Blood-borne Pathogens
|
|
|
- Tabitha Potter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Blood-borne Pathogens
2 Objectives: Identify what BBPs are and how they are transmitted List why health care workers are a risk Protection strategies
3 What are BBP? Hepatitis B (Hep B) Hepatitis C (Hep C) HIV/AIDS They are tranported by infected blood of a person Blood borne pathogens are microorganisms such as viruses, bacteria, or parasites which can enter the human blood stream causing diseases.
4 These microorganisms may be transmitted when mucous membranes or non-intact skin (cuts, abrasions, burns) come in contact with human blood or body fluids. Other modes of transmission include blood splashes, handling contaminated items, needle sticks, or cuts from contaminated sharps.
5 Hepatitis Viruses Hepatitis is inflammation (pain and swelling) of the liver. Viruses that cause inflammation of the liver are called Hepatitis viruses. Hepatitis means inflammation, redness, swelling and soreness of the liver.
6 Hepatitis B HBV is transmitted by sharing needles, razors, and toothbrushes. Body fluids, saliva and semen which are exchanged during sexual interactions cause transmission. HBV is also transmitted from mother to infant during her pregnancy. Symptoms: Symptoms may begin as early as 60 days or up to 150 days after exposure to HBV. 95% of the adults recover completely from HBV and do not become chronically infected. In contrast, 90% of infants and 35% of children under the age of 5 years will remain chronically (life -long) ill with HBV. Most of the people newly infected with Hepatitis B do not show any symptoms. Most common symptoms if present include: Fever Fatigue Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and/or eyes) Nausea and vomiting Abdominal pain Dark urine Clay-colored bowel movements Loss of appetite
7 Who is at risk for Hepatitis B? Intravenous drug users Health care and public safety workers, who have contact with blood or body fluids or blood contaminated products Sexual contact with partner infected with Hepatitis B Living with someone with chronic Hepatitis B Traveling to a country with high rates of Hepatitis B Hemodialysis patients Birth of a child to a Hepatitis B infected mother
8 Long-term with Hep B: Chronic Hep B can result in liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, or liver failure Treatment options: There are no specific treatments available Many antivirals can be used Protection strategies: Wearing PPE available Use safety precautions available Hep B vaccination
9 Hep B vaccination 3 vaccinations in the series Hep B vaccination vouchers are available Employee records either need to have Hep B vaccination documentation or a declination statement
10 Hepatitis C Causes inflammation of the liver Hepatitis C is transmitted by needle stick injury, blood, blood products, sharing needles, razors, toothbrushes, sexual contact with Hepatitis C infected person, and birth of a child to an infected Hepatitis C mother. What are the signs and symptoms of HCV? Most of the people newly infected with Hepatitis C do not show any symptoms. Most common symptoms if present include: Fever Fatigue Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and/or eyes) Nausea and vomiting Abdominal pain Dark urine Clay-colored bowel movements Loss of appetite
11 HIV/AIDS Human Immunodeficiency Virus/ Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome HIV is the virus that causes AIDS HIV attacked the body and breaks down the body s immune systems making is susceptible for more infections and disease; at that state HIV is then know as AIDS
12 How is it spread? Blood, body fluids containing blood, breast milk, semen/vaginal secretions Contact with infected fluids Sharing of needles or equipment (drugs, tattoos, piercing) Sex Infected mother can pass to child during pregnancy, childbirth, breastfeeding
13 Signs/Symptoms: Early (weeks to months after exposure): -Flu-like illness Swollen lymph nodes Late (years after exposure) -Persistent fevers -Night sweats -Prolonged diarrhea -Unexplained weight loss -Purple bumps on skin or inside mouth and nose -Chronic fatigue -Swollen lymph nodes -Recurrent respiratory infections (MDH, 2017)
14 Testing/Treatment: Testing can be completed to determine HIV antibodies No treatment is available Early detection is helpful: medications are able to help immune systems, decrease risk of mother passing it to baby, treat illnesses that came with AIDS
15 Prevention/Protection: Personal Protective Equipment: gloves, gown, mask Sharps containers No sharing of needles Immediate care with an BBP exposure Proper handling of possible infected material Latex contraception
16 What are HCW s at risk: Nursing staff: handling/using needles Housekeeping: handling soiled linens Providing care to residents that could be infected
17 What is available to keep staff protected? PPE: gloves, mask, gown, gloves Cleaning products that kill BBPs Needle safety covers, sharps containers Education Hep B vaccination vouchers
18 Tuberculosis
19 TB An airborne disease caused by the M. tuberculosis bacterium The airborne particles get into circulation when a person with active (respiratory) TB cough, sneeze, shout, sings, etc Depending on the environment, the particles can remain in the air for several hours
20 How is TB transmitted? When the active particles are in the air and someone inhales the droplets The particles can NOT survive on a surface, so it is NOT spread by contact Probability of transmission depends on: susceptibility (immune system), infectiousness (how sick is the active person), environment (how many droplets, ventilation), exposure (duration, frequency, proximity)
21 TB in the body The disease can affect more than just the respiratory tract. It can also be found in the brain, lymph node, spine, bone/joints, or kidney Active TB in the respiratory tract is the only one transmitted through airborne particles (larynx, lungs), or in open lesions with a high concentration of active bacteria
22 TB Disease Large amount of active TB bacteria Contagious Feel sick, signs/symptoms Positive TB test (TST or blood) Positive chest x-ray Positive sputum Needs TB treatment Require airbone isolation (hospital) Qualifies as a reportable TB case
23 Latent TB Small amount of inactive TB bacteria in body Not contagious Not sick (but can become sick if inactive turns active) Positive TST or blood test Negative sputum, chest x-ray Consider treatment to prevent becoming active No airbone isolation needed Not considered a TB case
24 Who is at risk to change from Latent to Active? Young children People with HIV Infected with TB within 2 years; hx of TB untreated or poorly treated Immunocompromised Gastric bypass Smokers, drug/alcohol users
25 Signs/Symptoms: Cough lasting longer than 3 weeks Coughing up blood Loss of appetite Unexplained weight loss Fever Fatigue Night sweats Chest pain
26 Testing for TB: Due to our risk level as a facility all residents are required to completed a baseline TB testing upon admission and symptom screening annually Staff are required to completed a baseline TB testing upon hire and annually thereafter
27 TST (skin TB test): Known as a Mantoux Placed on the forarm Read between hours of placement 2 nd step required to be placed between 1-3 weeks from the first step Must be placed and read by a licensed professional (at Hayes, that will be a nurse)
28 When reading a TST, you ONLY feel for a hard induration (lump) Redness, rash, general swelling: do NOT indicate a positive test Positive test can be 5mm or greater (depending on the individuals risk factors/criteria); Always positive in greater than 20mm A positive TST indicates further testing to rule out active TB
29 TB Blood Tests: Ex: Quantiferon Gold Only requires the blood test once (for resident s admission) or annually (for staff) Can be used instead of the TST Positive blood test: infected with TB and further testing is needed to determine Latent or Active
30 Diagnosis of TB: History and Physical Symptom screening Testing for TB Chest x-ray Sputum smear or culture
31 Treatment for TB: Commonly, people diagnosed with Latent TB are also treated to help prevent them from becoming active Active TB usually treated with a 6-9 month course of INH plus 3 others Compliance with treatment is very important to eliminate Latent or Active TB bacteria
32 Airbone Precautions: Residents with suspected TB should be placed on airbone precautions and isolation until they can be transferred to the hospital for further testing/treatment Active TB requires an negative pressure isolation room to prevent spread (in the hospital) Masks (N-9) are required while in facility isolation until transport
33 Shelley Bhola RN-BC, BSN, PHN, MSN BREAKING THE CHAIN OF INFECTION
34 OBJECTIVES Explain the chain of infection Describe how to break the chain of infection Reflect on ways you can help stop the spread of infection
35 THE CHAIN OF INFECTION Infectious Agent Susceptible host Reservoir Portal of Entry Portal of Exit Mode of Transmission
36 COMMON SOURCES Infectious Agent Bacteria, Virus, Fungi, or Parasite Reservoir Dirty surfaces and equipment, people, water, animals or insects and soil Portal of Exit open wounds/skin, splatter of body fluids or aerosols Mode of Transmission Contact direct or indirect, ingestion, inhalation Portal of Entry Broken skin/incisions, respiratory tract, mucous membranes, catheters and tubes Susceptible host any person, especially those receiving healthcare.
37 The hands of healthcare workers continues to be the number 1 way infections are transmitted.
38 HOW DO WE BREAK THE CHAIN? The way to stop germs from spreading is by interrupting this chain where?
39 WAYS TO BREAK THE CHAIN Immunizations Treatment of underlying disease Health Insurance Education on illnesses and their effects Proper diagnosis and treatment Antibiotic Stewardship Cleaning and disinfecting Infection Prevention policies
40 WAYS TO BREAK THE CHAIN Hand hygiene Personal Protective Equipment Personal hygiene First Aid Removal of catheters and tubes Food safety Isolation when needed
41 WAYS TO BREAK THE CHAIN Control of aerosols and splatter Respiratory etiquette Waste disposal
42 Hand Hygiene A NON-NEGOTIABLE PART OF ALL OF OUR JOBS
43 DO S AND DON TS FOR GLOVES Non-sterile gloves are indicated for sitatuions when there is a potential for contact with infectious material, such as blood, other body fluids or microorganisms. They are part of Standard Precautions.
44 DO WEAR GLOVES To reduce risk of contamination or exposure to blood, other body fluids, hazardous materials, and transmission of infection. Clean hands prior to putting gloves on. Clean hands after removing gloves. Clean hands and change gloves between each task. Make sure that gloves fit you properly. Ensure the correct type of gloves are available. Follow community policy on the use of gloves.
45 DON T Re-use or wash gloves Substitute glove use for hand hygiene Use gloves if they are damaged or visibly soiled Touch your face when wearing gloves Wear the same pair of gloves from one resident to another Wear gloves in the hall Forget to remove and dispose of properly
46 Why are we Concerned? WE ARE ALL AT RISK
47 HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS million residents in more than 15,000 long term care settings per year 70% of residents in a nursing home are receiving one or more courses of systemic antibiotics 40-75% of antibiotics prescribed in nursing homes may be unnecessary or inappropriate Antibiotics are not without harm especially for our frail elderly
48 ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE Antibiotic resistance is the ability of microbes to resist the effects of drugs that is, the germs are not killed and their growth is not stopped. Although some people are at greater risk than others, no one can completely avoid the risk of antibiotic-resistant infections. Infections with resistant organisms are difficult to treat, requiring costly and sometimes toxic alternatives. (CDC, 2015, About Antibiotic Resistance).
49 ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE Bacteria will inevitably find ways of resisting the antibiotics developed by humans, which is why aggressive action is needed now to keep new resistance from developing and to prevent the resistance that already exists from spreading. (CDC, 2015, About Antibiotic Resistance).
50 THE FUTURE IS IN OUR HANDS Hands of healthcare workers is consistently the #1 cause of infection transmission. We ARE the key to safer care.
51 REFERENCES APIC, Infection Preventionist s Guide to Long-term Care, Washington, D.C. APIC, Break the Chain of Infection.
52 This slide set Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Settings- Core and accompanying speaker notes provide an overview of the Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Settings published in A second slide set Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Settings-Supplemental which can be obtained at provides additional slides that may be used in conjunction with the core slide set. The target audience for this slide set is healthcare workers in acute care hospitals.
53 Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Settings: An Overview Background Definitions Indications Selection of Agents Techniques Surgical Other Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
54 So Why All the Fuss About Hand Hygiene? Most common mode of transmission of pathogens is via hands! Infections acquired in healthcare Spread of antimicrobial resistance
55 Evidence of Relationship Between Hand Hygiene and Healthcare-Associated Infections Substantial evidence that hand hygiene reduces the incidence of infections Historical study: Semmelweis More recent studies: rates lower when antiseptic handwashing was performed Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
56 Hand Hygiene Adherence in Hospitals Year of Study Adherence Rate Hospital Area 1994 (1) 29% General and ICU 1995 (2) 41% General 1996 (3) 41% ICU 1998 (4) 30% General 2000 (5) 48% General 1. Gould D, J Hosp Infect 1994;28: Larson E, J Hosp Infect 1995;30: Slaughter S, Ann Intern Med 1996;3: Watanakunakorn C, Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 1998;19: Pittet D, Lancet 2000:356;
57 Self-Reported Factors for Poor Adherence with Hand Hygiene Handwashing agents cause irritation and dryness Sinks are inconveniently located/lack of sinks Lack of soap and paper towels Too busy/insufficient time Understaffing/overcrowding Patient needs take priority Low risk of acquiring infection from patients Adapted from Pittet D, Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2000;21:
58 Definitions Hand hygiene Performing handwashing, antiseptic handwash, alcohol-based handrub, surgical hand hygiene/antisepsis Handwashing Washing hands with plain soap and water Antiseptic handwash Washing hands with water and soap or other detergents containing an antiseptic agent Alcohol-based handrub Rubbing hands with an alcohol-containing preparation Surgical hand hygiene/antisepsis Handwashing or using an alcohol-based handrub before operations by surgical personnel Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
59 Indications for Hand Hygiene When hands are visibly dirty, contaminated, or soiled, wash with nonantimicrobial or antimicrobial soap and water. If hands are not visibly soiled, use an alcohol-based handrub for routinely decontaminating hands. Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
60 Specific Indications for Hand Hygiene Before: Patient contact Donning gloves when inserting a CVC Inserting urinary catheters, peripheral vascular catheters, or other invasive devices that don t require surgery After: Contact with a patient s skin Contact with body fluids or excretions, nonintact skin, wound dressings Removing gloves Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
61 Selection of Hand Hygiene Agents: Factors to Consider Efficacy of antiseptic agent Acceptance of product by healthcare personnel Characteristics of product Skin irritation and dryness Accessibility of product Dispenser systems Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
62 Efficacy of Hand Hygiene Preparations in Killing Bacteria Good Better Best Plain Soap Antimicrobial soap Alcohol-based handrub
63 Ability of Hand Hygiene Agents to Reduce Bacteria on Hands % 99.9 Time After Disinfection log minutes 3.0 Bacterial Reduction Alcohol-based handrub (70% Isopropanol) Antimicrobial soap (4% Chlorhexidine) Plain soap Baseline Adapted from: Hosp Epidemiol Infect Control, 2 nd Edition, 1999.
64 Effect of Alcohol-Based Handrubs on Skin Condition Dry Healthy Self-reported skin score Baseline Alcohol rub 2 weeks Soap and water Epidermal water content Baseline Alcohol rub 2 weeks Soap and water Healthy Dry ~ Alcohol-based handrub is less damaging to the skin ~ Boyce J, Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2000;21(7):
65 Time Spent Cleansing Hands: one nurse per 8 hour shift Hand washing with soap and water: 56 minutes Based on seven (60 second) handwashing episodes per hour Alcohol-based handrub: 18 minutes Based on seven (20 second) handrub episodes per hour ~ Alcohol-based handrubs reduce time needed for hand disinfection ~ Voss A and Widmer AF, Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 1997:18;
66 Handrubs Recommended Hand Hygiene Technique Apply to palm of one hand, rub hands together covering all surfaces until dry Volume: based on manufacturer Handwashing Wet hands with water, apply soap, rub hands together for at least 15 seconds Rinse and dry with disposable towel Use towel to turn off faucet Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
67 Surgical Hand Hygiene/Antisepsis Use either an antimicrobial soap or alcoholbased handrub Antimicrobial soap: scrub hands and forearms for length of time recommended by manufacturer Alcohol-based handrub: follow manufacturer s recommendations. Before applying, pre-wash hands and forearms with non-antimicrobial soap Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
68 Infection Rates: Surgical Handscrub vs. Handrub 2 Test of Class of No. SSI/No. Operations (%) Equivalence Contamination Handscrub Handrub (p-value) Clean 29/1485 (1.9) 32/1520 (2.1) 16.0 (<0.001) Clean- Contaminated 24/650 (3.7) 23/732 (3.1) 1.9 (0.09) All 53/2135 (2.5) 55/2252 (2.4) 19.5 (<0.001) Parienti et al. JAMA 2002: 288(6);
69 Skin Care Provide healthcare workers with hand lotions or creams Get information from manufacturers regarding effects that hand lotions, creams, or alcohol-based handrubs may have on the effectiveness of antimicrobial soaps Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
70 Fingernails and Artificial Nails Natural nail tips should be kept to ¼ inch in length Artificial nails should not be worn when having direct contact with high-risk patients (e.g., ICU, OR) Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
71 Unresolved Issues Routine use of nonalcohol-based handrubs Wearing rings in healthcare settings Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
72 Gloving Wear gloves when contact with blood or other potentially infectious materials is possible Remove gloves after caring for a patient Do not wear the same pair of gloves for the care of more than one patient Do not wash gloves Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
73 Education/Motivation Programs Monitor healthcare workers (HCWs) adherence with recommended hand hygiene practices and give feedback Implement a multidisciplinary program to improve adherence to recommended practices Encourage patients and their families to remind HCWs to practice hand hygiene Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
74 Administrative Measures to Improve Hand Hygiene Make improved hand hygiene an institutional priority Place alcohol-based handrubs at entrance to patient room, or at bedside Provide HCWs with pocket-sized containers Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
75 Alcohol and Flammability Alcohols are flammable Alcohol-based handrubs should be stored away from high temperatures or flames Europe: fire incidence low U.S.: one report of flash fire Application is key: Let It Dry! Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
76 Performance Indicators Monitor and record adherence to hand hygiene by ward or service Provide feedback to healthcare workers about their performance Monitor the volume of alcohol-based handrub used per 1,000 patient days Monitor adherence to policies on wearing artificial nails Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16.
77 Summary Alcohol-Based Handrubs: What benefits do they provide? Require less time More effective for standard handwashing than soap More accessible than sinks Reduce bacterial counts on hands Improve skin condition
78 PREVENTION IS PRIMARY! Protect patients protect healthcare personnel promote quality healthcare!
So Why All the Fuss About Hand Hygiene?
 CARING PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, INC. HAND HYGIENE In-Service So Why All the Fuss About Hand Hygiene? Most common mode of transmission of pathogens is via hands! Infections acquired in healthcare Spread of
CARING PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, INC. HAND HYGIENE In-Service So Why All the Fuss About Hand Hygiene? Most common mode of transmission of pathogens is via hands! Infections acquired in healthcare Spread of
Policy Forum. Environmental and Professional Hygiene: Toward the Prevention of Drug Resistant Infections
 Policy Forum Environmental and Professional Hygiene: Toward the Prevention of Drug Resistant Infections International Society of Microbial Resistance and Office of International Medical Policy School of
Policy Forum Environmental and Professional Hygiene: Toward the Prevention of Drug Resistant Infections International Society of Microbial Resistance and Office of International Medical Policy School of
Infection Control and Standard Precautions
 Home Care Aide Training Guide Infection Control and Standard Precautions Pre-Service Training Course #1 Home Care Aide Orientation Training Manual: Infection Control & Standard Precautions Page 2 Table
Home Care Aide Training Guide Infection Control and Standard Precautions Pre-Service Training Course #1 Home Care Aide Orientation Training Manual: Infection Control & Standard Precautions Page 2 Table
Hand. Hygiene LEARNING OBJECTIVES. List 5 moments for hand hygiene. Identify 3 reported factors for noncompliance with hand hygiene.
 Hand Hygiene LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1 Identify 3 reported factors for noncompliance with hand hygiene. 2 List 5 moments for hand hygiene. 3 Identify the amount of time for proper handwashing and use of ABHR.
Hand Hygiene LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1 Identify 3 reported factors for noncompliance with hand hygiene. 2 List 5 moments for hand hygiene. 3 Identify the amount of time for proper handwashing and use of ABHR.
Hand washing, Asepsis, Precautions and Infection Control
 Hand washing, Asepsis, Precautions and Infection Control FN Ch 12, NICS Ch4 Week 2 Lesa McArdle, MSN, RN Objectives Hand washing, Asepsis, Precautions & Infection Control Explain the chain of infection
Hand washing, Asepsis, Precautions and Infection Control FN Ch 12, NICS Ch4 Week 2 Lesa McArdle, MSN, RN Objectives Hand washing, Asepsis, Precautions & Infection Control Explain the chain of infection
Living with MRSA Learning how to control the spread of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
 Living with MRSA Learning how to control the spread of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) IMPORTANT MRSA is a serious infection that can become life-threatening if left untreated. If you
Living with MRSA Learning how to control the spread of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) IMPORTANT MRSA is a serious infection that can become life-threatening if left untreated. If you
DISCUSS HAND HYGIENE AND PERFORM HAND ANTISEPSIS
 DISCUSS HAND HYGIENE AND PERFORM HAND ANTISEPSIS 1. TITLE SLIDE: DISCUSS HAND HYGIENE AND PERFORM HAND ANTISEPSIS. Hands are one of the most common sources of the spread of pathogenic microorganisms. Hand
DISCUSS HAND HYGIENE AND PERFORM HAND ANTISEPSIS 1. TITLE SLIDE: DISCUSS HAND HYGIENE AND PERFORM HAND ANTISEPSIS. Hands are one of the most common sources of the spread of pathogenic microorganisms. Hand
Your Guide to Managing. Multi Drug-resistant Organisms (MDROs)
 Agency for Integrated Care 5 Maxwell Road #10-00 Tower Block MND Complex Singapore 069110 Singapore Silver Line: 1800-650-6060 Email: enquiries@aic.sg Website: www.silverpages.sg Facebook: www.facebook.com/carerssg
Agency for Integrated Care 5 Maxwell Road #10-00 Tower Block MND Complex Singapore 069110 Singapore Silver Line: 1800-650-6060 Email: enquiries@aic.sg Website: www.silverpages.sg Facebook: www.facebook.com/carerssg
2.0 Scope These guidelines refer to all Cheshire Ireland employees, service users, their relatives, carers and visitors.
 Status: Guideline: Offers direction and guidance on good practice, need not necessarily be strictly adhered to. Title: Guidelines for Hand Hygiene Written by: Clinical Practice Project Group Policy No:
Status: Guideline: Offers direction and guidance on good practice, need not necessarily be strictly adhered to. Title: Guidelines for Hand Hygiene Written by: Clinical Practice Project Group Policy No:
APPENDIX. Hand Hygiene Observation Tool (Suggest one observation session by one observer)
 APPENDIX Hand Hygiene Observation Tool (Suggest one observation session by one observer) Date of Observation Time Observed - Person Observed (RN, RT, NNP, MD, Surgeon, OT/PT, etc.) Opportunity Assessed
APPENDIX Hand Hygiene Observation Tool (Suggest one observation session by one observer) Date of Observation Time Observed - Person Observed (RN, RT, NNP, MD, Surgeon, OT/PT, etc.) Opportunity Assessed
Hand washing/hand hygiene reduces the number of microorganisms on the hands and is the most important practice to prevent the spread of infection.
 1. Hand Hygiene Quick Reference Chart Hand washing/hand hygiene reduces the number of microorganisms on the hands and is the most important practice to prevent the spread of infection. WHEN Before: Direct
1. Hand Hygiene Quick Reference Chart Hand washing/hand hygiene reduces the number of microorganisms on the hands and is the most important practice to prevent the spread of infection. WHEN Before: Direct
Hand disinfection Topics
 Hand disinfection Mongolia 2011 Walter Popp, Hospital Hygiene, University Clinics Essen, Germany 1 Topics History Hand washing vs. hand disinfection Importance of hand disinfection Compliance campaigns
Hand disinfection Mongolia 2011 Walter Popp, Hospital Hygiene, University Clinics Essen, Germany 1 Topics History Hand washing vs. hand disinfection Importance of hand disinfection Compliance campaigns
Staph and MRSA Skin Infections Fact Sheet for Schools
 Cape May County Department of Health 4 Moore Road, Cape May Court House, NJ 08210 Staph and MRSA Skin Infections Fact Sheet for Schools What is a staph/mrsa skin infection? Staphylococcus or staph bacteria
Cape May County Department of Health 4 Moore Road, Cape May Court House, NJ 08210 Staph and MRSA Skin Infections Fact Sheet for Schools What is a staph/mrsa skin infection? Staphylococcus or staph bacteria
TABLE OF CONTENTS. 1. Purpose of the WRHA Infection Prevention and Control Manual 2.1 and approval process
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Winnipeg Regional Health Authority Introduction Page Number 1. Purpose of the WRHA Infection Prevention and Control Manual 2.1 and approval process 2. WRHA Infection Prevention and Control
TABLE OF CONTENTS Winnipeg Regional Health Authority Introduction Page Number 1. Purpose of the WRHA Infection Prevention and Control Manual 2.1 and approval process 2. WRHA Infection Prevention and Control
Clinic Infectious Disease Control
 Chapter 2 - Lesson 4 Clinic Infectious Disease Control Introduction Infectious and parasitic disease control is important in veterinary clinics. The main objective is to prevent the spread of infections
Chapter 2 - Lesson 4 Clinic Infectious Disease Control Introduction Infectious and parasitic disease control is important in veterinary clinics. The main objective is to prevent the spread of infections
Guideline for Prevention of Brucellosis in Meat Packing Plant Workers
 Guideline for Prevention of Brucellosis in Meat Packing Plant Workers Introduction Brucellosis is a disease which may spread from animals to man. There is no evidence for person to person transmission.
Guideline for Prevention of Brucellosis in Meat Packing Plant Workers Introduction Brucellosis is a disease which may spread from animals to man. There is no evidence for person to person transmission.
Overview of Infection Control and Prevention
 Overview of Infection Control and Prevention Review of the Cesarean-section Antibiotic Prophylaxis Program in Jordan and Workshop on Rational Medicine Use and Infection Control Terry Green and Salah Gammouh
Overview of Infection Control and Prevention Review of the Cesarean-section Antibiotic Prophylaxis Program in Jordan and Workshop on Rational Medicine Use and Infection Control Terry Green and Salah Gammouh
Do Bugs Need Drugs? A community program for wise use of antibiotics
 Do Bugs Need Drugs? A community program for wise use of antibiotics June 2012 Antibiotics Most significant discovery of modern medicine Save millions of lives Antibiotic resistance Caused by overuse and
Do Bugs Need Drugs? A community program for wise use of antibiotics June 2012 Antibiotics Most significant discovery of modern medicine Save millions of lives Antibiotic resistance Caused by overuse and
Advice for those affected by MRSA outside of hospital If you have MRSA this booklet provides information to help manage your day-to-day life
 Registered Charity No 1115672 raising public awareness - campaigning for safe standards supporting sufferers and dependants Patron: Edwina Currie President: Professor Hugh Pennington Advice for those affected
Registered Charity No 1115672 raising public awareness - campaigning for safe standards supporting sufferers and dependants Patron: Edwina Currie President: Professor Hugh Pennington Advice for those affected
Infection Prevention Highlights for the Medical Staff. Pamela Rohrbach MSN, RN, CIC Director of Infection Prevention
 Highlights for the Medical Staff Pamela Rohrbach MSN, RN, CIC Director of Infection Prevention Standard Precautions every patient every time a. Hand Hygiene b. Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Highlights for the Medical Staff Pamela Rohrbach MSN, RN, CIC Director of Infection Prevention Standard Precautions every patient every time a. Hand Hygiene b. Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL. Hand Hygiene CHAPTER 6: Authors A. J. Stewardson, MBBS, PhD D. Pittet, MD, MS
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 6: Hand Hygiene Authors A. J. Stewardson, MBBS, PhD D. Pittet, MD, MS Chapter Editor Shaheen Mehtar, MD, MBBS, FRC Path, FCPath (Micro) Topic Outline
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 6: Hand Hygiene Authors A. J. Stewardson, MBBS, PhD D. Pittet, MD, MS Chapter Editor Shaheen Mehtar, MD, MBBS, FRC Path, FCPath (Micro) Topic Outline
Presented by: Mary McGoldrick, MS, RN, CRNI
 Managing Infection Control Challenges in the Home Mary McGoldrick, MS, RN, CRNI Home Care and Hospice Consultant Saint Simons Island, GA CE Credit in Five Easy Steps! 1. Scan your badge as you enter each
Managing Infection Control Challenges in the Home Mary McGoldrick, MS, RN, CRNI Home Care and Hospice Consultant Saint Simons Island, GA CE Credit in Five Easy Steps! 1. Scan your badge as you enter each
Model Infection Control Plan for Veterinary Practices, 2010
 Model Infection Control Plan for Veterinary Practices, 2010 National Association of State Public Health Veterinarians (NASPHV) Veterinary Infection Control Committee (VICC) This plan should be adapted
Model Infection Control Plan for Veterinary Practices, 2010 National Association of State Public Health Veterinarians (NASPHV) Veterinary Infection Control Committee (VICC) This plan should be adapted
In-Service Training Program. Managing Drug-Resistant Organisms in Long-Term Care
 In-Service Training Program Managing Drug-Resistant Organisms in Long-Term Care OBJECTIVES 1. Define the term antibiotic resistance. 2. Explain the difference between colonization and infection. 3. Identify
In-Service Training Program Managing Drug-Resistant Organisms in Long-Term Care OBJECTIVES 1. Define the term antibiotic resistance. 2. Explain the difference between colonization and infection. 3. Identify
ENVIRONMENT, HEALTH AND SAFETY POLICY
 ENVIRONMENT, HEALTH AND SAFETY POLICY Minimally Required Personal Protective Equipment for Animal Care and Use October 11, 2017 Revision: 04 Page 1 of 7 Purpose: To define minimum standards for personal
ENVIRONMENT, HEALTH AND SAFETY POLICY Minimally Required Personal Protective Equipment for Animal Care and Use October 11, 2017 Revision: 04 Page 1 of 7 Purpose: To define minimum standards for personal
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL. NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 705. Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 705 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF WOUNDS (FIRST AID) 1. PURPOSE: Proper
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 705 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF WOUNDS (FIRST AID) 1. PURPOSE: Proper
Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE)
 Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) September 21, 2017 Maryam Khan Peel Public Health Madeleine Ashcroft Public Health Ontario Objectives Differentiate the acronyms related to CPE (CPE,CPO,CRE,CRO)
Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) September 21, 2017 Maryam Khan Peel Public Health Madeleine Ashcroft Public Health Ontario Objectives Differentiate the acronyms related to CPE (CPE,CPO,CRE,CRO)
Healthy Hands at Work Being sick at work is everyone s business
 Healthy Hands at Work Being sick at work is everyone s business Introduction The Healthy Hands at Work resources were developed to meet the growing need to provide, and to be part of, a healthy work environment.
Healthy Hands at Work Being sick at work is everyone s business Introduction The Healthy Hands at Work resources were developed to meet the growing need to provide, and to be part of, a healthy work environment.
Invasive Group A Streptococcus (GAS)
 Invasive Group A Streptococcus (GAS) Cause caused by a bacterium commonly found on the skin and in the throat transmitted by direct, indirect or droplet contact with secretions from the nose, and throat
Invasive Group A Streptococcus (GAS) Cause caused by a bacterium commonly found on the skin and in the throat transmitted by direct, indirect or droplet contact with secretions from the nose, and throat
Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections. For National Patient Safety Goal
 Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections For National Patient Safety Goal 07.03.01 2009 Methicillin Resistant Staphlococcus aureus (MRSA) About 3-8% of the population at large is a carrier
Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections For National Patient Safety Goal 07.03.01 2009 Methicillin Resistant Staphlococcus aureus (MRSA) About 3-8% of the population at large is a carrier
Advice for those affected by MRSA outside of hospital
 Advice for those affected by MRSA outside of hospital If you have MRSA this leaflet provides information and advice for managing your day-to-day life. 2 About MRSA Understanding the difference between
Advice for those affected by MRSA outside of hospital If you have MRSA this leaflet provides information and advice for managing your day-to-day life. 2 About MRSA Understanding the difference between
Thank you for joining us to learn about preventing the spread of disease in foster
 Thank you for joining us to learn about preventing the spread of disease in foster homes 1 Thank you for sharing your home with foster pets! Most of you probably have pets of your own, and have wondered
Thank you for joining us to learn about preventing the spread of disease in foster homes 1 Thank you for sharing your home with foster pets! Most of you probably have pets of your own, and have wondered
Model Infection Control Plan for Veterinary Practices, 2015
 Appendix 4: Model Infection Control Plan 2015 Model Infection Control Plan for Veterinary Practices, 2015 National Association of State Public Health Veterinarians (NASPHV) Veterinary Infection Control
Appendix 4: Model Infection Control Plan 2015 Model Infection Control Plan for Veterinary Practices, 2015 National Association of State Public Health Veterinarians (NASPHV) Veterinary Infection Control
Safety Presentation Infection Control and Handwashing
 Infection Control and Handwashing Presenter's Notes These notes are provided as a presenter's guide and can be used alone or with the PowerPoint presentation entitled "". Numbered headings in these notes
Infection Control and Handwashing Presenter's Notes These notes are provided as a presenter's guide and can be used alone or with the PowerPoint presentation entitled "". Numbered headings in these notes
Implementation Guide: Higher Education
 Guiding You to Healthy Hand Hygiene Implementation Guide: Higher Education What this Guide Will Do Hand hygiene compliance is a Step 2 - Educating those chosen to serious issue. Approximately 80% of be
Guiding You to Healthy Hand Hygiene Implementation Guide: Higher Education What this Guide Will Do Hand hygiene compliance is a Step 2 - Educating those chosen to serious issue. Approximately 80% of be
About this presentation: Using this presen esen a t tion: This presentation includes information about:
 About this presentation: Handwashing in Schools was prepared by the Do Bugs Need Drugs? program in collaboration with Alberta Health and Alberta Education. The content has been reviewed by Alberta Education,
About this presentation: Handwashing in Schools was prepared by the Do Bugs Need Drugs? program in collaboration with Alberta Health and Alberta Education. The content has been reviewed by Alberta Education,
The Spread of the Superbug
 The Spread of the Superbug AST staff As technology continues to allow scientists to make medical advances that once were considered difficult, new threats to public health are rising. Superbugs are deadly
The Spread of the Superbug AST staff As technology continues to allow scientists to make medical advances that once were considered difficult, new threats to public health are rising. Superbugs are deadly
Today s Agenda: 9/30/14
 Today s Agenda: 9/30/14 1. Students will take C List Medical Abbreviation Quiz. 2. TO: Discuss MRSA. MRSA MRSA Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus What
Today s Agenda: 9/30/14 1. Students will take C List Medical Abbreviation Quiz. 2. TO: Discuss MRSA. MRSA MRSA Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus What
The role of Infection Control Nurse in Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI) April 2013
 The role of Infection Control Nurse in Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI) April 2013 Impact of SSI 2 nd common health- care associated infection (HCAI) 14-16% of HCAI Post operation SSI prolong
The role of Infection Control Nurse in Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI) April 2013 Impact of SSI 2 nd common health- care associated infection (HCAI) 14-16% of HCAI Post operation SSI prolong
Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms (MDRO)
 Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms (MDRO) 2016 What are MDROs? Multi-drug resistant organisms, or MDROs, are bacteria resistant to current antibiotic therapy and therefore difficult to treat. MDROs can cause
Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms (MDRO) 2016 What are MDROs? Multi-drug resistant organisms, or MDROs, are bacteria resistant to current antibiotic therapy and therefore difficult to treat. MDROs can cause
HOSPITAL-ACQUIRED INFECTION/MRSA EYERUSALEM KIFLE AND GIFT IMUETINYAN OMOBOGBE PNURSS15
 HOSPITAL-ACQUIRED INFECTION/MRSA EYERUSALEM KIFLE AND GIFT IMUETINYAN OMOBOGBE PNURSS15 INTRODUCTION DEFINITIONS SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS RISK FACTORS DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATIONS PREVENTIONS TREATMENT PATIENT EDUCATION
HOSPITAL-ACQUIRED INFECTION/MRSA EYERUSALEM KIFLE AND GIFT IMUETINYAN OMOBOGBE PNURSS15 INTRODUCTION DEFINITIONS SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS RISK FACTORS DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATIONS PREVENTIONS TREATMENT PATIENT EDUCATION
WASH YOUR HANDS! Resources for Schools. Developed by Do Bugs Need Drugs? A Community Program for Wise Use of Antibiotics
 WASH YOUR HANDS! Resources for Schools Developed by Do Bugs Need Drugs? A Community Program for Wise Use of Antibiotics Introduction Wash Your Hands! Resources for Schools provides information and tools
WASH YOUR HANDS! Resources for Schools Developed by Do Bugs Need Drugs? A Community Program for Wise Use of Antibiotics Introduction Wash Your Hands! Resources for Schools provides information and tools
Hand Hygiene Policy. January Hand Hygiene Policy and Procedure (an element of Standard Infection Control Precautions)
 Hand Hygiene Policy January 2011 1 Introduction People s hands are the most common way in which micro organisms, particularly bacteria, might be transported and cause infection, especially to those who
Hand Hygiene Policy January 2011 1 Introduction People s hands are the most common way in which micro organisms, particularly bacteria, might be transported and cause infection, especially to those who
Care and Handling of Pets
 Communicable Disease Outreach Program 3020 Rucker Avenue, Suite 300 Everett, WA 98201-3900 425.339.5278 Care and Handling of Pets Name of facility: WIWS Pet restrictions 1. Pets will be inaccessible to
Communicable Disease Outreach Program 3020 Rucker Avenue, Suite 300 Everett, WA 98201-3900 425.339.5278 Care and Handling of Pets Name of facility: WIWS Pet restrictions 1. Pets will be inaccessible to
Preventing Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI)
 1 Preventing Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) All Hands on Deck to Reduce CDI Skill Nursing Facility Conference July 28, 2017 Idamae Kennedy, MPH,BSN,RN,CIC Liaison Infection Preventionist Healthcare
1 Preventing Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) All Hands on Deck to Reduce CDI Skill Nursing Facility Conference July 28, 2017 Idamae Kennedy, MPH,BSN,RN,CIC Liaison Infection Preventionist Healthcare
A patient s guide to. MRSA - Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
 A patient s guide to MRSA - Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus 1 What is MRSA? There are lots of micro-organisms (germs) on our skin. They are in the air we breathe, the water we drink, and the
A patient s guide to MRSA - Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus 1 What is MRSA? There are lots of micro-organisms (germs) on our skin. They are in the air we breathe, the water we drink, and the
STERILIZATION, DESINFECTION PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTION (SSI)
 Semmelweis University Faculty of Medicine Department of Surgical Research and Techniques OPERATING ROOM (OR) - STRUCTURE, EQUIPMENTS STERILIZATION, DESINFECTION PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTION (SSI)
Semmelweis University Faculty of Medicine Department of Surgical Research and Techniques OPERATING ROOM (OR) - STRUCTURE, EQUIPMENTS STERILIZATION, DESINFECTION PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTION (SSI)
WASH YOUR HANDS. GRADE ONE Lesson Plan
 WASH YOUR HANDS GRADE ONE Lesson Plan Grade One October 2009 GRADE Glittery Hands Suggested Time: 50 minutes Overview Students will review the steps of handwashing and learn how germs are spread and can
WASH YOUR HANDS GRADE ONE Lesson Plan Grade One October 2009 GRADE Glittery Hands Suggested Time: 50 minutes Overview Students will review the steps of handwashing and learn how germs are spread and can
EcoHydra Antimicrobial Handwash. Product Overview. Physical Properties. Product Description. Regulatory Compliance. Key Features and Benefits
 EcoHydra Antimicrobial Handwash Product Overview Product Description The EcoHydra Antimicrobial Handwash is a liquid soap substitute for the wet method of washing and disinfecting to remove dirt and kill
EcoHydra Antimicrobial Handwash Product Overview Product Description The EcoHydra Antimicrobial Handwash is a liquid soap substitute for the wet method of washing and disinfecting to remove dirt and kill
CANINE PARVO VIRUS HEALTHY HINTS I S S U E 1 GET THE BEST FOR YOUR BEST FRIENDS!
 CANINE PARVO VIRUS I S S U E 1 HEALTHY HINTS GET THE BEST FOR YOUR BEST FRIENDS! WHAT IS CANINE PARVO VIRUS? Parvovirus is a HIGHLY CONTAGIOUS virus that attacks the intestines and causes sloughing of
CANINE PARVO VIRUS I S S U E 1 HEALTHY HINTS GET THE BEST FOR YOUR BEST FRIENDS! WHAT IS CANINE PARVO VIRUS? Parvovirus is a HIGHLY CONTAGIOUS virus that attacks the intestines and causes sloughing of
MRSA What We Need to Know Sharon Pearce, CRNA, MSN Carolina Anesthesia Associates
 MRSA What We Need to Know Sharon Pearce, CRNA, MSN Carolina Anesthesia Associates What is MRSA? Methicillin-resistant Staphylococus aureus This hardy bacterium has developed resistance to every antibiotic
MRSA What We Need to Know Sharon Pearce, CRNA, MSN Carolina Anesthesia Associates What is MRSA? Methicillin-resistant Staphylococus aureus This hardy bacterium has developed resistance to every antibiotic
Antibiotic stewardship in long term care
 Antibiotic stewardship in long term care Shira Doron, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Geographic Medicine and Infectious Diseases Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA Consultant to Massachusetts
Antibiotic stewardship in long term care Shira Doron, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Geographic Medicine and Infectious Diseases Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA Consultant to Massachusetts
Originally posted February 13, Update: March 26, 2018
 UPDATED: FDA Investigates Pattern of Contamination in Certain Raw Pet Foods Made by Arrow Reliance Inc., Including Darwin s Natural Pet Products and ZooLogics Pet Food Originally posted February 13, 2018
UPDATED: FDA Investigates Pattern of Contamination in Certain Raw Pet Foods Made by Arrow Reliance Inc., Including Darwin s Natural Pet Products and ZooLogics Pet Food Originally posted February 13, 2018
MRSA: How to Keep This Deadly Super Bug From Infecting You
 MRSA: How to Keep This Deadly Super Bug From Infecting You DR. MERCOLA $9.97 Mercola.com is the world s #1-ranked natural health website, with over one million subscribers to its free newsletter. Millions
MRSA: How to Keep This Deadly Super Bug From Infecting You DR. MERCOLA $9.97 Mercola.com is the world s #1-ranked natural health website, with over one million subscribers to its free newsletter. Millions
Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) for Fresh Fruit and Vegetable Growers. Worker health
 Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) for Fresh Fruit and Vegetable Growers Worker health Worker Health and Hygiene In the field In the packing house/processing facility Pick your own operations What is Health
Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) for Fresh Fruit and Vegetable Growers Worker health Worker Health and Hygiene In the field In the packing house/processing facility Pick your own operations What is Health
Hand Hygiene and MDRO (Multidrug-resistant Organisms) - Science and Myth PROF MARGARET IP DEPT OF MICROBIOLOGY
 Hand Hygiene and MDRO (Multidrug-resistant Organisms) - Science and Myth PROF MARGARET IP DEPT OF MICROBIOLOGY MDROs and Hand Hygiene Guidelines HH Apr14 The Science of Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Settings
Hand Hygiene and MDRO (Multidrug-resistant Organisms) - Science and Myth PROF MARGARET IP DEPT OF MICROBIOLOGY MDROs and Hand Hygiene Guidelines HH Apr14 The Science of Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Settings
Zoonotic Diseases. Risks of working with wildlife. Maria Baron Palamar, Wildlife Veterinarian
 Zoonotic Diseases Risks of working with wildlife www.cdc.gov Definition Zoonoses: infectious diseases of vertebrate animals that can be naturally transmitted to humans Health vs. Disease Transmission -
Zoonotic Diseases Risks of working with wildlife www.cdc.gov Definition Zoonoses: infectious diseases of vertebrate animals that can be naturally transmitted to humans Health vs. Disease Transmission -
WASH YOUR HANDS. GRADE TWO Lesson Plan
 WASH YOUR HANDS GRADE TWO Lesson Plan Grade Two October 2009 GRADE 2 Not All Bugs Need Drugs Suggested Time: 50 minutes Overview Students will learn that medications can help you get better when you are
WASH YOUR HANDS GRADE TWO Lesson Plan Grade Two October 2009 GRADE 2 Not All Bugs Need Drugs Suggested Time: 50 minutes Overview Students will learn that medications can help you get better when you are
MRSA CROSS INFECTION RISK: IS YOUR PRACTICE CLEAN ENOUGH?
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk MRSA CROSS INFECTION RISK: IS YOUR PRACTICE CLEAN ENOUGH? Author : CATHERINE F LE BARS Categories : Vets Date : February 25,
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk MRSA CROSS INFECTION RISK: IS YOUR PRACTICE CLEAN ENOUGH? Author : CATHERINE F LE BARS Categories : Vets Date : February 25,
Nosocomial Antibiotic Resistant Organisms MRSA & VRE
 Nosocomial Antibiotic Resistant Organisms MRSA & VRE Course Health Science Unit VII Infection Control Essential Question Does improved hand hygiene really reduce the spread of bacteria in healthcare settings?
Nosocomial Antibiotic Resistant Organisms MRSA & VRE Course Health Science Unit VII Infection Control Essential Question Does improved hand hygiene really reduce the spread of bacteria in healthcare settings?
Feline zoonoses. Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee 12/09
 Feline zoonoses Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee 12/09 Cat scratch disease Bacterial infection caused by Bartonella henselae Associated with a cat bite or scratch Infection at point of injury,
Feline zoonoses Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee 12/09 Cat scratch disease Bacterial infection caused by Bartonella henselae Associated with a cat bite or scratch Infection at point of injury,
MRSA Screening Programme National Targeted Rollout. MRSA Screening
 National Targeted Rollout. MRSA Screening A resource pack to support the training of healthcare staff 5th February 2010 Xxxx Learning Outcomes Xxxx On completion of this course you should be able to: Give
National Targeted Rollout. MRSA Screening A resource pack to support the training of healthcare staff 5th February 2010 Xxxx Learning Outcomes Xxxx On completion of this course you should be able to: Give
Infection Control & Prevention
 Infection Control & Prevention Objectives: Define the term multi-drug resistant organism (MDRO). Recognize risk factors for developing MDROs. Describe the clinical manifestations and medical treatment
Infection Control & Prevention Objectives: Define the term multi-drug resistant organism (MDRO). Recognize risk factors for developing MDROs. Describe the clinical manifestations and medical treatment
Lesson 6: Handwashing and Gloving
 Lesson 6: Handwashing and Gloving Transcript Title Slide Welcome Hello. My name is Barbara Breen, Training Coordinator for the DPW Medication Administration Program. I will be your narrator for this webcast.
Lesson 6: Handwashing and Gloving Transcript Title Slide Welcome Hello. My name is Barbara Breen, Training Coordinator for the DPW Medication Administration Program. I will be your narrator for this webcast.
Infection Prevention & Control: PPE and Beyond. Stacy Martin, RN, BSN, CIC Manager, Infection Prevention & Control
 Infection Prevention & Control: PPE and Beyond Stacy Martin, RN, BSN, CIC Manager, Infection Prevention & Control Objectives Describe the chain of infection Explain the role of personal protective equipment
Infection Prevention & Control: PPE and Beyond Stacy Martin, RN, BSN, CIC Manager, Infection Prevention & Control Objectives Describe the chain of infection Explain the role of personal protective equipment
The Spread of the Superbug
 The Spread of the Superbug AST staff As technology continues to allow scientists to make medical advances that once were considered difficult, new threats to public health are rising. Superbugs are deadly
The Spread of the Superbug AST staff As technology continues to allow scientists to make medical advances that once were considered difficult, new threats to public health are rising. Superbugs are deadly
Good Agriculture Practices (GAPs) for Food Safety Indiana University Condensed for IU Garden Volunteers
 Good Agriculture Practices (GAPs) for Food Safety Indiana University Condensed for IU Garden Volunteers Introduction Produce is often implicated in foodborne illness outbreaks. Produce from IU gardens
Good Agriculture Practices (GAPs) for Food Safety Indiana University Condensed for IU Garden Volunteers Introduction Produce is often implicated in foodborne illness outbreaks. Produce from IU gardens
Adventures in Handwashing
 Adventures in Handwashing A review of studies on handwashing, foodborne illness, and the effectiveness of food worker training on handwashing behaviors Many Foodborne Pathogens are Associated with Personal
Adventures in Handwashing A review of studies on handwashing, foodborne illness, and the effectiveness of food worker training on handwashing behaviors Many Foodborne Pathogens are Associated with Personal
FDA Consumer Antimicrobial Handwash Proposed Rule: What Does It Mean and Does It Impact Healthcare or Not? Megan J. DiGiorgio MSN, RN, CIC
 FDA Consumer Antimicrobial Handwash Proposed Rule: What Does It Mean and Does It Impact Healthcare or Not? Megan J. DiGiorgio MSN, RN, CIC Foreword The following whitepaper is designed for healthcare professionals
FDA Consumer Antimicrobial Handwash Proposed Rule: What Does It Mean and Does It Impact Healthcare or Not? Megan J. DiGiorgio MSN, RN, CIC Foreword The following whitepaper is designed for healthcare professionals
Infection control in intensive care. Sandra Fairley Senior Nurse, Neurocritical Care
 Infection control in intensive care Sandra Fairley Senior Nurse, Neurocritical Care sandra.fairley@uclh.nhs.uk Risks to the patient of health care acquired infection (HCAI) Patient admitted to hospital
Infection control in intensive care Sandra Fairley Senior Nurse, Neurocritical Care sandra.fairley@uclh.nhs.uk Risks to the patient of health care acquired infection (HCAI) Patient admitted to hospital
APIC CHAPTER PRESENTATION 7/2014
 2014 CRE THE SUPER BUG - WHY ALL THE BUZZ? Susan Burns BS, MT, CIC, VA-BC Medical Science Liaison DISCLOSURE I am a paid employee of the clinical team of PDI Healthcare. The content of this presentation
2014 CRE THE SUPER BUG - WHY ALL THE BUZZ? Susan Burns BS, MT, CIC, VA-BC Medical Science Liaison DISCLOSURE I am a paid employee of the clinical team of PDI Healthcare. The content of this presentation
Running head: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE 1
 Running head: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE 1 Clostridium difficile Infection Christy Lee Fenton Mountainland Applied Technology College CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE 2 Clostridium difficile Infection Approximately 200,000
Running head: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE 1 Clostridium difficile Infection Christy Lee Fenton Mountainland Applied Technology College CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE 2 Clostridium difficile Infection Approximately 200,000
FLORIDA ATLANTIC UNIVERSITY
 FLORIDA ATLANTIC UNIVERSITY Medical Monitoring Program for Animal Use Environmental Health and Safety Florida Atlantic University 777 Glades Rd., C.O.B., Rm. 112 Boca Raton, FL 33431 Phone: 561-297-3129
FLORIDA ATLANTIC UNIVERSITY Medical Monitoring Program for Animal Use Environmental Health and Safety Florida Atlantic University 777 Glades Rd., C.O.B., Rm. 112 Boca Raton, FL 33431 Phone: 561-297-3129
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. AMOXICILLIN 250mg and 500mg CAPSULES BP Amoxicillin (as amoxicillin trihydrate)
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER AMOXICILLIN 250mg and 500mg CAPSULES BP Amoxicillin (as amoxicillin trihydrate) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER AMOXICILLIN 250mg and 500mg CAPSULES BP Amoxicillin (as amoxicillin trihydrate) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because
CHAPTER:1 THE RATIONAL USE OF ANTIBIOTICS. BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
 CHAPTER:1 THE RATIONAL USE OF ANTIBIOTICS BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Antibiotics One of the most commonly used group of drugs In USA 23
CHAPTER:1 THE RATIONAL USE OF ANTIBIOTICS BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Antibiotics One of the most commonly used group of drugs In USA 23
Feline Vaccines: Benefits and Risks
 Feline Vaccines: Benefits and Risks Deciding which vaccines your cat should receive requires that you have a complete understanding of the benefits and risks of the procedure. For this reason, it is extremely
Feline Vaccines: Benefits and Risks Deciding which vaccines your cat should receive requires that you have a complete understanding of the benefits and risks of the procedure. For this reason, it is extremely
What is Antibiotic Resistance. Antibiotic Resistance A Public Health Issue
 What is Antibiotic Resistance Antibiotic Resistance A Public Health Issue Antibiotic resistance is the ability of a bacteria, to stop an antibiotics from working against it. As a result, standard treatments
What is Antibiotic Resistance Antibiotic Resistance A Public Health Issue Antibiotic resistance is the ability of a bacteria, to stop an antibiotics from working against it. As a result, standard treatments
Conflict of interest: We have no conflict of interest to report on this topic of SSI reduction for total knees.
 Reducing SSI- Knees TIFFANY KENNERK MBA, MSN, RN, NE -BC, ONC CYNTHIA SEAMAN BSN, RN, ONC, CMSRN ~COMMUNITY HOSPITALS AND WELLNESS CENTERS~ Conflict of interest: We have no conflict of interest to report
Reducing SSI- Knees TIFFANY KENNERK MBA, MSN, RN, NE -BC, ONC CYNTHIA SEAMAN BSN, RN, ONC, CMSRN ~COMMUNITY HOSPITALS AND WELLNESS CENTERS~ Conflict of interest: We have no conflict of interest to report
Importance of handwashing prior to wound dressings in prevention of nosocomial infection in surgical wards
 International Surgery Journal Athavale VS et al. Int Surg J. 218 Apr;5(4):1422-1427 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-335 eissn 2349-292 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.1823/2349-292.isj2181123
International Surgery Journal Athavale VS et al. Int Surg J. 218 Apr;5(4):1422-1427 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-335 eissn 2349-292 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.1823/2349-292.isj2181123
This protocol pertains to clinicians, interns and anyone with direct patient contact.
 Adopted 8/12 Hand Hygiene A significant body of evidence exists to show that pathogens can be transferred from patient to health care worker. Much of this evidence details the transfer of pathogens from
Adopted 8/12 Hand Hygiene A significant body of evidence exists to show that pathogens can be transferred from patient to health care worker. Much of this evidence details the transfer of pathogens from
Multidrug Resistant Organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff)
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Multidrug Resistant Organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff) This information explains multidrug resistant organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff),
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Multidrug Resistant Organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff) This information explains multidrug resistant organisms (MDROs) and Clostridium difficile (C. diff),
ACTIVITIES GRADE TWO
 ACTIVITIES GRADE TWO October 2009 ACTIVITIES GRADE TWO ITEM # OF PAGES Picture of Bugsy --------------------------------------------------------- 1 Bacteria and Virus Overhead -----------------------------------------
ACTIVITIES GRADE TWO October 2009 ACTIVITIES GRADE TWO ITEM # OF PAGES Picture of Bugsy --------------------------------------------------------- 1 Bacteria and Virus Overhead -----------------------------------------
Clean machine: your guide to brilliant practice hygiene
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Clean machine: your guide to brilliant practice hygiene Author : JENNY WRIGHT Categories : Business Date : December 1, 2012
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Clean machine: your guide to brilliant practice hygiene Author : JENNY WRIGHT Categories : Business Date : December 1, 2012
Role of the nurse in diagnosing infection: The right sample, every time
 BROUGHT TO YOU BY Role of the nurse in diagnosing infection: The right sample, every time The module has been written by Shanika Anne-Marie Crusz and Amelia Joseph Authors affiliation: Department of Clinical
BROUGHT TO YOU BY Role of the nurse in diagnosing infection: The right sample, every time The module has been written by Shanika Anne-Marie Crusz and Amelia Joseph Authors affiliation: Department of Clinical
Amoxicillin 250mg Hard Capsules Amoxicillin 500mg Hard Capsules
 Package leaflet: Information for the user Amoxicillin 250mg Hard Capsules Amoxicillin 500mg Hard Capsules Amoxicillin Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it
Package leaflet: Information for the user Amoxicillin 250mg Hard Capsules Amoxicillin 500mg Hard Capsules Amoxicillin Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it
Version Control Sheet
 PROCEDURE FOR MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH MULTI DRUG RESISTANT ORGANISMS PROCEDURE NUMBER IC/02 DATE RATIFIED OCTOBER 2018 NEXT REVIEW DATE OCTOBER 2020 POLICY AUTHOR Infection Control Nurse ACCOUNTABLE
PROCEDURE FOR MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH MULTI DRUG RESISTANT ORGANISMS PROCEDURE NUMBER IC/02 DATE RATIFIED OCTOBER 2018 NEXT REVIEW DATE OCTOBER 2020 POLICY AUTHOR Infection Control Nurse ACCOUNTABLE
Sites of IM injections : 1. Ventrogluteal site: site is in the gluteus medius muscle, which lies over the gluteus minimus. 2. Vastus lateralis site:
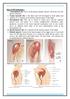 Sites of IM injections : 1. Ventrogluteal site: site is in the gluteus medius muscle, which lies over the gluteus minimus. 2. Vastus lateralis site: is the thick and well developed in both adults and children.
Sites of IM injections : 1. Ventrogluteal site: site is in the gluteus medius muscle, which lies over the gluteus minimus. 2. Vastus lateralis site: is the thick and well developed in both adults and children.
03/09/2014. Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course. Talk outline
 Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course 2014 What is healthcare-associated infection (HCAI), antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs)? Why we should be worried?
Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course 2014 What is healthcare-associated infection (HCAI), antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs)? Why we should be worried?
General Prevention Practices for Beef and dairy Producers
 for Beef and dairy Producers Minimizing or preventing disease entry and spread on farms is the goal of an effective Biological Risk Management plan. To accomplish this, there are several general management
for Beef and dairy Producers Minimizing or preventing disease entry and spread on farms is the goal of an effective Biological Risk Management plan. To accomplish this, there are several general management
: "INFECTION CONTROL: WHAT'S COMING IN 2017?" LISA THOMAS RN-BC STATE TRAINING COORDINATOR OFFICE OF LONG TERM CARE
 : "INFECTION CONTROL: WHAT'S COMING IN 2017?" LISA THOMAS RN-BC STATE TRAINING COORDINATOR OFFICE OF LONG TERM CARE OBJECTIVES REVIEW STATISTICS ASSOCIATED WITH OLDER ADULTS AND THEIR RISK OF INFECTIONS
: "INFECTION CONTROL: WHAT'S COMING IN 2017?" LISA THOMAS RN-BC STATE TRAINING COORDINATOR OFFICE OF LONG TERM CARE OBJECTIVES REVIEW STATISTICS ASSOCIATED WITH OLDER ADULTS AND THEIR RISK OF INFECTIONS
Antibiotic Stewardship in Nursing Homes SAM GUREVITZ PHARM D, CGP ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR BUTLER UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF PHARMACY AND HEALTH SCIENCE
 Antibiotic Stewardship in Nursing Homes SAM GUREVITZ PHARM D, CGP ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR BUTLER UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF PHARMACY AND HEALTH SCIENCE Crisis: Antibiotic Resistance Success Strategy WWW.optimistic-care.org
Antibiotic Stewardship in Nursing Homes SAM GUREVITZ PHARM D, CGP ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR BUTLER UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF PHARMACY AND HEALTH SCIENCE Crisis: Antibiotic Resistance Success Strategy WWW.optimistic-care.org
Antimicrobial Stewardship in the Long Term Care and Outpatient Settings. Carlos Reyes Sacin, MD, AAHIVS
 Antimicrobial Stewardship in the Long Term Care and Outpatient Settings Carlos Reyes Sacin, MD, AAHIVS Disclosure Speaker and consultant in HIV medicine for Gilead and Jansen Pharmaceuticals Objectives
Antimicrobial Stewardship in the Long Term Care and Outpatient Settings Carlos Reyes Sacin, MD, AAHIVS Disclosure Speaker and consultant in HIV medicine for Gilead and Jansen Pharmaceuticals Objectives
Hospital Infection. Mongolia, October Walter Popp Hospital Hygiene University Clinics Essen, Germany
 Hospital Infection Mongolia, October 2011 Walter Popp Hospital Hygiene University Clinics Essen, Germany 1 2 1 3 4 2 Tuberculosis Mongolia: 4,218 new cases in 2010. 156 per 100,000. 000 Transmission possible
Hospital Infection Mongolia, October 2011 Walter Popp Hospital Hygiene University Clinics Essen, Germany 1 2 1 3 4 2 Tuberculosis Mongolia: 4,218 new cases in 2010. 156 per 100,000. 000 Transmission possible
Hurricane Animal Hospital 2120 Mount Vernon Road Hurricane, WV or
 Hurricane Animal Hospital 2120 Mount Vernon Road Hurricane, WV 25526 304-757-5937 or 304-757-2287 www.hurricaneanimalhospital.com Feline Leukemia Virus (FELV) This information handout is designed as a
Hurricane Animal Hospital 2120 Mount Vernon Road Hurricane, WV 25526 304-757-5937 or 304-757-2287 www.hurricaneanimalhospital.com Feline Leukemia Virus (FELV) This information handout is designed as a
Surveillance of Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms
 Surveillance of Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms Karen Hoffmann, RN, MS, CIC Associate Director Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) University of North Carolina School of Medicine
Surveillance of Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms Karen Hoffmann, RN, MS, CIC Associate Director Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) University of North Carolina School of Medicine
4/28/2017. Scientific Basis for Current Hand Hygiene Guidelines and Future Trends. Presentation Objectives
 Scientific Basis for Current Hand Hygiene Guidelines and Future Trends John M. Boyce, MD J.M. Boyce Consulting, LLC Middletown, CT www.jmboyceconsulting.com 1 Presentation Objectives Review of evidence
Scientific Basis for Current Hand Hygiene Guidelines and Future Trends John M. Boyce, MD J.M. Boyce Consulting, LLC Middletown, CT www.jmboyceconsulting.com 1 Presentation Objectives Review of evidence
ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP: THE ROLE OF THE CLINICIAN SAM GUREVITZ PHARM D, CGP BUTLER UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF PHARMACY AND HEALTH SCIENCES
 ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP: THE ROLE OF THE CLINICIAN SAM GUREVITZ PHARM D, CGP BUTLER UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF PHARMACY AND HEALTH SCIENCES 1 Crisis: Antibiotic Resistance Success Strategy 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss
ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP: THE ROLE OF THE CLINICIAN SAM GUREVITZ PHARM D, CGP BUTLER UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF PHARMACY AND HEALTH SCIENCES 1 Crisis: Antibiotic Resistance Success Strategy 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss
DO BUGS NEED DRUGS? GRADE ONE
 DO BUGS NEED DRUGS? GRADE ONE Grade One May 2010 GRADE Do Bugs Need Drugs? 1 Overview In this lesson, students review the steps of handwashing and further explore how germs can spread and cause illness
DO BUGS NEED DRUGS? GRADE ONE Grade One May 2010 GRADE Do Bugs Need Drugs? 1 Overview In this lesson, students review the steps of handwashing and further explore how germs can spread and cause illness
Overcoming Barriers to Antimicrobial Stewardship
 Overcoming Barriers to Antimicrobial Stewardship New guidelines and core elements Learning Objectives: 1) Establish common definitions of infectious and antibiotic stewardship terminology. 2) Define and
Overcoming Barriers to Antimicrobial Stewardship New guidelines and core elements Learning Objectives: 1) Establish common definitions of infectious and antibiotic stewardship terminology. 2) Define and
MRSA Screening (Elective Patients)
 What is MRSA? MRSA stands for Meticillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. It is a type of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (germ) that is very resistant to antibiotics so infections due to MRSA can be quite
What is MRSA? MRSA stands for Meticillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. It is a type of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (germ) that is very resistant to antibiotics so infections due to MRSA can be quite
