Molecular epidemiology and antibiotic susceptibility pattern of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from children in a Turkish university hospital
|
|
|
- Coral Lambert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2014; 56: Original Molecular epidemiology and antibiotic susceptibility pattern of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from children in a Turkish university hospital Özlem Özgür Gündeşlioğlu 1, Tülin Güven Gökmen 2, Özden Özgür Horoz 3, Necmi Aksaray 1, Fatih Köksal 2, Akgün Yaman 2, Rıza Dinçer Yıldızdaş 3, Emre Alhan 1, Emine Kocabaş 1, Derya Alabaz 1 Division of 1 Pediatric Infectious Diseases and 3 Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Department of Pediatrics, and 2 Department of Clinical Microbiology, Cukurova University Faculty of Medicine, Adana, Turkey ozlemozgur1978@yahoo.com SUMMARY: Gündeşlioğlu ÖÖ, Gökmen TG, Horoz ÖÖ, Aksaray N, Köksal F, Yaman A, Yıldızdaş RD, Alhan E, Kocabaş E, Alabaz D. Molecular epidemiology and antibiotic susceptibility pattern of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from children in a Turkish university hospital. Turk J Pediatr 2014; 56: The aim of the present study is to investigate the types of healthcareassociated infections (HC-AIs) caused by Acinetobacter baumannii and the related antibiotic susceptibility patterns as well as the genotypic characteristics of the Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from our center. Sixty-nine Acinetobacter baumannii isolates originating from various samples collected from 69 pediatric patients during their hospital stays were included in the study. The types of healthcare-associated infections caused by these isolates were evaluated, and the antibiotic susceptibility pattern and the genotypic characteristics of the isolates were determined using the pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) method. Fifty of the 69 children were observed to have HC-AIs, and 19 children had Acinetobacter baumannii colonization. Healthcare-associated pneumonia (58%) was the most common type of these infections. The rate of carbapenem resistance was found as 91.3%, while tigecycline resistance was found as 18.84%. No colistin resistance was observed in any of the isolates. A total of 10 groups, comprising eight major and two minor groups, were determined using the pulsed-field gel electrophoresis method. Acinetobacter baumannii isolates are the leading cause of healthcare-associated infections, and they show high rates of multidrug antibiotic resistance. Molecular epidemiological evaluation using PFGE plays an important role in preventing healthcare-associated infections. Key words: Acinetobacter baumanni, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, healthcareassociated infections, antibiotic resistance, children. Members of the genus Acinetobacter have been increasingly responsible for healthcareassociated infections, especially in intensive care units, in recent years 1. The most frequently isolated type of Acinetobacter from clinical samples, Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii), has a low virulence and usually leads to opportunistic infections, including primarily ventilator-associated pneumonia and bacteremia, urinary system infections, meningitis and skin and soft tissue infections in patients admitted to intensive care units 2-4. A. baumannii has developed resistance to various types of antibiotics, including carbapenems, and multi-resistant epidemics of A. baumannii have recently been reported 5-8. In order to control HC-AIs and epidemics, it is of vital importance to know the origins and transmission routes of the isolates. In the past, phenotypic methods were used in order to compare the similarities and differences among isolates originating from different sources in healthcare-associated infections or epidemics. In recent years, this approach has changed in parallel to the progress in the molecular typing methods based on deoxyribonucleic acid
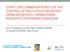
2 Volume 56 Number 4 Acinetobacter baumannii Infections in Children 361 (DNA). Today, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) is accepted as the gold standard among the frequently used DNA-based molecular typing methods 9. Material and Methods The present study was conducted at the Cukurova University Medical Faculty Hospital between February 2010 and October For the purposes of the study, approval was granted by the Cukurova University Medical Faculty Ethics Committee. The study had a prospective design based on the A. baumannii strains isolated from various clinical samples routinely sent to the microbiology laboratory from pediatric patients admitted to the Cukurova University Medical Faculty Hospital. In cases where more than one A. baumannii isolate was derived from a single patient, only one of the isolates was included in the study. The epidemiologic, clinical and demographic characteristics of the patients were recorded. The clinical data gathered included the patient s age, gender, duration of hospital stay, sites of infection, time from admission until collection of the sample, and any comorbidities or major risk factors (e.g., intensive care unit stay, intravenous catheterization, mechanical ventilation). The definitions of healthcare-associated infections and colonization were based on the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) criteria 10. Assessment of Antibiotic Susceptibility Antibiotic susceptibility was tested using the Vitek-2 Compact automated system. The MIC values of the antibiotics are presented in Table I 11. Intermediate-level susceptible strains were also accepted as resistant. The Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Method Plug preparation, lysis, cell washing, restriction digestion and electrophoresis were performed as has been previously described 12. For the electrophoresis, a CHEF-DR II (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Nazareth, Belgium) device was used. The band profiles were analyzed using GelCompar II software (version 5.0; Applied Maths, Sint-Martens-Latem, Belgium). The band and profile tolerance was taken as 1.5% in the calculation of the similarity coefficient. The isolates where the band profiles showed an 80% similarity were evaluated within the same group and designated with capital letters. Subtypes within the same group were indicated with numbers. Results Sixty-nine Acinetobacter baumannii isolates originating from various clinical samples collected from 69 pediatric patients during their hospital stays were included in the study. When the patients were assessed in terms of the infections that developed due to A. baumannii and the risk factors for colonization, all of them were observed to be under treatment with extended-spectrum antibiotics. The risk factors are presented in Table II. In this study, 50 among the 69 isolates (72.74%) were the agents of healthcareassociated infections; the most frequently observed infection (50%) was ventilatorassociated pneumonia. In 19 patients (27.53%), the isolated A. baumannii was accepted as colonization. The diagnoses of the patients are presented in Table III. Antibiotic susceptibility results Among the isolates included in the study, 67 (100%) were observed to be susceptible to colistin. No antibiogram was performed against colistin for the two isolates included in the study. The antibiotic susceptibility of the isolates included in the study is presented in Table IV. Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Results The pulsed-field gel electrophoresis results indicated 10 different clones (A-J), including eight major groups and two separate isolates, with more than 80% band profile similarity among the 69 isolates. The largest group among these clones was group D, with 23 isolates. Seven subtypes were detected within group D (D1-D7). Group F was the second largest group, with 16 isolates and nine subtypes (F1-F9). Group C included seven isolates and seven subtypes (C1-C7); group E had three isolates and three subtypes (E1-E3); group G comprised five isolates and three subtypes (G1-G3); group H had three isolates and three subtypes (H1-H3); group I included five isolates and four subtypes (I1-I4), and group J comprised five isolates and four subtypes (J1-J4). The dendrogram obtained through the pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analysis is presented in Figure 1.
3 362 Gündeşlioğlu ÖÖ, et al The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics July-August 2014 Fig. 1. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis dendrogram of the isolates included in the study
4 Volume 56 Number 4 Acinetobacter baumannii Infections in Children 363 Our study has demonstrated that different clones may be present within the same hospital units, while the same clones may be present in different units. The clone with the longest lifespan was in group D, and these isolates were first detected in the pediatric intensive care unit and last in the burn unit. This clone has been demonstrated to have persisted in different services in our hospital between 28 March 2010 and 09 May Also, we have observed that the PFGE type C clone persisted in the pediatric intensive care unit in the period between 16 July 2010 and 16 March Discussion Healthcare-associated infections caused by resistant microorganisms and especially by carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii strains have become an important cause of morbidity and mortality in hospitals in recent years 13. According to the data from the infection control committee of our hospital, A. baumannii was the most frequently observed microorganism, with a ratio of 16.34% in terms of the distribution according to the species of the agents isolated from the infections originating in the Intensive Care Units of our hospital during our study. A prolonged hospital stay, surgical intervention, wounds, previous infections and extendedspectrum antibiotic use, central venous or urinary system catheterization, an intensive care stay, a burn unit stay, parenteral nutrition, mechanical ventilation and shortcomings in the infection control program are the risk factors for healthcare-associated infections caused by Acinetobacter baumanni In our study, the most common risk factor was extendedspectrum antibiotic use, which was observed in all of the patients. The other risk factors found in our patients were (in descending order) use of a central venous catheter, mechanical ventilation, an intensive care stay, surgical intervention, total parenteral nutrition, urinary system catheterization, presence of wounds disrupting the integrity of the skin, and a burn unit stay. Healthcare-associated infections due to A. baumannii may involve any site. In most institutions, A. baumannii is an increasingly important cause of healthcare-associated pneumonia in the intensive care unit, particularly in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia, representing between 5% and 10% of the cases 9,17. A. baumannii may lead to healthcare-associated bacteremia and infections of the skin and soft tissue, genitourinary system or intracranial system 2,9,18. Among the 69 A. baumannii isolates in our study, 19 (27.53%) were defined as colonizations. More than half (58%) of the 50 isolates thought to have Table I. The Antibiotics and MIC Values 11 Antibiotic MIC Interpretation Ampicillin/Sulbactam 32 Resistant Piperacillin 128 Resistant Piperacillin/tazobactam 128 Resistant Ceftazidime 64 Resistant Cefoperazone/sulbactam 32 Intermediate-level susceptible Cefepime 64 Resistant Imipenem 16 Resistant Meropenem 16 Resistant Amikacin 32 Intermediate-level susceptible Gentamicin 1 Susceptible Netilmicin 8 Susceptible Ciprofloxacin 4 Resistant Levofloxacin 4 Intermediate-level susceptible Tetracycline 16 Resistant Tigecycline 2 Susceptible Colistin 0.5 Susceptible Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole 320 Resistant
5 364 Gündeşlioğlu ÖÖ, et al The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics July-August 2014 Table II. Frequency of the Risk Factors That May Lead to Acinetobacter baumannii Infections in the Patients Included in the Study Risk Factors Number of patients % Underlying disease Surgical intervention Wounds on the body Treatment with extended-spectrum antibiotics Central venous catheter Urinary system catheter Intensive care stay Burn unit stay Total parenteral nutrition Mechanical ventilation caused healthcare-associated infections were assessed to be agents associated with ventilatorassociated pneumonia. Although this ratio is in correlation with the studies reporting that A. baumannii most often leads to healthcareassociated pneumonia, it seems to be higher than the ratios reported in the literature. This higher ratio observed in our patients may be explained by the fact that the majority of our patients were mechanically ventilated or in the ICU. The other infections observed in our patients related to A. baumannii were (in descending order) central line-associated bloodstream infections, laboratory-evidenced bacteremia, meningitis, surgical site infections, burn wounds, permanent catheter-related bloodstream infections, infected decubitus ulcers, urinary system infections and rectal abscesses. As in rest of the world, the A.baumannii strains were multi-antibiotic resistant. In a multicenter study conducted in Europe in 1999, susceptibility among the Acinetobacter strains isolated from intensive care units was observed to be greatest to imipenem 19. Similarly, according to the industry-supported MYSTIC (Meropenem Yearly Susceptibility Test Information Collection) report, which evaluated antibiotic resistance in 490 Acinetobacter baumannii isolates collected between 1997 and 2000 from 37 centers in 11 European countries, imipenem and meropenem were the two most effective antibiotics against A. baumanni, although resistance was also observed in ratios of 16% and 14%, respectively 20. However, according to the MYSTIC report dated 2006, the resistance against these two antibiotics had shown a significant increase and reached 40% 21. Studies supporting these data and observing carbapenem resistance rates Table III. Types of Infection Caused by the Strains Included in the Study, and Colonization Rates Number of patients (n=69) % Type of healthcare-associated infection (n=50; 72.47%) Ventilator-associated pneumonia Catheter-associated bloodstream infection 6 12 Laboratory-confirmed bloodstream infection 4 8 Meningitis or ventriculitis 3 6 Incisional surgical site infection 3 6 Burn wound infection 2 4 Decubitus ulcer infection 1 2 Catheter-related urinary tract infection 1 2 Gastrointestinal tract infection (rectal abscess) 1 2 Colonization 19 (27.53%)
6 Volume 56 Number 4 Acinetobacter baumannii Infections in Children 365 Antibiotic Table IV. Antibiotic Susceptibility of the Isolates Included in the Study Susceptible isolate Resistant isolate n % n % Amikacin Ampicillin/Sulbactam Ciprofloxacin Colistin Ceftriaxone Cefepime Gentamicin Imipenem Meropenem Levofloxacin Piperacillin Piperacillin/tazobactam Ceftazidime Cefoperazone/sulbactam Ticarcillin Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole Tetracycline Tigecycline Tobramycin up to 100% have been reported from various geographical regions around the world 22,23,24. Studies from Turkey have reported carbapenem resistance rates of 78% for imipenem and 71% for meropenem 25,26. Parallel to these data, our study has also pointed out high rates of imipenem and meropenem resistance, both reaching 91.3%. The carbapenem resistance we observed in the strains isolated from our patients seems to be higher than the ratios reported by other centers in our country. This high resistance against carbapenems may be explained by a number of factors. Firstly, the majority of our subjects were ICU patients. Secondly, all the patients had a history of treatment with extended-spectrum antibiotics. And finally, they were frequently hospitalized patients due to other underlying diseases. The high carbapenem resistance observed in Acinetobacter baumannii has led to a search for new treatment options. Certain studies have reported a % susceptibility to colistin On the other hand, some studies have reported no resistance to colistin 25,31,32, while a study from our country has reported a 12.1% resistance 33. In different studies, the resistance rates to tigecycline varied from 5 to 78% In a study that evaluated 492 carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from various regions in the world, including Turkey, susceptibility to tigecycline and minocycline was reported to be over 80%, although the susceptibility to other antibiotics was low (38%). As observed in these studies, the antibiotics with the lowest resistance rates for the treatment of multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections are colistin and tigecycline In line with the literature, our study has also shown high resistance rates to other antibiotics, while the resistance to tigecycline was only 18.84%, and no colistin resistance was observed in any of the strains. Numerous publications have reported the phenotypic and genotypic features of the strains isolated during epidemics. The most common method currently used for the genotyping of A. baumannii is pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Although certain clones are present with widespread dissemination, isolates of A. baumannii from hospitals in the same country or even from a single hospital may show significant genetic diversity 12, 24,31,39-45.
7 366 Gündeşlioğlu ÖÖ, et al The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics July-August 2014 Our study also revealed that many different PFGE genotypes were present during the 1.5 year period. We have determined that clonally related strains can survive for a long time in our hospital and cause healthcareassociated infections at different times. The PFGE molecular typing of the Acinetobacter baumannii strains isolated during the 1.5 year period of our study has revealed that the same isolates were found in different units and some isolates persisted in the units for long periods. These findings point to the transmission of infections between the units and a lack of efficient measures for infection control. In conclusion, it can be claimed that A. baumannii plays an important role in healthcare-associated infections, and high antibiotic resistance is observed in this agent. The increasing costs of the morbidity, mortality and treatment related to healthcare-associated infections call for the implementation of infection control strategies. For every center, studying the patient profile, the microorganisms composing the hospital flora together with their resistance patterns, and the distribution and frequency of healthcareassociated infections in each unit will help in developing the right strategies. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis, which is the gold standard among molecular typing methods, should be employed in long-term surveillance in order to prevent healthcare-associated infections, determine the transmission sources and routes of microorganisms, and monitor the spread of these strains throughout the hospital. REFERENCES 1. Fournier PE, Richet H. The epidemiology and control of Acinetobacter baumannii in health care facilities. Clin Infect Dis 2006; 42: Allen DM, Hartman BJ. Acinetobacter species. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R (eds). Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases (7th ed). Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone; 2010: Towner KJ. Acinetobacter: an old friend, but a new enemy. J Hosp Infect 2009; 73: Garnacho-Montero J, Ortiz-Leyba C, Fernández- Hinojosa, et al. Acinetobacter baumannii ventilatorassociated pneumonia: epidemiological and clinical findings. Intensive Care Med 2005; 31: Gordon NC, Wareham DW. A review of clinical and microbiological outcomes following treat ment of infections involving multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii with tigecycline. J Antimicrob Chemother 2009; 63: Poirel L, Nordmann P. Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: mechanisms and epidemiology. Clin Microbiol Infect 2006; 12: Peleg AY, Potoski BA, Rea R, et al. Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infection while receiving tigecycline: a cautionary report. J Antimicrob Chemother 2007; 59: Zarrilli R, Giannouli M, Tomasone F, Triassi M, Tsakris A. Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: the molecular epidemic features of an emerging problem in health care facilities. J Infect Dev Ctries 2009; 3: Peleg AY, Seifert H, Paterson DL. Acinetobacter baumannii: emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev 2008; 21: Horan TC, Andrus M, Dudeck MA. CDC/NHSN surveillance definition of healthcare-associated infection and criteria for specific types of infections in the acute care setting. Am J Infect Control 2008; 36: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twentieth Informational Supplement, M100-S20-U. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2010: Seifert H, Dolzani L, Bressan R, et al. Standardization and interlaboratory reproducibility assessment of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis-generated fingerprints of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol 2005; 43: Giamarellou H, Poulakou G. Multidrug-resistant Gramnegative infections: what are the treatment options? Drugs 2009; 69: Anstey NM, Currie BJ, Withnall KM. Communityacquired Acinetobacter pneumonia in the Northern Territory of Australia. Clin Infect Dis 1992; 14: Lortholary O, Fagon JY, Hoi AB, et al. Nosocomial acquisition of multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii: risk factors and prognosis. Clin Infect Dis 1995; 20: Donskey CJ. Antibiotic regimens and intestinal colonization with antibiotic-resistant gram-negative bacilli. Clin Infect Dis 2006; 43 (Suppl 2:) S McDonald LC, Banerjee SN, Jarvis WR. Seasonal variation of Acinetobacter infections: Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System. Clin Infect Dis 1999; 29: Manchanda V, Sanchaita S, Singh NP. Multidrug resistant Acinetobacter. J Glob Infect Dis 2010; 2: Hanberger H, Garcia-Rodriguez JA, Gobernado M, Goossens H, Nilsson LE, Struelens MJ. Antibiotic susceptibility among aerobic gram-negative bacilli in intensive care units in 5 European countries. French and Portuguese ICU Study Groups. JAMA 1999; 281: Turner PJ, Greenhalgh JM; MYSTIC Study Group (Europe) The activity of meropenem and comparators against Acinetobacter strains isolated from European hospitals, Clin Microbiol Infect 2003; 9:
8 Volume 56 Number 4 Acinetobacter baumannii Infections in Children Turner PJ. Meropenem activity against European isolates: report on the MYSTIC (Meropenem Yearly Susceptibility Test Information Collection) 2006 results. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2008; 60: Cisneros JM, Rodríguez-Baño J. Nosocomial bacteremia due to Acinetobacter baumannii: epidemiology, clinical features and treatment. Clin Microbiol Infect 2002; 8: Trottier V, Segura PG, Namias N, King D, Pizano LR, Schulman CI. Outcomes of Acinetobacter baumannii infection in critically ill burned patients. J Burn Care Res 2007; 28: Irfan S, Turton JF, Mehraj J, et al. Molecular and epidemiological characterisation of clinical isolates of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii from public and private sector intensive care units in Karachi, Pakistan. J Hosp Infect 2011; 78: Kurtoğlu MG, Opuş A, Kaya M, Keşli R, Güzelant A, Yüksekkaya Ş. Bir eğitim ve araştırma hastanesinde klinik örneklerden izole edilen Acinetobacter baumannii suşlarında antibakteriyel direnç ( ). Ankem Derg 2011; 25: Bacakoğlu F, Korkmaz Ekren P, Taşbakan MS, et al. Solunumsal yoğun bakım ünitesinde çoklu antibiyotik dirençli Acinetobacter baumannii enfeksiyonu. Mikrobiyol Bült 2009; 43: Henwood CJ, Gatward T, Warner M, et al. Antibiotic resistance among clinical isolates of Acinetobacter in the UK, and in vitro evaluation of tigecycline (GAR- 936). J Antimicrob Chemother 2002; 49: Luyt CE, Combes A, Nieszkowska A, Trouillet JL, Chastre J. Aerosolized antibiotics to treat ventilatorassociated pneumonia. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2009; 22: Gales AC, Jones RN, Sader HS. Global assessment of the antimicrobial activity of polymyxin B against clinical isolates of Gram-negative bacilli: report from the SENTRY antimicrobial surveillance programme ( ). Clin Microbiol Infect 2006; 12: Souli M, Kontopidou FV, Koratzanis E, et al. İn vitro activity of tigecycline against multiple-drugresistant, including pan-resistant, gram-negative and gram-positive clinical isolates from Greek hospitals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2006; 50: Schimith Bier KE, Luiz SO, Scheffer CM, et al. Temporal evolution of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Curitiba, southern Brazil. Am J Infect Control 2010; 38: Falagas ME, Kasiakou SK. Colistin: the revival of polymyxins for the management of multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40: Çetin ES, Durmaz R, Tetik T, Otlu B, Kaya S, Çalışkan A. Epidemiologic characterization of nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii infections in a Turkish university hospital by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Am J Infect Control 2009; 37: Peterson LR: A review of tigecycline - the first glycylcycline. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2008; 32 Suppl 4: S Dominguez EA: Single-agent therapy with tigecy cline in the treatment of complicated skin and skin structure and complicated intraabdominal infecti ons. Infect Dis Clin Pract 2009; 17: Seifert H, Stefanik D, Wisplinghoff H. Comparative in vitro activities of tigecycline and 11 other antimicrobial agents against 215 epidemiologically defined multidrugresistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother 2006; 58: Dizbay M, Altuncekic A, Sezer BE, Ozdemir K, Arman D. Colistin and tigecycline susceptibility among multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from ventilator-associated pneumonia. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2008; 32: Higgins PG, Dammhayn C, Hackel M, Seifert H. Global spread of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J Antimicrob Chemother 2010; 65: Nemec A, Dijkshoorn L, van der Reijden TJ. Long-term predominance of two pan-european clones among multi-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains in the Czech Republic. J Med Microbiol 2004; 53: Abbo A, Navon-Venezia S, Hammer-Muntz O, Krichali T, Siegman-Igra Y, Carmeli Y. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Emerg Infect Dis 2005; 11: Zarrilli R, Vitale D, Di Popolo A, et al. A plasmidborne blaoxa-58 gene confers imipenem resistance to Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from a Lebanese hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2008; 52: Runnegar N, Sidjabat H, Goh HM, Nimmo GR, Schembri MA, Paterson DL. Molecular epidemiology of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a single institution over a 10-year period. J Clin Microbiol 2010; 48: Dijkshoorn L, Aucken H, Gerner-Smidt P, et al. Comparison of outbreak and nonoutbreak Acinetobacter baumannii strains by genotypic and phenotypic methods. J Clin Microbiol 1996; 34: Di Popolo A, Giannouli M, Triassi M, Brisse S, Zarrilli R. Molecular epidemiological investigation of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains in four Mediterranean countries with a multilocus sequence typing scheme. Clin Microbiol Infect 2011; 17: Carretto E, Barbarini D, Dijkshoorn L, et al. Widespread carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clones in Italian hospitals revealed by a multicenter study. Infect Genet Evol 2011; 11:
DRUG-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII A GROWING SUPERBUG POPULATION. Cara Wilder Ph.D. Technical Writer March 13 th 2014
 DRUG-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII A GROWING SUPERBUG POPULATION Cara Wilder Ph.D. Technical Writer March 13 th 2014 ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit organization with headquarters in Manassas,
DRUG-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII A GROWING SUPERBUG POPULATION Cara Wilder Ph.D. Technical Writer March 13 th 2014 ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit organization with headquarters in Manassas,
What does multiresistance actually mean? Yohei Doi, MD, PhD University of Pittsburgh
 What does multiresistance actually mean? Yohei Doi, MD, PhD University of Pittsburgh Disclosures Merck Research grant Clinical context of multiresistance Resistance to more classes of agents Less options
What does multiresistance actually mean? Yohei Doi, MD, PhD University of Pittsburgh Disclosures Merck Research grant Clinical context of multiresistance Resistance to more classes of agents Less options
Antimicrobial susceptibility of Acinetobacter clinical isolates and emerging antibiogram trends for nosocomial infection management
 doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0111-2016 Major Article Antimicrobial susceptibility of Acinetobacter clinical isolates and emerging antibiogram trends for nosocomial infection management Muhammad Sohail [1],[2],
doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0111-2016 Major Article Antimicrobial susceptibility of Acinetobacter clinical isolates and emerging antibiogram trends for nosocomial infection management Muhammad Sohail [1],[2],
Nosocomial Infections: What Are the Unmet Needs
 Nosocomial Infections: What Are the Unmet Needs Jean Chastre, MD Service de Réanimation Médicale Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, AP-HP, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris 6, France www.reamedpitie.com
Nosocomial Infections: What Are the Unmet Needs Jean Chastre, MD Service de Réanimation Médicale Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, AP-HP, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris 6, France www.reamedpitie.com
A review on multidrug - resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 2 (2014) pp. 9-13 http://www.ijcmas.com Review Article A review on multidrug - resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Pavani Gandham* Department of Microbiology, Apollo Institute
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 2 (2014) pp. 9-13 http://www.ijcmas.com Review Article A review on multidrug - resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Pavani Gandham* Department of Microbiology, Apollo Institute
Multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA) Surveillance and Control. Alison Holmes
 Multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA) Surveillance and Control Alison Holmes The organism and it s epidemiology Surveillance Control What is it? What is it? What is it? What is it? Acinetobacter :
Multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA) Surveillance and Control Alison Holmes The organism and it s epidemiology Surveillance Control What is it? What is it? What is it? What is it? Acinetobacter :
Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance among Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Hospitalized Patients at Chiang Mai University Hospital,
 Original Article Vol. 28 No. 1 Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance:- Chaiwarith R, et al. 3 Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance among Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Hospitalized Patients at
Original Article Vol. 28 No. 1 Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance:- Chaiwarith R, et al. 3 Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance among Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Hospitalized Patients at
Acinetobacter Resistance in Turkish Tertiary Care Hospitals. Zeliha KOCAK TUFAN, MD, Assoc. Prof.
 Acinetobacter Resistance in Turkish Tertiary Care Hospitals Zeliha KOCAK TUFAN, MD, Assoc. Prof. Acinetobacter Problem Countries that have reported hospital outbreaks of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter
Acinetobacter Resistance in Turkish Tertiary Care Hospitals Zeliha KOCAK TUFAN, MD, Assoc. Prof. Acinetobacter Problem Countries that have reported hospital outbreaks of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter
Overview of Nosocomial Infections Caused by Gram-Negative Bacilli
 HEALTHCARE EPIDEMIOLOGY Robert A. Weinstein, Section Editor INVITED ARTICLE Overview of Nosocomial Infections Caused by Gram-Negative Bacilli Robert Gaynes, Jonathan R. Edwards, and the National Nosocomial
HEALTHCARE EPIDEMIOLOGY Robert A. Weinstein, Section Editor INVITED ARTICLE Overview of Nosocomial Infections Caused by Gram-Negative Bacilli Robert Gaynes, Jonathan R. Edwards, and the National Nosocomial
Appropriate antimicrobial therapy in HAP: What does this mean?
 Appropriate antimicrobial therapy in HAP: What does this mean? Jaehee Lee, M.D. Kyungpook National University Hospital, Korea KNUH since 1907 Presentation outline Empiric antimicrobial choice: right spectrum,
Appropriate antimicrobial therapy in HAP: What does this mean? Jaehee Lee, M.D. Kyungpook National University Hospital, Korea KNUH since 1907 Presentation outline Empiric antimicrobial choice: right spectrum,
Prevalence of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its antibiogram in a tertiary care centre
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 952-956 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 952-956 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase
ESBL Producers An Increasing Problem: An Overview Of An Underrated Threat
 ESBL Producers An Increasing Problem: An Overview Of An Underrated Threat Hicham Ezzat Professor of Microbiology and Immunology Cairo University Introduction 1 Since the 1980s there have been dramatic
ESBL Producers An Increasing Problem: An Overview Of An Underrated Threat Hicham Ezzat Professor of Microbiology and Immunology Cairo University Introduction 1 Since the 1980s there have been dramatic
Molecular characterization of carbapenemase genes in Acinetobacter baumannii in China
 Molecular characterization of carbapenemase genes in Acinetobacter baumannii in China F. Fang 1 *, S. Wang 2 *, Y.X. Dang 3, X. Wang 3 and G.Q. Yu 3 1 The CT Room, Nanyang City Center Hospital, Nanyang,
Molecular characterization of carbapenemase genes in Acinetobacter baumannii in China F. Fang 1 *, S. Wang 2 *, Y.X. Dang 3, X. Wang 3 and G.Q. Yu 3 1 The CT Room, Nanyang City Center Hospital, Nanyang,
Aerobic bacterial infections in a burns unit of Sassoon General Hospital, Pune
 Original article Aerobic bacterial infections in a burns unit of Sassoon General Hospital, Pune Patil P, Joshi S, Bharadwaj R. Department of Microbiology, B.J. Medical College, Pune, India. Corresponding
Original article Aerobic bacterial infections in a burns unit of Sassoon General Hospital, Pune Patil P, Joshi S, Bharadwaj R. Department of Microbiology, B.J. Medical College, Pune, India. Corresponding
GENERAL NOTES: 2016 site of infection type of organism location of the patient
 GENERAL NOTES: This is a summary of the antibiotic sensitivity profile of clinical isolates recovered at AIIMS Bhopal Hospital during the year 2016. However, for organisms in which < 30 isolates were recovered
GENERAL NOTES: This is a summary of the antibiotic sensitivity profile of clinical isolates recovered at AIIMS Bhopal Hospital during the year 2016. However, for organisms in which < 30 isolates were recovered
Available online at ISSN No:
 Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(4): 36-42 Comparative Evaluation of In-Vitro Doripenem Susceptibility with Other
Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(4): 36-42 Comparative Evaluation of In-Vitro Doripenem Susceptibility with Other
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times
 Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
Safe Patient Care Keeping our Residents Safe 2016 Use Standard Precautions for ALL Residents at ALL times #safepatientcare Do bugs need drugs? Dr Deirdre O Brien Consultant Microbiologist Mercy University
Update on Resistance and Epidemiology of Nosocomial Respiratory Pathogens in Asia. Po-Ren Hsueh. National Taiwan University Hospital
 Update on Resistance and Epidemiology of Nosocomial Respiratory Pathogens in Asia Po-Ren Hsueh National Taiwan University Hospital Ventilator-associated Pneumonia Microbiological Report Sputum from a
Update on Resistance and Epidemiology of Nosocomial Respiratory Pathogens in Asia Po-Ren Hsueh National Taiwan University Hospital Ventilator-associated Pneumonia Microbiological Report Sputum from a
Antibiotic utilization and Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistance in intensive care units
 NEW MICROBIOLOGICA, 34, 291-298, 2011 Antibiotic utilization and Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistance in intensive care units Vladimíra Vojtová 1, Milan Kolář 2, Kristýna Hricová 2, Radek Uvízl 3, Jan Neiser
NEW MICROBIOLOGICA, 34, 291-298, 2011 Antibiotic utilization and Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistance in intensive care units Vladimíra Vojtová 1, Milan Kolář 2, Kristýna Hricová 2, Radek Uvízl 3, Jan Neiser
RISK FACTORS AND CLINICAL OUTCOMES OF MULTIDRUG-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII BACTEREMIA AT A UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL IN THAILAND
 RISK FACTORS AND CLINICAL OUTCOMES OF MULTIDRUG-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII BACTEREMIA AT A UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL IN THAILAND Siriluck Anunnatsiri 1 and Pantipa Tonsawan 2 1 Division of Infectious
RISK FACTORS AND CLINICAL OUTCOMES OF MULTIDRUG-RESISTANT ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII BACTEREMIA AT A UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL IN THAILAND Siriluck Anunnatsiri 1 and Pantipa Tonsawan 2 1 Division of Infectious
Intrinsic, implied and default resistance
 Appendix A Intrinsic, implied and default resistance Magiorakos et al. [1] and CLSI [2] are our primary sources of information on intrinsic resistance. Sanford et al. [3] and Gilbert et al. [4] have been
Appendix A Intrinsic, implied and default resistance Magiorakos et al. [1] and CLSI [2] are our primary sources of information on intrinsic resistance. Sanford et al. [3] and Gilbert et al. [4] have been
MDR Acinetobacter baumannii. Has the post antibiotic era arrived? Dr. Michael A. Borg Infection Control Dept Mater Dei Hospital Malta
 MDR Acinetobacter baumannii Has the post antibiotic era arrived? Dr. Michael A. Borg Infection Control Dept Mater Dei Hospital Malta 1 The Armageddon recipe Transmissible organism with prolonged environmental
MDR Acinetobacter baumannii Has the post antibiotic era arrived? Dr. Michael A. Borg Infection Control Dept Mater Dei Hospital Malta 1 The Armageddon recipe Transmissible organism with prolonged environmental
Original Articles. K A M S W Gunarathne 1, M Akbar 2, K Karunarathne 3, JRS de Silva 4. Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2011; 40(4):
 Original Articles Analysis of blood/tracheal culture results to assess common pathogens and pattern of antibiotic resistance at medical intensive care unit, Lady Ridgeway Hospital for Children K A M S
Original Articles Analysis of blood/tracheal culture results to assess common pathogens and pattern of antibiotic resistance at medical intensive care unit, Lady Ridgeway Hospital for Children K A M S
Received: February 29, 2008 Revised: July 22, 2008 Accepted: August 4, 2008
 J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 29;42:317-323 In vitro susceptibilities of aerobic and facultative anaerobic Gram-negative bacilli isolated from patients with intra-abdominal infections at a medical center
J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 29;42:317-323 In vitro susceptibilities of aerobic and facultative anaerobic Gram-negative bacilli isolated from patients with intra-abdominal infections at a medical center
Fighting MDR Pathogens in the ICU
 Fighting MDR Pathogens in the ICU Dr. Murat Akova Hacettepe University School of Medicine, Department of Infectious Diseases, Ankara, Turkey 1 50.000 deaths each year in US and Europe due to antimicrobial
Fighting MDR Pathogens in the ICU Dr. Murat Akova Hacettepe University School of Medicine, Department of Infectious Diseases, Ankara, Turkey 1 50.000 deaths each year in US and Europe due to antimicrobial
National Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates Obtained from Intensive Care Unit Patients from 1993 to 2002
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Dec. 2004, p. 4606 4610 Vol. 48, No. 12 0066-4804/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.12.4606 4610.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Dec. 2004, p. 4606 4610 Vol. 48, No. 12 0066-4804/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.12.4606 4610.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
Outline. Antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrobial resistance in gram negative bacilli. % susceptibility 7/11/2010
 Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms Is Combination Therapy the Way to Go? Sutthiporn Pattharachayakul, PharmD Prince of Songkhla University, Thailand Outline Prevalence of anti-microbial resistance in Acinetobacter
Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms Is Combination Therapy the Way to Go? Sutthiporn Pattharachayakul, PharmD Prince of Songkhla University, Thailand Outline Prevalence of anti-microbial resistance in Acinetobacter
4/3/2017 CLINICAL PEARLS: UPDATES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF NOSOCOMIAL PNEUMONIA DISCLOSURE LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 CLINICAL PEARLS: UPDATES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF NOSOCOMIAL PNEUMONIA BILLIE BARTEL, PHARMD, BCCCP APRIL 7 TH, 2017 DISCLOSURE I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial
CLINICAL PEARLS: UPDATES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF NOSOCOMIAL PNEUMONIA BILLIE BARTEL, PHARMD, BCCCP APRIL 7 TH, 2017 DISCLOSURE I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial
Does Screening for MRSA Colonization Have A Role In Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevention Programs?
 Does Screening for MRSA Colonization Have A Role In Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevention Programs? John A. Jernigan, MD, MS Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Centers for Disease Control and
Does Screening for MRSA Colonization Have A Role In Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevention Programs? John A. Jernigan, MD, MS Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Centers for Disease Control and
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(3):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 3 (2017) pp. 891-895 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.603.104
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 3 (2017) pp. 891-895 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.603.104
DR. MICHAEL A. BORG DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION & CONTROL MATER DEI HOSPITAL - MALTA
 DR. MICHAEL A. BORG DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION & CONTROL MATER DEI HOSPITAL - MALTA The good old days The dread (of) infections that used to rage through the whole communities is muted Their retreat
DR. MICHAEL A. BORG DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION & CONTROL MATER DEI HOSPITAL - MALTA The good old days The dread (of) infections that used to rage through the whole communities is muted Their retreat
Prevalence of Acinetobacter infections among Intensive Care Unit's patients in Najran
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 5-2017 Prevalence of Acinetobacter
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 5-2017 Prevalence of Acinetobacter
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
 International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 35 (2010) 19 24 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents journal homepage: http://www.elsevier.com/locate/ijantimicag
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 35 (2010) 19 24 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents journal homepage: http://www.elsevier.com/locate/ijantimicag
Summary of the latest data on antibiotic resistance in the European Union
 Summary of the latest data on antibiotic resistance in the European Union EARS-Net surveillance data November 2017 For most bacteria reported to the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network
Summary of the latest data on antibiotic resistance in the European Union EARS-Net surveillance data November 2017 For most bacteria reported to the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network
Jump Starting Antimicrobial Stewardship
 Jump Starting Antimicrobial Stewardship Amanda C. Hansen, PharmD Pharmacy Operations Manager Carilion Roanoke Memorial Hospital Roanoke, Virginia March 16, 2011 Objectives Discuss guidelines for developing
Jump Starting Antimicrobial Stewardship Amanda C. Hansen, PharmD Pharmacy Operations Manager Carilion Roanoke Memorial Hospital Roanoke, Virginia March 16, 2011 Objectives Discuss guidelines for developing
Dissecting the epidemiology of resistant Enterobacteriaceae and non-fermenters
 Dissecting the epidemiology of resistant Enterobacteriaceae and non-fermenters Jon Otter, PhD Centre for Clinical Infection and Diagnostics Research (CIDR), King's College London & Guy's and St. Thomas'
Dissecting the epidemiology of resistant Enterobacteriaceae and non-fermenters Jon Otter, PhD Centre for Clinical Infection and Diagnostics Research (CIDR), King's College London & Guy's and St. Thomas'
Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version
 Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED 2018 Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY NO. IC-122 Policy Group Infection Control
Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms POLICY REVIEW DATE EXTENDED 2018 Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY NO. IC-122 Policy Group Infection Control
Ventilator associated Pneumonia due to Multi Drug Resistant, Colistin-S Acinetobacter baumannii: Successful Revival of Colistin, A Forgotten Drug
 Case Study Ventilator associated Pneumonia due to Multi Drug Resistant, Colistin-S Acinetobacter baumannii: Successful Revival of Colistin, A Forgotten Drug *Deepak Juyal, Shekhar Pal, Jyoti Sangwan, Neelam
Case Study Ventilator associated Pneumonia due to Multi Drug Resistant, Colistin-S Acinetobacter baumannii: Successful Revival of Colistin, A Forgotten Drug *Deepak Juyal, Shekhar Pal, Jyoti Sangwan, Neelam
Sepsis is the most common cause of death in
 ADDRESSING ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE IN THE INTENSIVE CARE UNIT * John P. Quinn, MD ABSTRACT Two of the more common strategies for optimizing antimicrobial therapy in the intensive care unit (ICU) are antibiotic
ADDRESSING ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE IN THE INTENSIVE CARE UNIT * John P. Quinn, MD ABSTRACT Two of the more common strategies for optimizing antimicrobial therapy in the intensive care unit (ICU) are antibiotic
Florida Health Care Association District 2 January 13, 2015 A.C. Burke, MA, CIC
 Florida Health Care Association District 2 January 13, 2015 A.C. Burke, MA, CIC 11/20/2014 1 To describe carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. To identify laboratory detection standards for carbapenem-resistant
Florida Health Care Association District 2 January 13, 2015 A.C. Burke, MA, CIC 11/20/2014 1 To describe carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. To identify laboratory detection standards for carbapenem-resistant
Summary of unmet need guidance and statistical challenges
 Summary of unmet need guidance and statistical challenges Daniel B. Rubin, PhD Statistical Reviewer Division of Biometrics IV Office of Biostatistics, CDER, FDA 1 Disclaimer This presentation reflects
Summary of unmet need guidance and statistical challenges Daniel B. Rubin, PhD Statistical Reviewer Division of Biometrics IV Office of Biostatistics, CDER, FDA 1 Disclaimer This presentation reflects
Antimicrobial stewardship in managing septic patients
 Antimicrobial stewardship in managing septic patients November 11, 2017 Samuel L. Aitken, PharmD, BCPS (AQ-ID) Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Infectious Diseases slaitken@mdanderson.org Conflict of interest
Antimicrobial stewardship in managing septic patients November 11, 2017 Samuel L. Aitken, PharmD, BCPS (AQ-ID) Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Infectious Diseases slaitken@mdanderson.org Conflict of interest
Source: Portland State University Population Research Center (
 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Surveillance Report 2010 Oregon Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Office of Disease Prevention & Epidemiology Oregon Health Authority Updated:
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Surveillance Report 2010 Oregon Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Office of Disease Prevention & Epidemiology Oregon Health Authority Updated:
Testing for antimicrobial activity against multi-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. For. Forbo Flooring B.V. Final Report. Work Carried Out By
 Technical Report Testing for antimicrobial activity against multi-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii For Forbo Flooring B.V. Final Report Work Carried Out By A. Smith Group Leader Peter Collins PRA Ref:
Technical Report Testing for antimicrobial activity against multi-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii For Forbo Flooring B.V. Final Report Work Carried Out By A. Smith Group Leader Peter Collins PRA Ref:
Detecting / Reporting Resistance in Nonfastidious GNR Part #2. Janet A. Hindler, MCLS MT(ASCP)
 Detecting / Reporting Resistance in Nonfastidious GNR Part #2 Janet A. Hindler, MCLS MT(ASCP) Methods Described in CLSI M100-S21 for Testing non-enterobacteriaceae Organism Disk Diffusion MIC P. aeruginosa
Detecting / Reporting Resistance in Nonfastidious GNR Part #2 Janet A. Hindler, MCLS MT(ASCP) Methods Described in CLSI M100-S21 for Testing non-enterobacteriaceae Organism Disk Diffusion MIC P. aeruginosa
Acinetobacter species-associated infections and their antibiotic susceptibility profiles in Malaysia.
 Biomedical Research 12; 23 (4): 571-575 ISSN 97-938X Scientific Publishers of India Acinetobacter species-associated infections and their antibiotic susceptibility profiles in Malaysia. Nazmul MHM, Jamal
Biomedical Research 12; 23 (4): 571-575 ISSN 97-938X Scientific Publishers of India Acinetobacter species-associated infections and their antibiotic susceptibility profiles in Malaysia. Nazmul MHM, Jamal
Learning Points. Raymond Blum, M.D. Antimicrobial resistance among gram-negative pathogens is increasing
 Raymond Blum, M.D. Learning Points Antimicrobial resistance among gram-negative pathogens is increasing Infection with antimicrobial-resistant pathogens is associated with increased mortality, length of
Raymond Blum, M.D. Learning Points Antimicrobial resistance among gram-negative pathogens is increasing Infection with antimicrobial-resistant pathogens is associated with increased mortality, length of
Lack of Change in Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Pediatric Hospital Despite Marked Changes in Antibiotic Utilization
 Infect Dis Ther (2014) 3:55 59 DOI 10.1007/s40121-014-0028-8 BRIEF REPORT Lack of Change in Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Pediatric Hospital Despite Marked Changes in Antibiotic Utilization
Infect Dis Ther (2014) 3:55 59 DOI 10.1007/s40121-014-0028-8 BRIEF REPORT Lack of Change in Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Pediatric Hospital Despite Marked Changes in Antibiotic Utilization
Detection and Quantitation of the Etiologic Agents of Ventilator Associated Pneumonia in Endotracheal Tube Aspirates From Patients in Iran
 Letter to the Editor Detection and Quantitation of the Etiologic Agents of Ventilator Associated Pneumonia in Endotracheal Tube Aspirates From Patients in Iran Mohammad Rahbar, PhD; Massoud Hajia, PhD
Letter to the Editor Detection and Quantitation of the Etiologic Agents of Ventilator Associated Pneumonia in Endotracheal Tube Aspirates From Patients in Iran Mohammad Rahbar, PhD; Massoud Hajia, PhD
INCIDENCE OF BACTERIAL COLONISATION IN HOSPITALISED PATIENTS WITH DRUG-RESISTANT TUBERCULOSIS
 INCIDENCE OF BACTERIAL COLONISATION IN HOSPITALISED PATIENTS WITH DRUG-RESISTANT TUBERCULOSIS 1 Research Associate, Drug Utilisation Research Unit, Nelson Mandela University 2 Human Sciences Research Council,
INCIDENCE OF BACTERIAL COLONISATION IN HOSPITALISED PATIENTS WITH DRUG-RESISTANT TUBERCULOSIS 1 Research Associate, Drug Utilisation Research Unit, Nelson Mandela University 2 Human Sciences Research Council,
Measure Information Form
 Release Notes: Measure Information Form Version 3.0b **NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE** Measure Set: Pneumonia (PN) Performance Measure Identifier: Measure Information Form
Release Notes: Measure Information Form Version 3.0b **NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE** Measure Set: Pneumonia (PN) Performance Measure Identifier: Measure Information Form
Clonal Diversity of Nosocomial Epidemic Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Isolated in Spain
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 2011, p. 875 882 Vol. 49, No. 3 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01026-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Clonal Diversity
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 2011, p. 875 882 Vol. 49, No. 3 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01026-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Clonal Diversity
(DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
 (DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE John Ferguson (Hunter New England, NSW) on behalf of MRGN Task Force Acknowledgement
(DRAFT) RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVES: CARBAPENEM RESISTANT ENTEROBACTERIACEAE John Ferguson (Hunter New England, NSW) on behalf of MRGN Task Force Acknowledgement
Antimicrobial Cycling. Donald E Low University of Toronto
 Antimicrobial Cycling Donald E Low University of Toronto Bad Bugs, No Drugs 1 The Antimicrobial Availability Task Force of the IDSA 1 identified as particularly problematic pathogens A. baumannii and
Antimicrobial Cycling Donald E Low University of Toronto Bad Bugs, No Drugs 1 The Antimicrobial Availability Task Force of the IDSA 1 identified as particularly problematic pathogens A. baumannii and
crossm Global Assessment of the Activity of Tigecycline against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-negative pathogens between
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Clinical Science and Epidemiology crossm Global Assessment of the Activity of Tigecycline against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Pathogens between 2004 and 2014 as Part of the Tigecycline
RESEARCH ARTICLE Clinical Science and Epidemiology crossm Global Assessment of the Activity of Tigecycline against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Pathogens between 2004 and 2014 as Part of the Tigecycline
Emerging antimicrobial resistance and clinical relevance of Acinetobacter isolates in a tertiary care hospital of rural area of Punjab, India
 8 P a g e Emerging antimicrobial resistance and clinical relevance of Acinetobacter isolates in a tertiary care hospital of rural area of Punjab, India POONAM SHARMA 1, YOUSUF UL BASHIR 1, SARJIWAN KAUR
8 P a g e Emerging antimicrobial resistance and clinical relevance of Acinetobacter isolates in a tertiary care hospital of rural area of Punjab, India POONAM SHARMA 1, YOUSUF UL BASHIR 1, SARJIWAN KAUR
Other Enterobacteriaceae
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER NUMBER 50: Other Enterobacteriaceae Author Kalisvar Marimuthu, MD Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH Topic Outline Topic outline - Key Issues Known
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER NUMBER 50: Other Enterobacteriaceae Author Kalisvar Marimuthu, MD Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH Topic Outline Topic outline - Key Issues Known
Epidemiological characterization and distribution of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in Italy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Epidemiological characterization and distribution of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in Italy M. L. Mezzatesta 1, M. M. D Andrea 2, R. Migliavacca
ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Epidemiological characterization and distribution of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in Italy M. L. Mezzatesta 1, M. M. D Andrea 2, R. Migliavacca
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, ; doi: /ijerph
 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 1462-1473; doi:10.3390/ijerph10041462 OPEN ACCESS Article International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health ISSN 1660-4601 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijerph
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 1462-1473; doi:10.3390/ijerph10041462 OPEN ACCESS Article International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health ISSN 1660-4601 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijerph
Preserving bacterial susceptibility Implementing Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs Debra A. Goff, Pharm.D., FCCP
 Preserving bacterial susceptibility Implementing Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs Debra A. Goff, Pharm.D., FCCP Clinical Associate Professor Infectious Diseases Specialist The Ohio State University Medical
Preserving bacterial susceptibility Implementing Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs Debra A. Goff, Pharm.D., FCCP Clinical Associate Professor Infectious Diseases Specialist The Ohio State University Medical
Active Bacterial Core Surveillance Site and Epidemiologic Classification, United States, 2005a. Copyright restrictions may apply.
 Impact of routine surgical ward and intensive care unit admission surveillance cultures on hospital-wide nosocomial methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in a university hospital: an interrupted
Impact of routine surgical ward and intensive care unit admission surveillance cultures on hospital-wide nosocomial methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in a university hospital: an interrupted
Sustaining an Antimicrobial Stewardship
 Sustaining an Antimicrobial Stewardship Much needless expense, untoward effect, harm and disappointment can be prevented by better judgment in the use of antimicrobials Whitney A. Jones, PharmD Antimicrobial
Sustaining an Antimicrobial Stewardship Much needless expense, untoward effect, harm and disappointment can be prevented by better judgment in the use of antimicrobials Whitney A. Jones, PharmD Antimicrobial
Acinetobacter baumannii
 28 2010 1 4 IMP-19 IMP-1 -b- Acinetobacter baumannii 1) 2) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1) 3) 1) 1, 2) 1) 2) 3) 21 7 28 21 11 20 2004 2007 -b- (MBL) 67.6 Acinetobacter baumannii MBL A. baumannii 49 MBL A. baumannii
28 2010 1 4 IMP-19 IMP-1 -b- Acinetobacter baumannii 1) 2) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1) 3) 1) 1, 2) 1) 2) 3) 21 7 28 21 11 20 2004 2007 -b- (MBL) 67.6 Acinetobacter baumannii MBL A. baumannii 49 MBL A. baumannii
03/09/2014. Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course. Talk outline
 Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course 2014 What is healthcare-associated infection (HCAI), antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs)? Why we should be worried?
Infection Prevention and Control A Foundation Course 2014 What is healthcare-associated infection (HCAI), antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs)? Why we should be worried?
Antimicrobial Stewardship Strategy: Antibiograms
 Antimicrobial Stewardship Strategy: Antibiograms A summary of the cumulative susceptibility of bacterial isolates to formulary antibiotics in a given institution or region. Its main functions are to guide
Antimicrobial Stewardship Strategy: Antibiograms A summary of the cumulative susceptibility of bacterial isolates to formulary antibiotics in a given institution or region. Its main functions are to guide
Protocol for Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Urinary Isolates in Scotland
 Protocol for Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Urinary Isolates in Scotland Version 1.0 23 December 2011 General enquiries and contact details This is the first version (1.0) of the Protocol
Protocol for Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Urinary Isolates in Scotland Version 1.0 23 December 2011 General enquiries and contact details This is the first version (1.0) of the Protocol
PrevalenceofAntimicrobialResistanceamongGramNegativeIsolatesinanAdultIntensiveCareUnitataTertiaryCareCenterinSaudiArabia
 : K Interdisciplinary Volume 17 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2017 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618 & Print ISSN:
: K Interdisciplinary Volume 17 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2017 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618 & Print ISSN:
Received 21 June 2002/Returned for modification 23 July 2002/Accepted 24 September 2002
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 2002, p. 4571 4575 Vol. 40, No. 12 0095-1137/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.12.4571 4575.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 2002, p. 4571 4575 Vol. 40, No. 12 0095-1137/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.12.4571 4575.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 1598-1603 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.196
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 1598-1603 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.196
HEALTHCARE-ACQUIRED INFECTIONS AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE
 Universidade de São Paulo Departamento de Moléstias Infecciosas e Parasitárias HEALTHCARE-ACQUIRED INFECTIONS AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE Anna S. Levin 4 main lines! Epidemiology of HAS and resistance!
Universidade de São Paulo Departamento de Moléstias Infecciosas e Parasitárias HEALTHCARE-ACQUIRED INFECTIONS AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE Anna S. Levin 4 main lines! Epidemiology of HAS and resistance!
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile of E. coli Isolates Causing Urosepsis: Single Centre Experience
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 05 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.705.298
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 05 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.705.298
Longitudinal Analysis of the Temporal Evolution of Acinetobacter baumannii Strains in Ohio, USA, by Using Rapid Automated Typing Methods
 Longitudinal Analysis of the Temporal Evolution of Acinetobacter baumannii Strains in Ohio, USA, by Using Rapid Automated Typing Methods Brooke K. Decker, Case Western Reserve University Federico Perez,
Longitudinal Analysis of the Temporal Evolution of Acinetobacter baumannii Strains in Ohio, USA, by Using Rapid Automated Typing Methods Brooke K. Decker, Case Western Reserve University Federico Perez,
2015 Antimicrobial Susceptibility Report
 Gram negative Sepsis Outcome Programme (GNSOP) 2015 Antimicrobial Susceptibility Report Prepared by A/Professor Thomas Gottlieb Concord Hospital Sydney Jan Bell The University of Adelaide Adelaide On behalf
Gram negative Sepsis Outcome Programme (GNSOP) 2015 Antimicrobial Susceptibility Report Prepared by A/Professor Thomas Gottlieb Concord Hospital Sydney Jan Bell The University of Adelaide Adelaide On behalf
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN OF ESBL PRODUCING GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI ABSTRACT
 Research Article Microbiology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN OF ESBL PRODUCING GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI * PRABHAKAR C MAILAPUR, DEEPA
Research Article Microbiology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERN OF ESBL PRODUCING GRAM NEGATIVE BACILLI * PRABHAKAR C MAILAPUR, DEEPA
Acinetobacter Outbreaks: Experience from a Neurosurgery Critical Care Unit. Jumoke Sule Consultant Microbiologist 19 May 2010
 Acinetobacter Outbreaks: Experience from a Neurosurgery Critical Care Unit Jumoke Sule Consultant Microbiologist 19 May 2010 Epidemiology of Acinetobacter spp At least 32 different species Recovered from
Acinetobacter Outbreaks: Experience from a Neurosurgery Critical Care Unit Jumoke Sule Consultant Microbiologist 19 May 2010 Epidemiology of Acinetobacter spp At least 32 different species Recovered from
ORIGINAL ARTICLE /j x. Mallorca, Spain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01251.x Contribution of clonal dissemination and selection of mutants during therapy to Pseudomonas aeruginosa antimicrobial resistance in an intensive care unit
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01251.x Contribution of clonal dissemination and selection of mutants during therapy to Pseudomonas aeruginosa antimicrobial resistance in an intensive care unit
Evaluating the Role of MRSA Nasal Swabs
 Evaluating the Role of MRSA Nasal Swabs Josh Arnold, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Pharmacy Grand Rounds February 28, 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Identify the pathophysiology of MRSA nasal colonization
Evaluating the Role of MRSA Nasal Swabs Josh Arnold, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Pharmacy Grand Rounds February 28, 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Identify the pathophysiology of MRSA nasal colonization
Should we test Clostridium difficile for antimicrobial resistance? by author
 Should we test Clostridium difficile for antimicrobial resistance? Paola Mastrantonio Department of Infectious Diseases Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome,Italy Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) (first
Should we test Clostridium difficile for antimicrobial resistance? Paola Mastrantonio Department of Infectious Diseases Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome,Italy Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) (first
A retrospective analysis of urine culture results issued by the microbiology department, Teaching Hospital, Karapitiya
 A retrospective analysis of urine culture results issued by the microbiology department, Teaching Hospital, Karapitiya LU Edirisinghe 1, D Vidanagama 2 1 Senior Registrar in Medicine, 2 Consultant Microbiologist,
A retrospective analysis of urine culture results issued by the microbiology department, Teaching Hospital, Karapitiya LU Edirisinghe 1, D Vidanagama 2 1 Senior Registrar in Medicine, 2 Consultant Microbiologist,
Doxycycline and Co-trimethoxazole: A new combination for treatment of MDR Acinetobacter baumannii. Does it work?
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 1(2016) pp. 157-164 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.501.013 Doxycycline and Co-trimethoxazole:
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 1(2016) pp. 157-164 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.501.013 Doxycycline and Co-trimethoxazole:
Diversity in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from paediatric cancer patients in Egypt
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Diversity in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from paediatric cancer patients in Egypt L. Al-Hassan 1, H. El Mehallawy 2 and S.G.B. Amyes 1 1) Medical Microbiology, University
ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Diversity in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from paediatric cancer patients in Egypt L. Al-Hassan 1, H. El Mehallawy 2 and S.G.B. Amyes 1 1) Medical Microbiology, University
NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE. Measure Information Form
 Last Updated: Version 3.2a NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Set: Pneumonia (PN) Performance Measure Identifier: Measure Information Form Organization Set Measure ID#
Last Updated: Version 3.2a NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Set: Pneumonia (PN) Performance Measure Identifier: Measure Information Form Organization Set Measure ID#
Michael Hombach*, Guido V. Bloemberg and Erik C. Böttger
 J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: 622 632 doi:10.1093/jac/dkr524 Advance Access publication 13 December 2011 Effects of clinical breakpoint changes in CLSI guidelines 2010/2011 and EUCAST guidelines 2011
J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: 622 632 doi:10.1093/jac/dkr524 Advance Access publication 13 December 2011 Effects of clinical breakpoint changes in CLSI guidelines 2010/2011 and EUCAST guidelines 2011
ORIGINAL ARTICLE /j x
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01184.x Hospital outbreak caused by a carbapenem-resistant strain of Acinetobacter baumannii: patient prognosis and risk-factors for colonisation and infection
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01184.x Hospital outbreak caused by a carbapenem-resistant strain of Acinetobacter baumannii: patient prognosis and risk-factors for colonisation and infection
Molecular Epidemiology of Nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates. Rasha A. Nasr, Makram F. Attalah
 Molecular Epidemiology of Nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates Rasha A. Nasr, Makram F. Attalah Department of Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Cairo,
Molecular Epidemiology of Nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates Rasha A. Nasr, Makram F. Attalah Department of Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Cairo,
OPTIMIZATION OF PK/PD OF ANTIBIOTICS FOR RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVE ORGANISMS
 HTIDE CONFERENCE 2018 OPTIMIZATION OF PK/PD OF ANTIBIOTICS FOR RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVE ORGANISMS FEDERICO PEA INSTITUTE OF CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE, UNIVERSITY OF UDINE, ITALY SANTA
HTIDE CONFERENCE 2018 OPTIMIZATION OF PK/PD OF ANTIBIOTICS FOR RESISTANT GRAM-NEGATIVE ORGANISMS FEDERICO PEA INSTITUTE OF CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE, UNIVERSITY OF UDINE, ITALY SANTA
Antimicrobial Resistance & Wound Infections. Li Yang Hsu 8 th April 2015
 Antimicrobial Resistance & Wound Infections Li Yang Hsu 8 th April 2015 Potential Conflicts of Interest Research Funding: Pfizer Singapore AstraZeneca Janssen-Cilag Merck, Sharpe & Dohme Advisory Board:
Antimicrobial Resistance & Wound Infections Li Yang Hsu 8 th April 2015 Potential Conflicts of Interest Research Funding: Pfizer Singapore AstraZeneca Janssen-Cilag Merck, Sharpe & Dohme Advisory Board:
Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections. For National Patient Safety Goal
 Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections For National Patient Safety Goal 07.03.01 2009 Methicillin Resistant Staphlococcus aureus (MRSA) About 3-8% of the population at large is a carrier
Preventing Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) Infections For National Patient Safety Goal 07.03.01 2009 Methicillin Resistant Staphlococcus aureus (MRSA) About 3-8% of the population at large is a carrier
Acinetobacter baumannii Infection and Colonization among Pediatric Patients at Chiang Mai University Hospital
 Original Article Vol. 24 No. 2 Acinetobacter baumannii infection among pediatric patients;- Oberdorfer P & Oberdorfer P. 63 Acinetobacter baumannii Infection and Colonization among Pediatric Patients at
Original Article Vol. 24 No. 2 Acinetobacter baumannii infection among pediatric patients;- Oberdorfer P & Oberdorfer P. 63 Acinetobacter baumannii Infection and Colonization among Pediatric Patients at
Resistant Gram-negative Bacteria
 Introduction Antibiotic-resistant bacteria aren t new. But gram-negative bacteria, like Enterobacteriaceae, are becoming more resistant to our last-line antibiotics. Some people are calling these bacteria
Introduction Antibiotic-resistant bacteria aren t new. But gram-negative bacteria, like Enterobacteriaceae, are becoming more resistant to our last-line antibiotics. Some people are calling these bacteria
a. 379 laboratories provided quantitative results, e.g (DD method) to 35.4% (MIC method) of all participants; see Table 2.
 AND QUANTITATIVE PRECISION (SAMPLE UR-01, 2017) Background and Plan of Analysis Sample UR-01 (2017) was sent to API participants as a simulated urine culture for recognition of a significant pathogen colony
AND QUANTITATIVE PRECISION (SAMPLE UR-01, 2017) Background and Plan of Analysis Sample UR-01 (2017) was sent to API participants as a simulated urine culture for recognition of a significant pathogen colony
A pilot integrative knowledgebase for the characterization and tracking of multi resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Colombian hospitals
 A pilot integrative knowledgebase for the characterization and tracking of multi resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Colombian hospitals Our funding partners: EPFL Leading House Swiss Bilateral Programmes
A pilot integrative knowledgebase for the characterization and tracking of multi resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Colombian hospitals Our funding partners: EPFL Leading House Swiss Bilateral Programmes
SURVEILLANCE AND INFECTION CONTROL IN AN INTENSIVE CARE UNIT
 Vol. 26 No. 3 INFECTION CONTROL AND HOSPITAL EPIDEMIOLOGY 1 SURVEILLANCE AND INFECTION CONTROL IN AN INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Giovanni Battista Orsi, MD; Massimiliano Raponi, MD; Cristiana Franchi, MD; Monica
Vol. 26 No. 3 INFECTION CONTROL AND HOSPITAL EPIDEMIOLOGY 1 SURVEILLANCE AND INFECTION CONTROL IN AN INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Giovanni Battista Orsi, MD; Massimiliano Raponi, MD; Cristiana Franchi, MD; Monica
ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing microorganisms; state of the art. Laurent POIREL
 ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing microorganisms; state of the art Laurent POIREL Medical and Molecular Microbiology Unit Dept of Medicine University of Fribourg Switzerland INSERM U914 «Emerging Resistance
ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing microorganisms; state of the art Laurent POIREL Medical and Molecular Microbiology Unit Dept of Medicine University of Fribourg Switzerland INSERM U914 «Emerging Resistance
Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE)
 Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) September 21, 2017 Maryam Khan Peel Public Health Madeleine Ashcroft Public Health Ontario Objectives Differentiate the acronyms related to CPE (CPE,CPO,CRE,CRO)
Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) September 21, 2017 Maryam Khan Peel Public Health Madeleine Ashcroft Public Health Ontario Objectives Differentiate the acronyms related to CPE (CPE,CPO,CRE,CRO)
ETX2514SUL (sulbactam/etx2514) for the treatment of Acinetobacter baumannii infections
 ETX2514SUL (sulbactam/etx2514) for the treatment of Acinetobacter baumannii infections Robin Isaacs Chief Medical Officer, Entasis Therapeutics Dr. Isaacs is a full-time employee of Entasis Therapeutics.
ETX2514SUL (sulbactam/etx2514) for the treatment of Acinetobacter baumannii infections Robin Isaacs Chief Medical Officer, Entasis Therapeutics Dr. Isaacs is a full-time employee of Entasis Therapeutics.
Prevalence and Resistance pattern of Pseudomonas strains isolated from ICU Patients
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 3 (2014) pp. 527-534 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence and Resistance pattern of Pseudomonas strains isolated from ICU Patients T.Raakhee 1 * and
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 3 (2014) pp. 527-534 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence and Resistance pattern of Pseudomonas strains isolated from ICU Patients T.Raakhee 1 * and
Infection Control & Prevention
 Infection Control & Prevention Objectives: Define the term multi-drug resistant organism (MDRO). Recognize risk factors for developing MDROs. Describe the clinical manifestations and medical treatment
Infection Control & Prevention Objectives: Define the term multi-drug resistant organism (MDRO). Recognize risk factors for developing MDROs. Describe the clinical manifestations and medical treatment
ESCMID elibrary. Symposium: Acinetobacter Infections from East to West. Molecular Epidemiology Worldwide
 Symposium: Acinetobacter Infections from East to West Molecular Epidemiology Worldwide Harald Seifert Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie, Immunologie und Hygiene der Universität zu Köln 26 th ECCMID,
Symposium: Acinetobacter Infections from East to West Molecular Epidemiology Worldwide Harald Seifert Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie, Immunologie und Hygiene der Universität zu Köln 26 th ECCMID,
Is biocide resistance already a clinical problem?
 Is biocide resistance already a clinical problem? Stephan Harbarth, MD MS University of Geneva Hospitals and Faculty of Medicine, Geneva, Switzerland Important points Biocide resistance exists Antibiotic
Is biocide resistance already a clinical problem? Stephan Harbarth, MD MS University of Geneva Hospitals and Faculty of Medicine, Geneva, Switzerland Important points Biocide resistance exists Antibiotic
