|
|
|
- Cody Reeves
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EEB 2208: LECTURE TOPIC 10 INVASIVE SPECIES & DISEASE Reading for this lecture Primack: Chapter 10 (second half). Discussion reading: Gibson et al Near-complete extinction of native small mammal fauna 25 years after forest fragmentation. Science 341: On-line at: pdf Movie: Watch the movie cane toads (on YouTube in 5 parts link on the web site to the first part.) 1. What are invasive species? A) DEFINITIONS i) Native applies to a species that is found within its natural range. Introduced applies to species that have been moved to a new area (usually by humans). i Exotic or alien applies to species when found outside of their natural range (i.e., after being introduced). iv) The terms non-native, introduced, exotic and alien are often used interchangeably. v) Invasive species that spread rapidly, and undergo explosive population increases, such that they dominate a community. Usually things that are called invasive cause some problem (from the perspective of humans). Usually invasive species are also introduced, but sometimes the term is used for species that are native to an area. B) WHY ARE INTRODUCTIONS/INVASIVES A PROBLEM? i) Because they alter species interactions, often to the detriment of native species. For example, invasive species can affect other species by preying upon them, by out-competing them, by causing disease, etc. They also can have effects indirectly, e.g., by altering the way in which the ecosystem functions. For example, beavers have been introduced into southern Chile what kind of consequences do you think this would have given what I ve told you in earlier lectures? i Note that the interactions among native species can change dramatically as a result of human activities, creating effects that are similar to those of introduced invasive species. Examples, to think about include: removing a key predator and allowing its prey to increase dramatically (e.g., wiping out wolves resulted in a big increase in coyotes and other medium sized predators); increasing the food available for some species (e.g., waste grain in the farm-belt has caused massive increases in various geese populations); altering the habitat (e.g., cowbirds, discussed in a previous lecture, have increased because of forest fragmentation and increased cattle populations). C) BUT, INTRODUCTIONS ARE NOT ALWAYS A PROBLEM i) Most fail and only a very small proportion of all introduced species become invasive. But, a small proportion of a big number of introductions can still result in a lot of invasive species. 1
2 i For a species to become invasive it must overcome three (big) challenges: (a) it must get somewhere new (which means somehow being transported there), (b) it must become established once it has arrived (which requires conditions conducive to avoiding rapid extinction), and (c) it must undergo explosive population growth. At each of these steps, most species fail. In some cases, introductions can be beneficial, for example: Some very rare species have been introduced to new areas where they do not face the threats that exist in their native range. Sometimes introduced species provide valuable habitat for threatened species. Some species are introduced for very specific purposes that are considered valuable (maybe even necessary) for humans e.g., nearly all agricultural crops are introduced somewhere. D) CAN WE PREDICT WHICH SPECIES WILL BE INVASIVE? i) In a very general sense we can determine which species are likely to become invasive. Successful invaders have a host of typical characteristics: abundant in original range short generation times larger than most relatives habitat generalist polyphagous (diet generalist) much genetic variability fertilized female able to colonize associated with humans disturbed habitat users Not all invasives have all of these features, but most probably have at least a few. Why might each of the things listed help species to become invasive? i Even though there are a host of biological characteristics that are correlated with invasion success, there are many exceptions, and many invasions that cannot be explained as easily as we would like. iv) Some of the things that influence invasion success have nothing to do with the biological characteristics of the organisms. For example, one of the best studies of what it is that allows a species to become established after being introduced looked at introduced birds in New Zealand. This study was especially good because there were very detailed records about the earliest stage of the invasion (something we typically know little about). In this study, none of the biological factors considered helped to predict which species would become established. But, two other variables did correlate with the success of a species. Species for which a lot of individuals were released, or for which there had been multiple attempts at introduction were most likely to become established. v) Another study of 600 bird introductions around the world showed a similar result: that the primary factor influencing whether introductions were successful was the propagule pressure, or introduction effort. 2. Why do people move species to new areas? A) FOOD i) Example: The lakes of the Rift Valley in East Africa have incredibly high fish diversity. This small area contains as many fish species as all 2
3 of Europe and North America combined. The Nile perch, however, was introduced to provide food for the people who lived in the area. This species is a voracious predator and has contributed to the widespread loss of many fish species. In Lake Victoria there were 300 species of cichlid fish before Nile perch was introduced. Now there are fewer than 100 species. Example: European rabbits were introduced to Australia as a source of food. But, the population rapidly took off (they bred like rabbits), and within a few decades they had spread across the entire continent and numbered in the hundreds of millions. B) AESTHETIC REASONS i) Example: Eurasian starlings (and many other species) have been introduced into North America and other places around the world. Originally, these birds were introduced by organized groups that wanted to populate the New World with familiar species from home some of these societies had the goal of trying to introduce all the birds mentioned in Shakespeare s plays. In many places, starlings have become very common and now compete with native species for nest sites (starlings nest in tree cavities, which usually occur in limited numbers) and maybe also for food. In North America, about 100 birds were initially released in New York City. Now there are estimated to be well over 100 million, and they occur across the entire continent. Example: Species brought in as pets can also wreck havoc on native populations. In one especially dramatic example, the cat belonging to a local lighthouse keeper is thought to have largely wiped out an entire species: the Stephen s Island wren, which was found only on a small island near New Zealand. i Many (probably most) invasive plants were initially introduced as plantings in peoples gardens (or other ornamental settings). Most species grown in gardens have stayed in gardens, but many have not. iv) Example: Purple loosestrife is a species that you can easily find around Storrs (e.g., Mirror Lake). It is a very attractive plant and is consequently favored as a garden ornamental, but it tends to take over wetlands completely, out-competing all other species. It is now a dominant wetland plant in many parts of North America. v) Other invasive plants include: a) Kudzu, which is now found in the southeastern US and which completely overgrows everything it encounters. b) Tamarix (also known as salt cedar), which is introduced into the deserts of the southwest and helps to displace native trees, while also lowering the water table and making it harder for native species to survive (but to complicate matters also providing habitat for rare birds such as the southwestern willow flycatcher). c) Many, many others, e.g., see the UConn-based Invasive Plant Atlas of New England (IPANE) project C) ACCIDENTAL TRANSPORT i) Example: The brown tree snake is an Australasian species that was introduced to the island of Guam (in the Pacific) after World War II. It is thought to have got there accidentally, probably by stowing away on military aircraft. After a period of rarity, the population suddenly exploded with the result that there were snakes everywhere. Coincident with this population increase, all species of forest birds and other vertebrates (including some found nowhere else in the world) began to decline. Now many of the bird species are all gone from the island; predation by the snakes is thought to be the primary reason. 3
4 i One major way in which aquatic species get transported around the world is in the ballast water that large ships take on-board. This water may be taken onto a ship in one part of the world, and then discharged (along with all the organisms it contains) thousands of miles away. It has been estimated that 40,000 gallons of foreign ballast water is discharged into US waters every minute. Many other routes for accidental transport exist. These include: via the mail, on airplanes (see above), in the dirt on someone s boots (seeds, fungal spores), in shipped products (e.g., various forest insect pests probably get around in wood shipments), etc., etc. 3. Do all invasions involve introduced species? A) INVASIVE POPULATION GROWTH DUE TO HUMAN ACTIVITES i) Most species that are termed invasive are introduced. But sometimes the term is used for native species that have expanded their ranges (e.g., brown-headed cowbirds, which have spread into the Northeast following forest loss and fragmentation), or that have simply undergone i massive population growth. Example: An example of the latter, involves two species of North American geese snow and Ross s geese (collectively: white geese). These birds breed in the Arctic and winter in the US. Their populations have steadily increased in recent decades, largely because of increased food at wintering/migration sites, which tend to be agricultural areas where there is now a lot of spilled grain available after harvest (e.g., California, mid-west, Gulf Coast). Predation during these periods is also lower than it was historically (both because there is much less human hunting and because many natural predators have declined). A consequence of these population increases is widespread damage to Arctic breeding grounds, where the geese overgraze the tundra. For instance, it has been estimated that 65% of the inter-tidal habitat in southern and western Hudson Bay has been badly damaged by these geese. In addition to having harmful effects on the plant species that live in these areas, this grazing affects many other species of animal that live in this habitat. Can you think of any similar New England examples? Hint: there s a very well known one involving a forest herbivore. 4. Solutions A) EARLY DETECTION Once invasive species are established it is very difficult to get rid of them. Even when it is possible, it can be expensive. Consequently, the best solution to the problem is to prevent establishment and spread in the first place. i) Doing this is not easy and requires controls to movement and methods for early detection. Projects like IPANE can help us to better understand patterns and mechanisms of spread, which can help to determine which species are likely to be problems, and where they are likely to become invasive. These projects also help train large numbers of people who can then look for early signs of spread into new areas. B) BIOLOGICAL CONTROL i) Once introduced species have become widespread and extremely common, mechanical (e.g., pulling up plants) and chemical (e.g., herbicides) control are difficult to implement. 4
5 At this stage, one of the few options is the use of some biological agent (usually introduced from elsewhere). Typically, these agents are a herbivore, predator, or parasite that specializes on the invasive species. i A common argument for doing this is that an important thing that allows a species to become invasive is that it is released from the effects of key predators or parasites that keep its population in check in its native range. So, the argument goes, bringing in the predator will help control the invasive. iv) The history of biological control, however, is checkered. Some attempts have been very successful, but others have turned into complete environmental disasters. v) Example: The prickly pear cactus, which became invasive after being introduced to Australia, was effectively controlled by the introduction of Cactoblastis moths which feed on the cactus. This moth, however, has subsequently become invasive itself (e.g., in the southern US where it is impacting various native cacti). vi) Example: Mongoose were introduced to Hawaii (and elsewhere) to help control the (introduced) rats that had become very abundant in sugar cane (also introduced) fields. Unfortunately, mongooses are diurnal while rats are nocturnal so it didn t work! Not only did the mongoose not control the rats, but they started to prey on native bird species that they could find during the day instead. Today mongooses are the subject of major predator control programs (designed to protect native species) in many parts of Hawaii. v In general, biological control is most likely to work (and to not cause other problems) when the species brought in has a very specific effect on only the species that needs to be controlled (specialist herbivores and parasites are good examples). Extensive testing prior to release is consequently an important part of most modern biological control programs. As a result, these programs are generally more effective than some of those in the past. 5. Disease A) INTRODUCTION i) Diseases affect a relatively small proportion of endangered species, compared to most of the things we have talked out. Nonetheless, 1 in 10 endangered vertebrates in the US are affected by disease. It is quite likely that the very low percentages for invertebrates and plants are a i iv) result of our poor knowledge of disease in these groups. Probably the greatest threats come from emerging new diseases. Very often these will be diseases that are also introduced species. Changing conditions can also result in new outbreaks of diseases that have been present in an area for a long time. For example, if changes in habitat availability concentrate individuals into a small area, the rate of transmission is likely to go up, making a large outbreak more likely. The effects of existing diseases in an area can also be amplified by the fact that a species has become endangered through other means. For example, if a species is so rare that it must be brought into captivity, then it is likely to be exposed to diseases that it might not otherwise encounter. As populations decrease in size, they are likely to become more inbred (especially if in captivity), which might make them more vulnerable to disease. In fact, simply by having a small population a species is increasingly vulnerable to a disease outbreak, just because there are fewer individuals that are likely to have the genetic ability, overall good health, or simply good luck, to avoid succumbing to the disease. 5
6 B) EMERGING DISEASES i) Example: Chytrid disease in amphibians was only discovered in the late 1990s, but has rapidly spread worldwide and has caused rapid declines of many different species. Example: Devil Facial Tumor Disease in Tasmanian devils was also discovered only in the 1990s. The disease is a cancer that can be transmitted from one individual to another (via bites during fighting). All devils that get the cancer die and it is predicted that the disease will have spread throughout the entire range by the end of the decade. In areas where DFTD is present there have been declines of up to 90%. i Example: A century ago, the American chestnut was a dominant tree in eastern forests. Now it is almost entirely gone, due to the introduction of a fungal disease that kills mature trees. Chestnut blight was introduced to North America from Asia in It rapidly spread throughout the range of the tree in only a few decades. Chestnuts persist, but only in isolated places or as root sprouts. C) CONTROLLING DISEASE i) In some cases it is possible to address disease problems through direct intervention. Example: The Ethiopian wolf has a small population and has suffered serious declines due to rabies. Researchers, however, have shown that it should be possible to slow the spread of the disease by vaccinating as few as 30% of the animals in the population. The trick is to identify when/where outbreaks occur and then target those individuals that are most likely to contribute to disease spread (i.e., basic biological knowledge about the population is needed). i This study is important because vaccinating entire populations is often impractical, but the research suggests that it is not always necessary. 6
EEB 2208: TOPIC 10 INVASIVE SPECIES
 EEB 2208: TOPIC 10 INVASIVE SPECIES Reading for this topic Primack: Chapter 10 (second half). Watch Cane Toads: An Unnatural History: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6sblf1tsoaw 1. What are invasive species?
EEB 2208: TOPIC 10 INVASIVE SPECIES Reading for this topic Primack: Chapter 10 (second half). Watch Cane Toads: An Unnatural History: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6sblf1tsoaw 1. What are invasive species?
Turtle Research, Education, and Conservation Program
 Turtle Population Declines Turtle Research, Education, and Conservation Program Turtles are a remarkable group of animals. They ve existed on earth for over 200 million years; that s close to 100 times
Turtle Population Declines Turtle Research, Education, and Conservation Program Turtles are a remarkable group of animals. They ve existed on earth for over 200 million years; that s close to 100 times
Invasive Species Videos
 Invasive Species Videos Starling Asian Carp Great Lakes Kudzu Lionfish Python in Everglades Invasive Species Videos Starling Asian Carp Great Lakes Kudzu Lionfish Python in Everglades 1 The Brown Tree
Invasive Species Videos Starling Asian Carp Great Lakes Kudzu Lionfish Python in Everglades Invasive Species Videos Starling Asian Carp Great Lakes Kudzu Lionfish Python in Everglades 1 The Brown Tree
Grade 5. Practice Test. Invasion of the Pythons
 Name Date Grade 5 Invasion of the Pythons Today you will read the following passage. Read this passage carefully to gather information to answer questions and write an essay. Introduction Excerpt from
Name Date Grade 5 Invasion of the Pythons Today you will read the following passage. Read this passage carefully to gather information to answer questions and write an essay. Introduction Excerpt from
Biodiversity and Extinction. Lecture 9
 Biodiversity and Extinction Lecture 9 This lecture will help you understand: The scope of Earth s biodiversity Levels and patterns of biodiversity Mass extinction vs background extinction Attributes of
Biodiversity and Extinction Lecture 9 This lecture will help you understand: The scope of Earth s biodiversity Levels and patterns of biodiversity Mass extinction vs background extinction Attributes of
Where Animals and Plants Are Found
 Section 8: Physical Systems Where Animals and Plants Are Found About Animals and Plants What I Need to Know Vocabulary ecosystem food chain food web marine prairie Many animals live on Earth. Many plants
Section 8: Physical Systems Where Animals and Plants Are Found About Animals and Plants What I Need to Know Vocabulary ecosystem food chain food web marine prairie Many animals live on Earth. Many plants
Between 1850 and 1900, human population increased, and 99% of the forest on Puerto Rico was cleared.
 Case studies, continued. 9) Puerto Rican Parrot Low point was 13 parrots in 1975. Do not breed until 4 years old. May be assisted by helpers at the nest, but this is not clear. Breeding coincides with
Case studies, continued. 9) Puerto Rican Parrot Low point was 13 parrots in 1975. Do not breed until 4 years old. May be assisted by helpers at the nest, but this is not clear. Breeding coincides with
Why should we care about biodiversity? Why does it matter?
 1 Why should we care about biodiversity? Why does it matter? 1. Write one idea on your doodle sheet in the first box. (Then we ll share with a neighbor.) What do we know is happening to biodiversity now?
1 Why should we care about biodiversity? Why does it matter? 1. Write one idea on your doodle sheet in the first box. (Then we ll share with a neighbor.) What do we know is happening to biodiversity now?
Extinction. Extinction occurs when all individuals of a species are gone and have left no descendants. If all the species within a genus are
 Extinction Extinction occurs when all individuals of a species are gone and have left no descendants. If all the species within a genus are extinct then the genus is extinct. If all genera in a family
Extinction Extinction occurs when all individuals of a species are gone and have left no descendants. If all the species within a genus are extinct then the genus is extinct. If all genera in a family
Erin Maggiulli. Scientific Name (Genus species) Lepidochelys kempii. Characteristics & Traits
 Endangered Species Common Name Scientific Name (Genus species) Characteristics & Traits (s) Kemp s Ridley Sea Turtle Lepidochelys kempii Triangular head w/ hooked beak, grayish green color. Around 100
Endangered Species Common Name Scientific Name (Genus species) Characteristics & Traits (s) Kemp s Ridley Sea Turtle Lepidochelys kempii Triangular head w/ hooked beak, grayish green color. Around 100
AN APPLIED CASE STUDY of the complexity of ecological systems and process: Why has Lyme disease become an epidemic in the northeastern U.S.
 AN APPLIED CASE STUDY of the complexity of ecological systems and process: Why has Lyme disease become an epidemic in the northeastern U.S. over the last few decades? What causes Lyme disease? 1 Frequency
AN APPLIED CASE STUDY of the complexity of ecological systems and process: Why has Lyme disease become an epidemic in the northeastern U.S. over the last few decades? What causes Lyme disease? 1 Frequency
Waterfowl managers now believe that the continental lesser snow goose population may exceed 15 million birds.
 Waterfowl managers now believe that the continental lesser snow goose population may exceed 15 million birds. 38 Ducks Unlimited March/April 2013 Light Goose Dilemma Despite increased harvests, populations
Waterfowl managers now believe that the continental lesser snow goose population may exceed 15 million birds. 38 Ducks Unlimited March/April 2013 Light Goose Dilemma Despite increased harvests, populations
FERAL. Copyright David Manning s Animal Ark
 FERAL What is a Feral Animal? A feral animal is a domesticated creature that has escaped, or been deliberately released, into the wild where it now lives and breeds. When talking about ferals we also often
FERAL What is a Feral Animal? A feral animal is a domesticated creature that has escaped, or been deliberately released, into the wild where it now lives and breeds. When talking about ferals we also often
Michael R. Rochford, Jennifer Ketterlin Eckles, and Frank J. Mazzotti
 Relationship between invasive reptiles and ecosystem restoration in the Florida Everglades: How do we move from behind the eight ball to ahead of the curve? Michael R. Rochford, Jennifer Ketterlin Eckles,
Relationship between invasive reptiles and ecosystem restoration in the Florida Everglades: How do we move from behind the eight ball to ahead of the curve? Michael R. Rochford, Jennifer Ketterlin Eckles,
Most amphibians begin life as aquatic organisms and then live on land as adults.
 Section 3: Most amphibians begin life as aquatic organisms and then live on land as adults. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What were the kinds of adaptations
Section 3: Most amphibians begin life as aquatic organisms and then live on land as adults. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What were the kinds of adaptations
Module 2.4: Small Mammals Interpreting with Chinchillas
 Module 2.4: Small Mammals Interpreting with Chinchillas Interpreting with Chinchillas: The theme of your conversations may differ from group to group depending on the program, and the age of your audience.
Module 2.4: Small Mammals Interpreting with Chinchillas Interpreting with Chinchillas: The theme of your conversations may differ from group to group depending on the program, and the age of your audience.
Conserving Birds in North America
 Conserving Birds in North America BY ALINA TUGEND Sanderlings Andrew Smith November 2017 www.aza.org 27 Throughout the country, from California to Maryland, zoos and aquariums are quietly working behind
Conserving Birds in North America BY ALINA TUGEND Sanderlings Andrew Smith November 2017 www.aza.org 27 Throughout the country, from California to Maryland, zoos and aquariums are quietly working behind
SLOW DOWN, LOVE WIZARD. HERE S WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT THE HORNED LIZARD.
 SLOW DOWN, LOVE WIZARD. HERE S WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT THE HORNED LIZARD. Horned lizards predominately eat ants. In small doses the ants venom does not harm the lizard; however, a swarm can kill an
SLOW DOWN, LOVE WIZARD. HERE S WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT THE HORNED LIZARD. Horned lizards predominately eat ants. In small doses the ants venom does not harm the lizard; however, a swarm can kill an
Maritime Shipping on the Great Lakes and the Lake Erie Water Snake
 Activity for Biology Lesson #2 Name Period Date Maritime Shipping on the Great Lakes and the Lake Erie Water Snake Background Information on Lake Erie water snake and round goby: Lake Erie water snake:
Activity for Biology Lesson #2 Name Period Date Maritime Shipping on the Great Lakes and the Lake Erie Water Snake Background Information on Lake Erie water snake and round goby: Lake Erie water snake:
Unit 19.3: Amphibians
 Unit 19.3: Amphibians Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in amphibians. Outline the reproduction and development of amphibians. Identify the three living amphibian orders. Describe how amphibians
Unit 19.3: Amphibians Lesson Objectives Describe structure and function in amphibians. Outline the reproduction and development of amphibians. Identify the three living amphibian orders. Describe how amphibians
Northern Copperhead Updated: April 8, 2018
 Interpretation Guide Northern Copperhead Updated: April 8, 2018 Status Danger Threats Population Distribution Habitat Diet Size Longevity Social Family Units Reproduction Our Animals Scientific Name Least
Interpretation Guide Northern Copperhead Updated: April 8, 2018 Status Danger Threats Population Distribution Habitat Diet Size Longevity Social Family Units Reproduction Our Animals Scientific Name Least
EUROPEAN STARLING HOUSE FINCH
 EUROPEAN STARLING Scientific Name: Sturnus vulgaris Size: 7.5-8.5 " (19-21 cm) Shape: Short tail; plump body Color: Blackbird with shiny feathers; yellow bill in springtime. Habitat: Cities, parks, farms,
EUROPEAN STARLING Scientific Name: Sturnus vulgaris Size: 7.5-8.5 " (19-21 cm) Shape: Short tail; plump body Color: Blackbird with shiny feathers; yellow bill in springtime. Habitat: Cities, parks, farms,
Mute Swans. Invading Michigan s Waters. A growing threat to native animals, habitat, and humans. Photo by Jessie Turner
 Mute Swans Invading Michigan s Waters A growing threat to native animals, habitat, and humans Photo by Jessie Turner Definitions Native: species that occur naturally in a given area or region Non-Native:
Mute Swans Invading Michigan s Waters A growing threat to native animals, habitat, and humans Photo by Jessie Turner Definitions Native: species that occur naturally in a given area or region Non-Native:
Reptile conservation in Mauritius
 Reptile conservation in Mauritius Pristine Mauritius Nik Cole 671 species of plant 46% endemic to Mauritius The forests supported 22 types of land bird, 12 endemic to Mauritius, such as the dodo The Mauritius
Reptile conservation in Mauritius Pristine Mauritius Nik Cole 671 species of plant 46% endemic to Mauritius The forests supported 22 types of land bird, 12 endemic to Mauritius, such as the dodo The Mauritius
Captive Versus Wild. My last few papers have been on the subject of wild-caught versus captive-bred
 Chris Newman Malory Klocke Argument Captive Versus Wild My last few papers have been on the subject of wild-caught versus captive-bred exotic pets. I have presented information and explained both sides
Chris Newman Malory Klocke Argument Captive Versus Wild My last few papers have been on the subject of wild-caught versus captive-bred exotic pets. I have presented information and explained both sides
Dealing with the devil
 If we get their numbers back up, the devils themselves will sort it out. They re a very capable animal. They ve been here 10,000 years. It s their island. Dr David Pemberton Dealing with the devil writer
If we get their numbers back up, the devils themselves will sort it out. They re a very capable animal. They ve been here 10,000 years. It s their island. Dr David Pemberton Dealing with the devil writer
Ssssneaky, Pesssky, S speciesss! Objectives: Sneak Peek Aligned with the following Sunshine State Standards and FCAT Benchmarks for grades 6-8:
 Ssssneaky, Pesssky, S sspeciesss! ` Sneak Peek Students will be introduced to the concepts and issues surrounding Invasive Species. A potential Florida invader is the Brown Tree Snake, Boiga irregularis.
Ssssneaky, Pesssky, S sspeciesss! ` Sneak Peek Students will be introduced to the concepts and issues surrounding Invasive Species. A potential Florida invader is the Brown Tree Snake, Boiga irregularis.
Current Status of Amphibian Populations. Amphibian biology - characteristics making
 Global Amphibian Declines: What Have We Done? Mike Tyler Steve Holmer Nikki Maxwell University of Tennessee Knoxville Department of Forestry, Wildlife and Fisheries Graduate Student Seminar 15 October
Global Amphibian Declines: What Have We Done? Mike Tyler Steve Holmer Nikki Maxwell University of Tennessee Knoxville Department of Forestry, Wildlife and Fisheries Graduate Student Seminar 15 October
Hawaii s Forest. Concepts Competition Invasive Species How organisms affect other organisms in the same environment. HCPS III Benchmarks S.C.4.5.
 Hawaii s Forest Concepts Competition Invasive Species How organisms affect other organisms in the same environment. HCPS III Benchmarks S.C.4.5.3 Duration Part 1: 45 Min. Part 2: 40 Min. Part 3: 35 Min.
Hawaii s Forest Concepts Competition Invasive Species How organisms affect other organisms in the same environment. HCPS III Benchmarks S.C.4.5.3 Duration Part 1: 45 Min. Part 2: 40 Min. Part 3: 35 Min.
Little Brown Bat Myotis lucifugus
 Bat Management Little Brown Bat Myotis lucifugus Biology Nocturnal Approximately 8-9cm long and weighs 3-14 grams depending on age and time of year Bats have a very low reproductive rate May live for 30+
Bat Management Little Brown Bat Myotis lucifugus Biology Nocturnal Approximately 8-9cm long and weighs 3-14 grams depending on age and time of year Bats have a very low reproductive rate May live for 30+
Who Am I? What are some things you can do to help protect my home? Track: Ohio Department of Natural Resources Photo: Cottonwood Canyons Foundation
 Who Am I? What are some things you can do to help protect my home? Track: Ohio Department of Natural Resources Photo: Cottonwood Canyons Foundation I am a Red Squirrel! I live here in Alta. I build my
Who Am I? What are some things you can do to help protect my home? Track: Ohio Department of Natural Resources Photo: Cottonwood Canyons Foundation I am a Red Squirrel! I live here in Alta. I build my
Commercial Collection. & Pit Fall Trap Updates. Jason L. Jones Herpetologist 23 June 2017 Commission Update
 Commercial Collection & Pit Fall Trap Updates Jason L. Jones Herpetologist 23 June 2017 Commission Update Everyone collects Everyone collects Some collections require permits Some are illegal. 16-17th
Commercial Collection & Pit Fall Trap Updates Jason L. Jones Herpetologist 23 June 2017 Commission Update Everyone collects Everyone collects Some collections require permits Some are illegal. 16-17th
Bullfrogs - a Trojan horse for a deadly fungus?
 December OCTOBER 2017 2018 Bullfrogs - a Trojan horse for a deadly fungus? Authors: Susan Crow, Meghan Pawlowski, Manyowa Meki, Lara Authors: LaDage, Timothy Roth II, Cynthia Downs, Barry Tiffany Sinervo
December OCTOBER 2017 2018 Bullfrogs - a Trojan horse for a deadly fungus? Authors: Susan Crow, Meghan Pawlowski, Manyowa Meki, Lara Authors: LaDage, Timothy Roth II, Cynthia Downs, Barry Tiffany Sinervo
ECOSYSTEMS Wolves in Yellowstone
 ECOSYSTEMS Wolves in Yellowstone Adapted from Background Two hundred years ago, around 1800, Yellowstone looked much like it does today; forest covered mountain areas and plateaus, large grassy valleys,
ECOSYSTEMS Wolves in Yellowstone Adapted from Background Two hundred years ago, around 1800, Yellowstone looked much like it does today; forest covered mountain areas and plateaus, large grassy valleys,
THE WOLF WATCHERS. Endangered gray wolves return to the American West
 CHAPTER 7 POPULATION ECOLOGY THE WOLF WATCHERS Endangered gray wolves return to the American West THE WOLF WATCHERS Endangered gray wolves return to the American West Main concept Population size and makeup
CHAPTER 7 POPULATION ECOLOGY THE WOLF WATCHERS Endangered gray wolves return to the American West THE WOLF WATCHERS Endangered gray wolves return to the American West Main concept Population size and makeup
A Conversation with Mike Phillips
 A Conversation with Mike Phillips Clockwise from top: Lynn Rogers, Evelyn Mercer, Kevin Loader, Jackie Fallon 4 Fall 2011 www.wolf.org Editor s Note: Tom Myrick, communications director for the International
A Conversation with Mike Phillips Clockwise from top: Lynn Rogers, Evelyn Mercer, Kevin Loader, Jackie Fallon 4 Fall 2011 www.wolf.org Editor s Note: Tom Myrick, communications director for the International
Get ready to start your Expedition!
 Get ready to start your Expedition! What is an Expedition? An Expedition is a guided, themed interactive tour of a specific area of the Zoo. Please note: You will not see the entire Zoo on your Expedition.
Get ready to start your Expedition! What is an Expedition? An Expedition is a guided, themed interactive tour of a specific area of the Zoo. Please note: You will not see the entire Zoo on your Expedition.
Striped Skunk Updated: April 8, 2018
 Striped Skunk Updated: April 8, 2018 Interpretation Guide Status Danger Threats Population Distribution Habitat Diet Size Longevity Social Family Units Reproduction Our Animals Scientific Name Least Concern
Striped Skunk Updated: April 8, 2018 Interpretation Guide Status Danger Threats Population Distribution Habitat Diet Size Longevity Social Family Units Reproduction Our Animals Scientific Name Least Concern
Pygmy Rabbit (Brachylagus idahoensis)
 Pygmy Rabbit (Brachylagus idahoensis) Conservation Status: Near Threatened. FIELD GUIDE TO NORTH AMERICAN MAMMALS Pygmy Rabbits dig extensive burrow systems, which are also used by other animals. Loss
Pygmy Rabbit (Brachylagus idahoensis) Conservation Status: Near Threatened. FIELD GUIDE TO NORTH AMERICAN MAMMALS Pygmy Rabbits dig extensive burrow systems, which are also used by other animals. Loss
S7L Algal blooms that pollute streams, rivers, and lakes are caused by the presence of
 S7L-4 1. Algal blooms that pollute streams, rivers, and lakes are caused by the presence of A. lead. B. oxygen. C. mercury. D. phosphates. 2. Plants with spines and waxy leaves are well-suited for life
S7L-4 1. Algal blooms that pollute streams, rivers, and lakes are caused by the presence of A. lead. B. oxygen. C. mercury. D. phosphates. 2. Plants with spines and waxy leaves are well-suited for life
State of the Turtle Raising Awareness for Turtle Conservation
 State of the Turtle Raising Awareness for Turtle Conservation 1 January 2011 Trouble for Turtles The fossil record shows us that turtles, as we know them today, have been on our planet since the Triassic
State of the Turtle Raising Awareness for Turtle Conservation 1 January 2011 Trouble for Turtles The fossil record shows us that turtles, as we know them today, have been on our planet since the Triassic
Acknowledgements. Revised by: Richard W. Gleason, Adjunct Assistant, Florida 4-H Department, IFAS, University of Florida.
 li i Circular 545 i By: Carolee Boyles, 4-H IPM Coordinator, Florida 4-H Department, and Dr. Philip G. Koehler, Extension Entomologist, Department of Entomology and Nematology,lFAS, University of Florida,
li i Circular 545 i By: Carolee Boyles, 4-H IPM Coordinator, Florida 4-H Department, and Dr. Philip G. Koehler, Extension Entomologist, Department of Entomology and Nematology,lFAS, University of Florida,
VANCOUVER ISLAND MARMOT
 VANCOUVER ISLAND MARMOT STATUS: CRITICALLY ENDANGERED The Vancouver Island marmot is one of the rarest mammals in the world and can be found only in the alpine meadows on Vancouver Island. By 2003, there
VANCOUVER ISLAND MARMOT STATUS: CRITICALLY ENDANGERED The Vancouver Island marmot is one of the rarest mammals in the world and can be found only in the alpine meadows on Vancouver Island. By 2003, there
RABIES CONTROL INTRODUCTION
 RABIES CONTROL INTRODUCTION Throughout human history, few illnesses have provoked as much anxiety as has rabies. Known as a distinct entity since at least 500 B.C., rabies has been the subject of myths
RABIES CONTROL INTRODUCTION Throughout human history, few illnesses have provoked as much anxiety as has rabies. Known as a distinct entity since at least 500 B.C., rabies has been the subject of myths
How do dogs make trouble for wildlife in the Andes?
 How do dogs make trouble for wildlife in the Andes? Authors: Galo Zapata-Ríos and Lyn C. Branch Associate editors: Gogi Kalka and Madeleine Corcoran Abstract What do pets and wild animals have in common?
How do dogs make trouble for wildlife in the Andes? Authors: Galo Zapata-Ríos and Lyn C. Branch Associate editors: Gogi Kalka and Madeleine Corcoran Abstract What do pets and wild animals have in common?
Reptiles of Mauritius
 Reptiles of Pristine Imagine 371 years ago Before people lived in Nik Cole Prior to 1638 much of the island was covered in forest Pristine 671 species of plant 46% (endemic) found only in The forests supported
Reptiles of Pristine Imagine 371 years ago Before people lived in Nik Cole Prior to 1638 much of the island was covered in forest Pristine 671 species of plant 46% (endemic) found only in The forests supported
VANCOUVER ISLAND MARMOT
 VANCOUVER ISLAND MARMOT STATUS: CRITICALLY ENDANGERED The Vancouver Island marmot is one of the rarest mammals in the world and can be found only in the alpine meadows on Vancouver Island. By 2003, there
VANCOUVER ISLAND MARMOT STATUS: CRITICALLY ENDANGERED The Vancouver Island marmot is one of the rarest mammals in the world and can be found only in the alpine meadows on Vancouver Island. By 2003, there
November 6, Introduction
 TESTIMONY OF DAN ASHE, DEPUTY DIRECTOR, U.S. FISH AND WILDLIFE SERVICE, DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR, BEFORE THE HOUSE JUDICIARY SUBCOMMITTEE ON CRIME, TERRORISM, AND HOMELAND SECURITY ON H.R. 2811, TO AMEND
TESTIMONY OF DAN ASHE, DEPUTY DIRECTOR, U.S. FISH AND WILDLIFE SERVICE, DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR, BEFORE THE HOUSE JUDICIARY SUBCOMMITTEE ON CRIME, TERRORISM, AND HOMELAND SECURITY ON H.R. 2811, TO AMEND
Beaver. Mammal Rodent
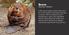 Beaver Rodent Is the second largest rodent in the world. It is a semi-aquatic rodent that is primarily nocturnal. They are mainly known for building dams, canals, and lodges(their homes). Large sharp front
Beaver Rodent Is the second largest rodent in the world. It is a semi-aquatic rodent that is primarily nocturnal. They are mainly known for building dams, canals, and lodges(their homes). Large sharp front
Evolution and Selection
 Why? Evolution and Selection What mechanisms lead to diversity of species on Earth? The idea of selection involves a variety of options with one option coming to the forefront while other options are eliminated.
Why? Evolution and Selection What mechanisms lead to diversity of species on Earth? The idea of selection involves a variety of options with one option coming to the forefront while other options are eliminated.
Biodiversity and Distributions. Lecture 2: Biodiversity. The process of natural selection
 Lecture 2: Biodiversity What is biological diversity? Natural selection Adaptive radiations and convergent evolution Biogeography Biodiversity and Distributions Types of biological diversity: Genetic diversity
Lecture 2: Biodiversity What is biological diversity? Natural selection Adaptive radiations and convergent evolution Biogeography Biodiversity and Distributions Types of biological diversity: Genetic diversity
Biological Invasions and Herpetology. 4/18/13 Chris Thawley
 Biological Invasions and Herpetology 4/18/13 Chris Thawley What are some invasive species? http://news.discovery.com/animals/videos/animals-jumping-carp-attack-explained.htm What is an Invasive species?
Biological Invasions and Herpetology 4/18/13 Chris Thawley What are some invasive species? http://news.discovery.com/animals/videos/animals-jumping-carp-attack-explained.htm What is an Invasive species?
Chapter 22 Darwin and Evolution by Natural Selection
 Anaerobic Bacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria Dinosaurs Green Algae Multicellular Animals Flowering Molluscs Arthropods Chordates Jawless Fish Teleost Fish Amphibians Insects Reptiles Mammals Birds Land Plants
Anaerobic Bacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria Dinosaurs Green Algae Multicellular Animals Flowering Molluscs Arthropods Chordates Jawless Fish Teleost Fish Amphibians Insects Reptiles Mammals Birds Land Plants
2012 Quail Season Outlook By Doug Schoeling, Upland Game Biologist Oklahoma Department of Wildlife Conservation
 2012 Quail Season Outlook By Doug Schoeling, Upland Game Biologist Oklahoma Department of Wildlife Conservation The Oklahoma Department of Wildlife Conservation has conducted annual roadside surveys in
2012 Quail Season Outlook By Doug Schoeling, Upland Game Biologist Oklahoma Department of Wildlife Conservation The Oklahoma Department of Wildlife Conservation has conducted annual roadside surveys in
Fundamentals to be considered when choosing your reptile pet.
 Reptiles Before you make a decision about adding a reptile to your family, be sure you know whether or not reptiles are allowed where you live! Many areas have laws pertaining to dangerous reptiles, including
Reptiles Before you make a decision about adding a reptile to your family, be sure you know whether or not reptiles are allowed where you live! Many areas have laws pertaining to dangerous reptiles, including
Evolution. Geology. Objectives. Key Terms SECTION 2
 SECTION 2 Evolution Organisms tend to be well suited to where they live and what they do. Figure 7 shows a chameleon (kuh MEEL ee uhn) capturing an insect. Insects are not easy to catch, so how does the
SECTION 2 Evolution Organisms tend to be well suited to where they live and what they do. Figure 7 shows a chameleon (kuh MEEL ee uhn) capturing an insect. Insects are not easy to catch, so how does the
Table of Threatened Animals in Amazing Animals in Australia s National Parks and Their Traffic-light Conservation Status
 Table of Threatened Animals in Amazing Animals in Australia s National Parks and Their Traffic-light Conservation Status Note: Traffic-light conservation status for the book was determined using a combination
Table of Threatened Animals in Amazing Animals in Australia s National Parks and Their Traffic-light Conservation Status Note: Traffic-light conservation status for the book was determined using a combination
Writing a Research Paper
 by Bill L. of Washington High School in South Bend, Indiana Barry Holstun Lopez The Naturalist INTRODUCTION Background information Thesis statement BODY First main point: Travels Summary Barry Lopez began
by Bill L. of Washington High School in South Bend, Indiana Barry Holstun Lopez The Naturalist INTRODUCTION Background information Thesis statement BODY First main point: Travels Summary Barry Lopez began
Introduced Species & Endangered Species
 Topic: Introduced Species & Endangered Species Notes Introduced Species & Endangered Species What is bioinvasion? The introduction of species, by direct or indirect human actions, to areas where they did
Topic: Introduced Species & Endangered Species Notes Introduced Species & Endangered Species What is bioinvasion? The introduction of species, by direct or indirect human actions, to areas where they did
Our Neighbors the Coyotes. Presented by: First Landing State Park
 Our Neighbors the Coyotes Presented by: First Landing State Park Basic Facts Weigh 25-35lbs Smaller than a grey wolf, more like a medium sized dog Can live up to 14 years, though most wild coyotes don
Our Neighbors the Coyotes Presented by: First Landing State Park Basic Facts Weigh 25-35lbs Smaller than a grey wolf, more like a medium sized dog Can live up to 14 years, though most wild coyotes don
ROGER IRWIN. 4 May/June 2014
 BASHFUL BLANDING S ROGER IRWIN 4 May/June 2014 4 May/June 2014 NEW HAMPSHIRE PROVIDES REGIONALLY IMPORTANT HABITAT FOR THE STATE- ENDANGERED BLANDING'S TURTLE BY MIKE MARCHAND A s a child, I loved to explore
BASHFUL BLANDING S ROGER IRWIN 4 May/June 2014 4 May/June 2014 NEW HAMPSHIRE PROVIDES REGIONALLY IMPORTANT HABITAT FOR THE STATE- ENDANGERED BLANDING'S TURTLE BY MIKE MARCHAND A s a child, I loved to explore
Name: Per. Date: 1. How many different species of living things exist today?
 Name: Per. Date: Life Has a History We will be using this website for the activity: http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/explorations/tours/intro/index.html Procedure: A. Open the above website and click
Name: Per. Date: Life Has a History We will be using this website for the activity: http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/explorations/tours/intro/index.html Procedure: A. Open the above website and click
10/24/2016 B Y E M I LY T I L L E Y
 ALL ABOUT ANIMALS B Y E M I LY T I L L E Y 1 M A M M A LS: H A V E A B A C K B O N E, A R E W A R M - B L O O D E D, H A V E H A I R O N T H E I R B O D I E S, A N D P R O D U C E M I L K T O F E E D T
ALL ABOUT ANIMALS B Y E M I LY T I L L E Y 1 M A M M A LS: H A V E A B A C K B O N E, A R E W A R M - B L O O D E D, H A V E H A I R O N T H E I R B O D I E S, A N D P R O D U C E M I L K T O F E E D T
A.13 BLAINVILLE S HORNED LIZARD (PHRYNOSOMA BLAINVILLII)
 A. BLAINVILLE S HORNED LIZARD (PHRYNOSOMA BLAINVILLII) A.. Legal and Other Status Blainville s horned lizard is designated as a Department of Fish and Game (DFG) Species of Concern. A.. Species Distribution
A. BLAINVILLE S HORNED LIZARD (PHRYNOSOMA BLAINVILLII) A.. Legal and Other Status Blainville s horned lizard is designated as a Department of Fish and Game (DFG) Species of Concern. A.. Species Distribution
Science Class 4 Topic: Habitats Reinforcement Worksheet. Name: Sec: Date:
 Science Class 4 Topic: Habitats Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the correct answer. 1. Which of these things are you NOT likely to find in a park or a garden? A. An earthworm B. An
Science Class 4 Topic: Habitats Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the correct answer. 1. Which of these things are you NOT likely to find in a park or a garden? A. An earthworm B. An
Evolution by Natural Selection
 Evolution by Natural Selection 2006-2007 DOCTRINE TINTORETTO The Creation of the Animals 1550 But the Fossil record OBSERVATION Anaerobic Bacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria Dinosaurs Green Algae Multicellular
Evolution by Natural Selection 2006-2007 DOCTRINE TINTORETTO The Creation of the Animals 1550 But the Fossil record OBSERVATION Anaerobic Bacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria Dinosaurs Green Algae Multicellular
Cane toads and Australian snakes
 Cane toads and Australian snakes This activity was adapted from an activity developed by Dr Thomas Artiss (Lakeside School, Seattle, USA) and Ben Phillips (University of Sydney). Cane toads (Bufo marinus)
Cane toads and Australian snakes This activity was adapted from an activity developed by Dr Thomas Artiss (Lakeside School, Seattle, USA) and Ben Phillips (University of Sydney). Cane toads (Bufo marinus)
An Ancient Reptile by Guy Belleranti
 What are their homes like? Tuatara live in underground burrows. Usually they don't dig their burrows, but instead live in burrows made by nesting sea birds. The two might even live in the burrow at the
What are their homes like? Tuatara live in underground burrows. Usually they don't dig their burrows, but instead live in burrows made by nesting sea birds. The two might even live in the burrow at the
The Gopher Tortoise (Gopherus polyphemus) A Species in Decline
 The Gopher Tortoise (Gopherus polyphemus) A Species in Decline History Gopher tortoises, or "gophers" as they are commonly called, belongs to a group of land tortoises that originated in western North
The Gopher Tortoise (Gopherus polyphemus) A Species in Decline History Gopher tortoises, or "gophers" as they are commonly called, belongs to a group of land tortoises that originated in western North
PORTRAIT OF THE AMERICAN BALD EAGLE
 PORTRAIT OF THE AMERICAN BALD EAGLE Objectives: To know the history of the bald eagle and the cause of it's decline. To understand what has been done to improve Bald Eagle habitat. To know the characteristics
PORTRAIT OF THE AMERICAN BALD EAGLE Objectives: To know the history of the bald eagle and the cause of it's decline. To understand what has been done to improve Bald Eagle habitat. To know the characteristics
Raptor Ecology in the Thunder Basin of Northeast Wyoming
 Raptor Ecology in the Thunder Basin Northeast Wyoming 121 Kort Clayton Thunderbird Wildlife Consulting, Inc. My presentation today will hopefully provide a fairly general overview the taxonomy and natural
Raptor Ecology in the Thunder Basin Northeast Wyoming 121 Kort Clayton Thunderbird Wildlife Consulting, Inc. My presentation today will hopefully provide a fairly general overview the taxonomy and natural
SEA TURTLES ARE AFFECTED BY PLASTIC SOFIA GIRALDO SANCHEZ AMALIA VALLEJO RAMIREZ ISABELLA SALAZAR MESA. Miss Alejandra Gómez
 SEA TURTLES ARE AFFECTED BY PLASTIC SOFIA GIRALDO SANCHEZ AMALIA VALLEJO RAMIREZ ISABELLA SALAZAR MESA Miss Alejandra Gómez CUMBRES SCHOOL 7 B ENVIGADO 2017 INDEX Pag. 1. Objectives.1 2. Questions...2
SEA TURTLES ARE AFFECTED BY PLASTIC SOFIA GIRALDO SANCHEZ AMALIA VALLEJO RAMIREZ ISABELLA SALAZAR MESA Miss Alejandra Gómez CUMBRES SCHOOL 7 B ENVIGADO 2017 INDEX Pag. 1. Objectives.1 2. Questions...2
Scholarship 2017 Biology
 93101Q 931012 S Scholarship 2017 Biology 9.30 a.m. Monday 20 November 2017 Time allowed: Three hours Total marks: 24 QUESTION BOOKLET There are THREE questions in this booklet. Answer ALL questions. Write
93101Q 931012 S Scholarship 2017 Biology 9.30 a.m. Monday 20 November 2017 Time allowed: Three hours Total marks: 24 QUESTION BOOKLET There are THREE questions in this booklet. Answer ALL questions. Write
Bobcat Interpretive Guide
 Interpretive Guide Exhibit Talking Point: Our job as interpreters is to link what the visitors are seeing to The Zoo's conservation education messages. Our goal is to spark curiosity, create emotional
Interpretive Guide Exhibit Talking Point: Our job as interpreters is to link what the visitors are seeing to The Zoo's conservation education messages. Our goal is to spark curiosity, create emotional
The GB Invasive Non-native Species Strategy. Olaf Booy GB Non-native Species Secretariat
 The GB Invasive Non-native Species Strategy Olaf Booy GB Non-native Species Secretariat Who am I? 4.2 staff What are we talking about? Non-native = animals or plants that have been introduced by human
The GB Invasive Non-native Species Strategy Olaf Booy GB Non-native Species Secretariat Who am I? 4.2 staff What are we talking about? Non-native = animals or plants that have been introduced by human
The Truth About. Rodents. by Kate Johanns HOUGHTON MIFFLIN
 The Truth About Rodents by Kate Johanns HOUGHTON MIFFLIN The Truth About Rodents by Kate Johanns PHOTOGRAPHY CREDITS: Cover Arco Images/Alamy; tp Anthony Bannister/Animals Animals Earth Scenes All rights
The Truth About Rodents by Kate Johanns HOUGHTON MIFFLIN The Truth About Rodents by Kate Johanns PHOTOGRAPHY CREDITS: Cover Arco Images/Alamy; tp Anthony Bannister/Animals Animals Earth Scenes All rights
MAMMAL SPECIES SEEN AT SCOTTSDALE COMMUNITY COLLEGE INDEX OF 14 SPECIES
 MAMMAL SPECIES SEEN AT SCOTTSDALE COMMUNITY COLLEGE INDEX OF 14 SPECIES References at end. Text written by staff. Photos by Roy Barnes, Emma Olsen and Dr. John Weser. Bailey's Pocket Mouse Black-tailed
MAMMAL SPECIES SEEN AT SCOTTSDALE COMMUNITY COLLEGE INDEX OF 14 SPECIES References at end. Text written by staff. Photos by Roy Barnes, Emma Olsen and Dr. John Weser. Bailey's Pocket Mouse Black-tailed
AN APPLIED CASE STUDY of the complexity of ecological systems and process: Why has Lyme disease become an epidemic in the northeastern U.S.
 AN APPLIED CASE STUDY of the complexity of ecological systems and process: Why has Lyme disease become an epidemic in the northeastern U.S. over the last few decades? What causes Lyme disease? 1 Frequency
AN APPLIED CASE STUDY of the complexity of ecological systems and process: Why has Lyme disease become an epidemic in the northeastern U.S. over the last few decades? What causes Lyme disease? 1 Frequency
Dinosaur Safari Junior: A Walk in Jurassic Park ver060113
 Dinosaur Safari Junior: A Walk in Jurassic Park ver060113 Introduction The rules used are a simplified variant of the Saurian Safari rules developed by Chris Peers and published by HLBS publishing 2002.
Dinosaur Safari Junior: A Walk in Jurassic Park ver060113 Introduction The rules used are a simplified variant of the Saurian Safari rules developed by Chris Peers and published by HLBS publishing 2002.
People around the world should be striving to preserve a healthy environment for both humans and
 People around the world should be striving to preserve a healthy environment for both humans and animals. However, factors such as pollution, climate change and exploitation are causing an increase in
People around the world should be striving to preserve a healthy environment for both humans and animals. However, factors such as pollution, climate change and exploitation are causing an increase in
Major Developments ( )
 Major Developments (1206-1340) Mongols (Genghis Khan) established a massive empire running from Eastern Europe, through Mesopotamia, across central Europe to China between 1206-1340. Silk road re-opened
Major Developments (1206-1340) Mongols (Genghis Khan) established a massive empire running from Eastern Europe, through Mesopotamia, across central Europe to China between 1206-1340. Silk road re-opened
Social media kit for World Wildlife Day 2018
 Social media kit for World Wildlife Day 2018 Date: 3 March 2018 Theme: Big Cats predators under threat Main hashtags: #WorldWildlifeDay, #PredatorsUnderThreat, #WWD2018 Supplementary hashtags: #DoOneThingToday
Social media kit for World Wildlife Day 2018 Date: 3 March 2018 Theme: Big Cats predators under threat Main hashtags: #WorldWildlifeDay, #PredatorsUnderThreat, #WWD2018 Supplementary hashtags: #DoOneThingToday
State of resources reporting
 Ministry of Natural Resources State of resources reporting Rabies in Ontario What is Rabies? Rabies is a disease that affects the nervous system of mammals. The virus that causes rabies is usually passed
Ministry of Natural Resources State of resources reporting Rabies in Ontario What is Rabies? Rabies is a disease that affects the nervous system of mammals. The virus that causes rabies is usually passed
Island Fox Update 2011
 ! page 1 of 5 The island fox offers a dramatic example of how people can come together to make a positive difference for an endangered species. In 1998, s were plummeting on four of the California Channel
! page 1 of 5 The island fox offers a dramatic example of how people can come together to make a positive difference for an endangered species. In 1998, s were plummeting on four of the California Channel
1.5 C: Role of the Environment in Evolution Quiz
 1. Numbers of reported cases of bedbug infestations have been increasing over the past ten years in the United States. In an attempt to combat the infestations, people began using pesticides to kill the
1. Numbers of reported cases of bedbug infestations have been increasing over the past ten years in the United States. In an attempt to combat the infestations, people began using pesticides to kill the
Physical Description Meadow voles are small rodents with legs and tails, bodies, and ears.
 A Guide to Meadow Voles Identification, Biology and Control Methods Identification There are 5 species of Meadow Vole common to California. They are the California Vole, Long-tailed Vole, Creeping Vole,
A Guide to Meadow Voles Identification, Biology and Control Methods Identification There are 5 species of Meadow Vole common to California. They are the California Vole, Long-tailed Vole, Creeping Vole,
Coyote (Canis latrans)
 Coyote (Canis latrans) Coyotes are among the most adaptable mammals in North America. They have an enormous geographical distribution and can live in very diverse ecological settings, even successfully
Coyote (Canis latrans) Coyotes are among the most adaptable mammals in North America. They have an enormous geographical distribution and can live in very diverse ecological settings, even successfully
SALAMANDERS. Helpful Hints: What is a Salamander: Physical Characteristics:
 SALAMANDERS Helpful Hints: This study guide will focus on s found in Illinois as well as those widespread in North America. The Eco-Meet test may consist of multiple choice, true/false, fill in the blank,
SALAMANDERS Helpful Hints: This study guide will focus on s found in Illinois as well as those widespread in North America. The Eco-Meet test may consist of multiple choice, true/false, fill in the blank,
Ecological Studies of Wolves on Isle Royale
 Ecological Studies of Wolves on Isle Royale 2017-2018 I can explain how and why communities of living organisms change over time. Summary Between January 2017 and January 2018, the wolf population continued
Ecological Studies of Wolves on Isle Royale 2017-2018 I can explain how and why communities of living organisms change over time. Summary Between January 2017 and January 2018, the wolf population continued
THE CHILDREN S ZOO. Scavenger Hunt GRADES K-3
 THE CHILDREN S ZOO Scavenger Hunt GRADES K-3 Scavenger Hunt The Children s Zoo (K-3) Teacher s Guide Updated Summer 2011 APPROXIMATE TIME: 60 Minutes Suggestions for Teachers: 1. Allow your children about
THE CHILDREN S ZOO Scavenger Hunt GRADES K-3 Scavenger Hunt The Children s Zoo (K-3) Teacher s Guide Updated Summer 2011 APPROXIMATE TIME: 60 Minutes Suggestions for Teachers: 1. Allow your children about
Activity for Biology. Background Information on Lake Erie water snake and round goby:
 Activity for Biology Lesson #2 Name Period Date Maritime Shipping on the Great Lakes and the link to the Lake Erie Water Snake Background Information on Lake Erie water snake and round goby: Lake Erie
Activity for Biology Lesson #2 Name Period Date Maritime Shipping on the Great Lakes and the link to the Lake Erie Water Snake Background Information on Lake Erie water snake and round goby: Lake Erie
Rufous hare-wallaby Lagorchestes hirsutus
 Rufous hare-wallaby Lagorchestes hirsutus Wild populations of the rufous hare-wallaby remain only on Bernier and Dorre islands in Shark Bay. There is also a translocated population of the central Australian
Rufous hare-wallaby Lagorchestes hirsutus Wild populations of the rufous hare-wallaby remain only on Bernier and Dorre islands in Shark Bay. There is also a translocated population of the central Australian
Gambel s Quail Callipepla gambelii
 Photo by Amy Leist Habitat Use Profile Habitats Used in Nevada Mesquite-Acacia Mojave Lowland Riparian Springs Agriculture Key Habitat Parameters Plant Composition Mesquite, acacia, salt cedar, willow,
Photo by Amy Leist Habitat Use Profile Habitats Used in Nevada Mesquite-Acacia Mojave Lowland Riparian Springs Agriculture Key Habitat Parameters Plant Composition Mesquite, acacia, salt cedar, willow,
Objectives: Outline: Idaho Amphibians and Reptiles. Characteristics of Amphibians. Types and Numbers of Amphibians
 Natural History of Idaho Amphibians and Reptiles Wildlife Ecology, University of Idaho Fall 2005 Charles R. Peterson Herpetology Laboratory Department of Biological Sciences, Idaho Museum of Natural History
Natural History of Idaho Amphibians and Reptiles Wildlife Ecology, University of Idaho Fall 2005 Charles R. Peterson Herpetology Laboratory Department of Biological Sciences, Idaho Museum of Natural History
Recognizing that the government of Mexico lists the loggerhead as in danger of extinction ; and
 RESOLUTION URGING THE REPUBLIC OF MEXICO TO END HIGH BYCATCH MORTALITY AND STRANDINGS OF NORTH PACIFIC LOGGERHEAD SEA TURTLES IN BAJA CALIFORNIA SUR, MEXICO Recalling that the Republic of Mexico has worked
RESOLUTION URGING THE REPUBLIC OF MEXICO TO END HIGH BYCATCH MORTALITY AND STRANDINGS OF NORTH PACIFIC LOGGERHEAD SEA TURTLES IN BAJA CALIFORNIA SUR, MEXICO Recalling that the Republic of Mexico has worked
Paratenic and Accidental Hosts
 Hawaii Island Rat Lungworm Working Group Daniel K. Inouye College of Pharmacy University of Hawaii, Hilo Rat Lungworm IPM RLWL-7 Paratenic and Accidental Hosts Standards addressed: Language Arts Common
Hawaii Island Rat Lungworm Working Group Daniel K. Inouye College of Pharmacy University of Hawaii, Hilo Rat Lungworm IPM RLWL-7 Paratenic and Accidental Hosts Standards addressed: Language Arts Common
Guidelines for including species of conservation concern in the Environmental Assessment process
 Guidelines for including species of conservation concern in the Environmental Assessment process Introduction To date not all provinces are including species of conservation concern as targets in their
Guidelines for including species of conservation concern in the Environmental Assessment process Introduction To date not all provinces are including species of conservation concern as targets in their
Presentation Guidelines
 Presentation Guidelines 12 minute PowerPoint, leaving 3 minutes to answer questions Between 8-15 slides, but there is no slide requirement Presentations will be graded by. Content Follow the format: introduction,
Presentation Guidelines 12 minute PowerPoint, leaving 3 minutes to answer questions Between 8-15 slides, but there is no slide requirement Presentations will be graded by. Content Follow the format: introduction,
How Animals Live. Chapter 2 Review
 How Animals Live Chapter 2 Review What do animals need to survive? Water Food Air (oxygen) Shelter Butterfly life cycle During the larva stage, the butterfly is called a caterpillar. During the pupa stage,
How Animals Live Chapter 2 Review What do animals need to survive? Water Food Air (oxygen) Shelter Butterfly life cycle During the larva stage, the butterfly is called a caterpillar. During the pupa stage,
Lecture 15. Biology 5865 Conservation Biology. Ex-Situ Conservation
 Lecture 15 Biology 5865 Conservation Biology Ex-Situ Conservation Exam 2 Review Concentration on Chapters 6-12 & 14 but not Chapter 13 (Establishing New Populations) Applied Population Biology Chapter
Lecture 15 Biology 5865 Conservation Biology Ex-Situ Conservation Exam 2 Review Concentration on Chapters 6-12 & 14 but not Chapter 13 (Establishing New Populations) Applied Population Biology Chapter
