Preventing Surgical Site Infections Loretta Litz Fauerbach, Shands Hospital at the University of Florida Sponsored by 3M Canada
|
|
|
- Nicholas French
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Preventing Surgical Site Infections Loretta Litz Fauerbach, MS, CIC Hosted by Paul Webber Sponsored by: 3M Canada Surgical Site Infections (SSIs) General Background 2.6% of 30 million operations complicated by SSIs SSIs second most common healthcare associated infection accounting for 17% of all hospital acquired infections SSIs most common healthcare associated infection in surgical patients (38%) CDC, 2003 Consequences of SSI Increased hospital stay by up to 10 days Increased hospital costs Increased readmission rates Increased pain and suffering Page 1
2 Prevention of SSI: Process MD to treat any existing infection at remote site (urine, bloodstream, etc.) Remove hair only when necessary Do not shave When necessary, use clippers or depilatories Control hyperglycemia Implement preoperative showers- CHG preferred Administer surgical prophylaxis according to guidelines Maintain appropriate oxygenation control Maintain normothermia/control of hypothermia CDC SSI Guideline 1999 CDC Prevention of Surgical Site Infections, Infection Prevention & Control Risk Assessment 30% of SSI are preventable with appropriate use of preoperative antibiotics* *Dellinger EP Page 2
3 Risk Prevention Patient Characteristics Diabetes Nicotine use Steroid Use Malnutrition Prolonged Hospital Stay Pre-operative nares colonization with Staph aureus Peri-operative Transfusions Risk Prevention Operative Characteristics: Preoperative Issues Preoperative antiseptic showering Preoperative hair removal Patient skin prep in the OR Preoperative hand/forearm antisepsis Management of infected or colonized surgical personnel Antimicrobial prophylaxis Peri-Operative Encourage smoking sensation. At a minimum, instruct patient to abstain for a at least 30 days before elective operation from smoking cigarettes, cigars, pipes or any other form of tobacco consumption. Category IB Do not withhold necessary blood products surgical patients as a means to prevent SSI. CategoryIB Page 3
4 Peri-Operative Treat remote site infections prior to elective surgery Category IA Do not remove hair preopertatively unless the hair at or around the incision will interfere with the operation. Category IA If hair is removed remove immediately before the operation, preferably with electric clippers. Category IB Skin Prep Wash site to remove gross contamination Use appropriate antiseptic skin agent Alcohol, CHG, iodine/iodophors, combo agents Concentric circles or manufacturer recommendations for use Risk Prevention Operative characteristics: Intraoperative issues Operating Room environment Ventilation Environmental surfaces Microbial sampling do not do routinely Conventional sterilization of surgical instruments Flash sterilization of surgical instruments Surgical attire and drapes Scrub suits Masks Surgical caps/hoods and shoe covers Sterile gloves Gowns and Drapes Asepsis and surgical technique Asepsis Surgical technique Page 4
5 Intraoperative - OR Environment Ventilation Positive pressure to corridors A minimum of air exchanges per hour Filter air Ceiling supply vents and exhaust near floor Humidity 30-60% Temp F AIA, 2006 Cleaning, Disinfection & Sterilization Environmental cleaning EPA approved hospital disinfectant Patient care equipment and instruments Sterilization Sterilize all surgical instruments according to published guidelines Perform flash sterilization only for patient care items that will be used immediately Do not use flash sterilization for convenience or for inventory control Biological monitoring for sterilizers Rapid readouts 48 hour test Steris Dress Codes & Drapes Gloves Masks Sterile Gowns determine the level of impermeability needed per procedure Shoe covers not infection prevention for SSI but prevents blood contamination Drapes impervious! Page 5
6 Gloving Aspects of Hand Hygiene Wear gloves when contact with blood or other potentially infectious materials, mucous membranes, & nonintact skin could occur. Category IC Change gloves during patient care if moving from a contaminated body site to a clean body site. Category II Remove gloves after caring for a patient. Do not wear the same pair of gloves for the care of more than one patient, Do not wash gloves between uses with different patients. Category IB Sterile Technique Adhere to principles of asepsis Assemble sterile equipment and solutions immediately prior to use. Handle tissues gently, maintain homeostasis, minimize devitalized tissues and foreign bodies and eradicate dead space at the surgical site Use delayed primary skin closure or an incision open to heal by secondary intention if the surgeon considers the surgical site to be heavily contaminated If drainage is necessary, use a closed suction drain. Place a drain through a separate incision distant from the operative incision. Remove the drain as soon as possible. Surgical Hand Hygiene/Antisepsis Use either an antimicrobial soap or alcoholbased handrub Antimicrobial soap: scrub hands and forearms for length of time recommended by manufacturer Alcohol- based handrub: follow manufacturer s recommendations. Before applying, pre- wash hands and forearms with non- antimicrobial soap Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-care Settings. MMWR 2002; vol. 51, no. RR-16. CDC HH slides Page 6
7 Risk Reduction: Antimicrobial Pre- Operative Shower Chlorhexidene Gluconate Primary choice Iodophor Hexachlorophene Risk Prevention Operative Characteristics: Postoperative Issues Incision care Protect with a sterile dressing for 24 to 48 hours postoperatively an incision that has been closed primarily. Wash hands before and after dressing changes any contact with surgical site When an incision dressing must be changed, use sterile technique. Discharge planning Educate the patient and family regarding proper incision care, symptoms of SSI, and the need to report those symptoms Surgical Site Infection: Clinical Signs and Symptoms Febrile? Erythema/redness? Swelling? Warm? Tender? Drainage? (Serosanquinous/purulent) Note: Amount, color, odor of drainage Page 7
8 SSI Surveillance Concepts Issues Surveillance methods Inpatient SSI surveillance Post discharge SSI surveillance Outpatient SSI surveillance Risk stratify patients according to NNIS Surgical wound class, ASA class, and duration of operation Report numbers back to surgical team SENIC Nosocomial Infection Risk Factors: Surgical Site Infections Reoperation Hematoma Obesity Diabetes Contaminated Surgery Abdominal Surgery Prolonged Surgery (>2 hours) Cross-section of abdominal wall depicting CDC classifications of surgical site infection Page 8
9 Classification of the Operative Wound by American College of Surgeons Class I - Clean remove eye/insert implant total knee Class II - Clean-Contaminated removal of tonsils and adenoids cystoscopy, stone removal Class III - Contaminated accidental wound Class IV - Dirty drainage of abdominal mass Unclassified Infection Rate by Class American College of Surgeons Class Infection Rate (%) Class I 1.5 Class II 7.7 Class III 15.2 Class IV 40 Overall 4.7 NNIS Risk Factors: Surgical Site Infections ASA score >3 Class III or Class IV Procedure T= >75 percentile of t for procedure Page 9
10 Physical Status Classification, (ASA) American Society of Anesthesiologist 1 Normally healthy patient 2 Patient with mild systemic disease 3 Patient with severe systemic disease that is not incapacitating 4 Patient with an incapacitating systemic disease that is a constant threat to life 5 Moribund patient who is not expected to survive for 24 hours with or without operation Common SSI Pathogens Staphylococcus aureus Coagulase negative staphylococci Enterococcus sp. E. coli Pseudomonas aeruginosa Enterobacter spp. Proteus mirabilis Klebsiella pneumonia Other Strep species Candida albicans Group D strep (non-enterococci) Other gram-positive aerobes Bacteroides fragilis Surgical Infection Prophylaxis (SIP) Justification Incidence of SSI. Extra-abdominal procedures 2 5%. Intra-abdominal procedures up to 20% Estimated 40-60% of SSI are preventable. Inappropriate use of antibiotics in 25-50% of cases (overuse, underuse, misuse, timing). Page 10
11 SIP Measures SIP 1 timing of prophylactic antibiotics. Patients should receive their prophylactic antibiotics within one hour of skin incision. (Vancomycin and the fluoroquinolones should be started within two hours of incision given their longer infusion times). SIP 2 selection of appropriate prophylactic antibiotics. Patients should receive the appropriate prophylactic antibiotic (as dictated by the current recommendations). SIP 3 cessation of prophylactic antibiotics. The prophylactic antibiotics should be discontinued within 24 hours after surgery with the exception of patients undergoing CABG or other cardiac procedures in which they should be discontinued within 48 hours. Targeted Surgical Procedures Cardiac. Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG). Colon. Hip and knee arthroplasty. Abdominal and vaginal hysterectomy. Vascular surgery. * Common procedures, antibiotics clearly indicated. Timing of Antibiotics Experimental Mode Lesion Size, mm (24 Hours) Penicillin, 40,000 U Control Staph + Penicillin Chloramphenicol, 0.1 mg/kg Control Staph + Chloramphenicol Erythromycin, 0.1 mg/kg Control Tetracycline, 0.1 mg/kg Control Staph + Erythromycin Staph + Tetracycline Age of Lesion at Antibiotic Injection (Hours) Burke JF. Surgery. 1961;50: Page 11
12 Timing of Antibiotics GI Surgery 20% 15% 10% 5% 0% 12 hr Preop 1 hr Preop Postop Placebo Stone HH et al. Ann Surg. 1976;184: Timing of Antibiotics Cardiac Surgery 4 Infections (%) Infections (%) < >5 Hours from Incision Hours from Incision Classen, et al. N Engl J Med. 1992;328: Page 12
13 Surgical Procedure Cardiac or Vascular Hip/Knee Arthroplasty Colon Hysterectomy Approved Antibiotics at Shands UF Cefazolin β lactam allergy or other risk factors*: Vancomycin Cefazolin β lactam allergy or other risk factors*: Vancomycin ORAL: Neomycin Sulfate + Erythromycin base PARENTERAL: Cefoxitin OR Cefazolin + Metronidazole β lactam allergy: Levofloxacin + Metronidazole Cefazolin OR Cefoxitin β lactam allergy: Clindamycin *Risk factors for vancomycin - Hospital stay > 24 hrs, MRSA colonization, hospitalized or in LCTF in past year, chronic HD or wound care, other. Duration of Antibiotic Prophylaxis Most studies confirmed efficacy of 12 hrs. Many confirm efficacy of a single dose. Shorter course results in less antibiotic resistance. Systemic review- single vs Multiple dose prophylaxis showed no benefit McDonald. Aust NZ J Surg 1998;68:388 Page 13
14 Surgical Care Improvement Project Partnership of providers and national organizations (CMS, CDC, ACS, others). Opportunity to improve surgical care beyond surgical site infection. SCIP goal To reduce preventable surgical morbidity and mortality 25% by SCIP Justification Incidence of complications. Noncardiac surgery 6%. High- risk surgical procedures 30% Sequelae of postoperative complications. Increased length of stay. Increased hospital costs. Increased mortality. SCIP Justification Annual estimated opportunities among Medicare beneficiaries undergoing major surgical procedures. 271,055 perioperative complications. 13,027 perioperative deaths. Page 14
15 SCIP SSI Prevention 2006 SIP measures (Initial Measures) Timing of prophylactic antibiotics. Appropriate prophylactic antibiotics. Cessation of prophylactic antibiotics. Blood glucose control in cardiac surgery patients (6 AM glucose < 200 mg/dl on POD 1, 2). Proper hair removal (clippers, depilatory or none). Normothermia in colorectal surgery patients (temp ⁰ F first postoperative hour). SCIP Modules Surgical site infection prevention. Venous thromboembolism prevention. Cardiac events prevention. Respiratory complication prevention. NISQIP 30 Day Complications Complication Surgical site infection Pneumonia Failure to wean < 48 hours Unplanned intubation Urinary tract infection Systemic sepsis Wound dehiscence Cardiac arrest Prolonged ileus Acute myocardial infarction Progressive renal insufficiency Bleeding Renal failure Deep vein thrombosis Graft/prosthesis failure Stroke Pulmonary embolism Coma % Best WR, et a. J Am Coll Surg. 2002;194: Page 15
16 Glucose Control Cardiac Surgery Latham R, et al. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol Proper Hair Removal Razors induce small skin lacerations. Potential sites for infection. Disturbs hair follicles colonized with S. aureus. Risk greatest when done the night before. Hair Removal Method Shaving vs Clipping Hair Removal Method Shaved with razor Clipped Electric razor Not shaved, not clipped Depilatories Clean Wound Infection Rate (%) Cruce and Forde, 1981 The increased risk with shaving prior to the operation is associated with microscopic cuts and shaving immediately before seriously reduces the SSI risk ( 20% risk if shaved > 24hrs--CDC, 1999). Page 16
17 Normothermia Colorectal Surgery Experimental design (N = 200) Control - routine care (mean 34.7 C) Treatment - active warming (mean 36.6 C) Results Control - 19% SSI (18/96) Treatment - 6% SSI (6/104), P=0.009 Kurz A, et al. N Engl J Med Surgical Care Improvement Project Implementation Communication is KEY! Set up system to assure delivery of antibiotics at right dose, right time and right stop time Outline steps and pathways for success Document no shaving Establish aggressive glucose control protocol ICU and on units Portland protocol or develop your own Surgical Site Infections: Proper Skin Prep through No Shaving & Pre-Operative Antimicrobial Showering- The Keys to Prevention Reduce risk of surgical site infections by 1. Educating healthcare providers to improve understanding and compliance with no shaving and pre-operative showering protocols as well as other ways to prevent Surgical Site Infections 2. Educating and providing patient with tools to understand the need not to shave and how to perform pre-op showering 3. Improving documentation of these activities 4. Monitoring surgical site infections and noting impact of these activities and report to OR and surgical staff Page 17
18 Education via Patient Safety Handout Points Discussed / Questions asked in Handout: -Will I receive and antibiotic prior to surgery? -Should I take a shower with antibacterial soap or shave prior to surgery? Infection Control Tips: -Keep your hands clean -Do not hesitate to ask your healthcare provider if he/she has washed their hands -Cover your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze. Discard the tissue and then clean your hands -Safely care for wounds and catheters by learning proper aseptic or clean techniques -Handle needles and other sharp items safely and discard into a sharps container to prevent injury to you and others SSI Prevention Guidelines Preparation of Patient Category 1A: Do Not Remove Hair at the incision site, unless it will interfere with surgery itself. If the hair must be removed, do it directly beforehand, preferably with electric clippers. Category 1B: Pre-surgical patients should perform an antiseptic shower at least the night before and preferably also the morning of the scheduled surgery. Wash and clean the incision site area, scrubbing lightly to remove any gross skin contamination prior to antiseptic surgical preparation. CDC, 1999 Preoperative Showering Info Preoperative shower or bath with CHG reduces skin microbial counts more effectively than povidone- iodine or other antimicrobial soaps Bathing 2 times with CHG (once the evening before & then the morning of ) is recommended to increase effectiveness. Develop and provide bathing instructions for patients Develop education and visual reminders for staff to provide information to patient Page 18
19 Patient Preoperative Shower Packet The packet given in the clinics or during preop testing should contain: -Instruction sheet -Patient Safety Handout -Packet or container with Hibiclens or other CHG product Other areas for pre-operative showering: -Pre-op Admissions or Pre-Op Holding Area -Pre-admission on a floor or ICU Documentation of pre-operative showering: -Pre-op nursing notes in holding area -Clinic notes -Transplant coordinator notes -Unit nurse who assisted with bath Summary No Shaving/Pre- operative showering is an important patient safety activity to reduce the risk of post operative infections Healthcare providers preparing a patient for surgery should provide education. Please provide a CHG product for the patient to use at home or in the hospital for a shower the night before and the morning of the procedure Remember to document education and record the patient s report of not saving and pre- op showering. Summary/Conclusions There are significant opportunities for improvement in surgical care. SIP and SCIP represent broad national commitment to improve quality. Hospitals and health care providers are encouraged to participate in these efforts. Page 19
20 References CDC Prevention of Surgical Site Infections, Altemeir WA, Burke JF, Pruitt, BA, Sandusky,WR and the American College of Surgeons, Committee on Control of Surgical Infections of the Committee on Pre-and Postoperative Care. Manual on Control of Infection in Surgical Patients.Second Edition. JB Lippincott Company. Philadelphia Janelle J, Howard, RJ, and Fry D. Chapter 23 Surgical Site Infections. APIC Text of Infection Control and Epidemiology, 2nd Edition, Mangram AJ, Horan TC, Person ML, Silver LC, Jarvis WR. The Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Guideline for prevention of surgical site infection. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology 1999;20: LeFrock, SHEA Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, Bratzler, DW. Surgical Infection Prevention and Surgical Care Improvement: National Initiatives to Improve Care for Medicare Patients Teleclass Schedule Page 20
Patient Preparation. Surgical Team
 January 2019 www.nursingcenter.com Surgical Site Infection Prevention Surgical site infections (SSIs) are one of the most common and costly healthcare-associated infections in the United States (Smith
January 2019 www.nursingcenter.com Surgical Site Infection Prevention Surgical site infections (SSIs) are one of the most common and costly healthcare-associated infections in the United States (Smith
Developed by Kathy Wonderly RN, MSEd,CPHQ Developed: October 2009 Most recently updated: December 2014
 Developed by Kathy Wonderly RN, MSEd,CPHQ Developed: October 2009 Most recently updated: December 2014 The Center for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) is moving away from collecting data on the process of care
Developed by Kathy Wonderly RN, MSEd,CPHQ Developed: October 2009 Most recently updated: December 2014 The Center for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) is moving away from collecting data on the process of care
The role of Infection Control Nurse in Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI) April 2013
 The role of Infection Control Nurse in Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI) April 2013 Impact of SSI 2 nd common health- care associated infection (HCAI) 14-16% of HCAI Post operation SSI prolong
The role of Infection Control Nurse in Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI) April 2013 Impact of SSI 2 nd common health- care associated infection (HCAI) 14-16% of HCAI Post operation SSI prolong
Preventing Surgical Site Infections. Edward L. Goodman, MD September 16, 2013
 Preventing Surgical Site Infections Edward L. Goodman, MD September 16, 2013 Outline NHSN Reporting and Definitions Magnitude of the Problem Risk Factors Non Pharmacologic Interventions Pharmacologic Interventions
Preventing Surgical Site Infections Edward L. Goodman, MD September 16, 2013 Outline NHSN Reporting and Definitions Magnitude of the Problem Risk Factors Non Pharmacologic Interventions Pharmacologic Interventions
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis in the Surgical Patient. M. J. Osgood
 Antimicrobial Prophylaxis in the Surgical Patient M. J. Osgood Outline Definitions surgical site infection (SSI) Risk factors Wound classification Microbiology of SSIs Strategies for prevention of SSIs
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis in the Surgical Patient M. J. Osgood Outline Definitions surgical site infection (SSI) Risk factors Wound classification Microbiology of SSIs Strategies for prevention of SSIs
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis in Digestive Surgery
 Antimicrobial Prophylaxis in Digestive Surgery Toar JM. Lalisang, MD, PhD Digestive Surgery Division Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital Medical Faculty Universitas Indonesia Antibiotic must be present before
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis in Digestive Surgery Toar JM. Lalisang, MD, PhD Digestive Surgery Division Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital Medical Faculty Universitas Indonesia Antibiotic must be present before
Surgical Site Infection (SSI) Prevention: The Latest, Greatest and Unanswered Questions
 Surgical Site Infection (SSI) Prevention: The Latest, Greatest and Unanswered Questions Keith S. Kaye, MD, MPH Corporate Vice President of Quality and Patient Safety Corporate Medical Director, Infection
Surgical Site Infection (SSI) Prevention: The Latest, Greatest and Unanswered Questions Keith S. Kaye, MD, MPH Corporate Vice President of Quality and Patient Safety Corporate Medical Director, Infection
Beyond SCIP: Leading the Way to SSI Reduction. House Keeping. House Keeping. Questions. Dianne Rawson, RN, MA Hugo, MN May 14, 2013
 3M Learning Connection 5/7/2013 3M Infection Prevention Solutions Learning Connection Beyond SCIP: Leading the Way to SSI Reduction Dianne Rawson, RN, MA Hugo, MN May 14, 2013 2012. All Rights Reserved.
3M Learning Connection 5/7/2013 3M Infection Prevention Solutions Learning Connection Beyond SCIP: Leading the Way to SSI Reduction Dianne Rawson, RN, MA Hugo, MN May 14, 2013 2012. All Rights Reserved.
Prevention of Surgical Site Infection 2017 Guidelines & Antimicrobial Stewardship
 Prevention of Surgical Site Infection 2017 Guidelines & Antimicrobial Stewardship Phenelle Segal RN, CIC, FAPIC President Infection Control Consulting Services www.iccs home.com 215 692 3485 info@iccs
Prevention of Surgical Site Infection 2017 Guidelines & Antimicrobial Stewardship Phenelle Segal RN, CIC, FAPIC President Infection Control Consulting Services www.iccs home.com 215 692 3485 info@iccs
Prevention of Perioperative Surgical Infections
 Prevention of Perioperative Surgical Infections Michael A. West, MD, PhD, FACS Department of Surgery University California San Francisco San Francisco, CA, USA Surgical Site Infections (SSI) 2-5% of operated
Prevention of Perioperative Surgical Infections Michael A. West, MD, PhD, FACS Department of Surgery University California San Francisco San Francisco, CA, USA Surgical Site Infections (SSI) 2-5% of operated
Conflict of interest: We have no conflict of interest to report on this topic of SSI reduction for total knees.
 Reducing SSI- Knees TIFFANY KENNERK MBA, MSN, RN, NE -BC, ONC CYNTHIA SEAMAN BSN, RN, ONC, CMSRN ~COMMUNITY HOSPITALS AND WELLNESS CENTERS~ Conflict of interest: We have no conflict of interest to report
Reducing SSI- Knees TIFFANY KENNERK MBA, MSN, RN, NE -BC, ONC CYNTHIA SEAMAN BSN, RN, ONC, CMSRN ~COMMUNITY HOSPITALS AND WELLNESS CENTERS~ Conflict of interest: We have no conflict of interest to report
Learning Objectives:
 Preventing Surgical Site Infections (SSI) Learning Objectives: Discuss risk factors for surgical site infections in healthcare settings. Review current strategies and emerging guidelines for SSI prevention.
Preventing Surgical Site Infections (SSI) Learning Objectives: Discuss risk factors for surgical site infections in healthcare settings. Review current strategies and emerging guidelines for SSI prevention.
2006 COURSE TITLE: Preventing Surgical Site Infections
 COURSE INTRODUCTION It has been approximately 150 years since Joseph Lister introduced the principles of asepsis and Louis Pasteur conducted research that confirmed the germ theory. One would think that
COURSE INTRODUCTION It has been approximately 150 years since Joseph Lister introduced the principles of asepsis and Louis Pasteur conducted research that confirmed the germ theory. One would think that
Proc. related Joseph Lister - antiseptic principles Zoutman et al Inf Contr Hosp Epi 1999
 Dick Zoutman, MD, FRCPC Queen s University School of Medicine & Kingston General Hospital, Kingston, Ontario, Canada Hosted by Paul Webber paul@webbertraining.com www.webbertraining.com Practical Meaning
Dick Zoutman, MD, FRCPC Queen s University School of Medicine & Kingston General Hospital, Kingston, Ontario, Canada Hosted by Paul Webber paul@webbertraining.com www.webbertraining.com Practical Meaning
In an effort to help reduce surgical site infections, Surgical Services associates will be expected to observe the following guidelines:
 To: Dept. of Surgery Associates From: Gloria Karr, Dir. Infection Prevention Date: May, 2012 Re: Guidelines for Infection Control in In an effort to help reduce surgical site infections, Surgical Services
To: Dept. of Surgery Associates From: Gloria Karr, Dir. Infection Prevention Date: May, 2012 Re: Guidelines for Infection Control in In an effort to help reduce surgical site infections, Surgical Services
Prevention of Perioperative Surgical Infections
 Prevention of Perioperative Surgical Infections Michael A. West, MD, PhD, FACS Department of Surgery University California San Francisco San Francisco, CA, USA Surgical Site Infections (SSI) 2-5% of operated
Prevention of Perioperative Surgical Infections Michael A. West, MD, PhD, FACS Department of Surgery University California San Francisco San Francisco, CA, USA Surgical Site Infections (SSI) 2-5% of operated
Antibiotic prophylaxis guideline for colorectal, hepatobiliary and vascular surgery for adult patients.
 Antibiotic prophylaxis guideline for colorectal, hepatobiliary and vascular surgery for adult patients. Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience,
Antibiotic prophylaxis guideline for colorectal, hepatobiliary and vascular surgery for adult patients. Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience,
Reducing Infections in Surgical Practice. Fred A Sweet, MD Rockford Spine Center Illinois, USA
 Reducing Infections in Surgical Practice Fred A Sweet, MD Rockford Spine Center Illinois, USA Introduction: How bacteria get in The Host The Surgeon The Procedure The STAFF Skin PREP Prophylactic Antibiotics
Reducing Infections in Surgical Practice Fred A Sweet, MD Rockford Spine Center Illinois, USA Introduction: How bacteria get in The Host The Surgeon The Procedure The STAFF Skin PREP Prophylactic Antibiotics
SURGICAL ANTIBIOTIC PROPHYLAXIS GUIDELINES WITHIN ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY FOR ADULT PATIENTS
 SURGICAL ANTIBIOTIC PROPHYLAXIS GUIDELINES WITHIN ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY FOR ADULT PATIENTS Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if
SURGICAL ANTIBIOTIC PROPHYLAXIS GUIDELINES WITHIN ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY FOR ADULT PATIENTS Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if
Prophylactic antibiotic timing and dosage. Dr. Sanjeev Singh AIMS, Kochi
 Prophylactic antibiotic timing and dosage Dr. Sanjeev Singh AIMS, Kochi Meaning - Webster Medical Definition of prophylaxis plural pro phy lax es \-ˈlak-ˌsēz\play : measures designed to preserve health
Prophylactic antibiotic timing and dosage Dr. Sanjeev Singh AIMS, Kochi Meaning - Webster Medical Definition of prophylaxis plural pro phy lax es \-ˈlak-ˌsēz\play : measures designed to preserve health
PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTION
 PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTION Montreal, March 29 2011 Chantal Bellerose P. Dt., BScHN, M.Sc. Adm Claude Laflamme MD, FRCPC, MHSC(c) Sandra Savery BScN, M.Sc.Adm Disclosure Financial disclosure:
PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTION Montreal, March 29 2011 Chantal Bellerose P. Dt., BScHN, M.Sc. Adm Claude Laflamme MD, FRCPC, MHSC(c) Sandra Savery BScN, M.Sc.Adm Disclosure Financial disclosure:
Prevention of Surgical Site Infections
 Prevention of Surgical Site Infections A Review of Recent Evidence and Guidelines Dale W. Bratzler, DO, MPH, MACOI, FIDSA Professor and Associate Dean, College of Public Health Professor, College of Medicine
Prevention of Surgical Site Infections A Review of Recent Evidence and Guidelines Dale W. Bratzler, DO, MPH, MACOI, FIDSA Professor and Associate Dean, College of Public Health Professor, College of Medicine
Prevention of Surgical Site Infections
 Prevention of Surgical Site Infections Adverse Clinical and Economic Outcomes Attributable to Surgical Site Infections Cohort Study Madhuri M. Sopirala, MD The Ohio State University Medical Center Engemann
Prevention of Surgical Site Infections Adverse Clinical and Economic Outcomes Attributable to Surgical Site Infections Cohort Study Madhuri M. Sopirala, MD The Ohio State University Medical Center Engemann
Perioperative Infection. Surgical site infections: How to prevent them. Surgical site infections
 Surgical site infections: How to prevent them Raghuvender Ganta MD, FRCA. Associate Professor, Anesthesiology Adjunct Associate Professor, OUMC Director Pain Management, VAMC Surgical site infections 17%
Surgical site infections: How to prevent them Raghuvender Ganta MD, FRCA. Associate Professor, Anesthesiology Adjunct Associate Professor, OUMC Director Pain Management, VAMC Surgical site infections 17%
Gynaecological Surgery in Adults Surgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis
 Gynaecological Surgery in Adults Surgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date
Gynaecological Surgery in Adults Surgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date
Overview of Infection Control and Prevention
 Overview of Infection Control and Prevention Review of the Cesarean-section Antibiotic Prophylaxis Program in Jordan and Workshop on Rational Medicine Use and Infection Control Terry Green and Salah Gammouh
Overview of Infection Control and Prevention Review of the Cesarean-section Antibiotic Prophylaxis Program in Jordan and Workshop on Rational Medicine Use and Infection Control Terry Green and Salah Gammouh
Surgical Site Infections (SSIs)
 Surgical Site Infections (SSIs) Postoperative infections presenting at any level Incisional superficial (skin, subcutaneous tissue) Incisional deep (fascial plane and muscles) Organ/space related (anatomic
Surgical Site Infections (SSIs) Postoperative infections presenting at any level Incisional superficial (skin, subcutaneous tissue) Incisional deep (fascial plane and muscles) Organ/space related (anatomic
During the second half of the 19th century many operations were developed after anesthesia
 Continuing Education Column Surgical Site Infection and Surveillance Tae Jin Lim, MD Department of Surgery, Keimyung University College of Medicine E mail : tjlim@dsmc.or.kr J Korean Med Assoc 2007; 50(10):
Continuing Education Column Surgical Site Infection and Surveillance Tae Jin Lim, MD Department of Surgery, Keimyung University College of Medicine E mail : tjlim@dsmc.or.kr J Korean Med Assoc 2007; 50(10):
Treatment of Surgical Site Infection Meeting Quality Statement 6. Prof Peter Wilson University College London Hospitals
 Treatment of Surgical Site Infection Meeting Quality Statement 6 Prof Peter Wilson University College London Hospitals TEG Quality Standard 6 Treatment and effective antibiotic prescribing: People with
Treatment of Surgical Site Infection Meeting Quality Statement 6 Prof Peter Wilson University College London Hospitals TEG Quality Standard 6 Treatment and effective antibiotic prescribing: People with
Prevention of surgical site infections (SSI) nosocomial infection * - Lead to prolonged hospital stay and increased coasts
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Surgery Birgit Ross, MD Dep. of Hospital Hygiene University Hospital and Clinics, Essen Prevention of surgical site infections (SSI) - Surgical site infections account for approximately
Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Surgery Birgit Ross, MD Dep. of Hospital Hygiene University Hospital and Clinics, Essen Prevention of surgical site infections (SSI) - Surgical site infections account for approximately
Antimicrobial prophylaxis. Bs Lưu Hồ Thanh Lâm Bv Nhi Đồng 2
 Antimicrobial prophylaxis Bs Lưu Hồ Thanh Lâm Bv Nhi Đồng 2 Definition The United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has developed criteria that define surgical site infection (SSI)
Antimicrobial prophylaxis Bs Lưu Hồ Thanh Lâm Bv Nhi Đồng 2 Definition The United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has developed criteria that define surgical site infection (SSI)
Antimicrobial Selection and Therapy for Equine Musculoskeletal Trauma
 Antimicrobial Selection and Therapy for Equine Musculoskeletal Trauma Lucio Petrizzi DVM DECVS Università degli Studi di Teramo Surgical site infections (SSI) Microbial contamination unavoidable Infection
Antimicrobial Selection and Therapy for Equine Musculoskeletal Trauma Lucio Petrizzi DVM DECVS Università degli Studi di Teramo Surgical site infections (SSI) Microbial contamination unavoidable Infection
Scottish Surveillance of Healthcare Infection Programme (SSHAIP) Health Protection Scotland SSI Surveillance Protocol 7th Edition 2017 Question &
 Contents General... 4 Pre-op... 4 Peri-op... 5 Post-op... 8 Caesarean Section... 12 Orthopaedics... 14 Large Bowel:... 15 Vascular... 17 General Pre-op Q: If a patient is an emergency admission is the
Contents General... 4 Pre-op... 4 Peri-op... 5 Post-op... 8 Caesarean Section... 12 Orthopaedics... 14 Large Bowel:... 15 Vascular... 17 General Pre-op Q: If a patient is an emergency admission is the
CURRENT CONCEPTS IN THE PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS
 CURRENT CONCEPTS IN THE PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS Walter L. Biffl, M.D. Assistant Director, Patient Quality and Safety Denver Health Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery University
CURRENT CONCEPTS IN THE PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS Walter L. Biffl, M.D. Assistant Director, Patient Quality and Safety Denver Health Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery University
 1) Mangram AJ,Horan TC,Pearson ML, et al:guideline for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection.Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 1999;20:247-278. 1a) Perl TM, Cullen JJ, Wenzel RP, et al.: Intranasal mupirocin
1) Mangram AJ,Horan TC,Pearson ML, et al:guideline for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection.Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 1999;20:247-278. 1a) Perl TM, Cullen JJ, Wenzel RP, et al.: Intranasal mupirocin
Neurosurgery Antibiotic Prophylaxis Guideline
 Neurosurgery Antibiotic Prophylaxis Guideline Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date (when this version
Neurosurgery Antibiotic Prophylaxis Guideline Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date (when this version
NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE. Measure Information Form Collected For: CMS Voluntary Only
 Last Updated: Version 4.4a NQF-ENORSE VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANARS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Information Form Collected For: CMS Voluntary Only Measure Set: Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) Set
Last Updated: Version 4.4a NQF-ENORSE VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANARS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Information Form Collected For: CMS Voluntary Only Measure Set: Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) Set
The surgical site infection risk in developing countries. Yves BUISSON Société de Pathologie Exotique
 The surgical site infection risk in developing countries Yves BUISSON Société de Pathologie Exotique Surgical site infections Health-care-associated infections occurring within 30 days after surgery, or
The surgical site infection risk in developing countries Yves BUISSON Société de Pathologie Exotique Surgical site infections Health-care-associated infections occurring within 30 days after surgery, or
Responders as percent of overall members in each category: Practice: Adult 490 (49% of 1009 members) 57 (54% of 106 members)
 Infectious Diseases Society of America Emerging Infections Network 6/2/10 Report for Query: Perioperative Staphylococcus aureus Screening and Decolonization Overall response rate: 674/1339 (50.3%) physicians
Infectious Diseases Society of America Emerging Infections Network 6/2/10 Report for Query: Perioperative Staphylococcus aureus Screening and Decolonization Overall response rate: 674/1339 (50.3%) physicians
CURRENT CONCEPTS IN THE PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS
 CURRENT CONCEPTS IN THE PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS Walter L. Biffl, M.D. Director, Surgical Quality Denver Health Medical Center Professor of Surgery University of Colorado SURGICAL INFECTIONS
CURRENT CONCEPTS IN THE PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS Walter L. Biffl, M.D. Director, Surgical Quality Denver Health Medical Center Professor of Surgery University of Colorado SURGICAL INFECTIONS
Preventing Surgical Site Infections
 Preventing Surgical Site Infections BC Hip & Knee Arthroplasty Collaborative February 7, 2006 Felicia Laing, BSc MSc CIC, Infection Control Anisha Lakhani, BScPharm Pharm D Fraser Health Authority It s
Preventing Surgical Site Infections BC Hip & Knee Arthroplasty Collaborative February 7, 2006 Felicia Laing, BSc MSc CIC, Infection Control Anisha Lakhani, BScPharm Pharm D Fraser Health Authority It s
Use And Misuse Of Antibiotics In Neurosurgery
 Use And Misuse Of Antibiotics In Neurosurgery CSF infection in the United States after neurosurgery from 1992 to 2003 0.86% to 2.32% * *National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System: National Nosocomial
Use And Misuse Of Antibiotics In Neurosurgery CSF infection in the United States after neurosurgery from 1992 to 2003 0.86% to 2.32% * *National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System: National Nosocomial
Summary of major changes
 1 Summary of major changes The first SSI surveillance protocol was produced in 2002. Changes have been applied, either based on the issue of Scottish Government directives or to align Scotland s SSI surveillance
1 Summary of major changes The first SSI surveillance protocol was produced in 2002. Changes have been applied, either based on the issue of Scottish Government directives or to align Scotland s SSI surveillance
So Why All the Fuss About Hand Hygiene?
 CARING PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, INC. HAND HYGIENE In-Service So Why All the Fuss About Hand Hygiene? Most common mode of transmission of pathogens is via hands! Infections acquired in healthcare Spread of
CARING PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, INC. HAND HYGIENE In-Service So Why All the Fuss About Hand Hygiene? Most common mode of transmission of pathogens is via hands! Infections acquired in healthcare Spread of
03/09/2014. Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course. Talk outline
 Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course 2014 What is healthcare-associated infection (HCAI), antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs)? Why we should be worried?
Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course 2014 What is healthcare-associated infection (HCAI), antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs)? Why we should be worried?
VCH PHC SURGICAL PROPHYLAXIS RECOMMENDATIONS
 VCH PHC SURGICAL PROPHYLAXIS RECOMMENDATIONS CARDIAC Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, except for For patients with known MRSA colonization, recommend decolonization with Antimicrobial Photodynamic
VCH PHC SURGICAL PROPHYLAXIS RECOMMENDATIONS CARDIAC Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, except for For patients with known MRSA colonization, recommend decolonization with Antimicrobial Photodynamic
SHC Surgical Antimicrobial Prophylaxis Guidelines
 SHC Surgical Antimicrobial Prophylaxis Guidelines I. Purpose/Background This document is based upon the 2013 consensus guidelines from American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP), the Infectious
SHC Surgical Antimicrobial Prophylaxis Guidelines I. Purpose/Background This document is based upon the 2013 consensus guidelines from American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP), the Infectious
Antimicrobial Stewardship. We cannot afford to go back
 Antimicrobial Stewardship We cannot afford to go back Objectives What is antimicrobial stewardship? Why the concern over antibiotic resistance? Discuss the role and use of antibacterial medical devices
Antimicrobial Stewardship We cannot afford to go back Objectives What is antimicrobial stewardship? Why the concern over antibiotic resistance? Discuss the role and use of antibacterial medical devices
Measure Information Form
 Release Notes: Measure Information Form Version 2.4 **NQF-NORS VOLUNTARY CONSNSUS STANARS FOR HOSPITAL CAR** Measure Information Form Measure Set: Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) Set Measure I
Release Notes: Measure Information Form Version 2.4 **NQF-NORS VOLUNTARY CONSNSUS STANARS FOR HOSPITAL CAR** Measure Information Form Measure Set: Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) Set Measure I
Systemic Antimicrobial Prophylaxis Issues
 Systemic Antimicrobial Prophylaxis Issues Pierre Moine Department of Anesthesiology University of Colorado Denver 3 rd International Conference on Surgery and Anesthesia OMICs Group Conference The Surgical
Systemic Antimicrobial Prophylaxis Issues Pierre Moine Department of Anesthesiology University of Colorado Denver 3 rd International Conference on Surgery and Anesthesia OMICs Group Conference The Surgical
2017 SURVEILLANCE OF SURGICAL SITES INFECTIONS FOLLOWING TOTAL HIP AND KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program 2017 SURVEILLANCE OF SURGICAL SITES INFECTIONS FOLLOWING TOTAL HIP AND KNEE ARTHROPLASTY FINAL Working Group: E. Henderson, M. John, I. Davis, S. Dunford,
Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program 2017 SURVEILLANCE OF SURGICAL SITES INFECTIONS FOLLOWING TOTAL HIP AND KNEE ARTHROPLASTY FINAL Working Group: E. Henderson, M. John, I. Davis, S. Dunford,
Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections. For National Patient Safety Goal
 Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections For National Patient Safety Goal 07.03.01 2009 Methicillin Resistant Staphlococcus aureus (MRSA) About 3-8% of the population at large is a carrier
Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections For National Patient Safety Goal 07.03.01 2009 Methicillin Resistant Staphlococcus aureus (MRSA) About 3-8% of the population at large is a carrier
Measure Information Form
 Release Notes: Measure Information Form Version 2.0 **NQF-NDORSD VOLUNTRY CONSNSUS STNDRDS FOR HOSPITL CR** Measure Information Form Measure Set: Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) Set Measure ID
Release Notes: Measure Information Form Version 2.0 **NQF-NDORSD VOLUNTRY CONSNSUS STNDRDS FOR HOSPITL CR** Measure Information Form Measure Set: Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) Set Measure ID
Infection Control for the Surgeon
 Infection Control for the Surgeon Gonzalo Bearman, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine & Epidemiology Associate Hospital Epidemiologist Michael Edmond, MD, MPH, MPA Professor of Internal Medicine
Infection Control for the Surgeon Gonzalo Bearman, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine & Epidemiology Associate Hospital Epidemiologist Michael Edmond, MD, MPH, MPA Professor of Internal Medicine
NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE. Measure Information Form Collected For: CMS Voluntary Only
 Last Updated: Version 4.4a NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Infmation Fm Collected F: CMS Voluntary Only Measure Set: Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) Set Measure
Last Updated: Version 4.4a NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Infmation Fm Collected F: CMS Voluntary Only Measure Set: Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) Set Measure
Measure Information Form
 Release Notes: Measure Information Form Version 2.0 **NQF-ENDORSED VOUNTRY CONSENSUS STNDRDS FOR HOSPIT CRE** Measure Information Form Measure Set: Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) Set Measure
Release Notes: Measure Information Form Version 2.0 **NQF-ENDORSED VOUNTRY CONSENSUS STNDRDS FOR HOSPIT CRE** Measure Information Form Measure Set: Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) Set Measure
Infection Prevention Highlights for the Medical Staff. Pamela Rohrbach MSN, RN, CIC Director of Infection Prevention
 Highlights for the Medical Staff Pamela Rohrbach MSN, RN, CIC Director of Infection Prevention Standard Precautions every patient every time a. Hand Hygiene b. Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Highlights for the Medical Staff Pamela Rohrbach MSN, RN, CIC Director of Infection Prevention Standard Precautions every patient every time a. Hand Hygiene b. Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Management and Prevention of. Infection in Orthopedic Surgical Procedures
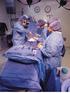 Management and Prevention of Infection in Orthopedic Surgical Procedures by Amy Broussard, CST, CFA In orthopedic operating rooms, even one surgical-site infection is too many. In today s operating rooms,
Management and Prevention of Infection in Orthopedic Surgical Procedures by Amy Broussard, CST, CFA In orthopedic operating rooms, even one surgical-site infection is too many. In today s operating rooms,
Horizontal vs Vertical Infection Control Strategies
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL Chapter 14 Horizontal vs Vertical Infection Control Strategies Author Salma Abbas, MBBS Michael Stevens, MD, MPH Chapter Editor Shaheen Mehtar, MBBS. FRC Path,
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL Chapter 14 Horizontal vs Vertical Infection Control Strategies Author Salma Abbas, MBBS Michael Stevens, MD, MPH Chapter Editor Shaheen Mehtar, MBBS. FRC Path,
General Surgery Small Group Activity (Facilitator Notes) Curriculum for Antimicrobial Stewardship
 General Surgery Small Group Activity (Facilitator Notes) Curriculum for Antimicrobial Stewardship Facilitator instructions: Read through the facilitator notes and make note of discussion points for each
General Surgery Small Group Activity (Facilitator Notes) Curriculum for Antimicrobial Stewardship Facilitator instructions: Read through the facilitator notes and make note of discussion points for each
An Evidence Based Approach to Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Oral Surgery
 An Evidence Based Approach to Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Oral Surgery Nicholas Makhoul DMD. MD. FRCD(C). Dip ABOMS. FACS. Director, Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Assistant Professor McGill
An Evidence Based Approach to Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Oral Surgery Nicholas Makhoul DMD. MD. FRCD(C). Dip ABOMS. FACS. Director, Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Assistant Professor McGill
Top Ten Articles Infection Prevention and Control
 Top Ten Articles Infection Prevention and Control 2017-2018 John M Conly MD Chingiz Amirov Just wash em! May 2018 Objectives Research or evidence-based guidelines in IPC Critique strengths and weaknesses
Top Ten Articles Infection Prevention and Control 2017-2018 John M Conly MD Chingiz Amirov Just wash em! May 2018 Objectives Research or evidence-based guidelines in IPC Critique strengths and weaknesses
This is the use of antibiotics before, during and after a diagnostic, therapeutic or surgical procedure to prevent infectious complications.
 Antibiotic prophylaxis in surgery CSu2 Policy Antimicrobial prophylaxis is used to reduce the incidence of post operative wound infection; patients undergoing procedures associated with high infection
Antibiotic prophylaxis in surgery CSu2 Policy Antimicrobial prophylaxis is used to reduce the incidence of post operative wound infection; patients undergoing procedures associated with high infection
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Bennett-Guerrero E, Pappas TN, Koltun WA, et al. Gentamicin
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Bennett-Guerrero E, Pappas TN, Koltun WA, et al. Gentamicin
Antibiotic Prophylaxis Update
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis Update Choosing Surgical Antimicrobial Prophylaxis Peri-Procedural Administration Surgical Prophylaxis and AMS at Epworth HealthCare Mr Glenn Valoppi Dr Trisha Peel Dr Joseph Doyle
Antibiotic Prophylaxis Update Choosing Surgical Antimicrobial Prophylaxis Peri-Procedural Administration Surgical Prophylaxis and AMS at Epworth HealthCare Mr Glenn Valoppi Dr Trisha Peel Dr Joseph Doyle
Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Spinal Surgery Antibiotic Guidelines. Contents
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Spinal Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine Unique
Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Spinal Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine Unique
Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance and Healthcare-associated Infections in Europe
 Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance and Healthcare-associated Infections in Europe Carl Suetens, ECDC Presented by Håkan Hanberger ecdc.europa.eu Message/Questions from C Suetens to Workshop 7, MIE2009
Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance and Healthcare-associated Infections in Europe Carl Suetens, ECDC Presented by Håkan Hanberger ecdc.europa.eu Message/Questions from C Suetens to Workshop 7, MIE2009
Animal Studies Committee Policy Rodent Survival Surgery
 Animal Studies Committee Policy Rodent Survival Surgery ASC Policy: To optimize animal health and well-being, survival surgery in rodents must be performed using sterile instruments, surgical gloves, masks
Animal Studies Committee Policy Rodent Survival Surgery ASC Policy: To optimize animal health and well-being, survival surgery in rodents must be performed using sterile instruments, surgical gloves, masks
Chapter Anaerobic infections (individual fields): prevention and treatment of postoperative infections
 J Infect Chemother (2011) 17 (Suppl 1):62 66 DOI 10.1007/s10156-010-0141-x GUIDELINES Chapter 2-5-1. Anaerobic infections (individual fields): prevention and treatment of postoperative infections Ó Japanese
J Infect Chemother (2011) 17 (Suppl 1):62 66 DOI 10.1007/s10156-010-0141-x GUIDELINES Chapter 2-5-1. Anaerobic infections (individual fields): prevention and treatment of postoperative infections Ó Japanese
Perioperative Care of Swine
 Swine are widely used in protocols that involve anesthesia and invasive surgical procedures. In order to ensure proper recovery of animals, preoperative, intraoperative and postoperative techniques specific
Swine are widely used in protocols that involve anesthesia and invasive surgical procedures. In order to ensure proper recovery of animals, preoperative, intraoperative and postoperative techniques specific
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times
 Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
The Impact of Timing, Selection, and Dosage of Preoperative Prophylactic Antibiotics on Preventable Surgical Site Infections
 Rhode Island College Digital Commons @ RIC Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers Overview Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers 1-1-2012 The Impact
Rhode Island College Digital Commons @ RIC Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers Overview Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers 1-1-2012 The Impact
3 Infection Prevention Solutions
 3 Infection Prevention Solutions 3M DuraPrep Surgical Solution Nothing is faster, easier or more effective. We can all make a difference. Fast Not only did 3M design an applicator that is fast to activate
3 Infection Prevention Solutions 3M DuraPrep Surgical Solution Nothing is faster, easier or more effective. We can all make a difference. Fast Not only did 3M design an applicator that is fast to activate
Post-operative surgical wound infection
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 45 No. 4 December 1990 Post-operative surgical wound infection Yasmin Abu Hanifah, MBBS, MSc. (London) Lecturer Department of Medical Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 45 No. 4 December 1990 Post-operative surgical wound infection Yasmin Abu Hanifah, MBBS, MSc. (London) Lecturer Department of Medical Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Surgical site infections. J Scott Weese DVM DVSc DipACVIM
 Surgical site infections J Scott Weese DVM DVSc DipACVIM Adapted from Mandell et al 2005 Risk of SSI Microbial concentration and virulence X Tissue injury X Foreign material X Antimicrobial resistance
Surgical site infections J Scott Weese DVM DVSc DipACVIM Adapted from Mandell et al 2005 Risk of SSI Microbial concentration and virulence X Tissue injury X Foreign material X Antimicrobial resistance
Invasive Group A Streptococcus (GAS)
 Invasive Group A Streptococcus (GAS) Cause caused by a bacterium commonly found on the skin and in the throat transmitted by direct, indirect or droplet contact with secretions from the nose, and throat
Invasive Group A Streptococcus (GAS) Cause caused by a bacterium commonly found on the skin and in the throat transmitted by direct, indirect or droplet contact with secretions from the nose, and throat
Cefuroxime 1.5gm IV and Metronidazole 500mg IV. Metronidazole 500mg IV/Ampicillin-sulbactam e 3g/Ceftriaxone 2gm. +Metronidazole 500mg/Ertapenem 1gm
 SURGICAL ANTIBIOTIC PROPHYLAXIS GENERAL SURGERY* PROCEDURE RECOMMENDED AGENTS a,b Clean None None ALTERNATIVE AGENTS (If allergic to penicillin or colonized/infected with MRSA at any site) Clean with potential
SURGICAL ANTIBIOTIC PROPHYLAXIS GENERAL SURGERY* PROCEDURE RECOMMENDED AGENTS a,b Clean None None ALTERNATIVE AGENTS (If allergic to penicillin or colonized/infected with MRSA at any site) Clean with potential
Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Adult Orthopaedic Surgery. Formulary/prescribing guideline
 Document type: Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Adult Orthopaedic Surgery Version: 2.0 Author (name): Author (designation): Validated by Formulary/prescribing guideline Dr Celia Chu, Dr Katy Edwards, Dr Pradeep
Document type: Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Adult Orthopaedic Surgery Version: 2.0 Author (name): Author (designation): Validated by Formulary/prescribing guideline Dr Celia Chu, Dr Katy Edwards, Dr Pradeep
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections Activity C: ELC Prevention Collaboratives
 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections Activity C: ELC Prevention Collaboratives John Jernigan, MD, MS Alex Kallen, MD, MPH Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Centers for Disease
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections Activity C: ELC Prevention Collaboratives John Jernigan, MD, MS Alex Kallen, MD, MPH Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Centers for Disease
Infection Control for the Orthopedic Surgeon
 Infection Control for the Orthopedic Surgeon Gonzalo Bearman, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine & Epidemiology Associate Hospital Epidemiologist VCU Medical Center Summer 2007 Outline Paradigm
Infection Control for the Orthopedic Surgeon Gonzalo Bearman, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine & Epidemiology Associate Hospital Epidemiologist VCU Medical Center Summer 2007 Outline Paradigm
Antibiotic Updates: Part II
 Antibiotic Updates: Part II Fredrick M. Abrahamian, DO, FACEP, FIDSA Health Sciences Clinical Professor of Emergency Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, California Financial Disclosures
Antibiotic Updates: Part II Fredrick M. Abrahamian, DO, FACEP, FIDSA Health Sciences Clinical Professor of Emergency Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, California Financial Disclosures
ESSENTIAL SKILLS: SURGICAL NURSING
 1 Students should have experience with the following surgical procedures, but not necessarily limited to these procedures. Canine ovariohysterectomy Feline ovariohysterectomy Cesarean section Orthopedic
1 Students should have experience with the following surgical procedures, but not necessarily limited to these procedures. Canine ovariohysterectomy Feline ovariohysterectomy Cesarean section Orthopedic
Policy Forum. Environmental and Professional Hygiene: Toward the Prevention of Drug Resistant Infections
 Policy Forum Environmental and Professional Hygiene: Toward the Prevention of Drug Resistant Infections International Society of Microbial Resistance and Office of International Medical Policy School of
Policy Forum Environmental and Professional Hygiene: Toward the Prevention of Drug Resistant Infections International Society of Microbial Resistance and Office of International Medical Policy School of
STERILIZATION, DESINFECTION PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTION (SSI)
 Semmelweis University Faculty of Medicine Department of Surgical Research and Techniques OPERATING ROOM (OR) - STRUCTURE, EQUIPMENTS STERILIZATION, DESINFECTION PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTION (SSI)
Semmelweis University Faculty of Medicine Department of Surgical Research and Techniques OPERATING ROOM (OR) - STRUCTURE, EQUIPMENTS STERILIZATION, DESINFECTION PREVENTION OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTION (SSI)
STUDY OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS AMONGST ORTHOPAEDIC PATIENTS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
 Page283 IJPBS Volume 5 Issue 2 APR-JUN 2015 283-287 Research Article Pharmaceutical Sciences STUDY OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS AMONGST ORTHOPAEDIC PATIENTS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL Chitralekha Saikumar,
Page283 IJPBS Volume 5 Issue 2 APR-JUN 2015 283-287 Research Article Pharmaceutical Sciences STUDY OF SURGICAL SITE INFECTIONS AMONGST ORTHOPAEDIC PATIENTS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL Chitralekha Saikumar,
Infection control in intensive care. Sandra Fairley Senior Nurse, Neurocritical Care
 Infection control in intensive care Sandra Fairley Senior Nurse, Neurocritical Care sandra.fairley@uclh.nhs.uk Risks to the patient of health care acquired infection (HCAI) Patient admitted to hospital
Infection control in intensive care Sandra Fairley Senior Nurse, Neurocritical Care sandra.fairley@uclh.nhs.uk Risks to the patient of health care acquired infection (HCAI) Patient admitted to hospital
Hand washing/hand hygiene reduces the number of microorganisms on the hands and is the most important practice to prevent the spread of infection.
 1. Hand Hygiene Quick Reference Chart Hand washing/hand hygiene reduces the number of microorganisms on the hands and is the most important practice to prevent the spread of infection. WHEN Before: Direct
1. Hand Hygiene Quick Reference Chart Hand washing/hand hygiene reduces the number of microorganisms on the hands and is the most important practice to prevent the spread of infection. WHEN Before: Direct
OBSTETRICS & GYNAECOLOGY. Penicillin G 5 million units IV ; followed by 2.5 million units 4hourly upto delivery
 OBSTETRICS & GYNAECOLOGY A.OBSTETRICS Infection/Condition/likely organism Intrapartum Group B Streptococcal (GBS) infection; positive mothers Suggested treatment Preferred Penicillin G 5 million units
OBSTETRICS & GYNAECOLOGY A.OBSTETRICS Infection/Condition/likely organism Intrapartum Group B Streptococcal (GBS) infection; positive mothers Suggested treatment Preferred Penicillin G 5 million units
Hospital Acquired Infections in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance
 Hospital Acquired Infections in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance Datuk Dr Christopher KC Lee Infectious Diseases Unit Department of Medicine Sungai Buloh Hospital Patient Story 23 Year old female admitted
Hospital Acquired Infections in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance Datuk Dr Christopher KC Lee Infectious Diseases Unit Department of Medicine Sungai Buloh Hospital Patient Story 23 Year old female admitted
Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis
 Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis 1. Definition of Peritonitis: a. Cloudy effluent. b. WBC > 100 cells/mm3 with >50% polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells with minimum 2 hour dwell. c.
Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis 1. Definition of Peritonitis: a. Cloudy effluent. b. WBC > 100 cells/mm3 with >50% polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells with minimum 2 hour dwell. c.
Staph and MRSA Skin Infections Fact Sheet for Schools
 Cape May County Department of Health 4 Moore Road, Cape May Court House, NJ 08210 Staph and MRSA Skin Infections Fact Sheet for Schools What is a staph/mrsa skin infection? Staphylococcus or staph bacteria
Cape May County Department of Health 4 Moore Road, Cape May Court House, NJ 08210 Staph and MRSA Skin Infections Fact Sheet for Schools What is a staph/mrsa skin infection? Staphylococcus or staph bacteria
National Hospital Quality Measures Measure Definitions
 National Hospital Quality Measures Measure efinitions Excerpts from the Specifications Manual for National Hospital Quality Measures for Surgical Care Improvement Project Measure Set Applicable to Cases
National Hospital Quality Measures Measure efinitions Excerpts from the Specifications Manual for National Hospital Quality Measures for Surgical Care Improvement Project Measure Set Applicable to Cases
Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis
 Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis 1. Definition of Peritonitis: a. Cloudy effluent. b. WBC > 100 cells/mm3 with >50% polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells with minimum 2 hour dwell. c.
Standing Orders for the Treatment of Outpatient Peritonitis 1. Definition of Peritonitis: a. Cloudy effluent. b. WBC > 100 cells/mm3 with >50% polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells with minimum 2 hour dwell. c.
The Effect of Perioperative Use of Prophylactic Antibiotics on Surgical Wound Infection
 THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL PROPHYLACTIC ANTIBIOTICS ON SURGICAL WOUND INFECTION The Effect of Perioperative Use of Prophylactic Antibiotics on Surgical Wound Infection Ahmed Hamid Jasim*, Nabeel
THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL PROPHYLACTIC ANTIBIOTICS ON SURGICAL WOUND INFECTION The Effect of Perioperative Use of Prophylactic Antibiotics on Surgical Wound Infection Ahmed Hamid Jasim*, Nabeel
Give the Right Antibiotics in Trauma Mitchell J Daley, PharmD, BCPS
 Give the Right Antibiotics in Trauma Mitchell J Daley, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Critical Care Dell Seton Medical Center at the University of Texas and Seton Healthcare Family Clinical
Give the Right Antibiotics in Trauma Mitchell J Daley, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Critical Care Dell Seton Medical Center at the University of Texas and Seton Healthcare Family Clinical
Responsible use of antibiotics
 Responsible use of antibiotics Uga Dumpis MD, PhD Department of Infectious Diseases and Infection Control Pauls Stradiņs Clinical University Hospital Challenges in the hospitals Antibiotics are still effective
Responsible use of antibiotics Uga Dumpis MD, PhD Department of Infectious Diseases and Infection Control Pauls Stradiņs Clinical University Hospital Challenges in the hospitals Antibiotics are still effective
Antibiotic Stewardship Program (ASP) CHRISTUS SETX
 Antibiotic Stewardship Program (ASP) CHRISTUS SETX Program Goals I. Judicious use of antibiotics Decrease use of broad spectrum antibiotics and deescalate use based on clinical symptoms Therapeutic duplication:
Antibiotic Stewardship Program (ASP) CHRISTUS SETX Program Goals I. Judicious use of antibiotics Decrease use of broad spectrum antibiotics and deescalate use based on clinical symptoms Therapeutic duplication:
UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee
 UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee Policy: Surgical Guidelines EFFECTIVE ISSUE DATE: 2/21/2005 REVISION DATE(s): 2/14/15; 3/19/2018 SCOPE To describe guidelines and considerations
UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee Policy: Surgical Guidelines EFFECTIVE ISSUE DATE: 2/21/2005 REVISION DATE(s): 2/14/15; 3/19/2018 SCOPE To describe guidelines and considerations
Approach to Antibiotics in Obstetrics: Surgical Prophylaxis for Cesareans
 Approach to Antibiotics in Obstetrics: Surgical Prophylaxis for Cesareans Amy Murtha, MD Associate Professor Vice Chair for Research Department of Ob/Gyn Objectives Review antibiotic prophylaxis for
Approach to Antibiotics in Obstetrics: Surgical Prophylaxis for Cesareans Amy Murtha, MD Associate Professor Vice Chair for Research Department of Ob/Gyn Objectives Review antibiotic prophylaxis for
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australians with Renal Impairment. 8. Prophylactic antibiotics for insertion of peritoneal dialysis catheter
 8. Prophylactic antibiotics for insertion of peritoneal dialysis catheter Date written: February 2003 Final submission: May 2004 Guidelines (Include recommendations based on level I or II evidence) Antibiotic
8. Prophylactic antibiotics for insertion of peritoneal dialysis catheter Date written: February 2003 Final submission: May 2004 Guidelines (Include recommendations based on level I or II evidence) Antibiotic
