The Significance (Socio-Economic Impact) and Control of Echinococcosis/Hydatidosis: A Review
|
|
|
- Georgina Fisher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Journal of Biological Sciences 9 (2): 58-66, 2017 ISSN IDOSI Publications, 2017 DOI: /idosi.ejbs The Significance (Socio-Economic Impact) and Control of Echinococcosis/Hydatidosis: A Review Ahmed Nur, Birhanu Abera and Teshome Gunse 1 East Shoa Zone Livestock and Fishery Resource Development Office, Adama, Ethiopia 2 Asella Regional Veterinary Laboratory, P.O. Box: 212, Asella, Ethiopia 3 Arsi Zone Livestoke and Fishery Resource Development Office, Asella Ethiopia Abstract: Echinococcosis/hydatidosis is a cosmopolitan zoonosis caused by adult or larval (metacestode) stage of Cestodes belonging to the genus Echinococcus, family Taeniidae. At present, five species of the genus Echinococcus are regarded. These are E. granulosus, E. multilocularis, E. oligarthus, E. vogeli and E. shiquicus. Recently E. shiquicus had been discovered only in a specific region of the People s Republic of China. Two major species of veterinary and public health importance are E. granulosus and E. multilocularis cause cystic echinococcosis (CE) and alveolar echinococcosis (AE) respectively. Unilocular hydatid disease (cystic hydatidosis) caused by the larval stage of E. granulosus is recognized as being one of the world s major zoonosis. Carnivores are definite hosts for the parasite with livestock acting as intermediate hosts and human as intermediate aberrant host. It has both economic and public health significance and are associated with sever morbidity and disability. The pathogenecity of hydatidosis heavily depends on the extent and severity of the infection and the organ on which it is situated. The two most common involved organs are liver and lung. In livestock hydatidosis results in reduction of yield and quality of milk, wool, reduced birth rate, delayed performance and growth; condemnation of organs and possible indirect consequences such as ban of animal export and their products. Hydatidosis in humans is an infection which results in asymptomatic infection to fatal disease. It is well known that the main factor for the persistent of the disease is the feeding of hydatid cysts infested offals of ruminants to dogs. Breaking the life cycle is one of the main control measures. This however, largely requires awareness creation and public education. Key words: Adama Hydatidosis Echinococcus species Public health INTRODUCTION echinococcosis (AE), respectively. Both CE and AE are serious and severe diseases, the latter especially so, with Echinococcosis/hydatidosis is one of the important high fatality rates and poor prognosis if managed parasitic diseases of livestock that has both financial and incorrectly. Unilocular hydatid disease or cystic public health significance. It is associated with severe echinococcosis (CE), caused by the larval stage of morbidity and disability. It is zoonosis caused by adult or E. granulosus is recognized as being one of the world s larval (metacestode) stage of Cestodes belonging to the major zoonosis [5]. genus Echinococcus (family Taeniidae) [1]. At present, The distributions of E. granulosus is wider in five species of the genus Echinococcus are regarded. developing countries especially in rural communities These are E. granulosus, E. multilocularis, E. oligarthus, where there is close contacts between the dog, the E. vogeli and E. shiquicus. Recently E. shiquicus had definitive host and various domestic animals, which may been discovered only in a specific region of the People s act as intermediate hosts [6]. Republic of China [2-4]. In Ethiopia, the status of hydatidosis in animals is not Two major species of veterinary and public health well documented and explored in the country. In some importance are E. granulosus and E. multilocularis that, regions according to Jobre et al. [7] prevalence rate of cause cystic echinococcosis (CE) and alveolar 46.5%, 25.7% and 24.3% in cattle and 2.45%, 25.7% and Corresponding Author: Birhanu Abera, Asella Regional Veterinary Laboratory, P.O. Box: 212, Asella, Ethiopia. 58
2 0% in sheep slaughtered in DebreZeit, South Omo and Gondar abattoirs, respectively were reported. Kebede et al. [8] found a prevalence of 34.05% and 10.6% in cattle and sheep, respectively in Bahir Dar. Ahmed et al. [9] found prevalence rate of 48.7% in cattle slaughtered in Adama Town municipal abattoir. The pathogenecity of hydatidosis heavily depends on the extent and severity of the infection and the organ on which it is situated. The outcome of infection in livestock is hydatid cyst development in the lung, liver or other organs [10, 11]. The occasional rupture of hydatid cysts often lead to sudden death due to anaphylaxis, haemorrhage and Fig. 1: Adult stage of Echinococcus spp. metastasis [7, 12, 13]. Source: Parija, [16]. The absence of proper meat inspection procedures and the presence of large stray dog population are thought to contribute significantly to the prevalence of the disease in Ethiopia. Hence, it is essential to pay a due attention to the disease and establishment of all possible control programmes are of major importance. Therefore, the objective of this paper includes: Review the epidemiology of echinococcosis /hydatidosis Assessing control method employed to the control of echinococcosis /hydatidosis. Description of the Parasite Fig. 2: Metacestode of Echinococcus granulosus Taxonomy: Echinococcus species and its metacestode Source: Parija, [16]. hydatid cyst, belongs to the class Cestoda order Cyclophyllidea family Taeniidae and genus Echinococcus The Major Metacestodes (Larval Stages) of [14]. The genus Echinococcus has 5 species, which Echinococcus: Hydatid disease is characterized by cyst include Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato, Echinococcus multilocularis, Echinococcus vogeli, Echinococcus oligarthrus and possibly Echinococcus shiquicus. [2, 4, 15]. Parasite Biology Adult Parasite: The adult E. granulosus inhabits in the small intestine of dog and wild canids. It is small tapeworm, measures 3 mm to 6 mm in length. It consists of head (scolex), neck and body (strobila). The scolex has 4 muscular suckers and two rows of hooks on the rostellum. The neck is short and thick; the body usually consists of three proglottids (segments). The first is immature segment the second mature segment and third terminal gravid segment. The terminal gravid segment is the largest and broadest and it contains several hundreds of eggs. This segment always bursts open before or after passage in the stool, to release hundreds of eggs (Fig. 1) [15, 16]. containing numerous tiny protoscolices that most often develop in the liver and lungs and also develop in the kidneys, spleen, nervous tissue and bone and other organs. In humans, the disease is initially without any symptoms until gradually the cyst increased in size, causing local pressure effects. In animals, the disease does not produce any clinical signs and is usually only discovered during meat inspection at the slaughter house, where the affected organs (mainly liver and lung) are condemned [17]. Cysts are formed mostly in the liver and lungs. In E. granulosus large tubular hydatid occur, whereas in E. multilocularis a tubular system infiltrates the whole organ (giving rise to alveolar aspects in sections). In brood capsules of both cyst types protoscolices are formed, which may become evaginated even inside their cysts. Evaginated or not, protoscolices are fully capable of infecting final hosts when they feed on infected organs of intermediate hosts [18]. 59
3 Echinococcus granulosus (Cystic Echinococcosis): Unilocular hydatid disease, hydatidosis, caused by the larval stage of E.granulosus is recognized as being one of the world s major zoonosis [6]. The definitive host of the parasite, E. granulosus, is dogs which harbor the adult parasite and excrete the parasite eggs along with their feces, while livestock and human are the intermediate hosts. Hydatid disease is characterized by cyst containing numerous tiny protoscolices that most often develop in the liver and lungs and also develop in the kidneys, spleen, nervous tissue, bone and other organs [17, 19]. The larva develops into a large cystic form or hydatid cyst, referred to as a unilocular cyst, which gives rise to unilocular hydatid disease in man. This is characterized as having only one bladder, or many completely separated bladders, each enclosed in its own well developed envelope. Echinococcosis multilocularis/ Alveolar Echinococcosis: Alveolar Echinococcosis (AE) in humans is caused by a larval stage (metacestode) of E. multilocularis, which exhibits a tumour like growth, initially in the liver, with the potential to induce serious disease. Red foxes are the principal definitive hosts of E. multilocularis and source of human infection, but dogs and cats can also be infected. Growing population of foxes and their increasing immigration to urban areas are new risk factors. Human alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is rare but its potential high fatality rate. It is characterized by a tumour like proliferation which leads to infiltration of the affected organs, primarily the liver and in progressive cases to sever disease and even death. The larval cyst, referred to as an alveolar or multilocularis hydatid cyst, which develops in man and animals, does not form a uniform, well- defined cyst (as in E. granulosus) but a multicystic structure made up of proliferating vesicles embedded in to a dense fibrous stroma, the whole resembling and often mistaken for hepatic sarcoma [16, 21]. Fig. 3: Metacestode of Echinococcosis multilocularis Source: Parija, [16]. Fig. 4: Egg of Echinococcus spp. Source: Parija, Eggs: The Echinococcus eggs are excreted with faeces of the infected dog and are infective to man, sheep, cattle and other intermediate hosts. They are spherical in shape, brown in colour, measures ìm in diameter and consist of two layers, an outer thin wall and inner embryophore. Each egg consists of a hexacanth embryo with three pairs of hooklet (Fig. 4). The eggs are morphologically indistinguishable from those of Taenia species. Eggs may survive for several months in pasture, garden and on household fomites; survives in water and damp sand for 3 weeks at 30 C, 225 days at 6 C and 32 days at C [14]. Life Cycle of Hydatidosis/Echinococcosis: The life cycle of these parasites involve carnivores as definitive hosts and food animals (cattle, sheep, goats, pigs and camel) and humans as intermediate hosts. The adult cestodes inhibit the small intestine of carnivores (definitive host) and produce eggs containing infective oncospheres. Either cestode segments, proglottids containing eggs or free eggs are released from the intestinal tract of the carnivores in to the environment [22]. Man and animals become infected by consuming faecal eggs containing water, or food stuffs or from handling infected dogs. The eggs hatch in the intestine and the released oncosphere penetrate the mucosa. On entering a mesenteric venule or a capillary, oncospheres are transported to and trapped largely in the liver, but may reach and develop in any of the viscera leading to the formation of cyst. The final host, dogs and other canids, acquires infection by ingestion of hydatid cyst containing fertile cyst present in the intermediate hosts. In the small intestine protoscolices envaginate, penetrate deep between villi and enter crypts of liberkhun [16]. The wide spread tradition of offering un-cooked infected offals to pet animals around home stead, poor public awareness about the diseases, the absence of proper fencing and disposal pits for slaughter houses (where dogs and other 60
4 Fig. 5: Life cycle of Echinococcus spp.source: [16]. carnivores get an easy access) and the habit of disposing most cases of the disease in the USA and Central Europe dead wild or domestic animals, unburied and left open for in immigrants from endemic countries. With the exception scavenging carnivores creates favorable condition for an of Turkana in Kenya, the Mediterranean Basin is the environmental contamination by maintaining the life cycle largest and most focus of human and animals hydatidosis of echinococcosis in stray dogs and wild carnivores [22]. with regard to incidence in human veterinary medicine [23]. Epidemiology, Transmission and Geographic Gemmel et al. [26] pointed out that the parasite Distribution: Dog plays a major role in the epidemiology population, which consists of three sub-populations of the disease. As it is known dog lives in close quarters namely the adults in the definitive hosts, larva with man, feeding on scrapes, on the offal of wild (metacestodes) in the intermediate host and eggs in the herbivores hunted by his master or domestic herbivores environment, play important role in the stability of the for butchering. [23]. Dogs infected with echinococcosis disease and therefore the contributions made by each tape worms pass eggs in their faeces and humans become segment of the parasite population need to be thoroughly infected through faecal-oral contacts [1]. Indirect means understood. of contact via soil, water and contaminated vegetables, or The highest prevalence of hydatid disease in the through the intermediary of flies and other arthropods, world occurs in Kenya where unusual conditions prevail, may also result in human infections. Eckert et al. [24] in that the Turkana tribe traditionally has a very close described that the disease has a worldwide distribution association with dogs. Most households keep a dog and is found in all continents i.e. temperate, tropical and which they utilize to lick clean their babies after sub tropical with the highest prevalence is found in parts defecation. A further factor is that human dead bodies of Eurasia, Africa, Australia and South America. Within (Which may contain hydatid cysts) are often buried in the endemic zones, the prevalence of the parasite varies shallow graved in the bush where they may be scavenged from sporadic to high, but only a few countries are by dogs or wild carnivores [5]. considered as free of Echinococcus granulosus [24]. The highest human incidence rate of CE is found in Morar and Felman, [25] indicated that considerable public areas where the greatest numbers of sheep are kept [27]. health problems are encountered in endemic areas and Schantz, [28] indicated that socio-economic and cultural 61
5 characteristics, uncontrolled slaughter of livestock and Clinical Manifestations: Dogs and other definitive hosts insanitary living condition and uncontrolled dogs living may have thousands Echinococcus tapeworms in their closely with people are among the best defined risk intestine without developing signs of infection. Rarely factors for human infection. there may be diarrhea [33]. In Ethiopia, the status of hydatidosis both in Sheep and other intermediate hosts with hydatid humans and animals is not well documented and explored. cysts are indistinguishable from uninfected animals In Southwestern Ethiopia (e.g. Borena and Hamer) CE is (no obvious signs). However, the results of some studies prevalent among transhumant pastoralists [29]. The have shown that infection can reduce meat, milk and wool incidence of hydatid disease slaughtered in various parts production. Sometimes depending on localization of cyst of the country has been reported by many individuals, the following signs can be seen bronchopneumonia, which ranges from 21.1% in Addis Ababa to 75.1% in hepatic disorder leading to ascites and jaundice, heart Gonder [30, 31, 32]. The variation in prevalence rate in failure, slow growing, weakness and lameness [21]. different regions may be attributed to difference in culture, In humans the clinical manifestation depends on the practice of back yard slaughtering coupled with provision site of organ involvement, organ involved and size of the of infected offal to dogs, social activities and other related cyst, stage of cyst development and viability of cyst factors [8]. contents. The majorities of cysts produce no symptoms Human hydatidosis in Ethiopia is very well known and are detected as incidental finding on routine imaging that hydatid disease is becoming a problem of human or at autopsy (surgery). Symptoms are related to concern throughout the world. But in Ethiopia information expanding mass, pressure on adjacent structure, infection and compile data is lacking in most hospitals and health and rupture of cyst contents in to surrounding body centers due to the absence of well equipped diagnostic cavity [33]. Accidental rupture of cysts can be followed facilities, asymptomatic and chronic nature of the disease. by massive involvement of cyst fluid and dissemination However, based on community base survey for CE, during of protoscolices, resulting occasionally in anaphylactic 1987 in Southwest Ethiopia 1970 people were screened reaction and or multiple secondary CE [34]. with ultrasound and 31 CE cases were detected with The incubation period is highly variable, the cyst may prevalence of 1.6%. In addition, 3224 persons were produce clinical symptoms even 5 years to 20 years after screened with ultrasound survey in Southern Ethiopia and infection when it attains sufficient size to cause 16 (0.5%) were positive for CE in 1996 [24]. disturbances by mechanical pressure on surrounding tissue. The cysts situated in vital organs interfere with the Pathogenesis: Depending on the mode of development function of the affected organ [16]. Hydatid cyst of the CE is of two types, primary CE and secondary CE. Primary liver causes hepatomegaly with or without palpable CE occurs after per oral infection with E. granulosus egg abdominal mass, the condition is associated with which gives rise to hydatid cyst in different parts of the abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, portal hypertension body while secondary CE occurs by rupture of primary and biliary peritonitis [16]. Intact hydatid cysts in the lung hydatid cyst due to trauma. In this condition the often cause no symptom. However, a large cyst may protoscolices are carried by the blood to different body cause pressure symptoms and lead to cough and parts and develop into secondary hydatid cyst [16]. haemoptysis. Complication arise when cyst rupture either Calcification can occur in pericyst, mother cyst and in to bronchial tree or pleura and may cause allergic daughter cyst. Calcification of endocyst indicates the reaction including an aphylaxis, pleural effusion, cyst is non viable. However, calcification of pericyst is emphysema [33]. found in one third of cysts and occurs in all stages of cyst development [33]. Importance of the Disease During natural course of infection some cysts may Veterinary Health and Financial Losses: The importance grow to certain size and continue to remain so without producing any pathological change for many years. Other of echinococcosis is mainly due to its impact on the animal production and economic losses due to disability cysts may rupture spontaneously or collapse and and death and losses from costs of applying control. The disappear completely [16]. Pressure effect by cyst may develop in sensitive areas. Hydatids may cause blocking effect and mechanical compression leading to collapse of infected bones, blindness, rupture of cyst induce sudden anaphylactic shock [24]. reduced yield and quality of meat, milk and wool, reduced birth rate, delayed performance and growth condemnation of organs, especially of liver and lung. Costs for destruction of infected and dead animals, ban on export of animals and their products and cost of control. 62
6 Losses in sheep with echniococcosis have been tree leads asthma like symptoms, coughing, dyspnoea and reported to approximate 7%-10% of milk yield, 5%-20% of haemoptysis, fever [36]. The socio-economic meat or total carcass weight and 10%-40% of wool consequences of echniococcosis in human is mainly due production. to: Researchers estimated that birth weight of lambs from Cost for diagnosis of the infection. Medical and infected sheep may be 20%-30% less than that of lambs surgical fees and costs of hospitalization nursing and from healthy sheep. The financial impact in domestic food drugs. Loss of working days or production. Cost of animals due to condemnation of offals in local abattoir in travel to seek treatment for both patient and family Chile between (liver and kidney) alone were members. Mortality (potential years of life lost). Suffering valued USD 6, 364, 563 [35]. With respect to a reduction and social consequences of disability. Abandonment of in the production of milk studies in Sardinia may amount farming or agricultural activities by affected or at risk to a loss of 20, 075 billion litres per annum [26]. persons. Costs of control programs [26]. Public Health Importance and Financial Losses: Cystic echinococcosis (CE) in humans is an infection, which is caused by larval stage, the metacestode of Echinococcus species and may result in asymptomatic infection to severe disease, which may be fatal. The metacestode all five recognized Echinococcus species can infect humans and cause varies forms of the disease. Among these forms CE caused by Echinococcus granulosus and alveolar echinococcus (AE) caused by Echinococcus multilocularis are of special importance [34]. Echinococcus granulosus following primary infection may inhibit many anatomic sites. The two most common organs involved are liver ( 65%) and lung (25%) other less common sites affected by cysts include the muscle (5%), spleen ( 1%), bone ( 3%), kidneys ( 2%), heart (1%) and CNS (1%). The majorities of patients have single organ involvement (18.7%) and harbor solitary cyst (72%) [33]. The presence of hydatid cyst in liver, lung and other organ can lead to varied clinical manifestations such as: In the liver: Tumor, hepatomegaly, cholestasis, jaundice, secondary biliary cirrhosis, biliary colic like symptoms, liver abscess, calcified lesions in the liver, portal hypertension and thrombosis. In the lung: Lung tumour, chest pain, chronic cough, dyspnoea, haemoptysis, pneumothorax, pleuritis and lung abscess. In the heart: Pain, tumour, cardiac insufficiency and embolism. In the bone and muscles: Pain, bone out growth, bone fragility, muscle cyst. In the brain and spine: Head each, tumour with neurological symptoms and back pain. In the eyes: Pain, ptosis and visual disturbances [36]. Cyst rupture in the liver to the biliary tree leads to biliary colic, cholesteotic jaundice, cholangitis, fever, pancreatitis and anaphylaxis. Cyst rupture in the bronchial Diagnosis: In dogs diagnosis can be made based on detection of eggs and proglottids in the faeces. Definitive diagnosis to the species is difficult because eggs of all Echinococcus and Taenia species are morphologically indistinguishable and characteristic small segments of Echinococcus species may be absent from faeces or can be easily over looked. Purgation with arecoline hydrobromide and necropsy of small intestine has been extensively used for diagnosis in dogs. Immunodiagnosis/coproantigen test based on faecal antigen detection, antibody sandwich ELISA can be used with 70% and 98% sensitivity and specificity, respectively [4]. Diagnosis of CE in livestock is mainly based on necropsy findings. Clinical symptoms may frequently be overlooked. Ultrasound examination for cystic structure may be used for diagnosis in small animals. In Kenya, ultrasound examination of lung and liver was used for detecting hydatid cyst in sheep and goats, sensitivity and specificity were 54% and 97% respectively. Immunological tests can be tried with various sensitivity and specificity [36]. Diagnosis of CE in humans can be done by microscopic examination of aspirated hydatid fluid specimen to demonstrate brood capsule and protoscolices (hooks), but aspiration is not recommended because of danger of spillage viable protoscolices. Occasionally protoscolices may be demonstrated in urine, bile, stool or sputum by acid fast staining after rupture of cyst in liver, lung or kidney [16]. Serological tests detect specific serum antibodies or circulating antigens by various methods. Currently indirect hemagglutination antibody (IHA) and double diffusion immunoelectrophoresis tests are frequently used with variable sensitivity and specificity [37]. ELISA employing hydatid fluid antigen for detection of 63
7 echinococcus antibody (IgG) in serum is most widely surgery, in patients with multiple peritoneal cysts after used. This test has sensitivity of % and specificity spillage during surgery and as concomitant therapy with of 88-96% in hepatic cyst. However, sensitivity of this test percutaneous drainage [33, 36]. is around 50-60% in pulmonary cyst and 25-26% in cysts PAIR (Puncture, Aspiration and Installation of involving other organs [33]. scolicidal agent and Reaspiration) is the treatment of Casoni skin test is an immediate hypersensitivity skin choice in patients with hepatic hydatid cyst who either test performed in injecting 0.2 ml of sterile hydatid fluid refuse surgery or have significant co-morbid disease. intradermally in one arm. Sterile normal saline (0.2 ml) is The procedure is minimally invasive, cost effective; injected on other arm as control. Development of large reduce hospital stay and less morbidity and mortality than wheal greater than 5 cm in diameter indicates positive surgery [33]. reaction but with limited diagnostic value due to low sensitivity and specificity (55-75%) [16]. Control Measures: Control of hydatidosis is less Imaging to detect hydatid cyst, plain radiography effective without the support of dog owners and this (x-ray) has role in lung and bone cysts [33, 36]. support can only be contained if the people have clear Ultrasonography- abdominal cysts, particularly in the liver understanding of the life cycle of the hydatid disease. and cysts in soft tissue are well visualized by ultrasound The following are important measures for the control [33, 37]. In epidemiological studies ultrasound used to preventing access by dogs to uncooked organs of study prevalence of CE in population [16]. livestock and dead human body, removal of unwanted dogs (or stray dogs), regular treatment of dogs with Treatment: In the definitive host the choice of drug is praziquante, persecution of illegal slaughtering, movement praziquantel and purging with arecoline hydro bromide is control of dogs and food animal, changing animal possible [38]. husbandry practices to limit the number of old animals, In the intermediate domestic animals promising vaccinating sheep and goats (Eg 95 vaccine), education results were obtained with anthelminthics benzimidazole and surveillance, avoidance of intimate contact with dogs, group (albendazole and mebendazole). At present no monitoring control changes in age/ incidence of new routine treatment of domestic animals against CE since human infections and the statistics of the parasite in application of benzimidazole in effective dosage would be slaughtered live stock [39, 40]. too expensive. Trials with benzimidazole in sheep and pig Public education program educate hotel owners and have only been carried out using mebendazole other citizens to have their animals slaughtered in administered daily at 50 mg/kg for up to 3 months. slaughter house. Educate and convey message to people Praziquantel has also been tested for hydatid cyst in (farms, children) that infected dogs present danger to animals but results were discouraging [36]. human population and livestock and prevention of In humans surgery is the treatment of choice in large infections in dogs. hepatic cysts with multiple daughter cysts, subcapsular Slaughter houses facilities should have properly or pedenculated liver cyst, infected liver cysts, cysts trained meat inspector, dog proof fencing and have communicating with bile ducts and cysts in lungs, brain, adequate, deep and wide disposal pits. kidney, bone and other organ [33]. Meat inspections and effective disposal of offal at Chemotherapy with albendazole given orally at a abattoir and prevention of clandestine leakage of offals, dose rate of 10 mg/kg body weight daily in two divided banning dogs form abattoir and closure if necessary, doses for minimum of 3 months and mebendazole given prevention of feeding raw offal to dogs including orally at a dose rate of mg thrice daily for 21 days inspection of offal disposal facilities on farm or other to 30 days are effective against CE, have scolicidal premises where live stock are killed, control of dogs activity [16]. including registration and elimination of un wanted (stray) Praziquantel administered at dose of 40 mg/kg once dogs and quarantine of premises with infected livestock. a week concomitantly with benzimidazole has shown to increase scolicidal activity of imidazoles [33]. CONCLUSION Chemotherapy is effective in smaller cysts (less than 4 cm in diameter), cysts with thin wall and in younger The wide spread tradition of offering uncooked patients. It is indicated in patients who are at high risk of infected offals to pet animals around homestead, poor 64
8 public awareness about the diseases, the absence of 7. Jobre, Y., F. Lobago, R. Tiruneh, G. Abebe and proper fencing and disposal pits for slaughter houses P.H. Dorchies, Hydatidosis in three selected (where dogs and other carnivores get an easy access) and regions in Ethiopia: An assessment trial on its the habit of disposing dead wild or domestic animals, prevalence, economic and public health importance. unburied and left open for scavenging carnivores creates Rev. Med. Vet., 11: favorable condition for environmental contamination by 8. a Kebede, N., A. Mitiku and G. Tilahun, maintaining the life cycle of Echinococcus granulosus in Hydatidosis of slaughtered animals in Bahir Dar stray dogs and wild carnivores. Echinococcosis is Abattoir, northwestern Ethiopia. Trop Anim Hlth zoonosis whose successful control and resulting Prod, 41(1): reduction of socio-economic impact demand continuous 9. Ahmed, N., L. Diriba, E. Eyob A. Birhanu A. Guluma resources and activities in long term, specially because and K. Lamessa, Prevalence, Organ it is often necessary to influence habits, customs, Condemnation and Financial Losses Due to traditions, cultures and living working environment which Fasciolosis and Hydatidosis in Cattle cannot be changed in short time. Slaughtered in Adama Municipal Abattoir, Ethiopia. In order to formulate and implement feasible control African Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences, program and reduce the economic and public health 8(5): impact caused by the disease strong continual 10. Eckert, J. and P. Deplazes, Biological, commitment and the collaboration of several professional Epidemiological and Clinical Aspects of categories such as veterinarians, physicians, public health Echinococcosis, a Zoonosis of Increasing Concern. personals, teachers, polices, wildlife attendants, waste Clin. Microbiol. Rev., 17(1): disposal personals, dog owners and community leaders 11. Jenkins, D.J., T. Romig and R.C.A. Thompson, and public administrators is recommended. Emergence/ re-emergence of Echinococcus spp.a global update. Int. J. Parasitol., 35: Competing Interests: The authors declare that they have 12. Azlaf, R. and A. Dakkak, Epidemiological study no competing interests. of the cystic Echinococcosis in Morocco. Vet. Parasitol., 137: REFERENCES 13. Elshazly, A.M., S.E. Awad, M.A. Hegazy, K.A. Mohammad and T.A. Morsy, Schantz, P.M., P. Kern and E. Brunetti, Tropical Echinococcus granulosus/hydatidosis an endemic infectious diseases: principles, pathogens and zoonotic disease in Egypt. Egp. society. J. Parasitol., practice.philadelphia, WB Saunders, pp: pp: Xiao N., J. Qiu, M. Nakao, T. Li, W.Yang, X. Chen, 14. Urquhart, G. M., J. Armour, J.L. Duncan, A.M. Dunn PM. Schantz, P.S. Craig and A. Ito, nd and F.W. Jennings, Veterinary Parasitology 2 Echinococcus shiquicus, a new species from the Ed. Oxford, Longman Scientific and technical press, qinghai-tibet plateau region of china: discovery UK., pp: and epidemiological implications. Parasitol. Int., a 15. Thompson, R.C.A. and D.P. McManus, : Aetiology: parasites and life cycles. WHO/OIE 3. Thompson, b R.C.A. and D.P. McManus, Manual in Echinococcosis in Humans and Animals, Towards a taxonomic revision of the genus pp: Echinococcus. Trends Parasitol., 18: Parija, S.C., Text book of medical 4. Francais, E., Manual of diagnostic tests and parasitology. Protozoology and helmenthology. vaccines for terrestrial animals. Echinococcosis / nd 2 ed. India Publishers and Distributors, India, New th Hydatidosis. 5 ed. Delhi. 5. Smith, M., Animal Parasitology. University of 17. Magambo, J., E. Njoroge and E. Zeyhle, Cambridge. Uk. Epidemiology and control of echinococcosis in 6. Radfar, M.H. and N. Iranyar, Biochemical sub-saharan Africa. Parasitol Int., 55: S193-S195. profiles of hydatid cyst fluids of E. granulosus of 18. Mehlhorn, H., Echinococcosus, Encyclopidia human and animal origin in Iran. Veterinarski Arhir, Reference of parasitology, berg:springer, Berlin, 74/61: I&II:
9 19. Anderson, F.L., H. Ouhelli and M. Kashani, Bersissa, K., Hydatidosis in Nekemte Compendium on cystic echinococcosis in Africa and prevalence in slaughtered cattle and sheep estimated in Middle Eastern countries with special reference to economic loss and incidence in stray dogs. A DVM Morocco. Provo Brigham Young University. thesis, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Addis Ababa 21. Grant, P.S. and D.P. McManus, Parasitology University, pp: 23. echinococcsis: Transmission, biology and 32. Zeleke, G., Prevalence and Financial Effects of epidemiology. CambridgeUniversity Press. Hydatidosis in Cattle Slaughtered in Birre-Sheleko 22. Kebede, N., H. Mekonnen, A. Wossene and and Dangila Abattoirs, Northwestern Ethiopia. Aklilu b G. Tilahun, Hydatidosis of slaughtered cattle Lemma Institute of Pathobiology, Addis Ababa in Wolaita Sodo Abattoir, southern Ethiopia. Trop University. Anim Hlth Prod., 41(4): Khuroo, M.S., Hydatid disease, current 23. Jean, N.P., Hydatidosis in the ancient world, status and recent advances. Ann. Saudi Med., The origin and Dispersion of human parasitic 122(1-2): diseases in the Old world (Africa, Europe and 34. Gottstein, B., Molecular and immunological Madagascar) virtychatillon, Paris, France. diagnosis of echinococcosis (hydatid disease), 24. Eckert, J., P.M. Schantz, R.B. Gasser, P.R. Torgerson, pp: 1-6. A.S. Bessonou, S.O. Movscsian, A. Thakur, F. Grimm 35. Budke, C.M., P. Deplazes and P.R. Torgerson, and M.A. Nikogossian, Geographic distribution Global socio-economic impact of cystic and prevalence.who/oie Manual in Echinococcosis echinococcosis. Vet. Pasitol., 12(2): 11. in Humans and Animals, pp: Pawlowski, Z.S., J. Eckert, D.A. Vuitton, 25. Morar, R. and C. Feldman, Pulmunary R.W. Amman, P. Kern, P.S. Eraig, K.F. Dars, echinococcosis. Eur Respir. J., 21: F. Dehosa, C. Filee, W. Gottstein and H. Wen, Gemmell, M.A., M.G. Roberts, T.C. Beard, D.S. Echnococcosis in humans. Clinical aspects, Campano, J.R. Lawson and J.M. Nonnemaker, diagnosis and treatment.who/oie Manual in Control of echinococcosis. WHO/OIE Manual in Echinococcosis in Humans and Animals, pp: Echinococcosis in Humans and Animals, pp: Brunetti E., Echinococcosis hydatidosis. HON 27. Torgerson, P.R., D.H. Williams and M.N. Abo- Code Principles of the Health on the Net Foundation, Shehada, Modelling the prevalence of pp: 12. Echinococcus and Taenia species in small ruminnts 38. Soulsby, E.J.L., Helminth, Arthropod and of different ages in northern Jordan. Vet. Parasitol., th Protozoa of Domestic Animals. 7 Ed. Baillere Tindall, 79: London, Uk, pp: Schantz, P.M., J. Chai and P.S. Craig, Macpherson, C.N.L., E. Zeyhle and T. Roming, Epidemiology and control.in Thompson, R.C.A., A.J. An echinococcosis pilot control programme for nd Lymbery, 2 ed. Echinococcosis and Hydatidosis Northwest Turkana, Kenya. Ann. Trop. Med. Disease.London, CAB., pp: 233. Parasitol., 78: Stenning, D.J., Transhumance, migratory drift, 40. Battelli, G., Evaluation of the economic costs of migration: Patterns of pastoral Fulani nomadism. echinococcosis. Int., Arch Hydatid, 32: Culters and societies of Africa. Random house, New York, pp: Mitiku, A., Prevalence, economic and Public Health significance of Hydatidosis Echinococcosis at Bahir Dar abattoir. Msc projec, Aklilu Lemma Institute of pathobioloigy, Addis Ababa Universty. 66
Hydatid Disease. Overview
 Hydatid Disease Overview Hydatid disease in man is caused principally by infection with the larval stage of the dog tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus. It is an important pathogenic zoonotic parasitic infection
Hydatid Disease Overview Hydatid disease in man is caused principally by infection with the larval stage of the dog tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus. It is an important pathogenic zoonotic parasitic infection
ECHINOCOCCOSIS. By Dr. Ameer kadhim Hussein. M.B.Ch.B. FICMS (Community Medicine).
 ECHINOCOCCOSIS By Dr. Ameer kadhim Hussein. M.B.Ch.B. FICMS (Community Medicine). INTRODUCTION Species under genus Echinococcus are small tapeworms of carnivores with larval stages known as hydatids proliferating
ECHINOCOCCOSIS By Dr. Ameer kadhim Hussein. M.B.Ch.B. FICMS (Community Medicine). INTRODUCTION Species under genus Echinococcus are small tapeworms of carnivores with larval stages known as hydatids proliferating
Hydatid Cyst Dr. Nora L. El-Tantawy
 Hydatid Cyst Dr. Nora L. El-Tantawy Ass. Prof. of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura university, Egypt Echinococcus granulosus Geographical Distribution: cosmopolitan especially in sheep raising
Hydatid Cyst Dr. Nora L. El-Tantawy Ass. Prof. of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura university, Egypt Echinococcus granulosus Geographical Distribution: cosmopolitan especially in sheep raising
1.0 INTRODUCTION. Echinococcosis, a cyclozoonotic helminthosis caused by the dwarf dog
 INTRODUCTION 1.0 INTRODUCTION Echinococcosis, a cyclozoonotic helminthosis caused by the dwarf dog tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus is highly endemic and is considered to be one of the most important parasitic
INTRODUCTION 1.0 INTRODUCTION Echinococcosis, a cyclozoonotic helminthosis caused by the dwarf dog tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus is highly endemic and is considered to be one of the most important parasitic
This is the smallest tapeworm that can affect human being but it s not really proper human tapeworm (the human is not the primary host).
 Echinococcus Granulosus Small Tapeworm (1 cm), Cestode. This is the smallest tapeworm that can affect human being but it s not really proper human tapeworm (the human is not the primary host). The primary
Echinococcus Granulosus Small Tapeworm (1 cm), Cestode. This is the smallest tapeworm that can affect human being but it s not really proper human tapeworm (the human is not the primary host). The primary
HYDATID CYST DISEASE
 HYDATID CYST DISEASE Hydatid disease, also called hydatidosis or echinococcosis, is a cystforming disease resulting from an infection with the metacestode, or larval form, of parasitic dog tapeworms from
HYDATID CYST DISEASE Hydatid disease, also called hydatidosis or echinococcosis, is a cystforming disease resulting from an infection with the metacestode, or larval form, of parasitic dog tapeworms from
ECHINOCOCCUS GRANULOSUS
 48 ECHINOCOCCUS GRANULOSUS 48.1 INTRODUCTION E granulosus are small tape worms that parasitize the intestines of carnivores like dogs. About one million people are infected with this tape worm worldwide.
48 ECHINOCOCCUS GRANULOSUS 48.1 INTRODUCTION E granulosus are small tape worms that parasitize the intestines of carnivores like dogs. About one million people are infected with this tape worm worldwide.
Schistosoma mansoni, S. japonicum, S. haematobium
 Schistosoma mansoni, S. japonicum, S. haematobium The Organisms More than 200 million people are infected worldwide with Schistosoma species. The adult worms are long and slender (males are 6 12 mm in
Schistosoma mansoni, S. japonicum, S. haematobium The Organisms More than 200 million people are infected worldwide with Schistosoma species. The adult worms are long and slender (males are 6 12 mm in
Scientific background concerning Echinococcus multilocularis. Muza Kirjušina, Daugavpils University, Latvia
 Scientific background concerning Echinococcus multilocularis Muza Kirjušina, Daugavpils University, Latvia Echinococcus multilocularis Infection with the larval form causes alveolar echinococcosis (AE).
Scientific background concerning Echinococcus multilocularis Muza Kirjušina, Daugavpils University, Latvia Echinococcus multilocularis Infection with the larval form causes alveolar echinococcosis (AE).
Contains most of the medically important tapeworms Scolex has 4 suckers and compact vitelline gland are characteristic Range from mm to >10m
 Cyclophyllidae Contains most of the medically important tapeworms Scolex has 4 suckers and compact vitelline gland are characteristic Range from mm to >10m Family Taeniidae Taenia saginata: beef tapeworm
Cyclophyllidae Contains most of the medically important tapeworms Scolex has 4 suckers and compact vitelline gland are characteristic Range from mm to >10m Family Taeniidae Taenia saginata: beef tapeworm
Prevalence Survey on Hydatidosis and its Financial Loss in Small Ruminants Slaughtered at Addis Ababa Abattoirs Enterprise
 ISSN 079-018 IDOSI Publications, 015 DOI: 10.589/idosi.apg.015.6.3.950 Prevalence Survey on Hydatidosis and its Financial Loss in Small Ruminants Slaughtered at Addis Ababa Abattoirs Enterprise Simegnew
ISSN 079-018 IDOSI Publications, 015 DOI: 10.589/idosi.apg.015.6.3.950 Prevalence Survey on Hydatidosis and its Financial Loss in Small Ruminants Slaughtered at Addis Ababa Abattoirs Enterprise Simegnew
Parasitology. Echinococcus Spp.
 Parasitology المحاضرة الثالثت ا. صباح النجار Echinococcus Spp. Genus Echinococcus include three different species in which man acts as intermediate host and infecting by the larval stage of these species.
Parasitology المحاضرة الثالثت ا. صباح النجار Echinococcus Spp. Genus Echinococcus include three different species in which man acts as intermediate host and infecting by the larval stage of these species.
Hazem.K.Al-Khafaji FICMS College of medicine- Al-Qadissyia university
 Hazem.K.Al-Khafaji FICMS College of medicine- Al-Qadissyia university Cestodes(Tapeworms) - Morphology - Tapeworm parts: Flat, segmented body with various length (several mm,25mm as hymenolepis nana ~
Hazem.K.Al-Khafaji FICMS College of medicine- Al-Qadissyia university Cestodes(Tapeworms) - Morphology - Tapeworm parts: Flat, segmented body with various length (several mm,25mm as hymenolepis nana ~
Antihelminthic Trematodes (flukes): Cestodes (tapeworms): Nematodes (roundworms, pinworm, whipworms and hookworms):
 Antihelminthic Drugs used to treat parasitic worm infections: helminthic infections Unlike protozoa, helminthes are large and have complex cellular structures It is very important to identify the causative
Antihelminthic Drugs used to treat parasitic worm infections: helminthic infections Unlike protozoa, helminthes are large and have complex cellular structures It is very important to identify the causative
Economic and Zoonotic Importance of Bovine Hydatidosis in Shire Municipal Abattoir, North West Zone, Tigary Region, Ethiopia
 ISSN 2079-2018 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.apg.2013.4.3.7531 Economic and Zoonotic Importance of Bovine Hydatidosis in Shire Municipal Abattoir, North West Zone, Tigary Region, Ethiopia
ISSN 2079-2018 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.apg.2013.4.3.7531 Economic and Zoonotic Importance of Bovine Hydatidosis in Shire Municipal Abattoir, North West Zone, Tigary Region, Ethiopia
Prevalence, Organ Condemnation and Financial Losses Due to Fasciolosis and Hydatidosis in Cattle Slaughtered in Adama Municipal Abattoir, Ethiopia
 African Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences 8 (5): 276-282, 2016 ISSN 2079-2034 IDOSI Publications, 2016 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajbas.2016.276.282 Prevalence, Organ Condemnation and Financial Losses Due to
African Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences 8 (5): 276-282, 2016 ISSN 2079-2034 IDOSI Publications, 2016 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajbas.2016.276.282 Prevalence, Organ Condemnation and Financial Losses Due to
Cystic echinococcosis in a domestic cat: an Italian case report
 13th NRL Workshop, Rome, 24-25 May, 2018 Cystic echinococcosis in a domestic cat: an Italian case report Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale (IZS) of Sardinia National Reference Laboratory for Cistic
13th NRL Workshop, Rome, 24-25 May, 2018 Cystic echinococcosis in a domestic cat: an Italian case report Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale (IZS) of Sardinia National Reference Laboratory for Cistic
Report and Opinion 2017;9(11) Birara Ayalneh 1, Balemual Abebaw 2
 Major causes of organ condemnation in cattle and sheep slaughtered at Motta abattoir North-West Ethiopia. Birara Ayalneh 1, Balemual Abebaw 2 1. College of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science, Department
Major causes of organ condemnation in cattle and sheep slaughtered at Motta abattoir North-West Ethiopia. Birara Ayalneh 1, Balemual Abebaw 2 1. College of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science, Department
Magnitude of Echinococcus granulosus in Dogs, Through the Infection Rate of Hydatid Cyst in Cattles and Humans
 African Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences 8 (6): 314-30, 016 ISSN 079-034 IDOSI Publications, 016 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ajbas.016.314.30 Magnitude of Echinococcus granulosus in Dogs, Through the Infection
African Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences 8 (6): 314-30, 016 ISSN 079-034 IDOSI Publications, 016 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ajbas.016.314.30 Magnitude of Echinococcus granulosus in Dogs, Through the Infection
Presentation of Quiz #85
 Presentation of Quiz #85 ***Reminder: Slides are copyrighted and cannot be copied for publication. A 36 year old male from Columbia was admitted to the hospital with seizures. This patient had previously
Presentation of Quiz #85 ***Reminder: Slides are copyrighted and cannot be copied for publication. A 36 year old male from Columbia was admitted to the hospital with seizures. This patient had previously
Bovine Hydatidosis in Eastern Part of Ethiopia
 Bovine Hydatidosis in Eastern Part of Ethiopia Miheret Mulatu, Biruk Mekonnen, Habtamu Tassew and Ashwani Kumar* Department of Veterinary Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Mekelle University, Mekelle,
Bovine Hydatidosis in Eastern Part of Ethiopia Miheret Mulatu, Biruk Mekonnen, Habtamu Tassew and Ashwani Kumar* Department of Veterinary Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Mekelle University, Mekelle,
General introduction
 Spirometra mansoni General introduction Distributed worldwide, mainly in southeast Asia. Larval infection of S. mansoni may cause serious clinical disease ---Sparganosis Morphology Adult worm measures
Spirometra mansoni General introduction Distributed worldwide, mainly in southeast Asia. Larval infection of S. mansoni may cause serious clinical disease ---Sparganosis Morphology Adult worm measures
by author Cystic Echinococcosis Rogelio López-Vélez MD, DTM&H, PhD National Referral Unit for Tropical Diseases Infectious Diseases Department
 Cystic Echinococcosis Rogelio López-Vélez MD, DTM&H, PhD National Referral Unit for Tropical Diseases Infectious Diseases Department Ramón y Cajal University Hospital. Madrid. Spain National Referral Unit
Cystic Echinococcosis Rogelio López-Vélez MD, DTM&H, PhD National Referral Unit for Tropical Diseases Infectious Diseases Department Ramón y Cajal University Hospital. Madrid. Spain National Referral Unit
Cystic Hydatid Disease in Southern Sudan
 Original Article Cystic Hydatid Disease in Southern Sudan D.K. Lado, MBBS, FS SMSB, Juba Teaching Hospital, Juba, South Sudan Correspondence and reprint requests to: Dr. D.K. Lado, Juba Teaching Hospital,
Original Article Cystic Hydatid Disease in Southern Sudan D.K. Lado, MBBS, FS SMSB, Juba Teaching Hospital, Juba, South Sudan Correspondence and reprint requests to: Dr. D.K. Lado, Juba Teaching Hospital,
The role of multidispinary team in management of Hydatid disease
 The role of multidispinary team in management of Hydatid disease Dr/ Rasheed ALEEZI (JBGS, MHPBS) Departmement of general surgery, USThospital Sana`a-YEMEN 58 years old, female patient, housewif. Complaints
The role of multidispinary team in management of Hydatid disease Dr/ Rasheed ALEEZI (JBGS, MHPBS) Departmement of general surgery, USThospital Sana`a-YEMEN 58 years old, female patient, housewif. Complaints
Cestodes. Tapeworms from man and animals
 Cestodes Tapeworms from man and animals Taenia sp. The common (beef) tapeworm is several meters long. Courtesy Peters W. & Gilles H. Courtesy CDC Courtesy CDC Taenia sp. Unstained egg with four (visible)
Cestodes Tapeworms from man and animals Taenia sp. The common (beef) tapeworm is several meters long. Courtesy Peters W. & Gilles H. Courtesy CDC Courtesy CDC Taenia sp. Unstained egg with four (visible)
Understanding the Lifecycle of the Hydatid Tapeworm
 Hydatid Tapeworm The Hydatid Tapeworm (scientific name Echinococcus granulosis) is one of a number of tapeworms that infect dogs. The reason this tapeworm is considered the most significant is that, unlike
Hydatid Tapeworm The Hydatid Tapeworm (scientific name Echinococcus granulosis) is one of a number of tapeworms that infect dogs. The reason this tapeworm is considered the most significant is that, unlike
Prevalence and Economic Importance of Hydatidosis in Cattle Slaughtered at North Gonder Elfora Abattoir
 European Journal of Applied Sciences 5 (1): 29-35, 2013 ISSN 2079-2077 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ejas.2013.5.1.6564 Prevalence and Economic Importance of Hydatidosis in Cattle Slaughtered
European Journal of Applied Sciences 5 (1): 29-35, 2013 ISSN 2079-2077 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ejas.2013.5.1.6564 Prevalence and Economic Importance of Hydatidosis in Cattle Slaughtered
Feline and Canine Internal Parasites
 Feline and Canine Internal Parasites Internal parasites are a very common problem among dogs. Almost all puppies are already infected with roundworm when still in the uterus, or get the infection immediately
Feline and Canine Internal Parasites Internal parasites are a very common problem among dogs. Almost all puppies are already infected with roundworm when still in the uterus, or get the infection immediately
Old Disease New Location Surgeons Be Alerted
 Old Disease New Location Surgeons Be Alerted K. B. Ashok Vol. 3 No. 4 (April 2011) International Journal of Collaborative Research on Internal Medicine & Public Health (IJCRIMPH) ISSN 1840-4529 Journal
Old Disease New Location Surgeons Be Alerted K. B. Ashok Vol. 3 No. 4 (April 2011) International Journal of Collaborative Research on Internal Medicine & Public Health (IJCRIMPH) ISSN 1840-4529 Journal
National Research Center
 National Research Center Update of immunodiagnosis of cystic echinococcosis cysts Global distribution of zoonotic strains of Echinococcus granulosus (Adapted from Eckert and Deplazes, 2004) Echinococcus
National Research Center Update of immunodiagnosis of cystic echinococcosis cysts Global distribution of zoonotic strains of Echinococcus granulosus (Adapted from Eckert and Deplazes, 2004) Echinococcus
Coproantigen prevalence of Echinococcus spp. in rural dogs from Northwestern Romania
 Coproantigen prevalence of Echinococcus spp. in rural dogs from Northwestern Romania Ştefania Seres 1, Eugeniu Avram 1, Vasile Cozma 2 1 Parasitology Department of Sanitary Veterinary and Food Safety Direction,
Coproantigen prevalence of Echinococcus spp. in rural dogs from Northwestern Romania Ştefania Seres 1, Eugeniu Avram 1, Vasile Cozma 2 1 Parasitology Department of Sanitary Veterinary and Food Safety Direction,
et.al -Al-Abassyet.al (1988) Al-Autabbi (1983) -Dawood et. al ( ) 20
 .8 00.7 7.3 Ibrahim Dailey and and Graig, (998) Himonas Islam (979) Sweatman (9) Ibrahim Pandey et.al (988) et.al (987) and Graig,(998) Abdel- Hafez and Al-Yaman,(989) 997( ( 7 Al- Abassy et.al,(980) Al-
.8 00.7 7.3 Ibrahim Dailey and and Graig, (998) Himonas Islam (979) Sweatman (9) Ibrahim Pandey et.al (988) et.al (987) and Graig,(998) Abdel- Hafez and Al-Yaman,(989) 997( ( 7 Al- Abassy et.al,(980) Al-
Management of Echinococcus Multilocularis Infections in Animals Guideline, 2018
 Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Management of Echinococcus Multilocularis Infections in Animals Guideline, 2018 Population and Public Health Division, Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Effective:
Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Management of Echinococcus Multilocularis Infections in Animals Guideline, 2018 Population and Public Health Division, Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Effective:
On the Occurrence and Significance of Hydatid Cysts in the Ceylon Sambhur Rusa unicolor unicolor.*
 CEYLON J. MBD. SCI. (D) Vol. XI, Pt. 1 (May 1962) On the Occurrence and Significance of Hydatid Cysts in the Ceylon Sambhur Rusa unicolor unicolor.* by A. S. DISSANAIKE AND D. C. PARAMANANTHAN** Department
CEYLON J. MBD. SCI. (D) Vol. XI, Pt. 1 (May 1962) On the Occurrence and Significance of Hydatid Cysts in the Ceylon Sambhur Rusa unicolor unicolor.* by A. S. DISSANAIKE AND D. C. PARAMANANTHAN** Department
EXPERIMENTAL HYDATIDOSIS IN THE SUDAN: TRANSMISSION AND NATURAL INFECTION
 EXPERIMENTAL HYDATIDOSIS IN THE SUDAN: TRANSMISSION AND NATURAL INFECTION By Nadia Ahmed Ali Mohamed B.Sc. (Assuit University -Egypt) M.Sc. (Parasitology) University of Khartoum Supervisor: Prof. Mohamed
EXPERIMENTAL HYDATIDOSIS IN THE SUDAN: TRANSMISSION AND NATURAL INFECTION By Nadia Ahmed Ali Mohamed B.Sc. (Assuit University -Egypt) M.Sc. (Parasitology) University of Khartoum Supervisor: Prof. Mohamed
Title. Author(s)YAMASHITA, Jiro; OHBAYASHI, Masashi; KONNO, Seiji. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 4(3): Issue Date
 Title STUDIES ON ECHINOCOCCOSIS : III. ON EXPERIMENTAL INF DEVELOPMENT OF ECHINOCOCCUS GRANULOSUS (BATSCH, 1786 Author(s)YAMASHITA, Jiro; OHBAYASHI, Masashi; KONNO, Seiji CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary
Title STUDIES ON ECHINOCOCCOSIS : III. ON EXPERIMENTAL INF DEVELOPMENT OF ECHINOCOCCUS GRANULOSUS (BATSCH, 1786 Author(s)YAMASHITA, Jiro; OHBAYASHI, Masashi; KONNO, Seiji CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary
Echinococcus multilocularis Diagnosis. Peter Deplazes. Medical Faculty. Swiss TPH Winter Symposium 2017
 Medical Faculty Swiss TPH Winter Symposium 2017 Helminth Infection from Transmission to Control Echinococcus multilocularis Diagnosis Peter Deplazes Global distribution of E. multilocularis Deplazes et
Medical Faculty Swiss TPH Winter Symposium 2017 Helminth Infection from Transmission to Control Echinococcus multilocularis Diagnosis Peter Deplazes Global distribution of E. multilocularis Deplazes et
Biomedicine and Nursing 2017;3(2) Review On Bovine Hydatidosis
 Review On Bovine Hydatidosis Geda Shendo 1, Birhanu Ayele 2, Mengestie Abebaw 1 and Genene Girma 1 1 Faculity of Veterinary Medicine, College of Medical and Health science, University of Gondar, P.O. Box.
Review On Bovine Hydatidosis Geda Shendo 1, Birhanu Ayele 2, Mengestie Abebaw 1 and Genene Girma 1 1 Faculity of Veterinary Medicine, College of Medical and Health science, University of Gondar, P.O. Box.
Cestodes (tapeworms) Pro. Dr. Mohammed Sabri
 Cestodes (tapeworms) Pro. Dr. Mohammed Sabri Characters (general):- Tape worms consist of a round head, called a scolex, and a flat body of multiple segments called proglottides. The scolex has specialized
Cestodes (tapeworms) Pro. Dr. Mohammed Sabri Characters (general):- Tape worms consist of a round head, called a scolex, and a flat body of multiple segments called proglottides. The scolex has specialized
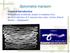
Breast Mass on Mammography
 Breast Mass on Mammography Bobbi Pritt, MD 2014 MFMER slide-1 Clinical Presentation 68 year old woman was noted to have 2 adjacent masses in the right breast on screening mammography Well-circumscribed,
Breast Mass on Mammography Bobbi Pritt, MD 2014 MFMER slide-1 Clinical Presentation 68 year old woman was noted to have 2 adjacent masses in the right breast on screening mammography Well-circumscribed,
Prevalence of Bovine Hydatidosis and Its Economic Significance in Harar Municipality Abattoir, Eastern Ethiopia
 American-Eurasian Journal of Scientific Research 9 (5): 143-149, 2014 ISSN 1818-6785 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.aejsr.2014.9.5.9144 Prevalence of Bovine Hydatidosis and Its Economic Significance
American-Eurasian Journal of Scientific Research 9 (5): 143-149, 2014 ISSN 1818-6785 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.aejsr.2014.9.5.9144 Prevalence of Bovine Hydatidosis and Its Economic Significance
The prevalence of anti-echinococcus antibodies in the North-Western part of Romania
 The prevalence of anti-echinococcus antibodies in the North-Western part of Romania Anca Florea 1, Zoe Coroiu 2, Rodica Radu 2 1 Prof. dr. Octavian Fodor Regional Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,
The prevalence of anti-echinococcus antibodies in the North-Western part of Romania Anca Florea 1, Zoe Coroiu 2, Rodica Radu 2 1 Prof. dr. Octavian Fodor Regional Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,
SHORT RESEARCH NOTE. Anca Florea 1. , Liviu Vlad 2, Vasile Cozma 3, Zoe Coroiu 4. Introduction
 Serological diagnosis of cystic echinococcosis by the ELISA technique, in the cases hospitalized in the Surgical Clinic no. III and Internal Medicine no. III of Cluj-Napoca, during October 2006 December
Serological diagnosis of cystic echinococcosis by the ELISA technique, in the cases hospitalized in the Surgical Clinic no. III and Internal Medicine no. III of Cluj-Napoca, during October 2006 December
Bovine Hydatidosis: Occurrence, Economic and Public Health Importance in Gondar ELFORA Abattoir
 European Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (2): 11-19, 2014 ISSN 2079-2077 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ejas.2014.6.2.8585 Bovine Hydatidosis: Occurrence, Economic and Public Health Importance
European Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (2): 11-19, 2014 ISSN 2079-2077 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ejas.2014.6.2.8585 Bovine Hydatidosis: Occurrence, Economic and Public Health Importance
Rare presentations and Complications of Hepatic Hydatid Cysts
 Rare presentations and Complications of Hepatic Hydatid Cysts Poster No.: C-1926 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kapoor, A. Arora, N. GUPTA, S. K. Puri ; Delhi/IN, NEW 1 2 3 3
Rare presentations and Complications of Hepatic Hydatid Cysts Poster No.: C-1926 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kapoor, A. Arora, N. GUPTA, S. K. Puri ; Delhi/IN, NEW 1 2 3 3
Research Article Risk Factors Associated with Prevalence of Bovine Hydatidosis in Cattle Slaughtered at Khartoum State
 Journal of Applied and Industrial Sciences, 2016,4(1): 21-26, ISSN: 2328-4595 (PRINT), ISSN: 2328-4609 (ONLINE) 21 Research Article Risk Factors Associated with Prevalence of Bovine Hydatidosis in Cattle
Journal of Applied and Industrial Sciences, 2016,4(1): 21-26, ISSN: 2328-4595 (PRINT), ISSN: 2328-4609 (ONLINE) 21 Research Article Risk Factors Associated with Prevalence of Bovine Hydatidosis in Cattle
Guard against intestinal worms with Palatable All-wormer
 Guard against intestinal worms with Palatable All-wormer WHIPWORMS HOOKWORMS TAPEWORMS ROUNDWORMS Palatable All-wormer, for superior, flexible protection of dogs and cats. GENTLE ON PETS, TOUGH ON WORMS.
Guard against intestinal worms with Palatable All-wormer WHIPWORMS HOOKWORMS TAPEWORMS ROUNDWORMS Palatable All-wormer, for superior, flexible protection of dogs and cats. GENTLE ON PETS, TOUGH ON WORMS.
Prevalence and Economic Loss due to Hydatidosis in Slaughtered Animals in Juba South Sudan
 International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 3, Issue 3, March 2015, PP 177-182 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Prevalence and Economic Loss
International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 3, Issue 3, March 2015, PP 177-182 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Prevalence and Economic Loss
Surveillance of animal brucellosis
 Surveillance of animal brucellosis Assoc.Prof.Dr. Theera Rukkwamsuk Department of large Animal and Wildlife Clinical Science Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Kasetsart University Review of the epidemiology
Surveillance of animal brucellosis Assoc.Prof.Dr. Theera Rukkwamsuk Department of large Animal and Wildlife Clinical Science Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Kasetsart University Review of the epidemiology
DEPARTMENT: AGRICULTURE REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA PARASITIC CYSTS AND LESIONS IN MEAT JENNY TURTON
 DEPARTMENT: AGRICULTURE REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA PARASITIC CYSTS AND LESIONS IN MEAT JENNY TURTON Information provided by Animal Health for Developing Farmers, ARC-Onderstepoort Veterinary Institute, Private
DEPARTMENT: AGRICULTURE REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA PARASITIC CYSTS AND LESIONS IN MEAT JENNY TURTON Information provided by Animal Health for Developing Farmers, ARC-Onderstepoort Veterinary Institute, Private
FAO-APHCA/OIE/USDA Regional Workshop on Prevention and Control of Neglected Zoonoses in Asia July, 2015, Obihiro, Japan.
 FAO-APHCA/OIE/USDA Regional Workshop on Prevention and Control of Neglected Zoonoses in Asia 15-17 July, 2015, Obihiro, Japan Dr Gillian Mylrea 1 Overview What is a Neglected Zoonotic Disease? The important
FAO-APHCA/OIE/USDA Regional Workshop on Prevention and Control of Neglected Zoonoses in Asia 15-17 July, 2015, Obihiro, Japan Dr Gillian Mylrea 1 Overview What is a Neglected Zoonotic Disease? The important
Oxfendazole Treatment for Cystic Hydatid Disease in Naturally Infected Animals
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Mar. 1998, p. 601 605 Vol. 42, No. 3 0066-4804/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology Oxfendazole Treatment for Cystic Hydatid Disease in Naturally
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Mar. 1998, p. 601 605 Vol. 42, No. 3 0066-4804/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology Oxfendazole Treatment for Cystic Hydatid Disease in Naturally
Prevalence of Liver Fluke in Sheep and Goat Slaughtered at Abattoirs in Zaria, Kaduna State, Nigeria
 Prevalence of Liver Fluke in Sheep and Goat Slaughtered at Abattoirs in Zaria, Kaduna State, Nigeria Rafindadi, M. N. Yusuf, Z. H. ABSTRACT A survey on the prevalence of liver fluke in sheep and goat slaughtered
Prevalence of Liver Fluke in Sheep and Goat Slaughtered at Abattoirs in Zaria, Kaduna State, Nigeria Rafindadi, M. N. Yusuf, Z. H. ABSTRACT A survey on the prevalence of liver fluke in sheep and goat slaughtered
Cross-Sectional Study on The Prevalence of Stilesia Hepatica on Small Ruminants Slaughtered at Modjo Modern Export Abattoir, Ethiopia
 Cross-Sectional Study on The Prevalence of Stilesia Hepatica on Small Ruminants Slaughtered at Modjo Modern Export Abattoir, Ethiopia Tesfaye Bejiga*, Taye Solomon and Niguagus Leben Veterinary Drug and
Cross-Sectional Study on The Prevalence of Stilesia Hepatica on Small Ruminants Slaughtered at Modjo Modern Export Abattoir, Ethiopia Tesfaye Bejiga*, Taye Solomon and Niguagus Leben Veterinary Drug and
EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF CYSTIC ECHINOCOCCOSIS IN WALES. Mariel Stefhanie Aybar Espinoza
 EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF CYSTIC ECHICOCCOSIS IN WALES Mariel Stefhanie Aybar Espinoza Supervisor: Eileen Devaney A dissertation submitted to obtain the degree of Master of Veterinary
EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE CONTROL OF CYSTIC ECHICOCCOSIS IN WALES Mariel Stefhanie Aybar Espinoza Supervisor: Eileen Devaney A dissertation submitted to obtain the degree of Master of Veterinary
LAO PEOPLE S DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC. Instruction on the Regulation on Livestock Management in the Lao PDR
 Page 1 LAO PEOPLE S DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC PEACE INDEPENDENCE DEMOCRACY UNITY PROSPERITY Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry Instruction on the Regulation on Livestock Management in the Lao PDR 1. Principles
Page 1 LAO PEOPLE S DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC PEACE INDEPENDENCE DEMOCRACY UNITY PROSPERITY Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry Instruction on the Regulation on Livestock Management in the Lao PDR 1. Principles
The EU thanks the OIE TAHSC, the APSFWW and the ad hoc group for their work.
 1 Annex 34 Original: English October 2010 REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE OIE AD HOC GROUP ON ZOONOTIC PARASITES Paris (France), 57 October 2010 s The EU thanks the OIE TAHSC, the APSFWW and the ad hoc group
1 Annex 34 Original: English October 2010 REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE OIE AD HOC GROUP ON ZOONOTIC PARASITES Paris (France), 57 October 2010 s The EU thanks the OIE TAHSC, the APSFWW and the ad hoc group
Fertility of Hydatid Cysts and Viability of Protoscoleces in Slaughtered Animals in Qazvin, Iran
 Journal of Agricultural Science; Vol. 5, No. 1; 2013 ISSN 1916-9752 E-ISSN 1916-9760 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Fertility of Hydatid Cysts and Viability of Protoscoleces in Slaughtered
Journal of Agricultural Science; Vol. 5, No. 1; 2013 ISSN 1916-9752 E-ISSN 1916-9760 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Fertility of Hydatid Cysts and Viability of Protoscoleces in Slaughtered
THE STRUCTURE OF ECHINOCOCCAL CYSTS AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN LIVER
 THE STRUCTURE OF ECHINOCOCCAL CYSTS AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN LIVER Michal Juszynski Helena Palenga, Danuta Cielecka PhD Department of General Biology and Parasitology Medical University of Warsaw
THE STRUCTURE OF ECHINOCOCCAL CYSTS AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN LIVER Michal Juszynski Helena Palenga, Danuta Cielecka PhD Department of General Biology and Parasitology Medical University of Warsaw
The Prevalence and Economic Significance of Bovine Fasciolosis at Jimma, Abattoir, Ethiopia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Veterinary Medicine Volume 3 Number 2 The Prevalence and Economic Significance of Bovine Fasciolosis at Jimma, Abattoir, Ethiopia T Tolosa, W Tigre Citation T Tolosa,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Veterinary Medicine Volume 3 Number 2 The Prevalence and Economic Significance of Bovine Fasciolosis at Jimma, Abattoir, Ethiopia T Tolosa, W Tigre Citation T Tolosa,
"Serpent" Sign, "Double Arch" Sign and "Air-Bubble"Sign in a case of Ruptured Hydatid Cyst-A Case Report
 Article ID: WMC004602 ISSN 2046-1690 "Serpent" Sign, "Double Arch" Sign and "Air-Bubble"Sign in a case of Ruptured Hydatid Cyst-A Case Report Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Dipti Gothi,
Article ID: WMC004602 ISSN 2046-1690 "Serpent" Sign, "Double Arch" Sign and "Air-Bubble"Sign in a case of Ruptured Hydatid Cyst-A Case Report Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Dipti Gothi,
Report on the third NRL Proficiency Test to detect adult worms of Echinococcus sp. in the intestinal mucosa of the definitive host.
 Report on the third NRL Proficiency Test to detect adult worms of Echinococcus sp. in the intestinal mucosa of the definitive host March-April, 2011 page 1 of 11 Table of contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Scope
Report on the third NRL Proficiency Test to detect adult worms of Echinococcus sp. in the intestinal mucosa of the definitive host March-April, 2011 page 1 of 11 Table of contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Scope
Tadesse Birhanu and Sultan Abda
 American-Eurasian Journal of Scientific Research 9 (4): 87-97, 2014 ISSN 1818-6785 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.aejsr.2014.9.4.86128 Prevalence, Economic Impact and Public Perception of
American-Eurasian Journal of Scientific Research 9 (4): 87-97, 2014 ISSN 1818-6785 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.aejsr.2014.9.4.86128 Prevalence, Economic Impact and Public Perception of
 Liver Fluke Infestation; What You Need to Know Mamoon Rashid, Sheep and Goat Specialist Manitoba Agriculture, Food and Rural Initiatives Liver fluke is an internal parasite (worm) that affects sheep and
Liver Fluke Infestation; What You Need to Know Mamoon Rashid, Sheep and Goat Specialist Manitoba Agriculture, Food and Rural Initiatives Liver fluke is an internal parasite (worm) that affects sheep and
CRANIAL HYDATID CYST
 Thi-Qar Medical Journal (TQMJ): Vol(6) No(1):2012(48-52) OBJECT: CRANIAL HYDATID CYST Dr. Haitham Handhal* HYDATID disease is caused by infestation by larvae of the tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus. The
Thi-Qar Medical Journal (TQMJ): Vol(6) No(1):2012(48-52) OBJECT: CRANIAL HYDATID CYST Dr. Haitham Handhal* HYDATID disease is caused by infestation by larvae of the tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus. The
Introduction to Helminthology
 Introduction to Helminthology HELMINTHES (WORMS) - Characteristics Eukaryotic, multicellular animals that usually have digestive, circulatory, nervous, excretory, and reproductive systems. Worms with bilateral
Introduction to Helminthology HELMINTHES (WORMS) - Characteristics Eukaryotic, multicellular animals that usually have digestive, circulatory, nervous, excretory, and reproductive systems. Worms with bilateral
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE CYSTIC ECHINOCOCCOSIS OF THE LIVER A CASE REPORT DR. S.VENKATESWARA RAO, 1 DR. BASETTY NAGARAJA, 2 DR. MUCHUKOTA BABU 3 1. Assistant Professor,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE CYSTIC ECHINOCOCCOSIS OF THE LIVER A CASE REPORT DR. S.VENKATESWARA RAO, 1 DR. BASETTY NAGARAJA, 2 DR. MUCHUKOTA BABU 3 1. Assistant Professor,
NATIONAL SHEEP HEALTH MONITORING PROJECT SNAPSHOT REPORT
 NATIONAL SHEEP HEALTH MONITORING PROJECT SNAPSHOT REPORT 216 SNAPSHOT SUMMARY 216 4,552,116 sheep inspected (Table 1) 21,332 lines inspected (Table 1) 7,211 PICs inspected (Table 1) The sheep industry
NATIONAL SHEEP HEALTH MONITORING PROJECT SNAPSHOT REPORT 216 SNAPSHOT SUMMARY 216 4,552,116 sheep inspected (Table 1) 21,332 lines inspected (Table 1) 7,211 PICs inspected (Table 1) The sheep industry
Study on gross pulmonary lesions in lungs of slaughtered animals and their economic importance in Tigray, Ethiopia
 Study on gross pulmonary lesions in lungs of slaughtered animals and their economic importance in Tigray, Ethiopia Gebrehiwot, T., Verma, P.C and Berhanu, H. College of Veterinary Medicine, Mekelle University,
Study on gross pulmonary lesions in lungs of slaughtered animals and their economic importance in Tigray, Ethiopia Gebrehiwot, T., Verma, P.C and Berhanu, H. College of Veterinary Medicine, Mekelle University,
Taking your pets abroad
 Taking your pets abroad Your guide to diseases encountered abroad Produced by the BVA Animal Welfare Foundation www.bva-awf.org.uk BVA AWF is a registered charity (287118) Prevention is better than cure!
Taking your pets abroad Your guide to diseases encountered abroad Produced by the BVA Animal Welfare Foundation www.bva-awf.org.uk BVA AWF is a registered charity (287118) Prevention is better than cure!
Isolated primary hydatid cyst of small intestinal mesentery: an exceptional location of hydatid disease
 Case report Open Access Isolated primary hydatid cyst of small intestinal mesentery: an exceptional location of hydatid disease Mohammed Najih 1,&, Ali Chabni 1, Gilles Attoulou 1, Rajae Yamoul 1, Mbarek
Case report Open Access Isolated primary hydatid cyst of small intestinal mesentery: an exceptional location of hydatid disease Mohammed Najih 1,&, Ali Chabni 1, Gilles Attoulou 1, Rajae Yamoul 1, Mbarek
Cestodes P & S, Joshua Stillman MD, MPH Department of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor, Columbia University. Helminths
 Cestodes P & S, 2008 Joshua Stillman MD, MPH Department of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor, Columbia University Helminths Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) - Nematodes Pinworm, Whipworm, Ascaris + VLM,
Cestodes P & S, 2008 Joshua Stillman MD, MPH Department of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor, Columbia University Helminths Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) - Nematodes Pinworm, Whipworm, Ascaris + VLM,
Prevalence of Taenia in selected Canids and felids living within wildlife sanctuaries in Kenya
 International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Research ISSN: 2393-8870 www.ijarm.com DOI: 10.22192/ijamr Volume 4, Issue 9-2017 Research Article Prevalence of Taenia in selected Canids and felids
International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Research ISSN: 2393-8870 www.ijarm.com DOI: 10.22192/ijamr Volume 4, Issue 9-2017 Research Article Prevalence of Taenia in selected Canids and felids
Prevalence of some parasitic helminths among slaughtered ruminants in Kirkuk slaughter house, Kirkuk, Iraq
 Prevalence of some parasitic helminths among slaughtered ruminants in Kirkuk slaughter house, Kirkuk, Iraq M. A. Kadir*, S. A. Rasheed** *College of Medicine, Tikrit, Iraq, **Technical Institute, Kirkuk,
Prevalence of some parasitic helminths among slaughtered ruminants in Kirkuk slaughter house, Kirkuk, Iraq M. A. Kadir*, S. A. Rasheed** *College of Medicine, Tikrit, Iraq, **Technical Institute, Kirkuk,
CYSTIC ECHINOCOCCOSIS IN AUSTRALIA: THE CURRENT SITUATION
 CYSTIC ECHINOCOCCOSIS IN AUSTRALIA: THE CURRENT SITUATION David J Jenkins Australian Hydatid Control and Epidemiology Program, Fyshwick; School of Botany and Zoology, Australian National University, Canberra,
CYSTIC ECHINOCOCCOSIS IN AUSTRALIA: THE CURRENT SITUATION David J Jenkins Australian Hydatid Control and Epidemiology Program, Fyshwick; School of Botany and Zoology, Australian National University, Canberra,
ECHINOCOCCOSIS AND CYSTICERCOSIS IN ASIA: EVALUATION OF THE MODERN TECHNOLOGY FOR EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY
 ECHINOCOCCOSIS AND CYSTICERCOSIS IN ASIA: EVALUATION OF THE MODERN TECHNOLOGY FOR EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY Akira Ito 1, Hiroshi Yamasaki 1, Minoru Nakao 1, Yasuhito Sako 1, Kazuhiro Nakaya 2, Wulamu Mamuti
ECHINOCOCCOSIS AND CYSTICERCOSIS IN ASIA: EVALUATION OF THE MODERN TECHNOLOGY FOR EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY Akira Ito 1, Hiroshi Yamasaki 1, Minoru Nakao 1, Yasuhito Sako 1, Kazuhiro Nakaya 2, Wulamu Mamuti
Hydatid disease (Echinococcus granulosus) in Australian Wildlife FACT SHEET
 Hydatid disease (Echinococcus granulosus) in Australian Wildlife FACT SHEET Introductory Statement Echinococcus granulosus is widespread in Australian wildlife where its reproductive potential may be greater
Hydatid disease (Echinococcus granulosus) in Australian Wildlife FACT SHEET Introductory Statement Echinococcus granulosus is widespread in Australian wildlife where its reproductive potential may be greater
Diagnosing intestinal parasites. Clinical reference guide for Fecal Dx antigen testing
 Diagnosing intestinal parasites Clinical reference guide for Fecal Dx antigen testing Screen every dog at least twice a year The Companion Animal Parasite Council (CAPC) guidelines recommend including
Diagnosing intestinal parasites Clinical reference guide for Fecal Dx antigen testing Screen every dog at least twice a year The Companion Animal Parasite Council (CAPC) guidelines recommend including
HOOKWORM FAQ SHEET (rev ) Adapted from the CDC Fact Sheet
 HOOKWORM FAQ SHEET (rev 3-1-10) Adapted from the CDC Fact Sheet Hookworm Infection FAQ Sheet Contents What is hookworm? Where are hookworms commonly found? How do I get a hookworm infection? Who is at
HOOKWORM FAQ SHEET (rev 3-1-10) Adapted from the CDC Fact Sheet Hookworm Infection FAQ Sheet Contents What is hookworm? Where are hookworms commonly found? How do I get a hookworm infection? Who is at
Characterization, Prevalence and Economic Significance of Hydatidosis in Cattle Slaughtered at Masha Municipal Abattoir, Southern Ethiopia
 Advances in Biological Research 11 (6): 319-326, 2017 ISSN 1992-0067 IDOSI Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.abr.2017.319.326 Characterization, Prevalence and Economic Significance of Hydatidosis in
Advances in Biological Research 11 (6): 319-326, 2017 ISSN 1992-0067 IDOSI Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.abr.2017.319.326 Characterization, Prevalence and Economic Significance of Hydatidosis in
Cestodes P & S, Joshua Stillman MD, MPH Department of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor, Columbia University. Helminths
 Cestodes P & S, 2009 Joshua Stillman MD, MPH Department of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor, Columbia University Helminths Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) - Nematodes Pinworm, Whipworm, Ascaris + VLM,
Cestodes P & S, 2009 Joshua Stillman MD, MPH Department of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor, Columbia University Helminths Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) - Nematodes Pinworm, Whipworm, Ascaris + VLM,
PART V WHAT TO DO? Knowing is not enough; we must apply. Willing is not enough; we must do. Johan Wolfgang von Goethe ( )
 PART V WHAT TO DO? Knowing is not enough; we must apply. Willing is not enough; we must do. Johan Wolfgang von Goethe (1749 1832) Thus, although predators have the most obvious role in the ongoing drama
PART V WHAT TO DO? Knowing is not enough; we must apply. Willing is not enough; we must do. Johan Wolfgang von Goethe (1749 1832) Thus, although predators have the most obvious role in the ongoing drama
Still and Moving Image Evidences for Mating of Echinococcus granulosus Reared in Culture Media
 Iranian J Parasitol: Vol. 9, No. 1, Jan -Mar 2014, pp.129-133 Short Communication Still and Moving Image Evidences for Mating of Echinococcus granulosus Reared in Culture Media Tahereh MOHAMMADZADEH, *Seyed
Iranian J Parasitol: Vol. 9, No. 1, Jan -Mar 2014, pp.129-133 Short Communication Still and Moving Image Evidences for Mating of Echinococcus granulosus Reared in Culture Media Tahereh MOHAMMADZADEH, *Seyed
HUSK, LUNGWORMS AND CATTLE
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk HUSK, LUNGWORMS AND CATTLE Author : Alastair Hayton Categories : Vets Date : July 20, 2009 Alastair Hayton discusses how best
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk HUSK, LUNGWORMS AND CATTLE Author : Alastair Hayton Categories : Vets Date : July 20, 2009 Alastair Hayton discusses how best
Global diversity of cystic echinococcosis. Thomas Romig Universität Hohenheim Stuttgart, Germany
 Global diversity of cystic echinococcosis Thomas Romig Universität Hohenheim Stuttgart, Germany Echinococcus: generalized lifecycle Cystic echinococcosis: geographical spread Acephalocystis cystifera
Global diversity of cystic echinococcosis Thomas Romig Universität Hohenheim Stuttgart, Germany Echinococcus: generalized lifecycle Cystic echinococcosis: geographical spread Acephalocystis cystifera
We Check Your Pets For Internal Parasites
 We Check Your Pets For Internal Parasites Why have a fecal exam done twice yearly? Hookworm egg, whipworm egg, roundworm egg Question: Vets typically want to a microscopic exam of a stool sample from our
We Check Your Pets For Internal Parasites Why have a fecal exam done twice yearly? Hookworm egg, whipworm egg, roundworm egg Question: Vets typically want to a microscopic exam of a stool sample from our
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 1, 2018,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 1, 2018, 116 120 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) A SLAUGHTER HOUSE REPORT OF OESOPHAGOSTOMOSIS IN GOAT Amit Gamit Navsari Agricultural
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 1, 2018, 116 120 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) A SLAUGHTER HOUSE REPORT OF OESOPHAGOSTOMOSIS IN GOAT Amit Gamit Navsari Agricultural
Diagnosing intestinal parasites. Clinical reference guide for Fecal Dx antigen testing
 Diagnosing intestinal parasites Clinical reference guide for Fecal Dx antigen testing Screen every dog at least twice a year The Companion Animal Parasite Council (CAPC) guidelines recommend including
Diagnosing intestinal parasites Clinical reference guide for Fecal Dx antigen testing Screen every dog at least twice a year The Companion Animal Parasite Council (CAPC) guidelines recommend including
Hydatidosis as a major cause of liver condemnation among parasitic diseases in goats and sheep in Keren slaughterhouse, Anseba zone, Eritrea
 Veterinary World, EISSN: 2231-0916 Available at www.veterinaryworld.org/vol.7/april-2014/16.pdf RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Hydatidosis as a major cause of liver condemnation among parasitic diseases
Veterinary World, EISSN: 2231-0916 Available at www.veterinaryworld.org/vol.7/april-2014/16.pdf RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Hydatidosis as a major cause of liver condemnation among parasitic diseases
Epidemiology of Opisthorchis felineus in the European Union
 Epidemiology of Opisthorchis felineus in the European Union Edoardo Pozio European Union Reference Laboratory for Parasites Istituto Superiore di Sanità Rome, Italy World distribution and human prevalence
Epidemiology of Opisthorchis felineus in the European Union Edoardo Pozio European Union Reference Laboratory for Parasites Istituto Superiore di Sanità Rome, Italy World distribution and human prevalence
CONTAGIOUS BOVINE PLEURO- PNEUMONIA steps towards control of the disease. Rose Matua -Department of Veterinary Services, Kenya
 CONTAGIOUS BOVINE PLEURO- PNEUMONIA steps towards control of the disease Rose Matua -Department of Veterinary Services, Kenya Introduction CBPP is a highly contagious acute, subacute or chronic disease
CONTAGIOUS BOVINE PLEURO- PNEUMONIA steps towards control of the disease Rose Matua -Department of Veterinary Services, Kenya Introduction CBPP is a highly contagious acute, subacute or chronic disease
Helminth Infections. Pinworms
 Helminth Infections Pinworms Helminths Worm classified as a parasite Contaminate food, water, air, feces, pets, wild animals, toilet seats and door handles Prevention: Frequent hand washing Frequent cleaning
Helminth Infections Pinworms Helminths Worm classified as a parasite Contaminate food, water, air, feces, pets, wild animals, toilet seats and door handles Prevention: Frequent hand washing Frequent cleaning
Multiple Organ Involvement with Hydatid Cysts
 Iranian J Parasitol: Vol. 5, No.2, 2010, pp. 65-70 Tehran University of Medical Sciences Publication http://tums.ac.ir Case Report Iranian J Parasitol Open access Journal at http://ijpa.tums.ac.ir Iranian
Iranian J Parasitol: Vol. 5, No.2, 2010, pp. 65-70 Tehran University of Medical Sciences Publication http://tums.ac.ir Case Report Iranian J Parasitol Open access Journal at http://ijpa.tums.ac.ir Iranian
COMMISSION DELEGATED REGULATION (EU)
 L 296/6 Official Journal of the European Union 15.11.2011 COMMISSION DELEGATED REGULATION (EU) No 1152/2011 of 14 July 2011 supplementing Regulation (EC) No 998/2003 of the European Parliament and of the
L 296/6 Official Journal of the European Union 15.11.2011 COMMISSION DELEGATED REGULATION (EU) No 1152/2011 of 14 July 2011 supplementing Regulation (EC) No 998/2003 of the European Parliament and of the
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (102)
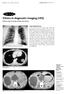 M e d i c a l E d u c a t i o n Singapore Med J 2005; 46(2) : 93 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (102) M Azeemuddin, T UI-Haq, H Ahsan, W A Memon Fig. 1 Chest radiograph (posteroanterior projection).
M e d i c a l E d u c a t i o n Singapore Med J 2005; 46(2) : 93 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (102) M Azeemuddin, T UI-Haq, H Ahsan, W A Memon Fig. 1 Chest radiograph (posteroanterior projection).
Prevalence of Various Intestinal Zoonotic Parasites in Dogs of Jammu Region of Jammu and Kashmir
 Page116 Original Research Prevalence of Various Intestinal Zoonotic Parasites in Dogs of Jammu Region of Jammu and Kashmir Irfan Ali Shah*, H.K. Sharma, M. A. Shah 1, R. Katoch 2 and M. A. Malik Department
Page116 Original Research Prevalence of Various Intestinal Zoonotic Parasites in Dogs of Jammu Region of Jammu and Kashmir Irfan Ali Shah*, H.K. Sharma, M. A. Shah 1, R. Katoch 2 and M. A. Malik Department
V. Subclass Eucestoida (Chapters 20 & 21, BLY 459, 2010)
 V. Subclass Eucestoida (Chapters 20 & 21, BLY 459, 2010) A. Characteristics (Ignore Cestodaria) 1. Differences from trematodes a. No digestive tract (1) No mouth, gut, nor anus (2) All nutrients absorbed
V. Subclass Eucestoida (Chapters 20 & 21, BLY 459, 2010) A. Characteristics (Ignore Cestodaria) 1. Differences from trematodes a. No digestive tract (1) No mouth, gut, nor anus (2) All nutrients absorbed
Eukaryotic Parasites. An Illustrated Guide to Parsitic Life Cycles to Accompany Lecture. By Noel Ways
 Eukaryotic Parasites An Illustrated Guide to Parsitic Life Cycles to Accompany Lecture By Noel Ways Giardia lamblia Life Cycle Reservoir: Beavers strongly implicated. Also, many other wild animals as well
Eukaryotic Parasites An Illustrated Guide to Parsitic Life Cycles to Accompany Lecture By Noel Ways Giardia lamblia Life Cycle Reservoir: Beavers strongly implicated. Also, many other wild animals as well
