealworms and learned about how the external
Comparing Life Cycles
 Image from Wikimedia Commons Pre-Visit Activity Grade Two Comparing Life Cycles Specific Learning Outcomes 2-1-01: Use appropriate vocabulary related to the investigations of growth and changes in animals.
Image from Wikimedia Commons Pre-Visit Activity Grade Two Comparing Life Cycles Specific Learning Outcomes 2-1-01: Use appropriate vocabulary related to the investigations of growth and changes in animals.
Adaptations of Insects
 Adaptations of Insects Teacher s Booklet Texas AgriLife Extenwsion Part of the Texas A&M University System Molly Keck Extension Program Specialist 3355 Cherry Ridge, Suite 212 San Antonio, TX 78230 Email:
Adaptations of Insects Teacher s Booklet Texas AgriLife Extenwsion Part of the Texas A&M University System Molly Keck Extension Program Specialist 3355 Cherry Ridge, Suite 212 San Antonio, TX 78230 Email:
by the authors and illustrators in Ms. Pyle s kindergarten class
 by the authors and illustrators in Ms. Pyle s kindergarten class Stony Point Elementary School February 2015 We dedicate this book to Ms. Pyle because she s a good teacher, she lets us make stuff, she
by the authors and illustrators in Ms. Pyle s kindergarten class Stony Point Elementary School February 2015 We dedicate this book to Ms. Pyle because she s a good teacher, she lets us make stuff, she
Raptors: Birds of Prey Lapbook
 Raptors: Birds of Prey Lapbook L-RBP Designed by Cyndi Kinney Raptors: Birds of Prey in North America Lapbook Copyright 2013 Knowledge Box Central www.knowledgeboxcentral.com ISBN # Ebook: 978-1-61625-547-3
Raptors: Birds of Prey Lapbook L-RBP Designed by Cyndi Kinney Raptors: Birds of Prey in North America Lapbook Copyright 2013 Knowledge Box Central www.knowledgeboxcentral.com ISBN # Ebook: 978-1-61625-547-3
Good Idea, Mother Nature!
 Good Idea, Mother Nature! Storytime by Kathy Ross King Grades PK 2 Mother Nature is full of good ideas for helping all kinds of plants and animals survive and grow. Sometimes, these species adaptive qualities
Good Idea, Mother Nature! Storytime by Kathy Ross King Grades PK 2 Mother Nature is full of good ideas for helping all kinds of plants and animals survive and grow. Sometimes, these species adaptive qualities
INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR DEPARTMENT OF EVS ( ) REVISION WORKSHEET NAME: CLASS: III SEC: ROLL NO:
 REVISION WORKSHEET INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR DEPARTMENT OF EVS (2017 2018) DATE: NAME: CLASS: III SEC: ROLL NO: I. Fill in the blanks to complete the statements. 1. The makes an untidy nest of sticks.
REVISION WORKSHEET INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR DEPARTMENT OF EVS (2017 2018) DATE: NAME: CLASS: III SEC: ROLL NO: I. Fill in the blanks to complete the statements. 1. The makes an untidy nest of sticks.
Grade 3: Animal Lifecycles Presentation
 Grade 3: Animal Lifecycles Presentation Table of Contents: Learning Objectives & Curriculum Connections... 2 Lesson Plan Script... 3 Extra Activities... 9 Appendix A: Lifecycle Match-up Cards... 11 Appendix
Grade 3: Animal Lifecycles Presentation Table of Contents: Learning Objectives & Curriculum Connections... 2 Lesson Plan Script... 3 Extra Activities... 9 Appendix A: Lifecycle Match-up Cards... 11 Appendix
ADAPTATION IN ANIMALS. 1. Which body feature of a frog MAINLY helps it to capture a flying insect? Ans
 Name : Subject : Science Class : V Roll No. : Date : SECTION A Choose the correct alternative ADAPTATION IN ANIMALS 1. Which body feature of a frog MAINLY helps it to capture a flying insect? a. Long,
Name : Subject : Science Class : V Roll No. : Date : SECTION A Choose the correct alternative ADAPTATION IN ANIMALS 1. Which body feature of a frog MAINLY helps it to capture a flying insect? a. Long,
Remember to stay SAFE. Stay Away From the Edge
 Remember to stay SAFE Stay Away From the Edge , LET S GO ON A QUEST Whether you want to go on a duck discovery or build the fastest leaf boat ever, our canals and rivers are the perfect place to go on
Remember to stay SAFE Stay Away From the Edge , LET S GO ON A QUEST Whether you want to go on a duck discovery or build the fastest leaf boat ever, our canals and rivers are the perfect place to go on
Inferring #1 This diagram shows the beak of several different species of birds. Make observations about the beaks and answer the questions.
 Observing #1 1. Record a qualitative observation of the scene in the illustration. 2. Record a quantitative observation of the scene in the illustration. 3. Observation or inference? The house collapsed.
Observing #1 1. Record a qualitative observation of the scene in the illustration. 2. Record a quantitative observation of the scene in the illustration. 3. Observation or inference? The house collapsed.
Animal Identification. Compiled by Lindsay Magill March 2017
 Animal Identification Compiled by Lindsay Magill March 2017 Birds Pigeon/Dove Passerine Corvid (Passerine) Hummingbird (Caprimulgiformes) Other Caprimulgiformes Bird of Prey Wading/Shorebird Woodpecker
Animal Identification Compiled by Lindsay Magill March 2017 Birds Pigeon/Dove Passerine Corvid (Passerine) Hummingbird (Caprimulgiformes) Other Caprimulgiformes Bird of Prey Wading/Shorebird Woodpecker
Birds, Beaks and Adaptations 4 hour curriculum
 Birds, Beaks and Adaptations 4 hour curriculum Habitats Ask students if they know what a habitat is. (Hint: they each have one!) A habitat is a place where animals (and people) can get everything they
Birds, Beaks and Adaptations 4 hour curriculum Habitats Ask students if they know what a habitat is. (Hint: they each have one!) A habitat is a place where animals (and people) can get everything they
Reproduction in Seed Plants (pp )
 Structure and Function of Plants Reading/Notetaking Guide Reproduction in Seed Plants (pp. 388 397) This section gives examples of the group of seed plants known as gymnosperms and angiosperms and describes
Structure and Function of Plants Reading/Notetaking Guide Reproduction in Seed Plants (pp. 388 397) This section gives examples of the group of seed plants known as gymnosperms and angiosperms and describes
All About Birds. Life Science. Scott Foresman Reading Street 3.2.5
 Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. Life Science All About Birds Genre Nonfiction Comprehension Skills and
Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. Life Science All About Birds Genre Nonfiction Comprehension Skills and
You are about to go on a journey of discovery around the park to find out more about how different animals are suited to their environment.
 Name: Adaptation Trail Welcome to Marwell Wildlife! You are about to go on a journey of discovery around the park to find out more about how different animals are suited to their environment. First, let
Name: Adaptation Trail Welcome to Marwell Wildlife! You are about to go on a journey of discovery around the park to find out more about how different animals are suited to their environment. First, let
BirdWalk Newsletter
 BirdWalk Newsletter 4.15.2018 Walk Conducted by Perry Nugent and Ray Swagerty Newsletter Written by Jayne J. Matney Cover Photo by Angie Bridges It s not only fine feathers that make fine birds. Aesop
BirdWalk Newsletter 4.15.2018 Walk Conducted by Perry Nugent and Ray Swagerty Newsletter Written by Jayne J. Matney Cover Photo by Angie Bridges It s not only fine feathers that make fine birds. Aesop
Bird Species Fact Sheets
 MODULE 1: LEARNING ABOUT BIRDS Bird Species Fact Sheets The following fact sheets cover 4 different birds, Blue tit, Chaffinch, Sand martin and House martin. These 4 species are featured because they can
MODULE 1: LEARNING ABOUT BIRDS Bird Species Fact Sheets The following fact sheets cover 4 different birds, Blue tit, Chaffinch, Sand martin and House martin. These 4 species are featured because they can
Meet the Larvae BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN. SC.F The student knows the basic needs of all living things FOR PERSONAL USE
 activity 21 Meet the Larvae BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade K Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.1.1 The student knows the basic needs of all living things SC.H.1.1.1 The student knows
activity 21 Meet the Larvae BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade K Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.1.1 The student knows the basic needs of all living things SC.H.1.1.1 The student knows
BirdWalk Newsletter. Magnolia Plantation and Gardens Walks Conducted by Perry Nugent and Ray Swagerty Newsletter Written by Jayne J.
 BirdWalk Newsletter Magnolia Plantation and Gardens Walks Conducted by Perry Nugent and Ray Swagerty Newsletter Written by Jayne J. Matney 3.11.2018 Carolina Wren Fledgling Photo by Guenter Weber Bird
BirdWalk Newsletter Magnolia Plantation and Gardens Walks Conducted by Perry Nugent and Ray Swagerty Newsletter Written by Jayne J. Matney 3.11.2018 Carolina Wren Fledgling Photo by Guenter Weber Bird
Bones and Bellies Clue Card 1
 Bones and Bellies Clue Card 1 Land Animals to the land food web. Animal A I am a carnivorous marsupial. My upper canine teeth are slightly larger than the lower canines. My molar teeth are sharp and pointy
Bones and Bellies Clue Card 1 Land Animals to the land food web. Animal A I am a carnivorous marsupial. My upper canine teeth are slightly larger than the lower canines. My molar teeth are sharp and pointy
students a hint to which habitat the animal could live in. If this information is above your students reading level, you may want
 tocutthecardsinhalfandonlyusethepictures. Note to teacher: The text on these cards is designed to give students a hint to which habitat the animal could live in. If this information is above your students
tocutthecardsinhalfandonlyusethepictures. Note to teacher: The text on these cards is designed to give students a hint to which habitat the animal could live in. If this information is above your students
Minnesota Bird Coloring Book
 Minnesota Bird Coloring Book Check out these links: How to look for birds! What s in a Bird Song? Listen to bird songs. State Park Bird Checklists 2015, State of Minnesota, mndnr.gov. This is a publication
Minnesota Bird Coloring Book Check out these links: How to look for birds! What s in a Bird Song? Listen to bird songs. State Park Bird Checklists 2015, State of Minnesota, mndnr.gov. This is a publication
Trunk Contents. Crane Flight Feathers (3)
 Trunk Contents Learning occurs not only with the mind, but also with the eyes, the hands the whole child (or adult!). Items contained in the trunk are meant to be examined, handled, and shared with your
Trunk Contents Learning occurs not only with the mind, but also with the eyes, the hands the whole child (or adult!). Items contained in the trunk are meant to be examined, handled, and shared with your
National Geographic Explorer. Lesson 1 Raising Raptors
 National Geographic Explorer Lesson 1 Raising Raptors Different kinds of raptors Raptors are birds of prey More than 500 species of raptors around the world Eagles, hawks, falcons, snowy owls and kestrels
National Geographic Explorer Lesson 1 Raising Raptors Different kinds of raptors Raptors are birds of prey More than 500 species of raptors around the world Eagles, hawks, falcons, snowy owls and kestrels
LESSON-7 NEST OF BIRDS Subject :- EVS
 LESSON-7 NEST OF BIRDS Subject :- EVS I. FILL IN THE BLANKS: 1. Birds build their nests during spring season. 2. Birds like fowls and partridges build shallow nest on the ground. 3. The cradle like nest
LESSON-7 NEST OF BIRDS Subject :- EVS I. FILL IN THE BLANKS: 1. Birds build their nests during spring season. 2. Birds like fowls and partridges build shallow nest on the ground. 3. The cradle like nest
HUMAN APPENDIX BATS & TROPICAL FLOWERS
 HUMAN APPENDIX In humans, the appendix is a short piece of tissue off the large intestine. It is not used by humans for digestive functions. In other mammals, like rabbits and deer, the cecum is a large
HUMAN APPENDIX In humans, the appendix is a short piece of tissue off the large intestine. It is not used by humans for digestive functions. In other mammals, like rabbits and deer, the cecum is a large
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH SA-I WORK SHEET CLASS: III EVS (LESSON-3, 4, 7, 12, 5)
 INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH SA-I WORK SHEET- 2016-2017 CLASS: III EVS (LESSON-3, 4, 7, 12, 5) LESSON-3, ANIMAL WORLD 1. FILL IN THE BANKS 1. A bird makes a. 2. A lion lives in a 3. A lives both
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH SA-I WORK SHEET- 2016-2017 CLASS: III EVS (LESSON-3, 4, 7, 12, 5) LESSON-3, ANIMAL WORLD 1. FILL IN THE BANKS 1. A bird makes a. 2. A lion lives in a 3. A lives both
What do these strange words mean?
 Bugs What do I need to start? How to draw them Drawing bugs takes practice, so don t expect to draw a perfect picture the first time. Use a notebook and write the date each time you draw to see how your
Bugs What do I need to start? How to draw them Drawing bugs takes practice, so don t expect to draw a perfect picture the first time. Use a notebook and write the date each time you draw to see how your
ì<(sk$m)=bdibjh< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Draw Conclusions Captions Call Outs Labels Glossary Plants and Animals Scott Foresman Science 3.4 ì
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Draw Conclusions Captions Call Outs Labels Glossary Plants and Animals Scott Foresman Science 3.4 ì
Where Animals and Plants Are Found
 Section 8: Physical Systems Where Animals and Plants Are Found About Animals and Plants What I Need to Know Vocabulary ecosystem food chain food web marine prairie Many animals live on Earth. Many plants
Section 8: Physical Systems Where Animals and Plants Are Found About Animals and Plants What I Need to Know Vocabulary ecosystem food chain food web marine prairie Many animals live on Earth. Many plants
FOOD WEB FOREST MUNCHERS
 FOOD WEB FOREST MUNCHERS Subject: Science Skills: Classification, Comparison, Discussion, Kinesthetic, Large group, Modeling, Simulation Duration: -2 Class Periods Setting: Outside or Large Open Area Materials:
FOOD WEB FOREST MUNCHERS Subject: Science Skills: Classification, Comparison, Discussion, Kinesthetic, Large group, Modeling, Simulation Duration: -2 Class Periods Setting: Outside or Large Open Area Materials:
KS3 Adaptation. KS3 Adaptation. Adaptation dominoes Trail
 KS3 Adaptation KS3 Adaptation Adaptation dominoes Trail Adaptation Trail The Adaptation Trail is a journey of discovery through Marwell which allows students to develop and apply their knowledge and understanding
KS3 Adaptation KS3 Adaptation Adaptation dominoes Trail Adaptation Trail The Adaptation Trail is a journey of discovery through Marwell which allows students to develop and apply their knowledge and understanding
Grade 1 Winter 12/08 1. GRADE 1 WINTER NATURE WALK Animals and What They Need to Survive
 Grade 1 Winter 12/08 1 GRADE 1 WINTER NATURE WALK Animals and What They Need to Survive OBJECTIVES: Observe seasonal changes in schoolyard since fall. Learn what happens in winter to animals typically
Grade 1 Winter 12/08 1 GRADE 1 WINTER NATURE WALK Animals and What They Need to Survive OBJECTIVES: Observe seasonal changes in schoolyard since fall. Learn what happens in winter to animals typically
It s All About Birds! Grade 7 Language Arts
 It s All About Birds! Grade 7 Language Arts I. Introduction to Birds Standard 1:1 Words in Context Verify the meaning of a word in its context, even when its meaning is not directly stated, through the
It s All About Birds! Grade 7 Language Arts I. Introduction to Birds Standard 1:1 Words in Context Verify the meaning of a word in its context, even when its meaning is not directly stated, through the
Adaptations of Insects
 Adaptationsof Insects Texas AgriLife Extension Part of the Texas A&M University System Molly Keck Extension Program Specialist 3355 Cherry Ridge, Suite 212 San Antonio, TX 78230 Email: mekeck@ag.tamu.edu
Adaptationsof Insects Texas AgriLife Extension Part of the Texas A&M University System Molly Keck Extension Program Specialist 3355 Cherry Ridge, Suite 212 San Antonio, TX 78230 Email: mekeck@ag.tamu.edu
SALAMANDERS. Helpful Hints: What is a Salamander: Physical Characteristics:
 SALAMANDERS Helpful Hints: This study guide will focus on s found in Illinois as well as those widespread in North America. The Eco-Meet test may consist of multiple choice, true/false, fill in the blank,
SALAMANDERS Helpful Hints: This study guide will focus on s found in Illinois as well as those widespread in North America. The Eco-Meet test may consist of multiple choice, true/false, fill in the blank,
The Blimp. DOWN 1 To steer, the pilot into a place under the air bag. 2 The large air bag is made of. 4 What is floating in the sky?
 The Blimp 1 2 3 3 It is not a plane by. This gas helps the blimp. A is an airship. People blimps to see if the enemy was close. 1 To steer, the pilot into a place under the air bag. 2 The large air bag
The Blimp 1 2 3 3 It is not a plane by. This gas helps the blimp. A is an airship. People blimps to see if the enemy was close. 1 To steer, the pilot into a place under the air bag. 2 The large air bag
Unit 5 Lesson 5: Mouse Mess
 Focus Areas: Pest Control Mechanical, Cultural; Science, Language Arts Focus Skills: critical thinking, observing, listening comprehension Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Objective To determine safe ways
Focus Areas: Pest Control Mechanical, Cultural; Science, Language Arts Focus Skills: critical thinking, observing, listening comprehension Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Objective To determine safe ways
Station #4. All information Adapted from:http://school.discoveryeducation.com/lessonplans/activities/makeitahabitat/adaptations.html and other sites
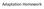 Adaptation Homework Station #1 GOAL: Avoid the Sun s heat and keep themselves cool. Animals spend the daylight hours hiding in burrows or behind boulders. They come out at night to hunt and forage for
Adaptation Homework Station #1 GOAL: Avoid the Sun s heat and keep themselves cool. Animals spend the daylight hours hiding in burrows or behind boulders. They come out at night to hunt and forage for
eastern meadowlark American woodcock brown thrasher
 Eastern Deciduous Forest Fish Pond / Stream Management Practices American woodcock brown thrasher eastern meadowlark golden- winged warbler great horned owl mourning dove northern bobwhite ovenbird wild
Eastern Deciduous Forest Fish Pond / Stream Management Practices American woodcock brown thrasher eastern meadowlark golden- winged warbler great horned owl mourning dove northern bobwhite ovenbird wild
Forests. By: Elyse Jacoby-Jacoby Jungle
 Forests There are forests in North America, Europe, Asia, South America, Africa, and Australia. The growing season in these forests is about 6 months long. Temperature and Precipitation: The average temperature
Forests There are forests in North America, Europe, Asia, South America, Africa, and Australia. The growing season in these forests is about 6 months long. Temperature and Precipitation: The average temperature
Songbird Rehabilitation
 Songbird Rehabilitation Federal Migratory Bird Treaty Act Creative Commons - Lambtonwyrm Creative Commons Sergey Yiliseev All birds are protected except: English Sparrow Rock Dove (pigeon) European Starling
Songbird Rehabilitation Federal Migratory Bird Treaty Act Creative Commons - Lambtonwyrm Creative Commons Sergey Yiliseev All birds are protected except: English Sparrow Rock Dove (pigeon) European Starling
Great Science Adventures
 Great Science Adventures What is complete metamorphosis? Lesson 10 Insect Concepts: Nearly all insects pass through changes in their body form and structure as they grow. The process of developing in stages
Great Science Adventures What is complete metamorphosis? Lesson 10 Insect Concepts: Nearly all insects pass through changes in their body form and structure as they grow. The process of developing in stages
Red-Tailed Hawk Buteo jamaicensis
 Red-Tailed Hawk Buteo jamaicensis This large, dark headed, broad-shouldered hawk is one of the most common and widespread hawks in North America. The Red-tailed hawk belongs to the genus (family) Buteo,
Red-Tailed Hawk Buteo jamaicensis This large, dark headed, broad-shouldered hawk is one of the most common and widespread hawks in North America. The Red-tailed hawk belongs to the genus (family) Buteo,
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL- RIYADH HALF YEARLY WORKSHEET CLASS: III. SUBJECT: EVS LESSONS: 3,4,5,6,7,12,17
 INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL- RIYADH HALF YEARLY WORKSHEET- 2018-2019 CLASS: III. SUBJECT: EVS LESSONS: 3,4,5,6,7,12,17 LESSON: 3- ANIMAL WORLD FILL IN THE BLANKS 1. A lives in the shade of trees. 2. A
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL- RIYADH HALF YEARLY WORKSHEET- 2018-2019 CLASS: III. SUBJECT: EVS LESSONS: 3,4,5,6,7,12,17 LESSON: 3- ANIMAL WORLD FILL IN THE BLANKS 1. A lives in the shade of trees. 2. A
By Doris L. Mueller Illustrations by Sherry Neidigh
 By Doris L. Mueller Illustrations by Sherry Neidigh Long ago, the magpies nests were the envy of all other birds. To help the other birds, Maggie Magpie patiently explained how to build a nest. But some
By Doris L. Mueller Illustrations by Sherry Neidigh Long ago, the magpies nests were the envy of all other birds. To help the other birds, Maggie Magpie patiently explained how to build a nest. But some
Santa Rosa Plateau Ecological Reserve
 Dear Third Grade Students, On your visit to the Plateau, we probably won t meet. I am nocturnal, which means I sleep all day long and come out at night. Since I m a male (or boy), when the sun starts to
Dear Third Grade Students, On your visit to the Plateau, we probably won t meet. I am nocturnal, which means I sleep all day long and come out at night. Since I m a male (or boy), when the sun starts to
Nonfiction. by Diane Furuichi PAIRED. Poetry READ
 Nonfiction by Diane Furuichi PAIRED READ Poetry STRATEGIES & SKILLS Comprehension Strategy: Ask and Answer Questions Skill: Main Idea and Key Details Vocabulary find, food, more, over, search, seek, start,
Nonfiction by Diane Furuichi PAIRED READ Poetry STRATEGIES & SKILLS Comprehension Strategy: Ask and Answer Questions Skill: Main Idea and Key Details Vocabulary find, food, more, over, search, seek, start,
Life Cycle of a Goose
 Life Cycle of a Goose By 1 2 3 Learn Curriculum Honk! Honk! Honk! Honk! THANK YOU for downloading this product. I hope you enjoy it as much as I did creating it! I value your feedback, so please don't
Life Cycle of a Goose By 1 2 3 Learn Curriculum Honk! Honk! Honk! Honk! THANK YOU for downloading this product. I hope you enjoy it as much as I did creating it! I value your feedback, so please don't
Amazing arthropods. Kindergarten-Second. Life Science TEKS. Life Science Vocabulary
 Amazing arthropods Kindergarten-Second Life Science TEKS Kindergarten: K.9A, K.9B, K.10A, K.10B First Grade: 1.9A, 1.9B, 1.9C, 10A, 1.10C, 1.10D Second Grade: 2.9A, 2.9B, 2.9C, 2.10A, 2.10C Life Science
Amazing arthropods Kindergarten-Second Life Science TEKS Kindergarten: K.9A, K.9B, K.10A, K.10B First Grade: 1.9A, 1.9B, 1.9C, 10A, 1.10C, 1.10D Second Grade: 2.9A, 2.9B, 2.9C, 2.10A, 2.10C Life Science
What is going on in this picture? (Turn and talk.)
 What is going on in this picture? (Turn and talk.) Was the animal in that last slide a crocodile or alligator? It s a crocodile! In nature, organisms live together in long-term relationships. SYMBIOSIS
What is going on in this picture? (Turn and talk.) Was the animal in that last slide a crocodile or alligator? It s a crocodile! In nature, organisms live together in long-term relationships. SYMBIOSIS
Biodiversity Trail Birds and Insects
 Biodiversity Trail Birds and Insects Self guided program Birds & Insects exhibition Student Activities Illustration: Sara Estrada-Arevalo, Australian Museum. Produced by Learning Services, Australian Museum,
Biodiversity Trail Birds and Insects Self guided program Birds & Insects exhibition Student Activities Illustration: Sara Estrada-Arevalo, Australian Museum. Produced by Learning Services, Australian Museum,
Primary Activity #1. The Story of Noir, the Black-footed Ferret. Description: Procedure:
 50 Primary Activity #1 The Story of Noir, the Black-footed Ferret Description: Students will learn about the habitat and life of a black-footed ferret as they read the story of Noir, the black-footed ferret.
50 Primary Activity #1 The Story of Noir, the Black-footed Ferret Description: Students will learn about the habitat and life of a black-footed ferret as they read the story of Noir, the black-footed ferret.
Wonders of Nature. Wonders of Nature J O R LEVELED READER O. Visit for thousands of books and materials.
 Wonders of Nature A Reading A Z Level O Leveled Reader Word Count: 710 LEVELED READER O Wonders of Nature Q J O R Written by Cheryl Ryan Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com
Wonders of Nature A Reading A Z Level O Leveled Reader Word Count: 710 LEVELED READER O Wonders of Nature Q J O R Written by Cheryl Ryan Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com
BirdWalk Newsletter
 BirdWalk Newsletter 2.26.2017 Walk Conducted by Perry Nugent Written by Jayne J. Matney Hark, love, while through this wood we walk, Beneath melodious trees, How wrens with redbreasts ever talk What tuneful
BirdWalk Newsletter 2.26.2017 Walk Conducted by Perry Nugent Written by Jayne J. Matney Hark, love, while through this wood we walk, Beneath melodious trees, How wrens with redbreasts ever talk What tuneful
Mini 4-H Wildlife Project
 Mini 4-H Wildlife Project Name Club Wildlife Project Instructions: Make 1 of the following: 1. An Animal Book 2. A Poster 3. A Model Animal 4. A Birdhouse Complete 2 of the following: 1. Word Search Puzzle
Mini 4-H Wildlife Project Name Club Wildlife Project Instructions: Make 1 of the following: 1. An Animal Book 2. A Poster 3. A Model Animal 4. A Birdhouse Complete 2 of the following: 1. Word Search Puzzle
