Invertebrates. Brain. Brain 12/2/2017. The Invertebrate Brain. The Invertebrate Brain. Invertebrate brain general layouts some specific functions
|
|
|
- Abigayle Sherman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brain Invertebrate brain general layouts some specific functions Vertebrate brain general layout cortical fields evolutionary theory Brain Brain size Invertebrates 1) No brain (only nerve net) jellyfish, hydra, anemones 2) No brain (only central ganglia) worms, snails, clams, crabs 3) Centralized brain insects 1) No brain (only nerve net) jellyfish, hydra, anemones 2) No brain (only central ganglia) worms, snails, clams, crabs Gangliaare collections of neurons that control a few local functions (e.g., moving eyes & mouth in sync). 3) Centralized brain insects Acentralized brain communicates with the whole body. 1
2 No Centralized Brain (only ganglia) pharynx Earthworms 302 neurons total (humans have 100,000,000,000) Test: No food present, Choose the side with Chloride or Sodium Naïve Food Only Random Sodium & Chloride Chloride with food, Sodium no food Sodium with food, Chloride no food Earthworm Stats 959 cells total 302 are neurons Most of the neurons are in the head 20 neurons in pharynx (like a tongue) 68 chemosensory neurons in head Most neurons are simple, unbranched Earthworms learn with only 302 neurons total. No preferences Centralized Brain Honeybee 960,000 neurons total (humans have 100,000,000,000) 60 % Change in Neuropilof Optic Lobes Centralized Brain 1week 1 week precocious 2 weeks weathered Mushroom body volume depends on foraging experience (NOT AGE) The mushroom bodies are the ONLY brain region that increases with foraging experience. The mushroom bodies are specialized for foraging (potentially spatial cognition). % Change in Neuropilof Effect is not just due to age because both have 1 week of experience but the precocious bees are much younger week 1 week precocious 2 weeks weathered Octopuses have more neurons and more connections among different parts of the nervous system than all other invertebrates. 300,000,000 neurons 2
3 Centralized Brain Vertebrates The Vertebrate Brain The Vertebrate Brain All vertebrates have the same basic brain structures. 1) Forebrain: Telencephalon & Diencephalon 2) Midbrain: Mesencephalon 3) Hindbrain: Cerebellum, Pons, Medulla Forebrain(Cerebrum & Olfactory Bulb) Midbrain (Optic Tectum) Hindbrain (Cerebellum) Hindbrain (Brainstem) The same general brain subdivisions exist across species. Braun and Northcutt (1999) The Vertebrate Brain Embryonic Brain: As embryos, ALL VERTEBRATES have a brain than looks like this (sharks, frogs, monkeys, humans, all of them). This shows the parts of the embryonic brain that ultimately become the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Only mammalshave a cerebral cortex (part of the forebrain). Human 3
4 Mammals Human Vision Vision Auditory Auditory Somatosensory Somatosensory Same basic organization of cortex across species. Same basic organization in human cortex as other mammals. Across species, cortex has the same general layout, but different species have an emphasis on different cortical regions. Mouse: Somatosensory (whiskers) Bat: Auditory (echolocation) Opossum: Vision (nocturnal) Leah Krubitzer The Old View of Vertebrate Brain Evolution Paul D. MacLean Until recently, the dominant view was that the brain evolved from hindbrain to forebrain (simple to complex). Midbrain + Hindbrain Forebrain + The Modern View of Vertebrate Brain Evolution Out-dated The modern view is that all vertebrates have the same basic brain parts but the parts vary in size and complexity. Modern The Modern View of Vertebrate Brain Evolution Among vertebrates, the main thing that has changed is size, not organization. 1) Relative Sizes of Regions 2) Overall Brain Size More than doubled in last 2 million years. Emery and Clayton
5 Brain size Absolute Brain Size Measures to compare brain size among species: 1) Absolute Brain Size 2) Relative Brain Size 3) Encephalization Quotient 4) Cortical Neurons Humans do not have the largest brain or most total neurons. Larger animals generally have larger brains and more neurons. Abigger body needs a bigger brain to control it. Relative Brain Size (compared to body size) Ratio of Brain Size to Body Size Relative Brain Size (compared to body size) Mammals have more brain for their body than other vertebrates. The line represents the average brain size per body size. Species above the line have more brain for their body than average. Species below the line have less brain for their body than average. Species on the line have an average amount of brain for their body size. Encephalization Quotient Encephalization Quotient (EQ) EQ is calculated relative to a standard species. For mammals, the standard is the cat. If a cat had the same body size as a human, how big would its brain be? The human brain is about 7 times bigger than a cat s brain would be at a human body size. Can compare any animal to the standard (cat) to get EQ. Encephalization Quotient Primates & dolphins are highest. Humans = ~7 Non-human primates = ~2-4 Dolphins = ~4-5 5
6 Cortical neurons Literally count up the number of neurons in cortex. Brain Size & Intelligence The general pattern that emerges from all of these measures of brain size is that humans, non-human primates, and dolphins (and sometimes elephants) have more brain power than other animals. There is a possible link between brain size and intelligence. Humans do have the most cortical neurons. Apes, dolphins, and elephants also rank high. We ll talk more about brain size and cognition across species in the next class. Why doesn t everyone have a big brain? Human brain accounts for 2% of body weightbut consumes 20% of metabolic energy at rest alone. Not all species can afford this energy expense. Smart Why doesn t everyone have a big brain? Breed the smart ones with smart ones Larger brains Survive Less Tadeusz J. Kawecki Dumb (+ bad quinine) Breed the dumb ones with dumb ones Smaller brains Survive Better Why doesn t everyone have a big brain? Tadeusz J. Kawecki Smart animals have larger brains but less intelligent flies with smaller brains survive better. How did humans afford such a big brain? + = Neural material is costly too much neural material can decrease survival. Small-brained animals will survive better under some circumstances, because neural material is so costly. Chimpanzee Human Current Hypothesis: Meat eating allowed humans to afford big brains Meat eating yields more calories and amino acids per bite than eating fruits and vegetables 6
7 Cooking (600,000 years ago) It takes less energy to digest cooked food more energy to the brain New Method for Comparing Brains between species 100 percent of a cooked meal is metabolized by the body 30 to 40 percent of raw food meal is metabolized Summary Invertebrate brain Layouts: nerve nets, ganglia, centralized brain Learning in earthworms with 302 neurons Foraging cognition in mushroom bodies of bees Vertebrate brain General layout is the same across species Cortical fields have same layout in mammals Size (of specific regions and overall) is most important factor in species differences Brain size Measurements: Absolute Size, Relative Size, Encephalization Quotient, Number of Cortical Neurons Humans, Apes, other Primates, Dolphins, and sometimes Elephants Diet determines whether a species can afford more neural tissue 7
The Brain and Senses. Birds perceive the world differently than humans. Avian intelligence. Novel feeding behaviors
 The Brain and Senses Birds perceive the world differently than humans Color and IR vision are highly developed Hearing is superior, owls track prey in total darkness Birds navigate using abilities to sense:
The Brain and Senses Birds perceive the world differently than humans Color and IR vision are highly developed Hearing is superior, owls track prey in total darkness Birds navigate using abilities to sense:
Diversity of Animals
 Classifying Animals Diversity of Animals Animals can be classified and grouped based on similarities in their characteristics. Animals make up one of the major biological groups of classification. All
Classifying Animals Diversity of Animals Animals can be classified and grouped based on similarities in their characteristics. Animals make up one of the major biological groups of classification. All
Overall structure is similar to humans, but again there are differences. Some features that are unique to mammals: Found in eutherian mammals.
 Mammalian anatomy and physiology (part II): Nervous system: Brain: Sensory input: Overall structure is similar to humans, but again there are differences. Some features that are unique to mammals: Smell:
Mammalian anatomy and physiology (part II): Nervous system: Brain: Sensory input: Overall structure is similar to humans, but again there are differences. Some features that are unique to mammals: Smell:
Name Date When you put food away in the kitchen, you sort the food into groups. You put foods that are alike in certain ways into the same
 1 Name Date When you put food away in the kitchen, you sort the food into groups. You put foods that are alike in certain ways into the same group. Scientists do the same thing with animals, plants and
1 Name Date When you put food away in the kitchen, you sort the food into groups. You put foods that are alike in certain ways into the same group. Scientists do the same thing with animals, plants and
NAME: DATE: SECTION:
 NAME: DATE: SECTION: MCAS PREP PACKET EVOLUTION AND BIODIVERSITY 1. Which of the following observations best supports the conclusion that dolphins and sharks do not have a recent common ancestor? A. Dolphins
NAME: DATE: SECTION: MCAS PREP PACKET EVOLUTION AND BIODIVERSITY 1. Which of the following observations best supports the conclusion that dolphins and sharks do not have a recent common ancestor? A. Dolphins
#8964 Standards-Based Science Investigations 2 Teacher Created Resources, Inc.
 Introduction...4 Locating Simple Science Materials...5 Standards Correlation....7 Thinking About Inquiry Investigations...9 Inquiry Assessment Rubric...12 Student Inquiry Worksheets...13 Sample Inquiry
Introduction...4 Locating Simple Science Materials...5 Standards Correlation....7 Thinking About Inquiry Investigations...9 Inquiry Assessment Rubric...12 Student Inquiry Worksheets...13 Sample Inquiry
Human Uniqueness. Human Uniqueness. Why are we so different? 12/6/2017. Four Candidates
 Our Hominid Ancestors In humans, brain tissue has more than doubled over the past 2 million years. Break from chimps 3-5 million Our Hominid Ancestors Our Hominid Ancestors Relative Brain Size in Our Ancestors
Our Hominid Ancestors In humans, brain tissue has more than doubled over the past 2 million years. Break from chimps 3-5 million Our Hominid Ancestors Our Hominid Ancestors Relative Brain Size in Our Ancestors
AP Biology. Animal Characteristics. Kingdom: Animals. Body Cavity. Animal Evolution. Invertebrate: Porifera. Invertebrate: Cnidaria.
 Kingdom: Animals Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Animal Characteristics Heterotrophs must ingest others for nutrients Multicellular complex bodies No cell walls allows active movement Sexual reproduction
Kingdom: Animals Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Animal Characteristics Heterotrophs must ingest others for nutrients Multicellular complex bodies No cell walls allows active movement Sexual reproduction
A. Body Temperature Control Form and Function in Mammals
 Taxonomy Chapter 22 Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Mammals Characteristics Evolution of Mammals Have hair and First appear in the mammary glands Breathe air, 4chambered heart, endotherms
Taxonomy Chapter 22 Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Mammals Characteristics Evolution of Mammals Have hair and First appear in the mammary glands Breathe air, 4chambered heart, endotherms
Let s learn about ANIMALS. Level : School:.
 Let s learn about ANIMALS Name: Level : School:. 1. CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS There are many different animals and we can classify them according to: Their skeleton: Vertebrates have a skeleton but Invertebrates
Let s learn about ANIMALS Name: Level : School:. 1. CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS There are many different animals and we can classify them according to: Their skeleton: Vertebrates have a skeleton but Invertebrates
Your Eye, My Eye, and the Eye of the Aye Aye: Evolution of Human Vision from 65 Million Years Ago to the Present
 # 75 Your Eye, My Eye, and the Eye of the Aye Aye: Evolution of Human Vision from 65 Million Years Ago to the Present Dr. Christopher Kirk December 2, 2011 Produced by and for Hot Science - Cool Talks
# 75 Your Eye, My Eye, and the Eye of the Aye Aye: Evolution of Human Vision from 65 Million Years Ago to the Present Dr. Christopher Kirk December 2, 2011 Produced by and for Hot Science - Cool Talks
Classification of Animals. adapted from
 Classification of Animals Animals With Backbones AMPHIBIAN FISH MAMMAL BIRD REPTILE Animals With Backbones Animals with backbones are called vertebrates. Vertebrates include many different kinds of animals.
Classification of Animals Animals With Backbones AMPHIBIAN FISH MAMMAL BIRD REPTILE Animals With Backbones Animals with backbones are called vertebrates. Vertebrates include many different kinds of animals.
Ch 34: Vertebrate Objective Questions & Diagrams
 Ch 34: Vertebrate Objective Questions & Diagrams Invertebrate Chordates and the Origin of Vertebrates 1. Distinguish between the two subgroups of deuterostomes. 2. Describe the four unique characteristics
Ch 34: Vertebrate Objective Questions & Diagrams Invertebrate Chordates and the Origin of Vertebrates 1. Distinguish between the two subgroups of deuterostomes. 2. Describe the four unique characteristics
Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection. Hunting for evolution clues Elementary, my dear, Darwin!
 Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection Hunting for evolution clues Elementary, my dear, Darwin! 2006-2007 Evidence supporting evolution Fossil record shows change over time Anatomical record comparing
Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection Hunting for evolution clues Elementary, my dear, Darwin! 2006-2007 Evidence supporting evolution Fossil record shows change over time Anatomical record comparing
Mammals. Introduction (page 821) Evolution of Mammals (page 821) Form and Function in Mammals (pages ) Chapter 32.
 Chapter 32 Mammals Section 32 1 Introduction to the Mammals (pages 821 827) This section describes the characteristics common to all mammals, as well as how mammals carry out life functions. It also briefly
Chapter 32 Mammals Section 32 1 Introduction to the Mammals (pages 821 827) This section describes the characteristics common to all mammals, as well as how mammals carry out life functions. It also briefly
Lab 9: Inventing Life Forms
 Name: Section: Date: Lab 9: Inventing Life Forms 1 Instructions The purpose of this lab is to create a life form that may have evolved on a planet other than Earth. Follow the instructions below detailing
Name: Section: Date: Lab 9: Inventing Life Forms 1 Instructions The purpose of this lab is to create a life form that may have evolved on a planet other than Earth. Follow the instructions below detailing
Name: Per. Date: 1. How many different species of living things exist today?
 Name: Per. Date: Life Has a History We will be using this website for the activity: http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/explorations/tours/intro/index.html Procedure: A. Open the above website and click
Name: Per. Date: Life Has a History We will be using this website for the activity: http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/explorations/tours/intro/index.html Procedure: A. Open the above website and click
Vertebrates. What is a vertebrate?
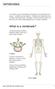 Vertebrates In a modern system of classification, all animals can be divided into two groups vertebrates and invertebrates. Vertebrates are animals that have a skeleton inside their bodies. Biologists
Vertebrates In a modern system of classification, all animals can be divided into two groups vertebrates and invertebrates. Vertebrates are animals that have a skeleton inside their bodies. Biologists
2018 Copyright Jolie Canoli and Friends. For personal and educational use only. Find more resources at joliecanoli.com
 PHYLUM: BODY PLANS After the classification of Kingdom comes the category Phylum. The Phylum category of Animals puts animals with similar body types together. There are many phylum, but we will study
PHYLUM: BODY PLANS After the classification of Kingdom comes the category Phylum. The Phylum category of Animals puts animals with similar body types together. There are many phylum, but we will study
Unit 19.3: Amphibians
 Unit 19.3: Amphibians Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in amphibians. Outline the reproduction and development of amphibians. Identify the three living amphibian orders. Describe how amphibians
Unit 19.3: Amphibians Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in amphibians. Outline the reproduction and development of amphibians. Identify the three living amphibian orders. Describe how amphibians
Animal phyla. Prior Knowledge Questions:
 1 Name: Animal phyla Core: Prior Knowledge Questions: What do Tim & Moby say about Invertebrates? 2 Want to watch the video again? Go to Invertebrates Brainpop (Username: nfmsbrain password: pop) Word
1 Name: Animal phyla Core: Prior Knowledge Questions: What do Tim & Moby say about Invertebrates? 2 Want to watch the video again? Go to Invertebrates Brainpop (Username: nfmsbrain password: pop) Word
Taste and Smell. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Taste, also called gustation, and smell, also called olfaction, are the most interconnected senses in that both involve molecules of the stimulus entering the body and bonding to receptors.
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Taste, also called gustation, and smell, also called olfaction, are the most interconnected senses in that both involve molecules of the stimulus entering the body and bonding to receptors.
Topic Page: Invertebrates
 Topic Page: Invertebrates Definition: invertebrate from The Penguin Dictionary of Science General term of convenience given to an animal species that is not a member of the chordate subphylum Vertebrata.
Topic Page: Invertebrates Definition: invertebrate from The Penguin Dictionary of Science General term of convenience given to an animal species that is not a member of the chordate subphylum Vertebrata.
Comparative Zoology Portfolio Project Assignment
 Comparative Zoology Portfolio Project Assignment Using your knowledge from the in class activities, your notes, you Integrated Science text, or the internet, you will look at the major trends in the evolution
Comparative Zoology Portfolio Project Assignment Using your knowledge from the in class activities, your notes, you Integrated Science text, or the internet, you will look at the major trends in the evolution
Animals Classification
 Animals Classification By Piyush & Ilaxi Grouping & Identifying Living Things 2 Classifying Living Things Classifying Living Things Biological Classification is the way in which scientists use to categorize
Animals Classification By Piyush & Ilaxi Grouping & Identifying Living Things 2 Classifying Living Things Classifying Living Things Biological Classification is the way in which scientists use to categorize
Some Facts about... Amphibians
 Amphibians Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates that live part of their lives in water and part on land. Amphibians eggs are laid in water and they are born there. They begin their lives with gills
Amphibians Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates that live part of their lives in water and part on land. Amphibians eggs are laid in water and they are born there. They begin their lives with gills
All living things are classified into groups based on the traits they share. Taxonomy is the study of classification. The largest groups into which
 All living things are classified into groups based on the traits they share. Taxonomy is the study of classification. The largest groups into which the scientists divide the groups are called kingdoms.
All living things are classified into groups based on the traits they share. Taxonomy is the study of classification. The largest groups into which the scientists divide the groups are called kingdoms.
Read the following texts 1. Living Things. Both animals and plants are living things because they are born, grow up, reproduce and die.
 Read the following texts 1. Living Things. Both animals and plants are living things because they are born, grow up, reproduce and die. All living things perform all of these functions. A tiger, a deer,
Read the following texts 1. Living Things. Both animals and plants are living things because they are born, grow up, reproduce and die. All living things perform all of these functions. A tiger, a deer,
Resources. Visual Concepts. Chapter Presentation. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Vertebrates Table of Contents Section 1 Vertebrates in the Sea and on Land Section 2 Terrestrial Vertebrates Section
Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Vertebrates Table of Contents Section 1 Vertebrates in the Sea and on Land Section 2 Terrestrial Vertebrates Section
Science Class 4 Topic: Habitats Reinforcement Worksheet. Name: Sec: Date:
 Science Class 4 Topic: Habitats Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the correct answer. 1. Which of these things are you NOT likely to find in a park or a garden? A. An earthworm B. An
Science Class 4 Topic: Habitats Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the correct answer. 1. Which of these things are you NOT likely to find in a park or a garden? A. An earthworm B. An
DEVELOPMENT OF THE HEAD AND NECK PLACODES
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE HEAD AND NECK Placodes and the development of organs of special sense L. Moss-Salentijn PLACODES Localized thickened areas of specialized ectoderm, lateral to the neural crest, at the
DEVELOPMENT OF THE HEAD AND NECK Placodes and the development of organs of special sense L. Moss-Salentijn PLACODES Localized thickened areas of specialized ectoderm, lateral to the neural crest, at the
I m so happy I just want to shout with joy It s what I ve always wanted the most fantastic toy!
 Written by Fiona Jackson. My Robot I m so happy I just want to shout with joy It s what I ve always wanted the most fantastic toy! It s made out of shiny steel I can t believe it s real. Happy Kismet Sad
Written by Fiona Jackson. My Robot I m so happy I just want to shout with joy It s what I ve always wanted the most fantastic toy! It s made out of shiny steel I can t believe it s real. Happy Kismet Sad
Name Class Date. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 14 2 The Animal Kingdom SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is diversity? What are vertebrates? What
CHAPTER 14 2 The Animal Kingdom SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is diversity? What are vertebrates? What
Color Vision: How Our Eyes Reflect Primate Evolution
 Scientific American Magazine - March 16, 2009 Color Vision: How Our Eyes Reflect Primate Evolution Analyses of primate visual pigments show that our color vision evolved in an unusual way and that the
Scientific American Magazine - March 16, 2009 Color Vision: How Our Eyes Reflect Primate Evolution Analyses of primate visual pigments show that our color vision evolved in an unusual way and that the
Animal Adaptations Woodland Animal Fact Sheet
 Post Visit Resource 5 Animal Adaptations Woodland Animal Fact Sheet Fox Food: Foxes will eat almost anything they can get hold of. They eat small mammals such as rabbits and voles, insects and invertebrates,
Post Visit Resource 5 Animal Adaptations Woodland Animal Fact Sheet Fox Food: Foxes will eat almost anything they can get hold of. They eat small mammals such as rabbits and voles, insects and invertebrates,
Characteristics of a Reptile. Vertebrate animals Lungs Scaly skin Amniotic egg
 Reptiles Characteristics of a Reptile Vertebrate animals Lungs Scaly skin Amniotic egg Characteristics of Reptiles Adaptations to life on land More efficient lungs and a better circulator system were develope
Reptiles Characteristics of a Reptile Vertebrate animals Lungs Scaly skin Amniotic egg Characteristics of Reptiles Adaptations to life on land More efficient lungs and a better circulator system were develope
UTILITY OF THE NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION IN RATS
 ACTA NEUROBIOL. ELW. 1980, 40 : 999-3 Short communication UTILITY OF THE NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION IN RATS David E. TUPPER and Robert B. WALLACE Laboratory of Developmental Psychobiology, University of
ACTA NEUROBIOL. ELW. 1980, 40 : 999-3 Short communication UTILITY OF THE NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION IN RATS David E. TUPPER and Robert B. WALLACE Laboratory of Developmental Psychobiology, University of
Animals WORKSHEET 3.1 Animals
 Animals WORKSHEET 3.1 Animals 1. Are these sentences true or false? Correct the false ones. a) A butterfly is a non-living thing. b) Water is a non-living thing. c) Living things are born, die, reproduce
Animals WORKSHEET 3.1 Animals 1. Are these sentences true or false? Correct the false ones. a) A butterfly is a non-living thing. b) Water is a non-living thing. c) Living things are born, die, reproduce
Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals
 Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish,
Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals Compare the characteristic structures of invertebrate animals (including sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods) and vertebrate animals (fish,
Science Magazine Podcast Transcript, 6 September 2013
 Science Magazine Podcast Transcript, 6 September 2013 http://podcasts.aaas.org/science_news/sciencepodcast_130906_sciencenow.mp3 Promo The following is an excerpt from the Science Podcast. To hear the
Science Magazine Podcast Transcript, 6 September 2013 http://podcasts.aaas.org/science_news/sciencepodcast_130906_sciencenow.mp3 Promo The following is an excerpt from the Science Podcast. To hear the
The Rat Lungworm Lifecycle
 Hawaii Island Rat Lungworm Working Group Daniel K. Inouye College of Pharmacy University of Hawaii, Hilo The Rat Lungworm Lifecycle Rat Lungworm IPM RLWL-3 It is important to understand the lifecycle of
Hawaii Island Rat Lungworm Working Group Daniel K. Inouye College of Pharmacy University of Hawaii, Hilo The Rat Lungworm Lifecycle Rat Lungworm IPM RLWL-3 It is important to understand the lifecycle of
Question Set 1: Animal EVOLUTIONARY BIODIVERSITY
 Biology 162 LAB EXAM 2, AM Version Thursday 24 April 2003 page 1 Question Set 1: Animal EVOLUTIONARY BIODIVERSITY (a). We have mentioned several times in class that the concepts of Developed and Evolved
Biology 162 LAB EXAM 2, AM Version Thursday 24 April 2003 page 1 Question Set 1: Animal EVOLUTIONARY BIODIVERSITY (a). We have mentioned several times in class that the concepts of Developed and Evolved
Time of Day. Teacher Lesson Plan Nocturnal Animals Pre-Visit Lesson. Overview
 Teacher Lesson Plan Nocturnal Animals Pre-Visit Lesson Duration: 40-50 minutes Minnesota State Science Standard Correlations: 3.4.1.1.2. Wisconsin State Science Standard Correlations: B 4.6, C.4.1, C.4.2
Teacher Lesson Plan Nocturnal Animals Pre-Visit Lesson Duration: 40-50 minutes Minnesota State Science Standard Correlations: 3.4.1.1.2. Wisconsin State Science Standard Correlations: B 4.6, C.4.1, C.4.2
Chapter 20: Mammals Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata. Class: Mammalia (~4800 spp.) Subclass: 2 Order: 17
 Chapter 20: Mammals Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Mammalia (~4800 spp.) Subclass: 2 Order: 17 most highly differentiated group in animal kingdom Mammals Key mammalian characteristics hair
Chapter 20: Mammals Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Class: Mammalia (~4800 spp.) Subclass: 2 Order: 17 most highly differentiated group in animal kingdom Mammals Key mammalian characteristics hair
Essential Question: What are the characteristics of invertebrate animals? What are the characteristics of vertebrate animals?
 Essential Question: What are the characteristics of invertebrate animals? What are the characteristics of vertebrate animals? Key Concept: The animal kingdom is divided up into 35 phyla. These phyla can
Essential Question: What are the characteristics of invertebrate animals? What are the characteristics of vertebrate animals? Key Concept: The animal kingdom is divided up into 35 phyla. These phyla can
ANTHR 1L Biological Anthropology Lab
 ANTHR 1L Biological Anthropology Lab Name: DEFINING THE ORDER PRIMATES Humans belong to the zoological Order Primates, which is one of the 18 Orders of the Class Mammalia. Today we will review some of
ANTHR 1L Biological Anthropology Lab Name: DEFINING THE ORDER PRIMATES Humans belong to the zoological Order Primates, which is one of the 18 Orders of the Class Mammalia. Today we will review some of
Owl Pellet Dissection A Study of Food Chains & Food Webs
 NAME Owl Pellet Dissection A Study of Food Chains & Food Webs INTRODUCTION: Owl pellets are masses of bone, teeth, hair, feathers and exoskeletons of various animals preyed upon by raptors, or birds of
NAME Owl Pellet Dissection A Study of Food Chains & Food Webs INTRODUCTION: Owl pellets are masses of bone, teeth, hair, feathers and exoskeletons of various animals preyed upon by raptors, or birds of
Vertebrate Structure and Function
 Vertebrate Structure and Function Part 1 - Comparing Structure and Function Classification of Vertebrates a. Phylum: Chordata Common Characteristics: Notochord, pharyngeal gill slits, hollow dorsal nerve
Vertebrate Structure and Function Part 1 - Comparing Structure and Function Classification of Vertebrates a. Phylum: Chordata Common Characteristics: Notochord, pharyngeal gill slits, hollow dorsal nerve
Shedding Light on the Dinosaur-Bird Connection
 Shedding Light on the Dinosaur-Bird Connection This text is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History. When people think of dinosaurs, two types generally come to mind: the huge herbivores
Shedding Light on the Dinosaur-Bird Connection This text is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History. When people think of dinosaurs, two types generally come to mind: the huge herbivores
Comparing DNA Sequences Cladogram Practice
 Name Period Assignment # See lecture questions 75, 122-123, 127, 137 Comparing DNA Sequences Cladogram Practice BACKGROUND Between 1990 2003, scientists working on an international research project known
Name Period Assignment # See lecture questions 75, 122-123, 127, 137 Comparing DNA Sequences Cladogram Practice BACKGROUND Between 1990 2003, scientists working on an international research project known
What is the evidence for evolution?
 What is the evidence for evolution? 1. Geographic Distribution 2. Fossil Evidence & Transitional Species 3. Comparative Anatomy 1. Homologous Structures 2. Analogous Structures 3. Vestigial Structures
What is the evidence for evolution? 1. Geographic Distribution 2. Fossil Evidence & Transitional Species 3. Comparative Anatomy 1. Homologous Structures 2. Analogous Structures 3. Vestigial Structures
8/25/ Opening Questions: Are you an animal? What traits do you share with a jellyfish? Chapter 10 Biodiversity 3: Animals
 Chapter 10 Biodiversity 3: Animals 10.1 Animals are consumers 10.2 Sponges and cnidarians 10.3 Three phyla of worms 10.4 Mollusks 10.5 Arthropods 10.6 Echinoderms 10.7 Vertebrates 10.8 Fishes 10.9 Amphibians
Chapter 10 Biodiversity 3: Animals 10.1 Animals are consumers 10.2 Sponges and cnidarians 10.3 Three phyla of worms 10.4 Mollusks 10.5 Arthropods 10.6 Echinoderms 10.7 Vertebrates 10.8 Fishes 10.9 Amphibians
Weekly Schedule of Neuroscience (2018/2019) Week 1
 Week 1 27/1/2019 28/1/2019 29/1/2019 30/1/2019 31/1/2019 9:00 10:00 Introductory lecture Gross morphology of the brain Gross morphology of spinal cord Health politics & Blood supply of the CNS Language
Week 1 27/1/2019 28/1/2019 29/1/2019 30/1/2019 31/1/2019 9:00 10:00 Introductory lecture Gross morphology of the brain Gross morphology of spinal cord Health politics & Blood supply of the CNS Language
Weekly Schedule of Neuroscience (2017/2018) Week 1
 Week 1 28/1/2018 29/1/2018 30/1/2018 31/1/2018 1/2/2018 8:00 9:00 Health politics & 9:00 10:00 Introductory lecture Gross morphology of the brain Gross morphology of spinal cord Health politics & Blood
Week 1 28/1/2018 29/1/2018 30/1/2018 31/1/2018 1/2/2018 8:00 9:00 Health politics & 9:00 10:00 Introductory lecture Gross morphology of the brain Gross morphology of spinal cord Health politics & Blood
Page # Diversity of Arthropoda Crustacea Morphology. Diversity of Arthropoda. Diversity of Arthropoda. Diversity of Arthropoda. Arthropods, from last
 Arthropods, from last time Crustacea are the dominant marine arthropods Crustacea are the dominant marine arthropods any terrestrial crustaceans? Should we call them shellfish? sowbugs 2 3 Crustacea Morphology
Arthropods, from last time Crustacea are the dominant marine arthropods Crustacea are the dominant marine arthropods any terrestrial crustaceans? Should we call them shellfish? sowbugs 2 3 Crustacea Morphology
Sense of Smell. By: Liz, Gen, Ethan, and Meakena
 Sense of Smell By: Liz, Gen, Ethan, and Meakena Function of smell The sense and function of smell is also called olfactometry, the testing and measurement of the sensitivity of the sense of smell. Smell
Sense of Smell By: Liz, Gen, Ethan, and Meakena Function of smell The sense and function of smell is also called olfactometry, the testing and measurement of the sensitivity of the sense of smell. Smell
MAMMAL LESSON PLAN. Understanding (s)/goals Students will understand that mammals are a unique group within the animal kingdom.
 MAMMAL LESSON PLAN Lesson Topic: Mammals Grade level: Elementary Grades Length of lesson: Approximately 5 days; will vary based on age and ability Curriculum Developer: Jennifer Mooney, M.Ed. Stage 1 Desired
MAMMAL LESSON PLAN Lesson Topic: Mammals Grade level: Elementary Grades Length of lesson: Approximately 5 days; will vary based on age and ability Curriculum Developer: Jennifer Mooney, M.Ed. Stage 1 Desired
Kingdom Animalia. All animals are multicellular organisms with real tissues and heterotrophic nutrition
 Keywords Kingdom Animalia Poriferan, -s Coelenterate,-s Echinoderm, -s Mollusc, -s Medusa, -s Polyp, -s Arthropod, -s Arachnid, -s Crustacean, -s Myriapod, -s Radula Exoskeleton / endoskeleton Atrial cavity
Keywords Kingdom Animalia Poriferan, -s Coelenterate,-s Echinoderm, -s Mollusc, -s Medusa, -s Polyp, -s Arthropod, -s Arachnid, -s Crustacean, -s Myriapod, -s Radula Exoskeleton / endoskeleton Atrial cavity
UNIT: INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS 1º ESO BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY
 UNIT: INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS 1º ESO BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 2015/2016 What do they have in common? What are their differences? What is the theme for the next unit? Vertebrates and Invertebrates 1 Label the animals
UNIT: INVERTEBRATE ANIMALS 1º ESO BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 2015/2016 What do they have in common? What are their differences? What is the theme for the next unit? Vertebrates and Invertebrates 1 Label the animals
PSY 2364 Animal Communication. Elk (Cervus canadensis) Extra credit assignment. Sad Underwing (Catocala maestosa) 10/11/2017
 PSY 2364 Animal Communication Elk (Cervus canadensis) Kingdom: Phylum: Class: Order: Family: Genus: Species: Animalia Chordata Mammalia Artiodactyla Cervidae Cervus canadensis Extra credit assignment Sad
PSY 2364 Animal Communication Elk (Cervus canadensis) Kingdom: Phylum: Class: Order: Family: Genus: Species: Animalia Chordata Mammalia Artiodactyla Cervidae Cervus canadensis Extra credit assignment Sad
2/11/2015. Body mass and total Glomerular area. Body mass and medullary thickness. Insect Nephridial Structure. Salt Gland Structure
 Body mass and medullary thickness Thicker medulla in mammals from dry climate Negative allometry why? Body mass and total Glomerular area Glomerular area is a measure of total ultrafiltration rate Slope
Body mass and medullary thickness Thicker medulla in mammals from dry climate Negative allometry why? Body mass and total Glomerular area Glomerular area is a measure of total ultrafiltration rate Slope
CHAPTER 26. Animal Evolution The Vertebrates
 CHAPTER 26 Animal Evolution The Vertebrates Impacts, Issues: Interpreting and Misinterpreting the Past No one was around to witness the transitions in the history of life Fossils allow us glimpses into
CHAPTER 26 Animal Evolution The Vertebrates Impacts, Issues: Interpreting and Misinterpreting the Past No one was around to witness the transitions in the history of life Fossils allow us glimpses into
VERTEBRATE READING. Fishes
 VERTEBRATE READING Fishes The first vertebrates to become a widespread, predominant life form on earth were fishes. Prior to this, only invertebrates, such as mollusks, worms and squid-like animals, would
VERTEBRATE READING Fishes The first vertebrates to become a widespread, predominant life form on earth were fishes. Prior to this, only invertebrates, such as mollusks, worms and squid-like animals, would
HUMAN APPENDIX BATS & TROPICAL FLOWERS
 HUMAN APPENDIX In humans, the appendix is a short piece of tissue off the large intestine. It is not used by humans for digestive functions. In other mammals, like rabbits and deer, the cecum is a large
HUMAN APPENDIX In humans, the appendix is a short piece of tissue off the large intestine. It is not used by humans for digestive functions. In other mammals, like rabbits and deer, the cecum is a large
Honey Bees. Anatomy and Function 9/26/17. Similar but Different. Honey Bee External Anatomy. Thorax (Human Chest): 4 Wings & 6 Legs
 Honey Bee Anatomy and Function How Honey Bees are Built and How the Function People Eat: Everything - Meat and Potatoes Omnivores Meat and Vegetables Digest: Stomach & Intestines Excrete: Feces and Urine
Honey Bee Anatomy and Function How Honey Bees are Built and How the Function People Eat: Everything - Meat and Potatoes Omnivores Meat and Vegetables Digest: Stomach & Intestines Excrete: Feces and Urine
Magic Story-telling Souvenir Coloring Books
 Magic Story-telling Souvenir Coloring Books The following are a few pages from our second book My Zoo Adventure Coloring Book. Actual page sizes are approximately 8.5 x 12 For wholesale prices to the souvenir
Magic Story-telling Souvenir Coloring Books The following are a few pages from our second book My Zoo Adventure Coloring Book. Actual page sizes are approximately 8.5 x 12 For wholesale prices to the souvenir
Animal. ì<(sk$m)=bdhhdc< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U. Groups. Life Science. by Carol Levine. Scott Foresman Science 2.2
 Life Science Animal Groups by Carol Levine Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Alike and Different Call Outs Glossary Vertebrates and Invertebrates Scott Foresman Science
Life Science Animal Groups by Carol Levine Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Alike and Different Call Outs Glossary Vertebrates and Invertebrates Scott Foresman Science
What Can I Learn From a Skull?
 What Can I Learn From a Skull? Pennsylvania Envirothon 2018 Skulls- Herbivores, Omnivores, and Carnivores Lesson Overview Grade level(s): Elementary School (K-5), Middle School Subjects(s): Biology/Life
What Can I Learn From a Skull? Pennsylvania Envirothon 2018 Skulls- Herbivores, Omnivores, and Carnivores Lesson Overview Grade level(s): Elementary School (K-5), Middle School Subjects(s): Biology/Life
! Three things needed to survive on land were: ! 1. Have lungs and breathe air. ! 2. Have a body resistant to drying out.
 Marine Reptiles, Birds and Mammals Vertebrates! Invaded the land and are descendants from the bony fish and were able to withstand the conditions on the land.! They evolved two sets of limbs (even snakes)
Marine Reptiles, Birds and Mammals Vertebrates! Invaded the land and are descendants from the bony fish and were able to withstand the conditions on the land.! They evolved two sets of limbs (even snakes)
There are 35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical
 Name 1 There are 35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical characteristics. All animals share several common
Name 1 There are 35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical characteristics. All animals share several common
B. Good, C.V. Holland* and P. Stafford. Department of Zoology, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Ireland
 Journal of Helminthology (2001) 75, 175±181 DOI: 10.1079/JOH200178 The influence of inoculum size and time post-infection on the number and position of Toxocara canis larvae recovered from the brains of
Journal of Helminthology (2001) 75, 175±181 DOI: 10.1079/JOH200178 The influence of inoculum size and time post-infection on the number and position of Toxocara canis larvae recovered from the brains of
SAMPLE PAPER. SU BJ ECT- Science CLASS-V
 SAMPLE PAPER SU BJ ECT- Science CLASS-V TIME DURATION: 2 hrs MAXIMUM MARKS:60 General Instructions :- 1 Attempt all questions section wise. 2 Two marks have been allotted for handwriting and neatness.
SAMPLE PAPER SU BJ ECT- Science CLASS-V TIME DURATION: 2 hrs MAXIMUM MARKS:60 General Instructions :- 1 Attempt all questions section wise. 2 Two marks have been allotted for handwriting and neatness.
The Animal Kingdom. Animal Diversity. Key Concept Animals are a diverse group of organisms that have adaptations to live in water and on land.
 2 The Animal Kingdom Key Concept Animals are a diverse group of organisms that have adaptations to live in water and on land. What You Will Learn The animal kingdom is made up of many different kinds of
2 The Animal Kingdom Key Concept Animals are a diverse group of organisms that have adaptations to live in water and on land. What You Will Learn The animal kingdom is made up of many different kinds of
Topic 3: Animals Ch.17 Characteristics of Animals p.338. Distinguishing Characteristics pp
 Topic 3: Animals Ch.17 Characteristics of Animals p.338 - Animals are: - Multicellular. - Ingestive heterotrophs. - Have a division of labour (tissues, organs, systems). - Motile at some stage in their
Topic 3: Animals Ch.17 Characteristics of Animals p.338 - Animals are: - Multicellular. - Ingestive heterotrophs. - Have a division of labour (tissues, organs, systems). - Motile at some stage in their
Vertebrates. skull ribs vertebral column
 Vertebrates skull ribs vertebral column endoskeleton in cells working together tissues tissues working together organs working together organs systems Blood carries oxygen to the cells carries nutrients
Vertebrates skull ribs vertebral column endoskeleton in cells working together tissues tissues working together organs working together organs systems Blood carries oxygen to the cells carries nutrients
Most amphibians begin life as aquatic organisms and then live on land as adults.
 Section 3: Most amphibians begin life as aquatic organisms and then live on land as adults. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What were the kinds of adaptations
Section 3: Most amphibians begin life as aquatic organisms and then live on land as adults. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What were the kinds of adaptations
Comparing DNA Sequence to Understand
 Comparing DNA Sequence to Understand Evolutionary Relationships with BLAST Name: Big Idea 1: Evolution Pre-Reading In order to understand the purposes and learning objectives of this investigation, you
Comparing DNA Sequence to Understand Evolutionary Relationships with BLAST Name: Big Idea 1: Evolution Pre-Reading In order to understand the purposes and learning objectives of this investigation, you
Evolutionary Trade-Offs in Mammalian Sensory Perceptions: Visual Pathways of Bats. By Adam Proctor Mentor: Dr. Emma Teeling
 Evolutionary Trade-Offs in Mammalian Sensory Perceptions: Visual Pathways of Bats By Adam Proctor Mentor: Dr. Emma Teeling Visual Pathways of Bats Purpose Background on mammalian vision Tradeoffs and bats
Evolutionary Trade-Offs in Mammalian Sensory Perceptions: Visual Pathways of Bats By Adam Proctor Mentor: Dr. Emma Teeling Visual Pathways of Bats Purpose Background on mammalian vision Tradeoffs and bats
Shared Humanity Written by Marilee Joy Mayfield
 Lesson: The Gorillas of Uganda Lesson Topic: Shared Humanity Shared Humanity Written by Marilee Joy Mayfield We often don t think of ourselves as animals, but we are. Humans are more similar to other animals
Lesson: The Gorillas of Uganda Lesson Topic: Shared Humanity Shared Humanity Written by Marilee Joy Mayfield We often don t think of ourselves as animals, but we are. Humans are more similar to other animals
Our Origins Discovering Physical Anthropology
 W. W. Norton & Company Our Origins Discovering Physical Anthropology Second Edition by Clark Spencer Larsen Chapter 7 Clark Spencer Larsen Our Origins DISCOVERING PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY C. Milner-Rose Chapter
W. W. Norton & Company Our Origins Discovering Physical Anthropology Second Edition by Clark Spencer Larsen Chapter 7 Clark Spencer Larsen Our Origins DISCOVERING PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY C. Milner-Rose Chapter
The Evolutionary Tree
 jonathanpark book2 9/22/04 6:01 PM Page 29 The Mysterious Stranger The Evolutionary Tree Have you ever seen the evolutionary tree? This diagram is used by evolutionists to try and figure out what animals
jonathanpark book2 9/22/04 6:01 PM Page 29 The Mysterious Stranger The Evolutionary Tree Have you ever seen the evolutionary tree? This diagram is used by evolutionists to try and figure out what animals
Homework: 1. Catalyst 2. Cladogram Building 3. Jigsaw Reading. Agenda:
 Friday/Monday, October 6/9, 2017 Your Learning Goal: SWBAT compare relationships between species to place them on a modified family tree called a cladogram. Table of Contents: Lines of Descent - 9R+L Key
Friday/Monday, October 6/9, 2017 Your Learning Goal: SWBAT compare relationships between species to place them on a modified family tree called a cladogram. Table of Contents: Lines of Descent - 9R+L Key
WHAT DO SEA STARS EAT EPUB
 02 June, 2018 WHAT DO SEA STARS EAT EPUB Document Filetype: PDF 375.58 KB 0 WHAT DO SEA STARS EAT EPUB We don't have as many fish as we used too because. It has been estimated that an adult Ochre sea star
02 June, 2018 WHAT DO SEA STARS EAT EPUB Document Filetype: PDF 375.58 KB 0 WHAT DO SEA STARS EAT EPUB We don't have as many fish as we used too because. It has been estimated that an adult Ochre sea star
Biology. Slide 1of 50. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 50 2of 50 Phylogeny of Chordates Nonvertebrate chordates Jawless fishes Sharks & their relatives Bony fishes Reptiles Amphibians Birds Mammals Invertebrate ancestor 3of 50 A vertebrate dry,
Biology 1of 50 2of 50 Phylogeny of Chordates Nonvertebrate chordates Jawless fishes Sharks & their relatives Bony fishes Reptiles Amphibians Birds Mammals Invertebrate ancestor 3of 50 A vertebrate dry,
The evolutionary origin of the mammalian. Cerebral cortex
 Biol Res 25: 41-49(1992) 41 The evolutionary origin of the mammalian cerebral cortex FRANCISCO ABOITIZ* Neuroscience Program, Brain Research Institute, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90024-1761,
Biol Res 25: 41-49(1992) 41 The evolutionary origin of the mammalian cerebral cortex FRANCISCO ABOITIZ* Neuroscience Program, Brain Research Institute, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90024-1761,
Skulls & Evolution. 14,000 ya cro-magnon. 300,000 ya Homo sapiens. 2 Ma Homo habilis A. boisei A. robustus A. africanus
 Skulls & Evolution Purpose To illustrate trends in the evolution of humans. To demonstrate what you can learn from bones & fossils. To show the adaptations of various mammals to different habitats and
Skulls & Evolution Purpose To illustrate trends in the evolution of humans. To demonstrate what you can learn from bones & fossils. To show the adaptations of various mammals to different habitats and
Comparative Physiology 2007 Second Midterm Exam. 1) 8 pts. 2) 14 pts. 3) 12 pts. 4) 17 pts. 5) 10 pts. 6) 8 pts. 7) 12 pts. 8) 10 pts. 9) 9 pts.
 Name: Comparative Physiology 2007 Second Midterm Exam 1) 8 pts 2) 14 pts 3) 12 pts 4) 17 pts 5) 10 pts 6) 8 pts 7) 12 pts 8) 10 pts 9) 9 pts Total 1. Cells I and II, shown below, are found in the gills
Name: Comparative Physiology 2007 Second Midterm Exam 1) 8 pts 2) 14 pts 3) 12 pts 4) 17 pts 5) 10 pts 6) 8 pts 7) 12 pts 8) 10 pts 9) 9 pts Total 1. Cells I and II, shown below, are found in the gills
Pasig Catholic College. Grade School Department 103 S.Y Be with Jesus, be with the Poor. Science 5 SECOND QUARTER Activity Sheet # 1
 PCC @ 103 Be with Jesus, be with the Poor Activity Sheet # 1 TYPE OF ACTIVITY: Discussion on Animal Adaptations: Natural Habitat : Natural Habitat of Animals Learning Objectives : Describe the different
PCC @ 103 Be with Jesus, be with the Poor Activity Sheet # 1 TYPE OF ACTIVITY: Discussion on Animal Adaptations: Natural Habitat : Natural Habitat of Animals Learning Objectives : Describe the different
MANSFIELD SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL / SCIENCE / A. There is no God. B. All living things on Earth are related.
 The Evidence of Evolution Name: Date: 1. Biological Evolutions makes 2 very bold claims about living creatures.what are they circle 2. A. There is no God. B. All living things on Earth are related. C.
The Evidence of Evolution Name: Date: 1. Biological Evolutions makes 2 very bold claims about living creatures.what are they circle 2. A. There is no God. B. All living things on Earth are related. C.
B D. C D) Devonian E F. A) Cambrian. B) Ordovician. C) Silurian. E) Carboniferous. F) Permian. Paleozoic Era
 Paleozoic Era A) Cambrian A B) Ordovician B D C) Silurian C D) Devonian E) Carboniferous F) Permian E F The Cambrian explosion refers to the sudden appearance of many species of animals in the fossil record.
Paleozoic Era A) Cambrian A B) Ordovician B D C) Silurian C D) Devonian E) Carboniferous F) Permian E F The Cambrian explosion refers to the sudden appearance of many species of animals in the fossil record.
Animal Evolution The Chordates. Chapter 26 Part 2
 Animal Evolution The Chordates Chapter 26 Part 2 26.10 Birds The Feathered Ones Birds are the only animals with feathers Descendants of flying dinosaurs in which scales became modified as feathers Long
Animal Evolution The Chordates Chapter 26 Part 2 26.10 Birds The Feathered Ones Birds are the only animals with feathers Descendants of flying dinosaurs in which scales became modified as feathers Long
CLADISTICS Student Packet SUMMARY Phylogeny Phylogenetic trees/cladograms
 CLADISTICS Student Packet SUMMARY PHYLOGENETIC TREES AND CLADOGRAMS ARE MODELS OF EVOLUTIONARY HISTORY THAT CAN BE TESTED Phylogeny is the history of descent of organisms from their common ancestor. Phylogenetic
CLADISTICS Student Packet SUMMARY PHYLOGENETIC TREES AND CLADOGRAMS ARE MODELS OF EVOLUTIONARY HISTORY THAT CAN BE TESTED Phylogeny is the history of descent of organisms from their common ancestor. Phylogenetic
Nematoda. Round worms Feeding and Parasitism
 Nematoda Round worms Feeding and Parasitism Nematoda Have pseudocoelom Live in many environments Parasitic Important decomposers Covered with cuticle Trichinella spiralis see fig 18.8B Nematode Diets and
Nematoda Round worms Feeding and Parasitism Nematoda Have pseudocoelom Live in many environments Parasitic Important decomposers Covered with cuticle Trichinella spiralis see fig 18.8B Nematode Diets and
Species must be adapted to their habitat.
 Species must be adapted to their habitat. Species must protect themselves from the heat, cold, move around, feed themselves, communicate and reproduce. These are the types of adaptations which we will
Species must be adapted to their habitat. Species must protect themselves from the heat, cold, move around, feed themselves, communicate and reproduce. These are the types of adaptations which we will
Feeding Behavior of a Dog, Betta Fish, and Leopard Gecko. Shannon Hutchison
 Feeding Behavior of a Dog, Betta Fish, and Leopard Gecko Shannon Hutchison 05/07/2018 Background The feeding behavior for dogs is greatly influenced by the feeding habits of their wild ancestors. Most
Feeding Behavior of a Dog, Betta Fish, and Leopard Gecko Shannon Hutchison 05/07/2018 Background The feeding behavior for dogs is greatly influenced by the feeding habits of their wild ancestors. Most
Meet our Nurses. Winter Newsletter In this issue. In your genes Pets and arthritis History of colour vision
 Winter Newsletter 2016 In this issue In your genes Pets and arthritis History of colour vision 2 3 4 Fulham Garden Vets (08) 8255 5475 Unley Vet Surgery (08) 8272 3400 Fulham Gardens Vet Surgery Black
Winter Newsletter 2016 In this issue In your genes Pets and arthritis History of colour vision 2 3 4 Fulham Garden Vets (08) 8255 5475 Unley Vet Surgery (08) 8272 3400 Fulham Gardens Vet Surgery Black
Slide 1. Birds & Mammals. Chapter 15
 Slide 1 Birds & Mammals Chapter 15 Slide 2 What is a Bird? Vertebrate Endothermic Feathered 4 chambered heart Egg laying Fore-limbs adapted for flight Bones nearly hollow (allow for lighter weight) Slide
Slide 1 Birds & Mammals Chapter 15 Slide 2 What is a Bird? Vertebrate Endothermic Feathered 4 chambered heart Egg laying Fore-limbs adapted for flight Bones nearly hollow (allow for lighter weight) Slide
Mystery of Life Travelling Exhibition Vertebrate Kingdom
 Mystery of Life Travelling Exhibition Vertebrate Kingdom When science meets art, what will happen? Vertebrate exhibition, it s a perfect convergence of the technique and art, where you can learn not only
Mystery of Life Travelling Exhibition Vertebrate Kingdom When science meets art, what will happen? Vertebrate exhibition, it s a perfect convergence of the technique and art, where you can learn not only
Exceptions: Somebody liked snakes. Some people disliked dogs, geese, sharks
 Unit 1: ANIMALS Exceptions: Somebody liked snakes Some people disliked dogs, geese, sharks Both animals are fascinating & worthy of our interest ANIMAL NAMES Taxonomy is a branch of biology that categorizes
Unit 1: ANIMALS Exceptions: Somebody liked snakes Some people disliked dogs, geese, sharks Both animals are fascinating & worthy of our interest ANIMAL NAMES Taxonomy is a branch of biology that categorizes
35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external
 35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical characteristics. All animals share several common characteristics:
35 phyla of animals These phyla can be classified into two groups (vertebrates or invertebrates) based on external and internal physical characteristics. All animals share several common characteristics:
