Original Article Evolution of bacterial flora in burn wounds: key role of environmental disinfection in control of infection
|
|
|
- Carmel Curtis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Burn Trauma 2013;3(2): /ISSN: /IJBT Original Article Evolution of bacterial flora in burn wounds: key role of environmental disinfection in control of infection Neelam Taneja 1, PS Chari 2, Malkit Singh 1, Gagandeep Singh 1, Manisha Biswal 1, Meera Sharma 1 1 Department of Medical Microbiology, 2 Department of Burns and Plastic Surgery, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Sector 12, Chandigarh, India Received March 22, 2013; Accepted April 6, 2013; Epub April 18, 2013; Published April 30, 2013 Abstract: Bacterial flora in burn patients undergoes change over period of time and is dependent upon many factors. Study of burn flora is not only helpful in locating entry of multidrug resistant bacterial strains into the unit s usual flora but also in determining current antibiotic susceptibilities. Since no studies are available from India that have studied sequential emergence of different microorganisms in burn wound, present study was carried out to study evolution of bacterial flora in burn wounds and its correlation with invasive wound infection. Environmental sampling was also carried out for possible sources of infection. Patients with 20-70% of total burn surface were enrolled and followed up for entire duration of stay. Clinical & treatment details were noted. Surface wound swabs were collected on first, third, seventh, tenth and fourteenth day post admission. Environmental sampling was done every three months. Of 215 wound swabs collected from 71 patients, 72 were sterile and 143 yielded 214 isolates. Colonization rates were 33% on first day, 94% on 7th day and 100% by 14th day. 42% swabs grew gram negative bacteria. Overall Staphylococcus aureus was the predominant isolate (45%) followed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (13.9%), beta hemolytic Streptococci (9.4%). Maximum invasive infections were seen at the seventh day. A high level of environmental contamination was seen with S. aureus, a substantial portion being MRSA. Better control of environmental contamination and disinfection along with rigorous hand washing and barrier precautions are recommended to prevent infection of wounds. Keywords: Burns, infections, environmental, surveillance, disinfection Introduction It has been estimated that at least 50% of all deaths caused by burns are the result of wound infection [1]. Burn wounds are especially prone to infection because of loss of protective covering and presence of highly nutritive serum. The incidence of wound infection in burn patients appears to be correlated with both the extent and depth of injury as well as length of time the wound remains open [2]. Altered microbial ecology following burn injury is the result of the interaction of endogenous & exogenous microbial flora with injury induced physical and immunologic host defects [3]. The bacterial flora undergoes a change over a period of time [4] and is dependent upon length of hospitalization, environmental contamination, endogenous bacterial flora of patients and dressing procedures [5]. The determination of antibiotic susceptibility of the predominant isolated organisms or targeted organisms aids in recognizing the problems of cross contamination or introduction of multi-drug resistant bacterial strains into the unit s usual flora [5]. It is therefore desirable to carry out periodic reviews of the bacterial flora of burn wounds in all centers so that preventive strategies could be modified as necessary. No studies are available from India to date that have studied sequential emergence of different microorganisms in burn wound patients. Therefore, the present study was carried out in the burn unit of 1900 bed tertiary care referral centre in North India to study the evolution of bacterial flora of burn wounds. Environmental surveillance was also carried out to look for possible sources of wound contamination. Subjects and methods Patients presenting with 20-70% of total body surface area burned (TBSAB) were enrolled in
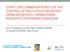
2 Figure 1. Graphic representation of colonization with Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter and beta hemolytic streptococci (BHS) and development of invasive wound infection over a period of 14 days. this study. Details of the burn unit have been described elsewhere [6]. Patients referred from other hospitals and nursing homes were not included. Patients were visited daily by the hospital infection nurse, and followed up to death/ discharge. Clinical and demographic details, which included age, sex, burn injury details, all investigations done, procedures and treatment details were filled up in a detailed proforma in consultation with resident doctors. Total surface area burned (TBSAB) was calculated by Lund and Browder chart [7]. Following investigations were done routinely and repeated as often as required: hemoglobin, total and differential leucocyte counts, renal and liver function tests, arterial blood gas analysis, urine microscopy, urine culture, blood culture, wound swab culture, tracheal aspirate culture. A surface wound swab was collected from the site marked on first, third, seventh, tenth, and fourteenth day post admission. Fifty ml sterile saline was poured over wound surface, a wet cotton tipped swab was collected and plated on blood and MacConkeys medium (Himedia Laboratories, Mumbai). The swabs were processed for aerobic organisms by standard conventional methods and antibiotic sensitivity tested by Kirby Bauers disc diffusion method as recommended by the CLSI [8]. The following definition based on CDC case definitions [9] was used to define invasive wound infection: 1. Change in burn wound appearance or character such as rapid eschar formation, discoloration of the eschar or edema at wound margin and 2. At least one of the following: a. Organisms cultured from blood in absence of other identifiable infections. b. Two of the following-fever>38 C or hypothermia, hypotension, oliguria, hyperglycemia at previously tolerated level of dietary carbohydrate or mental confusion. Environmental sampling During the study period an environmental sampling was done every three months. Samples were collected from various areas. Nasal swabs were collected from patients as well nursing staff to look for nasal carriage of S. aureus. Results Results of wound swab cultures In all, 215 wound swabs were collected from 71 patients of which 72 were sterile & 143 yielded 214 isolates. Single isolates were obtained from 89 sample and multiple isolates from 54 samples. Table 1 summarizes the findings of bacteriological cultures and correlation with gross appearance of wound and invasive wound infection. On first day post admission itself, 33% patients were colonized; S. aureus accounting for 50% of isolates, however, gram negative bacteria like P. aeruginosa, Acinetobacter, Klebsiella, Enterobacter and E. coli were isolated from 14 of 24 patients. By seventh day 94% of patients were colonized and 100% of patients were colonized by four- 103 Int J Burn Trauma 2013;3(2):
3 Table 1. Result of gross wound appearance, invasive wound infection, colonization of wounds & mortality Result Post admission time of sampling 1 st day 3 rd day 7 th day 10 th day 14 th day Number of patients (n) sampled Number of patients colonized 24 (33%) 44 (68.7%) 34 (94%) 34 (94%) 24 (100%) Grossly clean wound 71 (100%) 61 (95.3%) 17 (47.2%) 18 (50%) 06 (25%) Invasive wound infection 0 (nil) 04 (09.0%) 17 (50%) 8 (23.5%) 02 (8.3%) Polymicrobial wound colonization 6 (25%) 15 (34%) 08 (23.5%) 13 (38.2%) 14 (58.3) Patients died (n=16) * 0 (nil) 01 (6.25) 06 (37.5) 02 (12.5) 04 (25) * Three died after 14 th day. Table 2. Results of bacterial cultures from wounds on different days Organism 1 st day 3 rd day 7 th day 10 th day 14 th day No. of patients colonized S. aureus (n=101) 12 (50%) 29 (65.9%) 25 (73.5%) 17 (50%) 18 (75%) Pseudomonas (n=22) 4 (16.7%) 2 (8.3%) 8 (23.5 %) 4 (11.8%) 4 (16.7%) Acinetobacter (n=21) 5 (20.8%) 8 (59.2%) 4 (11.8%) 2 (5.9%) 2 (8.3%) β Hemolytic Streptococci (n=21) 1 (4.2%) 4 (9.1%) 4 (11.8%) 4 (11.8%) 8 (33.3%) Klebsiella (n=15) 2 (8.3%) 6 (13.6%) 3 (8.8%) 2 (5.9%) 2 (8.3%) Enterobacter (n=9) 2 (8.3%) 4 (9.1%) 3 (8.8%) Proteus mirabilis (n=8) -- 2 (4.5%) 4 (11.8%) 1 (2.9%) 1 (4.2%) E.coli (n=7) 1 (4.2%) 2 (4.5%) 1 (2.9%) 2 (5.9%) 1 (4.2%) Enterococci (n=7) 2 (8.3%) 3 (6.8%) 1 (2.9%) 1 (2.9%) -- Cirtobacter (n=2) (2.9%) 1 (4.2%) α-haemolytic Streptococci (n=1) (2.9%) -- n = number of isolates. teenth day. Table 2 shows the microorganisms isolated on different days. Out of 214 isolates 92(41.4%) were gram-negative bacteria. Overall S. aureus was the predominant isolate throughout (45.4%) followed by P. aeruginosa (13.9%), Beta-hemolytic streptococci (9.4%), Acinetobacter spp (9.4%), Klebsiella (6.3%), Enterobacter (4.3%), Proteus (3.6%), and E.coli (3.1%). All beta-hemolytic streptococci were group A. Figure 1 shows the graphic representation of colonization, invasive wound infection and acquiring S. aureus, P. aeruginosa over a period of 14 days. Maximum invasive wound infection occurred at seven days (range 3 to 21 days, median 7 days). Two infections occurred after 14 days. The peak of the invasive wound infection coincided with the peak of acquiring P. aeruginosa and peak of colonization coincided with peak of acquiring S. aureus. Antibiotic susceptibility results of isolates are shown in Table 3. Results of environmental surveillance MRSA was grown from disinfectant solution, air samples, bath and medicine trolleys, bed mattresses, a nurse s locker and nasal swab of a patient. However none of the health care worker carried MRSA in their nose. Some of the sterile dressing material and open saline bottles used for irrigation of wounds were found contaminated (Table 4). Discussion The microbial component of the burn wound is the variable most easily influenced by therapy [3]. The organisms involved in these infections can be either endogenous or exogenous in origin. The exogenous sources of cross transmission and outbreaks in ICUs may include other patients, colonized health care personnel, contaminated food, supplies, hospital equipment and air [10]. Colonization precedes infection as also shown in our study (median day of coloni- 104 Int J Burn Trauma 2013;3(2):
4 Table 3. Results of Antibiotic resistance of bacterial isolates from burn unit Organism Met G Cip Net Tmp-Sxt E Cef Ak Cefta Pip S. aureus (N=51) 13 (25.5%) 25 (49.2%) 12 (23.5%) 7 (13.7%) 21/30 (70%) 21/37 (56.7%) 12/40 (30%) P. aeruginosa (N=17) Acinetobcter (N=13) Klebsiella (N=6) Proteus (N=4) Enterobacter (N=4) 11 (64.7%) 7/13 (53.8%) 5/6 (83.3%) 3/4 (75%) 4/4 (100%) 2/17 (11.7%) 4/13 (30.7%) 2/6 (33.3%) 3/4 (75%) 2/4 (50%) 12/17 (70.5%) 3/13 (23.1%) 2/5 (40%) 1/4 (25%) 0/4 100%) 3/17 (17.6) 3/8 (37.5%) 5/13 (38.5%) 4/6 (66.6%) 4/4 (100%) 3/4 (75%) 2/4 (50%) 2/13 (15.4%) 3/6 (50%) 1/4 (25%) 8/17 (47%) 07/17 (41.2%) N=number of isolates tested, -not tested, Met-Methicillin, G-Gentamicin, Ak-Amikacin, Cef-Cefotaxime, Cip-Ciprofloxacin, Tmp-Sxt-trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole combination, Net-Netilmicin, E-Erythromycin, Pip-Piperacillin, Cefta-Ceftazidime. Table 4. Results of environment sampling, nasal and hand swabs Surface tested Total sample taken Organism isolated & no. of samples contaminated or showing growth of pathogens Medicine trolleys 05 S. aureus including MRSA (5), Acinetobacter spp. (5) Bath trolleys 10 S. aureus including MRSA (10), Acinetobacter spp. (10) Tap handles 08 MSSA (3) Air conditioning grille 05 MSSA (3) Wash basin 04 Acinetobacter spp., Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter spp. (4) Refrigerators 05 Citrobacter spp. (1) Enterobacter spp. (1) Sterile dressing material 13 E.coli (1) Enterobacter spp. (1) Silver sulphadiazene cream & saline bottles 13 Proteus mirabilis (1) Enterobacter spp. (1) Artery forceps 05 (0) Disinfectant solution- Betadine 10 MRSA (1) Bed mattresses 12 S. aureus including MRSA (12) Nurses lockers 03 MRSA (1) Electric switches 04 (0) Nasal swab-patients 20 MSSA (7), MRSA (1), βhs (1) Nasal swab-staff 10 MSSA (2) Hand swab/intact skin swab-patients 20 MSSA (8), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (1), Acinetobacter spp. (1), βhs (2) Hand webs-staff 10 MSSA (1) Air cfu of air including MRSA Water 05 Satisfactory on all occassions Total cfu-colony forming units, MSSA-Methicillin sensitive S. aureus, MRSA-Methicillin resistant S. aureus, βhs-beta hemolytic streptococci. zation 3 days, and median day of wound infection 7 days). Burn wound is highly susceptible to colonization; colonizing microorganisms can easily multiply to reach high densities on the wound [11]. In the present study, it was found that colonization started almost immediately on admission (46.5% on first day), more than 90% of patients was colonized by the 7 th day. 105 Int J Burn Trauma 2013;3(2):
5 The results are similar to other studies [4, 12] where by the end of first week 80.6%-87% patients were colonized. An important finding of our study is an apparent change in the microbiology of burns wounds away from the traditionally important gram-negative rods to grampositive cocci. P. aeruginosa which used to be the predominant colonizer and infective agent of burn wound have become uncommon due use of topical antibiotics [13]. In India many of the centers still have P. aeruginosa has been reported as the predominant organism from many centers in India [5, 14-16] however, at our center similar to developed countries S. aureus was the predominant organism throughout. Several studies have shown that flora of individual burn wound changes over time; grampositive organisms are generally replaced by gram negative ones after the first week. In one study, P. aeruginosa did not appear in burn wounds until an average of 21 days after admission [17]. In our study this trend was not seen. P. aeruginosa was the second most common colonizer and colonization remained at the same level over a period of two weeks. In epidemiological studies of MRSA, it has been shown that the majority of MRSA positive burn patients, both the air and the environment surfaces become heavily contaminated [18]. This was also true for our burn unit. Most of the MRSA infections are due to failure to prevent cross-transmission in hospital [13, 19]. Contrary to the finding in the literature about beta hemolytic streptococci becoming a rarity [20], this organism, which is a serious threat to skin grafting, was the most common colonizing organism. A significant number of contaminated wounds showed a polymicrobial etiology with multiple isolates (54/143, overall 33%), 25% on first day, 34% on 3 rd day, 32.5% on 7 th day, 38.2% o 10 th day, 58.3% on 14 th day. Polymicrobial infection is increasingly being reported in burn patients [21]. The relationship between the colonizing organisms and the ones causing invasive wound infection was studied. Blood stream isolates were taken into account as we had not taken the burn biopsies. In 10 patients the organism isolated from blood culture were the same as that isolated from wound swab. Though S. aureus was the predominant colonizer, surprisingly P. aeruginosa and other gram-negative organisms were more frequently isolated from blood culture. This may be due to the higher invasiveness of P. aeruginosa or due to high resistance in this organism. The results of antibiotic sensitivity patterns give serious cause for concern because many of the isolates were resistant to commonly available antibiotics. Gross clean appearance of the wounds had very poor correlation with wound colonization, but correlated well inversely with invasive wound infection. In 16 patients, nasal swab culture yielded S. aureus (MRSA in only 1). Antibiogram of these 16 strains did not match with S. aureus isolated from wound surface. None of the nursing staff had MRSA in their nose and none of the isolates matched in antibiogram with that isolated from wound surface. Another study with larger number of patients combined with epidemiological typing methods is warranted to know the exact source of S. aureus. However the source of S. aureus in burn patients may be exogenous. This finding is corroborated by high environment contamination of surfaces and air with S. aureus including MRSA. Since a high level of contamination of air and bath trolleys was seen it is obvious that control measures should be directed against contamination of environment with S. aureus. No environmental sources were found for P. aeruginosa. We suspect the gut of the patient to be a source as P. aeruginosa can colonize guts of 30% of the hospitalized patients [5]. Some of the sterile material used for dressing and disinfectants were also found contaminated. It is very important that all the dressing material be sterile and that dressings be done taking all sterile precautions. Patient housing in single bed in a room with a separate sink facility to wash hands and change in staffing pattern has been shown to prevent infection and reduce mortality [22]. Cohort separation has been found to be a practical way of elimination endemic resistant gram-negative organisms from burn [3]. We recommend nursing of severely burned patients in a purpose built burn unit rather than general surgical ward and cohort nursing to reduce the cross infection problem. Particular nurse/nurses can look after uninfected patients. Barrier precautions should be taken at all times of patient handling. Disinfection of the bath trolleys in between two patients and routine disinfection of the surfaces is highly desirable as also better compliance to hand washing. Infected and uninfected patients should be cared for by separate groups 106 Int J Burn Trauma 2013;3(2):
6 of nurses and residents should do the dressing of uninfected patients first and then proceed to infected patients. Competing interest statement The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests. Address correspondence to: Dr. Neelam Taneja, Department of Medical Microbiology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Sector 12, Chandigarh, India. Pin: Phone: ; Fax: ; drneelampgi@yahoo.com References [1] Monafo WW. Supportive therapy in burn care. An overview of infection control. J Trauma 1979; 19: [2] Kagan RJ, Matsuda T, Hanumadass M and Jonasson O. Serious wound infections in burned patients. Surgery 1985; 98: [3] McManus AT, McManus WF, Mason AD Jr, Aitcheson AR and Pruitt BA Jr. Microbial colonization in a new intensive care burn unit. A prospective cohort study. Arch Surg 1985; 120: [4] Atoyebi OA, Sowemimo GO and Odugbemi T. Bacterial flora of burn wounds in Lagos, Nigeria: a prospective study. Burns 1992; 18: [5] Pandit DV, Gore MA, Saileshwar N and Deodhar LP. Laboratory data from the surveillance of a burns ward for the detection of hospital infection. Burns 1993; 19: [6] Taneja N, Emmanuel R, Chari PS and Sharma M. A prospective study of hospital-acquired infections in burn patients at a tertiary care referral centre in North India. Burns 2004; 30: [7] Lund CC and Browder NC. The estimation of areas of burns. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1944; 79: [8] CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; 18th Informational Supplement, M100-S18, vol. 28, no. 1. In: editors. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; [9] Gaynes RP and Horan TC. Surveillance of nosocomial infections. Appendix A: CDC definitions of nosocomial infections. In: Mayhall CG, editors. Hospital epidemiology and infection control. Baltimore: William and Wilkins; pp: 1-4. [10] Chetchotisakd P, Phelps CL and Hartstein AI. Assessment of bacterial cross-transmission as a cause of infections in patients in intensive care units. Clin Infect Dis 1994; 18: [11] Kluytmans J. Surgical infections including burns. In: Wenzel RP, editors. Prevention and control of nosocomial infections. Pennsylvania: Williams and Wilkins; pp: [12] Yemul VL and Sengupta SR. Bacteriology of Burns. Burns 1981; 7: [13] Oncul O, Yuksel F, Altunay H, Acikel C, Celikoz B and Cavuslu S. The evaluation of nosocomial infection during 1-year-period in the burn unit of a training hospital in Istanbul, Turkey. Burns 2002; 28: [14] Mehta M, Dutta P and Gupta V. Bacterial isolates from burn wound infections and their antibiograms: A eight-year study. Indian J Plast Surg 2007; 40: [15] Rajput A, Singh KP, Kumar V, Sexena R and Singh RK. Antibacterial resistance pattern of aerobic bacteria isolates from burn patients in tertiary care hospital. Biomed Res 2008; 19: 1-4. [16] Revathi G, Puri J and Jain BK. Bacteriology of burns. Burns 1998; 24: [17] Manson WL, Pernot PC, Fidler V, Sauer EW and Klasen HJ. Colonization of burns and the duration of hospital stay of severely burned patients. J Hosp Infect 1992; 22: [18] Rutala WA, Katz EB, Sherertz RJ and Sarubbi FA Jr. Environmental study of a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus epidemic in a burn unit. J Clin Microbiol 1983; 18: [19] Chaudhary U, Goel N, Sharma M, Griwan MS and Kumar V. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection/Colonization at the Burn Care Unit of a Medical School in India. J Infect Dis Antimicrob Agents 2007; 24: [20] Bang RL, Sharma PN, Sanyal SC and Al Najjadah I. Septicaemia after burn injury: a comparative study. Burns 2002; 28: [21] Still JM Jr, Belcher K and Law EJ. Experience with polymicrobial sepsis in a regional burn unit. Burns 1993; 19: [22] Shirani KZ, McManus AT, Vaughan GM, McManus WF, Pruitt BA Jr and Mason AD Jr. Effects of environment on infection in burn patients. Arch Surg 1986; 121: Int J Burn Trauma 2013;3(2):
Aerobic bacterial infections in a burns unit of Sassoon General Hospital, Pune
 Original article Aerobic bacterial infections in a burns unit of Sassoon General Hospital, Pune Patil P, Joshi S, Bharadwaj R. Department of Microbiology, B.J. Medical College, Pune, India. Corresponding
Original article Aerobic bacterial infections in a burns unit of Sassoon General Hospital, Pune Patil P, Joshi S, Bharadwaj R. Department of Microbiology, B.J. Medical College, Pune, India. Corresponding
Bacteriological profile of burn patients and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of burn wound isolates
 International Surgery Journal Sharma L et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Mar;4(3):1019-1023 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20170854
International Surgery Journal Sharma L et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Mar;4(3):1019-1023 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20170854
Burn Infection & Laboratory Diagnosis
 Burn Infection & Laboratory Diagnosis Introduction Burns are one the most common forms of trauma. 2 million fires each years 1.2 million people with burn injuries 100000 hospitalization 5000 patients die
Burn Infection & Laboratory Diagnosis Introduction Burns are one the most common forms of trauma. 2 million fires each years 1.2 million people with burn injuries 100000 hospitalization 5000 patients die
Prevalence of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its antibiogram in a tertiary care centre
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 952-956 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 952-956 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase
BACTERIOLOGICAL PROFILE AND ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN OF ISOLATES OF NEONATAL SEPTICEMIA IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Research Article BACTERIOLOGICAL PROFILE AND ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN OF ISOLATES OF NEONATAL SEPTICEMIA IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Research Article BACTERIOLOGICAL PROFILE AND ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN OF ISOLATES OF NEONATAL SEPTICEMIA IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
A Study of Bacteriology of Burn Wound Infections
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 3611-3617 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.434
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 3611-3617 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.434
Bacterial Pathogens in Urinary Tract Infection and Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern from a Teaching Hospital, Bengaluru, India
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 11 (2015) pp. 731-736 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Bacterial Pathogens in Urinary Tract Infection and Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern from a Teaching
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 11 (2015) pp. 731-736 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Bacterial Pathogens in Urinary Tract Infection and Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern from a Teaching
Detection and Quantitation of the Etiologic Agents of Ventilator Associated Pneumonia in Endotracheal Tube Aspirates From Patients in Iran
 Letter to the Editor Detection and Quantitation of the Etiologic Agents of Ventilator Associated Pneumonia in Endotracheal Tube Aspirates From Patients in Iran Mohammad Rahbar, PhD; Massoud Hajia, PhD
Letter to the Editor Detection and Quantitation of the Etiologic Agents of Ventilator Associated Pneumonia in Endotracheal Tube Aspirates From Patients in Iran Mohammad Rahbar, PhD; Massoud Hajia, PhD
Aerobic Bacterial Profile and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Pus Isolates in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Hadoti Region
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 2866-2873 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.326
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 2866-2873 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.326
Bacteriological profile and antibiogram of aerobic burn wound isolates in a tertiary care hospital, Odisha, India
 International Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences ISSN: 2167-0404 Vol. 3 (5), pp. 460-463, July, 2013. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International Scholars Journals Full
International Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences ISSN: 2167-0404 Vol. 3 (5), pp. 460-463, July, 2013. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International Scholars Journals Full
Other Enterobacteriaceae
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER NUMBER 50: Other Enterobacteriaceae Author Kalisvar Marimuthu, MD Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH Topic Outline Topic outline - Key Issues Known
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER NUMBER 50: Other Enterobacteriaceae Author Kalisvar Marimuthu, MD Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH Topic Outline Topic outline - Key Issues Known
Study of Bacteriological Profile of Corneal Ulcers in Patients Attending VIMS, Ballari, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 7 (2016) pp. 200-205 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.507.020
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 7 (2016) pp. 200-205 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.507.020
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times
 Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
Bacteriological Profile of Burn Wounds and Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern in a Tertiary Care Hospital
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/447 Bacteriological Profile of Burn Wounds and Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern in a Tertiary Care Hospital
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/447 Bacteriological Profile of Burn Wounds and Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern in a Tertiary Care Hospital
BACTERIOLOGICALL STUDY OF MICROORGANISMS ON MOBILES AND STETHOSCOPES USED BY HEALTH CARE WORKERS IN EMERGENCY AND ICU S
 Research Article Harika A,, 2013; Volume 2(3): 290-297 ISSN: 2277-8713 BACTERIOLOGICALL STUDY OF MICROORGANISMS ON MOBILES AND STETHOSCOPES USED BY HEALTH CARE WORKERS IN EMERGENCY AND ICU S HARIKAA A,
Research Article Harika A,, 2013; Volume 2(3): 290-297 ISSN: 2277-8713 BACTERIOLOGICALL STUDY OF MICROORGANISMS ON MOBILES AND STETHOSCOPES USED BY HEALTH CARE WORKERS IN EMERGENCY AND ICU S HARIKAA A,
Prevalence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Surgical Site Infection in a Tertiary Care Centre
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 4 (2017) pp. 1202-1206 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.604.147
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 4 (2017) pp. 1202-1206 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.604.147
Bacteriological Profile and Antimicrobial Sensitivity of Wound Infections
 Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (215) 4(12): 248-254 ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 4 Number 12 (215) pp. 248-254 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Bacteriological Profile and Antimicrobial Sensitivity
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (215) 4(12): 248-254 ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 4 Number 12 (215) pp. 248-254 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Bacteriological Profile and Antimicrobial Sensitivity
Original Articles. K A M S W Gunarathne 1, M Akbar 2, K Karunarathne 3, JRS de Silva 4. Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2011; 40(4):
 Original Articles Analysis of blood/tracheal culture results to assess common pathogens and pattern of antibiotic resistance at medical intensive care unit, Lady Ridgeway Hospital for Children K A M S
Original Articles Analysis of blood/tracheal culture results to assess common pathogens and pattern of antibiotic resistance at medical intensive care unit, Lady Ridgeway Hospital for Children K A M S
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Screening of Critical Care Setting for Bacterial Colonization Arth Nath Dube 1, Dr. S.A. Samant
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Screening of Critical Care Setting for Bacterial Colonization Arth Nath Dube 1, Dr. S.A. Samant
2015 Antibiogram. Red Deer Regional Hospital. Central Zone. Alberta Health Services
 2015 Antibiogram Red Deer Regional Hospital Central Zone Alberta Health Services Introduction. This antibiogram is a cumulative report of the antimicrobial susceptibility rates of common microbial pathogens
2015 Antibiogram Red Deer Regional Hospital Central Zone Alberta Health Services Introduction. This antibiogram is a cumulative report of the antimicrobial susceptibility rates of common microbial pathogens
Post-operative surgical wound infection
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 45 No. 4 December 1990 Post-operative surgical wound infection Yasmin Abu Hanifah, MBBS, MSc. (London) Lecturer Department of Medical Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 45 No. 4 December 1990 Post-operative surgical wound infection Yasmin Abu Hanifah, MBBS, MSc. (London) Lecturer Department of Medical Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(3):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 3 (2017) pp. 891-895 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.603.104
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 3 (2017) pp. 891-895 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.603.104
2012 ANTIBIOGRAM. Central Zone Former DTHR Sites. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
 2012 ANTIBIOGRAM Central Zone Former DTHR Sites Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Medically Relevant Pathogens Based on Gram Morphology Gram-negative Bacilli Lactose Fermenters Non-lactose
2012 ANTIBIOGRAM Central Zone Former DTHR Sites Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Medically Relevant Pathogens Based on Gram Morphology Gram-negative Bacilli Lactose Fermenters Non-lactose
Emergence of multi-drug resistant strains among bacterial isolates in burn wound swabs in a tertiary care centre, Nanded, Maharashtra, India
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Rathod VS et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Mar;5(3):973-977 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20170645
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Rathod VS et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Mar;5(3):973-977 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20170645
BACTERIOLOGICAL PROFILE OF OSTEOMYELITIS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL AT VISAKHAPATNAM, ANDHRA PRADESH
 IJCRR Vol 05 issue 20 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 07/09/13 Revised on: 02/10/13 Accepted on: 24/10/13 BACTERIOLOGICAL PROFILE OF OSTEOMYELITIS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL AT VISAKHAPATNAM,
IJCRR Vol 05 issue 20 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 07/09/13 Revised on: 02/10/13 Accepted on: 24/10/13 BACTERIOLOGICAL PROFILE OF OSTEOMYELITIS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL AT VISAKHAPATNAM,
Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections. For National Patient Safety Goal
 Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections For National Patient Safety Goal 07.03.01 2009 Methicillin Resistant Staphlococcus aureus (MRSA) About 3-8% of the population at large is a carrier
Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections For National Patient Safety Goal 07.03.01 2009 Methicillin Resistant Staphlococcus aureus (MRSA) About 3-8% of the population at large is a carrier
2017 Antibiogram. Central Zone. Alberta Health Services. including. Red Deer Regional Hospital. St. Mary s Hospital, Camrose
 2017 Antibiogram Central Zone Alberta Health Services including Red Deer Regional Hospital St. Mary s Hospital, Camrose Introduction This antibiogram is a cumulative report of the antimicrobial susceptibility
2017 Antibiogram Central Zone Alberta Health Services including Red Deer Regional Hospital St. Mary s Hospital, Camrose Introduction This antibiogram is a cumulative report of the antimicrobial susceptibility
Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version
 Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED 2018 Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY NO. IC-122 Policy Group Infection Control
Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED 2018 Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY NO. IC-122 Policy Group Infection Control
RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI ISOLATES AMONG DIFFERENT CLINICAL SAMPLES FROM A DIAGNOSTIC CENTER OF KANPUR
 Original article RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI ISOLATES AMONG DIFFERENT CLINICAL SAMPLES FROM A DIAGNOSTIC CENTER OF KANPUR R.Sujatha 1,Nidhi Pal 2, Deepak S 3 1. Professor & Head, Department
Original article RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI ISOLATES AMONG DIFFERENT CLINICAL SAMPLES FROM A DIAGNOSTIC CENTER OF KANPUR R.Sujatha 1,Nidhi Pal 2, Deepak S 3 1. Professor & Head, Department
A retrospective analysis of urine culture results issued by the microbiology department, Teaching Hospital, Karapitiya
 A retrospective analysis of urine culture results issued by the microbiology department, Teaching Hospital, Karapitiya LU Edirisinghe 1, D Vidanagama 2 1 Senior Registrar in Medicine, 2 Consultant Microbiologist,
A retrospective analysis of urine culture results issued by the microbiology department, Teaching Hospital, Karapitiya LU Edirisinghe 1, D Vidanagama 2 1 Senior Registrar in Medicine, 2 Consultant Microbiologist,
Active Bacterial Core Surveillance Site and Epidemiologic Classification, United States, 2005a. Copyright restrictions may apply.
 Impact of routine surgical ward and intensive care unit admission surveillance cultures on hospital-wide nosocomial methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in a university hospital: an interrupted
Impact of routine surgical ward and intensive care unit admission surveillance cultures on hospital-wide nosocomial methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in a university hospital: an interrupted
A Study on Bacterial Flora on the Finger printing Surface of the Biometric Devices at a Tertiary Care Hospital
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 9 (2016) pp. 441-446 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.509.047
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 9 (2016) pp. 441-446 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.509.047
SURVIVABILITY OF HIGH RISK, MULTIRESISTANT BACTERIA ON COTTON TREATED WITH COMMERCIALLY AVAILABLE ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS
 SURVIVABILITY OF HIGH RISK, MULTIRESISTANT BACTERIA ON COTTON TREATED WITH COMMERCIALLY AVAILABLE ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS Adrienn Hanczvikkel 1, András Vígh 2, Ákos Tóth 3,4 1 Óbuda University, Budapest,
SURVIVABILITY OF HIGH RISK, MULTIRESISTANT BACTERIA ON COTTON TREATED WITH COMMERCIALLY AVAILABLE ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS Adrienn Hanczvikkel 1, András Vígh 2, Ákos Tóth 3,4 1 Óbuda University, Budapest,
Study of Microbiological Profile and their Antibiogram in Patients with Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 981-985 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Study of Microbiological Profile
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 981-985 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Study of Microbiological Profile
During the second half of the 19th century many operations were developed after anesthesia
 Continuing Education Column Surgical Site Infection and Surveillance Tae Jin Lim, MD Department of Surgery, Keimyung University College of Medicine E mail : tjlim@dsmc.or.kr J Korean Med Assoc 2007; 50(10):
Continuing Education Column Surgical Site Infection and Surveillance Tae Jin Lim, MD Department of Surgery, Keimyung University College of Medicine E mail : tjlim@dsmc.or.kr J Korean Med Assoc 2007; 50(10):
Isolation of Urinary Tract Pathogens and Study of their Drug Susceptibility Patterns
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 4 (2016) pp. 897-903 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.504.101
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 4 (2016) pp. 897-903 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.504.101
Approval Signature: Original signed by Dr. Michel Tetreault Date of Approval: July Review Date: July 2017
 WRHA Infection Prevention and Control Program Operational Directives Admission Screening for Antibiotic Resistant Organisms (AROs): Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Vancomycin Resistant
WRHA Infection Prevention and Control Program Operational Directives Admission Screening for Antibiotic Resistant Organisms (AROs): Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Vancomycin Resistant
Importance of handwashing prior to wound dressings in prevention of nosocomial infection in surgical wards
 International Surgery Journal Athavale VS et al. Int Surg J. 218 Apr;5(4):1422-1427 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-335 eissn 2349-292 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.1823/2349-292.isj2181123
International Surgery Journal Athavale VS et al. Int Surg J. 218 Apr;5(4):1422-1427 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-335 eissn 2349-292 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.1823/2349-292.isj2181123
Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms (MDRO)
 Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms (MDRO) 2016 What are MDROs? Multi-drug resistant organisms, or MDROs, are bacteria resistant to current antibiotic therapy and therefore difficult to treat. MDROs can cause
Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms (MDRO) 2016 What are MDROs? Multi-drug resistant organisms, or MDROs, are bacteria resistant to current antibiotic therapy and therefore difficult to treat. MDROs can cause
Irrational use of antimicrobial agents often
 Antibiotic Resistance of Isolated Bacteria in 1 and Abdo-Rabbo A. 2 Irrational use of antimicrobial agents often leads to the multi-drug resistance microorganisms. This study is aimed at investigating
Antibiotic Resistance of Isolated Bacteria in 1 and Abdo-Rabbo A. 2 Irrational use of antimicrobial agents often leads to the multi-drug resistance microorganisms. This study is aimed at investigating
2016 Antibiogram. Central Zone. Alberta Health Services. including. Red Deer Regional Hospital. St. Mary s Hospital, Camrose
 2016 Antibiogram Central Zone Alberta Health Services including Red Deer Regional Hospital St. Mary s Hospital, Camrose Introduction This antibiogram is a cumulative report of the antimicrobial susceptibility
2016 Antibiogram Central Zone Alberta Health Services including Red Deer Regional Hospital St. Mary s Hospital, Camrose Introduction This antibiogram is a cumulative report of the antimicrobial susceptibility
Overview of Infection Control and Prevention
 Overview of Infection Control and Prevention Review of the Cesarean-section Antibiotic Prophylaxis Program in Jordan and Workshop on Rational Medicine Use and Infection Control Terry Green and Salah Gammouh
Overview of Infection Control and Prevention Review of the Cesarean-section Antibiotic Prophylaxis Program in Jordan and Workshop on Rational Medicine Use and Infection Control Terry Green and Salah Gammouh
Intrinsic, implied and default resistance
 Appendix A Intrinsic, implied and default resistance Magiorakos et al. [1] and CLSI [2] are our primary sources of information on intrinsic resistance. Sanford et al. [3] and Gilbert et al. [4] have been
Appendix A Intrinsic, implied and default resistance Magiorakos et al. [1] and CLSI [2] are our primary sources of information on intrinsic resistance. Sanford et al. [3] and Gilbert et al. [4] have been
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Isolated From Various Clinical
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Isolated From Various Clinical
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(11):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 1167-1171 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.139
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 1167-1171 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.139
Surveillance of Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms
 Surveillance of Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms Karen Hoffmann, RN, MS, CIC Associate Director Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) University of North Carolina School of Medicine
Surveillance of Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms Karen Hoffmann, RN, MS, CIC Associate Director Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) University of North Carolina School of Medicine
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2018) 7(1):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.080
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.080
2010 ANTIBIOGRAM. University of Alberta Hospital and the Stollery Children s Hospital
 2010 ANTIBIOGRAM University of Alberta Hospital and the Stollery Children s Hospital Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Table of Contents Page Introduction..... 2 Antibiogram
2010 ANTIBIOGRAM University of Alberta Hospital and the Stollery Children s Hospital Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Table of Contents Page Introduction..... 2 Antibiogram
Comparison of Antibiotic Resistance and Sensitivity with Reference to Ages of Elders
 Daffodil International University Institutional Repository DIU Journal of Science and Technology Volume 10, Issue 1-2, July 2015 2016-06-16 Comparison of Antibiotic Resistance and Sensitivity with Reference
Daffodil International University Institutional Repository DIU Journal of Science and Technology Volume 10, Issue 1-2, July 2015 2016-06-16 Comparison of Antibiotic Resistance and Sensitivity with Reference
Florida Health Care Association District 2 January 13, 2015 A.C. Burke, MA, CIC
 Florida Health Care Association District 2 January 13, 2015 A.C. Burke, MA, CIC 11/20/2014 1 To describe carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. To identify laboratory detection standards for carbapenem-resistant
Florida Health Care Association District 2 January 13, 2015 A.C. Burke, MA, CIC 11/20/2014 1 To describe carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. To identify laboratory detection standards for carbapenem-resistant
Why should we care about multi-resistant bacteria? Clinical impact and
 Why should we care about multi-resistant bacteria? Clinical impact and public health implications Prof. Stephan Harbarth Infection Control Program Geneva, Switzerland and Ebola (in 2014/2015) Increased
Why should we care about multi-resistant bacteria? Clinical impact and public health implications Prof. Stephan Harbarth Infection Control Program Geneva, Switzerland and Ebola (in 2014/2015) Increased
Bacteriology of Surgical Site Infections and Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of the Isolates at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Karachi
 Abstract Bacteriology of Surgical Site Infections and Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of the Isolates at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Karachi Abid Mahmood ( Department of Pathology, PNS Shifa, Karachi.
Abstract Bacteriology of Surgical Site Infections and Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of the Isolates at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Karachi Abid Mahmood ( Department of Pathology, PNS Shifa, Karachi.
Infection Pattern, Etiological Agents And Their Antimicrobial Resistance At A Tertiary Care Hospital In Moshi, Tanzania
 Infection Pattern, Etiological Agents And Their Antimicrobial Resistance At A Tertiary Care Hospital In Moshi, Tanzania Happiness Kumburu PhD candidate KCMUCo 23 rd October,2014 Introduction O Resource
Infection Pattern, Etiological Agents And Their Antimicrobial Resistance At A Tertiary Care Hospital In Moshi, Tanzania Happiness Kumburu PhD candidate KCMUCo 23 rd October,2014 Introduction O Resource
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile of E. coli Isolates Causing Urosepsis: Single Centre Experience
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 05 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.705.298
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 05 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.705.298
Available online at ISSN No:
 Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(4): 36-42 Comparative Evaluation of In-Vitro Doripenem Susceptibility with Other
Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(4): 36-42 Comparative Evaluation of In-Vitro Doripenem Susceptibility with Other
Epidemiology and Microbiology of Surgical Wound Infections
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 2000, p. 918 922 Vol. 38, No. 2 0095-1137/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Epidemiology and Microbiology of Surgical
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 2000, p. 918 922 Vol. 38, No. 2 0095-1137/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Epidemiology and Microbiology of Surgical
Appropriate antimicrobial therapy in HAP: What does this mean?
 Appropriate antimicrobial therapy in HAP: What does this mean? Jaehee Lee, M.D. Kyungpook National University Hospital, Korea KNUH since 1907 Presentation outline Empiric antimicrobial choice: right spectrum,
Appropriate antimicrobial therapy in HAP: What does this mean? Jaehee Lee, M.D. Kyungpook National University Hospital, Korea KNUH since 1907 Presentation outline Empiric antimicrobial choice: right spectrum,
ESBL Producers An Increasing Problem: An Overview Of An Underrated Threat
 ESBL Producers An Increasing Problem: An Overview Of An Underrated Threat Hicham Ezzat Professor of Microbiology and Immunology Cairo University Introduction 1 Since the 1980s there have been dramatic
ESBL Producers An Increasing Problem: An Overview Of An Underrated Threat Hicham Ezzat Professor of Microbiology and Immunology Cairo University Introduction 1 Since the 1980s there have been dramatic
Evaluation of a computerized antimicrobial susceptibility system with bacteria isolated from animals
 J Vet Diagn Invest :164 168 (1998) Evaluation of a computerized antimicrobial susceptibility system with bacteria isolated from animals Susannah K. Hubert, Phouc Dinh Nguyen, Robert D. Walker Abstract.
J Vet Diagn Invest :164 168 (1998) Evaluation of a computerized antimicrobial susceptibility system with bacteria isolated from animals Susannah K. Hubert, Phouc Dinh Nguyen, Robert D. Walker Abstract.
Horizontal vs Vertical Infection Control Strategies
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL Chapter 14 Horizontal vs Vertical Infection Control Strategies Author Salma Abbas, MBBS Michael Stevens, MD, MPH Chapter Editor Shaheen Mehtar, MBBS. FRC Path,
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL Chapter 14 Horizontal vs Vertical Infection Control Strategies Author Salma Abbas, MBBS Michael Stevens, MD, MPH Chapter Editor Shaheen Mehtar, MBBS. FRC Path,
Concise Antibiogram Toolkit Background
 Background This toolkit is designed to guide nursing homes in creating their own antibiograms, an important tool for guiding empiric antimicrobial therapy. Information about antibiograms and instructions
Background This toolkit is designed to guide nursing homes in creating their own antibiograms, an important tool for guiding empiric antimicrobial therapy. Information about antibiograms and instructions
NASAL COLONIZATION WITH STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS IN BASRA MEDICAL AND DENTISTRY STUDENTS
 NASAL COLONIZATION WITH STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS IN BASRA MEDICAL AND DENTISTRY STUDENTS Wijdan Nazar Ibraheim Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, University of Basra, Iraq. ABSTRACT: Staphylococcus
NASAL COLONIZATION WITH STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS IN BASRA MEDICAL AND DENTISTRY STUDENTS Wijdan Nazar Ibraheim Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, University of Basra, Iraq. ABSTRACT: Staphylococcus
Microbial landscape of surgical hospital. Biology and Medicine
 eissn: 09748369 Microbial landscape of surgical hospital Biology and Medicine Research Article Volume 6, Issue 4, Article ID: BM-058-14, 2014 Indexed by Scopus (Elsevier) www.biolmedonline.com Microbial
eissn: 09748369 Microbial landscape of surgical hospital Biology and Medicine Research Article Volume 6, Issue 4, Article ID: BM-058-14, 2014 Indexed by Scopus (Elsevier) www.biolmedonline.com Microbial
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics
 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278 2648 IJRPP Vol.3 Issue 3 July-Sep-214 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access Study
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278 2648 IJRPP Vol.3 Issue 3 July-Sep-214 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access Study
Overview of Nosocomial Infections Caused by Gram-Negative Bacilli
 HEALTHCARE EPIDEMIOLOGY Robert A. Weinstein, Section Editor INVITED ARTICLE Overview of Nosocomial Infections Caused by Gram-Negative Bacilli Robert Gaynes, Jonathan R. Edwards, and the National Nosocomial
HEALTHCARE EPIDEMIOLOGY Robert A. Weinstein, Section Editor INVITED ARTICLE Overview of Nosocomial Infections Caused by Gram-Negative Bacilli Robert Gaynes, Jonathan R. Edwards, and the National Nosocomial
CONTAGIOUS COMMENTS Department of Epidemiology
 VOLUME XXIII NUMBER 1 July 2008 CONTAGIOUS COMMENTS Department of Epidemiology Bugs and Drugs Elaine Dowell, SM (ASCP), Marti Roe SM (ASCP), Ann-Christine Nyquist MD, MSPH Are the bugs winning? The 2007
VOLUME XXIII NUMBER 1 July 2008 CONTAGIOUS COMMENTS Department of Epidemiology Bugs and Drugs Elaine Dowell, SM (ASCP), Marti Roe SM (ASCP), Ann-Christine Nyquist MD, MSPH Are the bugs winning? The 2007
Antimicrobial Cycling. Donald E Low University of Toronto
 Antimicrobial Cycling Donald E Low University of Toronto Bad Bugs, No Drugs 1 The Antimicrobial Availability Task Force of the IDSA 1 identified as particularly problematic pathogens A. baumannii and
Antimicrobial Cycling Donald E Low University of Toronto Bad Bugs, No Drugs 1 The Antimicrobial Availability Task Force of the IDSA 1 identified as particularly problematic pathogens A. baumannii and
North West Neonatal Operational Delivery Network Working together to provide the highest standard of care for babies and families
 Document Title and Reference : Guideline for the management of multi-drug resistant organisms (MDRO) Main Author (s) Simon Power Ratified by: GM NSG Date Ratified: February 2012 Review Date: March 2017
Document Title and Reference : Guideline for the management of multi-drug resistant organisms (MDRO) Main Author (s) Simon Power Ratified by: GM NSG Date Ratified: February 2012 Review Date: March 2017
Detection of ESBL Producing Gram Negative Uropathogens and their Antibiotic Resistance Pattern from a Tertiary Care Centre, Bengaluru, India
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 12 (2015) pp. 578-583 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Detection of ESBL Producing Gram Negative Uropathogens and their Antibiotic Resistance Pattern from
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 12 (2015) pp. 578-583 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Detection of ESBL Producing Gram Negative Uropathogens and their Antibiotic Resistance Pattern from
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Advanced Course
 Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Advanced Course Cascade Reporting Cascade Reporting I. Selecting Antimicrobial Agents for Testing and Reporting Selection of the most appropriate antimicrobials to
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Advanced Course Cascade Reporting Cascade Reporting I. Selecting Antimicrobial Agents for Testing and Reporting Selection of the most appropriate antimicrobials to
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns
 Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns KNH SURGERY Department Masika M.M. Department of Medical Microbiology, UoN Medicines & Therapeutics Committee, KNH Outline Methodology Overall KNH data Surgery department
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns KNH SURGERY Department Masika M.M. Department of Medical Microbiology, UoN Medicines & Therapeutics Committee, KNH Outline Methodology Overall KNH data Surgery department
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2016) 5(12):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 12 (2016) pp. 644-649 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.512.071
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 12 (2016) pp. 644-649 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.512.071
STUDY OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS AMONGST ORTHOPAEDIC PATIENTS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
 Page283 IJPBS Volume 5 Issue 2 APR-JUN 2015 283-287 Research Article Pharmaceutical Sciences STUDY OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS AMONGST ORTHOPAEDIC PATIENTS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL Chitralekha Saikumar,
Page283 IJPBS Volume 5 Issue 2 APR-JUN 2015 283-287 Research Article Pharmaceutical Sciences STUDY OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS AMONGST ORTHOPAEDIC PATIENTS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL Chitralekha Saikumar,
Bacteriological profile of blood stream infections at a Rural tertiary care teaching hospital of Western Uttar Pradesh
 Original article: Bacteriological profile of blood stream infections at a Rural tertiary care teaching hospital of Western Uttar Pradesh Vijay Prakash Singh a, Abhishek Mehta b* a,bdepartment of Microbiology,
Original article: Bacteriological profile of blood stream infections at a Rural tertiary care teaching hospital of Western Uttar Pradesh Vijay Prakash Singh a, Abhishek Mehta b* a,bdepartment of Microbiology,
QUICK REFERENCE. Pseudomonas aeruginosa. (Pseudomonas sp. Xantomonas maltophilia, Acinetobacter sp. & Flavomonas sp.)
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonas sp. Xantomonas maltophilia, Acinetobacter sp. & Flavomonas sp.) Description: Greenish gray colonies with some beta-hemolysis around each colony on blood agar (BAP),
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonas sp. Xantomonas maltophilia, Acinetobacter sp. & Flavomonas sp.) Description: Greenish gray colonies with some beta-hemolysis around each colony on blood agar (BAP),
MDRO: Prevention in 7 Steps. Jeanette Harris MS, MSM, MT(ASCP), CIC MultiCare Health System Tacoma, Wa.
 MDRO: Prevention in 7 Steps Jeanette Harris MS, MSM, MT(ASCP), CIC MultiCare Health System Tacoma, Wa. Multi Drug Resistant Organism MDRO MDRO: What are we talking about? MRSA VRE ESBL (E.coli, Klebs pneum,
MDRO: Prevention in 7 Steps Jeanette Harris MS, MSM, MT(ASCP), CIC MultiCare Health System Tacoma, Wa. Multi Drug Resistant Organism MDRO MDRO: What are we talking about? MRSA VRE ESBL (E.coli, Klebs pneum,
Susceptibility Pattern of Some Clinical Bacterial Isolates to Selected Antibiotics and Disinfectants
 Polish Journal of Microbiology 2008, Vol. 57, No 3, 199 204 ORIGINAL PAPER Susceptibility Pattern of Some Clinical Bacterial Isolates to Selected Antibiotics and Disinfectants JUDE N. OGBULIE, IFECHUKWU
Polish Journal of Microbiology 2008, Vol. 57, No 3, 199 204 ORIGINAL PAPER Susceptibility Pattern of Some Clinical Bacterial Isolates to Selected Antibiotics and Disinfectants JUDE N. OGBULIE, IFECHUKWU
Original Article. Hossein Khalili a*, Rasool Soltani b, Sorrosh Negahban c, Alireza Abdollahi d and Keirollah Gholami e.
 Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research (22), (2): 559-563 Received: January 2 Accepted: June 2 Copyright 22 by School of Pharmacy Shaheed Beheshti University of Medical Sciences and Health Services
Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research (22), (2): 559-563 Received: January 2 Accepted: June 2 Copyright 22 by School of Pharmacy Shaheed Beheshti University of Medical Sciences and Health Services
Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis
 Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis 1. Definition of Peritonitis: a. Cloudy effluent. b. WBC > 100 cells/mm3 with >50% polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells with minimum 2 hour dwell. c.
Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis 1. Definition of Peritonitis: a. Cloudy effluent. b. WBC > 100 cells/mm3 with >50% polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells with minimum 2 hour dwell. c.
Antimicrobial Stewardship Strategy: Antibiograms
 Antimicrobial Stewardship Strategy: Antibiograms A summary of the cumulative susceptibility of bacterial isolates to formulary antibiotics in a given institution or region. Its main functions are to guide
Antimicrobial Stewardship Strategy: Antibiograms A summary of the cumulative susceptibility of bacterial isolates to formulary antibiotics in a given institution or region. Its main functions are to guide
Treatment of Surgical Site Infection Meeting Quality Statement 6. Prof Peter Wilson University College London Hospitals
 Treatment of Surgical Site Infection Meeting Quality Statement 6 Prof Peter Wilson University College London Hospitals TEG Quality Standard 6 Treatment and effective antibiotic prescribing: People with
Treatment of Surgical Site Infection Meeting Quality Statement 6 Prof Peter Wilson University College London Hospitals TEG Quality Standard 6 Treatment and effective antibiotic prescribing: People with
(DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
 (DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE John Ferguson (Hunter New England, NSW) on behalf of MRGN Task Force Acknowledgement
(DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE John Ferguson (Hunter New England, NSW) on behalf of MRGN Task Force Acknowledgement
Acinetobacter species-associated infections and their antibiotic susceptibility profiles in Malaysia.
 Biomedical Research 12; 23 (4): 571-575 ISSN 97-938X Scientific Publishers of India Acinetobacter species-associated infections and their antibiotic susceptibility profiles in Malaysia. Nazmul MHM, Jamal
Biomedical Research 12; 23 (4): 571-575 ISSN 97-938X Scientific Publishers of India Acinetobacter species-associated infections and their antibiotic susceptibility profiles in Malaysia. Nazmul MHM, Jamal
Isolation, identification and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of uropathogens isolated at a tertiary care centre
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 10 (2015) pp. 951-955 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Isolation, identification and antimicrobial
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 10 (2015) pp. 951-955 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Isolation, identification and antimicrobial
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 27/ Apr 02, 2015 Page 4644
 STUDY OF BACTERIAL FLORA OF HANDS OF HEALTH CARE GIVERS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN EASTERN INDIA Asim Sarfraz 1, Sayan Bhattacharyya 2, Mohammed Aftab Alam Ansari 3, Nitesh Kumar Jaiswal 4, Hema Roy
STUDY OF BACTERIAL FLORA OF HANDS OF HEALTH CARE GIVERS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN EASTERN INDIA Asim Sarfraz 1, Sayan Bhattacharyya 2, Mohammed Aftab Alam Ansari 3, Nitesh Kumar Jaiswal 4, Hema Roy
INCIDENCE OF BACTERIAL COLONISATION IN HOSPITALISED PATIENTS WITH DRUG-RESISTANT TUBERCULOSIS
 INCIDENCE OF BACTERIAL COLONISATION IN HOSPITALISED PATIENTS WITH DRUG-RESISTANT TUBERCULOSIS 1 Research Associate, Drug Utilisation Research Unit, Nelson Mandela University 2 Human Sciences Research Council,
INCIDENCE OF BACTERIAL COLONISATION IN HOSPITALISED PATIENTS WITH DRUG-RESISTANT TUBERCULOSIS 1 Research Associate, Drug Utilisation Research Unit, Nelson Mandela University 2 Human Sciences Research Council,
Antibiotic Susceptibility of Common Bacterial Pathogens in Canine Urinary Tract Infections
 Vol.1 No.2 Oct-Dec 2013 ISSN : 2321-6387 Antibiotic Susceptibility of Common Bacterial Pathogens in Canine Urinary Tract Infections S. Yogeshpriya*, Usha N.Pillai, S. Ajithkumar and N. Madhavan Unny Department
Vol.1 No.2 Oct-Dec 2013 ISSN : 2321-6387 Antibiotic Susceptibility of Common Bacterial Pathogens in Canine Urinary Tract Infections S. Yogeshpriya*, Usha N.Pillai, S. Ajithkumar and N. Madhavan Unny Department
Understanding the Hospital Antibiogram
 Understanding the Hospital Antibiogram Sharon Erdman, PharmD Clinical Professor Purdue University College of Pharmacy Infectious Diseases Clinical Pharmacist Eskenazi Health 5 Understanding the Hospital
Understanding the Hospital Antibiogram Sharon Erdman, PharmD Clinical Professor Purdue University College of Pharmacy Infectious Diseases Clinical Pharmacist Eskenazi Health 5 Understanding the Hospital
Animal Antibiotic Use and Public Health
 A data table from Nov 2017 Animal Antibiotic Use and Public Health The selected studies below were excerpted from Pew s peer-reviewed 2017 article Antimicrobial Drug Use in Food-Producing Animals and Associated
A data table from Nov 2017 Animal Antibiotic Use and Public Health The selected studies below were excerpted from Pew s peer-reviewed 2017 article Antimicrobial Drug Use in Food-Producing Animals and Associated
Does Screening for MRSA Colonization Have A Role In Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevention Programs?
 Does Screening for MRSA Colonization Have A Role In Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevention Programs? John A. Jernigan, MD, MS Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Centers for Disease Control and
Does Screening for MRSA Colonization Have A Role In Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevention Programs? John A. Jernigan, MD, MS Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Centers for Disease Control and
Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains Isolated from Various Clinical Specimens
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 03 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.703.217
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 03 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.703.217
RCH antibiotic susceptibility data
 RCH antibiotic susceptibility data The following represent RCH antibiotic susceptibility data from 2008. This data is used to inform antibiotic guidelines used at RCH. The data includes all microbiological
RCH antibiotic susceptibility data The following represent RCH antibiotic susceptibility data from 2008. This data is used to inform antibiotic guidelines used at RCH. The data includes all microbiological
Konsequenzen für Bevölkerung und Gesundheitssysteme. Stephan Harbarth Infection Control Program
 Konsequenzen für Bevölkerung und Gesundheitssysteme Stephan Harbarth Infection Control Program University of Geneva Hospitals Outline Introduction What data sources are available? AMR-associated outcomes
Konsequenzen für Bevölkerung und Gesundheitssysteme Stephan Harbarth Infection Control Program University of Geneva Hospitals Outline Introduction What data sources are available? AMR-associated outcomes
Felipe N. Gutierrez MD, MPH Chief, Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare
 Felipe N. Gutierrez MD, MPH Chief, Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare 100% of all wounds will yield growth If you get a negative culture you something is wrong! Pseudomonas while ubiquitous does
Felipe N. Gutierrez MD, MPH Chief, Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare 100% of all wounds will yield growth If you get a negative culture you something is wrong! Pseudomonas while ubiquitous does
2009 ANTIBIOGRAM. University of Alberta Hospital and the Stollery Childrens Hospital
 2009 ANTIBIOGRAM University of Alberta Hospital and the Stollery Childrens Hospital Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Table of Contents Page Introduction.....
2009 ANTIBIOGRAM University of Alberta Hospital and the Stollery Childrens Hospital Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Table of Contents Page Introduction.....
Taking Action to Prevent and Manage Multidrug-resistant Organisms and C. difficile in the Nursing Home: Part 1 Reviewing the organisms
 Taking Action to Prevent and Manage Multidrug-resistant Organisms and C. difficile in the Nursing Home: Part 1 Reviewing the organisms Nimalie D. Stone, MD,MS Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion National
Taking Action to Prevent and Manage Multidrug-resistant Organisms and C. difficile in the Nursing Home: Part 1 Reviewing the organisms Nimalie D. Stone, MD,MS Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion National
An evaluation of the susceptibility patterns of Gram-negative organisms isolated in cancer centres with aminoglycoside usage
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1991) 27, Suppl. C, 1-7 An evaluation of the susceptibility patterns of Gram-negative organisms isolated in cancer centres with aminoglycoside usage J. J. Muscato",
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1991) 27, Suppl. C, 1-7 An evaluation of the susceptibility patterns of Gram-negative organisms isolated in cancer centres with aminoglycoside usage J. J. Muscato",
Liofilchem Chromatic Chromogenic culture media for microbial identification and for the screening of antimicrobial resistance mechanisms
 Liofilchem Chromatic Chromogenic culture media for microbial identification and for the screening of antimicrobial resistance mechanisms Microbiology Products since 1983 Liofilchem Chromatic ESBL Selective
Liofilchem Chromatic Chromogenic culture media for microbial identification and for the screening of antimicrobial resistance mechanisms Microbiology Products since 1983 Liofilchem Chromatic ESBL Selective
Detection of Inducible AmpC β-lactamase-producing Gram-Negative Bacteria in a Teaching Tertiary Care Hospital in North India
 Original Article Vol. 25 No. 3 Ampc β-lactamase Production in Gram-Negative Bacilli:-Chaudhary U, et al. 129 Detection of Inducible AmpC β-lactamase-producing Gram-Negative Bacteria in a Teaching Tertiary
Original Article Vol. 25 No. 3 Ampc β-lactamase Production in Gram-Negative Bacilli:-Chaudhary U, et al. 129 Detection of Inducible AmpC β-lactamase-producing Gram-Negative Bacteria in a Teaching Tertiary
Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE)
 Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) September 21, 2017 Maryam Khan Peel Public Health Madeleine Ashcroft Public Health Ontario Objectives Differentiate the acronyms related to CPE (CPE,CPO,CRE,CRO)
Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) September 21, 2017 Maryam Khan Peel Public Health Madeleine Ashcroft Public Health Ontario Objectives Differentiate the acronyms related to CPE (CPE,CPO,CRE,CRO)
